

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 275-283.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21039 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21039
潘晨阳, 张月, 林晗, 陈芊羽, 杨凯如, 姜嘉骥, 李梦佳, 芦涛, 王珂欣, 路梅, 王盛, 叶涵斐, 饶玉春*( ), 胡海涛*(
), 胡海涛*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-22
接受日期:2021-03-26
出版日期:2021-05-01
发布日期:2021-04-30
通讯作者:
饶玉春,胡海涛
作者简介:haitao-hu@zjnu.cn基金资助:
Chenyang Pan, Yue Zhang, Han Lin, Qianyu Chen, Kairu Yang, Jiaji Jiang, Mengjia Li, Tao Lu, Kexin Wang, Mei Lu, Sheng Wang, Hanfei Ye, Yuchun Rao*( ), Haitao Hu*(
), Haitao Hu*( )
)
Received:2021-02-22
Accepted:2021-03-26
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Yuchun Rao,Haitao Hu
摘要: 为探究叶片水势(LWP)相关基因在水稻(Oryza sativa)抗旱中的作用及其遗传机制, 以热研2号(Nekken2)和华占(HZ)为亲本以及构建的120个重组自交系(RILs)群体为实验材料, 对水稻分蘖期叶片水势进行检测, 并利用前期基于高通量测序构建的分子遗传连锁图谱进行数量性状基因座(QTL)分析。结果表明, 共检测到5个与水稻分蘖期叶片水势相关的QTLs, 分别位于第2、3、4、11和12号染色体上, LOD值均达2.5以上, 其中位于4号染色体物理距离24 066 261- 30 847 136 bp内QTL的LOD值高达5.15。对这些QTL区间内与水势相关的候选基因进行定量分析, 发现LOC_Os02g56630、LOC_Os02g57720、LOC_Os02g57580、LOC_Os04g43730、LOC_Os04g46490、LOC_Os04g44570和LOC_Os04g44060这7个基因在双亲间表达量差异显著。位于4号染色体QTL区间内LOC_Os04g46490基因的表达在两亲本间存在显著差异。对基因LOC_Os04g46490进行测序分析, 发现该基因在两亲本间共存在6处差异, 从而导致氨基酸序列的改变。通过QTL挖掘及相关基因表达分析, 发现这些基因与水稻叶片水势调控相关, 可能间接影响水稻的抗旱性。检测到的QTL位点对水势相关基因精细定位和克隆具有重要参考价值, 有助于进一步理解水稻叶片水势的遗传基础, 并为培育耐旱水稻新品种提供有利的基因资源。
潘晨阳, 张月, 林晗, 陈芊羽, 杨凯如, 姜嘉骥, 李梦佳, 芦涛, 王珂欣, 路梅, 王盛, 叶涵斐, 饶玉春, 胡海涛. 水稻叶片水势的QTL定位与候选基因分析. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 275-283.
Chenyang Pan, Yue Zhang, Han Lin, Qianyu Chen, Kairu Yang, Jiaji Jiang, Mengjia Li, Tao Lu, Kexin Wang, Mei Lu, Sheng Wang, Hanfei Ye, Yuchun Rao, Haitao Hu. QTL Mapping and Candidate Gene Analysis on Rice Leaf Water Potential. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 275-283.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g56630-F-qrt | GATGCTACGGAGACTGCACA | 60.02 | 182 |
| LOC_Os02g56630-R-qrt | GAGCCAGAAGCACATGAACA | 59.99 | |
| LOC_Os02g57720-F-qrt | CTGACGTCGTGGTCGTTCTA | 59.90 | 101 |
| LOC_Os02g57720-R-qrt | GACTTGTTCACCCCCATCAC | 60.22 | |
| LOC_Os04g43730-F-qrt | ACCAAAGTGGGTGTTTCTCG | 60.01 | 153 |
| LOC_Os04g43730-R-qrt | TCGAGATCTGGCTTGTGTTG | 59.98 | |
| LOC_Os04g44060-F-qrt | CGGTGTTCATGGTTCACTTG | 60.00 | 182 |
| LOC_Os04g44060-R-qrt | CCTCAGGACGTACTGGTGGT | 60.03 | |
| LOC_Os04g46490-F-qrt | GCCTCGTCCTCCACTACATC | 59.69 | 123 |
| LOC_Os04g46490-R-qrt | CCGTGTACACCACCATGAAC | 59.73 | |
| LOC_Os02g57580-F-qrt | ACCTCTTCAGATGGGGTGTG | 59.96 | 101 |
| LOC_Os02g57580-R-qrt | CCAGTCAGTTTTGCAGACCA | 59.87 | |
| LOC_Os04g48230-F-qrt | GGGCACTACAAGTCCGTGAT | 60.00 | 199 |
| LOC_Os04g48230-R-qrt | CTTGGTAGCTTCCGATGAGC | 59.98 | |
| LOC_Os04g44570-F-qrt | CGCCACCACTGGGTTTACT | 60.96 | 123 |
| LOC_Os04g44570-R-qrt | CACGGGAAGCCGAGTATCT | 60.23 |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR的引物序列
Table 1 The primer sequences of real-time quantitative PCR
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Tm (°C) | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os02g56630-F-qrt | GATGCTACGGAGACTGCACA | 60.02 | 182 |
| LOC_Os02g56630-R-qrt | GAGCCAGAAGCACATGAACA | 59.99 | |
| LOC_Os02g57720-F-qrt | CTGACGTCGTGGTCGTTCTA | 59.90 | 101 |
| LOC_Os02g57720-R-qrt | GACTTGTTCACCCCCATCAC | 60.22 | |
| LOC_Os04g43730-F-qrt | ACCAAAGTGGGTGTTTCTCG | 60.01 | 153 |
| LOC_Os04g43730-R-qrt | TCGAGATCTGGCTTGTGTTG | 59.98 | |
| LOC_Os04g44060-F-qrt | CGGTGTTCATGGTTCACTTG | 60.00 | 182 |
| LOC_Os04g44060-R-qrt | CCTCAGGACGTACTGGTGGT | 60.03 | |
| LOC_Os04g46490-F-qrt | GCCTCGTCCTCCACTACATC | 59.69 | 123 |
| LOC_Os04g46490-R-qrt | CCGTGTACACCACCATGAAC | 59.73 | |
| LOC_Os02g57580-F-qrt | ACCTCTTCAGATGGGGTGTG | 59.96 | 101 |
| LOC_Os02g57580-R-qrt | CCAGTCAGTTTTGCAGACCA | 59.87 | |
| LOC_Os04g48230-F-qrt | GGGCACTACAAGTCCGTGAT | 60.00 | 199 |
| LOC_Os04g48230-R-qrt | CTTGGTAGCTTCCGATGAGC | 59.98 | |
| LOC_Os04g44570-F-qrt | CGCCACCACTGGGTTTACT | 60.96 | 123 |
| LOC_Os04g44570-R-qrt | CACGGGAAGCCGAGTATCT | 60.23 |
| QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qLpw2-8 | 2 | 34636269-35675126 | 148.48-152.93 | 3.27 |
| qLpw3-8 | 3 | 30389734-30481217 | 130.27-130.66 | 2.93 |
| qLpw4-8 | 4 | 24066261-30847136 | 103.17-132.23 | 5.15 |
| qLpw11-8 | 11 | 2051418-2119803 | 8.79-9.09 | 3.06 |
| qLpw12-8 | 12 | 25396321-25626163 | 108.87-109.85 | 3.34 |
表2 水稻分蘖期叶片水势的QTL分析
Table 2 QTL analysis of leaf water potential in rice at tillering stage
| QTL | Chromosome | Physical distance (bp) | Position of support (cM) | Likelihood of odd (LOD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qLpw2-8 | 2 | 34636269-35675126 | 148.48-152.93 | 3.27 |
| qLpw3-8 | 3 | 30389734-30481217 | 130.27-130.66 | 2.93 |
| qLpw4-8 | 4 | 24066261-30847136 | 103.17-132.23 | 5.15 |
| qLpw11-8 | 11 | 2051418-2119803 | 8.79-9.09 | 3.06 |
| qLpw12-8 | 12 | 25396321-25626163 | 108.87-109.85 | 3.34 |
| Chromosome | Gene | Function | Regulation object | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | LOC_Os02g56630 | Play an important regulatory role in the response of plants to abiotic stress | OsWAK24-OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g43730 | Play an important regulatory role in the response of plants to abiotic stress | OsWAK51-OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | |
| 2 | LOC_Os02g57580 | Maybe involved in anthocyanin vacuole storage, participate in osmotic adjustment | Anthocyanin permease | Aza-González et al., 2013 |
| 2 | LOC_Os02g57720 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g46490 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g44570 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g44060 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g48230 | Maybe involved in the perception, conduc- tion of plant dehydration and regulation of antidehydration substance synthesis | Dehydration response related protein | Shinozaki and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, 1997 |
表3 候选基因的功能注释
Table 3 The function annotation of candidate genes
| Chromosome | Gene | Function | Regulation object | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | LOC_Os02g56630 | Play an important regulatory role in the response of plants to abiotic stress | OsWAK24-OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g43730 | Play an important regulatory role in the response of plants to abiotic stress | OsWAK51-OsWAK receptor-like protein kinase | |
| 2 | LOC_Os02g57580 | Maybe involved in anthocyanin vacuole storage, participate in osmotic adjustment | Anthocyanin permease | Aza-González et al., 2013 |
| 2 | LOC_Os02g57720 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g46490 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g44570 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g44060 | Mediate the transport of water across the membrane, regulate water | Aquaporin | |
| 4 | LOC_Os04g48230 | Maybe involved in the perception, conduc- tion of plant dehydration and regulation of antidehydration substance synthesis | Dehydration response related protein | Shinozaki and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, 1997 |
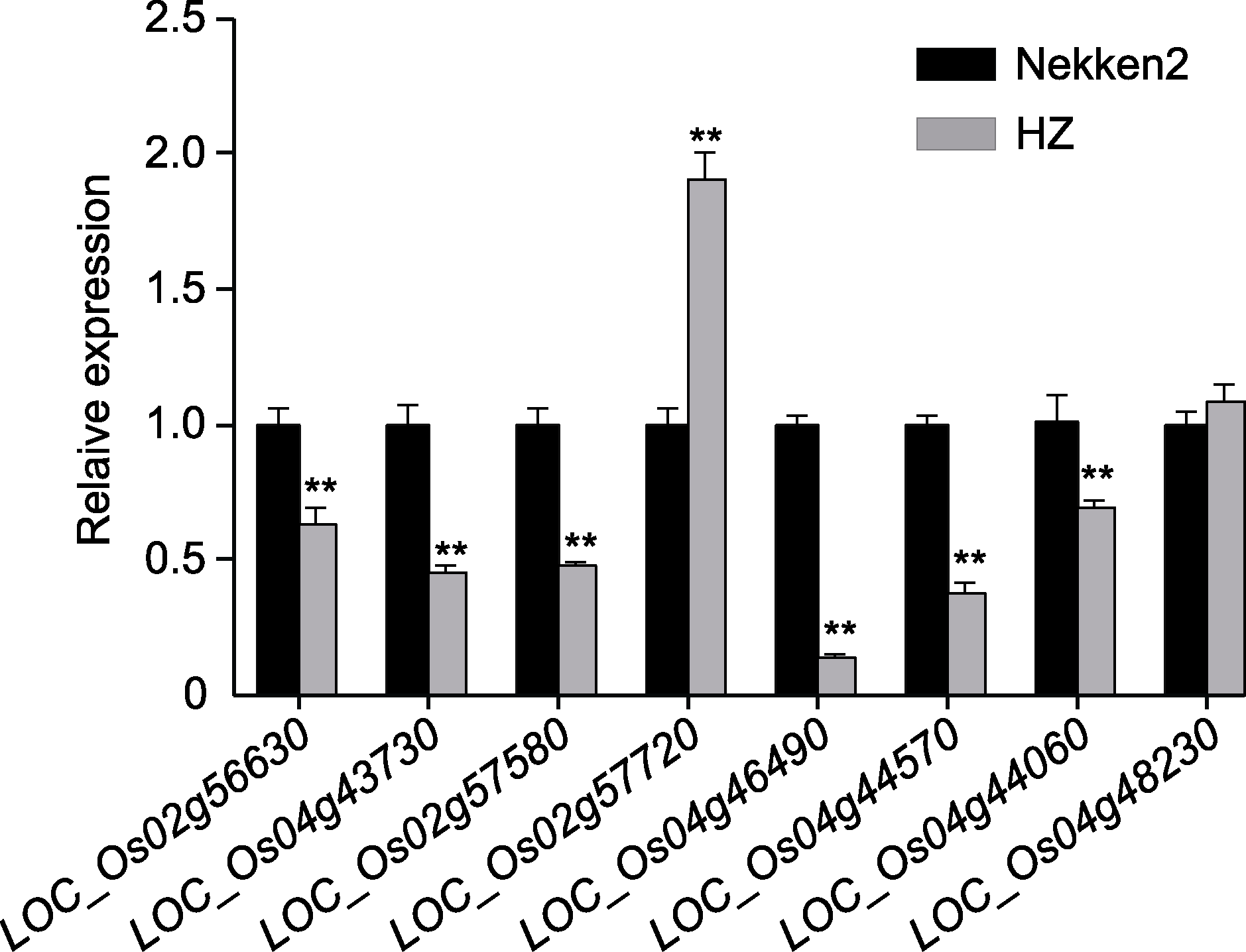
图4 水稻叶片水势相关候选基因表达量差异 **表示华占与热研2号基因表达量在0.01水平上差异显著。
Figure 4 Differences in the expression level of candidate genes involved in leaf water potential in rice ** indicate significant differences in genes expression level between HZ and Nekken2 at 0.01 level.
| 1 | 曹玉婷, 丁艳菲, 朱诚 (2014). 类受体蛋白激酶与植物非生物胁迫应答. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报 30, 241-247. |
| 2 | 高世斌, 冯质雷, 李晚忱, 荣廷昭 (2005). 干旱胁迫下玉米根系性状和产量的QTLs分析. 作物学报 31, 718-722. |
| 3 | 刘鸿艳, 邹桂花, 刘国兰, 胡颂平, 李明寿, 余新桥, 梅捍卫, 罗利军 (2005). 水分梯度下水稻CT, LWP和SF的相关及其QTL定位研究. 科学通报 50, 130-139. |
| 4 | 穆平 (2004). 水、旱稻DH和RIL群体抗旱性状相关分析及其QTL表达规律比较. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业大学. pp. 1-115. |
| 5 | 聂元元, 邹桂花, 李瑶, 刘国兰, 蔡耀辉, 毛凌华, 颜龙安, 刘鸿艳, 罗利军 (2012). 水稻第2染色体上抗旱相关性状QTL的精细定位. 作物学报 38, 988-995. |
| 6 |
潘琰, 龚吉蕊, 宝音陶格涛, 罗亲普, 翟占伟, 徐沙, 王忆慧, 刘敏, 杨丽丽 (2017). 季节放牧下内蒙古温带草原羊草根茎叶功能性状的权衡. 植物学报 52, 307-321.
DOI |
| 7 | 邱泽森, 朱庆森, 刘建国, 巫亚东, 杨建昌 (1993). 水稻在不同土水势下的生理反应. 江苏农学院学报 14(2), 7-11. |
| 8 | 曲延英, 穆平, 李雪琴, 田玉秀, 文峰, 张洪亮, 李自超 (2008). 水、旱栽培条件下水稻叶片水势与抗旱性的相关分析及其QTL定位. 作物学报 34, 198-206. |
| 9 | 王辉, 曹立勇, 郭玉华, 程式华 (2008). 水稻生理特性与抗旱性的相关分析及QTL定位. 中国水稻科学 22, 477-484. |
| 10 | 王兰, 黄李超, 代丽萍, 杨窑龙, 徐杰, 冷语佳, 张光恒, 胡江, 朱丽, 高振宇, 董国军, 郭龙彪, 钱前, 曾大力 (2014). 利用日本晴/9311重组自交系群体定位水稻成熟期叶形相关性状QTL. 中国水稻科学 28, 589-597. |
| 11 | 于利刚, 解莉楠, 李玉花 (2011). 植物抗逆反应中水孔蛋白的表达调控研究. 生物技术通报 27(8), 5-14. |
| 12 | 赵秀琴, 徐建龙, 朱苓华, 黎志康 (2008). 利用回交导入系定位干旱环境下水稻植株水分状况相关QTL. 作物学报 34, 1696-1703. |
| 13 | 朱鸿宇, 王盛, 张月, 林晗, 路梅, 吴先美, 李三峰, 朱旭东, 饶玉春, 王跃星 (2020). 水稻籽粒砷、铜、铁、汞、锌含量QTL挖掘及候选基因分析. 中国科学: 生命科学 50, 623-632. |
| 14 |
Aza-González C, Herrera-Isidrón L, Núñez-Palenius HG, De La Vega OM, Ochoa-Alejo N (2013). Anthocyanin accumulation and expression analysis of biosynthesis- related genes during chili pepper fruit development. Biol Plantarum 57, 49-55.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Hemamalini GS, Shashidhar HE, Hittalmani S (2000). Molecular marker assisted tagging of morphological and physiological traits under two contrasting moisture regimes at peak vegetative stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 112, 69-78.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Johansson I, Karlsson M, Shukla VK, Chrispeels MJ, Larsson C, Kjellbom P (1998). Water transport activity of the plasma membrane aquaporin PM28A is regulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell 10, 451-459.
PMID |
| 17 |
Johansson I, Larsson C, Ek B, Kjellbom P (1996). The major integral proteins of spinach leaf plasma membranes are putative aquaporins and are phosphorylated in response to Ca 2+ and apoplastic water potential . Plant Cell 8, 1181-1191.
PMID |
| 18 |
Jongdee B, Fukai S, Cooper M (2002). Leaf water potential and osmotic adjustment as physiological traits to improve drought tolerance in rice. Field Crops Res 76, 153-163.
DOI URL |
| 19 |
Li LG, Li SF, Tao Y, Kitagawa Y (2000). Molecular cloning of a novel water channel from rice: its products expression in Xenopus oocytes and involvement in chilling tolerance. Plant Sci 154, 43-51.
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 -ΔΔCT method . Methods 25, 402-408.
PMID |
| 21 |
Marrs KA, Alfenito MR, Lloyd AM, Walbot V (1995). A glutathione S-transferase involved in vacuolar transfer encoded by the maize gene Bronze-2. Nature 375, 397-400.
PMID |
| 22 |
Mathews H, Clendennen SK, Caldwell CG, Liu XL, Connors K, Matheis N, Schuster DK, Menasco DJ, Wago- ner W, Lightner J, Wagner DR (2003). Activation tagging in tomato identifies a transcriptional regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis, modification, and transport. Plant Cell 15, 1689-1703.
PMID |
| 23 | McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14, 11-13. |
| 24 |
Mueller LA, Goodman CD, Silady RA, Walbot V (2000). AN9, a petunia glutathione S-transferase required for anthocyanin sequestration, is a flavonoid-binding protein. Plant Physiol 123, 1561-1570.
PMID |
| 25 |
Pivovaroff AL, Pasquini SC, De Guzman ME, Alstad KP, Stemke JS, Santiago LS (2016). Multiple strategies for drought survival among woody plant species. Funct Ecol 30, 517-526.
DOI URL |
| 26 |
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (1997). Gene expression and signal transduction in water-stress response. Plant Physiol 115, 327-334.
DOI URL |
| 27 |
Wang YJ, Huang JK, Wang JX, Findlay C (2018). Miti-gating rice production risks from drought through improving irrigation infrastructure and management in China. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 62, 161-176.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Zhou Q, Ju CX, Wang ZQ, Zhang H, Liu LJ, Yang JC, Zhang JH (2017). Grain yield and water use efficiency of super rice under soil water deficit and alternate wetting and drying irrigation. J Integr Agric 16, 1028-1043.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [6] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [7] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [8] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [9] | 廖星鑫, 牛祎, 多兴武, 阿克也得力·居玛哈孜, 买热哈巴·阿不都克尤木, 热孜瓦尼姑丽·胡甫尔, 兰海燕, 曹婧. 异源表达异子蓬SaPEPC2基因提高烟草抗旱性和光合特性(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 585-599. |
| [10] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [11] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [12] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [13] | 王贺萍, 孙震, 刘雨辰, 苏彦龙, 杜锦瑜, 赵彦, 赵竑博, 王召明, 苑峰, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草肉桂醇脱氢酶基因序列鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 204-216. |
| [14] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [15] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||