

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (5): 738-751.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24065 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24065
所属专题: 大食物观
连锦瑾1,†, 唐璐瑶1,†, 张伊诺1, 郑佳兴1, 朱超宇1, 叶语涵1, 王跃星2, 商文楠3, 傅正浩1, 徐昕璇1, 吴日成1, 路梅1, 王长春1,*( ), 饶玉春1,*(
), 饶玉春1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-30
接受日期:2024-06-21
出版日期:2024-09-10
发布日期:2024-08-19
通讯作者:
王长春,饶玉春
作者简介:第一联系人: 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Jinjin Lian1,†, Luyao Tang1,†, Yinuo Zhang1, Jiaxing Zheng1, Chaoyu Zhu1, Yuhan Ye1, Yuexing Wang2, Wennan Shang3, Zhenghao Fu1, Xinxuan Xu1, Richeng Wu1, Mei Lu1, Changchun Wang1,*( ), Yuchun Rao1,*(
), Yuchun Rao1,*( )
)
Received:2024-04-30
Accepted:2024-06-21
Online:2024-09-10
Published:2024-08-19
Contact:
Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao
About author:First author contact: These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)是世界上最重要的粮食作物之一。提高水稻抗氧化性, 进而提高抗逆性是保障其高产稳产的重要途径。选用籼稻华占(HZ)和粳稻热研2号(Nekken2)及以其为亲本构建的120个重组自交系(RILs), 分别在分蘖期、灌浆期和成熟期测定亲本及其后代剑叶、颖壳及籽粒中羟基自由基清除率、总酚含量、黄酮含量和花青苷含量, 同时基于已构建的高密度遗传连锁图谱进行数量性状基因座(QTL)定位。结果共挖掘到62个与水稻抗氧化损伤有关的QTLs, 其中LOD值最高达4.36。对这些QTL区间内相关候选基因的表达进行定量分析, 结果表明LOC_Os06g01850、LOC_Os12g07820、LOC_ Os12g07830和LOC_Os03g60509等13个基因的表达在不同时期的双亲间差异显著。研究挖掘到众多与水稻抗氧化性相关的QTLs, 为进一步定位并克隆相关基因, 选育抗性强且营养价值高的水稻新品种奠定基础。
连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751.
Jinjin Lian, Luyao Tang, Yinuo Zhang, Jiaxing Zheng, Chaoyu Zhu, Yuhan Ye, Yuexing Wang, Wennan Shang, Zhenghao Fu, Xinxuan Xu, Richeng Wu, Mei Lu, Changchun Wang, Yuchun Rao. Genetic Locus Mining and Candidate Gene Analysis of Antioxidant Traits in Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 738-751.
| Physiological traits | Gene name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsActin | TGGCATCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA | |
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate | LOC_Os06g01850 | ACATGGTCTTCAGCACCGAG | CTTTGCCTACTGGTCCGGTT |
| LOC_Os06g48000 | TTCAACCTCGACCAGCTCAC | GGAGGTTCTGGTAGAAGGCG | |
| LOC_Os06g48020 | GTTGTGACGCGTCGATCATG | CCGCTCTGGTAGACGGATTC | |
| Total phenolic content | LOC_Os04g45210 | AGCTGGTCAAGACGTTCCAG | GAAGTAGACCATCTCGCCGG |
| LOC_Os12g07820 | GTTCGGTTAGGGTGGCATGA | CATTGTTCAGGGGCAGCAAC | |
| LOC_Os12g07830 | CCTCTCCCCTCCCTTCTCTC | GTCATGCCACCCTAACCGAA | |
| Flavonoid content | LOC_Os05g12190 | GACCTCAAGCTGGCATCACT | CCCAAACAGTCCATGACCGA |
| LOC_Os05g12210 | ATGCCCTCCCTTGAAACTCG | TCACGGTTGTTCTCGGTGAG | |
| LOC_Os05g12240 | GGCCTCAACCCTTCTGTCTC | AGGACCATCTCAAACAGCGG | |
| LOC_Os05g45120 | CTCATGGTGGAGGACATGGG | CAACAGGAACTCGGCAAACG | |
| LOC_Os12g16260 | TGATACGCAACTTCTACACTGCT | AGATGGCTCAGGTTGGTTGG | |
| Anthocyanin content | LOC_Os03g60509 | TGTGTTCCGTGTCAGTGGAG | CAGGATCATCGTCACCCTCG |
| LOC_Os03g62480 | CCATCCCCGCCTACTTCTTC | ATCGAAGCTGTTCACGAGCA |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Physiological traits | Gene name | Forward primer (5'-3') | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OsActin | TGGCATCTCAGCACATTCC | TGCACAATGGATGGGTCAGA | |
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate | LOC_Os06g01850 | ACATGGTCTTCAGCACCGAG | CTTTGCCTACTGGTCCGGTT |
| LOC_Os06g48000 | TTCAACCTCGACCAGCTCAC | GGAGGTTCTGGTAGAAGGCG | |
| LOC_Os06g48020 | GTTGTGACGCGTCGATCATG | CCGCTCTGGTAGACGGATTC | |
| Total phenolic content | LOC_Os04g45210 | AGCTGGTCAAGACGTTCCAG | GAAGTAGACCATCTCGCCGG |
| LOC_Os12g07820 | GTTCGGTTAGGGTGGCATGA | CATTGTTCAGGGGCAGCAAC | |
| LOC_Os12g07830 | CCTCTCCCCTCCCTTCTCTC | GTCATGCCACCCTAACCGAA | |
| Flavonoid content | LOC_Os05g12190 | GACCTCAAGCTGGCATCACT | CCCAAACAGTCCATGACCGA |
| LOC_Os05g12210 | ATGCCCTCCCTTGAAACTCG | TCACGGTTGTTCTCGGTGAG | |
| LOC_Os05g12240 | GGCCTCAACCCTTCTGTCTC | AGGACCATCTCAAACAGCGG | |
| LOC_Os05g45120 | CTCATGGTGGAGGACATGGG | CAACAGGAACTCGGCAAACG | |
| LOC_Os12g16260 | TGATACGCAACTTCTACACTGCT | AGATGGCTCAGGTTGGTTGG | |
| Anthocyanin content | LOC_Os03g60509 | TGTGTTCCGTGTCAGTGGAG | CAGGATCATCGTCACCCTCG |
| LOC_Os03g62480 | CCATCCCCGCCTACTTCTTC | ATCGAAGCTGTTCACGAGCA |
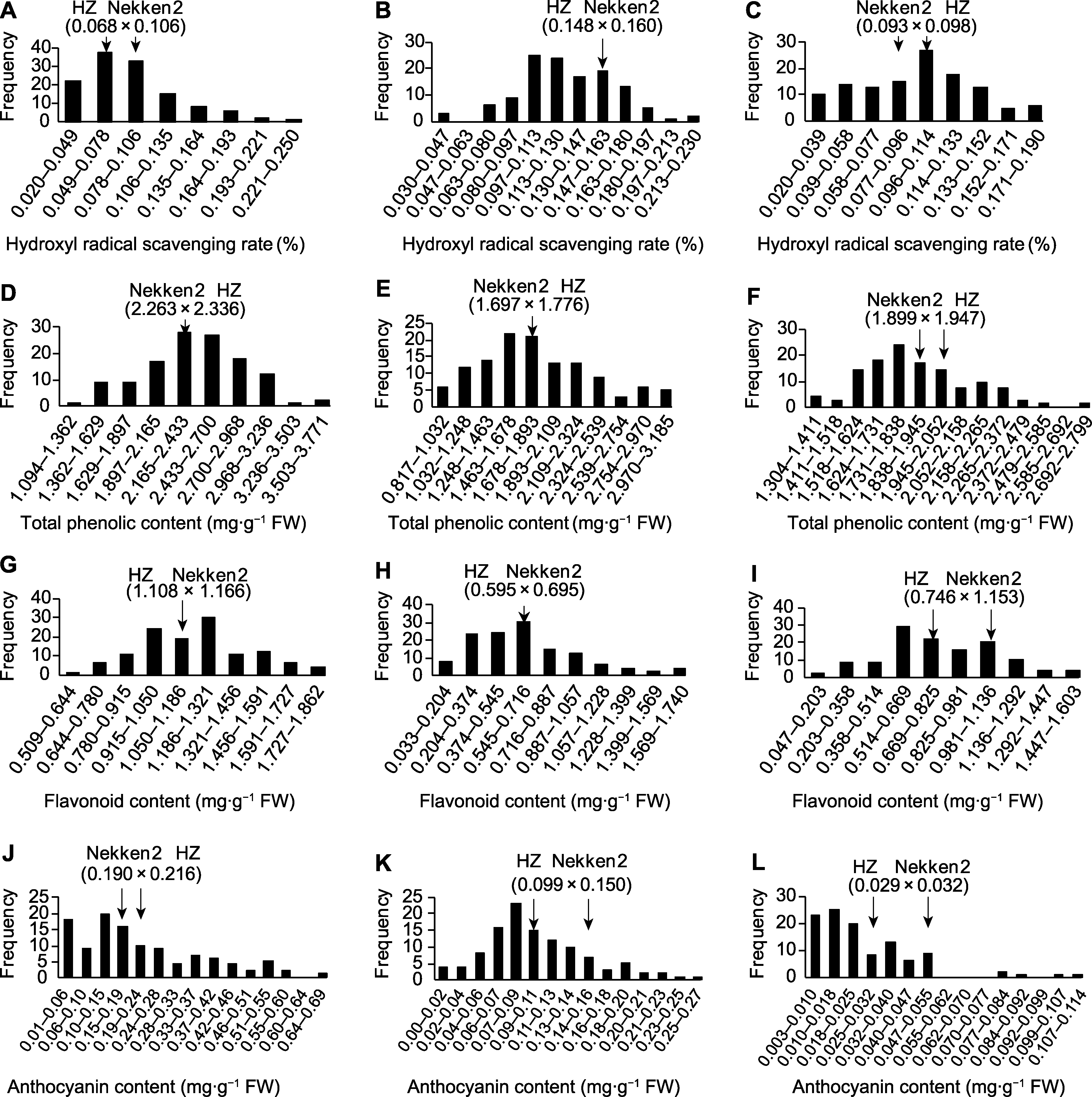
图2 水稻重组自交系抗氧化性状分布 (A) 分蘖期羟基自由基清除率; (B) 灌浆期羟基自由基清除率; (C) 成熟期羟基自由基清除率; (D) 分蘖期总酚含量; (E) 灌浆期总酚含量; (F) 成熟期总酚含量; (G) 分蘖期黄酮含量; (H) 灌浆期黄酮含量; (I) 成熟期黄酮含量; (J) 分蘖期花青苷含量; (K) 灌浆期花青苷含量; (L) 成熟期花青苷含量
Figure 2 Distribution of antioxidant traits in the recombinant inbred lines of rice (A) Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate at the tillering stage; (B) Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate at the grain filling stage; (C) Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate at the maturity stage; (D) Total phenolic content at the tillering stage; (E) Total phenolic content at the grain filling stage; (F) Total phenolic content at the maturity stage; (G) Flavonoid content at the tillering stage; (H) Flavonoid content at the grain filling stage; (I) Flavonoid content at the maturity stage; (J) Anthocyanin content at the tillering stage; (K) Anthocyanin content at the grain filling stage; (L) Anthocyanin content at the maturity stage
| Physiological traits | QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate | qHRSR1.1 | 1 | 2556386-2834929 | 10.96-12.15 | 2.14 |
| qHRSR2.1 | 2 | 3467582-4955784 | 14.87-21.24 | 4.36 | |
| qHRSR2.2 | 2 | 5098574-6084984 | 21.86-26.08 | 3.37 | |
| qHRSR2.3 | 2 | 27009300-27239796 | 115.78-116.77 | 2.75 | |
| qHRSR2.4 | 2 | 28427871-28664694 | 121.86-122.88 | 2.21 | |
| qHRSR3.1 | 3 | 12723031-12925845 | 54.54-55.41 | 2.22 | |
| qHRSR3.2 | 3 | 29949770-30321190 | 128.39-129.98 | 2.31 | |
| qHRSR4.1 | 4 | 23316226-23991142 | 99.95-102.84 | 3.35 | |
| qHRSR4.2 | 4 | 23680403-239113 17 | 101.51-102.50 | 2.00 | |
| qHRSR4.3 | 4 | 24725621-25022230 | 105.99-107.26 | 2.29 | |
| qHRSR5.1 | 5 | 26927610-27082669 | 115.43-116.10 | 2.30 | |
| qHRSR6.1 | 6 | 33441-781344 | 0.14-3.35 | 2.50 | |
| qHRSR6.2 | 6 | 26490081-27333693 | 113.56-117.17 | 2.24 | |
| qHRSR6.3 | 6 | 28674720-29130039 | 123.31-124.87 | 2.62 | |
| qHRSR8.1 | 8 | 1092742-2649021 | 4.68-11.36 | 2.97 | |
| qHRSR8.2 | 8 | 11086291-11153903 | 47.52-47.81 | 2.22 | |
| qHRSR8.3 | 8 | 14983464-15034055 | 64.23-64.45 | 2.36 | |
| qHRSR8.4 | 8 | 21388530-22202508 | 91.69-95.18 | 2.44 | |
| Total phenolic content | qTPC1.1 | 1 | 7667525-8235815 | 32.87-35.30 | 2.23 |
| qTPC3.1 | 3 | 15484683-16021103 | 66.38-68.68 | 3.07 | |
| qTPC3.2 | 3 | 16899768-17721978 | 72.45-75.97 | 3.58 | |
| qTPC3.3 | 3 | 25032115-25648379 | 107.31-109.95 | 2.50 | |
| qTPC4.1 | 4 | 26377931-27479589 | 113.07-117.80 | 2.44 | |
| qTPC12.1 | 12 | 2689107-3043767 | 11.53-13.05 | 2.52 | |
| qTPC12.2 | 12 | 3933801-4462301 | 16.86-19.13 | 2.08 | |
| qTPC12.3 | 12 | 11398960-11895586 | 48.86-50.99 | 2.00 | |
| qTPC12.4 | 12 | 13100229-14071703 | 56.16-60.32 | 2.00 | |
| qTPC12.5 | 12 | 14215593-15112427 | 60.94-64.78 | 2.11 | |
| qTPC12.6 | 12 | 16682032-1680484 | 71.51-72.19 | 2.47 | |
| Flavonoid content | qFC1.1 | 1 | 26148806-27178896 | 112.09-116.50 | 2.42 |
| qFC1.2 | 1 | 27178896-27631674 | 116.50-118.45 | 2.03 | |
| qFC1.3 | 1 | 37113012-37638053 | 159.09-161.34 | 2.12 | |
| qFC1.4 | 1 | 38157798-38395992 | 163.57-164.59 | 2.35 | |
| qFC2.1 | 2 | 21915215-22231364 | 93.94-95.30 | 2.30 | |
| qFC4.1 | 4 | 17472715-19028032 | 74.90-81.57 | 3.67 | |
| qFC4.2 | 4 | 19642144-19986484 | 84.20-85.68 | 2.70 | |
| qFC4.3 | 4 | 22019563-23235126 | 94.39-99.60 | 3.74 | |
| qFC4.4 | 4 | 26377931-26619819 | 113.07-114.11 | 2.87 | |
| qFC5.1 | 5 | 5206830-6439595 | 22.32-27.60 | 4.03 | |
| qFC5.2 | 5 | 6673100-7059585 | 28.61-30.26 | 4.12 | |
| qFC5.3 | 5 | 12422042-12794190 | 53.25-54.85 | 2.04 | |
| qFC5.4 | 5 | 26189817-26927610 | 112.27-115.43 | 2.59 | |
| qFC6.1 | 6 | 5187517-6015262 | 22.24-25.79 | 3.28 | |
| qFC6.2 | 6 | 6069227-6560451 | 26.02-28.12 | 2.68 | |
| qFC6.3 | 6 | 21068005-21507916 | 90.31-92.20 | 2.16 | |
| qFC6.4 | 6 | 27961504-28384769 | 119.86-121.68 | 2.51 | |
| qFC9.1 | 9 | 13119644-13620974 | 56.24-58.39 | 2.07 | |
| qFC10.1 | 10 | 21806620-22080253 | 93.48-94.65 | 2.02 | |
| qFC12.1 | 12 | 2351235-2689107 | 10.08-11.53 | 2.56 | |
| qFC12.2 | 12 | 4462301-6224960 | 19.13-26.68 | 2.95 | |
| qFC12.3 | 12 | 7508660-9990803 | 32.19-42.83 | 3.74 | |
| qFC12.4 | 12 | 11398960-14215593 | 48.86-60.94 | 3.04 | |
| qFC12.5 | 12 | 17056555-17574928 | 73.12-75.34 | 2.19 | |
| qFC12.6 | 12 | 23839134-24088353 | 102.19-103.26 | 2.39 | |
| Anthocyanin content | qAC2.1 | 2 | 35599368-35902152 | 152.60-153.90 | 2.42 |
| qAC3.1 | 3 | 31965505-32493480 | 137.03-138.32 | 2.25 | |
| qAC3.2 | 3 | 33386000-34509821 | 143.12-147.93 | 3.23 | |
| qAC3.3 | 3 | 35314343-35646346 | 151.38-152.81 | 2.30 | |
| qAC5.1 | 5 | 22147125-22524107 | 94.94-96.55 | 2.88 | |
| qAC11.1 | 11 | 9832804-10200412 | 42.15-43.73 | 2.28 | |
| qAC12.1 | 12 | 927518-2689107 | 3.98-11.53 | 2.31 | |
| qAC12.2 | 12 | 23013674-23469132 | 98.65-100.61 | 2.50 |
表2 水稻重组自交系群体抗氧化性生理指标QTL分析
Table 2 QTL analysis of physiological indicators of antioxidant properties in the recombinant inbred line population of rice
| Physiological traits | QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Limit of detection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate | qHRSR1.1 | 1 | 2556386-2834929 | 10.96-12.15 | 2.14 |
| qHRSR2.1 | 2 | 3467582-4955784 | 14.87-21.24 | 4.36 | |
| qHRSR2.2 | 2 | 5098574-6084984 | 21.86-26.08 | 3.37 | |
| qHRSR2.3 | 2 | 27009300-27239796 | 115.78-116.77 | 2.75 | |
| qHRSR2.4 | 2 | 28427871-28664694 | 121.86-122.88 | 2.21 | |
| qHRSR3.1 | 3 | 12723031-12925845 | 54.54-55.41 | 2.22 | |
| qHRSR3.2 | 3 | 29949770-30321190 | 128.39-129.98 | 2.31 | |
| qHRSR4.1 | 4 | 23316226-23991142 | 99.95-102.84 | 3.35 | |
| qHRSR4.2 | 4 | 23680403-239113 17 | 101.51-102.50 | 2.00 | |
| qHRSR4.3 | 4 | 24725621-25022230 | 105.99-107.26 | 2.29 | |
| qHRSR5.1 | 5 | 26927610-27082669 | 115.43-116.10 | 2.30 | |
| qHRSR6.1 | 6 | 33441-781344 | 0.14-3.35 | 2.50 | |
| qHRSR6.2 | 6 | 26490081-27333693 | 113.56-117.17 | 2.24 | |
| qHRSR6.3 | 6 | 28674720-29130039 | 123.31-124.87 | 2.62 | |
| qHRSR8.1 | 8 | 1092742-2649021 | 4.68-11.36 | 2.97 | |
| qHRSR8.2 | 8 | 11086291-11153903 | 47.52-47.81 | 2.22 | |
| qHRSR8.3 | 8 | 14983464-15034055 | 64.23-64.45 | 2.36 | |
| qHRSR8.4 | 8 | 21388530-22202508 | 91.69-95.18 | 2.44 | |
| Total phenolic content | qTPC1.1 | 1 | 7667525-8235815 | 32.87-35.30 | 2.23 |
| qTPC3.1 | 3 | 15484683-16021103 | 66.38-68.68 | 3.07 | |
| qTPC3.2 | 3 | 16899768-17721978 | 72.45-75.97 | 3.58 | |
| qTPC3.3 | 3 | 25032115-25648379 | 107.31-109.95 | 2.50 | |
| qTPC4.1 | 4 | 26377931-27479589 | 113.07-117.80 | 2.44 | |
| qTPC12.1 | 12 | 2689107-3043767 | 11.53-13.05 | 2.52 | |
| qTPC12.2 | 12 | 3933801-4462301 | 16.86-19.13 | 2.08 | |
| qTPC12.3 | 12 | 11398960-11895586 | 48.86-50.99 | 2.00 | |
| qTPC12.4 | 12 | 13100229-14071703 | 56.16-60.32 | 2.00 | |
| qTPC12.5 | 12 | 14215593-15112427 | 60.94-64.78 | 2.11 | |
| qTPC12.6 | 12 | 16682032-1680484 | 71.51-72.19 | 2.47 | |
| Flavonoid content | qFC1.1 | 1 | 26148806-27178896 | 112.09-116.50 | 2.42 |
| qFC1.2 | 1 | 27178896-27631674 | 116.50-118.45 | 2.03 | |
| qFC1.3 | 1 | 37113012-37638053 | 159.09-161.34 | 2.12 | |
| qFC1.4 | 1 | 38157798-38395992 | 163.57-164.59 | 2.35 | |
| qFC2.1 | 2 | 21915215-22231364 | 93.94-95.30 | 2.30 | |
| qFC4.1 | 4 | 17472715-19028032 | 74.90-81.57 | 3.67 | |
| qFC4.2 | 4 | 19642144-19986484 | 84.20-85.68 | 2.70 | |
| qFC4.3 | 4 | 22019563-23235126 | 94.39-99.60 | 3.74 | |
| qFC4.4 | 4 | 26377931-26619819 | 113.07-114.11 | 2.87 | |
| qFC5.1 | 5 | 5206830-6439595 | 22.32-27.60 | 4.03 | |
| qFC5.2 | 5 | 6673100-7059585 | 28.61-30.26 | 4.12 | |
| qFC5.3 | 5 | 12422042-12794190 | 53.25-54.85 | 2.04 | |
| qFC5.4 | 5 | 26189817-26927610 | 112.27-115.43 | 2.59 | |
| qFC6.1 | 6 | 5187517-6015262 | 22.24-25.79 | 3.28 | |
| qFC6.2 | 6 | 6069227-6560451 | 26.02-28.12 | 2.68 | |
| qFC6.3 | 6 | 21068005-21507916 | 90.31-92.20 | 2.16 | |
| qFC6.4 | 6 | 27961504-28384769 | 119.86-121.68 | 2.51 | |
| qFC9.1 | 9 | 13119644-13620974 | 56.24-58.39 | 2.07 | |
| qFC10.1 | 10 | 21806620-22080253 | 93.48-94.65 | 2.02 | |
| qFC12.1 | 12 | 2351235-2689107 | 10.08-11.53 | 2.56 | |
| qFC12.2 | 12 | 4462301-6224960 | 19.13-26.68 | 2.95 | |
| qFC12.3 | 12 | 7508660-9990803 | 32.19-42.83 | 3.74 | |
| qFC12.4 | 12 | 11398960-14215593 | 48.86-60.94 | 3.04 | |
| qFC12.5 | 12 | 17056555-17574928 | 73.12-75.34 | 2.19 | |
| qFC12.6 | 12 | 23839134-24088353 | 102.19-103.26 | 2.39 | |
| Anthocyanin content | qAC2.1 | 2 | 35599368-35902152 | 152.60-153.90 | 2.42 |
| qAC3.1 | 3 | 31965505-32493480 | 137.03-138.32 | 2.25 | |
| qAC3.2 | 3 | 33386000-34509821 | 143.12-147.93 | 3.23 | |
| qAC3.3 | 3 | 35314343-35646346 | 151.38-152.81 | 2.30 | |
| qAC5.1 | 5 | 22147125-22524107 | 94.94-96.55 | 2.88 | |
| qAC11.1 | 11 | 9832804-10200412 | 42.15-43.73 | 2.28 | |
| qAC12.1 | 12 | 927518-2689107 | 3.98-11.53 | 2.31 | |
| qAC12.2 | 12 | 23013674-23469132 | 98.65-100.61 | 2.50 |
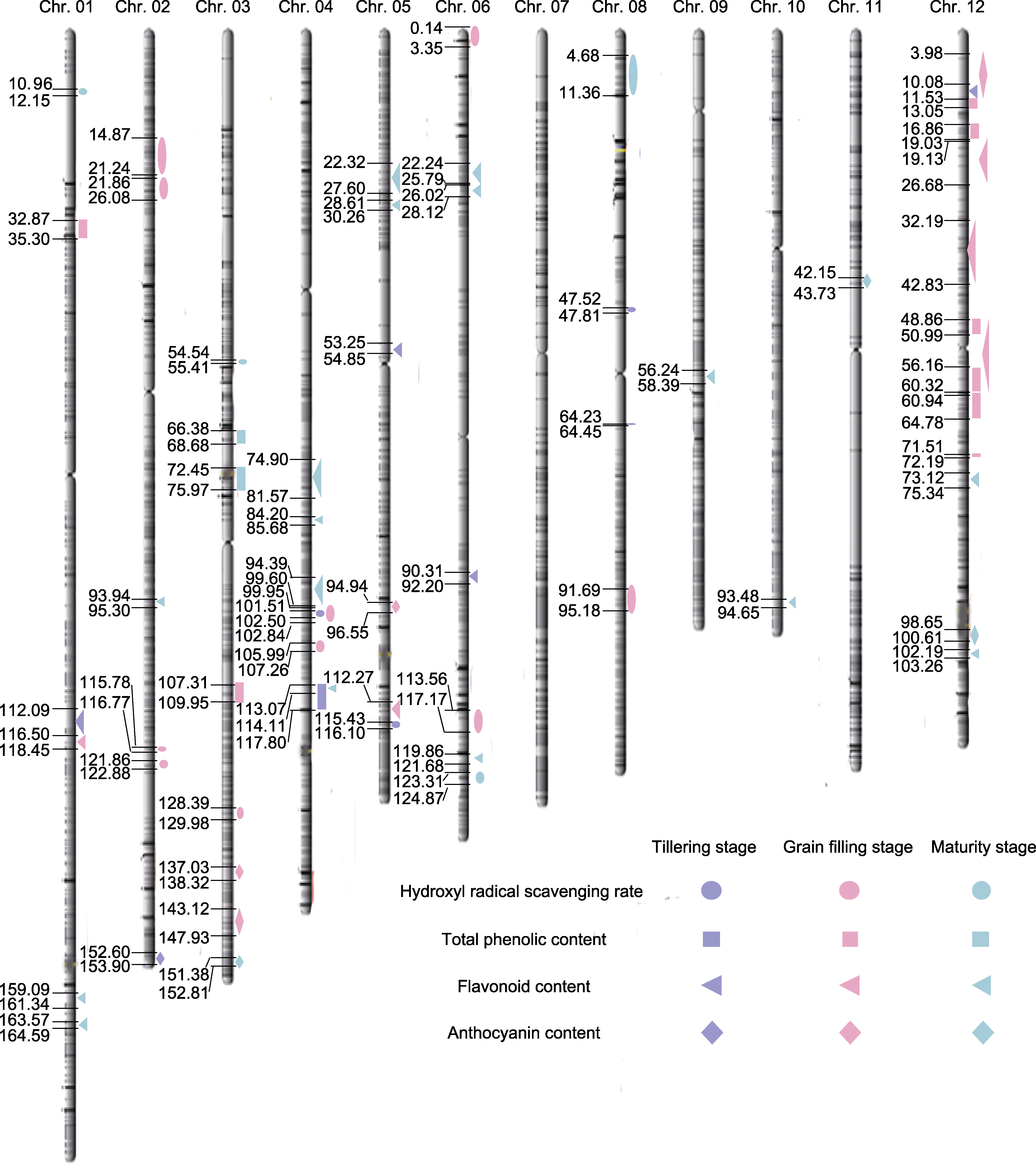
图3 水稻重组自交系群体抗氧化性生理指标QTL定位
Figure 3 Localization of QTLs for physiological indicators of antioxidant properties in the recombinant inbred line population of rice
| Antioxidant physiological indicators | Gene ID | QTL locus | Functional annotation | Gene name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate | LOC_Os06g01850 | qHRSR6.1 | Leaf-type ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase | OsLFNR2 (Da et al., |
| LOC_Os06g48000 | qHRSR6.3 | Peroxidase precursor | ||
| LOC_Os06g48020 | qHRSR6.3 | Peroxidase precursor | ||
| Total phenolic content | LOC_Os04g45210 | qTPC4.1 | Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11 | |
| LOC_Os12g07820 | qTPC12.2 | Ascorbate peroxidase gene | OsAPx6 (Chou et al., | |
| LOC_Os12g07830 | qTPC12.2 | Ascorbate peroxidase gene | OsAPx5 (Hong et al., | |
| Flavonoid content | LOC_Os05g12190 | qFC5.2 | Chalcone synthase | |
| LOC_Os05g12210 | qFC5.2 | Chalcone synthase | ||
| LOC_Os05g12240 | qFC5.2 | Chalcone synthase | ||
| LOC_Os05g45120 | qFC5.4 | Anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | ||
| LOC_Os12g16260 | qFC12.3 | Isoflavone reductase | ||
| Anthocyanin content | LOC_Os03g60509 | qAC3.2 | Chalcone isomerase gene | OsCHI (Lam et al., |
| LOC_Os03g62480 | qAC3.3 | UV-B-responsive glycosyltransferase; flavonoid 7-O-glycosyltransferase |
表3 水稻抗氧化性生理指标相关候选基因的功能
Table 3 Functions of candidate genes related to physiological indicators of antioxidant properties in rice
| Antioxidant physiological indicators | Gene ID | QTL locus | Functional annotation | Gene name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyl radical scavenging rate | LOC_Os06g01850 | qHRSR6.1 | Leaf-type ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase | OsLFNR2 (Da et al., |
| LOC_Os06g48000 | qHRSR6.3 | Peroxidase precursor | ||
| LOC_Os06g48020 | qHRSR6.3 | Peroxidase precursor | ||
| Total phenolic content | LOC_Os04g45210 | qTPC4.1 | Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 11 | |
| LOC_Os12g07820 | qTPC12.2 | Ascorbate peroxidase gene | OsAPx6 (Chou et al., | |
| LOC_Os12g07830 | qTPC12.2 | Ascorbate peroxidase gene | OsAPx5 (Hong et al., | |
| Flavonoid content | LOC_Os05g12190 | qFC5.2 | Chalcone synthase | |
| LOC_Os05g12210 | qFC5.2 | Chalcone synthase | ||
| LOC_Os05g12240 | qFC5.2 | Chalcone synthase | ||
| LOC_Os05g45120 | qFC5.4 | Anthocyanidin 5,3-O-glucosyltransferase | ||
| LOC_Os12g16260 | qFC12.3 | Isoflavone reductase | ||
| Anthocyanin content | LOC_Os03g60509 | qAC3.2 | Chalcone isomerase gene | OsCHI (Lam et al., |
| LOC_Os03g62480 | qAC3.3 | UV-B-responsive glycosyltransferase; flavonoid 7-O-glycosyltransferase |

图4 抗氧化性生理指标候选基因在双亲中的表达差异 (A) 分蘖期; (B) 灌浆期; (C) 成熟期。*P<0.05; ** P<0.01
Figure 4 Differences in the expression of candidate genes for physiological indicators of antioxidant properties in both parents (A) Tillering stage; (B) Grain filling stage; (C) Maturity stage. *P<0.05; ** P<0.01
| [1] | Abdel-Aal ESM, Hucl P (1999). A rapid method for quantifying total anthocyanins in blue aleurone and purple pericarp wheats. Cereal Chem 76, 350-354. |
| [2] | Cai YZ, Luo Q, Sun M, Corke H (2004). Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci 74, 2157-2184. |
| [3] | Chen MH, Pinson SRM, Jackson AK, Edwards JD (2023). Genetic loci regulating the concentrations of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins in the pericarps of purple and red rice. Plant Genome 16, e20338. |
| [4] | Chou TS, Chao YY, Kao CH (2012). Involvement of hydrogen peroxide in heat shock- and cadmium-induced expression of ascorbate peroxidase and glutathione reductase in leaves of rice seedlings. J Plant Physiol 169, 478-486. |
| [5] | Da XW, Guo JF, Yan P, Yang C, Zhao HF, Li W, Kong YZ, Jiang RR, He Y, Xu JM, Xu OY, Mao CZ, Mo XR (2023). Characterizing membrane anchoring of leaf-form ferredoxin-NADP+oxidoreductase in rice. Plant Cell Environ 46, 1195-1206. |
| [6] | Dai WD, Tie NY, Ma LY, Zhang C, Tang R, Wang SM, Yang B, Wang LL, Rao Y, Huang ZS (2021). QTL mapping of leaf anthocyanin and chlorophyll content in Brassica napus. Southwest China J Agric Sci 34, 2547-2556. (in Chinese) |
| 代文东, 铁拿优, 玛丽亚, 张超, 唐容, 王少铭, 杨斌, 王璐璐, 饶勇, 黄泽素 (2021). 甘蓝型油菜叶片花青素及叶绿素含量的QTL定位. 西南农业学报 34, 2547-2556. | |
| [7] | Fang CX, Li LL, Zhang PL, Wang DH, Yang LK, Reza BM, Lin WX (2019). Lsi1 modulates the antioxidant capacity of rice and protects against ultraviolet-B radiation. Plant Sci 278, 96-106. |
| [8] | Higuchi-Takeuchi M, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Matsui K, Hasegawa Y, Kawashima M, Sonoike K, Mori M, Hirochika, Matsui M (2011). Functional analysis of two isoforms of leaf-type ferredoxin-NADP+-oxidoreductase in rice using the heterologous expression system of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 157, 96-108. |
| [9] | Hong CY, Hsu YT, Tsai YC, Kao CH (2007). Expression of ASCORBATE PEROXIDASE 8 in roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings in response to NaCl. J Exp Bot 58, 3273-3283. |
| [10] | Hong LL, Qian Q, Tang D, Wang KJ, Li M, Cheng ZK (2012). A mutation in the rice chalcone isomerase gene causes the golden hull and internode 1phenotype. Planta 236, 141-151. |
| [11] | Huang J, Zhu L, Xue PB, Fu Q (2022). Research on mechanism and QTL mapping associated with cadmium accumulation in rice leaves and grains. Biotechnol Bull 38(8), 118-126. (in Chinese) |
| 黄婧, 朱亮, 薛蓬勃, 付强 (2022). 水稻叶和籽粒镉积累机制及QTL定位研究. 生物技术通报 38( 8), 118-126. | |
| [12] | Huang YJ, Yang ZY, Rao ZM, Deng JL, Liu YB (2000). Active oxygen damage effect and regulation of chlorophyll degradation in rice leaves at filling stage under high temperature stress. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxiensis 22(5), 1-6. (in Chinese) |
| 黄英金, 杨芝燕, 饶志明, 邓接楼, 刘宜柏 (2000). 灌浆期高温胁迫下水稻叶片叶绿素降解的活性氧损伤及调控研究. 江西农业大学学报 22(5), 1-6. | |
| [13] | Islam F, Khan MSS, Ahmed S, Abdullah M, Hannan F, Chen J (2023). OsLPXC negatively regulates tolerance to cold stress via modulating oxidative stress, antioxidant defense and JA accumulation in rice. Free Radical Biol Med 199, 2-16. |
| [14] | Jaksomsak P, Rerkasem B, Prom-U-Thai C (2021). Variation in nutritional quality of pigmented rice varieties under different water regimes. Plant Prod Sci 24, 244-255. |
| [15] | Jia QW, Zhong QQ, Gu YJ, Lu TQ, Li W, Yang S, Zhu CY, Hu CX, Li SF, Wang YX, Rao YC (2023). Mapping of QTL for cell wall related components in rice stem and analysis of candidate genes. Chin Bull Bot 58, 882-892. (in Chinese) |
| 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 58, 882- 892. | |
| [16] | Jiang HH, Wang T, Chen N, Yu SL, Chi XY, Wang M, Qi PS (2019). Research progress in PGPR improving plant’s resistance to salt and alkali. Biotechnol Bull 35(10), 189- 197. (in Chinese) |
| 姜焕焕, 王通, 陈娜, 禹山林, 迟晓元, 王冕, 祁佩时 (2019). 根际促生菌提高植物抗盐碱性的研究进展. 生物技术通报 35( 10), 189-197. | |
| [17] | Jin JY, Luo YT, Yang HM, Lu T, Ye HF, Xie JY, Wang KX, Chen QY, Fang Y, Wang YX, Rao YC (2023). Mapping of QTL for cell wall related components in rice stem and analysis of candidate genes. Chin Bull Bot 58, 394-403. (in Chinese) |
| 金佳怡, 罗怿婷, 杨惠敏, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 谢继毅, 王珂欣, 陈芊羽, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻叶绿素含量QTL定位与候选基因表达分析. 植物学报 58, 394-403. | |
| [18] | Jin L, Xiao P, Lu Y, Shao YF, Shen Y, Bao JS (2009). Quantitative trait loci for brown rice color, phenolics, flavonoid contents, and antioxidant capacity in rice grain. Cereal Chem 86, 609-615. |
| [19] | Kim B, Shim S, Zhang HJ, Lee C, Jang S, Jin Z, Seo J, Kwon SW, Koh HJ (2023). Dynamic transcriptome changes driven by the mutation of OsCOP1 underlie flavonoid biosynthesis and embryogenesis in the developing rice seed. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 4436-4452. |
| [20] | Lam PY, Wang LX, Lui ACW, Liu HJ, Takeda-Kimura Y, Chen MX, Zhu FY, Zhang JH, Umezawa T, Tobimatsu Y, Lo C (2022). Deficiency in flavonoid biosynthesis genes CHS, CHI, and CHIL alters rice flavonoid and lignin profiles. Plant Physiol 188, 1993-2011. |
| [21] | Li SC (2023). Novel insight into functions of ascorbate peroxidase in higher plants: more than a simple antioxidant enzyme. Redox Biol 64, 102789. |
| [22] | Li XY, Yin H, Zhan SY, Qiao Y (2017). Effects of enhanced UV-B radiation on photosynthetic characteristics and anti- oxidation of rice flag leaves in filling stage. J Shenyang Agric Univ 48, 271-276. (in Chinese) |
| 李雪莹, 殷红, 战莘晔, 乔媛 (2017). 添加UV-B辐射对灌浆期水稻剑叶光合特性及抗氧化能力的影响. 沈阳农业大学学报 48, 271-276. | |
| [23] | Liu M, Chu MJ, Ding YF, Wang SH, Liu ZH, Tang S, Ding CQ, Li GH (2015). Exogenous spermidine alleviates oxidative damage and reduce yield loss in rice submerged at tillering stage. Front Plant Sci 6, 919. |
| [24] | Liu Y, Xue XX, Zhao CL, Zhang J, Liu M, Li XY, Li YQ, Gao X (2021). Cloning and functional characterization of chalcone isomerase genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis in Clivia miniata. Ornam Plant Res 1, 2. |
| [25] | Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25, 402-408. |
| [26] | Lu T, Ye HF, Chu XJ, Lin H, Wang S, Pan CY, Li SF, Wang YX, Rao YC (2022). Identification of QTL brown rice rate to submergence in rice. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 45, 323-328. (in Chinese) |
| 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 褚晓洁, 林晗, 王盛, 潘晨阳, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2022). 水稻糙米率QTL检测及候选基因分析. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 45, 323-328. | |
| [27] | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet News 14, 11-13. |
| [28] | Mi YZ (2021). Mechanism of Anthocyanin Alleviates Cd Oxidative Damage of Rice Leaves and Inhibits Cd Accumulation in Rice Grains. PhD dissertation. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University. pp. 42. (in Chinese) |
| 米雅竹 (2021). 花青素缓解Cd胁迫下水稻叶片氧化损伤及抑制籽粒Cd累积机理研究. 博士论文. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. pp. 42. | |
| [29] | Ran YD, Moursy M, Hider RC, Cilibrizzi A (2023). The colorimetric detection of the hydroxyl radical. Int J Mol Sci 24, 4162. |
| [30] | Rao YC, Dai ZJ, Zhu YT, Jiang JJ, Ma RY, Wang YY, Wang YX (2020). Advances in research of drought resistance in rice. J Zhejiang Normal Univ (Nat Sci) 43, 417- 429. (in Chinese) |
| 饶玉春, 戴志俊, 朱怡彤, 姜嘉骥, 马若盈, 王予烨, 王跃星 (2020). 水稻抗干旱胁迫的研究进展. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版) 43, 417-429. | |
| [31] | Shi H, Wang RC, Wu XY, Liu Q (2018). Protective effect of Actinidia arguta flavonoid on hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in HaCaT cells. Food Sci 39(13), 229-234. (in Chinese) |
| 石浩, 王仁才, 吴小燕, 刘琼 (2018). 软枣猕猴桃黄酮对过氧化氢诱导HaCaT细胞损伤的保护作用. 食品科学 39(13), 229-234. | |
| [32] | Wang CC (2015). Study of Novel Functions of Arabidopsis AtSPXI Through Multi-dimension Omics Data-mining, and the Role of OsSPX1 Involved in Oxidative Stresses in Rice Seedlings. PhD dissertation. Beijing: China Agricultural University. pp. 77-79. (in Chinese) |
| 王春超 (2015). 基于多维组学数据挖掘研究拟南芥AtSPX1基因的新功能以及OsSPX1对苗期水稻抗氧化性的影响. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业大学. pp. 77-79. | |
| [33] | Wang L, Huang LC, Dai LP, Yang YL, Xu J, Leng YJ, Zhang GH, Hu J, Zhu L, Gao ZY, Dong GJ, Guo LB, Qian Q, Zeng DL (2014). QTL analysis for rice leaf morphology at maturity stage using a recombinant inbred line population derived from a cross between Nipponbare and 9311. Chin J Rice Sci 28, 589-597. (in Chinese) |
| 王兰, 黄李超, 代丽萍, 杨窑龙, 徐杰, 冷语佳, 张光恒, 胡江, 朱丽, 高振宇, 董国军, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力 (2014). 利用日本晴/9311重组自交系群体定位水稻成熟期叶形相关性状QTL. 中国水稻科学 28, 589-597. | |
| [34] | Wang LP, Zhou SM, Dai DL, Cao JS (2010). Progress in plant phenolic compounds. Acta Agric Zhejiangensis 22, 696-701. (in Chinese) |
| 王玲平, 周生茂, 戴丹丽, 曹家树 (2010). 植物酚类物质研究进展. 浙江农业学报 22, 696-701. | |
| [35] | Wang WS (2020). Identification and Function Analysis of Glycosyltransferase Genes Related to Flavonoids and Anthocyanins Metabolism in Rice. Master’s thesis. Jinan: Shandong University. pp. 11-13. (in Chinese) |
| 王文帅 (2020). 水稻黄酮和花青素代谢相关糖基转移酶基因的鉴定与作用分析. 硕士论文. 济南: 山东大学. pp. 11-13. | |
| [36] | Xie WB, Feng Q, Yu HH, Huang XH, Zhao Q, Xing YZ, Yu SB, Han B, Zhang QF (2010). Parent-independent genotyping for constructing an ultrahigh-density linkage map based on population sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 10578-10583. |
| [37] | Yang HX, Chen JL, Liu W (2019). Research progress on cadmium toxicity and detoxification mechanism in plants. Jiangsu Agric Sci 47(2), 1-8. (in Chinese) |
| 杨红霞, 陈俊良, 刘崴 (2019). 镉对植物的毒害及植物解毒机制研究进展. 江苏农业科学 47(2), 1-8. | |
| [38] | Zhao MY, Kang QF, Zhao Y, Li XY (2023). Identification and bioinformatic analyses of genes related to anthocyanin biosynthesis in Setaria italica. Mol Plant Breed 1-17. (in Chinese) |
| 赵孟瑶, 康庆芳, 赵影, 李雪垠 (2023). 谷子花青苷合成相关基因的鉴定与生物信息学分析. 分子植物育种 1-17. | |
| [39] | Zhong YH, Guo ZJ, Wei MY, Wang JC, Song SW, Chi BJ, Zhang YC, Liu JW, Li J, Zhu XY, Tang HC, Song LY, Xu CQ, Zheng HL (2023). Hydrogen sulfide upregulates the alternative respiratory pathway in mangrove plant Avicennia marina to attenuate waterlogging-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in a calcium-dependent manner. Plant Cell Environ 46, 1521-1539. |
| [40] | Zhou H, Finkemeier I, Guan WX, Tossounian MA, Wei B, Young D, Huang JJ, Messens J, Yang XB, Zhu J, Wilson MH, Shen WB, Xie YJ, Foyer CH (2018). Oxidative stress-triggered interactions between the succinyl- and acetyl-proteomes of rice leaves. Plant Cell Environ 41, 1139-1153. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [7] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [8] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [9] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [10] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [12] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| [13] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [14] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [15] | 刘裕强, 万建民. 寄主监控昆虫唾液蛋白平衡植物抗性与生长发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 353-355. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||