

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 342-353.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24047 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24047
赵凌1, 管菊1, 梁文化1, 张勇2, 路凯1, 赵春芳1, 李余生1, 张亚东1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-03-28
接受日期:2024-05-27
出版日期:2025-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-30
通讯作者:
*张亚东, 男, 汉族, 江苏省靖江人, 研究员, 硕士生导师。2001年6月本科毕业于扬州大学农学院; 2003年6月硕士研究生毕业于扬州大学作物遗传育种专业; 2014年6月博士研究生毕业于南京农业大学作物遗传育种专业。2003.08-至今在江苏省农业科学院粮食作物研究所工作, 从事水稻遗传育种研究。其中2003.08-2006.07任研究实习员, 2006.08-2012.08任助理研究员, 2012.09-2018.09任副研究员, 2018.10-至今任研究员。2014.08- 2015.12先后在美国密西西比州立大学、德州农工大学做访问学者, 从事作物科学研究。E-mail: zhangyd@jaas.ac.cn
基金资助:
Zhao Ling1, Guan Ju1, Liang Wenhua1, Zhang Yong2, Lu Kai1, Zhao Chunfang1, Li Yusheng1, Zhang Yadong1,*( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Accepted:2024-05-27
Online:2025-05-10
Published:2024-05-30
Contact:
*E-mail: zhangyd@jaas.ac.cn
摘要: 鉴定控制水稻(Oryza sativa)高温耐性的新位点和候选基因, 可为耐热遗传育种提供理论支撑, 具有重要的实践意义。利用粳稻(O. sativa subsp. japonica)品种TD70和籼稻(O. sativa subsp. indica)品种Kasalath衍生的重组自交系(RILs)群体为研究材料, 构建基于深度重测序的高密度Bin遗传图谱; 使用QTL IciMappingv软件基于完备复合区间作图法对水稻苗期高温胁迫下的幼苗存活率进行QTLs分析。共检测到26个控制苗期耐热性QTLs, 分布在除第3号染色体外的11条染色体上, LOD值为2.59-16.15, 其中4个QTLs的LOD值大于10, 7个QTLs与已知高温耐性QTLs的位置存在重叠或者部分重叠, 其主效QTL位点qHTSR5.2位于第5号染色体26.25-26.38 Mb区间, LOD值为16.15, 解释7.18%的表型贡献率。对4个主效QTLs区间进行基因功能注释和亲本间序列分析, 共发现27个注释有功能且在2个亲本间编码区存在非同义突变的基因。根据候选基因SNP的类型对RILs群体家系进行基因等位型分类和效应分析, 发现5个基因不同等位型的RILs群体家系高温处理后的幼苗存活率存在显著差异, 推测可能为候选基因, 可用于后续水稻高温耐性的分子机理研究。
赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353.
Zhao Ling, Guan Ju, Liang Wenhua, Zhang Yong, Lu Kai, Zhao Chunfang, Li Yusheng, Zhang Yadong. Mapping of QTLs for Heat Tolerance at the Seedling Stage in Rice Based on a High-density Bin Map. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(3): 342-353.
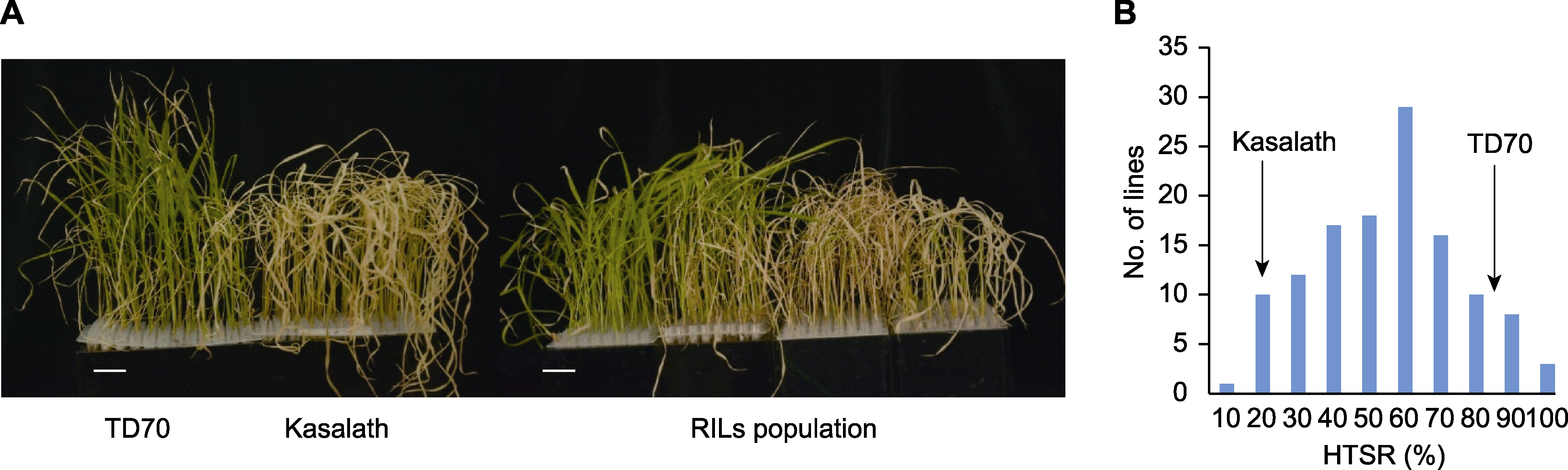

图1 亲本和重组自交系(RIL)群体的苗期耐热性 (A) 亲本和部分RILs群体的苗期耐热性表现(bars=2 cm); (B) RILs群体高温幼苗存活率的表型分布。HTSR: 高温幼苗存活率
Figure 1 Heat tolerance of parents and some recombinant inbred lines (RILs) during the seedling stage (A) Heat tolerance of parents and RILs population during seedling stage (bars=2 cm); (B) Distribution of high-temperature seedling survival rates in the RILs. HTSR: High-temperature seedling survival rate
| QTL | Chr. | Interval (Mb) | Genes | Annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qHTSR1.1 | 1 | 1.90-1.95 | Os01g0134800* | Glycosyl hydrolase family | |
| Os01g0134900* | Glycosyl hydrolase family | ||||
| Os01g0135000 | Similar to 1,4-beta-D xylan xylanohydrolase | ||||
| Os01g0135700* | OsCML16, calmodulin, calcium signaling during abiotic stress | Yang et al., | |||
| Os01g0135800* | HSP20, heat shock protein | ||||
| Os01g0135900* | HSP20, heat shock protein | Sarkar et al., | |||
| Os01g0136000* | OsHSP16.9C, HSP17.5 heat shock protein | Sarkar et al., | |||
| Os01g0136050 | 16.9 kDa heat shock protein | ||||
| qHTSR4.1 | 4 | 15.72-15.92 | Os04g0336600 | Peptidase aspartic, catalytic domain containing protein | |
| Os04g0337000* | Aspartyl protease domain containing protein | ||||
| Os04g0337201* | SAD2, sensitive to ABA and drought2 | ||||
| Os04g0337300 | SAD2, sensitive to ABA and drought2 | ||||
| Os04g0337500 | Oxidoreductase | ||||
| Os04g0337800* | IN2-2 protein | ||||
| Os04g0338000* | Aldo/keto reductase family protein | Kim et al., | |||
| qHTSR5.1 | 5 | 20.41-20.48 | Os05g0417000* | DUF260 domain containing protein | |
| Os05g0417100* | Deg Protease Protein, chloroplast development and maintenance of PSII function under high temperatures | Zheng et al., | |||
| Os05g0417800* | ulp1 protease family | ||||
| qHTSR5.2 | 5 | 26.25-26.39 | Os05g0418000* | GDP-dissociation inhibitor | Shad et al., |
| Os05g0528500 | OsWRKY58, WRKY transcription factor | ||||
| Os05g0528600 | OsYUCCA2, flavin monooxygenase-like enzyme, auxin biosynthesis | Yamamoto et al., | |||
| Os05g0528900 | Ribosomal protein | ||||
| Os05g0529000* | OsCOLE1, regulation of intracellular auxin transport | Liu et al., | |||
| Os05g0529200 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family protein | ||||
| Os05g0529300 | ER lumen protein retaining receptor | ||||
| Os05g0529400* | Ubiquitin domain-containing protein | ||||
| Os05g0529600* | ATP binding protein | ||||
| Os05g0529700 | Electron transporter/heat shock protein binding protein | ||||
| Os05g0529900 | Cell cycle control protein, OsHsfA4d; Heat stress transcription factor | Mittal et al., | |||
| Os05g0530400* | Plant growth and balancing reactive oxygen species du- ring biotic and abiotic stress | ||||
| Os05g0530500 | Snf1 protein kinase; sucrose non-fermenting-1 related protein kinase 1 | Kanegae et al., | |||
| Os05g0530701 | Leucine-rich repeat | ||||
| Os05g0531000* | A member of S40 gene family, regulation of crosstalk among abiotic and biotic and developmental senescence | ||||
| Os05g0531100 | A member of S40 gene family, regulation of crosstalk among abiotic and biotic and developmental senescence | ||||
| Os05g0531200 | Pollen Ole e I allergen and extensin family protein precursor | ||||
| Os05g0531400 | Pollen Ole e I allergen and extensin family protein precursor | ||||
| Os05g0531500 | Hydrolase |
表1 主效QTL区间内基因的注释
Table 1 Annotated genes within the interval of major QTLs
| QTL | Chr. | Interval (Mb) | Genes | Annotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qHTSR1.1 | 1 | 1.90-1.95 | Os01g0134800* | Glycosyl hydrolase family | |
| Os01g0134900* | Glycosyl hydrolase family | ||||
| Os01g0135000 | Similar to 1,4-beta-D xylan xylanohydrolase | ||||
| Os01g0135700* | OsCML16, calmodulin, calcium signaling during abiotic stress | Yang et al., | |||
| Os01g0135800* | HSP20, heat shock protein | ||||
| Os01g0135900* | HSP20, heat shock protein | Sarkar et al., | |||
| Os01g0136000* | OsHSP16.9C, HSP17.5 heat shock protein | Sarkar et al., | |||
| Os01g0136050 | 16.9 kDa heat shock protein | ||||
| qHTSR4.1 | 4 | 15.72-15.92 | Os04g0336600 | Peptidase aspartic, catalytic domain containing protein | |
| Os04g0337000* | Aspartyl protease domain containing protein | ||||
| Os04g0337201* | SAD2, sensitive to ABA and drought2 | ||||
| Os04g0337300 | SAD2, sensitive to ABA and drought2 | ||||
| Os04g0337500 | Oxidoreductase | ||||
| Os04g0337800* | IN2-2 protein | ||||
| Os04g0338000* | Aldo/keto reductase family protein | Kim et al., | |||
| qHTSR5.1 | 5 | 20.41-20.48 | Os05g0417000* | DUF260 domain containing protein | |
| Os05g0417100* | Deg Protease Protein, chloroplast development and maintenance of PSII function under high temperatures | Zheng et al., | |||
| Os05g0417800* | ulp1 protease family | ||||
| qHTSR5.2 | 5 | 26.25-26.39 | Os05g0418000* | GDP-dissociation inhibitor | Shad et al., |
| Os05g0528500 | OsWRKY58, WRKY transcription factor | ||||
| Os05g0528600 | OsYUCCA2, flavin monooxygenase-like enzyme, auxin biosynthesis | Yamamoto et al., | |||
| Os05g0528900 | Ribosomal protein | ||||
| Os05g0529000* | OsCOLE1, regulation of intracellular auxin transport | Liu et al., | |||
| Os05g0529200 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase/isomerase family protein | ||||
| Os05g0529300 | ER lumen protein retaining receptor | ||||
| Os05g0529400* | Ubiquitin domain-containing protein | ||||
| Os05g0529600* | ATP binding protein | ||||
| Os05g0529700 | Electron transporter/heat shock protein binding protein | ||||
| Os05g0529900 | Cell cycle control protein, OsHsfA4d; Heat stress transcription factor | Mittal et al., | |||
| Os05g0530400* | Plant growth and balancing reactive oxygen species du- ring biotic and abiotic stress | ||||
| Os05g0530500 | Snf1 protein kinase; sucrose non-fermenting-1 related protein kinase 1 | Kanegae et al., | |||
| Os05g0530701 | Leucine-rich repeat | ||||
| Os05g0531000* | A member of S40 gene family, regulation of crosstalk among abiotic and biotic and developmental senescence | ||||
| Os05g0531100 | A member of S40 gene family, regulation of crosstalk among abiotic and biotic and developmental senescence | ||||
| Os05g0531200 | Pollen Ole e I allergen and extensin family protein precursor | ||||
| Os05g0531400 | Pollen Ole e I allergen and extensin family protein precursor | ||||
| Os05g0531500 | Hydrolase |
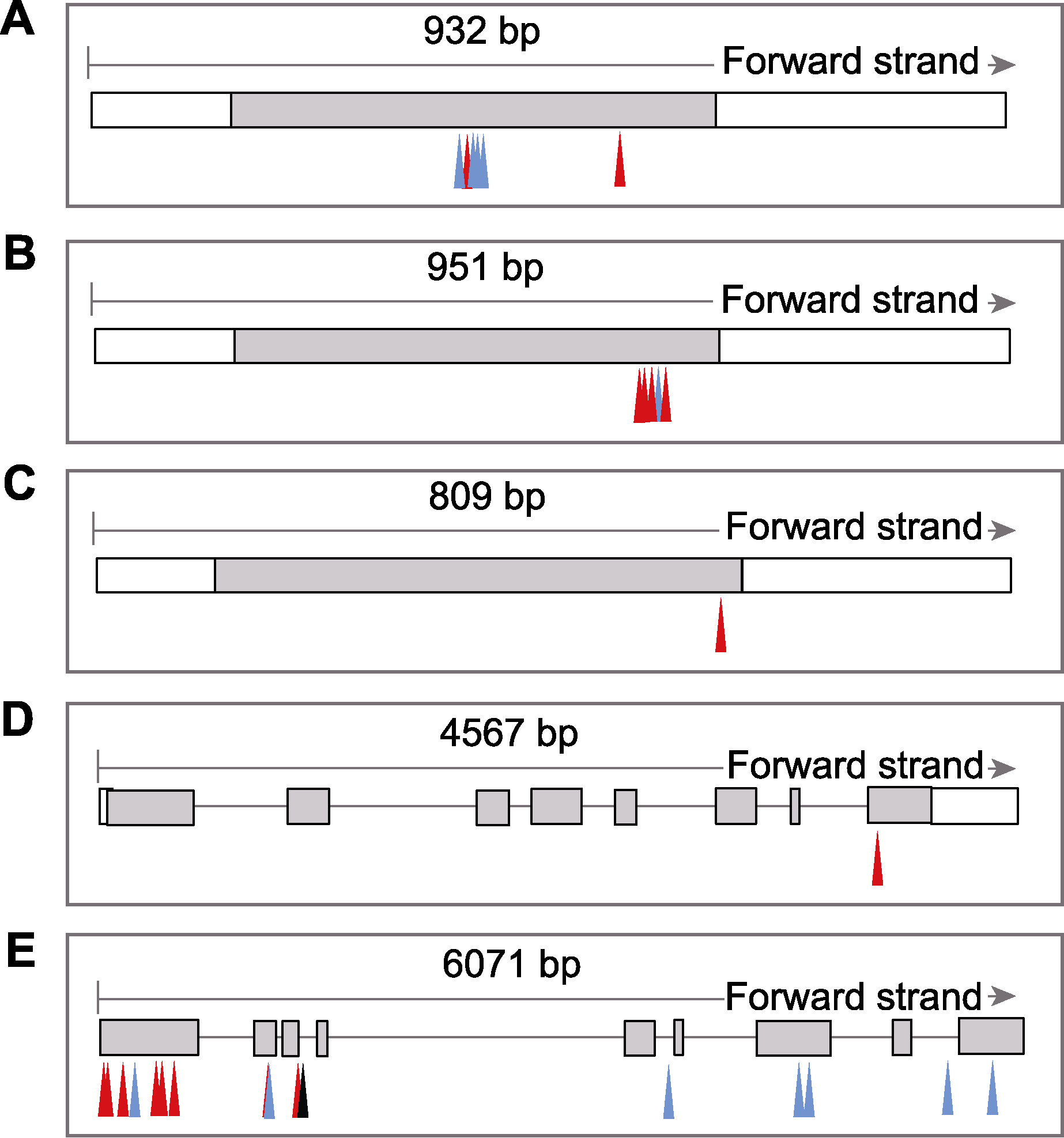
图3 TD70与Kasalath之间5个候选基因的结构和非同义突变 (A) LOC_Os01g04340; (B) LOC_Os01g04350; (C) LOC_ Os01g04360; (D) LOC_Os05g34460; (E) LOC_Os05g34520。黑色框: 外显子; 灰色部分: 蛋白编码序列; 红色箭头: 错义突变; 蓝色箭头: 移码突变; 黑色箭头: 同义突变
Figure 3 Gene structure and non-synonymous mutation of five candidate genes between TD70 and Kasalath (A) LOC_Os01g04340; (B) LOC_Os01g04350; (C) LOC_Os01g04360; (D) LOC_Os05g34460; (E) LOC_Os05g34520. Frames with black lines: Exon; Grey boxes: Protein coding sequence; Red arrow: Missense mutation; Blue arrow: Frameshift mutation; Black arrow: Synonymous mutation
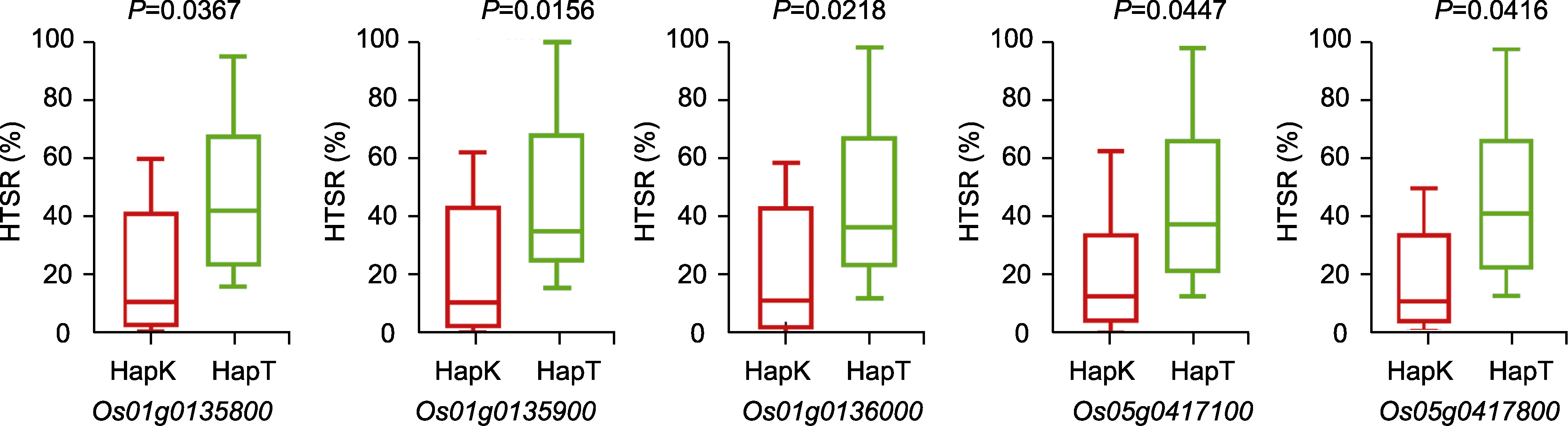
图4 候选基因不同等位型对重组自交系(RILs)群体高温幼苗存活率(HTSR)的影响 HapT: SNP位点核苷酸为TD70型; HapK: SNP位点核苷酸为Kasalath型。HTSR同图1。
Figure 4 Effects of different Haps of candidate genes on the HTSR of recombinant inbred lines (RILs) HapT: The SNP of the candidate genes are the same as those in TD70; HapK: The SNP of the candidate genes are the same as those in Kasalath. HTSR is the same as shown in Figure 1.
| QTL | This study | Known QTLs or genes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr. | Position (Mb) | Population | Traits | Position (Mb) | Reference | |
| qHTSR1.1 | 1 | 1.90-1.95 | Nipponbare/Kasalath backcross inbred lines (BILs) | HT during grain filling | 0.64-3.44 | 朱昌兰等, |
| Teqin/Yuanjiang Common Wild Rice BILs | HT at flowering stage | 0.38-2.18 | 奎丽梅等, | |||
| N22/IR64 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) | Shoot length under heat stress | 1.86-2.31 | Kilasi et al., | |||
| qHTSR1.2 | 1 | 39.82-39.86 | Longdao 5/Zhongyouzao 8RILs | HTSR | 37.6-39.08 | 刘进等, |
| Bala/Azucena RILs | HT at flowering stage | 38.35-40.66 | Jagadish et al., | |||
| qHTSR2.2 | 2 | 24.58-24.72 | 255 core materials | HTSR | 24.66 | 魏昭然, |
| qHTSR4.1 | 4 | 15.71-15.92 | 996/4628 RILs | HT at flowering stage | 15.74-18.82 | Xiao et al., |
| Bala/Azucena RILs | HT at flowering stage | 14.19-16.86 | Jagadish et al., | |||
| qHTSR 5.2 | 5 | 26.25-26.39 | Zhongyouzao 8/Fengjin RILs | HT at flowering stage | 3.08-26.85 | 张涛等, |
| Longdao 5/Zhongyouzao 8 RILs | HTSR | 25.78-26.28 | 刘进等, | |||
| R498/R3551 RILs | HT at flowering stage | 26.69-27.69 | 陶磊, | |||
| qHTSR9.1 | 9 | 9.42-9.46 | Nipponbare/Kasalath bils | Thermo-tolerance of amylose content | 5.27-21.85 | 朱昌兰等, |
| qHTSR10 | 10 | 22.57-22.63 | Bala/Azucena RILs | HT at flowering stage | 20.84-23.45 | Jagadish et al., |
| 233 core materials | HT during grain filling | 22.62 | 杨飞, | |||
| Sasanishiki/Habataki CSSLs | Pollen fertility under high temperature | 19.89-23.01 | Zhu et al., | |||
表2 本研究定位的QTL和已知耐热性相关位点的位置比较
Table 2 Overlap of known QTLs contributing to heat resistance with the QTLs detected in this study
| QTL | This study | Known QTLs or genes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chr. | Position (Mb) | Population | Traits | Position (Mb) | Reference | |
| qHTSR1.1 | 1 | 1.90-1.95 | Nipponbare/Kasalath backcross inbred lines (BILs) | HT during grain filling | 0.64-3.44 | 朱昌兰等, |
| Teqin/Yuanjiang Common Wild Rice BILs | HT at flowering stage | 0.38-2.18 | 奎丽梅等, | |||
| N22/IR64 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) | Shoot length under heat stress | 1.86-2.31 | Kilasi et al., | |||
| qHTSR1.2 | 1 | 39.82-39.86 | Longdao 5/Zhongyouzao 8RILs | HTSR | 37.6-39.08 | 刘进等, |
| Bala/Azucena RILs | HT at flowering stage | 38.35-40.66 | Jagadish et al., | |||
| qHTSR2.2 | 2 | 24.58-24.72 | 255 core materials | HTSR | 24.66 | 魏昭然, |
| qHTSR4.1 | 4 | 15.71-15.92 | 996/4628 RILs | HT at flowering stage | 15.74-18.82 | Xiao et al., |
| Bala/Azucena RILs | HT at flowering stage | 14.19-16.86 | Jagadish et al., | |||
| qHTSR 5.2 | 5 | 26.25-26.39 | Zhongyouzao 8/Fengjin RILs | HT at flowering stage | 3.08-26.85 | 张涛等, |
| Longdao 5/Zhongyouzao 8 RILs | HTSR | 25.78-26.28 | 刘进等, | |||
| R498/R3551 RILs | HT at flowering stage | 26.69-27.69 | 陶磊, | |||
| qHTSR9.1 | 9 | 9.42-9.46 | Nipponbare/Kasalath bils | Thermo-tolerance of amylose content | 5.27-21.85 | 朱昌兰等, |
| qHTSR10 | 10 | 22.57-22.63 | Bala/Azucena RILs | HT at flowering stage | 20.84-23.45 | Jagadish et al., |
| 233 core materials | HT during grain filling | 22.62 | 杨飞, | |||
| Sasanishiki/Habataki CSSLs | Pollen fertility under high temperature | 19.89-23.01 | Zhu et al., | |||
| [1] |
曹志斌, 李瑶, 曾博虹, 毛凌华, 蔡耀辉, 吴晓峰, 袁林峰 (2020). 非洲栽培稻垩白粒率耐热性QTL的定位. 中国水稻科学 34, 135-142.
DOI |
| [2] | 郭虹霞, 王创云, 赵丽, 王陆军, 张丽光, 邓妍 (2019). 水稻中2个小分子热激蛋白基因启动子的序列分析及功能鉴定. 西北农业学报 28, 1079-1086. |
| [3] |
郝立生, 马宁, 何丽烨 (2022). 2022年长江中下游夏季异常干旱高温事件之环流异常特征. 干旱气象 40, 721-732.
DOI |
| [4] |
胡时开, 钱前 (2016). RNA解旋酶调控rRNA内稳态: 水稻耐热新机制、分子育种新资源. 植物学报 51, 283-286.
DOI |
| [5] | 阚义, 林鸿宣 (2022). 水稻高温感知及响应机制的研究进展. 自然杂志 44, 411-421. |
| [6] | 奎丽梅, 谭禄宾, 涂建, 卢义宣, 孙传清 (2008). 云南元江野生稻抽穗开花期耐热QTL定位. 农业生物技术学报 16, 461-464. |
| [7] | 李林浩 (2023). 基于Meta-QTL和RNA-seq的整合分析挖掘水稻持续耐高温候选基因. 硕士论文. 荆州: 长江大学. pp. 26-30. |
| [8] |
栗振义, 龙瑞才, 张铁军, 杨青川, 康俊梅 (2016). 植物热激蛋白研究进展. 生物技术通报 32(2), 7-13.
DOI |
| [9] | 刘进, 崔迪, 余丽琴, 张立娜, 周慧颖, 马小定, 胡佳晓, 韩冰, 韩龙植, 黎毛毛 (2022a). 水稻苗期耐热种质资源筛选及QTL定位. 中国水稻科学 36, 259-268. |
| [10] | 刘进, 胡佳晓, 马小定, 陈武, 勒思, Sumin J, 崔迪, 周慧颖, 张立娜, Dongjin S, 黎毛毛, 韩龙植, 余丽琴 (2022b). 水稻RIL群体高密度遗传图谱的构建及苗期耐热性QTL定位. 中国农业科学 55, 4327-4341. |
| [11] | 盘毅, 陈立云, 肖应辉 (2008). 水稻耐热遗传育种及热激蛋白的研究综述. 作物研究 22(S1), 363-367. |
| [12] |
盘毅, 罗丽华, 邓化冰, 张桂莲, 唐文邦, 陈立云, 肖应辉 (2011). 水稻开花期高温胁迫下的花粉育性QTL定位. 中国水稻科学 25, 99-102.
DOI |
| [13] |
沈泓, 姚栋萍, 吴俊, 罗秋红, 吴志鹏, 雷东阳, 邓启云, 柏斌 (2022). 灌浆期不同时段高温对稻米淀粉理化特性的影响. 中国水稻科学 36, 377-387.
DOI |
| [14] |
宋有金, 吴超, 李子煜, 唐设, 李刚华, 王绍华, 丁艳锋 (2021). 水稻产量对生殖生长阶段不同时期高温的响应差异. 中国水稻科学 35, 177-186.
DOI |
| [15] | 陶磊 (2020). 水稻开花期耐高温QTL分析及精细定位. 硕士论文. 成都: 四川农业大学. pp. 25-27. |
| [16] |
王建康 (2009). 数量性状基因的完备区间作图方法. 作物学报 35, 239-245.
DOI |
| [17] | 魏昭然 (2020). 水稻苗期高温关键候选位点鉴定. 硕士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 21-23. |
| [18] | 杨飞 (2020). 水稻灌浆期耐热性及主要农艺性状的全基因组关联分析. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 27-29. |
| [19] |
杨军, 章毅之, 贺浩华, 李迎春, 陈小荣, 边建民, 金国花, 李翔翔, 黄淑娥 (2020). 水稻高温热害的研究现状与进展. 应用生态学报 31, 2817-2830.
DOI |
| [20] | 杨梯丰, 刘斌 (2009). 水稻耐热性QTL鉴定的研究进展. 广东农业科学 (6), 16-20. |
| [21] | 俞佳虹, 冯坤, 程远, 叶青静, 阮美颖, 王荣青, 李志邈, 周国治, 姚祝平, 魏家香, 杨悦俭, 万红建 (2017). 植物小热激蛋白的研究进展. 分子植物育种 15, 3016-3023. |
| [22] | 张涛, 杨莉, 蒋开锋, 黄敏, 孙群, 陈温福, 郑家奎 (2008). 水稻抽穗扬花期耐热性的QTL分析. 分子植物育种 6, 867-873. |
| [23] |
张亚东, 梁文化, 赫磊, 赵春芳, 朱镇, 陈涛, 赵庆勇, 赵凌, 姚姝, 周丽慧, 路凯, 王才林 (2021). 水稻RIL群体高密度遗传图谱构建及粒型QTL定位. 中国农业科学 54, 5163-5176.
DOI |
| [24] |
赵凌, 张勇, 魏晓东, 梁文化, 赵春芳, 周丽慧, 姚姝, 王才林, 张亚东 (2022). 利用高密度Bin图谱定位水稻抽穗期剑叶叶绿素含量QTL. 中国农业科学 55, 825-836.
DOI |
| [25] | 朱昌兰, 江玲, 张文伟, 王春明, 翟虎渠, 万建民 (2006). 稻米直链淀粉含量和胶稠度对高温耐性的QTL分析. 中国水稻科学 20, 248-252. |
| [26] | 朱昌兰, 肖应辉, 王春明, 江玲, 翟虎渠, 万建民 (2005). 水稻灌浆期耐热害的数量性状基因位点分析. 中国水稻科学 19, 117-121. |
| [27] |
Bauer D, Meinhold S, Jakob RP, Stigler J, Merkel U, Maier T, Rief M, Žoldák G (2018). A folding nucleus and minimal ATP binding domain of HSP70 identified by single-molecule force spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 4666-4671.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Cao ZB, Li Y, Tang HW, Zeng BH, Tang XY, Long QZ, Wu XF, Cai YH, Yuan LF, Wan JL (2020). Fine mapping of the qHTB1-1 QTL, which confers heat tolerance at the booting stage, using an Oryza rufipogon Griff. introgression line. Theor Appl Genet 133, 1161-1175. |
| [29] | Chen L, Wang Q, Tang MY, Zhang XL, Pan YH, Yang XH, Gao GQ, Lv RH, Tao W, Jiang LG, Liang TF (2021). QTL mapping and identification of candidate genes for heat tolerance at the flowering stage in rice. Front Genet 11, 621871. |
| [30] | Chen XG, Chen S (2018). China feels the heat: negative impacts of high temperatures on China's rice sector. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 62, 576-588. |
| [31] | Haq ul S, Khan A, Ali M, Khattak AM, Gai WX, Zhang HX, Wei AM, Gong ZH (2019). Heat shock proteins: dynamic biomolecules to counter plant biotic and abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 20, 5321. |
| [32] | IPCC (2021). Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 199-200. |
| [33] |
Jacob P, Hirt H, Bendahmane A (2017). The heat-shock protein/chaperone network and multiple stress resistance. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 405-414.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Jagadish SVK, Cairns J, Lafitte R, Wheeler TR, Price AH, Craufurd PQ (2010). Genetic analysis of heat tolerance at anthesis in rice. Crop Sci 50, 1633-1641. |
| [35] |
Kan Y, Mu XR, Zhang H, Gao J, Han JX, Ye WW, Lin HX (2022). TT2 controls rice thermotolerance through SCT1- dependent alteration of wax biosynthesis. Nat Plants 8, 53-67.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Kanegae H, Miyoshi K, Hirose T, Tsuchimoto S, Mori M, Nagato Y, Takano M (2005). Expressions of rice sucrose non-fermenting-1 related protein kinase 1 genes are differently regulated during the caryopsis development. Plant Physiol Biochem 43, 669-679. |
| [37] | Khan S, Anwar S, Ashraf MY, Khaliq B, Sun M, Hussain S, Gao ZQ, Noor H, Alam S (2019). Mechanisms and adaptation strategies to improve heat tolerance in rice. Plants 8, 508. |
| [38] | Kilasi NL, Singh J, Vallejos CE, Ye CR, Jagadish SVK, Kusolwa P, Rathinasabapathi B (2018). Heat stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.): identification of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for seedling growth under heat stress. Front Plant Sci 9, 1578. |
| [39] | Kim JH, Lim SD, Jang CS (2019). Oryza sativa heat-induced RING finger protein 1 (OsHIRP1) positively regulates plant response to heat stress. Plant Mol Biol 99, 545-559. |
| [40] |
Lee BH, Won SH, Lee HS, Miyao M, Chung WI, Kim IJ, Jo J (2000). Expression of the chloroplast-localized small heat shock protein by oxidative stress in rice. Gene 245, 283-290.
PMID |
| [41] | Li XM, Chao DY, Wu Y, Huang XH, Chen K, Cui LG, Su L, Ye WW, Chen H, Chen HC, Dong NQ, Guo T, Shi M, Feng Q, Zhang P, Han B, Shan JX, Gao JP, Lin HX (2015). Natural alleles of a proteasome α2 subunit gene contribute to thermotolerance and adaptation of African rice. Nat Genet 47, 827-833. |
| [42] | Liu F, Zhang L, Luo YZ, Xu MY, Fan YL, Wang L (2016a). Interactions of Oryza sativa OsCONTINUOUS VASCULAR RING-LIKE 1 (OsCOLE1) and OsCOLE1-INTERACTING PROTEIN reveal a novel intracellular auxin transport mechanism. New Phytol 212, 96-107. |
| [43] | Liu JP, Zhang CC, Wei CC, Liu X, Wang MG, Yu FF, Xie Q, Tu JM (2016b). The RING finger ubiquitin E3 ligase OsHTAS enhances heat tolerance by promoting H2O2-induced stomatal closure in rice. Plant Physiol 170, 429-443. |
| [44] | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| [45] |
Meng L, Li HH, Zhang LY, Wang JK (2015). QTL ICIMAPPING: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3, 269-283.
DOI |
| [46] | Mittal D, Chakrabarti S, Sarkar A, Singh A, Grover A (2009). Heat shock factor gene family in rice: genomic organization and transcript expression profiling in response to high temperature, low temperature and oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 47, 785-795. |
| [47] | Murakami T, Matsuba S, Funatsuki H, Kawaguchi K, Saruyama H, Tanida M, Sato Y (2004). Over-expression of a small heat shock protein, sHSP17.7, confers both heat tolerance and UV-B resistance to rice plants. Mol Breed 13, 165-175. |
| [48] | Murthy VS, Ravishankar KV (2016). Molecular mechanisms of heat shock proteins and thermotolerance in plants. In: SrinivasaRao NK, ShivashankaraKS, LaxmanRH, Abiotic Stress Physiology of Horticultural Crops.eds. New Delhi: Springer. pp. 71-83. |
| [49] |
Sarkar NK, Kim YK, Grover A (2009). Rice sHsp genes: genomic organization and expression profiling under stress and development. BMC Genomics 10, 393.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Sarkar NK, Kotak S, Agarwal M, Kim YK, Grover A (2020). Silencing of class I small heat shock proteins affects seed-related attributes and thermotolerance in rice seedlings. Planta 251, 26. |
| [51] | Shad MA, Wang YX, Zhang H, Zhai SS, Shalmani A, Li YB (2023). Genetic analysis of GEFs and GDIs in rice reveals the roles of OsGEF5, OsGDI1, and OsGEF3 in the regulation of grain size and plant height. Crop J 11, 345-360. |
| [52] | Siddique M, Gernhard S, von Koskull-Döring P, Vierling E, Scharf KD (2008). The plant sHSP superfamily: five new members in Arabidopsis thaliana with unexpected properties. Cell Stress Chaperones 13, 183-197. |
| [53] | Wang D, Qin BX, Li X, Tang D, Zhang YE, Cheng ZK, Xue YB (2016). Nucleolar DEAD-Box RNA helicase TOGR1 regulates thermos tolerant growth as a Pre-rRNA chaperone in rice. PLoS Genet 12, e1005844. |
| [54] | Xiao YH, Pan Y, Luo LH, Zhang GL, Deng HB, Dai LY, Liu XL, Tang WB, Chen LY, Wang GL (2011). Quantitative trait loci associated with seed set under high temperature stress at the flowering stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 178, 331-338. |
| [55] |
Yamamoto Y, Kamiya N, Morinaka Y, Matsuoka M, Sazuka T (2007). Auxin biosynthesis by the YUCCA genes in rice. Plant Physiol 143, 1362-1371.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Yang J, Ji LX, Zhu BH, Yuan XJ, Jin DM, Xie GS (2018). OsCML16 interacts with a novel CC-NBS-LRR protein OsPi304 in the Ca2+/Mg2+dependent and independent manner in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 504, 346-351. |
| [57] |
Zhang KM, Ezemaduka AN, Wang Z, Hu HL, Shi XD, Liu C, Lu XP, Fu XM, Chang ZY, Yin CC (2015). A novel mechanism for small heat shock proteins to function as molecular chaperones. Sci Rep 5, 8811.
DOI PMID |
| [58] | Zhang Y, Zou BH, Lu S, Ding Y, Liu H, Hua J (2016). Expression and promoter analysis of the OsHSP16.9C gene in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 479, 260-265. |
| [59] | Zheng KL, Zhao J, Lin DZ, Chen JY, Xu JL, Zhou H, Teng S, Dong YJ (2016). The rice TCM5 gene encoding a novel Deg protease protein is essential for chloroplast development under high temperatures. Rice 9, 13. |
| [60] | Zhu S, Huang RL, Wai HP, Xiong HL, Shen XH, He HH, Yan S (2017). Mapping quantitative trait loci for heat tolerance at the booting stage using chromosomal segment substitution lines in rice. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23, 817-825. |
| [1] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张蓉菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [2] | 陈钧, 徐江民, 周逸楠, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 金芊芸, 赵蓓蓓, 朱哲楠, 徐雨青, 张璐怡, 刘笑妍, 刘隽, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻白叶枯病抗性QTL的挖掘与候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [3] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [4] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [5] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [6] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [7] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [8] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [9] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [10] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [11] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [12] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [13] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [14] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [15] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||