

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (6): 882-892.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23100 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23100
贾绮玮1,†, 钟芊芊1,†, 顾育嘉1, 陆天麒1, 李玮1, 杨帅1, 朱超宇1, 胡程翔1, 李三峰2, 王跃星2,*( ), 饶玉春1,*(
), 饶玉春1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-07-28
接受日期:2023-11-02
出版日期:2023-11-01
发布日期:2023-11-27
通讯作者:
* E-mail: wangyuexing@caas.cn;ryc@zjnu.cn
作者简介:† 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Qiwei Jia1,†, Qianqian Zhong1,†, Yujia Gu1, Tianqi Lu1, Wei Li1, Shuai Yang1, Chaoyu Zhu1, Chengxiang Hu1, Sanfeng Li2, Yuexing Wang2,*( ), Yuchun Rao1,*(
), Yuchun Rao1,*( )
)
Received:2023-07-28
Accepted:2023-11-02
Online:2023-11-01
Published:2023-11-27
Contact:
* E-mail: wangyuexing@caas.cn;ryc@zjnu.cn
About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 水稻(Oryza sativa)倒伏是制约其生产的主要因素之一, 而茎秆的机械强度影响水稻抗倒伏能力, 且与茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量密切相关。通过调控水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量提高水稻抗倒伏能力, 是提高水稻产量与品质的有效途径。该研究用籼稻品种华占(O. sativa subsp. indica cv. ‘HZ’)和粳稻品种热研2号(O. sativa subsp. japonica cv. ‘Nekken2’)杂交获得F1代, 经连续多代自交得到120个重组自交系(RILs)群体, 并以此构建遗传连锁图谱。基于构建的高密度遗传图谱, 对水稻茎秆细胞壁中纤维素、半纤维素和木质素含量相关QTLs进行定位, 结果共检测到4个与纤维素含量相关的QTLs、12个与半纤维素含量相关的QTLs和8个与木质素含量相关的QTLs。对检测到的QTLs区间进行候选基因分析, 共筛选到13个候选基因。利用qRT-PCR检测候选基因的表达水平, 结果表明除LOC_Os02g58590和LOC_Os12g41720外, 其余候选基因的表达量在双亲间均存在显著差异。研究结果为挖掘调控水稻茎秆机械强度的基因, 进而筛选和培育抗倒伏能力强的水稻品种奠定了重要基础。
贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892.
Qiwei Jia, Qianqian Zhong, Yujia Gu, Tianqi Lu, Wei Li, Shuai Yang, Chaoyu Zhu, Chengxiang Hu, Sanfeng Li, Yuexing Wang, Yuchun Rao. Mapping of QTL for Cell Wall Related Components in Rice Stem and Analysis of Candidate Genes. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 882-892.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os01g04930-F-qrt | GAGGGGGAACTGGTTCATGG | 60.00 | 20 | 164 |
| LOC_Os01g04930-R-qrt | CGAGGTCCCTGAAGTGGTTC | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os01g08440-F-qrt | AGCAACGACCTCTTCAAGCA | 59.90 | 20 | 178 |
| LOC_Os01g08440-R-qrt | TCCTCAGCACCCACAAGAAC | 59.90 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os01g09850-F-qrt | CTCCTCCTACCAGCAACGTG | 60.10 | 20 | 180 |
| LOC_Os01g09850-R-qrt | GACCCAAGAAGTCCCTGGTG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os02g56460-F-qrt | CTGCTGGAGCGACTACGAAT | 59.90 | 20 | 182 |
| LOC_Os02g56460-R-qrt | CGTGGTTGGTGCTGAAGTTG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os02g58480-F-qrt | ACCGTCGGACTACCTCAAGA | 60.00 | 20 | 187 |
| LOC_Os02g58480-R-qrt | GTCGGTCAGCTTGGAAGACA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os02g58590-F-qrt | GCCTCGCACAAGCAGAAAAA | 60.00 | 20 | 183 |
| LOC_Os02g58590-R-qrt | AGGTCTGCACGCTCCTTTTT | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os04g52280-F-qrt | GGATGAGGGTGACGGTGATC | 59.90 | 20 | 179 |
| LOC_Os04g52280-R-qrt | TGCCAGGTAAGAGTGCATGG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os08g14760-F-qrt | AATACCAGTCGCCTTCGTGG | 60.10 | 20 | 186 |
| LOC_Os08g14760-R-qrt | AGATGTTGCAGCTGCTTCCT | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os11g04400-F-qrt | CAGTGCACCCATGGAGGATT | 60.00 | 20 | 183 |
| LOC_Os11g04400-R-qrt | TTCTCCAACATCTCGCCGAC | 60.10 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g29300-F-qrt | GTCTTCTTCGACTGCACCGA | 60.00 | 20 | 155 |
| LOC_Os12g29300-R-qrt | TCTTCTCCGAGTAGGCGACA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g36890-F-qrt | CTTCACCTCCGTGTTCCTCC | 60.00 | 20 | 162 |
| LOC_Os12g36890-R-qrt | CCGGACCACTTGATCTCGAG | 59.90 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g41720-F-qrt | CAACTACGTCCGCATCCAGG | 60.80 | 20 | 163 |
| LOC_Os12g41720-R-qrt | CCGGTTTGACTTCTCCGACA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g41780-F-qrt | TTCACTGGCATCCCGAAGTC | 60.00 | 20 | 187 |
| LOC_Os12g41780-R-qrt | CAATGCCTGATCTTCGCAGC | 60.00 | 20 |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os01g04930-F-qrt | GAGGGGGAACTGGTTCATGG | 60.00 | 20 | 164 |
| LOC_Os01g04930-R-qrt | CGAGGTCCCTGAAGTGGTTC | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os01g08440-F-qrt | AGCAACGACCTCTTCAAGCA | 59.90 | 20 | 178 |
| LOC_Os01g08440-R-qrt | TCCTCAGCACCCACAAGAAC | 59.90 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os01g09850-F-qrt | CTCCTCCTACCAGCAACGTG | 60.10 | 20 | 180 |
| LOC_Os01g09850-R-qrt | GACCCAAGAAGTCCCTGGTG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os02g56460-F-qrt | CTGCTGGAGCGACTACGAAT | 59.90 | 20 | 182 |
| LOC_Os02g56460-R-qrt | CGTGGTTGGTGCTGAAGTTG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os02g58480-F-qrt | ACCGTCGGACTACCTCAAGA | 60.00 | 20 | 187 |
| LOC_Os02g58480-R-qrt | GTCGGTCAGCTTGGAAGACA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os02g58590-F-qrt | GCCTCGCACAAGCAGAAAAA | 60.00 | 20 | 183 |
| LOC_Os02g58590-R-qrt | AGGTCTGCACGCTCCTTTTT | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os04g52280-F-qrt | GGATGAGGGTGACGGTGATC | 59.90 | 20 | 179 |
| LOC_Os04g52280-R-qrt | TGCCAGGTAAGAGTGCATGG | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os08g14760-F-qrt | AATACCAGTCGCCTTCGTGG | 60.10 | 20 | 186 |
| LOC_Os08g14760-R-qrt | AGATGTTGCAGCTGCTTCCT | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os11g04400-F-qrt | CAGTGCACCCATGGAGGATT | 60.00 | 20 | 183 |
| LOC_Os11g04400-R-qrt | TTCTCCAACATCTCGCCGAC | 60.10 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g29300-F-qrt | GTCTTCTTCGACTGCACCGA | 60.00 | 20 | 155 |
| LOC_Os12g29300-R-qrt | TCTTCTCCGAGTAGGCGACA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g36890-F-qrt | CTTCACCTCCGTGTTCCTCC | 60.00 | 20 | 162 |
| LOC_Os12g36890-R-qrt | CCGGACCACTTGATCTCGAG | 59.90 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g41720-F-qrt | CAACTACGTCCGCATCCAGG | 60.80 | 20 | 163 |
| LOC_Os12g41720-R-qrt | CCGGTTTGACTTCTCCGACA | 60.00 | 20 | |
| LOC_Os12g41780-F-qrt | TTCACTGGCATCCCGAAGTC | 60.00 | 20 | 187 |
| LOC_Os12g41780-R-qrt | CAATGCCTGATCTTCGCAGC | 60.00 | 20 |
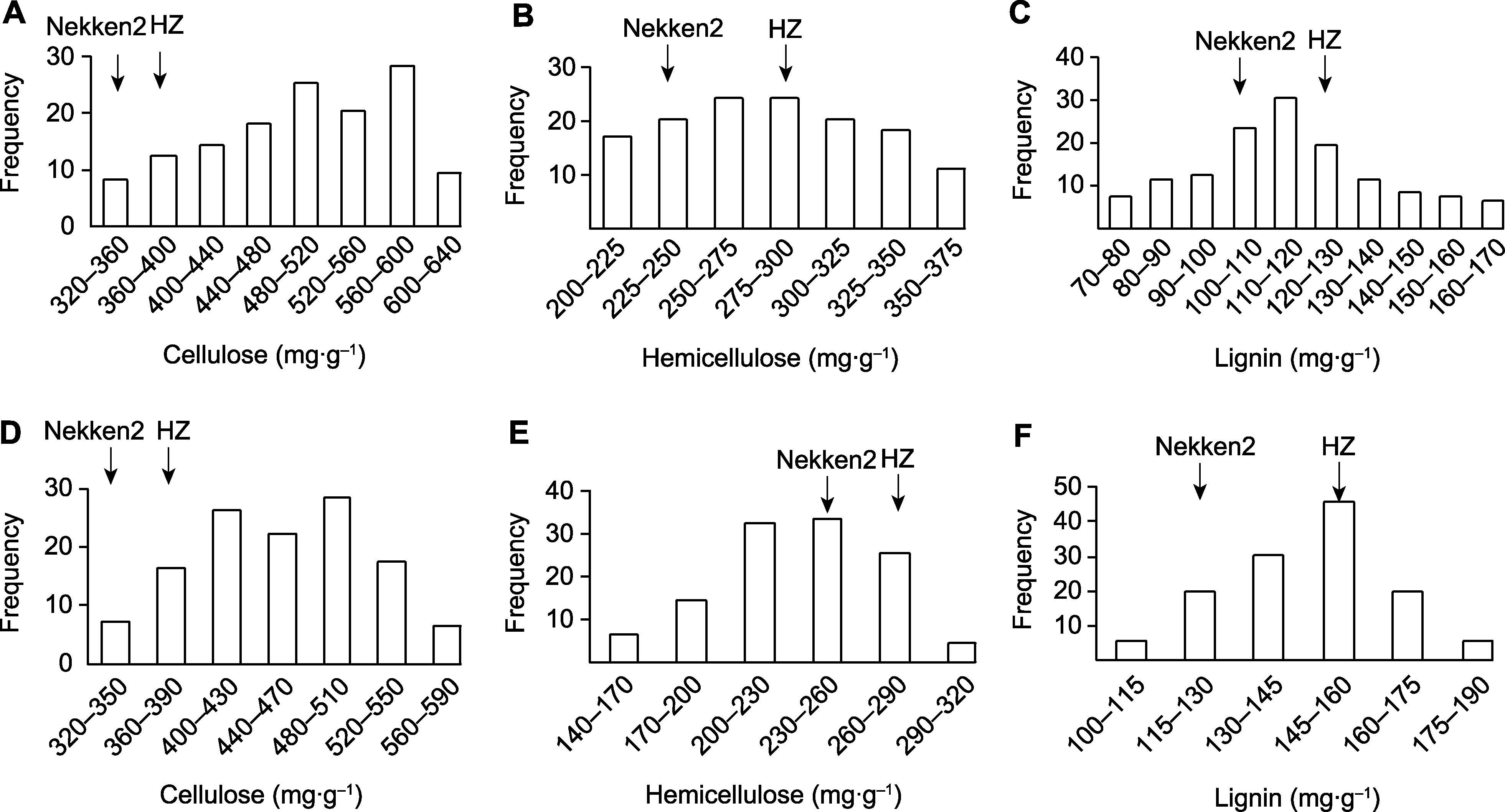
图2 水稻重组自交系群体茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量 (A) 2020年测定的纤维素含量; <BOLD>(B) </BOLD>2020年测定的半纤维素含量; <BOLD>(C)</BOLD> 2020年测定的木质素含量; <BOLD>(D)</BOLD> 2021年测定的纤维素含量; <BOLD>(E)</BOLD> 2021年测定的半纤维素含量; <BOLD>(F)</BOLD> 2021年测定的木质素含量
Figure 2 The contents of stem cell wall related components in rice recombinant inbred line population (A) The content of cellulose components in 2020; (B) The content of hemicellulose components in 2020; (C) The content of lignin components in 2020; (D) The content of cellulose components in 2021; (E) The content of hemicellulose components in 2021; (F) The content of lignin components in 2021
| Year | Cell wall component | QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Cellulose | qCel202 | 2 | 35381094-35599368 | 151.67-152.60 | 3.48 |
| qCel204 | 4 | 29276416-29507404 | 125.50-126.49 | 2.82 | ||
| Hemicellulose | qHem201 | 1 | 2070966-6568005 | 8.88-28.16 | 5.02 | |
| qHem203 | 3 | 29806859-30321190 | 127.77-129.99 | 2.53 | ||
| qHem208 | 8 | 4587694-8917564 | 19.67-38.23 | 3.48 | ||
| qHem2012-1 | 12 | 15484322-15779533 | 66.38-67.64 | 2.94 | ||
| qHem2012-2 | 12 | 22426037-27516985 | 96.13-117.95 | 5.52 | ||
| Lignin | qLig202 | 2 | 33583953-35902152 | 143.97-153.90 | 3.03 | |
| qLig204-1 | 4 | 27558155-28380156 | 118.13-121.66 | 3.19 | ||
| qLig204-2 | 4 | 31066903-31212801 | 133.18-133.80 | 3.25 | ||
| qLig2011 | 11 | 1449031-5404218 | 6.21-23.17 | 3.46 | ||
| qLig2012-1 | 12 | 24319945-24511904 | 104.25-105.66 | 3.45 | ||
| qLig2012-2 | 12 | 27434341-27516085 | 117.60-117.95 | 2.60 | ||
| 2021 | Cellulose | qCel211 | 1 | 2192312-2834929 | 9.39-12.15 | 3.34 |
| qCel2112 | 12 | 25510919-27516085 | 109.35-117.95 | 3.94 | ||
| Hemicellulose | qHem211 | 1 | 5699636-6152981 | 24.43-26.37 | 3.34 | |
| qHem213-1 | 3 | 8841716-8989609 | 37.90-38.53 | 2.55 | ||
| qHem213-2 | 3 | 20915784-21229182 | 89.66-91.00 | 3.07 | ||
| qHem214 | 4 | 2647701-5256057 | 11.34-22.53 | 3.81 | ||
| qHem218 | 8 | 1430252-1451568 | 6.13-6.22 | 2.50 | ||
| qHem2112-1 | 12 | 7276559-7573232 | 31.19-32.46 | 2.55 | ||
| qHem2112-2 | 12 | 17268215-18172857 | 74.02-77.90 | 3.40 | ||
| Lignin | qLig215-1 | 5 | 327464-853216 | 1.40-3.65 | 2.90 | |
| qLig215-2 | 5 | 25519701-27453301 | 109.39-117.68 | 3.35 |
表2 水稻重组自交系群体茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量的QTL分析
Table 2 QTL analysis of stem cell wall related components in rice recombinant inbred line population
| Year | Cell wall component | QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Cellulose | qCel202 | 2 | 35381094-35599368 | 151.67-152.60 | 3.48 |
| qCel204 | 4 | 29276416-29507404 | 125.50-126.49 | 2.82 | ||
| Hemicellulose | qHem201 | 1 | 2070966-6568005 | 8.88-28.16 | 5.02 | |
| qHem203 | 3 | 29806859-30321190 | 127.77-129.99 | 2.53 | ||
| qHem208 | 8 | 4587694-8917564 | 19.67-38.23 | 3.48 | ||
| qHem2012-1 | 12 | 15484322-15779533 | 66.38-67.64 | 2.94 | ||
| qHem2012-2 | 12 | 22426037-27516985 | 96.13-117.95 | 5.52 | ||
| Lignin | qLig202 | 2 | 33583953-35902152 | 143.97-153.90 | 3.03 | |
| qLig204-1 | 4 | 27558155-28380156 | 118.13-121.66 | 3.19 | ||
| qLig204-2 | 4 | 31066903-31212801 | 133.18-133.80 | 3.25 | ||
| qLig2011 | 11 | 1449031-5404218 | 6.21-23.17 | 3.46 | ||
| qLig2012-1 | 12 | 24319945-24511904 | 104.25-105.66 | 3.45 | ||
| qLig2012-2 | 12 | 27434341-27516085 | 117.60-117.95 | 2.60 | ||
| 2021 | Cellulose | qCel211 | 1 | 2192312-2834929 | 9.39-12.15 | 3.34 |
| qCel2112 | 12 | 25510919-27516085 | 109.35-117.95 | 3.94 | ||
| Hemicellulose | qHem211 | 1 | 5699636-6152981 | 24.43-26.37 | 3.34 | |
| qHem213-1 | 3 | 8841716-8989609 | 37.90-38.53 | 2.55 | ||
| qHem213-2 | 3 | 20915784-21229182 | 89.66-91.00 | 3.07 | ||
| qHem214 | 4 | 2647701-5256057 | 11.34-22.53 | 3.81 | ||
| qHem218 | 8 | 1430252-1451568 | 6.13-6.22 | 2.50 | ||
| qHem2112-1 | 12 | 7276559-7573232 | 31.19-32.46 | 2.55 | ||
| qHem2112-2 | 12 | 17268215-18172857 | 74.02-77.90 | 3.40 | ||
| Lignin | qLig215-1 | 5 | 327464-853216 | 1.40-3.65 | 2.90 | |
| qLig215-2 | 5 | 25519701-27453301 | 109.39-117.68 | 3.35 |
| Gene ID | Chromosome | Function | Cloned or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os01g04930 | 1 | MYB transcription factor | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os01g08440 | 1 | UDP glucoside transferase | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os01g09850 | 1 | C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor | Cloned (Huang et al., |
| LOC_Os02g56460 | 2 | Cinnamyl CoA reductase | Cloned (Kawasaki et al., |
| LOC_Os02g58480 | 2 | Sucrose synthase | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os02g58590 | 2 | N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I | Cloned (Fanata et al., |
| LOC_Os04g52280 | 4 | Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase | Cloned (Li et al., |
| LOC_Os08g14760 | 8 | 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase | Cloned (Gu et al., |
| LOC_Os11g04400 | 11 | GRAS family transcription factor | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os12g29300 | 12 | CESA10-cellulase synthesis | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os12g36890 | 12 | Cellulose synthase-like | Cloned (Hu et al., |
| LOC_Os12g41720 | 12 | Patatin-related phospholipase A | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os12g41780 | 12 | Glycosyltransferase | Not cloned |
表3 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量候选基因及其功能
Table 3 Rice stem cell wall related components candidate genes and their function
| Gene ID | Chromosome | Function | Cloned or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os01g04930 | 1 | MYB transcription factor | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os01g08440 | 1 | UDP glucoside transferase | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os01g09850 | 1 | C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor | Cloned (Huang et al., |
| LOC_Os02g56460 | 2 | Cinnamyl CoA reductase | Cloned (Kawasaki et al., |
| LOC_Os02g58480 | 2 | Sucrose synthase | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os02g58590 | 2 | N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I | Cloned (Fanata et al., |
| LOC_Os04g52280 | 4 | Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase | Cloned (Li et al., |
| LOC_Os08g14760 | 8 | 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase | Cloned (Gu et al., |
| LOC_Os11g04400 | 11 | GRAS family transcription factor | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os12g29300 | 12 | CESA10-cellulase synthesis | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os12g36890 | 12 | Cellulose synthase-like | Cloned (Hu et al., |
| LOC_Os12g41720 | 12 | Patatin-related phospholipase A | Not cloned |
| LOC_Os12g41780 | 12 | Glycosyltransferase | Not cloned |
| [1] | 白勇, 巩威, 刘天昀, 朱玉贤 (2003). 水稻肉桂酰辅酶A还原酶基因的克隆与表达分析. 科学通报 48, 1780-1784. |
| [2] |
陈桂华, 邓化冰, 张桂莲, 唐文帮, 黄璜 (2016). 水稻茎秆性状与抗倒性的关系及配合力分析. 中国农业科学 49, 407-417.
DOI |
| [3] | 代建秀, 唐子清, 吴春文, 史培康, 韦良艳, 施洁, 黎晟, 罗继景, 蔡中全 (2017). 水稻特异粗茎相关性状QTL的初步定位分析. 分子植物育种 15, 1395-1402. |
| [4] | 丰安徽 (2017). 控制水稻茎秆粗细的OsTB1等位基因发掘与功能分析. 硕士论文. 成都: 四川农业大学. pp. 1-47. |
| [5] | 冯春燕 (2010). 植物4-香豆酸:辅酶A连接酶(4CL)研究进展. 现代农业科技 (8), 39-40. |
| [6] | 韩雷锋, 周燃, 周涛, 林翠香, 甘泉, 倪大虎, 石英尧, 宋丰顺 (2023). 水稻抗倒伏和产量性状的相关性分析及QTLs定位. 生物学杂志 40(2), 65-70. |
| [7] | 胡文冉, 李晓东, 周小云, 杨洋, 李波, 李晓荣 (2019). 棉花肉桂醇脱氢酶基因在棉纤维中的表达及对其结构组分的影响. 西北植物学报 39, 1114-1120. |
| [8] |
金佳怡, 罗怿婷, 杨惠敏, 芦涛, 叶涵斐, 谢继毅, 王珂欣, 陈芊羽, 方媛, 王跃星, 饶玉春 (2023). 水稻叶绿素含量QTL定位与候选基因表达分析. 植物学报 58, 394-403.
DOI |
| [9] | 鞠晓晨, 胡杰, 高冠军, 张庆路, 何予卿 (2016). 水稻茎秆抗倒伏相关QTL定位与分析. 分子植物育种 14, 475-481. |
| [10] | 李丰成 (2015). 植物细胞壁结构特征与生物质高效利用分子机理研究. 博士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 1-136. |
| [11] |
刘畅, 李来庚 (2016). 水稻抗倒伏性状的分子机理研究进展. 中国水稻科学 30, 216-222.
DOI |
| [12] | 刘子玮 (2018). 水稻GRAS转录因子家族的系统分析与功能研究. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京大学. pp. 1-44. |
| [13] | 卢雯瑩, 崔贺云, 高杉, 崔顺梅, 吴营照 (2020). 肉桂醇脱氢酶基因研究进展及其在小麦抗倒伏中的应用. 天津农业科学 26(10), 7-10. |
| [14] | 罗兵, 韩永笑, 张淇鑫, 郭浩, 李红梅, 王静, 杨志刚, 孙海燕 (2018). 水稻UDP-N-乙酰葡萄糖胺酰基转移酶基因(OsLpxA) RNA干扰载体的构建及遗传转化. 分子植物育种 16, 5311-5317. |
| [15] | 穆平, 李自超, 李春平, 张洪亮, 王象坤 (2004). 水、旱条件下水稻茎秆主要抗倒伏性状的QTL分析. 遗传学报 31, 717-723. |
| [16] | 苏仕华, 王珏, 孙成亮, 成英, 卢红 (2008). 水稻倒伏对产量影响的调查与分析. 北方水稻 38, 41-43. |
| [17] | 王士强, 顾春梅, 沈巧梅, 赵黎明, 王丽萍, 王贺 (2011). 水稻倒伏发生规律及防御技术的研究进展. 北方水稻 41, 69-72. |
| [18] | 王晓飞, 陆展华, 刘维, 卢东柏, 王石光, 巫浩翔, 方志强, 何秀英 (2022). “绿色革命”以来水稻抗倒伏研究进展. 广东农业科学 49(3), 1-13. |
| [19] |
魏和平, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 邓飞, 朱浩, 岂泽华, 王玉玺, 叶涵斐, 殷文晶, 方媛, 穆丹, 饶玉春 (2022). 水稻抽穗期QTL定位及候选基因分析. 植物学报 57, 588-595.
DOI |
| [20] | 吴丹, 唐冬英, 李新梅, 李丽, 赵小英, 刘选明 (2015). F-box蛋白在植物生长发育中的功能研究进展. 生命科学研究 19, 362-367. |
| [21] | 肖应辉, 罗丽华, 闫晓燕, 高艳红, 王春明, 江玲, 矢野昌裕, 翟虎渠, 万建民 (2005). 水稻品种倒伏指数QTL分析. 作物学报 31, 348-354. |
| [22] |
辛良杰, 李秀彬 (2009). 近年来我国南方双季稻区复种的变化及其政策启示. 自然资源学报 24, 58-65.
DOI |
| [23] | 许作鹏 (2017). 水稻茎秆强度相关性状QTL分析及基因克隆. 硕士论文. 扬州: 扬州大学. pp. 19-78. |
| [24] | 杨波, 杨文钰 (2011). 水稻抗倒伏研究进展. 耕作与栽培 (2), 1-5, 9. |
| [25] | 杨德卫, 朱镇, 张亚东, 林静, 陈涛, 赵凌, 朱文银, 王才林 (2009). 基于CSSL的水稻穗颈长度QTL的代换作图. 遗传 31, 741-747. |
| [26] | 杨窑龙, 饶玉春, 李赓觅, 黄李超, 冷语佳, 张光恒, 高振宇, 胡江, 朱丽, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力 (2011). 水稻茎秆相关性状遗传分析. 分子植物育种 9, 160-168. |
| [27] | 袁新捷 (2021). 水稻抗倒伏研究及相关性状QTL初步定位分析. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 9-61. |
| [28] | 赵新勇, 邵在胜, 吴艳珍, 赵轶鹏, 王余龙, 王云霞, 杨连新 (2018). 花后人为模拟倒伏对超级稻生长、产量和品质的影响. 中国生态农业学报 26, 980-989. |
| [29] | 周雷 (2018). 一个水稻茎粗抗倒QTL的定位及其候选基因分析. 硕士论文. 成都: 四川农业大学. pp. 2-40. |
| [30] | Fanata WID, Lee KH, Son BH, Yoo JY, Harmoko R, Ko KS, Ramasamy NK, Kim KH, Oh DB, Jung HS, Kim JY, Lee SY, Lee KO (2013). N-glycan maturation is crucial for cytokinin-mediated development and cellulose synthesis in Oryza sativa. Plant J 73, 966-979. |
| [31] |
Gui JS, Shen JH, Li LG (2011). Functional characterization of evolutionarily divergent 4-coumarate: coenzyme A ligases in rice. Plant Physiol 157, 574-586.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Haigler CH, Ivanova-Datcheva M, Hogan PS, Salnikov VV, Hwang S, Martin K, Delmer DP (2001). Carbon partitioning to cellulose synthesis. Plant Mol Biol 47, 29-51.
PMID |
| [33] |
Hu J, Zhu L, Zeng DL, Gao ZY, Guo LB, Fang YX, Zhang GH, Dong GJ, Yan MX, Liu J, Qian Q (2010). Identification and characterization of NARROW AND ROLLED LEAF 1, a novel gene regulating leaf morphology and plant architecture in rice. Plant Mol Biol 73, 283-292.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Huang P, Yoshida H, Yano K, Kinoshita S, Kawai K, Koketsu E, Hattori M, Takehara S, Huang J, Hirano K, Ordonio RL, Matsuoka M, Ueguchi-Tanaka M (2018). OsIDD2, a zinc finger and INDETERMINATE DOMAIN protein, regulates secondary cell wall formation. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 130-143.
DOI |
| [35] |
Ishimaru K, Togawa E, Ookawa T, Kashiwagi T, Madoka Y, Hirotsu N (2008). New target for rice lodging resistance and its effect in a typhoon. Planta 227, 601-609.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Kashiwagi T, Togawa E, Hirotsu N, Ishimaru K (2008). Improvement of lodging resistance with QTLs for stem diameter in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 117, 749-757.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Kawasaki T, Koita H, Nakatsubo T, Hasegawa K, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Umemura K, Umezawa T, Shimamoto K (2006). Cinnamoyl-CoA reductase, a key enzyme in lignin biosynthesis, is an effector of small GTPase Rac in defense signaling in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 230-235.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Li M, Xiong GY, Li R, Cui JJ, Tang D, Zhang BC, Pauly M, Cheng ZK, Zhou YH (2009a). Rice cellulose synthase- like D4 is essential for normal cell-wall biosynthesis and plant growth. Plant J 60, 1055-1069.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Li XJ, Yang Y, Yao JL, Chen GX, Li XH, Zhang QF, Wu CY (2009b). FLEXIBLE CULM 1 encoding a cinnamyl- alcohol dehydrogenase controls culm mechanical strength in rice. Plant Mol Biol 69, 685-697.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Liu GM, Zhang K, Ai J, Deng XJ, Hong YY, Wang XM (2015). Patatin-related phospholipase A, pPLAIIIα, modulates the longitudinal growth of vegetative tissues and seeds in rice. J Exp Bot 66, 6945-6955.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| [43] |
Nixon BT, Mansouri K, Singh A, Du J, Davis JK, Lee JG, Slabaugh E, Vandavasi VG, O'Neill H, Roberts EM, Roberts AW, Yingling YG, Haigler CH (2016). Comparative structural and computational analysis supports eighteen cellulose synthases in the plant cellulose synthesis complex. Sci Rep 6, 28696.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Paredez AR, Somerville CR, Ehrhardt DW (2006). Visualization of cellulose synthase demonstrates functional association with microtubules. Science 312, 1491-1495.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Peng S, Cassman KG, Virmani SS, Sheehy J, Khush GS (1999). Yield potential trends of tropical rice since the release of IR8 and the challenge of increasing rice yield potential. Crop Sci 39, 1552-1559.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Rosinski JA, Atchley WR (1998). Molecular evolution of the MYB family of transcription factors: evidence for polyphyletic origin. J Mol Evol 46, 74-83.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Song XQ, Zhang BC, Zhou YH (2011). Golgi-localized UDP-glucose transporter is required for cell wall integrity in rice. Plant Signal Behav 6, 1097-1100.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA (1991). Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J Dairy Sci 74, 3583-3597.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Wang L, Wang AH, Huang XH, Zhao Q, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Sang T, Han B (2011). Mapping 49 quantitative trait loci at high resolution through sequencing-based genotyping of rice recombinant inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 122, 327-340.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
Zhang BL, Zhao TM, Yu WG, Kuang BQ, Yao Y, Liu TL, Chen XY, Zhang WH, Wu AM (2014). Functional conservation of the glycosyltransferase gene GT47A in the monocot rice. J Plant Res 127, 423-432.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [7] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [9] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [10] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [11] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [12] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [13] | 戴若惠, 钱心妤, 孙静蕾, 芦涛, 贾绮玮, 陆天麒, 路梅, 饶玉春. 水稻叶色调控机制及相关基因研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 799-812. |
| [14] | 田传玉, 方妍力, 沈晴, 王宏杰, 陈析丰, 郭威, 赵开军, 王春连, 纪志远. 2019-2021年我国南方稻区白叶枯病菌的毒力与遗传多样性调查研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 743-749. |
| [15] | 孙尚, 胡颖颖, 韩阳朔, 薛超, 龚志云. 水稻染色体双链寡核苷酸荧光原位杂交技术[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 433-439. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||