

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 150-158.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22108 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22108
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
叶卫军, 张阴, 王沛然, 张玲玲, 田东丰, 吴泽江, 周斌*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-25
接受日期:2022-07-25
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 18756019871@139.com
基金资助:
Weijun Ye, Yin Zhang, Peiran Wang, Lingling Zhang, Dongfeng Tian, Zejiang Wu, Bin Zhou*( )
)
Received:2022-05-25
Accepted:2022-07-25
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: 18756019871@139.com
摘要: 利用绿豆(Vigna radiata)品种苏绿16-10和潍绿11杂交构建的F2和F3群体发掘调控绿豆产量相关性状的遗传位点。同时对绿豆产量相关性状进行表型鉴定和相关性分析, 并利用构建的遗传连锁图谱进行QTL定位。结果表明, 单株产量与单株荚数、单荚粒数、百粒重和分枝数均呈正相关。单株产量与单株荚数的相关性最高, 这2个性状在F2和F3群体中的相关系数分别为0.950和0.914。在F2群体中, 共检测到8个与产量性状相关的QTL位点, 其中与单株荚数、单荚粒数和单株产量相关的QTL位点各1个, 分别解释11.09% (qNPP3)、17.93% (qNSP3)和14.18% (qYP3)的表型变异; 2个与分枝数相关的QTL位点qBMS3和qBMS11, 分别解释18.51%和7.06%的表型变异; 3个与百粒重相关的QTL位点qHSW3、qHSW7和qHSW10, 分别解释5.33%、46.07%和4.24%的表型变异。在F3群体中, qNSP3和qHSW7再次被检测到, 表明这2个QTLs有较好的遗传稳定性。同时, 开发了1个与百粒重主效QTL qHSW7紧密连锁的InDel标记R7-13.4, 并利用自然群体对该分子标记辅助筛选的有效性进行了验证。研究结果可为绿豆产量相关性状基因的定位、克隆及分子标记辅助育种提供参考。
叶卫军, 张阴, 王沛然, 张玲玲, 田东丰, 吴泽江, 周斌. 绿豆5个产量相关性状的QTL分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 150-158.
Weijun Ye, Yin Zhang, Peiran Wang, Lingling Zhang, Dongfeng Tian, Zejiang Wu, Bin Zhou. QTLs Analysis for Five Yield-related Traits in Mungbean. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 150-158.
| Year | Traits | Parental lines | F2 or F3 population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weilv11 | Sulv16-10 | Means±SD | Range | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
| 2019 (F2) | NPP | 11.0 | 20.2 ** | 18.26±8.86 | 5.0-46.0 | 48.52 | 1.27 | 1.26 |
| NSP | 10.1 | 12.0 ** | 10.62±0.98 | 9.6-14.3 | 7.77 | -0.84 | 0.55 | |
| HSW (g) | 5.00 | 7.42 ** | 6.33±0.69 | 4.77-8.19 | 10.95 | 0.27 | -0.45 | |
| BMS | 0.5 | 3.0 ** | 2.08±1.48 | 0.0-6.0 | 71.17 | 0.35 | -0.45 | |
| YP (g) | 5.21 | 14.95 ** | 11.48±5.95 | 2.67-28.96 | 51.80 | 1.16 | 0.82 | |
| 2020 (F3) | NPP | 9.4 | 23.2 ** | 16.94±8.65 | 5.0-48.0 | 51.05 | 1.38 | 2.01 |
| NSP | 9.8 | 12.3 ** | 10.41±1.30 | 8.5-15.0 | 10.15 | -0.73 | 0.80 | |
| HSW (g) | 5.06 | 7.02 ** | 5.47±0.68 | 3.40-7.20 | 12.51 | -0.44 | 0.27 | |
| BMS | 0.5 | 3.6 ** | 1.71±1.39 | 0.0-6.0 | 81.68 | -0.11 | -1.17 | |
| YP (g) | 4.62 | 16.89 ** | 8.94±4.71 | 2.00-5.40 | 52.70 | 1.15 | 1.18 | |
表1 绿豆亲本、F2和F3群体的表型分析
Table 1 Phenotype analysis for the mungbean parental lines, F2 and F3 populations
| Year | Traits | Parental lines | F2 or F3 population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weilv11 | Sulv16-10 | Means±SD | Range | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
| 2019 (F2) | NPP | 11.0 | 20.2 ** | 18.26±8.86 | 5.0-46.0 | 48.52 | 1.27 | 1.26 |
| NSP | 10.1 | 12.0 ** | 10.62±0.98 | 9.6-14.3 | 7.77 | -0.84 | 0.55 | |
| HSW (g) | 5.00 | 7.42 ** | 6.33±0.69 | 4.77-8.19 | 10.95 | 0.27 | -0.45 | |
| BMS | 0.5 | 3.0 ** | 2.08±1.48 | 0.0-6.0 | 71.17 | 0.35 | -0.45 | |
| YP (g) | 5.21 | 14.95 ** | 11.48±5.95 | 2.67-28.96 | 51.80 | 1.16 | 0.82 | |
| 2020 (F3) | NPP | 9.4 | 23.2 ** | 16.94±8.65 | 5.0-48.0 | 51.05 | 1.38 | 2.01 |
| NSP | 9.8 | 12.3 ** | 10.41±1.30 | 8.5-15.0 | 10.15 | -0.73 | 0.80 | |
| HSW (g) | 5.06 | 7.02 ** | 5.47±0.68 | 3.40-7.20 | 12.51 | -0.44 | 0.27 | |
| BMS | 0.5 | 3.6 ** | 1.71±1.39 | 0.0-6.0 | 81.68 | -0.11 | -1.17 | |
| YP (g) | 4.62 | 16.89 ** | 8.94±4.71 | 2.00-5.40 | 52.70 | 1.15 | 1.18 | |
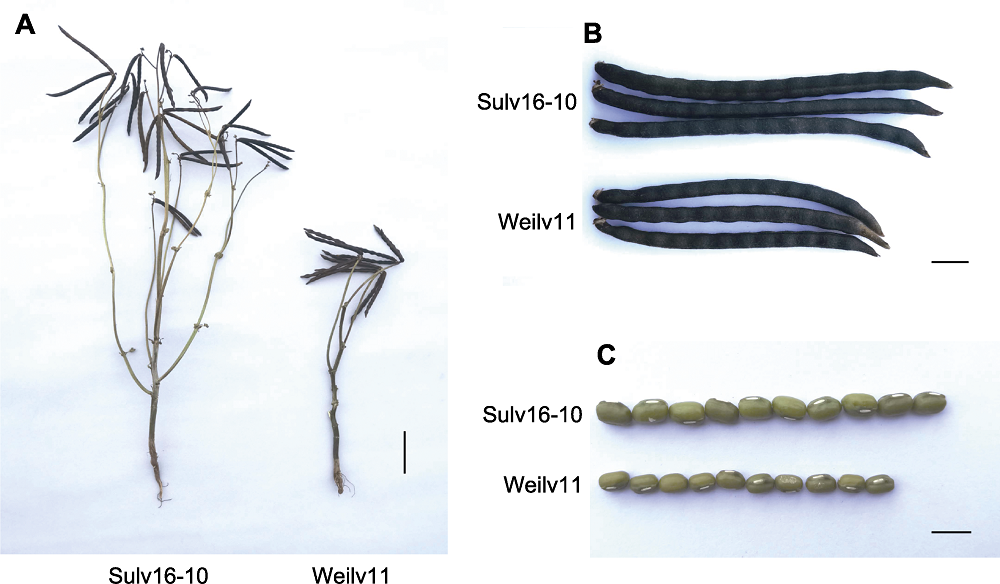
图1 绿豆亲本表型 (A) 成熟期亲本植株表型(bar=5 cm); (B) 亲本成熟荚表型(bar=1 cm); (C) 亲本籽粒表型(bar=5 mm)
Figure 1 Phenotype of mungbean parental lines (A) Phenotype of parental plants at mature stage (bar=5 cm); (B) Phenotype of the mature pods of parental lines (bar=1 cm); (C) Phenotype of parental seeds (bar=5 mm)
| Traits | NPP | NSP | HSW | BMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSP | 0.362 ** | |||
| 0.357 ** | ||||
| HSW | -0.005 | -0.049 | ||
| 0.149 | 0.125 | |||
| BMS | 0.403 ** | 0.190 * | 0.174 * | |
| 0.708 ** | 0.423 ** | 0.311 ** | ||
| YP | 0.950 ** | 0.409 ** | 0.163 | 0.425 ** |
| 0.914 ** | 0.464 ** | 0.318 ** | 0.701 ** |
表2 绿豆产量相关农艺性状的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis of yield-related agronomic traits in mungbean
| Traits | NPP | NSP | HSW | BMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSP | 0.362 ** | |||
| 0.357 ** | ||||
| HSW | -0.005 | -0.049 | ||
| 0.149 | 0.125 | |||
| BMS | 0.403 ** | 0.190 * | 0.174 * | |
| 0.708 ** | 0.423 ** | 0.311 ** | ||
| YP | 0.950 ** | 0.409 ** | 0.163 | 0.425 ** |
| 0.914 ** | 0.464 ** | 0.318 ** | 0.701 ** |
| Year | Traits | QTL name | Chromosome | Marker interval | Position (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) | Add effect | Phenotype variance explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | NPP | qNPP3 | 3 | ID3-8-ID3-9 | 30.60-31.34 | 3.47 | 4.62 | 11.09 |
| NSP | qNSP3 | 3 | ID3-5-ID3-6 | 13.16-23.40 | 5.92 | 0.58 | 17.93 | |
| HSW | qHSW3 | 3 | ID3-7-ID3-9 | 29.12-31.34 | 3.78 | 0.26 | 5.33 | |
| qHSW7 | 7 | ID7-10-ID7-7 | 100.12-103.50 | 23.15 | 0.71 | 46.07 | ||
| qHSW10 | 10 | ID10-3-ID10-4 | 6.84-9.08 | 2.90 | -0.09 | 4.24 | ||
| BMS | qBMS3 | 3 | ID3-8-ID3-9 | 30.60-31.34 | 6.44 | 1.03 | 18.51 | |
| qBMS11 | 11 | ID11-6-ID11-7 | 33.46-35.32 | 2.85 | 0.25 | 7.06 | ||
| YP | qYP3 | 3 | ID3-8-ID3-9 | 30.60-31.34 | 4.60 | 3.67 | 14.18 | |
| 2020 | NPP | qNPP3a | 3 | ID3-4-ID3-5 | 9.83-13.06 | 3.39 | 3.63 | 2.27 |
| NSP | qNSP3a | 3 | R3-9-R3-12 | 20.88-22.23 | 6.37 | 0.66 | 19.93 | |
| HSW | qHSW7a | 7 | ID7-10-ID7-7 | 29.77-31.76 | 8.80 | 0.42 | 30.17 |
表3 绿豆产量相关农艺性状的QTL分析
Table 3 QTL analysis for yield-related agronomic traits in mungbean
| Year | Traits | QTL name | Chromosome | Marker interval | Position (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) | Add effect | Phenotype variance explained (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | NPP | qNPP3 | 3 | ID3-8-ID3-9 | 30.60-31.34 | 3.47 | 4.62 | 11.09 |
| NSP | qNSP3 | 3 | ID3-5-ID3-6 | 13.16-23.40 | 5.92 | 0.58 | 17.93 | |
| HSW | qHSW3 | 3 | ID3-7-ID3-9 | 29.12-31.34 | 3.78 | 0.26 | 5.33 | |
| qHSW7 | 7 | ID7-10-ID7-7 | 100.12-103.50 | 23.15 | 0.71 | 46.07 | ||
| qHSW10 | 10 | ID10-3-ID10-4 | 6.84-9.08 | 2.90 | -0.09 | 4.24 | ||
| BMS | qBMS3 | 3 | ID3-8-ID3-9 | 30.60-31.34 | 6.44 | 1.03 | 18.51 | |
| qBMS11 | 11 | ID11-6-ID11-7 | 33.46-35.32 | 2.85 | 0.25 | 7.06 | ||
| YP | qYP3 | 3 | ID3-8-ID3-9 | 30.60-31.34 | 4.60 | 3.67 | 14.18 | |
| 2020 | NPP | qNPP3a | 3 | ID3-4-ID3-5 | 9.83-13.06 | 3.39 | 3.63 | 2.27 |
| NSP | qNSP3a | 3 | R3-9-R3-12 | 20.88-22.23 | 6.37 | 0.66 | 19.93 | |
| HSW | qHSW7a | 7 | ID7-10-ID7-7 | 29.77-31.76 | 8.80 | 0.42 | 30.17 |
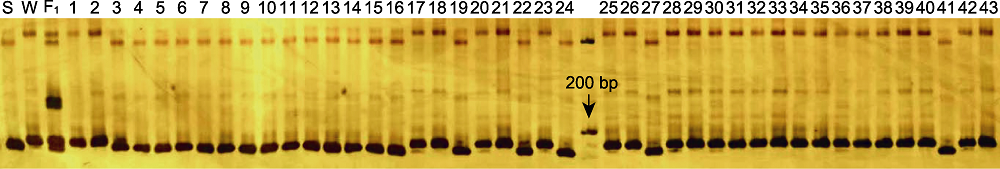
图3 利用标记R7-13.4分析绿豆资源的基因型 S: 苏绿16-10; W: 潍绿11。1-24为大粒型种质; 25-43为小粒型种质。
Figure 3 Genotype analysis for mungbean accessions using marker R7-13.4 S: Sulv16-10; W: Weilv11. 1-24 are accessions with large seed size; 25-43 are accessions with small seed size.
| No. | Variety name | HSW (g) | Genotype | No. | Variety name | HSW (g) | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baolv200520 | 7.13±0.21 | aa | 23 | Jilv0816 | 6.63±0.32 | aa |
| 2 | E1002 | 7.53±0.40 | aa | 24 | Sulv15-11 | 6.67±0.31 | AA |
| 3 | E1006 | 6.80±0.30 | AA | 25 | Bailv11 | 4.60±0.10 | aa |
| 4 | E1007 | 6.90±0.26 | AA | 26 | E1003 | 4.70±0.20 | aa |
| 5 | Elv3 | 7.13±0.31 | AA | 27 | Jinlv4 | 4.87±0.23 | AA |
| 6 | Jilv7 | 7.03±0.21 | AA | 28 | Jinlv6 | 4.30±0.10 | aa |
| 7 | Su2074 | 7.90±0.56 | AA | 29 | Lulv1002-3 | 4.83±0.15 | aa |
| 8 | Sukang4 | 7.03±0.23 | AA | 30 | Pinlv08116 | 4.67±0.15 | aa |
| 9 | Sukang1 | 7.37±0.25 | AA | 31 | Su09-8 | 4.37±0.31 | aa |
| 10 | Sulv016 | 7.13±0.31 | AA | 32 | Suhei2 | 4.30±0.00 | aa |
| 11 | Sulv023 | 7.07±0.35 | AA | 33 | Suheilv | 4.23±0.06 | aa |
| 12 | Sulv11-8 | 7.23±0.15 | AA | 34 | Sukang2 | 5.00±0.10 | aa |
| 13 | Sulv203 | 8.20±0.26 | AA | 35 | Taiyuan52 | 3.70±0.20 | aa |
| 14 | Sulv209 | 7.07±0.32 | AA | 36 | Taiyuanchuanfu | 4.73±0.15 | aa |
| 15 | Sulv4 | 8.23±0.64 | AA | 37 | Taiyuanzao2 | 5.00±0.36 | aa |
| 16 | Sulv9073 | 6.97±0.25 | AA | 38 | Tong1188326 | 3.80±0.26 | aa |
| 17 | Zhonglv1 | 7.27±0.35 | aa | 39 | Wei2117 | 4.60±0.44 | aa |
| 18 | Zhonglv3 | 6.90±0.44 | aa | 40 | Weilv12 | 4.80±0.35 | aa |
| 19 | Zhonglv5 | 6.87±0.45 | AA | 41 | Weilv2117 | 4.57±0.42 | AA |
| 20 | Baolv200810 | 6.53±0.58 | aa | 42 | Weilv8 | 4.93±0.23 | aa |
| 21 | E1009 | 6.63±0.40 | aa | 43 | Yinggelv | 4.57±0.15 | aa |
| 22 | E75-3 | 6.77±0.40 | AA |
表4 43份绿豆资源的表型和基因型
Table 4 Phenotype and genotype of 43 mungbean accessions
| No. | Variety name | HSW (g) | Genotype | No. | Variety name | HSW (g) | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baolv200520 | 7.13±0.21 | aa | 23 | Jilv0816 | 6.63±0.32 | aa |
| 2 | E1002 | 7.53±0.40 | aa | 24 | Sulv15-11 | 6.67±0.31 | AA |
| 3 | E1006 | 6.80±0.30 | AA | 25 | Bailv11 | 4.60±0.10 | aa |
| 4 | E1007 | 6.90±0.26 | AA | 26 | E1003 | 4.70±0.20 | aa |
| 5 | Elv3 | 7.13±0.31 | AA | 27 | Jinlv4 | 4.87±0.23 | AA |
| 6 | Jilv7 | 7.03±0.21 | AA | 28 | Jinlv6 | 4.30±0.10 | aa |
| 7 | Su2074 | 7.90±0.56 | AA | 29 | Lulv1002-3 | 4.83±0.15 | aa |
| 8 | Sukang4 | 7.03±0.23 | AA | 30 | Pinlv08116 | 4.67±0.15 | aa |
| 9 | Sukang1 | 7.37±0.25 | AA | 31 | Su09-8 | 4.37±0.31 | aa |
| 10 | Sulv016 | 7.13±0.31 | AA | 32 | Suhei2 | 4.30±0.00 | aa |
| 11 | Sulv023 | 7.07±0.35 | AA | 33 | Suheilv | 4.23±0.06 | aa |
| 12 | Sulv11-8 | 7.23±0.15 | AA | 34 | Sukang2 | 5.00±0.10 | aa |
| 13 | Sulv203 | 8.20±0.26 | AA | 35 | Taiyuan52 | 3.70±0.20 | aa |
| 14 | Sulv209 | 7.07±0.32 | AA | 36 | Taiyuanchuanfu | 4.73±0.15 | aa |
| 15 | Sulv4 | 8.23±0.64 | AA | 37 | Taiyuanzao2 | 5.00±0.36 | aa |
| 16 | Sulv9073 | 6.97±0.25 | AA | 38 | Tong1188326 | 3.80±0.26 | aa |
| 17 | Zhonglv1 | 7.27±0.35 | aa | 39 | Wei2117 | 4.60±0.44 | aa |
| 18 | Zhonglv3 | 6.90±0.44 | aa | 40 | Weilv12 | 4.80±0.35 | aa |
| 19 | Zhonglv5 | 6.87±0.45 | AA | 41 | Weilv2117 | 4.57±0.42 | AA |
| 20 | Baolv200810 | 6.53±0.58 | aa | 42 | Weilv8 | 4.93±0.23 | aa |
| 21 | E1009 | 6.63±0.40 | aa | 43 | Yinggelv | 4.57±0.15 | aa |
| 22 | E75-3 | 6.77±0.40 | AA |
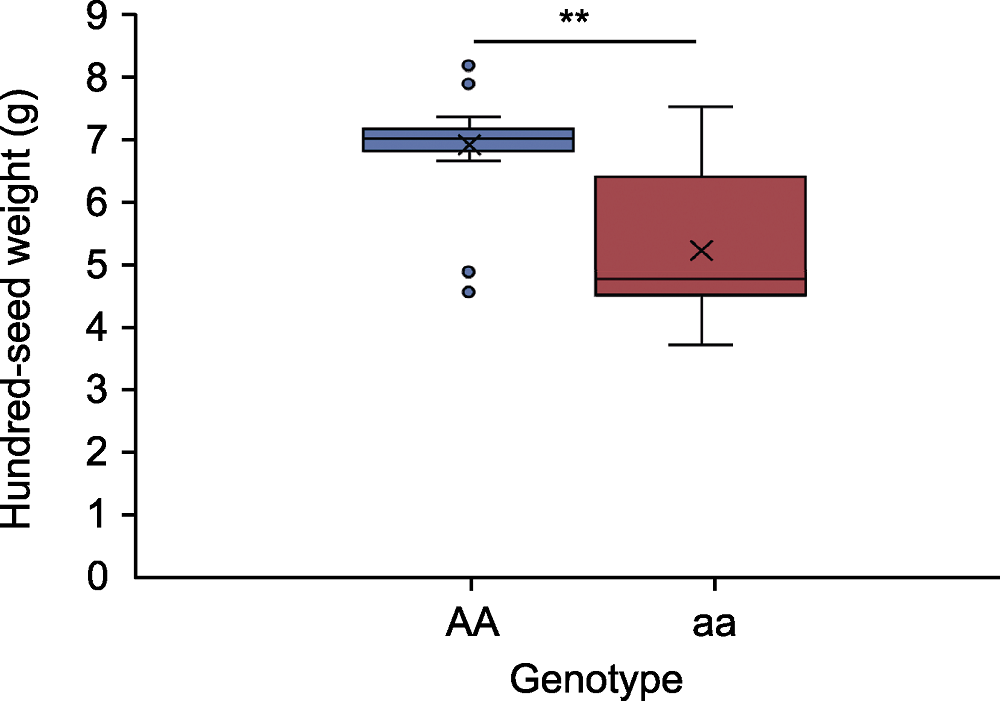
图4 43份绿豆资源基因型和表型统计分析 AA和aa分别代表苏绿16-10和潍绿11基因型。**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。
Figure 4 Statistical analysis of genotype and phenotype for 43 mungbean accessions AA and aa represent Sulv16-10 and Weilv11 genotype, respectively. ** indicates extremely significant difference (P<0.01).
| [1] | 陈红霖, 胡亮亮, 杨勇, 郝曦煜, 李姝彤, 王素华, 王丽侠, 程须珍 (2020). 481份国内外绿豆种质农艺性状及豆象抗性鉴定评价及遗传多样性分析. 植物遗传资源学报 21, 549-559. |
| [2] |
陈吉宝 (2020). 绿豆产量性状的QTL定位. 中国农业科技导报 22(10), 38-48.
DOI |
| [3] | 程须珍, 王素华, 王丽霞 (2006). 绿豆种质资源描述规范和数据标准. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 9-22. |
| [4] | 杜梦柯, 连文婷, 张晓, 李欣欣 (2021). 氮处理对大豆根瘤固氮能力及GmLbs基因表达的影响. 植物学报 56, 391-403. |
| [5] |
何恒斌, 贾桂霞 (2013). 豆科植物早期共生信号转导的研究进展. 植物学报 48, 665-675.
DOI |
| [6] | 侯小峰, 刘静, 王彩萍, 左联忠, 赵吉平, 郭鹏燕, 郭兆萍 (2015). 绿豆产量与主要农艺性状的灰色关联分析. 作物杂志 (1), 53-56. |
| [7] |
马秀杰 (2014). 间作对绿豆生物性状、产量和品质的影响. 核农学报 28, 546-551.
DOI |
| [8] | 梅丽, 程须珍, 王素华, 王丽侠, 蔡庆生, 刘春吉, 徐宁, 刘长友, 孙蕾 (2011). 绿豆产量相关农艺性状的QTL定位. 植物遗传资源学报 12, 948-956. |
| [9] | 王健康 (2009). 数量性状基因的完备区间作图方法. 作物学报 35, 239-245. |
| [10] | 王洁 (2020). 绿豆高密度遗传图谱构建及重要农艺性状QTL定位. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 22-26. |
| [11] | 徐东旭 (2015). 冀西北绿豆产量与主要农艺性状的灰色关联度分析. 农业科技通讯 (7), 96-98, 251. |
| [12] | 杨春玲, 王阔, 关立, 侯军红, 宋志均, 韩勇, 葛鹏飞 (2005). 绿豆主要农艺性状间的相关及通径分析. 杂粮作物 25, 314-315. |
| [13] | 杨芳, 杨媛, 冯高, 杨明君 (2012). 绿豆籽粒产量与主要农艺性状的相关分析. 农业科技通讯 (7), 95-97. |
| [14] | 杨勇, 周斌, 杨超华, 张丽亚 (2015). 夏播绿豆不同品种产量与主要农艺性状的相关分析. 作物杂志 (4), 65-68. |
| [15] | Alam MK, Islam MM, Salahin N, Hasanuzzaman M (2014). Effect of tillage practices on soil properties and crop productivity in wheat-mungbean-rice cropping system under subtropical climatic conditions. Sci World J 2014, 437283. |
| [16] |
Chankaew S, Somta P, Sorajjapinun W, Srinives P (2011). Quantitative trait loci mapping of Cercospora leaf spot resistance in mungbean, Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Mol Breeding 28, 255-264.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Chen HM, Ku HM, Schafleitner R, Bains TS, Kuo CG, Liu CA, Nair RM (2013). The major quantitative trait locus for mungbean yellow mosaic Indian virus resistance is tightly linked in repulsion phase to the major bruchid resistance locus in a cross between mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] and its wild relative Vigna radiata ssp. sublobata. Euphytica 192, 205-216. |
| [18] |
Chotechung S, Somta P, Chen JB, Yimram T, Chen X, Srinives P (2016). A gene encoding a polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) is a candidate gene for bruchid (Coleoptera: bruchidae) resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata). Theor Appl Genet 129, 1673-1683.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Fatokun CA, Menancio-Hautea DI, Danesh D, Young ND (1992). Evidence for orthologous seed weight genes in cowpea and mungbean based on RFLP mapping. Genetics 132, 841-846.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Ha J, Satyawan D, Jeong H, Lee E, Cho KH, Kim MY, Lee SH (2021). A near-complete genome sequence of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) provides key insights into the modern breeding program. Plant Genome 14, e20121. |
| [21] |
Humphry ME, Lambrides CJ, Chapman SC, Aitken EAB, Imrie BC, Lawn RJ, Mcintyre CL, Liu CJ (2005). Relationships between hard-seededness and seed weight in mungbean (Vigna radiata) assessed by QTL analysis. Plant Breeding 124, 292-298.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Humphry ME, Magner T, McIntyre CL, Aitken EAB, Liu CJ (2003). Identification of a major locus conferring resistance to powdery mildew (Erysiphe polygoni DC) in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) by QTL analysis. Genome 46, 738-744.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Isemura T, Kaga A, Tabata S, Somta P, Srinives P, Shimizu T, Jo U, Vaughan DA, Tomooka N (2012). Construction of a genetic linkage map and genetic analysis of domestication related traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata). PLoS One 7, e41304.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Kajonphol T, Sangsiri C, Somta P, Toojinda T, Srinives P (2012). SSR map construction and quantitative trait loci (QTL) identification of major agronomic traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek). SABRAO J Breed Genet 44, 71-86. |
| [25] |
Kang YJ, Kim SK, Kim MY, Lestari P, Kim KH, Ha BK, Jun TH, Hwang WJ, Lee T, Lee J, Shim S, Yoon MY, Jang YE, Han KS, Taeprayoon P, Yoon N, Somta P, Tanya P, Kim KS, Gwag JG, Moon JK, Lee YH, Park BS, Bombarely A, Doyle JJ, Jackson SA, Schafleitner R, Srinives P, Varshney RK, Lee SH (2014). Genome sequence of mungbean and insights into evolution within Vigna species. Nat Commun 5, 5443.
DOI |
| [26] |
Keatinge JDH, Easdown WJ, Yang RY, Chadha ML, Shanmugasundaram S (2011). Overcoming chronic malnutrition in a future warming world: the key importance of mungbean and vegetable soybean. Euphytica 180, 129-141.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Kim SK, Nair RM, Lee J, Lee SH (2015). Genomic resources in mungbean for future breeding programs. Front Plant Sci 6, 626.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Kitsanachandee R, Somta P, Chatchawankanphanich O, Akhtar KP, Shah TM, Nair RM, Bains TS, Sirari A, Kaur L, Srinives P (2013). Detection of quantitative trait loci for mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MYMIV) resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) in India and Pakistan. Breeding Sci 63, 367-373.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Mei L, Cheng XZ, Wang SH, Wang LX, Liu CY, Sun L, Xu N, Humphry ME, Lambrides CJ, Li HB, Liu CJ (2009). Relationship between bruchid resistance and seed mass in mungbean based on QTL analysis. Genome 52, 589-596.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Sompong U, Somta P, Raboy V, Srinives P (2012). Mapping of quantitative trait loci for phytic acid and phosphorus contents in seed and seedling of mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczed). Breed Sci 62, 87-92.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Somta P, Chankaew S, Kongjaimun A, Srinives P (2015). QTLs controlling seed weight and days to flowering in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek], their conservation in azuki bean [V. angularis (Ohwi) Ohwi & Ohashi] and rice bean [V. umbellata (Thunb.) Ohwi & Ohashi]. Agrivita 37, 159-168. |
| [32] |
Tuberosa R, Salvi S, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Maccaferri M, Conti S (2002). Mapping QTLs regulating morpho- physiological traits and yield: case studies, shortcomings and perspectives in drought-stressed maize. Ann Bot 89, 941-963.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Yaqub M, Mahmood T, Akhtar M, Iqbal MM, Ali S (2010). Induction of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] as a grain legume in the annual rice-wheat double cropping system. Pak J Bot 42, 3125-3135. |
| [34] |
Ye WJ, Yang Y, Wang PR, Zhang Y, Zhang LY, Tian DF, Zhang L, Zhang LL, Zhou B (2021). InDel marker development and QTL analysis of agronomic traits in mung- bean [Vigna radiate (L.) Wilczek]. Mol Breeding 41, 66.
DOI |
| [35] |
Yundaeng C, Somta P, Chen JB, Yuan XX, Chankaew S, Chen X (2021). Fine mapping of QTL conferring Cercospora leaf spot disease resistance in mungbean revealed TAF5 as candidate gene for the resistance. Theor Appl Genet 134, 701-714.
DOI |
| [36] |
Zhang MC, Wang DM, Zheng Z, Humphry M, Liu CJ (2008). Development of PCR-based markers for a major locus conferring powdery mildew resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata). Plant Breed 127, 429-432.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [2] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [3] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [4] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [5] | 金佳怡, 罗怿婷, 杨惠敏, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 谢继毅, 王珂欣, 陈芊羽, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻叶绿素含量QTL定位与候选基因表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 394-403. |
| [6] | 冯晓敏, 高翔, 臧华栋, 胡跃高, 任长忠, 郝志萍, 吕慧卿, 曾昭海. 燕麦-绿豆间作效应及氮素转移特性[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 122-131. |
| [7] | 魏和平, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 邓飞, 朱浩, 岂泽华, 王玉玺, 叶涵斐, 殷文晶, 方媛, 穆丹, 饶玉春. 水稻抽穗期QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 588-595. |
| [8] | 叶涵斐, 殷文晶, 管易安, 杨凯如, 陈芊羽, 俞淑颖, 朱旭东, 辛德东, 章薇, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻籽粒维生素E QTL挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 157-170. |
| [9] | 潘晨阳, 张月, 林晗, 陈芊羽, 杨凯如, 姜嘉骥, 李梦佳, 芦涛, 王珂欣, 路梅, 王盛, 叶涵斐, 饶玉春, 胡海涛. 水稻叶片水势的QTL定位与候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 275-283. |
| [10] | 潘晨阳, 叶涵斐, 周维永, 王盛, 李梦佳, 路梅, 李三峰, 朱旭东, 王跃星, 饶玉春, 戴高兴. 水稻籽粒镉积累QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 25-32. |
| [11] | 章怡兰, 林雪, 吴仪, 李梦佳, 张晟婕, 路梅, 饶玉春, 王跃星. 水稻根系遗传育种研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 382-393. |
| [12] | 王丽华, 薛晶月, 谢雨, 吴彦. 不同气候类型下四川草地土壤有机碳空间分布及影响因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 2018, 42(3): 297-306. |
| [13] | 姚炳楠, 陈报章, 车明亮. 鄱阳湖流域植被总初级生产力时空变化特征及其气候驱动因子分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 639-649. |
| [14] | 王迪, 李永祥, 王阳, 刘成, 刘志斋, 彭勃, 谭巍巍, 张岩, 孙宝成,石云素, 宋燕春, 王天宇, 黎裕. 控制玉米雄穗分枝数目和雄穗重的主效QTL的定位[J]. 植物学报, 2011, 46(1): 11-20. |
| [15] | 张现伟;杨莉;张涛;蒋开锋;王贵学;郑家奎;*;倪先林;田翠;曹应江. 水稻籽粒锌含量的QTL 定位[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(05): 594-600. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||