

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 122-131.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22176 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22176
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
冯晓敏1,2, 高翔1, 臧华栋2, 胡跃高2, 任长忠3, 郝志萍1, 吕慧卿1, 曾昭海2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-31
接受日期:2022-10-30
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: zengzhaohai@cau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xiaomin Feng1,2, Xiang Gao1, Huadong Zang2, Yuegao Hu2, Changzhong Ren3, Zhiping Hao1, Huiqing Lü1, Zhaohai Zeng2,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-31
Accepted:2022-10-30
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: zengzhaohai@cau.edu.cn
摘要: 为探究燕麦(Avena sativa)-绿豆(Phaseolus radiatus)间作效应及氮素转移特性, 在不施氮肥的大田试验条件下, 设置3种种植模式(燕麦单作、绿豆单作和燕麦-绿豆间作), 采用传统挖根法和15N同位素标记法进行研究。结果表明, 间作系统中燕麦侵袭力强于绿豆, 绿豆生长受到抑制。整个生育期, 间作燕麦地上部干物质积累量比单作增加14.9%-33.1%, 2年成熟期间作燕麦的氮素积累量比单作分别提高53.1%和44.8%; 间作减少了开花结荚期绿豆氮素积累量和根瘤重量, 降低了绿豆的固氮效率, 绿豆的固氮效率2年平均降低23.7%, 生物固氮量平均减少11.66%。间作绿豆向燕麦的氮素转移率2年平均值达31.7%, 氮素转移量为212.16 kg∙hm-2。燕麦-绿豆间作降低了开花结荚期绿豆的根瘤固氮酶活性和固氮效率, 但绿豆体内氮素转移增加了燕麦对氮素的吸收利用, 实现了地上部与地下部生长的相互调节和促进, 优化了农田生态系统的氮素管理。
冯晓敏, 高翔, 臧华栋, 胡跃高, 任长忠, 郝志萍, 吕慧卿, 曾昭海. 燕麦-绿豆间作效应及氮素转移特性. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 122-131.
Xiaomin Feng, Xiang Gao, Huadong Zang, Yuegao Hu, Changzhong Ren, Zhiping Hao, Huiqing Lü, Zhaohai Zeng. Intercropping Effect and Nitrogen Transfer Characteristics of Oat-Mungbean Intercrop. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 122-131.
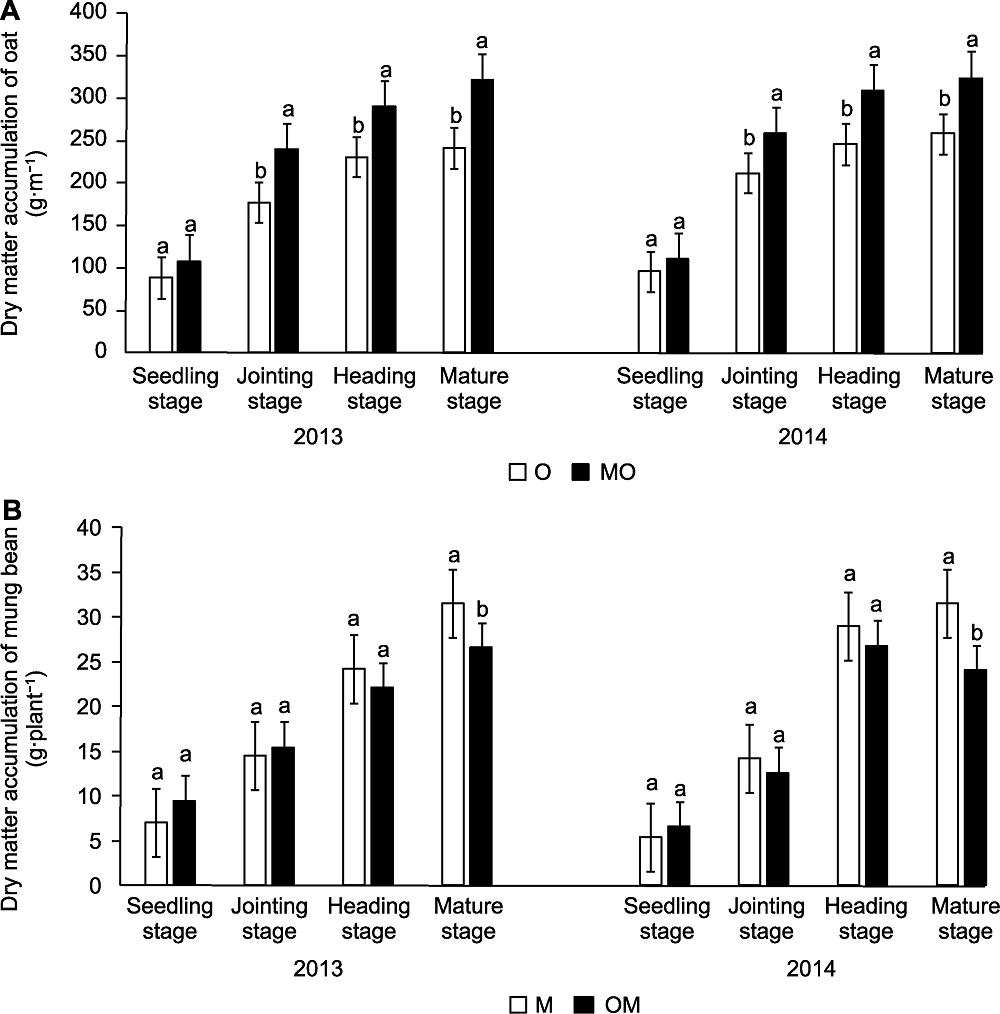
图3 不同种植方式下燕麦(A)和绿豆(B)各生育期地上部干物质的积累量 O: 单作燕麦; M: 单作绿豆; MO: 与绿豆间作的燕麦; OM: 与燕麦间作的绿豆。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 3 Dry matter accumulation amount of oat (A) and mungbean (B) in different growing stage under different cropping mode O: Oat monocropping; M: Mungbean monocropping; MO: Oat intercropped with mungbean; OM: Mungbean intercropped with oat. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
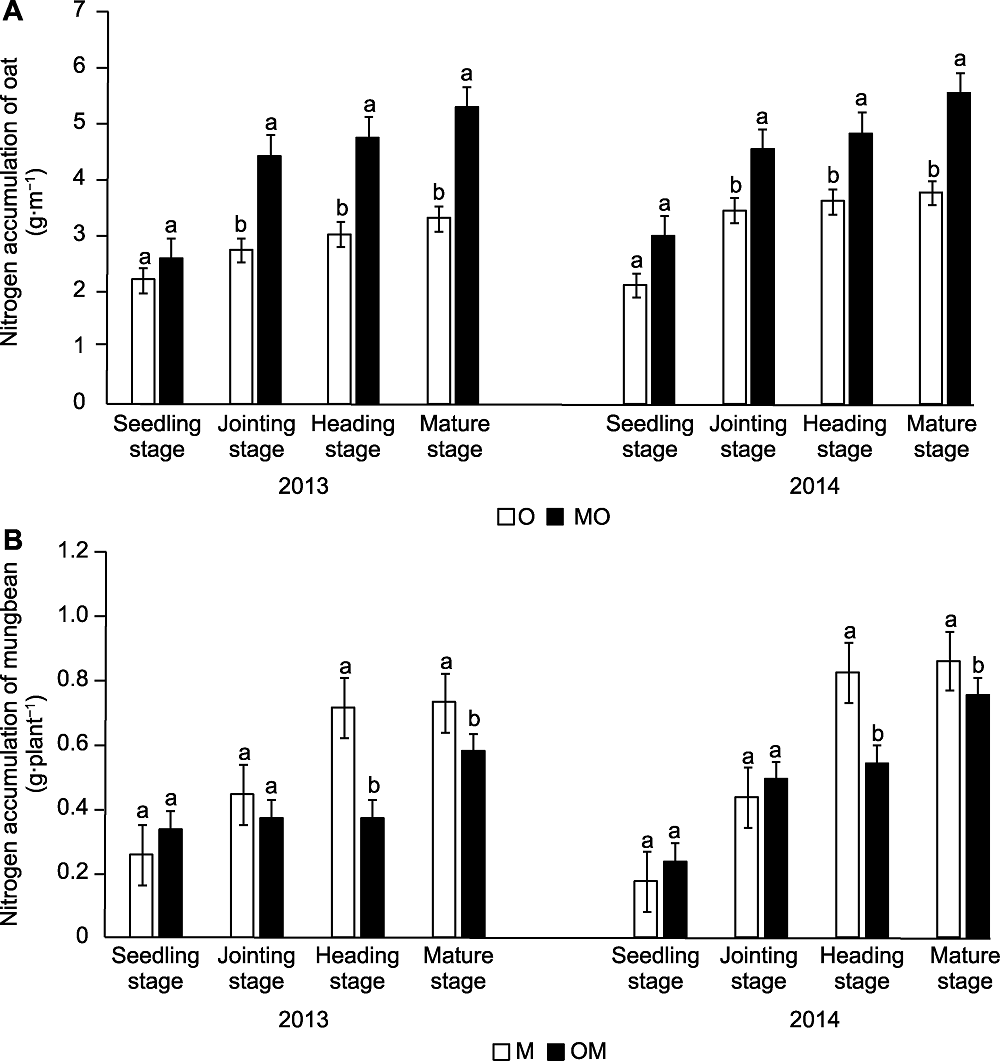
图4 间作对燕麦(A)和绿豆(B)地上部干物质氮素积累的影响 O、M、MO和OM同图3。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 4 Effect of the intercropping on nitrogen accumulation of oat (A) and mungbean (B) O, M, MO, and OM are the same as in Figure 3. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
| Year | Treatments | Weight of nodules (g) | Nitrogenase activity (nmol C2H2·h-1·plant-1) | %NDFA | Biological nitrogen fixation (g?plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | M | 3.29 a | 1.64 a | 66.23 a | 19.68 a |
| OM | 2.14 b | 1.48 a | 62.04 a | 15.56 b | |
| 2014 | M | 3.89 a | 3.11 b | 64.89 b | 17.05 a |
| OM | 2.79 b | 2.55 a | 58.56 a | 16.64 a |
表1 间作对绿豆结瘤固氮的影响
Table 1 Effect of intercropping on nodule and nitrogen fixation of mungbean
| Year | Treatments | Weight of nodules (g) | Nitrogenase activity (nmol C2H2·h-1·plant-1) | %NDFA | Biological nitrogen fixation (g?plant-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | M | 3.29 a | 1.64 a | 66.23 a | 19.68 a |
| OM | 2.14 b | 1.48 a | 62.04 a | 15.56 b | |
| 2014 | M | 3.89 a | 3.11 b | 64.89 b | 17.05 a |
| OM | 2.79 b | 2.55 a | 58.56 a | 16.64 a |
| Year | Treatments | 15N atom percent excess | 15N uptake (mg?plant-1) | %NTFL | N transfer (kg?hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | O | 0.5720 b | 0.36 a | - | - |
| MO | 0.7563 a | 0.39 a | 32.2 | 215.28 | |
| 2014 | O | 0.6102 b | 0.40 b | - | - |
| MO | 0.8010 a | 0.54 a | 31.2 | 209.04 |
表2 间作系统中氮素从绿豆向燕麦的转移
Table 2 Nitrogen translation from mungbean to oat in the intercropping system
| Year | Treatments | 15N atom percent excess | 15N uptake (mg?plant-1) | %NTFL | N transfer (kg?hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | O | 0.5720 b | 0.36 a | - | - |
| MO | 0.7563 a | 0.39 a | 32.2 | 215.28 | |
| 2014 | O | 0.6102 b | 0.40 b | - | - |
| MO | 0.8010 a | 0.54 a | 31.2 | 209.04 |
| [1] | 蔡倩, 孙占祥, 王文斌, 白伟, 杜桂娟, 张悦, 张哲, 冯晨, 向午燕, 赵凤艳 (2022). 辽西半干旱区玉米大豆间作对作物产量及水分利用的影响. 中国农业气象 43, 551-562. |
| [2] | 柴强, 胡发龙, 陈桂平 (2017). 禾豆间作氮素高效利用机理及农艺调控途径研究进展. 中国生态农业学报 25, 19-26. |
| [3] | 褚贵新, 沈其荣, 曹金留, 茆泽圣, 钟增涛, 赵龙 (2003). 旱作水稻与花生间作系统中的氮素固定与转移及其对土壤肥力的影响. 土壤学报 40, 717-723. |
| [4] | 董志新, 孙波, 殷士学, 隋跃宇 (2012). 气候条件和作物对黑土和潮土固氮微生物群落多样性的影响. 土壤学报 49, 130-138. |
| [5] | 房增国 (2004). 豆科/禾本科间作的氮铁营养效应及对结瘤固氮的影响. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业大学. pp. 65-66. |
| [6] | 房增国, 左元梅, 李隆, 张福锁 (2005). 玉米-花生混作对系统内氮营养的影响研究. 中国生态农业学报 13(3), 63-64. |
| [7] | 冯晓敏, 胡跃高, 张卫建, 曾昭海 (2015a). 不同豆科作物与燕麦间作对燕麦产量、光合特性和根际固氮微生物nifH基因丰度的影响. 中国作物学会——2015年学术年会论文摘要集. 哈尔滨: 中国作物学会. pp. 222. |
| [8] | 冯晓敏, 杨永, 任长忠, 胡跃高, 曾昭海 (2015b). 豆科-燕麦间作对作物光合特性及籽粒产量的影响. 作物学报 41, 1426-1434. |
| [9] | 郭丽琢, 张虎天, 何亚慧, 柴强, 黄高宝 (2012). 根瘤菌接种对豌豆/玉米间作系统作物生长及氮素营养的影响. 草业学报 21, 43-49. |
| [10] |
何纪桐, 马祥, 琚泽亮, 刘凯强, 赵继秀, 马小龙, 贾志锋 (2022). 高寒地区燕麦与蚕豆间作对作物生长发育及产量的影响. 草地学报 30, 2514-2521.
DOI |
| [11] | 纪祥龙, 张吉立, 蒋雨洲, 王鹏 (2022). 施氮量对绿豆光合特性、磷钾素吸收利用及产量的影响. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报 34(2), 1-9, 31. |
| [12] | 焦念元, 赵春, 宁堂原, 侯连涛, 付国占, 李增嘉, 陈明灿 (2008). 玉米-花生间作对作物产量和光合作用光响应的影响. 应用生态学报 19, 981-985. |
| [13] | 李玉英, 孙建好, 李春杰, 李隆, 程序, 张福锁 (2009). 施氮对蚕豆/玉米间作系统蚕豆农艺性状及结瘤特性的影响. 中国农业科学 42, 3467-3474. |
| [14] | 刘卫国, 蒋涛, 佘跃辉, 杨峰, 杨文钰 (2011). 大豆苗期茎秆对荫蔽胁迫响应的生理机制初探. 中国油料作物学报 33, 141-146. |
| [15] | 卢秉林, 车宗贤, 包兴国, 张久东, 曹卫东, 吴科生, 杨蕊菊, 崔恒 (2021). 不同氮肥减施量下玉米针叶豌豆间作体系的产量及效益. 植物营养与肥料学报 27, 1560-1570. |
| [16] | 马怀英, 王上, 杨亚东, 冯晓敏, 曾昭海, 任长忠, 臧华栋, 胡跃高 (2021). 燕麦与豆科作物间作的产量、经济效益与碳足迹分析. 中国农业大学学报 26(8), 23-32. |
| [17] | 秦亚洲, 王利立, 柴强, 殷文 (2015). 大麦间作豌豆的种间竞争力及产量对施氮量的响应. 农业现代化研究 36, 482-487. |
| [18] | 沈颖超, 张志肖, 孙素丽, 王彦, 范保杰, 刘长友, 王珅, 苏秋竹, 时会影, 朱振东, 田静 (2022). 绿豆种质资源枯萎病抗性鉴定及抗性资源筛选. 植物遗传资源学报 23, 1660-1669. |
| [19] | 王利立, 朱永永, 殷文, 郑德阳, 柴强 (2016). 大麦/豌豆间作系统种间竞争力及产量对地下作用和密度互作的响应. 中国生态农业学报 24, 265-273. |
| [20] | 王旭, 曾昭海, 朱波, 胡跃高, 林叶春, 陈恭, 芦金生, 袁喜兰 (2009). 燕麦与箭筈豌豆不同混作模式对根际土壤微生物数量的影响. 草业学报 18(6), 151-157. |
| [21] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静 (2021a). 紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作对燕麦碳、氮代谢及其物质积累的影响研究. 草地学报 29, 2258-2264. |
| [22] | 汪雪, 刘晓静, 赵雅姣, 王静 (2021b). 根系分隔方式下紫花苜蓿/燕麦间作氮素利用及种间互馈特征研究. 草业学报 30(8), 73-85. |
| [23] | 肖焱波, 李隆, 张福锁 (2005). 小麦/蚕豆间作体系中的种间相互作用及氮转移研究. 中国农业科学 38, 965-973. |
| [24] |
殷文, 赵财, 于爱忠, 柴强, 胡发龙, 冯福学 (2015). 秸秆还田后少耕对小麦/玉米间作系统中种间竞争和互补的影响. 作物学报 41, 633-641.
DOI |
| [25] | 赵雅姣, 刘晓静, 童长春, 吴勇 (2020). 紫花苜蓿/玉米间作对紫花苜蓿结瘤固氮特性的影响. 草业学报 29, 95-105. |
| [26] | 左元梅, 刘永秀, 张福锁 (2003). 与玉米混作改善花生铁营养对其根瘤形态结构及豆血红蛋白含量的影响. 植物生理与分子生物学学报 29, 33-38. |
| [27] |
Bellenger JP, Xu Y, Zhang X, Morel FMM, Kraepiel AML (2014). Possible contribution of alternative nitrogenases to nitrogen fixation by asymbiotic N2-fixing bacteria in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 69, 413-420.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Chapagain T, Riseman A (2014). Barley-pea intercropping: effects on land productivity, carbon and nitrogen transformations. Field Crops Res 166, 18-25.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Gong XW, Dang K, Lv SM, Zhao G, Tian LX, Luo Y, Feng BL (2020). Interspecific root interactions and water-use efficiency of intercropped proso millet and mungbean. Eur J Agron 115, 126034.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Hauggaard-Nielsen H, Gooding M, Ambus P, Corre-Hellou G, Crozat Y, Dahlmann C, Dibet A, von Fragstein P, Pristeri A, Monti M, Jensen ES (2009). Pea-barley intercropping for efficient symbiotic N2-fixation, soil N acquisition and use of other nutrients in European organic cropping systems. Field Crops Res 113, 64-71.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
He TG, Su LR, Li YR, Su TM, Qin F, Li Q (2018). Nutrient decomposition rate and sugarcane yield as influenced by mungbean intercropping and crop residue recycling. Sugar Tech 20, 154-162.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Hu FL, Zhao C, Feng FX, Chai Q, Mu YP, Zhang Y (2017). Improving N management through intercropping alleviates the inhibitory effect of mineral N on nodulation in pea. Plant Soil 412, 235-251.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Ledgard SF, Freney JR, Simpson JR (1985). Assessing nitrogen transfer from legumes to associated grasses. Soil Boil Biochem 17, 575-577.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Li SX, Wang ZH, Hu TT, Gao YJ, Stewart BA (2009). Nitrogen in dryland soils of China and its management. Adv Agron 101, 123-181. |
| [35] |
Liang JP, He ZJ, Shi WJ (2020). Cotton/mungbean intercropping improves crop productivity, water use efficiency, nitrogen uptake, and economic benefits in the arid area of Northwest China. Agric Water Manage 240, 106277.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Neugschwandtner RW, Kaul HP (2014). Sowing ratio and N fertilization affect yield and yield components of oat and pea in intercrops. Field Crops Res 155, 159-163.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Neumann A, Schmidtke K, Rauber R (2007). Effects of crop density and tillage system on grain yield and N uptake from soil and atmosphere of sole and intercropped pea and oat. Field Crops Res 100, 285-293.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Neumann A, Werner J, Rauber R (2009). Evaluation of yield-density relationships and optimization of intercrop compositions of field-grown pea-oat intercrops using the replacement series and the response surface design. Field Crops Res 114, 286-294.
DOI URL |
| [39] | Ofori F, Stern WR (1987). Cereal-legume intercropping systems. Adv Agron 41, 41-90. |
| [40] |
Rusinamhodzi L, Murwira HK, Nyamangara J (2006). Cotton-cowpea intercropping and its N2 fixation capacity improves yield of a subsequent maize crop under Zimbabwean rain-fed conditions. Plant Soil 287, 327-336.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Van Kessel C, Roskoski JP (1998). Row spacing effects on N2-fixation, N-yield and soil N uptake of intercropped cowpea and maize. Plant Soil 111, 17-23.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Willey RW (1979). Intercropping—its importance and research needs. Part II. Agronomy and research approaches. Field Crop Abstr 32, 73-85. |
| [43] |
Xie KY, Li XL, He F, Zhang YJ, Wan LQ, David BH, Wang D, Qin Y, Gamal MAF (2015). Effect of nitrogen fertilization on yield, N content, and nitrogen fixation of alfalfa and smooth bromegrass grown alone or in mixture in greenhouse pots. J Integr Agric 14, 1864-1876.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Zang HD, Yang XC, Feng XM, Qian X, Hu YG, Ren CZ, Zeng ZH (2015). Rhizodeposition of nitrogen and carbon by mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) and its contribution to intercropped oats (Avena nuda L.). PLoS One 10, e0121132. |
| [1] | 孔照胜, 杨文强, 王柏臣, 林荣呈. 豆科饲草碳氮高效固定、转运和同化利用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 764-773. |
| [2] | 刘恩科, 梅旭荣, 龚道枝, 严昌荣, 庄严. 不同生育时期干旱对冬小麦氮素吸收与利用的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2010, 34(5): 555-562. |
| [3] | 江立庚, 戴廷波, 韦善清, 甘秀芹, 徐建云, 曹卫星. 南方水稻氮素吸收与利用效率的基因型差异及评价[J]. 植物生态学报, 2003, 27(4): 466-471. |
| [4] | 由振国. 稗草阴蔽对大豆根瘤固氮速率的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 1993, 17(1): 33-37. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||