

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 586-596.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24148 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24148
叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇*( ), 张可伟*(
), 张可伟*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-25
接受日期:2024-12-14
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:1900-01-01
通讯作者:
*E-mail: wzhang@zjnu.edu.cn;kwzhang@zjnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Can Ye, Linbo Yao, Ying Jin, Rong Gao, Qi Tan, Xuying Li, Yanjun Zhang, Xifeng Chen, Bojun Ma, Wei Zhang*( ), Kewei Zhang*(
), Kewei Zhang*( )
)
Received:2024-09-25
Accepted:2024-12-14
Online:2025-07-10
Published:1900-01-01
Contact:
*E-mail: wzhang@zjnu.edu.cn;kwzhang@zjnu.edu.cn
摘要: 水杨酸(SA)是植物免疫的关键防御信号分子。植物SA的定量分析对于SA代谢途径及其生物学功能研究至关重要。利用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC)和液相-质谱联用仪(LC-MS)测定SA含量是目前常用方法, 但难以实现高通量测定。水稻(Oryza sativa)中SA合成代谢途径目前尚未完全解析, 高效筛选水稻SA相关突变体对于阐明其代谢途径具有重要意义。该文对已有基于SA生物传感菌株Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_lux估算SA的分析方法进行了改良, 建立了水稻SA高通量估算方法, 简化了样品采集和提取过程, 省去样品称重、组织研磨及离心等耗时步骤, 整个操作流程便捷且高效。同时, 利用已报道的水稻SA代谢相关遗传材料验证了该方法的可行性, 并使用该方法筛选了钴-60诱变的水稻突变体库, 获得一批水稻SA含量发生显著变化的突变体, 采用HPLC法对突变体内源SA进行了验证。该方法可用于SA代谢突变体的遗传筛选及其代谢相关酶鉴定, 对水稻等作物的SA代谢及生物学功能研究具有重要的应用价值。
叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 586-596.
Can Ye, Linbo Yao, Ying Jin, Rong Gao, Qi Tan, Xuying Li, Yanjun Zhang, Xifeng Chen, Bojun Ma, Wei Zhang, Kewei Zhang. Establishment and Application of a High-throughput Screening Method for Salicylic Acid Metabolic Mutants in Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 586-596.
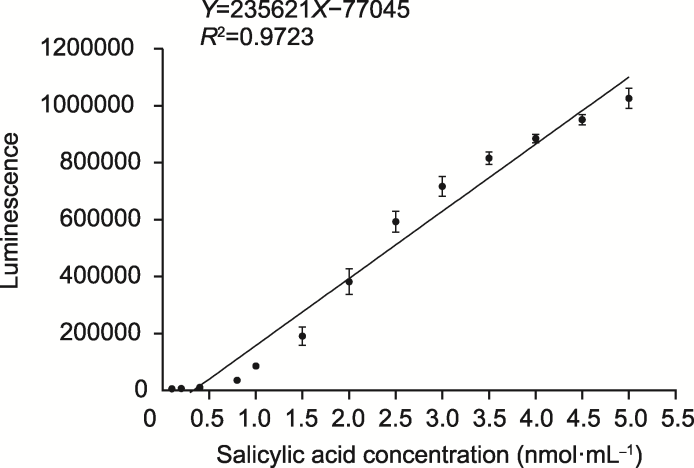
图1 Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_lux菌株的发光强度标准曲线 标准曲线方程是Y=235621X-77045, 决定系数R2 =0.9723。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。
Figure 1 Standard curve of luminescence of Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_lux strain Equation: Y=235621X-77045, Coefficient of determination: R2=0.9723. Data are means ± SD (n=3).
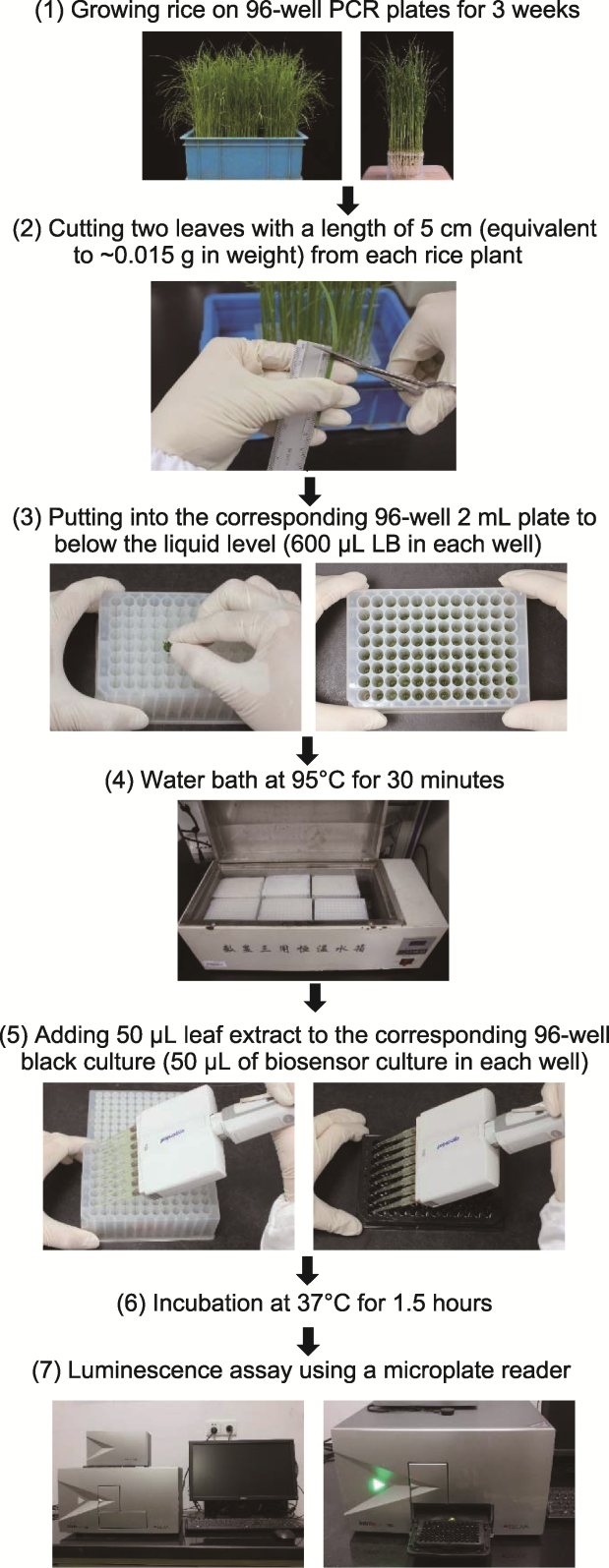
图2 利用水杨酸(SA)生物传感器Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_ lux菌株高通量测定水稻SA含量的改良操作流程(改自Marek et al., 2010) (1) 水稻在96孔PCR板(管底经切割处理)水培约3周(每板加入3株野生型, 1株oss5hDM/NIP和S5H1-OE作为对照); (2) 剪取每株水稻苗5 cm的叶片2枚(约0.015 g); (3) 揉成团塞入对应的已加600 μL LB的96孔2 mL板中, 96孔PCR板与96孔2 mL板位置一一对应; (4) 将96孔2 mL板在95°C下水浴30分钟, 每隔5分钟将96孔板盖子重新盖好(高温会使盖子顶开); (5) 待96孔2 mL板中的叶片提取液冷却至室温后, 吸取50 μL叶片提取液至已提前加入50 μL生物传感器的黑色酶标板中, 酶标板与96孔2 mL板位置一一对应(每次实验每板水稻苗做2板重复); (6) 37°C下恒温黑暗静置培养1.5小时; (7) 用酶联免疫检测仪测定相对发光值(每一酶标板需测2次)。
Figure 2 Modified manipulating process for high-throughput determination of salicylic acid (SA) content using SA biosensor Acinetobacter sp. ADPWH_lux strain in rice (adapted from Marek et al., 2010) (1) Rice was hydroponic for about 3 weeks in 96-well PCR plates (The bottom of tube was cut) (As controls, 3 wild type,1 oss5hDM/NIP and S5H1-OE plants were added to each plate); (2) Took two leaves of 5 cm (about 0.015 g) from each rice seedling; (3) Kneaded the leaf into a 2 mL 96-well plate with 600 μL LB, and the positions of the 96-well PCR plate and the 96-well 2 mL plate were one-to-one corresponding; (4) The 2 mL 96-well plate was bathed in water at 95°C for 30 minutes (the lid of the 96-well plate should be re-closed every 5 minutes, because high temperature would make the lid open); (5) After the leaf extract liquid from the 2 mL 96-well plate was cooled to room temperature, 50 μL of the extract liquid was pipetted into the black enzyme-labeled plate that had been added with 50 μL biosensor in advance, and the position of the enzyme-labeled plate was one-to-one corresponding to the 96-well 2 mL plate (two plates were repeated for each rice seedling in each experiment); (6) Incubation at 37°C in a incubator for 1.5 hours in the dark; (7) The relative luminescence value was measured with an enzyme-linked immunodetector (each enzyme plate needs to be measured twice).
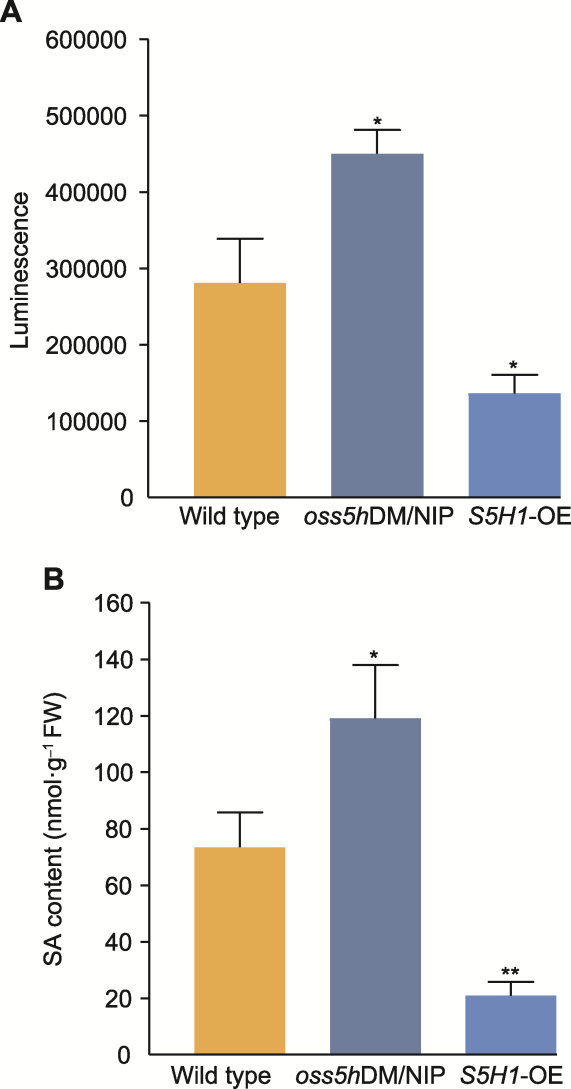
图3 NIP、oss5hDM/NIP和S5H1-OE的水杨酸(SA)发光强度(A)及内源性SA含量(B) 水稻在温室条件下培养, 培养条件完全相同。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。使用t检验进行统计学分析, *P<0.05; **P<0.01
Figure 3 The salicylic acid (SA) luminescence (A) and SA content (B) of wild type (NIP), oss5hDM/NIP and S5H1-OE Rice plants were cultured in greenhouse, and the culture conditions were the same. Data are means ± SD (n=3). The statistical significances were calculated by t-test, * P<0.05; **P<0.01
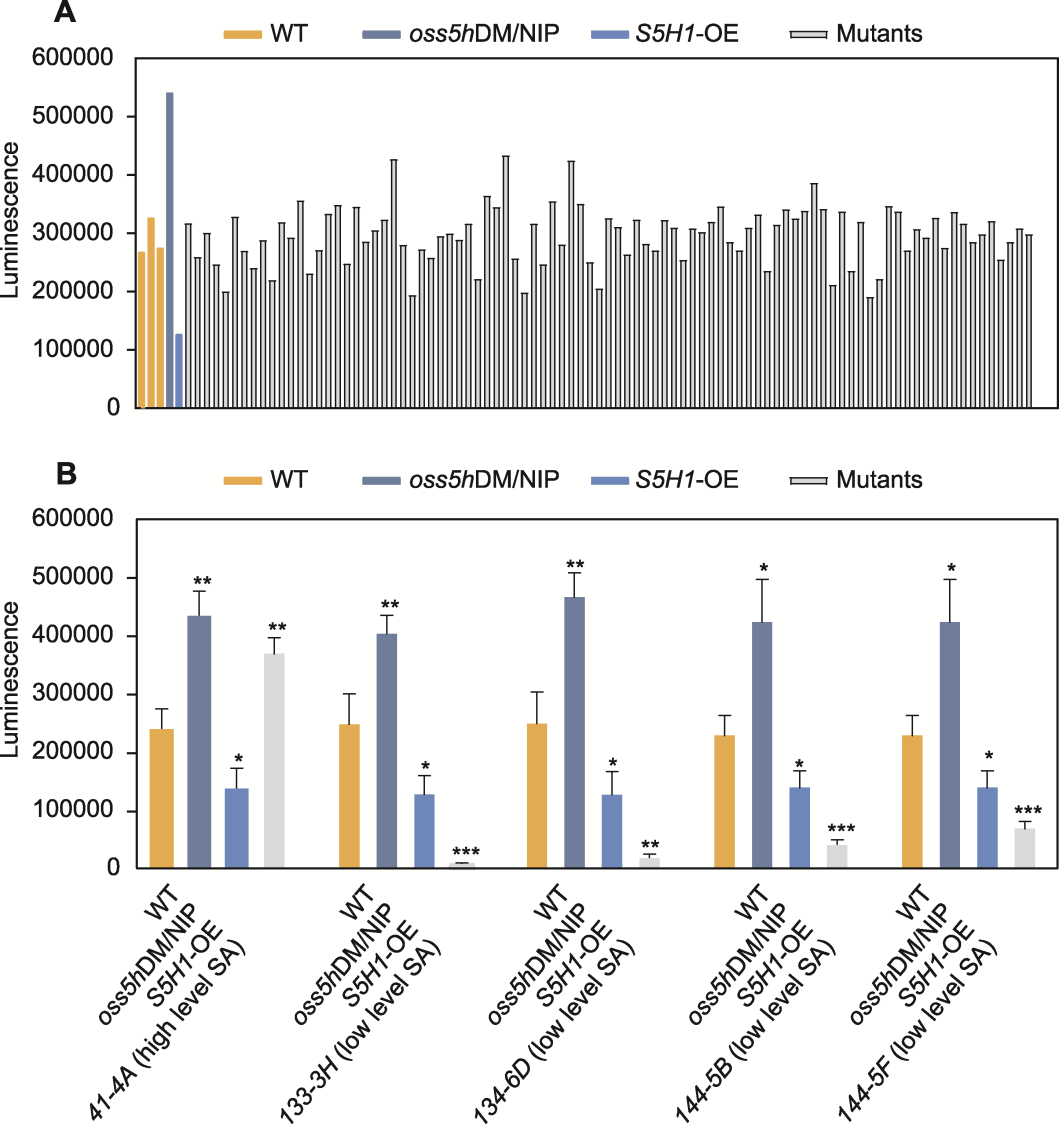
图4 96孔PCR板上所有水稻的水杨酸(SA)发光强度(A)及筛选候选突变体的SA发光强度(B) 数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。使用t检验进行统计学分析, * P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001
Figure 4 The salicylic acid (SA) luminescence of all rice on the 96-well PCR plate (A) and SA luminescence in the selected candidate mutants (B) Data are means ± SD (n=3). Statistical significance was calculated by t-test, * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
| No. | Sample name | Luminescence | SA concentration in extracting solution (nmol·mL-1) | Estimated SA content in rice leaves (nmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NIP | 240906.67±33164.52 | 1.35±0.14 | 53.98±5.63 |
| 41-4A | 373098.67±23587.55** | 1.91±0.10* | 76.42±4.00* | |
| 2 | NIP | 251577.33±48090.31 | 1.39±0.20 | 55.79±8.16 |
| 133-3H | 7778.33±1563.11*** | 0.36±0.01*** | 13.21±0.27*** | |
| 3 | NIP | 253330.67±50076.11 | 1.40±0.21 | 56.09±8.50 |
| 134-6D | 21748.67±2827.30** | 0.42±0.01** | 16.77±0.48** | |
| 4 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5B | 44528±4907.68*** | 0.52±0.02*** | 20.64±0.83*** | |
| 5 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5F | 72798.67±7982.44*** | 0.64±0.03*** | 25.44±1.36*** |
表1 突变体水杨酸(SA)发光强度在标准曲线中对应的SA浓度及估算的水稻叶片SA含量
Table 1 The salicylic acid (SA) concentration corresponding to the SA luminescence of mutant in the standard curve and estimated SA content in rice leaves
| No. | Sample name | Luminescence | SA concentration in extracting solution (nmol·mL-1) | Estimated SA content in rice leaves (nmol·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NIP | 240906.67±33164.52 | 1.35±0.14 | 53.98±5.63 |
| 41-4A | 373098.67±23587.55** | 1.91±0.10* | 76.42±4.00* | |
| 2 | NIP | 251577.33±48090.31 | 1.39±0.20 | 55.79±8.16 |
| 133-3H | 7778.33±1563.11*** | 0.36±0.01*** | 13.21±0.27*** | |
| 3 | NIP | 253330.67±50076.11 | 1.40±0.21 | 56.09±8.50 |
| 134-6D | 21748.67±2827.30** | 0.42±0.01** | 16.77±0.48** | |
| 4 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5B | 44528±4907.68*** | 0.52±0.02*** | 20.64±0.83*** | |
| 5 | NIP | 232799.67±29917.16 | 1.32±0.13 | 52.60±5.08 |
| 144-5F | 72798.67±7982.44*** | 0.64±0.03*** | 25.44±1.36*** |
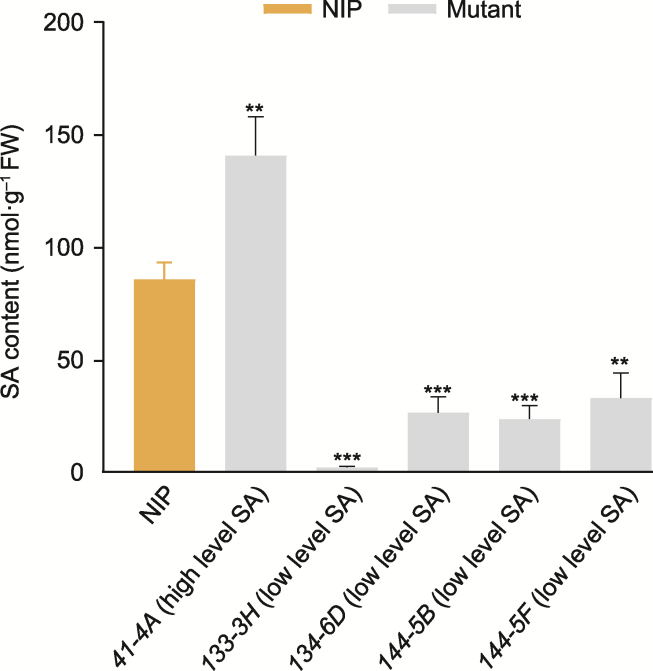
图5 野生型(NIP)和5个水杨酸(SA)水稻突变体的SA含量柱状图 FW: 鲜重。数据为平均值±标准差(n=3)。使用t检验进行统计学分析, **P<0.01; ***P<0.001
Figure 5 Histogram of salicylic acid (SA) content in wild type (NIP) and 5 SA rice mutant plants FW: Fresh weight. Data are means ± SD (n=3). The statistical significance was calculated by t-test, **P<0.01; ***P<0.001
| [1] | Aboul-Soud MAM, Cook K, Loake GJ (2004). Measurement of salicylic acid by a high-performance liquid chromatography procedure based on ion-exchange. Chromatographia 59, 129-133. |
| [2] | Ahmad P, Prasad MNV (2012). Abiotic Stress Responses in Plants:Metabolism, Productivity and Sustainability. New York: Springer Press. pp. 312-466. |
| [3] | Cao DD, Chen SY, Qin YB, Wu HP, Ruan GH, Huang YT (2020). Regulatory mechanism of salicylic acid on seed germination under salt stress in kale. Chin Bull Bot 55, 49-61. (in Chinese) |
|
曹栋栋, 陈珊宇, 秦叶波, 吴华平, 阮关海, 黄玉韬 (2020). 水杨酸调控盐胁迫下羽衣甘蓝种子萌发的机理. 植物学报 55, 49-61.
DOI |
|
| [4] | Dempsey DA, Vlot AC, Wildermuth MC, Klessig DF (2011). Salicylic acid biosynthesis and metabolism. Arabidopsis Book 9, e0156. |
| [5] |
Ding PT, Ding YL (2020). Stories of salicylic acid: a plant defense hormone. Trends Plant Sci 25, 549-565.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Ding XY, Zhang J, Su BL, Xu HF (2001). Role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Chin Bull Bot 18, 163-168. (in Chinese) |
| 丁秀英, 张军, 苏宝林, 徐惠风 (2001). 水杨酸在植物抗病中的作用. 植物学通报 18, 163-168. | |
| [7] |
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993). Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261, 754-756.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Huang WE, Huang LF, Preston GM, Naylor M, Carr JP, Li YH, Singer AC, Whiteley AS, Wang H (2006). Quantitative in situ assay of salicylic acid in tobacco leaves using a genetically modified biosensor strain of Acinetobacter sp. ADP1. Plant J 46, 1073-1083.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Huang WE, Wang H, Zheng HJ, Huang LF, Singer AC, Thompson I, Whiteley AS (2005). Chromosomally located gene fusions constructed in Acinetobacter sp. ADP1 for the detection of salicylate. Environ Microbiol 7, 1339-1348.
PMID |
| [10] |
Koo YM, Heo AY, Choi HW (2020). Salicylic acid as a safe plant protector and growth regulator. Plant Pathol J 36, 1-10.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Li C, Zhou L, Zhang YJ, Song FP, Zhang J (2009). Influence of ions conditions on salR gene in Acinetobacter sp. ADP1. Biotechnol Bull (9), 57-63. (in Chinese) |
| 李超, 周琳, 张永军, 宋福平, 张杰 (2009). 离子环境对Acinetobacter sp. ADP1的salR基因活性的影响. 生物技术通报 (9), 57-63. | |
| [12] |
Liu SJ, Wu YN, Fang CG, Cui Y, Jiang N, Wang H (2017). Simultaneous determination of 19 plant growth regulator residues in plant-originated foods by QuEChERS and stable isotope dilution-ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Sci 33, 1047-1052.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Malamy J, Carr JP, Klessig DF, Raskin I (1990). Salicylic acid: a likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection. Science 250, 1002-1004.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Marek G, Carver R, Ding YZ, Sathyanarayan D, Zhang XD, Mou ZL (2010). A high-throughput method for isolation of salicylic acid metabolic mutants. Plant Methods 6, 21.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Meighen EA (1993). Bacterial bioluminescence: organization, regulation, and application of the lux genes. FASEB J 7, 1016-1022.
PMID |
| [16] |
Métraux JP, Signer H, Ryals J, Ward E, Wyss-Benz M, Gaudin J, Raschdorf K, Schmid E, Blum W, Inverardi B (1990). Increase in salicylic acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science 250, 1004-1006.
PMID |
| [17] |
Peng YJ, Yang JF, Li X, Zhang YL (2021). Salicylic acid: biosynthesis and signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 761-791.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Rasmussen JB, Hammerschmidt R, Zook MN (1991). Systemic induction of salicylic acid accumulation in cucumber after inoculation with Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Plant Physiol 97, 1342-1347.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Rekhter D, Lüdke D, Ding YL, Feussner K, Zienkiewicz K, Lipka V, Wiermer M, Zhang YL, Feussner I (2019). Isochorismate-derived biosynthesis of the plant stress hormone salicylic acid. Science 365, 498-502.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Rivas-San Vicente M, Plasencia J (2011). Salicylic acid beyond defence: its role in plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 62, 3321-3338.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Saleem M, Fariduddin Q, Castroverde CDM (2021). Salicylic acid: a key regulator of redox signaling and plant immunity. Plant Physiol Biochem 168, 381-397. |
| [22] |
Sanders IO, Smith AR, Hall MA (1989). The measurement of ethylene binding and metabolism in plant tissue. Planta 179, 97-103.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Shields A, Shivnauth V, Castroverde CDM (2022). Salicylic acid and N-hydroxypipecolic acid at the fulcrum of the plant immunity-growth equilibrium. Front Plant Sci 13, 841688. |
| [24] |
van Butselaar T, Van den Ackerveken G (2020). Salicylic acid steers the growth-immunity tradeoff. Trends Plant Sci 25, 566-576.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Verberne MC, Brouwer N, Delbianco F, Linthorst HJM, Bol JF, Verpoorte R (2002). Method for the extraction of the volatile compound salicylic acid from tobacco leaf material. Phytochem Anal 13, 45-50. |
| [26] | Waadt R, Seller CA, Hsu PK, Takahashi Y, Munemasa S, Schroeder JI (2022). Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23, 680-694. |
| [27] | Wang YK, Jin GC, Song SY, Jin YJ, Wang XW, Yang SQ, Shen XX, Gan YB, Wang YX, Li R, Liu JX, Hu JP, Pan RH (2024). A peroxisomal cinnamate: CoA ligase-dependent phytohormone metabolic cascade in submerged rice germination. Dev Cell 59, 1363-1378. |
| [28] |
White RF (1979). Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) induces resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco. Virology 99, 410-412.
PMID |
| [29] | Xu L, Zhao HY, Wang JB, Wang XM, Jia XQ, Wang L, Xu Z, Li RL, Jiang K, Chen ZX, Luo J, Xie XD, Yi KK (2023). AIM1-dependent high basal salicylic acid accumulation modulates stomatal aperture in rice. New Phytol 238, 1420-1430. |
| [30] | Yang CK, Shen SQ, Zhou S, Li YF, Mao YY, Zhou JJ, Shi YH, An LX, Zhou QQ, Peng WJ, Lyu Y, Liu XM, Chen W, Wang SC, Qu LH, Liu XQ, Fernie AR, Luo J (2022). Rice metabolic regulatory network spanning the entire life cycle. Mol Plant 15, 258-275. |
| [31] | Zhang YJ, Yu QL, Gao SL, Yu NN, Zhao L, Wang JB, Zhao JZ, Huang P, Yao LB, Wang M, Zhang KW (2022). Disruption of the primary salicylic acid hydroxylases in rice enhances broad-spectrum resistance against pathogens. Plant Cell Environ 45, 2211-2225. |
| [32] |
Zhang YL, Li X (2019). Salicylic acid: biosynthesis, perception, and contributions to plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50, 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Zhao JZ, Yu NN, Ju M, Fan B, Zhang YJ, Zhu EG, Zhang MY, Zhang KW (2019). ABC transporter OsABCG18 controls the shootward transport of cytokinins and grain yield in rice. J Exp Bot 70, 6277-6291.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张蓉菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [2] | 陈钧, 徐江民, 周逸楠, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 金芊芸, 赵蓓蓓, 朱哲楠, 徐雨青, 张璐怡, 刘笑妍, 刘隽, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻白叶枯病抗性QTL的挖掘与候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [3] | 吴艾安, 陶一菲, 方思棋, 许欣悦, 朱珊珊, 陈诗颖, 王廷超, 郭威. 水稻细菌性条斑病菌致病与水稻抗病机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [4] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [5] | 吕加一, 李乐攻, 侯聪聪. 基于FRET原理的生物传感器: 小分子荧光探针在植物中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 283-293. |
| [6] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [7] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [8] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [9] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [10] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [11] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [12] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [13] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [14] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [15] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||