

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 831-845.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25059 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25059
陈钧1,†, 徐江民1,†, 周逸楠1, 江亚楠1, 胡程翔1, 金芊芸1, 赵蓓蓓1, 朱哲楠1, 徐雨青1, 张璐怡1, 刘笑妍1, 刘隽1, 李三峰2, 王跃星2,*( ), 饶玉春1,*(
), 饶玉春1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2025-04-08
接受日期:2025-06-03
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-06-10
通讯作者:
*饶玉春, 博士/博士后, 教授, 博士生导师, “双龙学者”特聘教授, 浙江省“高校领军人才培养计划”高层次拔尖人才(2022年), 金华市青年拔尖人才(2023年), 浙江省发明协会理事、植物遗传专业委员会副主任, 中国作物学会会员, 浙江省遗传学会会员。主要从事水稻等禾谷类作物的分子遗传学研究。以第一作者或通讯作者身份在Science Bulletin和New Phytologist等权威期刊发表论文80余篇, 以合作者身份在Nature Plants、Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America等杂志发表论文30余篇。主持转基因国家重大专项子课题、国家自然科学基金和浙江省自然科学基金等科研项目。授权国家发明专利25项(第一完成人)。ryc@zjnu.cn
王跃星, 博士, 研究员, 博士生导师, 中国水稻研究所超级稻育种创新团队首席科学家, 国家水稻改良中心副主任。入选国家高层次人才青年拔尖人才、浙江省高层次人才青年拔尖人才和“151”第二层次人才培养工程以及中国农业科学院“农科英才”杰出青年英才。主要从事水稻遗传育种工作, 已完成一系列水稻重要农艺性状基因的克隆和育种利用。以第一作者在Nature Genetics和Molecular Plant等国际著名期刊发表论文多篇。主持国家自然科学基金、浙江省自然科学基金杰出青年基金等项目。以第一或主要完成人选育水稻优质不育系和杂交水稻新品种7个, 获植物新品种权5项, 授权国家发明专利8项。荣获中国农学会青年科技奖。E-mail: wangyuexing@caas.cn
作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Chen Jun1,†, Xu Jiangmin1,†, Zhou Yinan1, Jiang Yanan1, Hu Chengxiang1, Jin Qianyun1, Zhao Beibei1, Zhu Zhenan1, Xu Yuqing1, Zhang Luyi1, Liu Xiaoyan1, Liu Jun1, Li Sanfeng2, Wang Yuexing2,*( ), Rao Yuchun1,*(
), Rao Yuchun1,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-08
Accepted:2025-06-03
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-06-10
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)白叶枯病是危害全球水稻生产的三大主要病害之一, 严重影响水稻的产量和品质。抗性基因的挖掘与利用是防治白叶枯病最有效的途径之一。为挖掘水稻白叶枯病抗性相关的数量性状位点(QTL), 以籼稻华占、粳稻热研2号及其构建的120个重组自交系(RILs)群体为实验材料, 在水稻分蘖盛期接种4种不同的白叶枯病致病小种并评价抗性表型。基于前期构建的高密度遗传图谱进行QTL定位, 共检测到19个QTLs, 其中最大LOD值为5.49。对检测到的QTL区间内候选基因进行筛选, 并利用qRT-PCR进行基因表达水平分析, 发现LOC_Os02g13270、LOC_Os02g13410、LOC_Os02g13420、LOC_Os02g13430和LOC_Os01g12130在双亲间的表达量差异显著, 且在接种白叶枯病菌后受诱导表达, 推测其为调控白叶枯病抗性的重点候选基因。研究结果为白叶枯病抗性相关基因的精细定位和克隆奠定了基础, 对于培育广谱抗病水稻品种有重要意义。
陈钧, 徐江民, 周逸楠, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 金芊芸, 赵蓓蓓, 朱哲楠, 徐雨青, 张璐怡, 刘笑妍, 刘隽, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻白叶枯病抗性QTL的挖掘与候选基因分析. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 831-845.
Chen Jun, Xu Jiangmin, Zhou Yinan, Jiang Yanan, Hu Chengxiang, Jin Qianyun, Zhao Beibei, Zhu Zhenan, Xu Yuqing, Zhang Luyi, Liu Xiaoyan, Liu Jun, Li Sanfeng, Wang Yuexing, Rao Yuchun. Identification of Candidate Genes for Rice Resistance to Bacterial Blight via QTL Mapping and Gene Expression Analysis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 831-845.
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin | TGGCATCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA |
| LOC_Os02g13270 | TGGCCATTTCCTCCATAAAG | TTGGTATCCTTCTTCCCTTTGA |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | AATGTCCATCGCACTGTTCA | GCTGCTTCAATCTCGGACTC |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | TCAATTATCCGGCAGACTCC | TGCCTGTGCTACTGATCCTG |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | TGCTCAGCTTTGGAGTTCCT | CCCAACGATAGCCTGTCAAT |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | CCGATGAGTGATGTTCTCCA | CGCTATGTGTTCCGCTATGA |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | TAATGGTACCAAGGGGGTGA | GAAGGCGATTCGTTGGATAA |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | AGCCCGACTTCAAGCTAACA | ATGGATTCATTGGCATGGTT |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | AATGGTGCTACCCGTTCTTG | CCGTGCGTATGAAACAGAAA |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | CATCGCCTACTTCGAGTTCA | CATGCATGATGAGGACGAAC |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | AGGTCCCGGAAAATACCACT | ATGGCATGAAGCCAATCATC |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | TGGTGAAGGAGGAGGTTGTC | TAGCTCCAGGTCAGGCATCT |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsActin | TGGCATCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA |
| LOC_Os02g13270 | TGGCCATTTCCTCCATAAAG | TTGGTATCCTTCTTCCCTTTGA |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | AATGTCCATCGCACTGTTCA | GCTGCTTCAATCTCGGACTC |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | TCAATTATCCGGCAGACTCC | TGCCTGTGCTACTGATCCTG |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | TGCTCAGCTTTGGAGTTCCT | CCCAACGATAGCCTGTCAAT |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | CCGATGAGTGATGTTCTCCA | CGCTATGTGTTCCGCTATGA |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | TAATGGTACCAAGGGGGTGA | GAAGGCGATTCGTTGGATAA |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | AGCCCGACTTCAAGCTAACA | ATGGATTCATTGGCATGGTT |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | AATGGTGCTACCCGTTCTTG | CCGTGCGTATGAAACAGAAA |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | CATCGCCTACTTCGAGTTCA | CATGCATGATGAGGACGAAC |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | AGGTCCCGGAAAATACCACT | ATGGCATGAAGCCAATCATC |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | TGGTGAAGGAGGAGGTTGTC | TAGCTCCAGGTCAGGCATCT |
| Race | Significance test for all traits between their parents (t-test) | Variation for all traits tested in the RILs population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | Nekken2 | P value | Means±SD | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
| P6 | 32.57±1.92 | 19.25±1.78 | 5.66E-08 | 22.01±7.71 | 0.50-46.83 | 0.33 | 1.54 |
| P10 | 4.08±0.58 | 2.92±0.38 | 2.11E-03 | 4.43±2.47 | 0.50-17.08 | 2.27 | 7.93 |
| C5 | 21.50±2.49 | 10.63±2.59 | 1.59E-04 | 14.89±5.98 | 0.45-32.40 | 0.19 | 0.62 |
| T1 | 11.83±1.29 | 15.25±1.51 | 1.78E-03 | 12.03±6.61 | 0.60-30.25 | 0.47 | -0.42 |
表2 各致病小种在水稻亲本及重组自交系(RILs)群体间的致病性情况
Table 2 Presentation of pathogenicity of pathogenic races in parents and recombinant inbred lines (RILs) population of rice
| Race | Significance test for all traits between their parents (t-test) | Variation for all traits tested in the RILs population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | Nekken2 | P value | Means±SD | Range | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
| P6 | 32.57±1.92 | 19.25±1.78 | 5.66E-08 | 22.01±7.71 | 0.50-46.83 | 0.33 | 1.54 |
| P10 | 4.08±0.58 | 2.92±0.38 | 2.11E-03 | 4.43±2.47 | 0.50-17.08 | 2.27 | 7.93 |
| C5 | 21.50±2.49 | 10.63±2.59 | 1.59E-04 | 14.89±5.98 | 0.45-32.40 | 0.19 | 0.62 |
| T1 | 11.83±1.29 | 15.25±1.51 | 1.78E-03 | 12.03±6.61 | 0.60-30.25 | 0.47 | -0.42 |
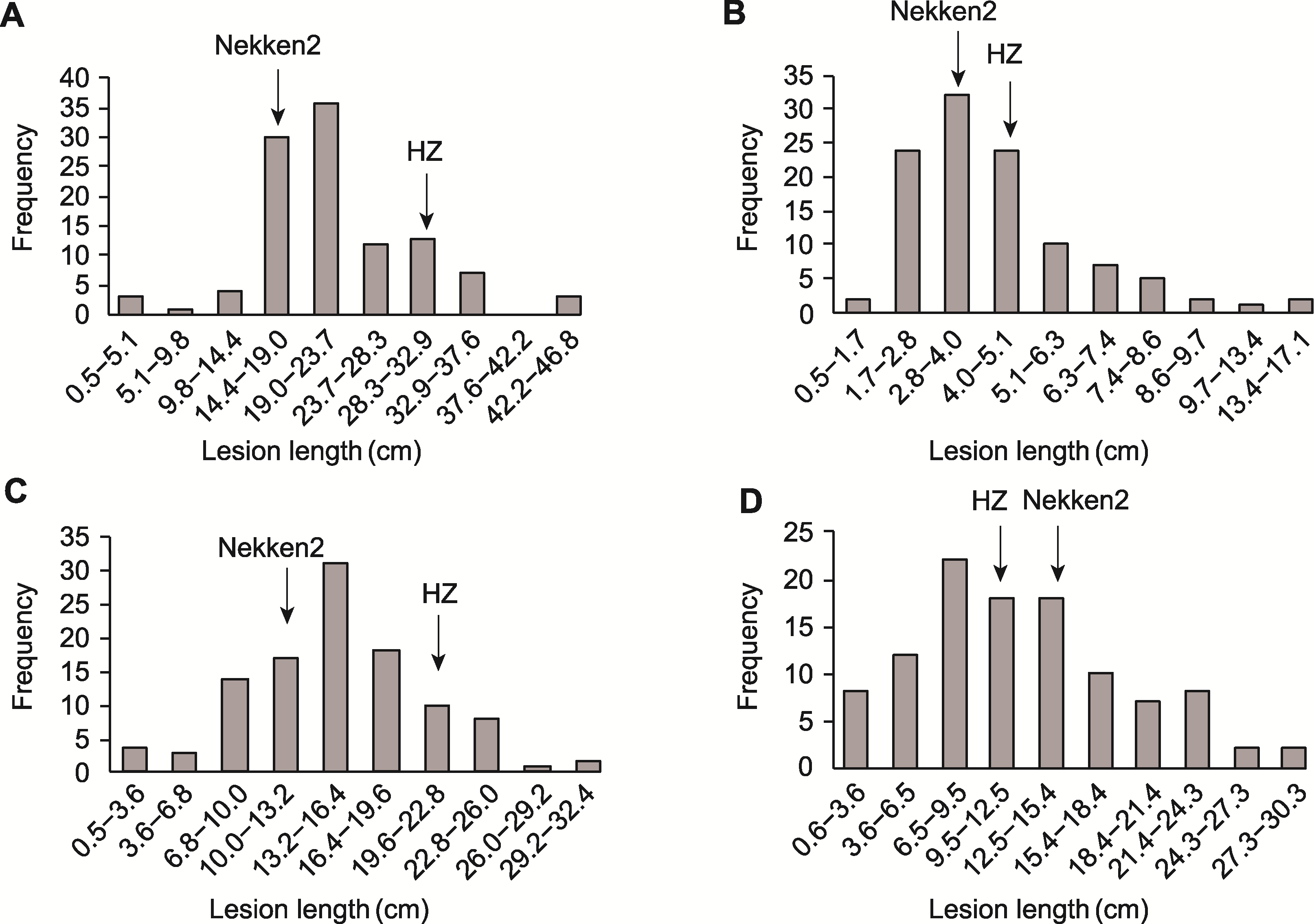
图1 各致病小种病斑长度在水稻重组自交系(RILs)群体中的分布 (A) P6; (B) P10; (C) C5; (D) T1
Figure 1 Distribution of lesion length generated by each race in recombinant inbred lines (RILs) population (A) P6; (B) P10; (C) C5; (D) T1
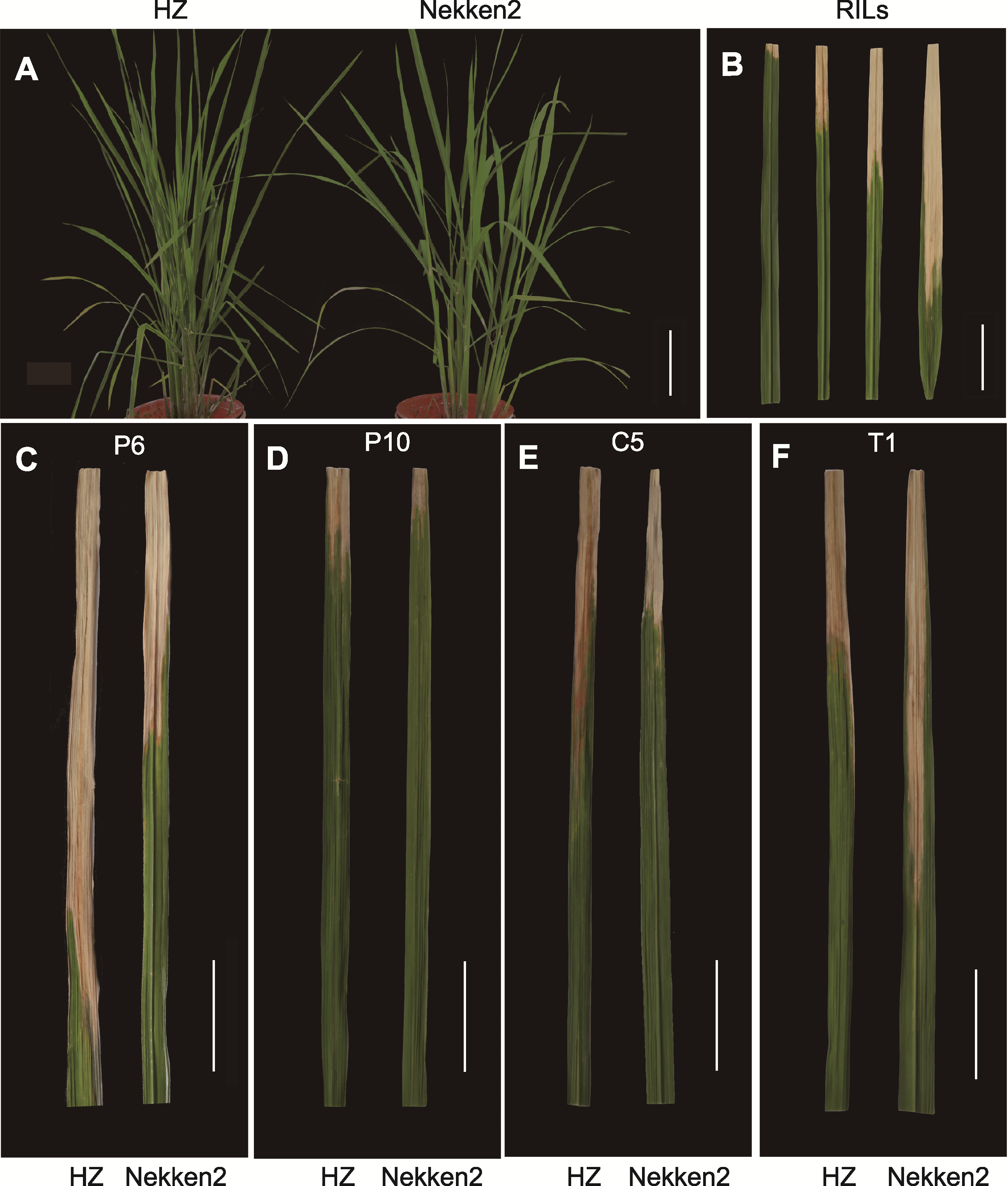

图2 水稻亲本及其重组自交系(RILs)群体表型 (A) 分蘖盛期父本华占与母本热研2号表型(bar=10 cm); (B) RILs群体中白叶枯病抗性水平对比(病斑长度小于5 cm为高抗病, 病斑长度在5-10 cm为中等抗病, 病斑长度在10-15 cm为中等感病, 病斑长度超过15 cm为感病, bar=5 cm); (C)-(F) 分蘖盛期华占与热研2号受4种白叶枯病小种(P6、P10、C5和T1)侵染后的病斑表型(bars=5 cm)
Figure 2 Phenotypes of rice parents and their recombinant inbred lines (RILs) population (A) The phenotypes of male parent HZ and maternal Nekken2 at full tillering stage (bar=10 cm); (B) Comparison of resistance levels of white leaf blight in RILs population (spot length less than 5 cm was high disease resistance, spot length between 5 cm and 10 cm was medium disease resistance, spot length between 10 cm and 15 cm was medium disease susceptibility, and more than 15 cm was susceptible, bar=5 cm); (C)-(F) Spot phenotypes of HZ and Nekken2 at the peak of tilling stage after infection by 4 types of bacterial leaf blight races (P6, P10, C5, and T1) (bars=5 cm)
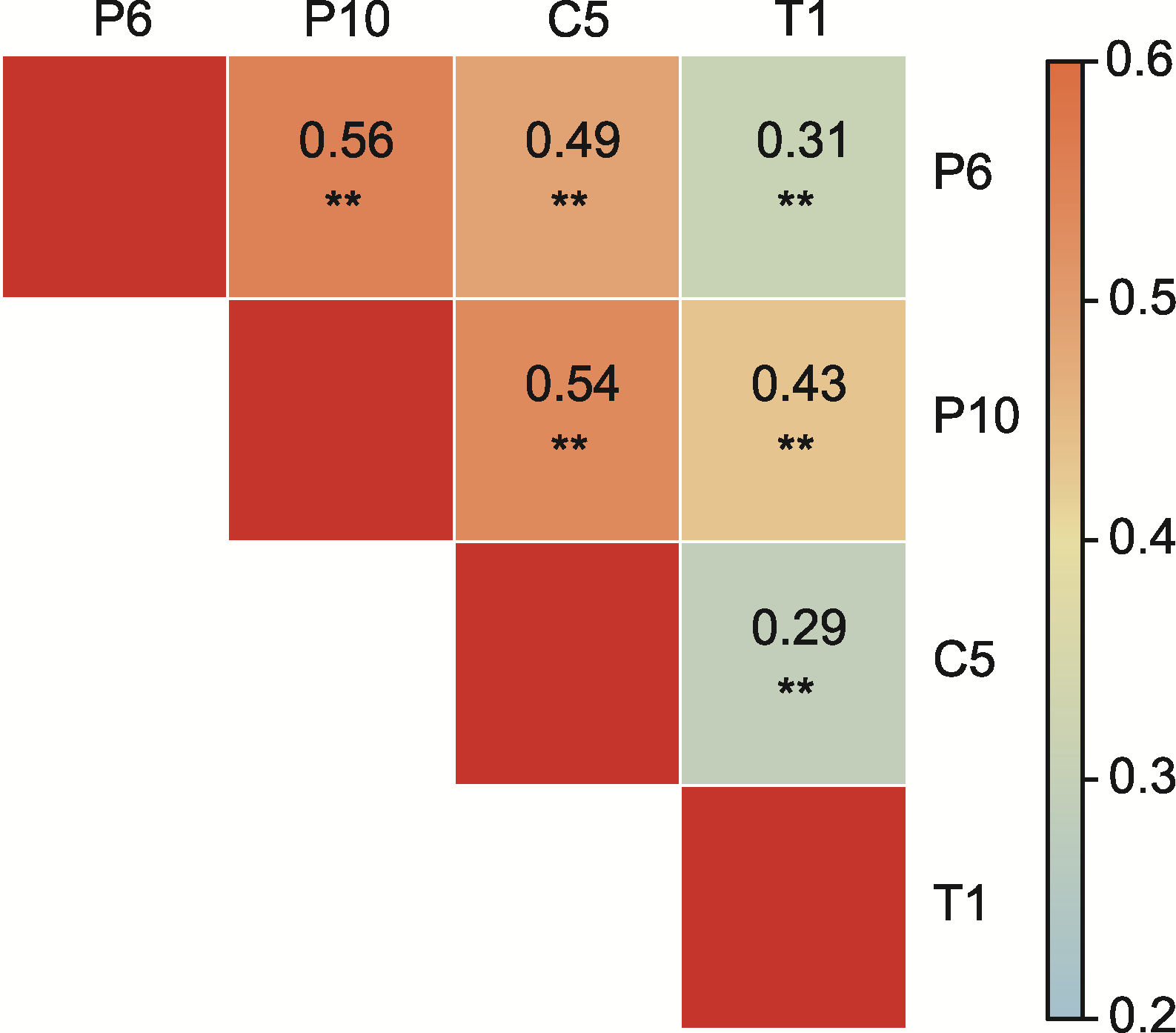
图3 重组自交系(RILs)群体中各致病小种致病相关性分析 ** 1%显著性水平
Figure 3 Correlation analysis of pathogenicity of each pathogenic race in recombinant inbred lines (RILs) population ** 1% significant level
| Race | QTL locus | Chromo- some | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection | Overlapped with known genes/QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P6 | qP6-2 | 2 | 6987519-7215671 | 29.95-30.93 | 2.82 | Novel |
| qP6-6 | 6 | 22540408-24198880 | 96.62-103.73 | 2.10 | Xa27 (Gu et al., | |
| P10 | qP10-4.1 | 4 | 46622-253174 | 0.20-1.09 | 4.09 | Novel |
| qP10-4.2 | 4 | 21662809-22843728 | 92.86-97.92 | 4.12 | OsABA1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-4.3 | 4 | 26889242-31662274 | 115.27-135.73 | 5.49 | Xa1 (Yoshimura et al., | |
| qP10-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.17 | Novel | |
| qP10-8 | 8 | 27210008-27435407 | 116.64-117.66 | 2.34 | OsPDR1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-9 | 9 | 11237877-11654883 | 48.17-49.96 | 2.50 | Novel | |
| qP10-11 | 11 | 4880924-5893190 | 20.92-25.26 | 3.23 | Novel | |
| qP10-12.1 | 12 | 3541703-5035843 | 15.18-21.59 | 3.52 | OsSGS3a (Gu et al., | |
| qP10-12.2 | 12 | 9212254-11302449 | 39.49-48.45 | 3.47 | ELL1 (Tian et al., | |
| C5 | qC5-1 | 1 | 6568005-6737416 | 28.16-28.88 | 2.41 | Novel |
| qC5-8 | 8 | 26765295-26912750 | 114.74-115.37 | 2.58 | Xa-45(t) (Neelam et al., | |
| T1 | qT1-1.1 | 1 | 2317764-2649258 | 9.94-11.36 | 2.25 | Novel |
| qT1-1.2 | 1 | 5747788-6006625 | 24.64-25.75 | 2.17 | TUT1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qT1-3 | 3 | 28465343-29876347 | 122.02-128.07 | 2.24 | Xa11 (Goto et al., | |
| qT1-4 | 4 | 23759183-23831009 | 101.85-102.16 | 2.48 | Novel | |
| qT1-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.51 | Novel | |
| qT1-12 | 12 | 19717421-19889567 | 84.52-85.26 | 2.12 | OsPR10a (Huang et al., |
表3 水稻白叶枯病抗性QTL分析
Table 3 QTL analysis of rice resistance to bacterial blight
| Race | QTL locus | Chromo- some | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection | Overlapped with known genes/QTL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P6 | qP6-2 | 2 | 6987519-7215671 | 29.95-30.93 | 2.82 | Novel |
| qP6-6 | 6 | 22540408-24198880 | 96.62-103.73 | 2.10 | Xa27 (Gu et al., | |
| P10 | qP10-4.1 | 4 | 46622-253174 | 0.20-1.09 | 4.09 | Novel |
| qP10-4.2 | 4 | 21662809-22843728 | 92.86-97.92 | 4.12 | OsABA1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-4.3 | 4 | 26889242-31662274 | 115.27-135.73 | 5.49 | Xa1 (Yoshimura et al., | |
| qP10-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.17 | Novel | |
| qP10-8 | 8 | 27210008-27435407 | 116.64-117.66 | 2.34 | OsPDR1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qP10-9 | 9 | 11237877-11654883 | 48.17-49.96 | 2.50 | Novel | |
| qP10-11 | 11 | 4880924-5893190 | 20.92-25.26 | 3.23 | Novel | |
| qP10-12.1 | 12 | 3541703-5035843 | 15.18-21.59 | 3.52 | OsSGS3a (Gu et al., | |
| qP10-12.2 | 12 | 9212254-11302449 | 39.49-48.45 | 3.47 | ELL1 (Tian et al., | |
| C5 | qC5-1 | 1 | 6568005-6737416 | 28.16-28.88 | 2.41 | Novel |
| qC5-8 | 8 | 26765295-26912750 | 114.74-115.37 | 2.58 | Xa-45(t) (Neelam et al., | |
| T1 | qT1-1.1 | 1 | 2317764-2649258 | 9.94-11.36 | 2.25 | Novel |
| qT1-1.2 | 1 | 5747788-6006625 | 24.64-25.75 | 2.17 | TUT1 (Zhang et al., | |
| qT1-3 | 3 | 28465343-29876347 | 122.02-128.07 | 2.24 | Xa11 (Goto et al., | |
| qT1-4 | 4 | 23759183-23831009 | 101.85-102.16 | 2.48 | Novel | |
| qT1-5 | 5 | 5860546-5932385 | 25.12-25.43 | 2.51 | Novel | |
| qT1-12 | 12 | 19717421-19889567 | 84.52-85.26 | 2.12 | OsPR10a (Huang et al., |
| QTL locus | Chromosome | Gene ID | Functional annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| qP6-2 | 2 | LOC_Os02g13270 | Mpv17/PMP22 family domain containing protein |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | NUDIX family | ||
| LOC_Os02g13410 | Leucine-rich repeat family protein | ||
| LOC_Os02g13420 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase EXS precursor | ||
| LOC_Os02g13430 | Receptor-like protein kinase 5 precursor | ||
| qP10-4.1 | 4 | LOC_Os04g01310 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor | ||
| qC5-1 | 1 | LOC_Os01g12130 | Enodulin MtN3 family protein |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | Ndole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | ||
| LOC_Os01g12320 | GDSL-like lipase/acylhydrolase | ||
| qT1-5 | 5 | LOC_Os05g10690 | Myb transcription factor |
表4 水稻白叶枯病抗性相关候选基因的功能
Table 4 The function of candidate genes associated with resistance of rice bacterial blight
| QTL locus | Chromosome | Gene ID | Functional annotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| qP6-2 | 2 | LOC_Os02g13270 | Mpv17/PMP22 family domain containing protein |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | NUDIX family | ||
| LOC_Os02g13410 | Leucine-rich repeat family protein | ||
| LOC_Os02g13420 | Leucine-rich repeat receptor protein kinase EXS precursor | ||
| LOC_Os02g13430 | Receptor-like protein kinase 5 precursor | ||
| qP10-4.1 | 4 | LOC_Os04g01310 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor precursor | ||
| qC5-1 | 1 | LOC_Os01g12130 | Enodulin MtN3 family protein |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | Ndole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | ||
| LOC_Os01g12320 | GDSL-like lipase/acylhydrolase | ||
| qT1-5 | 5 | LOC_Os05g10690 | Myb transcription factor |
| Gene ID | Length (bp) | Number of amino acids (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instabiliy index | Grand average of hydropathicity | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g13270 | 3105 | 205 | 23.61 | 10.47 | 55.17 | -0.063 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | 2612 | 297 | 32.69 | 5.47 | 44.45 | 0.056 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | 2761 | 508 | 57.34 | 8.05 | 51.52 | -0.406 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | 3070 | 611 | 66.79 | 5.75 | 29.68 | 0.077 | Extracellular |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | 3541 | 1004 | 110.39 | 5.21 | 38.88 | -0.049 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | 2758 | 828 | 91.62 | 6.01 | 40.39 | -0.016 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | 2927 | 813 | 90.71 | 6.15 | 43.94 | -0.170 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | 1563 | 252 | 28.17 | 9.25 | 36.00 | 0.538 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | 5501 | 591 | 64.19 | 5.90 | 39.85 | -0.059 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | 3688 | 379 | 40.97 | 5.13 | 41.35 | 0.061 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | 3818 | 287 | 30.46 | 9.35 | 64.91 | -0.298 | Mitochondrial |
表5 水稻白叶枯病抗性相关候选基因信息
Table 5 Information of candidate genes associated with resistance of rice bacterial blight
| Gene ID | Length (bp) | Number of amino acids (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical pI | Instabiliy index | Grand average of hydropathicity | Subcellular location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g13270 | 3105 | 205 | 23.61 | 10.47 | 55.17 | -0.063 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os02g13350 | 2612 | 297 | 32.69 | 5.47 | 44.45 | 0.056 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13410 | 2761 | 508 | 57.34 | 8.05 | 51.52 | -0.406 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os02g13420 | 3070 | 611 | 66.79 | 5.75 | 29.68 | 0.077 | Extracellular |
| LOC_Os02g13430 | 3541 | 1004 | 110.39 | 5.21 | 38.88 | -0.049 | Nuclear |
| LOC_Os04g01310 | 2758 | 828 | 91.62 | 6.01 | 40.39 | -0.016 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os04g01320 | 2927 | 813 | 90.71 | 6.15 | 43.94 | -0.170 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12130 | 1563 | 252 | 28.17 | 9.25 | 36.00 | 0.538 | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| LOC_Os01g12160 | 5501 | 591 | 64.19 | 5.90 | 39.85 | -0.059 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os01g12320 | 3688 | 379 | 40.97 | 5.13 | 41.35 | 0.061 | Cytoplasmic |
| LOC_Os05g10690 | 3818 | 287 | 30.46 | 9.35 | 64.91 | -0.298 | Mitochondrial |
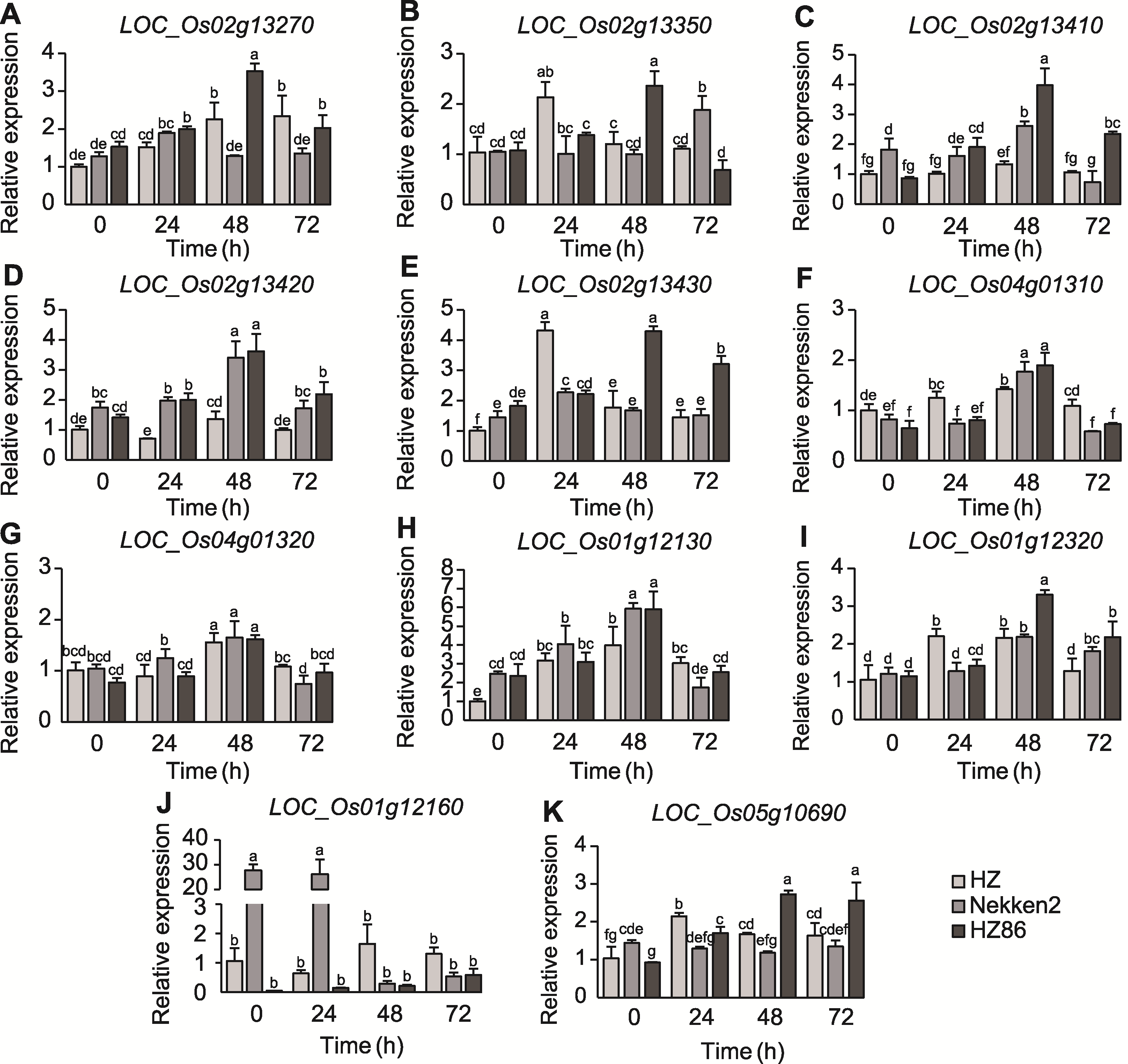
图5 白叶枯病抗性候选基因表达差异 不同小写字母表示基因表达在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 5 Differences in the expression of candidate genes for resistance to bacterial blight Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in gene expression at the 0.05 level.
| [1] | Antony G, Zhou JH, Huang S, Li T, Liu B, White F, Yang B (2010). Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 22, 3864-3876. |
| [2] | Bao SY, Tan MP, Lin XH (2010). Genetic mapping of a bacterial blight resistance gene Xa14 in rice. Acta Agron Sin 36, 422-427. (in Chinese) |
|
鲍思元, 谭明谱, 林兴华 (2010). 水稻抗白叶枯病基因Xa14的遗传定位. 作物学报 36, 422-427.
DOI |
|
| [3] | Bhasin H, Bhatia D, Raghuvanshi S, Lore JS, Sahi GK, Kaur B, Vikal Y, Singh K (2012). New PCR-based sequence-tagged site marker for bacterial blight resistance gene Xa38 of rice. Mol Breeding 30, 607-611. |
| [4] |
Bogdanove AJ, Schornack S, Lahaye T (2010). TAL effectors: finding plant genes for disease and defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13, 394-401.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chen XF, Liu PC, Mei L, He XL, Chen L, Liu H, Shen SR, Ji ZD, Zheng XX, Zhang YC, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Ma BJ (2021). Xa7, a new executor R gene that confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Commun 2, 100143. |
| [6] |
De Vleesschauwer D, Seifi HS, Filipe O, Haeck A, Huu SN, Demeestere K, Höfte M (2016). The DELLA protein SLR1 integrates and amplifies salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-dependent innate immunity in rice. Plant Physiol 170, 1831-1847.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Goto T, Matsumoto T, Furuya N, Tsuchiya K, Yoshimura A (2009). Mapping of bacterial blight resistance gene Xa11 on rice chromosome 3. Japan Agric Res Quart 43, 221-225. |
| [8] |
Gu K, Tian D, Yang F, Wu L, Sreekala C, Wang D, Wang GL, Yin Z (2004). High-resolution genetic mapping of Xa27(t), a new bacterial blight resistance gene in rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor Appl Genet 108, 800-807.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Gu KY, Yang B, Tian DS, Wu LF, Wang DJ, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu ZQ, Wang GL, White FF, Yin ZC (2005). R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 435, 1122-1125. |
| [10] | Gu XT, Si FY, Feng ZX, Li SJ, Liang D, Yang P, Yang C, Yan B, Tang J, Yang Y, Li T, Li L, Zhou JL, Li J, Feng LL, Liu JY, Yang YZ, Deng YW, Wu XN, Zhao ZG, Wan JM, Cao XF, Song XW, He ZH, Liu JZ (2023). The OsSGS3-tasiRNA-OsARF3 module orchestrates abiotic- biotic stress response trade-off in rice. Nat Commun 14, 4441. |
| [11] | Han YL, Cai MH, Zhang SQ, Chai JW, Sun MZ, Wang YW, Xie QY, Chen YH, Wang HZ, Chen T (2022). Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF transcription factor family and functional analysis of DcAP2/ERF#96 associated with abiotic stress in Dendrobium catenatum. Int J Mol Sci 23, 13603. |
| [12] | He Q, Li DB, Zhu YS, Tan MP, Zhang DP, Lin XH (2006). Fine mapping of Xa2, a bacterial blight resistance gene in rice. Mol Breeding 17, 1-6. |
| [13] |
Hu KM, Cao JB, Zhang J, Xia F, Ke YG, Zhang HT, Xie WY, Liu HB, Cui Y, Cao YL, Sun XL, Xiao JH, Li XH, Zhang QL, Wang SP (2017). Improvement of multiple agronomic traits by a disease resistance gene via cell wall reinforcement. Nat Plants 3, 17009.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Huang LF, Lin KH, He SL, Chen JL, Jiang JZ, Chen BH, Hou YS, Chen RS, Hong CY, Ho SL (2016). Multiple patterns of regulation and overexpression of a ribonuclease-like pathogenesis-related protein gene, OsPR10a, conferring disease resistance in rice and Arabidopsis. PLoS One 11, e0156414. |
| [15] |
Iyer-Pascuzzi AS, Jiang H, Huang L, Mccouch SR (2008). Genetic and functional characterization of the rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene xa5. Phytopathology 98, 289-295.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Ji CH, Ji ZY, Liu B, Cheng H, Liu H, Liu SZ, Yang B, Chen GY (2020). Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun 1, 100087. |
| [17] | Ji ZY, Guo W, Chen XF, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2022). Plant executor genes. Int J Mol Sci 23, 1524. |
| [18] | Jia QW, Zhong QQ, Gu YJ, Lu TQ, Li W, Yang S, Zhu CY, Hu CX, Li SF, Wang YX, Rao YC (2023). Mapping of QTL for cell wall related components in rice stem and analysis of candidate genes. Chin Bull Bot 58, 882-892. (in Chinese) |
|
贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 58, 882-892.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Jiang GH, Liu DF, Yin DD, Zhou ZZ, Shi Y, Li CR, Zhu LH, Zhai WX (2020). A rice NBS-ARC gene conferring quantitative resistance to bacterial blight is regulated by a pathogen effector-inducible miRNA. Mol Plant 13, 1752-1767. |
| [20] | Jin JY, Luo YT, Yang HM, Lu T, Ye HF, Xie JY, Wang KX, Chen QY, Fang Y, Wang YX, Rao YC (2023). QTL mapping and expression analysis on candidate genes related to chlorophyll content in rice. Chin Bull Bot 58, 394-403. (in Chinese) |
|
金佳怡, 罗怿婷, 杨惠敏, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 谢继毅, 王珂欣, 陈芊羽, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻叶绿素含量QTL定位与候选基因表达分析. 植物学报 58, 394-403.
DOI |
|
| [21] | Li XR, He XY, Chen H, Lu ZH, Wang XF, Wang SG, Fang ZQ, Wu HX, Liu W (2022). Mechanism and breeding application of bacterial blight gene in rice. Guangdong Agric Sci 49, 31-41. (in Chinese) |
| 李香荣, 何秀英, 陈浩, 陆展华, 王晓飞, 王石光, 方志强, 巫浩翔, 刘维 (2022). 水稻白叶枯病基因的作用机制与育种应用. 广东农业科学 49, 31-41. | |
| [22] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Lu YD, Zhong QF, Xiao SQ, Wang B, Ke X, Zhang Y, Yin FY, Zhang DY, Jiang C, Liu L, Li JL, Yu TQ, Wang LX, Cheng ZQ, Chen L (2022). A new NLR disease resistance gene Xa47confers durable and broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice. Front Plant Sci 13, 1037901. |
| [24] |
Luu DD, Joe A, Chen Y, Parys K, Bahar O, Pruitt R, Chan LJG, Petzold CJ, Long K, Adamchak C, Stewart V, Belkhadir Y, Ronald PC (2019). Biosynthesis and secretion of the microbial sulfated peptide RaxX and binding to the rice XA21 immune receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 8525-8534.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| [26] | Neelam K, Mahajan R, Gupta V, Bhatia D, Gill BK, Komal R, Lore JS, Mangat GS, Singh K (2020). High-resolution genetic mapping of a novel bacterial blight resistance gene xa-45(t) identified from Oryza glaberrima and transferred to Oryza sativa. Theor Appl Genet 133, 689-705. |
| [27] |
Oliva R, Ji CH, Atienza-Grande G, Huguet-Tapia JC, Perez-Quintero A, Li T, Eom JS, Li CH, Nguyen H, Liu B, Auguy F, Sciallano C, Luu VT, Dossa GS, Cunnac S, Schmidt SM, Slamet-Loedin IH, Vera Cruz C, Szurek B, Frommer WB, White FF, Yang B (2019). Broad-spectrum resistance to bacterial blight in rice using genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 37, 1344-1350.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Pan BH, Yin JJ, Wang S, Huang H, Gao P, Zhong W, Hu CR, He DP (2024). Research hotspots and evolution trends of rice bran oil. China Oils Fats 1-21. (in Chinese) |
| 潘保辉, 殷娇娇, 王澍, 黄何, 高盼, 钟武, 胡传荣, 何东平 (2024). 稻米油研究热点和演变趋势的分析. 中国油脂. 1-21. | |
| [29] | Peng XQ, Wang ML (2022). Research advances on resistance genes to bacterial blight disease in rice. Plant Physiol J 58, 472-482. (in Chinese) |
| 彭小群, 王梦龙 (2022). 水稻白叶枯病抗性基因研究进展. 植物生理学报 58, 472-482. | |
| [30] |
Pradhan SK, Barik SR, Nayak DK, Pradhan A, Pandit E, Nayak P, Das SR, Pathak H (2020). Genetics, molecular mechanisms and deployment of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Crit Rev Plant Sci 39, 360-385.
DOI |
| [31] | Pundir S, Singh R, Singh VK, Sharma S, Balyan HS, Gupta PK, Sharma S (2023). Mapping of QTLs and meta-QTLs for Heterodera avenae Woll. resistance in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 23, 529. |
| [32] | Rao YC, Wu RC, Liu FY, Dai RH (2024). On research progress of RNAi application in prevention and control of rice pests and diseases. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 47, 361-369. (in Chinese) |
| 饶玉春, 吴日成, 刘富远, 戴若惠 (2024). RNAi在水稻病虫害防控中的应用研究进展. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 47, 361-369. | |
| [33] | Sun XL, Cao YL, Yang ZF, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP, Zhang QF (2004). Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J 37, 517-527. |
| [34] | Tian DG, Yang F, Niu YQ, Lin Y, Chen ZJ, Li G, Luo Q, Wang F, Wang M (2020). Loss function of SL (sekiguchi lesion) in the rice cultivar Minghui 86 leads to enhanced resistance to (hemi) biotrophic pathogens. BMC Plant Biol 20, 507. |
| [35] | Tian DS, Wang JX, Zeng X, Gu KY, Qiu CX, Yang XB, Zhou ZY, Goh M, Luo YC, Murata-Hori M, White FF, Yin ZC (2014). The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 26, 497-515. |
| [36] | Wu T, Bi YY, Yu Y, Zhou Z, Yuan B, Ding XH, Zhang QX, Chen XS, Yang H, Liu HF, Chu ZH (2023). Activated expression of rice DMR6-like gene OsS3H partially explores the susceptibility to bacterial leaf streak mediated by knock-out OsF3H04g. Int J Mol Sci 24, 13263. |
| [37] | Wu XJ, Zhang XY, Xu M, Bu QY, Wang ZY (2024). Research advances on MYB transcription factor in rice stress response. J Northeast Agric Univ 55, 83-96. (in Chinese) |
| 吴秀菊, 张新颖, 许敏, 卜庆云, 王臻昱 (2024). MYB转录因子在水稻胁迫响应中的研究进展. 东北农业大学学报 55, 83-96. | |
| [38] | Xu ZY, Xu XM, Li Y, Liu LL, Wang Q, Wang YJ, Wang Y, Yan JL, Cheng GY, Zou LF, Zhu B, Chen GY (2023). Tal6b/AvrXa27A, a hidden TALE targeting the susceptibility gene OsSWEET11a and the resistance gene Xa27 in rice. Plant Commun 5, 100721. |
| [39] |
Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang ZX, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T (1998). Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 1663-1668.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Zhang DD, Tian CJ, Yin KQ, Wang WY, Qiu JL (2019). Postinvasive bacterial resistance conferred by open stomata in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 32, 255-266. |
| [41] | Zhang HS, Jing W, Zheng JM, Jin YY, Wu D, Cao CJ, Dong YM, Shi XY, Zhang WH (2020). The ATP-binding cassette transporter OsPDR1 regulates plant growth and pathogen resistance by affecting jasmonates biosynthesis in rice. Plant Sci 298, 110582. |
| [42] | Zhang Q (2009). Genetics and improvement of resistance to bacterial blight in hybrid rice in China. Chin J Rice Sci 23, 111-119. (in Chinese) |
| 章琦 (2009). 中国杂交水稻白叶枯病抗性的遗传改良. 中国水稻科学 23, 111-119. | |
| [43] | Zhong QQ, Huang JH, Yin WJ, Lu T, Gu YJ, Chen ZG, Ye HF, Rao YC (2023). QTLs mapping and expression analysis of candidate genes for root traits in rice. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 46, 425-432. (in Chinese) |
| 钟芊芊, 黄佳慧, 殷文晶, 芦涛, 顾育嘉, 陈振概, 叶涵斐, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻种子耐储藏性状QTLs挖掘及候选基因分析. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 46, 425-432. | |
| [44] | Zhu CY, Hu CX, Zhu ZN, Zhang ZN, Wang LH, Chen J, Li SF, Lian JJ, Tang LY, Zhong QQ, Yin WJ, Wang YX, Rao YC (2024). Mapping of QTLs associated with rice panicle traits and candidate gene analysis. Chin Bull Bot 59, 217-230. (in Chinese) |
|
朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2024). 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 59, 217-230.
DOI |
| [1] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张容菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 734-748. |
| [2] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 586-596. |
| [3] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [4] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [5] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [6] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [8] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [9] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [10] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [11] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [12] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [13] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [14] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [15] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||