

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 140-149.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22177 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22177
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
王菲菲, 周振祥, 洪益, 谷洋洋, 吕超, 郭宝健, 朱娟, 许如根*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-31
接受日期:2022-10-24
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: rgxu@yzu.edu.cn
作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Feifei Wang, Zhenxiang Zhou, Yi Hong, Yangyang Gu, Chao Lü, Baojian Guo, Juan Zhu, Rugen Xu*( )
)
Received:2022-07-31
Accepted:2022-10-24
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: rgxu@yzu.edu.cn
About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 核因子Y (NF-Y)是由NF-YA、NF-YB和NF-YC三个亚基组成的一类真核细胞转录因子, 主要参与植物生长发育调控和非生物胁迫信号传递。该研究利用生物信息学方法解析了大麦(Hordeum vulgare) NF-YC基因家族功能。首先, 基于大麦基因组数据库鉴定出11个HvNF-YC成员, 分布在除第2号染色体以外的其余6条染色体上, 内含子0-5个。系统进化分析显示, 大麦、拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)和水稻(Oryza sativa) NF-YC基因家族成员可分为5个亚家族。基因复制分析显示, 6个HvNF-YC基因存在片段复制, 3个HvNF-YC基因存在串联复制。启动子顺式作用元件分析显示, 大多数HvNF-YC基因启动子含有与非生物胁迫及激素响应相关的顺式作用元件。对HvNF-YC家族成员在不同组织不同时期的表达模式分析表明, 不同成员的时空表达存在明显差异, 其中HvNF-YC9和HvNF-YC11可能在籽粒发育初期发挥重要作用。通过分析耐盐型和盐敏感型大麦品种根和叶中HvNF-YC表达量变化, 发现HvNF-YC3、HvNF-YC6和HvNF-YC10主要在盐胁迫初期的根中行使功能, HvNF-YC9主要在长期盐胁迫处理后期的根中起作用。综上所述, 推测HvNF-YC9、10、11三个基因可作为后续探究大麦NF-YC参与耐盐作用机制的候选基因。该研究结果为进一步解析HvNF-YC在大麦中的耐盐调控功能奠定了基础。
王菲菲, 周振祥, 洪益, 谷洋洋, 吕超, 郭宝健, 朱娟, 许如根. 大麦NF-YC基因鉴定及在盐胁迫下的表达分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 140-149.
Feifei Wang, Zhenxiang Zhou, Yi Hong, Yangyang Gu, Chao Lü, Baojian Guo, Juan Zhu, Rugen Xu. Identification of the NF-YC Genes in Hordeum vulgare and Expression Analysis Under Salt Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 140-149.
| Gene name | Gene ID | Chromo- some | Location | Amino acid length (aa) | Protein molecular weight (kDa) | pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HvNF-YC1 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.1HG0069390.1 | 1 | 447067437- 447072149 | 282 | 31.44 | 5.4 | 48.23 | 75.07 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC2 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.1HG0081770.1 | 1 | 489164568- 489164978 | 136 | 14.07 | 9.5 | 38.39 | 79.78 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC3 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.3HG0237950.1 | 3 | 54989815- 54991052 | 371 | 39.09 | 4.74 | 52.22 | 66.66 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC4 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.4HG0364520.1 | 4 | 231786893- 231791804 | 255 | 28.09 | 5.93 | 59.67 | 65.76 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC5 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.4HG0391570.1 | 4 | 499791697- 499793529 | 241 | 25.63 | 5.32 | 60.13 | 66.18 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC6 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.5HG0489580.1 | 5 | 474074907- 474075856 | 203 | 21.78 | 5.39 | 59.79 | 72.91 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC7 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.6HG0571700.1 | 6 | 135835186- 135838701 | 260 | 28.59 | 4.87 | 81.41 | 71.81 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC8 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0677850.1 | 7 | 160202157- 160203122 | 199 | 21.57 | 5.52 | 65.36 | 71.86 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC9 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0737530.1 | 7 | 597862664- 597863461 | 265 | 29.76 | 4.79 | 69.77 | 63.06 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC10 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0737680.1 | 7 | 598086832- 598087587 | 251 | 27.85 | 6.22 | 68.44 | 73.19 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC11 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0737720.1 | 7 | 598116971- 598117753 | 260 | 28.62 | 4.66 | 80.61 | 68.81 | Nucleus |
表1 大麦NF-YC基因家族成员的序列信息
Table 1 Sequence information of HvNF-YCs gene family
| Gene name | Gene ID | Chromo- some | Location | Amino acid length (aa) | Protein molecular weight (kDa) | pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HvNF-YC1 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.1HG0069390.1 | 1 | 447067437- 447072149 | 282 | 31.44 | 5.4 | 48.23 | 75.07 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC2 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.1HG0081770.1 | 1 | 489164568- 489164978 | 136 | 14.07 | 9.5 | 38.39 | 79.78 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC3 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.3HG0237950.1 | 3 | 54989815- 54991052 | 371 | 39.09 | 4.74 | 52.22 | 66.66 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC4 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.4HG0364520.1 | 4 | 231786893- 231791804 | 255 | 28.09 | 5.93 | 59.67 | 65.76 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC5 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.4HG0391570.1 | 4 | 499791697- 499793529 | 241 | 25.63 | 5.32 | 60.13 | 66.18 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC6 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.5HG0489580.1 | 5 | 474074907- 474075856 | 203 | 21.78 | 5.39 | 59.79 | 72.91 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC7 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.6HG0571700.1 | 6 | 135835186- 135838701 | 260 | 28.59 | 4.87 | 81.41 | 71.81 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC8 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0677850.1 | 7 | 160202157- 160203122 | 199 | 21.57 | 5.52 | 65.36 | 71.86 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC9 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0737530.1 | 7 | 597862664- 597863461 | 265 | 29.76 | 4.79 | 69.77 | 63.06 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC10 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0737680.1 | 7 | 598086832- 598087587 | 251 | 27.85 | 6.22 | 68.44 | 73.19 | Nucleus |
| HvNF-YC11 | HORVU.MOREX.- r3.7HG0737720.1 | 7 | 598116971- 598117753 | 260 | 28.62 | 4.66 | 80.61 | 68.81 | Nucleus |
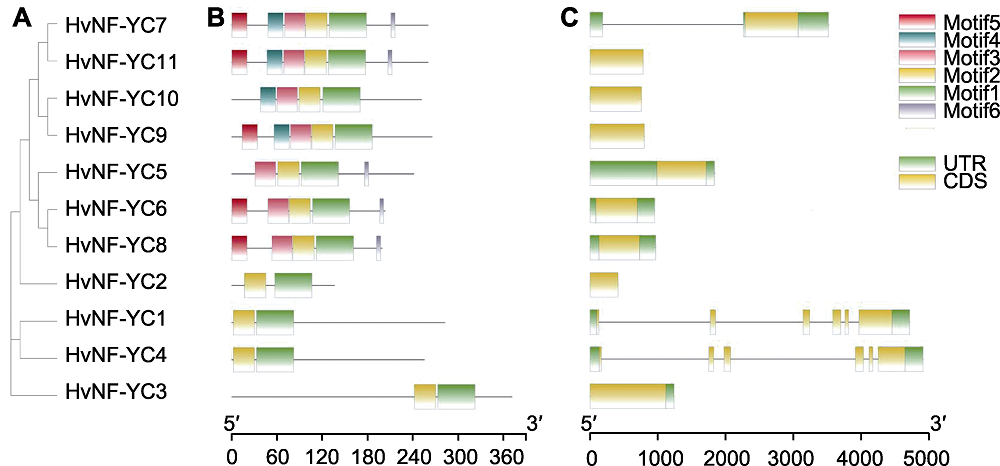
图1 大麦NF-YC家族成员的聚类分析(A)、保守基序(B)与基因结构(C) CDS: 编码序列; UTR: 非翻译区
Figure 1 Cluster analysis (A), conserved motif (B) and gene structure (C) of HvNF-YC family members CDS: Coding sequence; UTR: Untranslated region
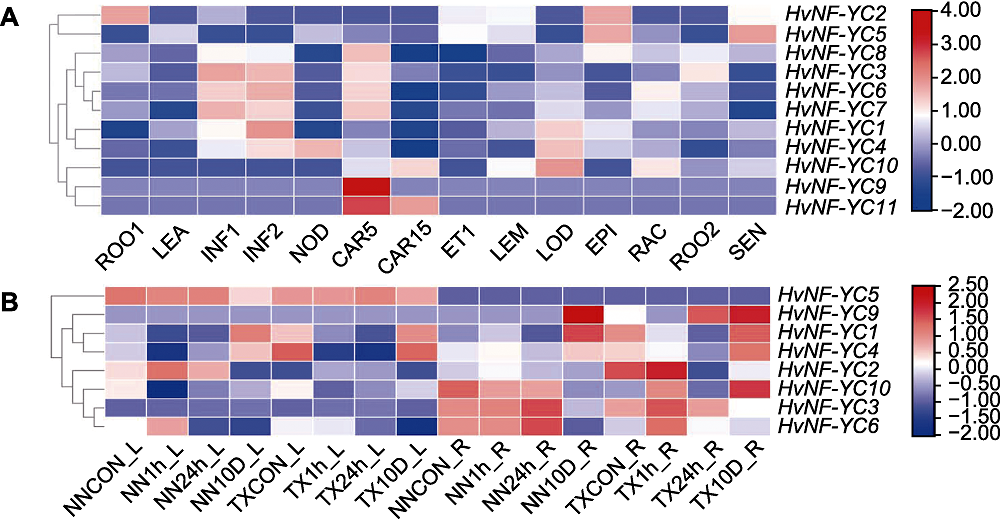
图8 大麦NF-YC基因家族成员的组织表达谱(A)及盐胁迫处理下NN和TX品种叶和根中HvNF-YC表达量(B) ROO1: 种子根(茎长10 cm, 幼苗阶段); LEA: 茎(10 cm, 幼苗阶段); INF1: 花序(5 mm); INF2: 花序(1-1.5 cm); NOD: 分蘖(第3节); CAR5: 籽粒(授粉后第5天); CAR15: 籽粒(授粉后第15天); ET1: 黄花幼苗(黑暗条件下10天); LEM: 花序(外稃, 授粉后42天); LOD: 花序(浆片, 授粉后42天); EPI: 表皮(授粉后28天); RAC: 花序(花轴, 授粉后35天); ROO2: 根(授粉后28天); SEN: 衰老叶片(授粉后56天)
Figure 8 Tissue expression profile of NF-YC gene family members in Hordeum vulgare (A) and HvNF-YC expressions in the leaf and root of NN and TX varieties under salt stress (B) ROO1: Roots from seedlings (10 cm shoot stage); LEA: Shoots from seedlings (10 cm shoot stage); INF1: Young developing inflorescences (5 mm); INF2: Developing inflorescences (1-1.5 cm); NOD: Developing tillers (3rd internode); CAR5: Developing grain (5 days after pollination (DAP)); CAR15: Developing grain (15 DAP); ET1: Etiolated seedling (dark condition,10 days); LEM: Inflorescences (lemma, 42 DAP); LOD: Inflorescences (lodicule, 42 DAP); EPI: Epidermal strips (28 DAP); RAC: Inflorescences (rachis, 35 DAP); ROO2: Roots (28 DAP); SEN: Senescing leaves (56 DAP)
| [1] | 陈国户, 庞小可, 李广, 王浩, 吴思文, 温宏伟, 尹倩, 袁凌云, 侯金锋, 唐小燕, 汪承刚 (2022). 白菜NAC基因家族全基因组鉴定及其应答春化反应的表达分析. 南京农业大学学报 45, 656-665. |
| [2] | 黄俊文, 南建宗, 阳成伟 (2020). NF-Y转录因子调控植物生长发育及胁迫响应的研究进展. 植物生理学报 56, 2595-2605. |
| [3] | 李娟, 高凯, 安新民 (2019). 转录因子NF-Y在植物生长发育和逆境胁迫响应中的作用. 中国细胞生物学学报 41, 2434-2442. |
| [4] | 李世贵, 马瑞, 王芳芳, 刘维刚, 杨江伟, 唐勋, 张宁, 司怀军 (2021). 植物NF-Y转录因子研究进展. 植物生理学报 57, 248-256. |
| [5] |
马鑫磊, 许瑞琪, 索晓曼, 李婧实, 顾鹏鹏, 姚锐, 林小虎, 高慧 (2022). 谷子III型PRX基因家族全基因组鉴定及干旱胁迫下表达分析. 作物学报 48, 2517-2532.
DOI |
| [6] | 桑璐曼, 汤沙, 张仁梁, 贾小平, 刁现民 (2022). 谷子热激蛋白HSP90基因家族鉴定及分析. 植物遗传资源学报 23, 1085-1097. |
| [7] |
Alam MM, Tanaka T, Nakamura H, Ichikawa H, Kobayashi K, Yaeno T, Yamaoka N, Shimomoto K, Takayama K, Nishina H, Nishiguchi M (2015). Overexpression of a rice heme activator protein gene (OsHAP2E) confers resistance to pathogens, salinity and drought, and increases photosynthesis and tiller number. Plant Biotechnol J 13, 85-96.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Dolfini D, Gatta R, Mantovani R (2012). NF-Y and the transcriptional activation of CCAAT promoters. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 47, 29-49.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Forsburg SL, Guarente L (1989). Identification and characterization of HAP4: a third component of the CCAAT- bound HAP2/HAP3 heteromer. Genes Dev 3, 1166-1178.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Frontini M, Imbriano C, Manni I, Mantovani R (2004). Cell cycle regulation of NF-YC nuclear localization. Cell Cycle 3, 217-222.
PMID |
| [11] |
Kong HZ, Landherr LL, Frohlich MW, Leebens-Mack J, Ma H, DePamphilis CW (2007). Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J 50, 873-885.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Laloum T, De Mita S, Gamas P, Baudin M, Niebel A (2013). CCAAT-box binding transcription factors in plants: Y so many? Trends Plant Sci 18, 157-166.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Li QP, Yan WH, Chen HX, Tan C, Han ZM, Yao W, Li GW, Yuan MQ, Xing YZ (2016). Duplication of OsHAP family genes and their association with heading date in rice. J Exp Bot 67, 1759-1768.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Li YJ, Fang Y, Fu YR, Huang JG, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2013). NFYA1 is involved in regulation of postgermina-tion growth arrest under salt stress in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 8, e61289.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Liang MX, Hole D, Wu JX, Blake T, Wu YJ (2012). Expres-sion and functional analysis of NUCLEAR FACTORY, subunit B genes in barley. Planta 235, 779-791. |
| [16] |
Mantovani R (1999). The molecular biology of the CCAAT- binding factor NF-Y. Gene 239, 15-27.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Nelson DE, Repetti PP, Adams TR, Creelman RA, Wu JR, Warner DC, Anstrom DC, Bensen RJ, Castiglioni PP, Donnarummo MG, Hinchey BS, Kumimoto RW, Maszle DR, Canales RD, Krolikowski KA, Dotson SB, Gutterson N, Ratcliffe OJ, Heard JE (2007). Plant nuclear factor Y (NF-Y) B subunits confer drought tolerance and lead to improved corn yields on water-limited acres. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 16450-16455.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Niu BX, Zhang ZY, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Chen C (2021). The rice LEC1-like transcription factor OsNF-YB9 interacts with SPK, an endosperm specific sucrose synthase pro-tein kinase, and functions in seed development. Plant J 106, 1233-1246.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Panahi B, Mohammadi SA, Ruzicka K, Abbasi Holaso H, Zare Mehrjerdi M (2019). Genome-wide identification and co-expression network analysis of nuclear factor-Y in barley revealed potential functions in salt stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25, 485-495.
DOI |
| [20] | Pelletier JM, Kwong RW, Park S, Le BH, Baden R, Cagliari A, Hashimoto M, Munoz MD, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2017). LEC1 sequentially regulates the transcription of genes involved in diverse developmental processes during seed development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E6710-E6719. |
| [21] |
Petroni K, Kumimoto RW, Gnesutta N, Calvenzani V, Fornari M, Tonelli C, Holt III BF, Mantovani R (2012). The promiscuous life of plant NUCLEAR FACTOR Y transcription factors. Plant Cell 24, 4777-4792.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Qu BY, He X, Wang J, Zhao YY, Teng W, Shao A, Zhao XQ, Ma WY, Wang JY, Li B, Li ZS, Tong YP (2015). A wheat CCAAT box-binding transcription factor increases the grain yield of wheat with less fertilizer input. Plant Physiol 167, 411-423.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Rogozin IB, Wolf YI, Sorokin AV, Mirkin BG, Koonin EV (2003). Remarkable interkingdom conservation of intron positions and massive, lineage-specific intron loss and gain in eukaryotic evolution. Curr Biol 13, 1512-1517.
PMID |
| [24] |
Romier C, Cocchiarella F, Mantovani R, Moras D (2003). The NF-YB/NF-YC structure gives insight into DNA binding and transcription regulation by CCAAT factor NF-Y. J Biol Chem 278, 1336-1345.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Siefers N, Dang KK, Kumimoto RW, Bynum WE, Tayrose G, Holt III BF (2009). Tissue-specific expression patterns of Arabidopsis NF-Y transcription factors suggest potential for extensive combinatorial complexity. Plant Physiol 149, 625-641.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Stephenson TJ, McIntyre CL, Collet C, Xue GP (2010). TaNF-YC11, one of the light-upregulated NF-YC members in Triticum aestivum, is co-regulated with photosynthesis-related genes. Funct Integr Genomics 10, 265-276.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Stephenson TJ, McIntyre CL, Collet C, Xue GP (2007). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y family of transcription factors in Triticum aesti-vum. Plant Mol Biol 65, 77-92.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Thirumurugan T, Ito Y, Kubo T, Serizawa A, Kurata N (2008). Identification, characterization and interaction of HAP family genes in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 279, 279-289.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Xing Y, Fikes JD, Guarente L (1993). Mutations in yeast HAP2/HAP3 define a hybrid CCAAT box binding domain. EMBO J 12, 4647-4655.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Yang WJ, Lu ZH, Xiong YF, Yao JL (2017). Genome-wide identification and co-expression network analysis of the OsNF-Y gene family in rice. Crop J 5, 21-31.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Yu TF, Liu Y, Fu JD, Ma J, Fang ZW, Chen J, Zheng L, Lu ZW, Zhou YB, Chen M, Xu ZS, Ma YZ (2021). The NF-Y-PYR module integrates the abscisic acid signal pathway to regulate plant stress tolerance. Plant Biotech-nol J 19, 2589-2605. |
| [32] |
Zhang ZB, Li XL, Zhang C, Zou HW, Wu ZY (2016). Isola-tion, structural analysis, and expression characteristics of the maize nuclear factor Y gene families. Biochem Bio-phys Res Commun 478, 752-758.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王子韵, 吕燕文, 肖钰, 吴超, 胡新生. 植物基因表达调控与进化机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 徐田甜, 杨培建, 周晓茜, 曹怡, 陈艳红, 刘国元, 张健, 魏辉. 紫薇GolS家族基因的理化特性与表达特征[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 393-406. |
| [3] | 赵来鹏, 王柏柯, 杨涛, 李宁, 杨海涛, 王娟, 闫会转. SlHVA22l基因调节番茄耐旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 558-573. |
| [4] | 杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [5] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [6] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [7] | 刘叶飞, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 邱锐, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥. 野大麦高效组培快繁及农杆菌介导的愈伤侵染体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 440-448. |
| [8] | 张琦, 张文静, 袁宪凯, 李明, 赵强, 杜艳丽, 杜吉到. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下普通菜豆芽期核酸修复的调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [9] | 范凯, 叶方婷, 毛志君, 潘鑫峰, 李兆伟, 林文雄. 被子植物小热激蛋白家族的比较基因组学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 245-261. |
| [10] | 车明哲, 王亚军, 马创新, 漆小泉. 大麦抗叶锈病慢锈性鉴定技术及抗性评价方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 573-576. |
| [11] | 谢露露, 崔青青, 董春娟, 尚庆茂. 植物嫁接愈合分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 634-643. |
| [12] | 张楠,刘自广,孙世臣,刘圣怡,林建辉,彭疑芳,张晓旭,杨贺,岑曦,吴娟. 拟南芥AtR8 lncRNA对盐胁迫响应及其对种子萌发的调节作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 421-429. |
| [13] | 曹栋栋,陈珊宇,秦叶波,吴华平,阮关海,黄玉韬. 水杨酸调控盐胁迫下羽衣甘蓝种子萌发的机理[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 49-61. |
| [14] | 王小龙,刘凤之,史祥宾,王孝娣,冀晓昊,王志强,王宝亮,郑晓翠,王海波. 葡萄NCED基因家族进化及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 474-485. |
| [15] | 范业赓,丘立杭,黄杏,周慧文,甘崇琨,李杨瑞,杨荣仲,吴建明,陈荣发. 甘蔗节间伸长过程赤霉素生物合成关键基因的表达及相关植物激素动态变化[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 486-496. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||