

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (1): 1-9.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23071 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23071
• 研究报告 • 下一篇
方妍力1,2,†, 田传玉1,2,†, 苏如意1, 刘亚培2, 王春连2, 陈析丰1, 郭威1,*( ), 纪志远2,*(
), 纪志远2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-31
接受日期:2023-12-19
出版日期:2024-01-10
发布日期:2024-01-10
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Yanli Fang1,2,†, Chuanyu Tian1,2,†, Ruyi Su1, Yapei Liu2, Chunlian Wang2, Xifeng Chen1, Wei Guo1,*( ), Zhiyuan Ji2,*(
), Zhiyuan Ji2,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-31
Accepted:2023-12-19
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2024-01-10
Contact:
*E-mail: About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 由稻黄单胞菌稻生致病变种(Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola, Xoc)引起的细菌性条斑病(BLS)是水稻(Oryza sativa)生产上的重要病害, 近年来其发病呈快速上升趋势, 特别是在我国南方(包括江苏、浙江、福建和广东等地)稻区危害严重。种植抗病品种是防治BLS最理想的措施, 但目前生产上严重缺乏可用于育种的优异抗病基因资源。通过人工接种鉴定筛选水稻种质资源, 挖掘到2份高抗BLS材料(M1和D1)。多菌株系接种结果表明, M1具有非小种特异性广谱抗病(RNS BSR)特征。经遗传群体分析表明, 栽培稻M1携带单个显性抗BLS新基因Xo-3。通过混池测序和关联分析, 将Xo-3基因初步定位在2号染色体上的一段候选区域内。抗BLS种质资源的挖掘及其抗性遗传基础的解析, 将有助于理解水稻-Xoc互作机理, 从而培育抗BLS水稻新品种和制定科学的防治BLS策略。
方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9.
Yanli Fang, Chuanyu Tian, Ruyi Su, Yapei Liu, Chunlian Wang, Xifeng Chen, Wei Guo, Zhiyuan Ji. Mining and Preliminary Mapping of Rice Resistance Genes Against Bacterial Leaf Streak. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 1-9.
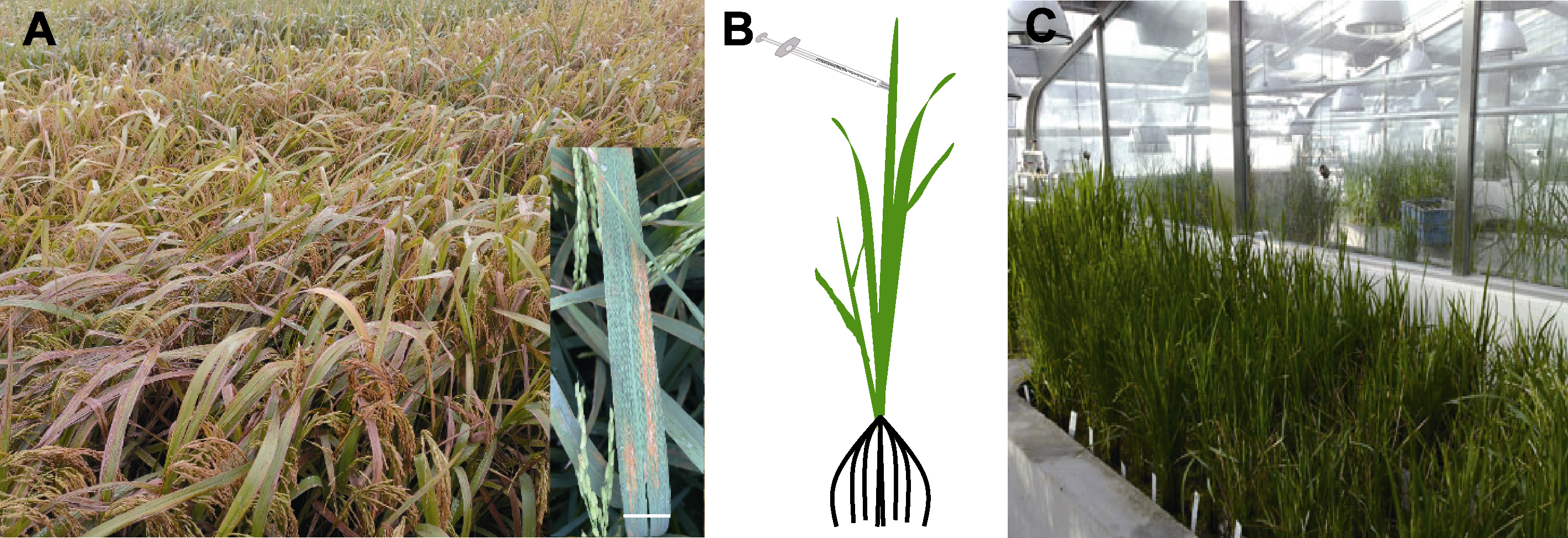

图1 水稻细菌性条斑病(BLS)抗性种质鉴定示意图 (A) 水稻细菌性条斑病发生田块(bar=1 cm); (B) 注射接种; (C) 水稻抗性种质材料鉴定
Figure 1 Diagram for the identification of rice germplasms that confer resistance to bacterial leaf streak (BLS) (A) Occurrence of bacterial leaf streak in paddy (bar=1 cm); (B) Syringe inoculation; (C) Rice materials for resistance identification
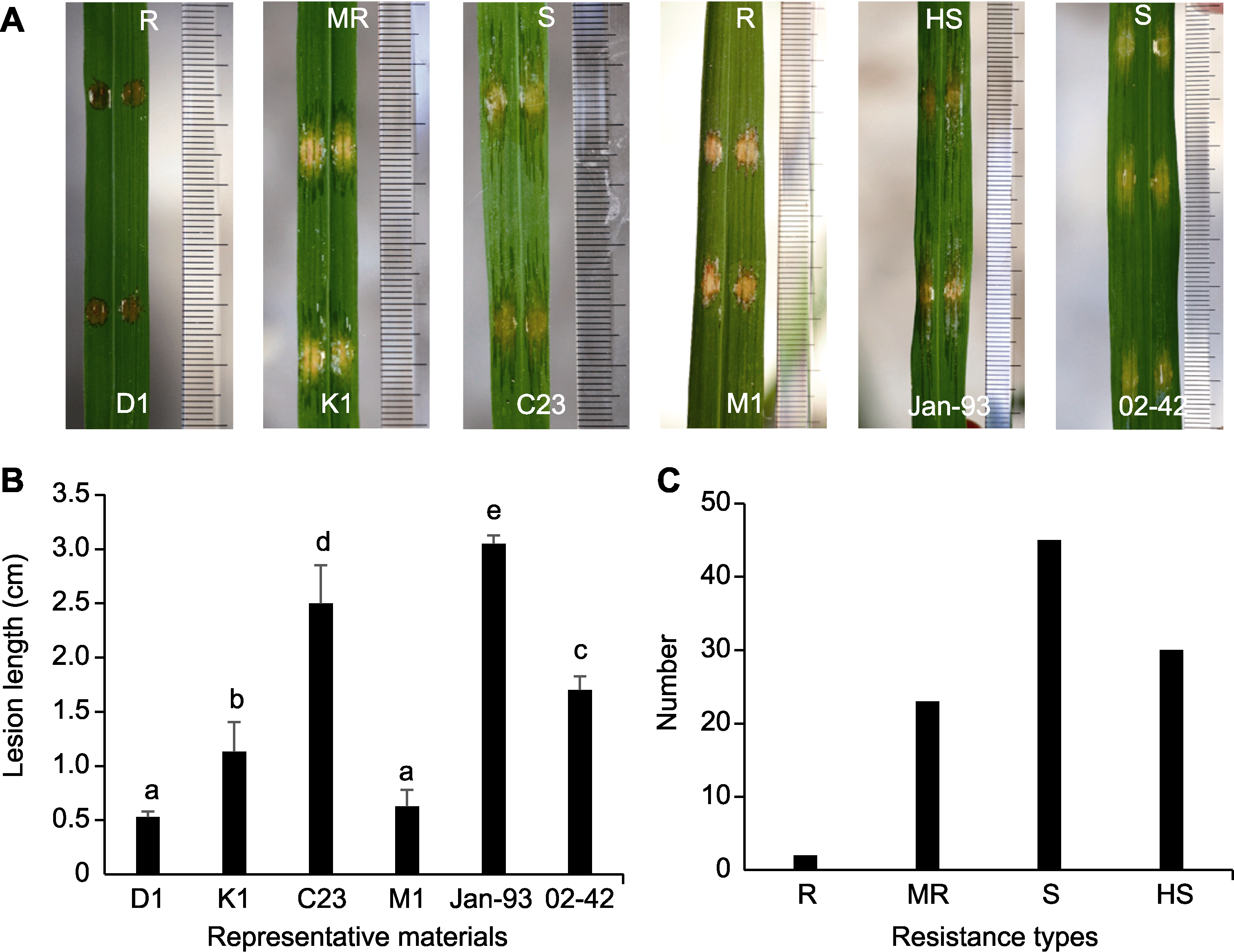
图2 水稻细菌性条斑病(BLS)抗性的无针注射接种鉴定 (A) 代表性材料病斑类型; (B) 代表性材料病斑长度(柱形图上方不同小写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)); (C) 测试材料的抗性类型分布(R: 高抗; MR: 中抗; S: 感病; HS: 高感)
Figure 2 Identification of rice germplasms that confer resistance to bacterial leaf streak (BLS) with needleless syringes (A) Phenotype of representative rice materials; (B) Lesion length of representative rice materials (different lowercase letters above horizontal columns indicate significant statistical differences at P<0.01); (C) Distribution of rice materials in BLS disease reactions (R: High resistance; MR: Middle resistance; S: Susceptibility; HS: High susceptibility)
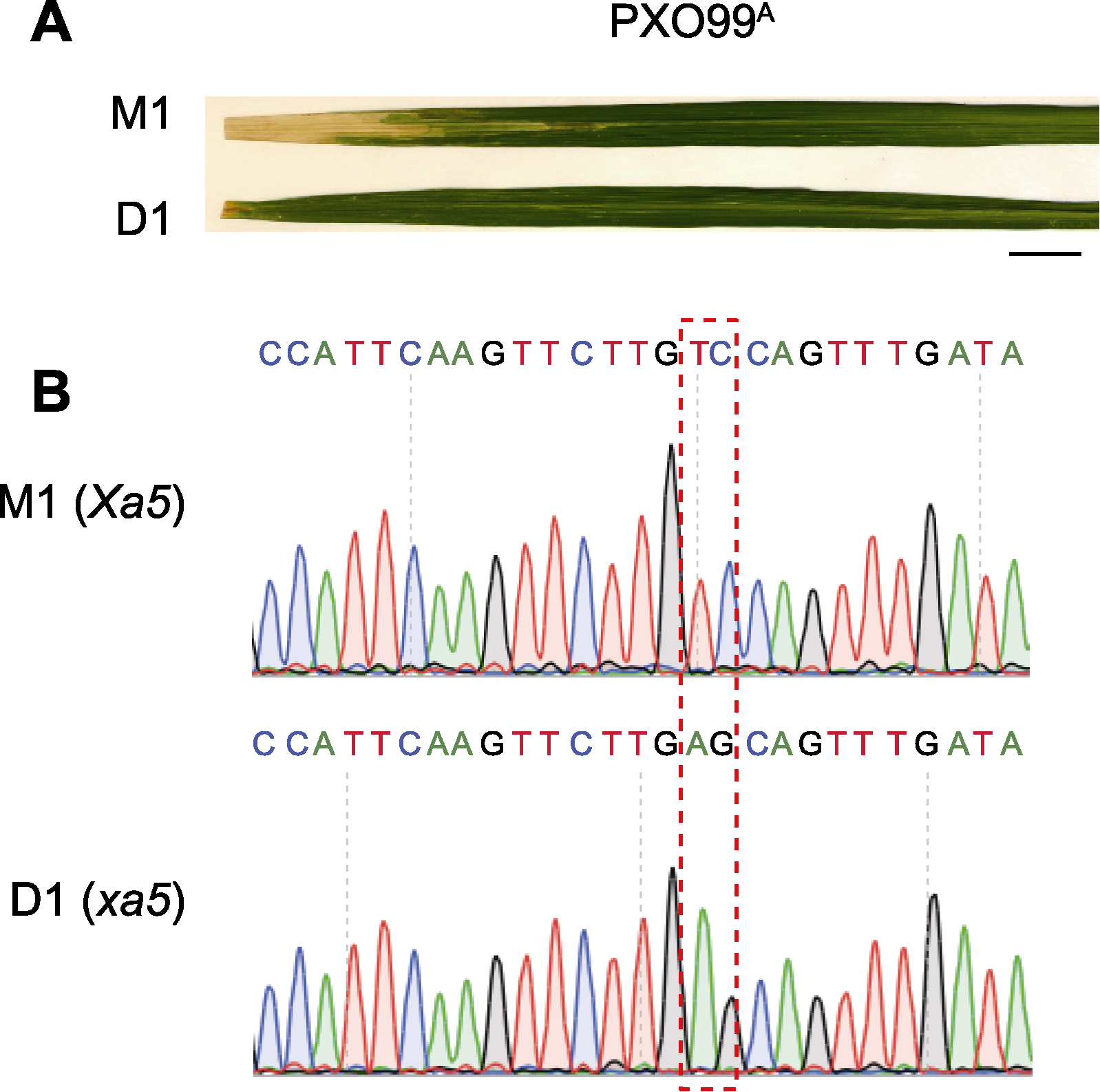
图3 M1和D1材料的白叶枯病(BB)抗性鉴定 (A) M1和D1接种白叶枯病菌(PXO99A)后的表型(bar=1 cm); (B) M1和D1的Xa5/xa5位点序列(红色虚线框表示变异位点)
Figure 3 Identification of M1 and D1 that confer resistance to bacterial blight (BB) (A) Disease response of M1 and D1 inoculated with Xoo (PXO99A) (bar=1 cm); (B) Sequence of Xa5/xa5 locus in M1 and D1 (the red dashed box represents the mutation sites)
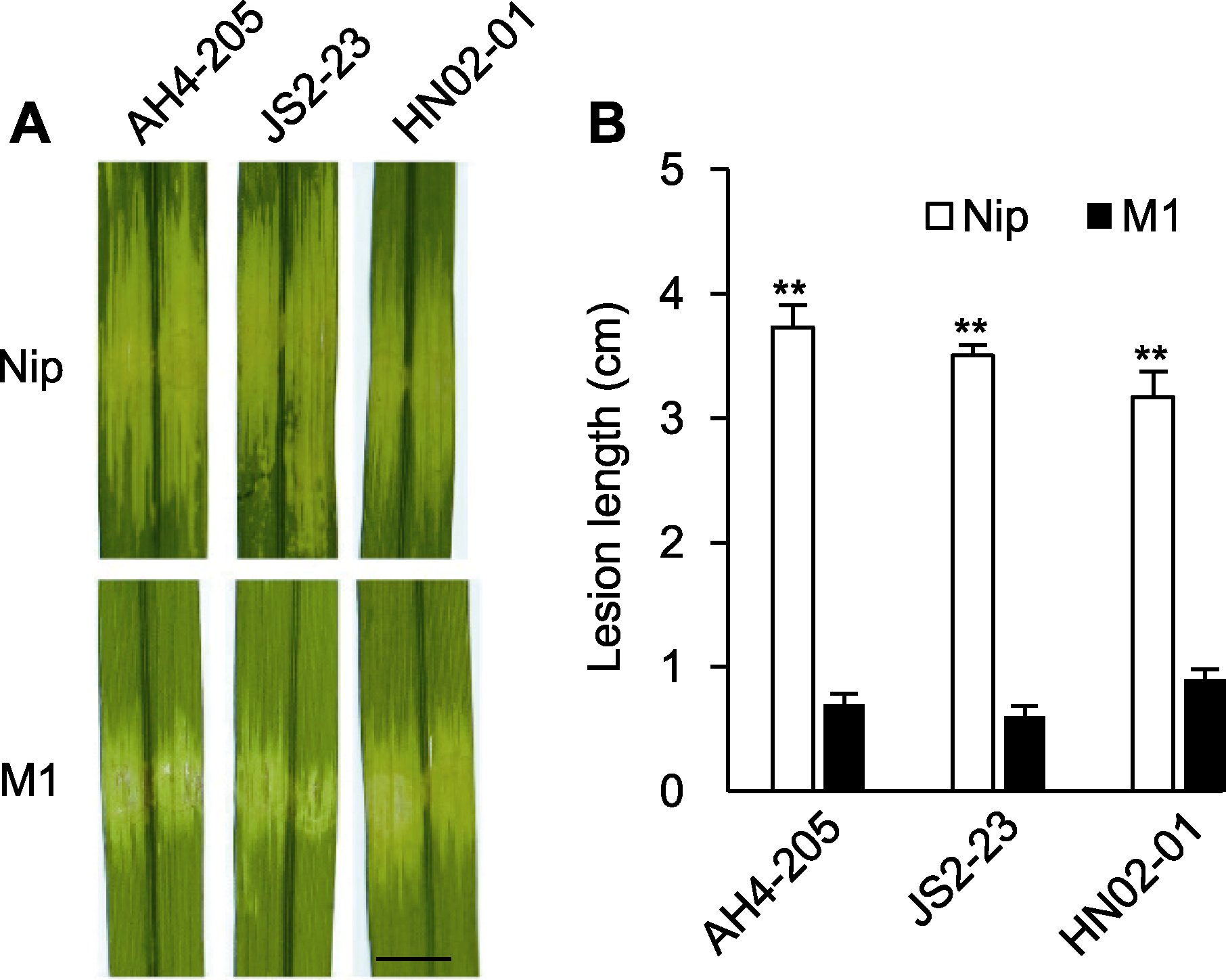
图4 M1的抗细菌性条斑病(BLS)病谱鉴定分析 (A) Xoc强毒菌株接种Nip和M1后的表型(bar=0.5 cm); (B) 病斑长度(**表示差异极显著(P<0.01))
Figure 4 Bacterial leaf streak (BLS) resistance spectrum assay of M1 (A) Phenotype of hypervirulent Xoc strains in Nip and M1 (bar=0.5 cm); (B) Lesion length of hypervirulent Xoc strains in Nip and M1 (** indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01))
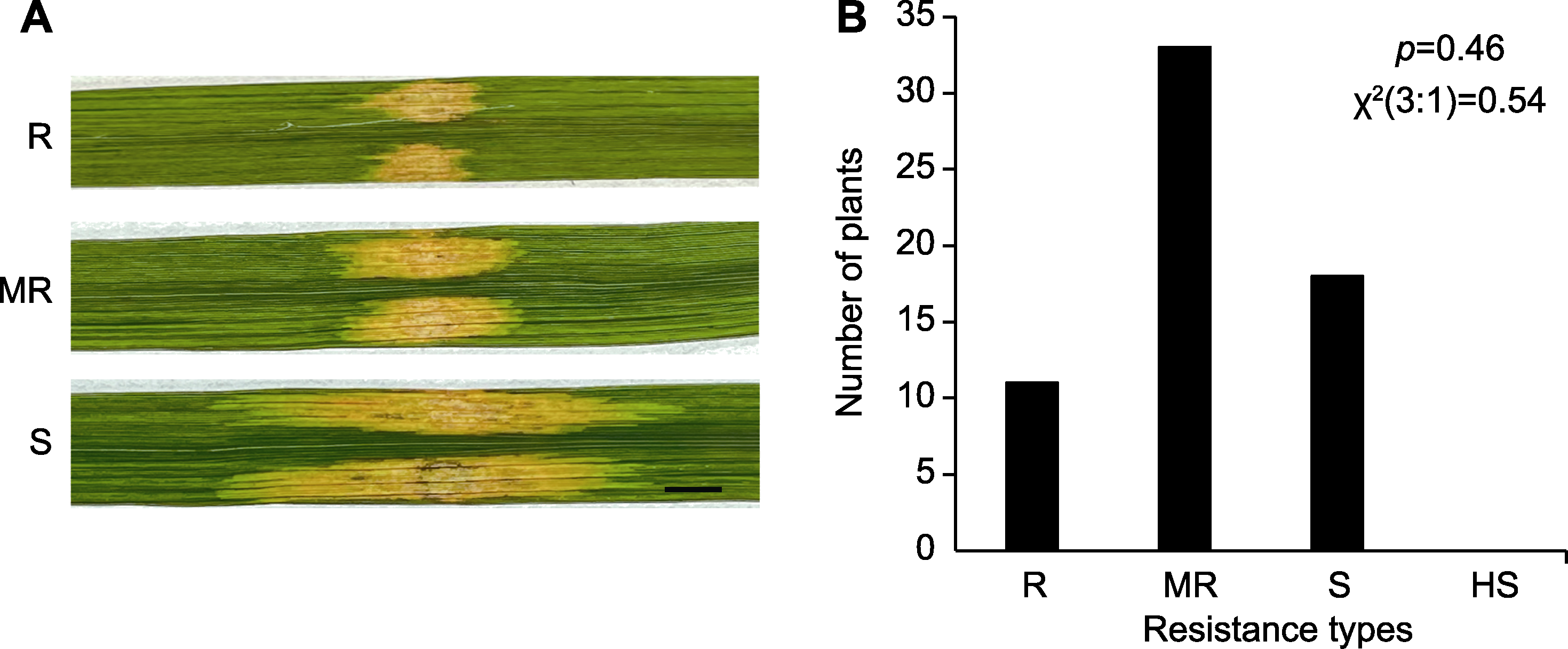
图5 M1材料的细菌性条斑病(BLS)抗性遗传分析 (A) Nipponbare × M1群体F2单株的BLS抗病反应(bar=0.5 cm); (B) F2群体抗感单株的统计分析。R、MR、S和HS同图2。
Figure 5 Genetic analysis of M1 that confers resistance to bacterial leaf streak (BLS) (A) Resistance identification of F2 plants derived from the cross between Nipponbare and M1 (bar=0.5 cm); (B) Statistical analysis of resistant and susceptible F2 plants. R, MR, S, and HS are the same as shown in Figure 2.
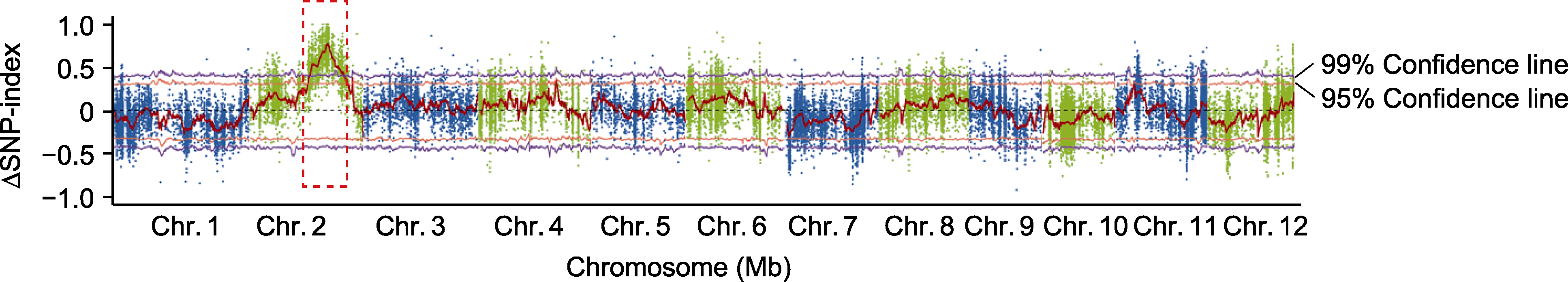
图6 M1携带抗细菌性条斑病(BLS)基因Xo-3的BSA-Seq定位分析 红色虚线框表示候选基因区间。
Figure 6 Mapping of bacterial leaf streak (BLS) resistance gene Xo-3 in M1 using BSA-Seq method The red dashed box represents the candidate gene region.
| [1] | 黄大辉, 岑贞陆, 刘驰, 贺文爱, 陈英之, 马增凤, 杨朗, 韦绍丽, 刘亚利, 黄思良, 杨新庆, 李容柏 (2008). 野生稻细菌性条斑病抗性资源筛选及遗传分析. 植物遗传资源学报 9, 11-14. |
| [2] | 林作晓, 龙梦玲, 唐洁瑜, 辛德育, 黄成宇 (2021). 广西2020年农作物主要病虫害发生实况. 广西植保 34, 25-32. |
| [3] |
马路, 方媛, 肖飒清, 周纯, 金哲伦, 叶雯澜, 饶玉春 (2018). 水稻条斑病抗性QTL的挖掘及相关基因的表达. 植物学报 53, 468-476.
DOI |
| [4] |
王田幸子, 朱峥, 陈悦, 刘玉晴, 燕高伟, 徐珊, 张彤, 马金姣, 窦世娟, 李莉云, 刘国振 (2021). 水稻OsWRKY42是Xa21介导的抗白叶枯病途径新元件. 植物学报 56, 687-698.
DOI |
| [5] |
Bogdanove AJ, Koebnik R, Lu H, Furutani A, Angiuoli SV, Patil PB, Van Sluys MA, Ryan RP, Meyer DF, Han SW, Aparna G, Rajaram M, Delcher AL, Phillippy AM, Puiu D, Schatz MC, Shumway M, Sommer DD, Trapnell C, Benahmed F, Dimitrov G, Madupu R, Radune D, Sullivan S, Jha G, Ishihara H, Lee SW, Pandey A, Sharma V, Sriariyanun M, Szurek B, Vera-Cruz CM, Dorman KS, Ronald PC, Verdier V, Dow JM, Sonti RV, Tsuge S, Brendel VP, Rabinowicz PD, Leach JE, White FF, Salzberg SL (2011). Two new complete genome sequences offer insight into host and tissue specificity of plant pathogenic Xanthomonas spp. J Bacteriol 193, 5450-5464.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Cai LL, Cao YY, Xu ZY, Ma WX, Zakria M, Zou LF, Cheng ZQ, Chen GY (2017). A transcription activator-like effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola activates rice gene Os09g29100 to suppress rice immunity. Sci Rep 7, 5089.
DOI |
| [7] |
Cernadas RA, Doyle EL, Niño-Liu DO, Wilkins KE, Bancroft T, Wang L, Schmidt CL, Caldo R, Yang B, White FF, Nettleton D, Wise RP, Bogdanove AJ (2014). Code-assisted discovery of TAL effector targets in bacterial leaf streak of rice reveals contrast with bacterial blight and a novel susceptibility gene. PLoS Pathog 10, e1003972.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Ji CH, Ji ZY, Liu B, Cheng H, Liu H, Liu SZ, Yang B, Chen GY (2020). Xa1 allelic R genes activate rice blight resistance suppressed by interfering TAL effectors. Plant Commun 1, 100087.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Ji ZY, Ji CH, Liu B, Zou LF, Chen GY, Yang B (2016). Interfering TAL effectors of Xanthomonas oryzae neutralize R-gene-mediated plant disease resistance. Nat Commun 7, 13435.
DOI |
| [10] |
Ji ZY, Wang CL, Zhao KJ (2018). Rice routes of countering Xanthomonas oryzae. Int J Mol Sci 19, 3008.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Ji ZY, Zakria M, Zou LF, Xiong L, Li Z, Ji GH, Chen GY (2014). Genetic diversity of transcriptional activator-like effector genes in Chinese isolates of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Phytopathology 104, 672-682.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Jiang GH, Xia ZH, Zhou YL, Wan J, Li DY, Chen RS, Zhai WX, Zhu LH (2006). Testifying the rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 by genetic complementation and further analyzing xa5 (Xa5) in comparison with its homolog TFIIAγ1. Mol Genet Genomics 275, 354-366.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Jiang N, Yan J, Liang Y, Shi YL, He ZZ, Wu YT, Zeng Q, Liu XL, Peng JH (2020). Resistance genes and their interactions with bacterial blight/leaf streak pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in rice (Oryza sativa L.)—an updated review. Rice 13, 3.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329.
DOI |
| [15] |
Li CY, Zhou L, Wu B, Li SH, Zha WJ, Li W, Zhou ZH, Yang LF, Shi L, Lin YJ, You AQ (2022). Improvement of bacterial blight resistance in two conventionally cultivated rice varieties by editing the noncoding region. Cells 11, 2535.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Liu HF, Chang QL, Feng WJ, Zhang BG, Wu T, Li N, Yao FY, Ding XH, Chu ZH (2014). Domain dissection of AvrRxo1 for suppressor, avirulence and cytotoxicity functions. PLoS One 9, e113875.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Ma ZF, Qin G, Zhang YX, Liu C, Wei MY, Cen ZL, Yan Y, Luo TP, Li ZJ, Liang HF, Huang DH, Deng GF (2021). Bacterial leaf streak 1 encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase confers resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Plant J 107, 1084-1101.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Makino S, Sugio A, White F, Bogdanove AJ (2006). Inhibition of resistance gene-mediated defense in rice by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19, 240-249.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Meyer M, Cox JA, Hitchings MDT, Burgin L, Hort MC, Hodson DP, Gilligan CA (2017). Quantifying airborne dispersal routes of pathogens over continents to safeguard global wheat supply. Nat Plants 3, 780-786.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Ni Z, Cao YQ, Jin X, Fu ZM, Li JY, Mo XY, He YQ, Tang JL, Huang S (2021). Engineering resistance to bacterial blight and bacterial leaf streak in rice. Rice 14, 38.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Niño-Liu DO, Ronald PC, Bogdanove AJ (2006). Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: model pathogens of a model crop. Mol Plant Pathol 7, 303-324.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Pruitt RN, Schwessinger B, Joe A, Thomas N, Liu FR, Albert M, Robinson MR, Chan LJG, Luu DD, Chen HM, Bahar O, Daudi A, De Vleesschauwer D, Caddell D, Zhang WG, Zhao XX, Li X, Heazlewood JL, Ruan DL, Majumder D, Chern M, Kalbacher H, Midha S, Patil PB, Sonti RV, Petzold CJ, Liu CC, Brodbelt JS, Felix G, Ronald PC (2015). The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci Adv 1, e1500245.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Shidore T, Broeckling CD, Kirkwood JS, Long JJ, Miao JM, Zhao BY, Leach JE, Triplett LR (2017). The effector AvrRxo1 phosphorylates NAD in planta. PLoS Pathog 13, e1006442.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Streubel J, Pesce C, Hutin M, Koebnik R, Boch J, Szurek B (2013). Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol 200, 808-819.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Tall H, Lachaux M, Diallo A, Wonni I, Tékété C, Verdier V, Szurek B, Hutin M (2022). Confirmation report of bacterial leaf streak disease of rice caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola in senegal. Plant Dis 106, 2253. |
| [26] |
Tian JJ, Hui SG, Shi YR, Yuan M (2019). The key residues of OsTFIIAγ5/Xa5 protein captured by the arginine-rich TFB domain of TALEs compromising rice susceptibility and bacterial pathogenicity. J Integr Agric 18, 1178-1188.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Timilsina S, Potnis N, Newberry EA, Liyanapathiranage P, Iruegas-Bocardo F, White FF, Goss EM, Jones JB (2020). Xanthomonas diversity, virulence and plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol 18, 415-427.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Triplett LR, Hamilton JP, Buell CR, Tisserat NA, Verdier V, Zink F, Leach JE (2011). Genomic analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae isolates from rice grown in the United States reveals substantial divergence from known X. oryzae pathovars. Appl Environ Microb 77, 3930-3937.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Triplett LR, Shidore T, Long J, Miao JM, Wu SC, Han Q, Zhou CH, Ishihara H, Li JY, Zhao BY, Leach JE (2016). AvrRxo1 is a bifunctional type III secreted effector and toxin-antitoxin system component with homologs in diverse environmental contexts. PLoS One 11, e0158856.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Wang CC, Yu H, Huang J, Wang WS, Faruquee M, Zhang F, Zhao XQ, Fu BY, Chen K, Zhang HL, Tai SS, Wei CC, McNally KL, Alexandrov N, Gao XY, Li JY, Li ZK, Xu JL, Zheng TQ (2020). Towards a deeper haplotype mining of complex traits in rice with RFGB v2.0. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 14-16.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Wang CL, Qin TF, Yu HM, Zhang XP, Che JY, Gao Y, Zheng CK, Yang B, Zhao KJ (2014). The broad bacterial blight resistance of rice line CBB23 is triggered by a novel transcription activator-like (TAL) effector of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol Plant Pathol 15, 333-341.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Wang WS, Mauleon R, Hu ZQ, Chebotarov D, Tai SS, Wu ZC, Li M, Zheng TQ, Fuentes RR, Zhang F, Mansueto L, Copetti D, Sanciangco M, Palis KC, Xu JL, Sun C, Fu BY, Zhang HL, Gao YM, Zhao XQ, Shen F, Cui X, Yu H, Li ZC, Chen ML, Detras J, Zhou YL, Zhang XY, Zhao Y, Kudrna D, Wang CC, Li R, Jia B, Lu JY, He XC, Dong ZT, Xu JB, Li YH, Wang M, Shi JX, Li J, Zhang DB, Lee S, Hu WS, Poliakov A, Dubchak I, Ulat VJ, Borja FN, Mendoza JR, Ali J, Li J, Gao Q, Niu YC, Yue Z, Naredo MEB, Talag J, Wang XQ, Li JJ, Fang XD, Yin Y, Glaszmann JC, Zhang JW, Li JY, Hamilton RS, Wing RA, Ruan J, Zhang GY, Wei CC, Alexandrov N, McNally KL, Li ZK, Leung H (2018). Genomic variation in 3,010 diverse accessions of Asian cultivated rice. Nature 557, 43-49. |
| [33] |
White FF, Yang B (2009). Host and pathogen factors controlling the rice-Xanthomonas oryzae interaction. Plant Physiol 150, 1677-1686.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Wu T, Zhang HM, Yuan B, Liu HF, Kong LG, Chu ZH, Ding XH (2022). Tal2b targets and activates the expression of OsF3H03g to hijack OsUGT74H4 and synergistically interfere with rice immunity. New Phytol 233, 1864-1880.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Xu XM, Xu ZY, Li ZY, Zakria M, Zou LF, Chen GY (2021). Increasing resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice by editing the promoter of susceptibility gene OsSULRT3;6. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1101-1103.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Xu ZY, Zou LF, Ma WX, Cai LL, Yang YY, Chen GY (2017). Action modes of transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) of Xanthomonas in plants. J Integr Agric 16, 2736-2745.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Yuan M, Ke YG, Huang RY, Ma L, Yang ZY, Chu ZH, Xiao JH, Li XH, Wang SP (2016). A host basal transcription factor is a key component for infection of rice by TALE- carrying bacteria. eLife 5, e19605.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Yugander A, Ershad M, Muthuraman PP, Prakasam V, Ladhalakshmi D, Sheshu Madhav M, Srinivas Prasad M, Sundaram RM, Laha GS (2022). Understanding the variability of rice bacterial blight pathogen, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in Andhra Pradesh, India. J Basic Microbiol 62, 185-196.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Zhang SH, He XY, Zhao JL, Cheng YS, Xie ZM, Chen YH, Yang TF, Dong JF, Wang XF, Liu Q, Liu W, Mao XX, Fu H, Chen ZM, Liao YP, Liu B (2017). Identification and validation of a novel major QTL for harvest index in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 10, 44.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Zhao BY, Lin XH, Poland J, Trick H, Leach J, Hulbert S (2005). A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 15383-15388.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [10] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [11] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [12] | 曾小宁, 王鹏行, 张梦帆, 苏静, 史志远, 高福玲, 李家美. 河南省野生木本植物名录[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(6): 22306-. |
| [13] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [14] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||