

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 132-143.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24001 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24001
• 专题论坛 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-01-02
接受日期:2024-05-04
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-05-16
通讯作者:
* 张文君, 华中农业大学资源与环境学院副教授, 博士生导师。主要利用生物学及环境化学交叉的技术手段进行土壤-植物养分循环转化及高效利用研究。主持国家自然科学基金以及国家重点研发计划子课题等项目。在New Phytologist、Plant Physiology、Journal of Experimental Botany和Environmental Science & Technology等期刊上发表研究论文30余篇, 相关论文被引用1 000余次。E-mail: wenjunzhang@mail.hzau.edu.cn基金资助:
Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang*( )
)
Received:2024-01-02
Accepted:2024-05-04
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-05-16
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)是全球重要的粮食作物。合理施肥是保障水稻持续稳产的必要农艺措施。磷是水稻生长必需的营养元素之一, 主要通过水稻根系吸收。而水稻长期生长在淹水环境中, 其根系表层形成富含铁氧化物的胶膜, 并在水稻根际磷的迁移和转化过程中扮演关键角色。该文综述了生物和非生物因素对水稻铁膜形成和转化的影响, 探讨了铁膜对磷吸收及转运的影响, 并对后续研究提出建议, 旨在为阐明水稻根际铁磷互作机制提供理论依据。
李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143.
Jianguo Li, Yi Zhang, Wenjun Zhang. Iron Plaque Formation and Its Effects on Phosphorus Absorption in Rice Roots. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 132-143.
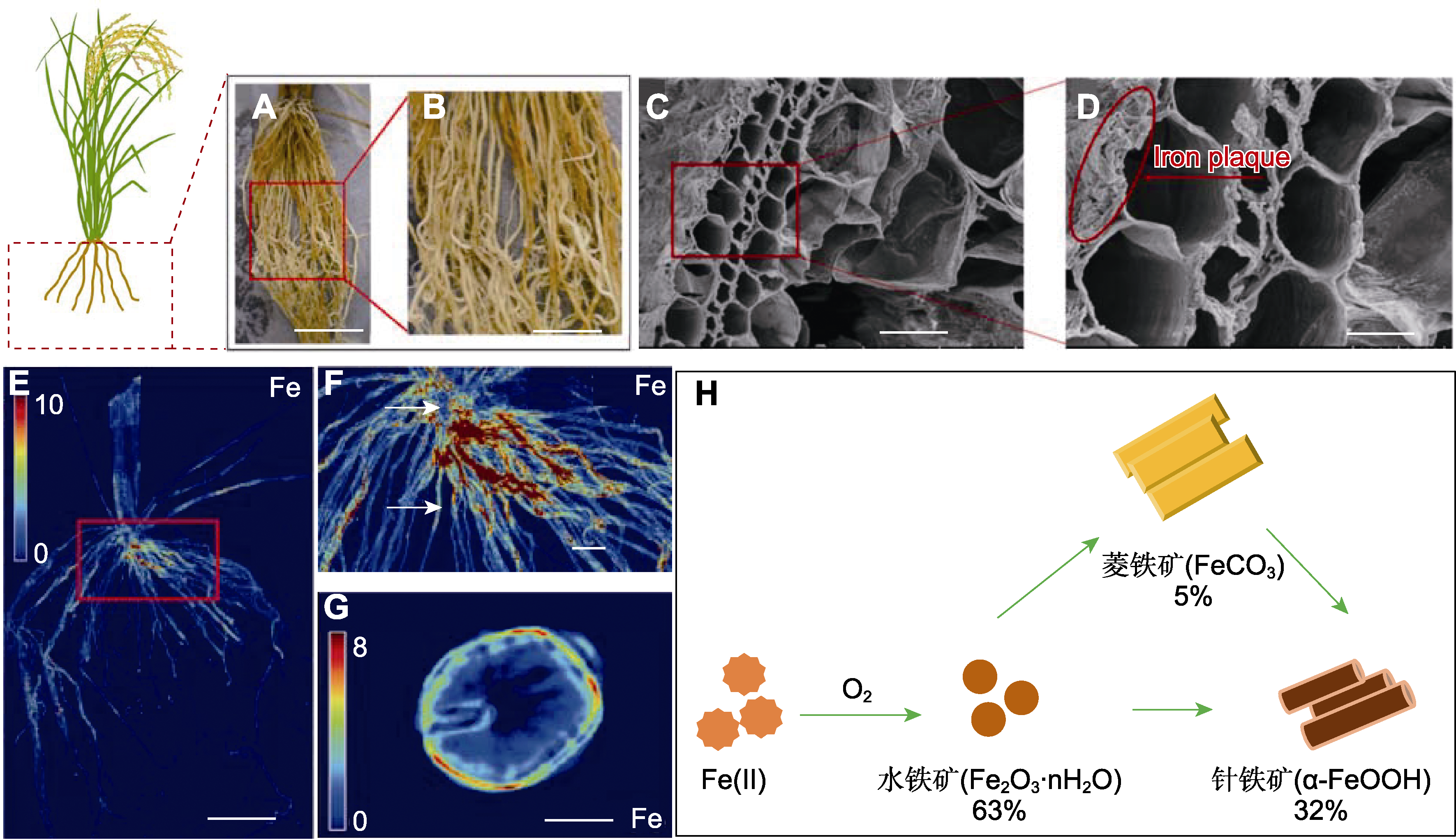
图1 水稻根表铁膜形貌及组分表征 (A), (B) 新鲜的水稻根部光学图像(Seyfferth et al., 2010); (C), (D) 水稻根横切面扫描电镜图(Tian et al., 2023); (E), (F) 水稻根部X-射线荧光(XRF)图像, (E)中红色方框及(F)中箭头均指示铁膜(Seyfferth et al., 2010); (G) X-射线断层扫描(XRT)图像(Seyfferth et al., 2010); (H) 铁膜形成过程及组分(Hansel et al., 2001)。(A) Bar=5 cm; (B) Bar=2 cm; (C) Bar=25 µm; (D) Bar=10 µm; (E) Bar=20 mm; (F) Bar=6 mm; (G) Bar= 200 µm
Figure 1 Morphology and component characterization of iron plaque on rice root surface (A), (B) Optical image of fresh rice root (Seyfferth et al., 2010); (C), (D) Scanning electron microscope image of rice root cross-section (Tian et al., 2023); (E), (F) X-ray fluorescence (XRF) images of rice roots, the red-outlined box in (E) and the arrows in (F) both represent iron plaques (Seyfferth et al., 2010); (G) X-ray tomography (XRT) images (Seyfferth et al., 2010); (H) Formation and composition of iron plaque (Hansel et al., 2001). (A) Bar=5 cm; (B) Bar=2 cm; (C) Bar=25 µm; (D) Bar=10 µm; (E) Bar= 20 mm; (F) Bar=6 mm; (G) Bar=200 µm
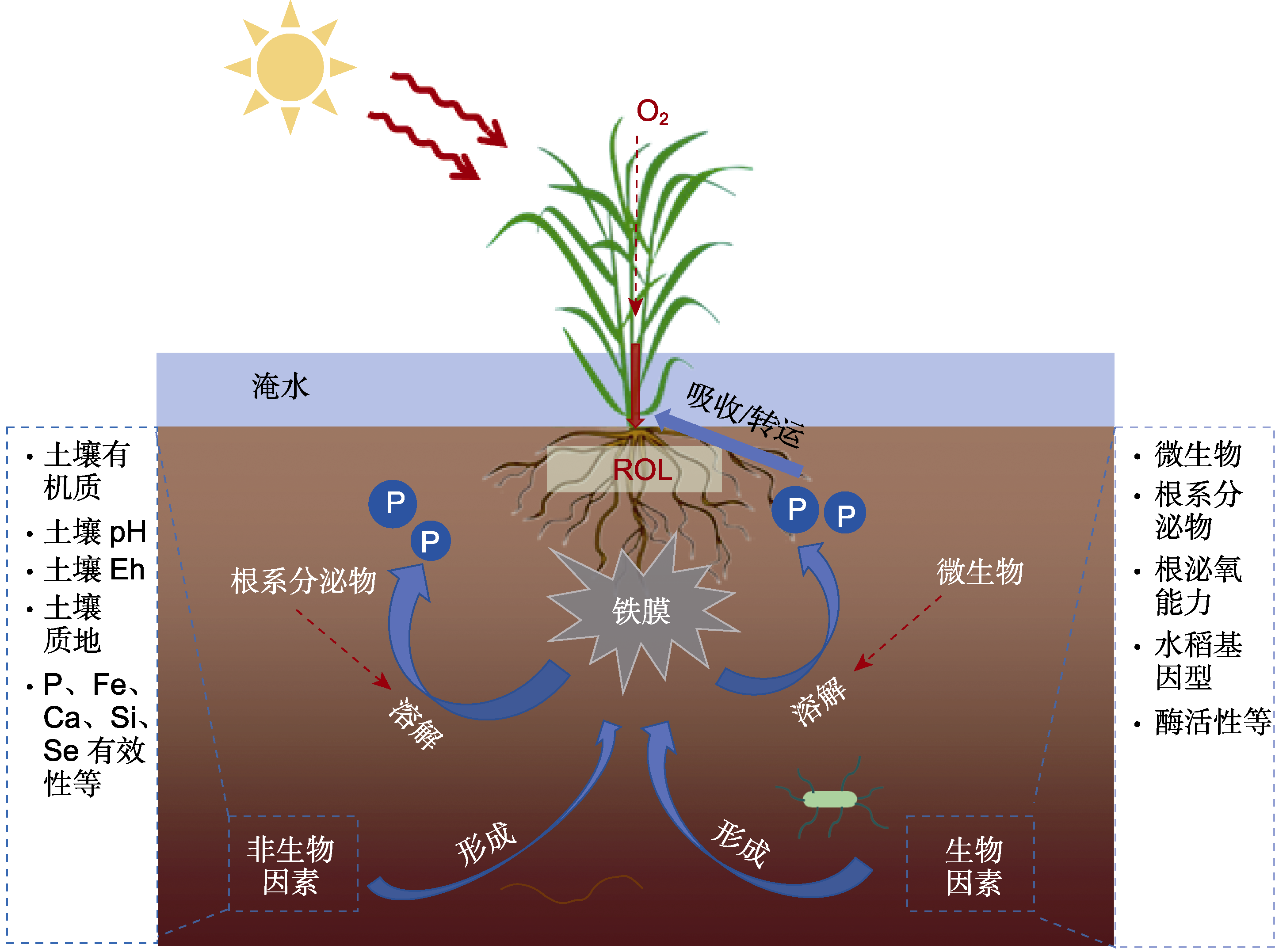
图2 水稻根际生物(微生物和根系分泌物等)及非生物(土壤pH和氧化还原电位(Eh)等)因素对根表铁膜形成的影响 在根系泌氧(ROL)等因素的调控下, 根系附近铁(II)被氧化后在根表沉积形成铁(III)膜, 铁膜对根际磷(P)养分具有富集效应, 并随着根系分泌物或微生物对铁膜结合态磷的溶解效应, 磷素被释放出来以供水稻吸收利用。
Figure 2 Effects of biotic (microbial, root exudates, etc.) and abiotic (soil pH, Eh, etc.) factors on the formation of iron plaque on rice root surface Under the regulation of radial oxygen loss (ROL) and other factors, iron (II) near the root can be oxidized and deposited on the root surface to form iron (III) plaque. Iron plaque has an enriching effect on rhizosphere phosphorus (P) nutrition, and with the dissolution effect of the root exudates or microorganisms on iron plaque-bound phosphorus, phosphorus will be released for rice absorption and utilization.
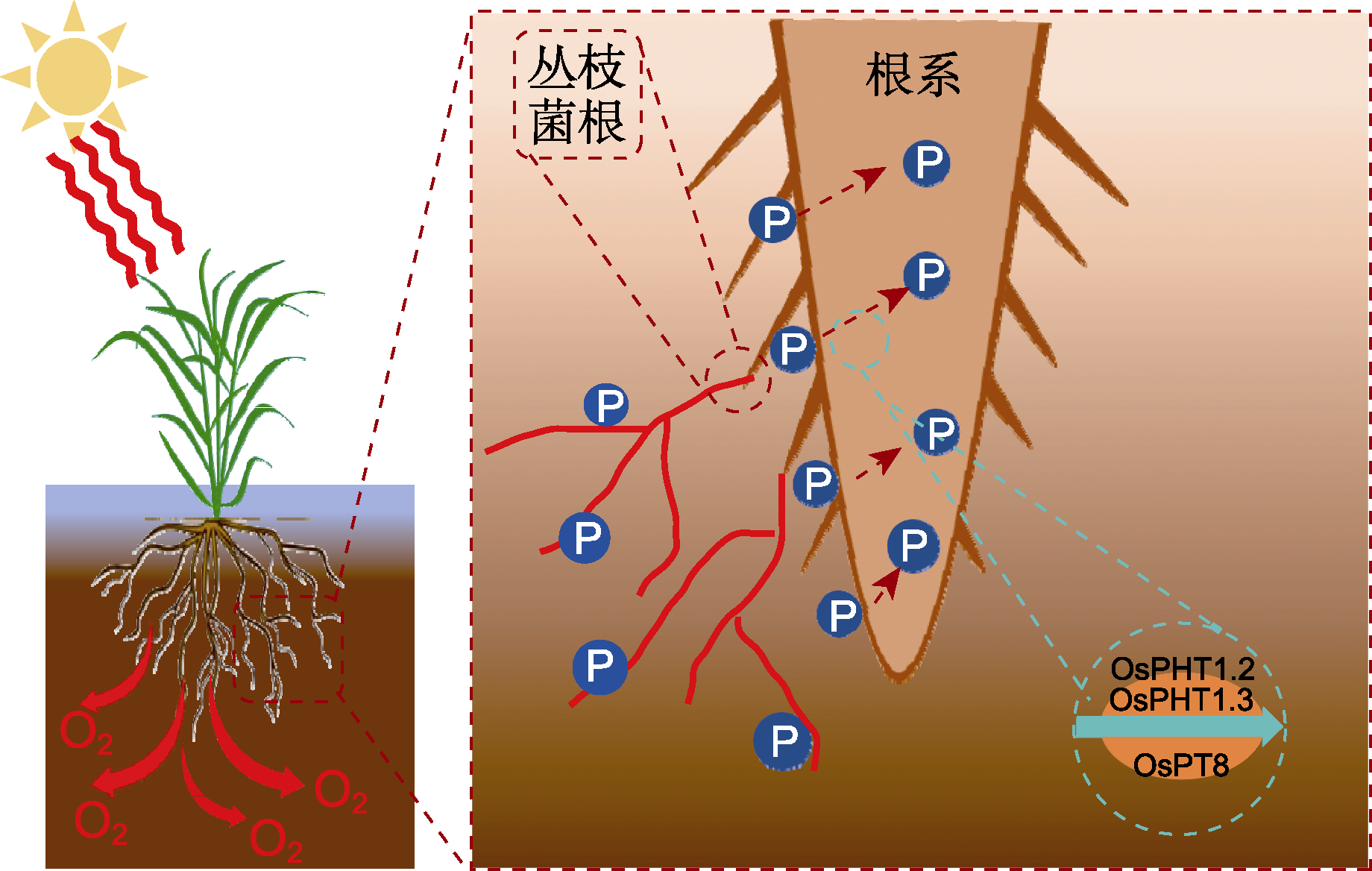
图3 水稻根系磷吸收相关机制示意图 水稻根系通过根表直接获取磷养分, 或通过铁膜及丛枝菌根等间接获取磷养分, 再通过转运蛋白吸收。
Figure 3 Schematic diagram of phosphorus absorption related mechanism in rice roots Rice roots acquire phosphorus nutrients directly through the root surface or indirectly through the iron plaque, and arbuscular mycorrhizae, and absorb them through transporters.
| [1] | Ai PH, Sun SB, Zhao JN, Fan XR, Xin WJ, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen QR, Wu P, Miller AJ, Xu GH (2009). Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J 57, 798-809. |
| [2] | Amaral DC, Lopes G, Guilherme LRG, Seyfferth AL (2017). A new approach to sampling intact Fe plaque reveals Si-induced changes in Fe mineral composition and shoot as in rice. Environ Sci Technol 51, 38-45. |
| [3] | Antoniadis V, Levizou E, Shaheen SM, Ok YS, Sebastian A, Baum C, Prasad MNV, Wenzel WW, Rinklebe J (2017). Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation—a review. Earth Sci Rev 171, 621-645. |
| [4] |
Armstrong J, Armstrong W (2001). Rice and Phragmites: effects of organic acids on growth, root permeability, and radial oxygen loss to the rhizosphere. Am J Bot 88, 1359-1370.
PMID |
| [5] | Badri DV, Chaparro JM, Zhang RF, Shen QR, Vivanco JM (2013). Application of natural blends of phytochemicals derived from the root exudates of Arabidopsis to the soil reveal that phenolic-related compounds predominantly modulate the soil microbiome. J Biol Chem 288, 4502-4512. |
| [6] | Batty LC, Younger PL (2003). Effects of external iron concentration upon seedling growth and uptake of Fe and phosphate by the common reed, Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel. Ann Bot 92, 801-806. |
| [7] | Boone CM, Bristow JM, Vanloon GW (1983). The relative efficiency of ionic iron (III) and iron (II) utilization by the rice plant. J Plant Nutr 6, 201-218. |
| [8] | Boxma R (1972). Bicarbonate as the most important soil factor in lime-induced chlorosis in the Netherlands. Plant Soil 37, 233-243. |
| [9] | Cai SY, Zhao X, Pittelkow CM, Fan MS, Zhang X, Yan XY (2023). Optimal nitrogen rate strategy for sustainable rice production in China. Nature 615, 73-79. |
| [10] |
Chang MX, Gu M, Xia YW, Dai XL, Dai CR, Zhang J, Wang SC, Qu HY, Yamaji N, Ma JF, Xu GH (2019). OsPHT1;3 mediates uptake, translocation, and remobilization of phosphate under extremely low phosphate regimes. Plant Physiol 179, 656-670.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Chen CC, Dixon JB, Turner FT (1980). Iron coatings on rice roots: morphology and models of development. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44, 1113-1119. |
| [12] |
Chen H, Wang Y, Yuan JH, Zhu WB, Chen GL, Wang SQ (2021). Effect of P fertilizer reduction regime on soil Olsen-P, root Fe-plaque P, and rice P uptake in rice-wheat rotation paddy fields. Pedosphere 31, 94-102.
DOI |
| [13] | Chen L, Lin Y, Chen PF, Wang SH, Ding YF (2019). Effect of iron deficiency on the protein profile of rice (Oryza sativa) phloem sap. Chin Bull Bot 54, 194-207. (in Chinese) |
|
陈琳, 林焱, 陈鹏飞, 王绍华, 丁艳锋 (2019). 水稻响应缺铁的韧皮部汁液蛋白质组学分析. 植物学报 54, 194-207.
DOI |
|
| [14] | Cheng BT (1982). Some significant functions of silicon to higher plants. J Plant Nutr 5, 1345-1353. |
| [15] | Christensen KK, Jensen HS, Andersen FØ, Holmer M, Wigand C (1998). Interferences between root plaque formation and phosphorus availability for isoetids in sediments of oligotrophic lakes. Biogeochemistry 43, 107-128. |
| [16] | Christensen KK, Sand-Jensen K (1998). Precipitated iron and manganese plaques restrict root uptake of phosphorus in Lobelia dortmanna. Can J Bot 76, 2158-2163. |
| [17] | Christensen KK, Wigand C (1998). Formation of root plaques and their influence on tissue phosphorus content in Lobelia dortmanna. Aquat Bot 61, 111-122. |
| [18] | Duan HY, Wang YH, Xu FS (2002). Advance on genetic aspects of phosphorus efficiency in plants. Chin Bull Bot 19, 432-438. (in Chinese) |
| 段海燕, 王运华, 徐芳森 (2002). 植物高效吸收和利用磷营养的遗传学研究进展. 植物学通报 19, 432-438. | |
| [19] | Elert E (2014). Rice by the numbers: a good grain. Nature 514, S50-S51. |
| [20] | Emerson D, Weiss JV, Megonigal JP (1999). Iron-oxidizing bacteria are associated with ferric hydroxide precipitates (Fe-plaque) on the roots of wetland plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 2758-2761. |
| [21] | Etesami H (2020). Enhanced phosphorus fertilizer use efficiency with microorganisms. In: Meena RS, ed. Nutrient Dynamics for Sustainable Crop Production. Singapore: Springer. pp. 215-245. |
| [22] | Etesami H, Jeong BR, Glick BR (2021). Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, and silicon to P uptake by plant. Front Plant Sci 12, 699618. |
| [23] | Fan YY, Sun SS, He SB (2023). Iron plaque formation and its effect on key elements cycling in constructed wetlands: functions and outlooks. Water Res 235, 119837. |
| [24] | Fink JR, Inda AV, Tiecher T, Barrón V (2016). Iron oxides and organic matter on soil phosphorus availability. Ciênc Agrotec 40, 369-379. |
| [25] | Fiorilli V, Lanfranco L, Bonfante P (2013). The expression of GintPT, the phosphate transporter of Rhizophagus irregularis, depends on the symbiotic status and phosphate availability. Planta 237, 1267-1277. |
| [26] | Ge XF, Wang LJ, Zhang WJ (2022). Direct observation of alginate-promoted soil phosphorus availability. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10, 8011-8021. |
| [27] | Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48, 909-930. |
| [28] | Giri J, Bhosale R, Huang GQ, Pandey BK, Parker H, Zappala S, Yang J, Dievart A, Bureau C, Ljung K, Price A, Rose T, Larrieu A, Mairhofer S, Sturrock CJ, White P, Dupuy L, Hawkesford M, Perin C, Liang WQ, Peret B, Hodgman CT, Lynch J, Wissuwa M, Zhang DB, Pridmore T, Mooney SJ, Guiderdoni E, Swarup R, Bennett MJ (2018). Rice auxin influx carrier OsAUX1 facilitates root hair elongation in response to low external phosphate. Nat Commun 9, 1408. |
| [29] | Graham ER (1973). Selective distribution and labile pools of micronutrient elements as factors affecting plant uptake. Soil Sci Soc Am J 37, 70-74. |
| [30] | Guo AN, Ding LJ, Tang Z, Zhao ZQ, Duan GL (2019). Microbial response to CaCO3 application in an acid soil in southern China. J Environ Sci 79, 321-329. |
| [31] | Guo W, Zhu YG, Liu WJ, Liang YC, Geng CN, Wang SG (2007). Is the effect of silicon on rice uptake of arsenate (AsV) related to internal silicon concentrations, iron plaque and phosphate nutrition? Environ Pollut 148, 251-257. |
| [32] | Hansel CM, Fendorf S, Sutton S, Newville M (2001). Characterization of Fe plaque and associated metals on the roots of mine-waste impacted aquatic plants. Environ Sci Technol 35, 3863-3868. |
| [33] | Huang AC, Jiang T, Liu YX, Bai YC, Reed J, Qu BY, Goossens A, Nützmann HW, Bai Y, Osbourn A (2019). A specialized metabolic network selectively modulates Arabidopsis root microbiota. Science 364, eaau6389. |
| [34] | Huang GX, Ding CF, Guo FY, Zhang TL, Wang XX (2018). The optimum Se application time for reducing Cd uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) and its mechanism. Plant Soil 431, 231-243. |
| [35] | Huang GX, Ding CF, Li YS, Zhang TL, Wang XX (2020). Selenium enhances iron plaque formation by elevating the radial oxygen loss of roots to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Hazard Mater 398, 122860. |
| [36] | Huang YN, Fu ZQ (2018). Study progress about the mechanism of cadmium uptake and accumulation in rice root exudates. Crop Res 32, 244-248, 264. (in Chinese) |
| 黄亚男, 傅志强 (2018). 水稻根系分泌物对镉吸收、积累影响机理研究进展. 作物研究 32, 244-248, 264. | |
| [37] | Huang YZ, Ji Z, Tao YJ, Wei SX, Jiao W, Fang YZ, Jian P, Shen CB, Qin YJ, Zhang SY, Li SQ, Liu X, Kang SM, Tian YN, Song QX, Harberd NP, Wang SK, Li S (2023). Improving rice nitrogen-use efficiency by modulating a novel monouniquitination machinery for optimal root plasticity response to nitrogen. Nat Plants 9, 1902-1914. |
| [38] | Isa M, Bai SQ, Yokoyama T, Ma JF, Ishibashi Y, Yuasa T, Iwaya-Inoue M (2010). Silicon enhances growth independent of silica deposition in a low-silica rice mutant, lsi1. Plant Soil 331, 361-375. |
| [39] | Jia HF, Ren HY, Gu M, Zhao JN, Sun SB, Zhang X, Chen JY, Wu P, Xu GH (2011). The phosphate transporter gene OsPht1;8 is involved in phosphate homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiol 156, 1164-1175. |
| [40] | Jiang FY, Chen X, Luo AC (2009). Iron plaque formation on wetland plants and its influence on phosphorus, calcium and metal uptake. Aquat Ecol 43, 879-890. |
| [41] | Kawashima C (1988). Root system formation in rice plant: III. Quantitative studies. Jpn J Crop Sci 57, 26-36. |
| [42] | Khan N, Seshadri B, Bolan N, Saint CP, Kirkham MB, Chowdhury S, Yamaguchi N, Lee DY, Li G, Kunhikrishnan A, Qi F, Karunanithi R, Qiu R, Zhu YG, Syu CH (2016). Root iron plaque on wetland plants as a dynamic pool of nutrients and contaminants. Adv Agron 138, 1-96. |
| [43] | Khashi U, Rahman M, Wang XX, Gao DM, Zhou XG, Wu FZ (2021). Root exudates increase phosphorus availability in the tomato/potato onion intercropping system. Plant Soil 464, 45-62. |
| [44] | King GM, Garey MA (1999). Ferric iron reduction by bacteria associated with the roots of freshwater and marine macrophytes. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 4393-4398. |
| [45] | Kuppe CW, Kirk GJD, Wissuwa M, Postma JA (2022). Rice increases phosphorus uptake in strongly sorbing soils by intra-root facilitation. Plant Cell Environ 45, 884-899. |
| [46] | Lazali M, Bargaz A (2017). Examples of belowground mechanisms enabling legumes to mitigate phosphorus deficiency. In: Sulieman S, Tran LSP, eds. Legume Nitrogen Fixation in Soils with Low Phosphorus Availability. Cham: Springer Cham. pp. 135-152. |
| [47] | Li J, Liu JC, Yan CL, Du DL, Lu HL (2019a). The alleviation effect of iron on cadmium phytotoxicity in mangrove A. marina. Alleviation effect of iron on cadmium phytotoxicity in mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Chemosphere 226, 413-420. |
| [48] |
Li LH, Liu C, Lian XM (2010). Gene expression profiles in rice roots under low phosphorus stress. Plant Mol Biol 72, 423-432.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Li WT, Chern M, Yin JJ, Wang J, Chen XW (2019b). Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50, 114-120. |
| [50] | Li X, Wang P, Li J, Wei SB, Yan YY, Yang J, Zhao M, Langdale JA, Zhou WB (2020). Maize GOLDEN2-LIKE genes enhance biomass and grain yields in rice by improving photosynthesis and reducing photoinhibition. Commun Biol 3, 151. |
| [51] | Li YC, Yu S, Strong J, Wang HL (2012). Are the biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus driven by the “FeIII-FeII redox wheel” in dynamic redox environments? J Soils Sediments 12, 683-693. |
| [52] | Liang Y, Zhu YG, Xia Y, Li Z, Ma Y (2006). Iron plaque enhances phosphorus uptake by rice (Oryza sativa) growing under varying phosphorus and iron concentrations. Ann Appl Biol 149, 305-312. |
| [53] | Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA, Smith SE (2004). Do phosphorus nutrition and iron plaque alter arsenate (As) uptake by rice seedlings in hydroponic culture? New Phytol 162, 481-488. |
| [54] | Loeppert RH, Hossner LR, Chmielewski MA (1984). Indigenous soil properties influencing the availability of Fe in calcareous hot spots. J Plant Nutr 7, 135-147. |
| [55] | Lovley DR (1995). Microbial reduction of iron, manganese, and other metals. Adv Agron 54, 175-231. |
| [56] | Lovley DR, Fraga JL, Blunt-Harris EL, Hayes LA, Phillips EJP, Coates JD (1998). Humic substances as a mediator for microbially catalyzed metal reduction. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 26, 152-157. |
| [57] |
Lovley DR, Holmes DE, Nevin KP (2004). Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Adv Microb Physiol 49, 219-286.
PMID |
| [58] | Lueder U, Jørgensen BB, Kappler A, Schmidt C (2020). Photochemistry of iron in aquatic environments. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 22, 12-24. |
| [59] | Lynch JP, Brown KM (2008). Root strategies for phosphorus acquisition. In: White PJ, Hammond JP, eds. The Ecophysiology of Plant-Phosphorus Interactions. Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 83-116. |
| [60] | Ma ZS (2016). Research, rethink and revolutionize rice breeding: an interview with Qifa Zhang. Natl Sci Rev 3, 328-330. |
| [61] | Mendelssohn IA, Kleiss BA, Wakeley JS (1995). Factors controlling the formation of oxidized root channels: a review. Wetlands 15, 37-46. |
| [62] | Meng FL, Zhang X, Hu Y, Sheng GP (2024). New barrier role of iron plaque: producing interfacial hydroxyl radicals to degrade rhizosphere pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 58, 795-804. |
| [63] | Mohamed I, Ahamadou B, Li M, Gong CX, Cai P, Liang W, Huang QY (2010). Fractionation of copper and cadmium and their binding with soil organic matter in a contaminated soil amended with organic materials. J Soils Sediments 10, 973-982. |
| [64] | Møller CL, Sand-Jensen K (2008). Iron plaques improve the oxygen supply to root meristems of the freshwater plant, Lobelia dortmanna. New Phytol 179, 848-856. |
| [65] | Mora-Macías J, Ojeda-Rivera JO, Gutiérrez-Alanís D, Yong- Villalobos L, Oropeza-Aburto A, Raya-González J, Jiménez-Domínguez G, Chávez-Calvillo G, Rellán- Álvarez R, Herrera-Estrella L (2017). Malate-dependent Fe accumulation is a critical checkpoint in the root developmental response to low phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E3563-E3572. |
| [66] | Qiao JT, Liu TX, Wang XQ, Li FB, Lv YH, Cui JH, Zeng XD, Yuan YZ, Liu CP (2018). Simultaneous alleviation of cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice by applying zero-valent iron and biochar to contaminated paddy soils. Chemosphere 195, 260-271. |
| [67] | Qin LH, Zhang WJ, Lu JW, Stack AG, Wang LJ (2013). Direct imaging of nanoscale dissolution of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate by an organic ligand: concentration matters. Environ Sci Technol 47, 13365-13374. |
| [68] | Raghothama KG (1999). Phosphate acquisition. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50, 665-693. |
| [69] |
Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (2011). Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol 156, 989-996.
DOI PMID |
| [70] | Saleque MA, Naher UA, Islam A, Pathan ABMBU, Hossain ATMS, Meisner CA (2004). Inorganic and organic phosphorus fertilizer effects on the phosphorus fractionation in wetland rice soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 68, 1635-1644. |
| [71] | Sánchez-Alcalá I, Del Campillo MC, del Torrent J, Straub KL, Kraemer SM (2011). Iron(III) reduction in anaerobically incubated suspensions of highly calcareous agricultural soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75, 2136-2146. |
| [72] | Sarkar AN, Wynjones RG (1982). Effect of rhizosphere pH on the availability and uptake of Fe, Mn and Zn. Plant Soil 66, 361-372. |
| [73] | Seppänen M, Turakainen M, Hartikainen H (2003). Selenium effects on oxidative stress in potato. Plant Sci 165, 311-319. |
| [74] | Seyfferth AL, Ross J, Webb SM (2017). Evidence for the root-uptake of arsenite at lateral root junctions and root apices in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Soils 1, 3. |
| [75] | Seyfferth AL, Webb SM, Andrews JC, Fendorf S (2010). Arsenic localization, speciation, and co-occurrence with iron on rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots having variable Fe coatings. Environ Sci Technol 44, 8108-8113. |
| [76] | Sha G, Sun P, Kong XJ, Han XY, Sun QP, Fouillen L, Zhao J, Li Y, Yang L, Wang Y, Gong QW, Zhou YR, Zhou WQ, Jain R, Gao J, Huang RL, Chen XY, Zheng L, Zhang WY, Qin ZT, Zhou Q, Zeng QD, Xie KB, Xu JD, Chiu TY, Guo L, Mortimer JC, Boutté Y, Li Q, Kang ZS, Ronald PC, Li GT (2023). Genome editing of a rice CDP-DAG synthase confers multipathogen resistance. Nature 618, 1017-1023. |
| [77] | Sharma SB, Sayyed RZ, Trivedi MH, Gobi TA (2013). Phosphate solubilizing microbes: sustainable approach for managing phosphorus deficiency in agricultural soils. Springer Plus 2, 587. |
| [78] |
Shaw LJ, Burns RG (2003). Biodegradation of organic pollutants in the rhizosphere. Adv Appl Microbiol 53, 1-60.
PMID |
| [79] | Shen JB, Bai Y, Wei Z, Chu CC, Yuan LX, Zhang L, Cui ZL, Cong WF, Zhang FS (2021). Rhizobiont: an interdisciplinary innovation and perspective for harmonizing resources, environment, and food security. Acta Pedol Sin 58, 805-813. (in Chinese) |
| 申建波, 白洋, 韦中, 储成才, 袁力行, 张林, 崔振岭, 丛汶峰, 张福锁 (2021). 根际生命共同体: 协调资源、环境和粮食安全的学术思路与交叉创新. 土壤学报 58, 805-813. | |
| [80] |
Shen JB, Yuan LX, Zhang JL, Li HG, Bai ZH, Chen XP, Zhang WF, Zhang FS (2011). Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant. Plant Physiol 156, 997-1005.
DOI PMID |
| [81] | Singha KT, Sebastian A, Prasad MNV (2019). Iron plaque formation in the roots of Pistia stratiotes L.: importance in phytoremediation of cadmium. Int J Phytorem 21, 120-128. |
| [82] |
Smith SE, Smith FA (2011). Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant nutrition and growth: new paradigms from cellular to ecosystem scales. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62, 227-250.
DOI PMID |
| [83] |
Sun FS, Polizzotto ML, Guan DX, Wu J, Shen QR, Ran W, Wang BR, Yu GH (2017). Exploring the interactions and binding sites between Cd and functional groups in soil using two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy and synchrotron radiation based spectromicroscopies. J Hazard Mater 326, 18-25.
DOI PMID |
| [84] | Sundby B, Vale C, Caçador Z, Catarino F, Madureira MJ, Caetano M (1998). Metal-rich concretions on the roots of salt marsh plants: mechanism and rate of formation. Limnol Oceanogr 43, 245-252. |
| [85] | Syu CH, Jiang PY, Huang HH, Chen WT, Lin TH, Lee DY (2013). Arsenic sequestration in iron plaque and its effect on As uptake by rice plants grown in paddy soils with high contents of As, iron oxides, and organic matter. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 59, 463-471. |
| [86] | Syu CH, Lee CH, Jiang PY, Chen MK, Lee DY (2014). Comparison of as sequestration in iron plaque and uptake by different genotypes of rice plants grown in As-contaminated paddy soils. Plant Soil 374, 411-422. |
| [87] | Tai YP, Tam NFY, Wang R, Yang Y, Lin JH, Wang JX, Yang YF, Li L, Sun YM (2018). Iron plaque formation on wetland-plant roots accelerates removal of water-borne antibiotics. Plant Soil 433, 323-338. |
| [88] | Tao Q, Zhao JW, Li JX, Liu YK, Luo JP, Yuan S, Li B, Li QQ, Xu Q, Yu XF, Huang HG, Li TQ, Wang CQ (2020). Unique root exudate tartaric acid enhanced cadmium mobilization and uptake in Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 383, 121177. |
| [89] | Tian XS, Chai GQ, Lu M, Xiao R, Xie Q, Luo LZ (2023). A new insight into the role of iron plaque in arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 254, 114714. |
| [90] |
Tisserant E, Kohler A, Dozolme-Seddas P, Balestrini R, Benabdellah K, Colard A, Croll D, Da Silva C, Gomez SK, Koul R, Ferrol N, Fiorilli V, Formey D, Franken P, Helber N, Hijri M, Lanfranco L, Lindquist E, Liu Y, Malbreil M, Morin E, Poulain J, Shapiro H, van Tuinen D, Waschke A, Azcón-Aguilar C, Bécard G, Bonfante P, Harrison MJ, Küster H, Lammers P, Paszkowski U, Requena N, Rensing SA, Roux C, Sanders IR, Shachar-Hill Y, Tuskan G, Young JPW, Gianinazzi-Pearson V, Martin F (2012). The transcriptome of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices (DAOM 197198) reveals functional tradeoffs in an obligate symbiont. New Phytol 193, 755-769.
DOI PMID |
| [91] | Wang CQ, Thielemann L, Dippold MA, Guggenberger G, Kuzyakov Y, Banfield CC, Ge TD, Guenther S, Bork P, Horn MA, Dorodnikov M (2022a). Can the reductive dissolution of ferric iron in paddy soils compensate phosphorus limitation of rice plants and microorganisms? Soil Biol Biochem 168, 108653. |
| [92] | Wang CQ, Thielemann L, Dippold MA, Guggenberger G, Kuzyakov Y, Banfield CC, Ge TD, Guenther S, Bork P, Horn MA, Dorodnikov M (2022b). Microbial iron reduction compensates for phosphorus limitation in paddy soils. Sci Total Environ 837, 155810. |
| [93] | Wang CQ, Thielemann L, Dippold MA, Guggenberger G, Kuzyakov Y, Banfield CC, Ge TD, Guenther S, Dorodnikov M (2023a). Reductive dissolution of iron phosphate modifies rice root morphology in phosphorus-deficient paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 177, 108904. |
| [94] | Wang LJ, Putnis CV, Hövelmann J, Putnis A (2018). Interfacial precipitation of phosphate on hematite and goethite. Minerals 8, 207. |
| [95] | Wang LJ, Putnis CV, Ruiz-Agudo E, Hövelmann J, Putnis A (2015). In situ imaging of interfacial precipitation of phosphate on goethite. Environ Sci Technol 49, 4184-4192. |
| [96] | Wang X, Li HG, Cheng LY, Wang BL, Shen JB (2017). Advances of root-soil interface effect of phosphorus and water interaction and mechanisms of their efficient use. J Plant Nutr Fert 23, 1054-1064. (in Chinese) |
| 王昕, 李海港, 程凌云, 王宝兰, 申建波 (2017). 磷与水分互作的根土界面效应及其高效利用机制研究进展. 植物营养与肥料学报 23, 1054-1064. | |
| [97] |
Wang Y, Yuan JH, Chen H, Zhao X, Wang DJ, Wang SQ, Ding SM (2019). Small-scale interaction of iron and phosphorus in flooded soils with rice growth. Sci Total Environ 669, 911-919.
DOI |
| [98] | Wang YY, Luo DH, Xiong ZY, Wang ZF, Gao M (2023b). Changes in rhizosphere phosphorus fractions and phosphate-mineralizing microbial populations in acid soil as influenced by organic acid exudation. Soil Tillage Res 225, 105543. |
| [99] | Wei T, Liu X, Dong MF, Lv X, Hua L, Jia HL, Ren XH, Yu SH, Guo JK, Li YT (2021). Rhizosphere iron and manganese-oxidizing bacteria stimulate root iron plaque formation and regulate Cd uptake of rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). J Environ Manage 278, 111533. |
| [100] | Weiss JV, Emerson D, Backer SM, Megonigal JP (2003). Enumeration of Fe(II)-oxidizing and Fe(III)-reducing bacteria in the root zone of wetland plants: implications for a rhizosphere iron cycle. Biogeochemistry 64, 77-96. |
| [101] |
Wu C, Zou Q, Xue SG, Pan WS, Huang L, Hartley W, Mo JY, Wong MH (2016). The effect of silicon on iron plaque formation and arsenic accumulation in rice genotypes with different radial oxygen loss (ROL). Environ Pollut 212, 27-33.
DOI PMID |
| [102] | Wu LB, Shhadi MY, Gregorio G, Matthus E, Becker M, Frei M (2014). Genetic and physiological analysis of tolerance to acute iron toxicity in rice. Rice 7, 8. |
| [103] |
Wu ZC, Ren HY, McGrath SP, Wu P, Zhao FJ (2011). Investigating the contribution of the phosphate transport pathway to arsenic accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 157, 498-508.
DOI PMID |
| [104] | Xiao SY, Luo M, Liu YX, Bai J, Yang Y, Zhai ZF, Huang JF (2021). Rhizosphere effect and its associated soil-microbe interactions drive iron fraction dynamics in tidal wetland soils. Sci Total Environ 756, 144056. |
| [105] |
Xing JJ, Zhang L, Duan ZK, Lin JX (2021). Coordination of phospholipid-based signaling and membrane trafficking in plant immunity. Trends Plant Sci 26, 407-420.
DOI PMID |
| [106] | Xu DF, Xu JM, He Y, Huang PM (2009). Effect of iron plaque formation on phosphorus accumulation and availability in the rhizosphere of wetland plants. Water Air Soil Pollut 200, 79-87. |
| [107] | Yan XJ, Chen XH, Ma CC, Cai YY, Cui ZL, Chen XP, Wu LQ, Zhang FS (2021). What are the key factors affecting maize yield response to and agronomic efficiency of phosphorus fertilizer in China? Field Crops Res 270, 108221. |
| [108] | Yoon DK, Ishiyama K, Suganami M, Tazoe Y, Watanabe M, Imaruoka S, Ogura M, Ishida H, Suzuki Y, Obara M, Mae T, Makino A (2020). Transgenic rice overproducing Rubisco exhibits increased yields with improved nitrogen- use efficiency in an experimental paddy field. Nat Food 1, 134-139. |
| [109] | Yu CX, Xie SR, Song ZL, Xia SP, Åström ME (2021). Biogeochemical cycling of iron (hydr-)oxides and its impact on organic carbon turnover in coastal wetlands: a global synthesis and perspective. Earth Sci Rev 218, 103658. |
| [110] | Zhang CH, Ge Y, Yao H, Chen X, Hu MK (2012). Iron oxidation-reduction and its impacts on cadmium bioavailability in paddy soils: a review. Front Environ Sci Eng 6, 509-517. |
| [111] | Zhang FS, Shen JB, Zhang JL, Zuo YM, Li L, Chen XP (2010). Rhizosphere processes and management for improving nutrient use efficiency and crop productivity: implications for China. Adv Agron 107, 1-32. |
| [112] | Zhang QQ, Yan ZZ, Li XZ (2021). Iron plaque formation and rhizosphere iron bacteria in Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis on the redoxcline of tidal flat in the Yangtze River Estuary. Geoderma 392, 115000. |
| [113] | Zhang QQ, Yan ZZ, Li XZ, Xu Y, Sun XL, Liang QY (2019). Formation of iron plaque in the roots of Spartina alterniflora and its effect on the immobilization of wastewater- borne pollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 168, 212-220. |
| [114] | Zhang XK, Zhang FS, Mao DR (1997). Effect of root iron plaque on phosphorus uptake by rice plant. Plant Nutr Fert Sci 3, 295-299. (in Chinese) |
| 张西科, 张福锁, 毛达如 (1997). 水稻根表铁氧化物胶膜对水稻吸收磷的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报 3, 295-299. | |
| [115] | Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Meharg AA (2010). Arsenic as a food chain contaminant: mechanisms of plant uptake and metabolism and mitigation strategies. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 535-559. |
| [116] | Zhou ZG, Wang JF, Zhou JM (2005). Current advances in the molecular biology of high efficient phosphorus nutrition in plants. Chin Bull Bot 22, 82-91. (in Chinese) |
| 周志高, 汪金舫, 周健民 (2005). 植物磷营养高效的分子生物学研究进展. 植物学通报 22, 82-91. | |
| [117] | Zhu Q, Riley WJ, Tang JY, Koven CD (2016). Multiple soil nutrient competition between plants, microbes, and mineral surfaces: model development, parameterization, and example applications in several tropical forests. Biogeosciences 13, 341-363. |
| [118] | Zou T, Zhang X, Davidson EA (2022). Global trends of cropland phosphorus use and sustainability challenges. Nature 611, 81-87. |
| [1] | 张静 陈洁 李艳朋 盘李军 许涵 李意德 何海生. 南亚热带针阔混交人工林植物生物量比较及其影响因子分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 0-0. |
| [2] | 张琳, 袁伟影, 宋创业, 吴冬秀. 1998~2010年中国典型生态系统环境要素、物种丰富度和生物量动态数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(典型生态系统数据集): 1-. |
| [3] | 朱瑞德, 杨俊薇, 刘宵含, 陈冰瑞, 池秀莲, 田地, 杨光, 程蒙, 戴亚峰, 王诗文, 陈仲. 霍山石斛设施和林下栽培模式中养分对植物-微生物关联的调控[J]. , 2025, 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 0-. |
| [4] | 韩菲, 王袼, 武帅楷, 林茂, 董宽虎, $\boxed{\hbox{王常慧}}$, 苏原. 极端降水对不同草原土壤总硝化及总氮矿化速率及其敏感性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 697-709. |
| [5] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [6] | 李欣怡, 张丽芳, 吴友贵, 郭静, 兰荣光, 吕洪飞, 于明坚. 不同海拔高度下百山祖冷杉幼苗的生长特征及其影响因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 610-623. |
| [7] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [8] | 马亮, 杨永青, 郭岩. “后绿色革命”基因——助力培育“气候智能”作物新品种[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 489-498. |
| [9] | 莫笑梅, 张琪, 杨嘉欣, 郑国, 胡中民, 张晓珂, 梁思维, 崔淑艳. 北方典型草地土壤线虫代谢速率及能量流动对氮沉降和降水模式改变的响应[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24341-. |
| [10] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 江智诚, 刘江慧, 闫江超. 短期氮、水添加和刈割减弱了苦豆子型退化草地土壤生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的联系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24305-. |
| [11] | 马尚飞, 龚鑫, 上官华媛, 姚海凤, 王滨, 李志鹏, 孙新. 城市化过程中不同用地类型对土壤真核生物多样性的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24540-. |
| [12] | 李冬梅, 孙龙, 韩宇, 胡同欣, 杨光, 蔡慧颖. 计划火烧对红松人工林生物多样性与生态系统多功能性关系的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(3): 379-392. |
| [13] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [14] | 葛小彩, 李锦隆, 孙俊, 武盼盼, 胡丹丹, 程栋梁, 钟全林. 武夷山亚高山草甸土壤呼吸组分特征及影响因素[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(3): 502-512. |
| [15] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||