

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 204-216.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23109 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23109
王贺萍1,2, 孙震2, 刘雨辰2, 苏彦龙2, 杜锦瑜2,5, 赵彦5, 赵竑博1, 王召明6, 苑峰6, 刘亚玲6, 吴振映2,3,4, 何峰2,3,4,*( ), 付春祥2,3,4,*(
), 付春祥2,3,4,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-09
接受日期:2023-12-19
出版日期:2024-03-10
发布日期:2024-03-10
通讯作者:
* E-mail: 基金资助:
Heping Wang1,2, Zhen Sun2, Yuchen Liu2, Yanlong Su2, Jinyu Du2,5, Yan Zhao5, Hongbo Zhao1, Zhaoming Wang6, Feng Yuan6, Yaling Liu6, Zhenying Wu2,3,4, Feng He2,3,4,*( ), Chunxiang Fu2,3,4,*(
), Chunxiang Fu2,3,4,*( )
)
Received:2023-08-09
Accepted:2023-12-19
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-10
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要: 肉桂醇脱氢酶(CAD)作为植物次生代谢尤其是木质素生物合成过程的关键酶, 在调控植物生长发育和抵御生物/非生物胁迫等过程中发挥关键作用。蒙古冰草(即沙芦草(Agropyron mongolicum))耐旱耐寒, 在我国北方荒漠草原区域广泛分布。为探讨CAD基因在蒙古冰草木质素合成和非生物胁迫抗性中的作用, 从蒙古冰草全长转录组数据中筛选并克隆到1个CAD基因, 序列长度1 083 bp, 命名为AmCAD。该基因编码361个氨基酸残基, 同源序列比对发现蛋白质序列保守区域含有2个Zn2+结合基序和NADP(H)辅因子结合基序, 属于典型的CAD蛋白, 且三维结构与AtCAD5相似。AmCAD在茎秆中高表达, 对AmCAD重组蛋白的酶学性质分析表明, 该蛋白对不同肉桂醛类底物均具有很强的催化能力, 其中对松柏醛和芥子醛的底物亲和力更强。用不同浓度甘露醇模拟干旱胁迫, 蒙古冰草AmCAD基因表达受到显著诱导。研究结果表明, AmCAD在蒙古冰草木质素合成和干旱胁迫抗性中发挥重要作用, 可为提高蒙古冰草品质和抗逆性分子育种提供有价值的基因资源。
王贺萍, 孙震, 刘雨辰, 苏彦龙, 杜锦瑜, 赵彦, 赵竑博, 王召明, 苑峰, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草肉桂醇脱氢酶基因序列鉴定及功能分析. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 204-216.
Heping Wang, Zhen Sun, Yuchen Liu, Yanlong Su, Jinyu Du, Yan Zhao, Hongbo Zhao, Zhaoming Wang, Feng Yuan, Yaling Liu, Zhenying Wu, Feng He, Chunxiang Fu. Sequence Identification and Functional Analysis of Cinnamyl Alcohol Dehydrogenase Gene from Agropyron mongolicum. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 204-216.
| Sequence ID | Number of amino acid | Molecular weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | Grand average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB.70108.1 | 360 | 38591.48 | 5.87 | 23.05 | 90.33 | 0.025 |
| PB.82665.1 | 354 | 38437.86 | 6.66 | 24.94 | 84.75 | -0.098 |
| PB.80567.1 | 358 | 38685.52 | 6.60 | 30.79 | 89.27 | 0.012 |
| PB.80906.1 | 355 | 38256.89 | 5.68 | 31.84 | 88.42 | 0.037 |
| PB.62308.1 | 269 | 28625.35 | 6.31 | 31.41 | 92.45 | 0.166 |
| PB.17482.1 | 344 | 36802.76 | 5.86 | 31.22 | 86.13 | 0.103 |
| PB.52032.1 | 373 | 38747.35 | 6.53 | 24.05 | 91.58 | 0.136 |
| PB.47633.2 | 421 | 44353.00 | 6.42 | 31.04 | 84.28 | 0.092 |
| PB.55683.1 | 421 | 44338.97 | 6.42 | 29.60 | 83.80 | 0.088 |
| PB.83678.1 | 356 | 37359.82 | 5.40 | 25.49 | 92.25 | 0.146 |
| PB.84043.1 | 356 | 37036.55 | 5.84 | 26.83 | 93.88 | 0.211 |
| PB.84184.1 | 356 | 37019.73 | 6.08 | 23.61 | 92.25 | 0.195 |
表1 蒙古冰草AmCAD蛋白理化性质分析
Table 1 Analysis of physicochemical properties of AmCAD proteins from Agropyron mongolicum
| Sequence ID | Number of amino acid | Molecular weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | Grand average of hydropathicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB.70108.1 | 360 | 38591.48 | 5.87 | 23.05 | 90.33 | 0.025 |
| PB.82665.1 | 354 | 38437.86 | 6.66 | 24.94 | 84.75 | -0.098 |
| PB.80567.1 | 358 | 38685.52 | 6.60 | 30.79 | 89.27 | 0.012 |
| PB.80906.1 | 355 | 38256.89 | 5.68 | 31.84 | 88.42 | 0.037 |
| PB.62308.1 | 269 | 28625.35 | 6.31 | 31.41 | 92.45 | 0.166 |
| PB.17482.1 | 344 | 36802.76 | 5.86 | 31.22 | 86.13 | 0.103 |
| PB.52032.1 | 373 | 38747.35 | 6.53 | 24.05 | 91.58 | 0.136 |
| PB.47633.2 | 421 | 44353.00 | 6.42 | 31.04 | 84.28 | 0.092 |
| PB.55683.1 | 421 | 44338.97 | 6.42 | 29.60 | 83.80 | 0.088 |
| PB.83678.1 | 356 | 37359.82 | 5.40 | 25.49 | 92.25 | 0.146 |
| PB.84043.1 | 356 | 37036.55 | 5.84 | 26.83 | 93.88 | 0.211 |
| PB.84184.1 | 356 | 37019.73 | 6.08 | 23.61 | 92.25 | 0.195 |
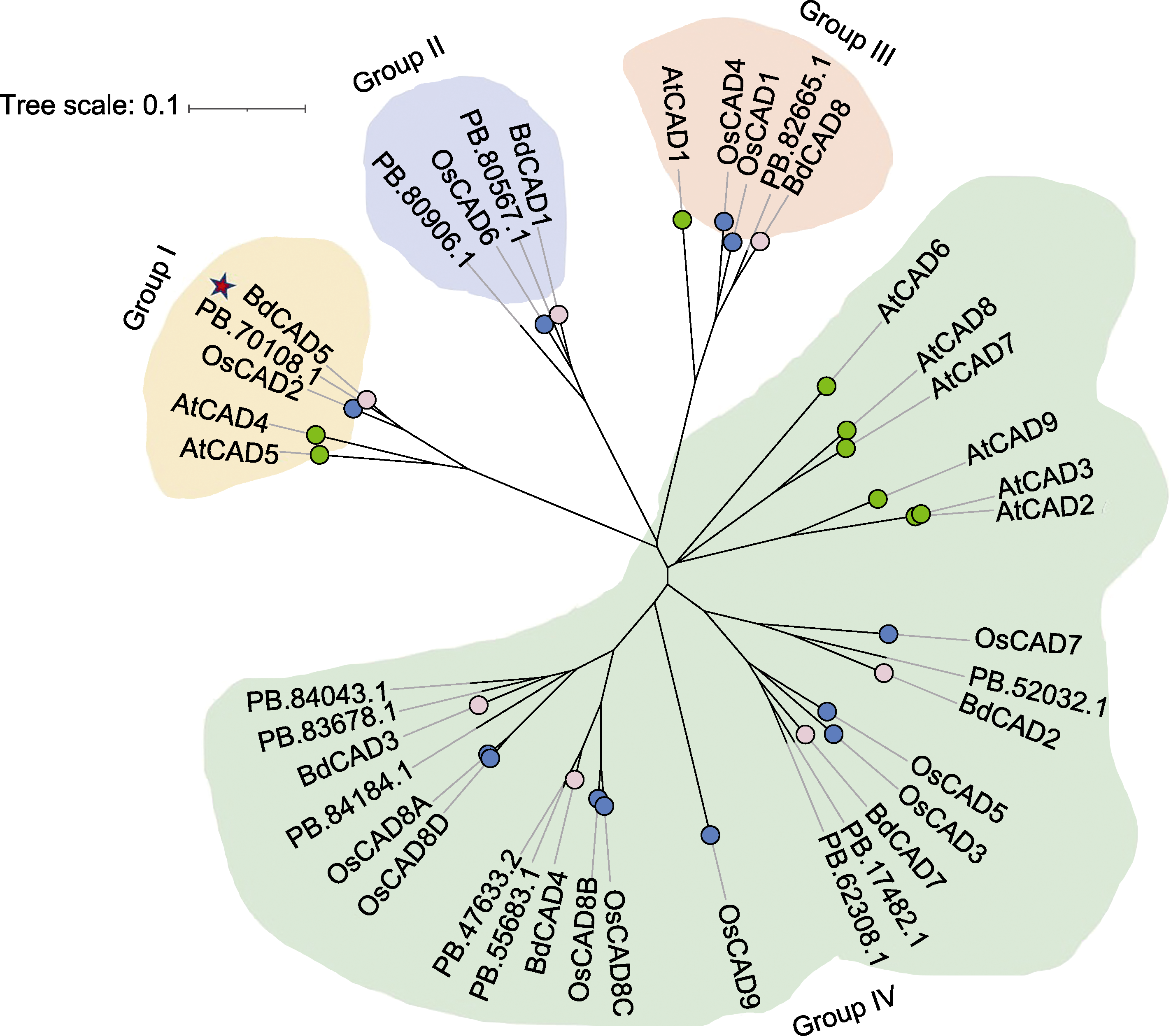
图2 蒙古冰草与拟南芥、水稻和二穗短柄草CAD的系统进化树 红色五角星代表可能参与木质素合成的蒙古冰草CAD蛋白; 粉色点代表二穗短柄草CAD蛋白; 绿色点代表拟南芥CAD蛋白; 蓝色点代表水稻CAD蛋白。
Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree of CADs in Agropyron mongolicum, Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, and Brachypodium distachyon The red pentagram represents the functional CAD protein of A. mongolicum that may be involved in lignin synthesis; the pink dots represent the CAD protein of B. distachyon; the green dots represent the CAD protein of A. thaliana; and the blue dots represent the CAD protein of O. sativa.
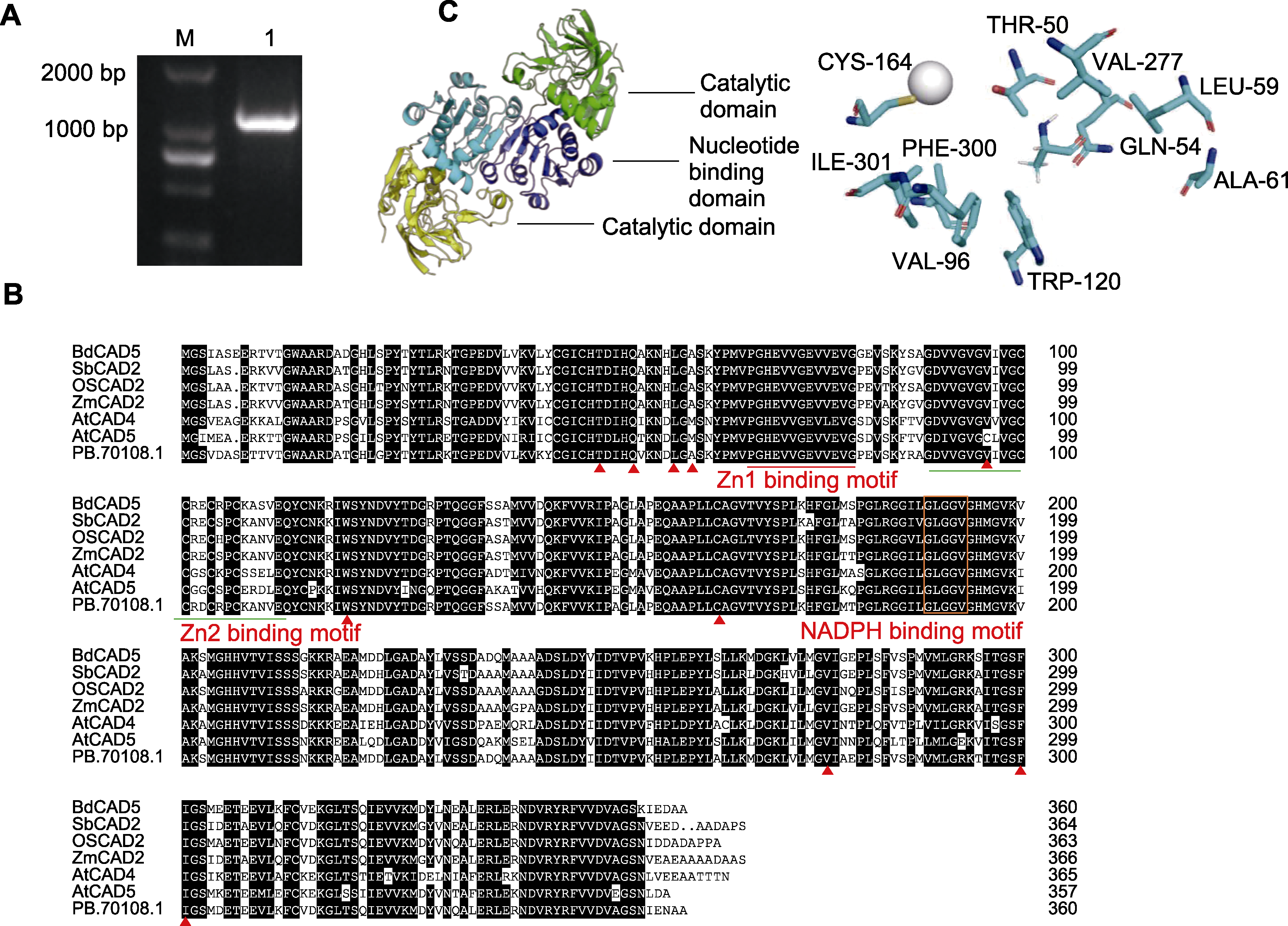
图3 蒙古冰草AmCAD基因扩增和蛋白结构分析 (A) AmCAD电泳图(M: DNA ladder; 1: 扩增序列); (B) 蒙古冰草与其它物种CAD氨基酸序列比对(构成底物结合口袋的残基用三角形(▲)标记); (C) AmCAD蛋白质三维结构模型和底物结合口袋(底部亚基的核苷酸结合和催化结构域分别呈黄色和蓝色, 在上部亚基中的对应结构分别以绿色和深蓝色显示, 锌离子用灰色球体表示)
Figure 3 Amplification of Agropyron mongolicum AmCAD and protein structure analysis (A) AmCAD gel map (M: DNA ladder; 1: Amplification sequence); (B) Comparison of CAD amino acid sequences among A. mongolicum and other species (the residue forming the substrate binding pocket is marked with a triangle (▲)); (C) Three-dimensional protein structure model and substrate binding pocket of AmCAD (the nucleotide binding and catalytic domains of the bottom subunit are colored yellow and blue, respectively, the corresponding compounds in the upper subunit are colored green and dark blue, while the zinc ions are indicated by gray spheres)
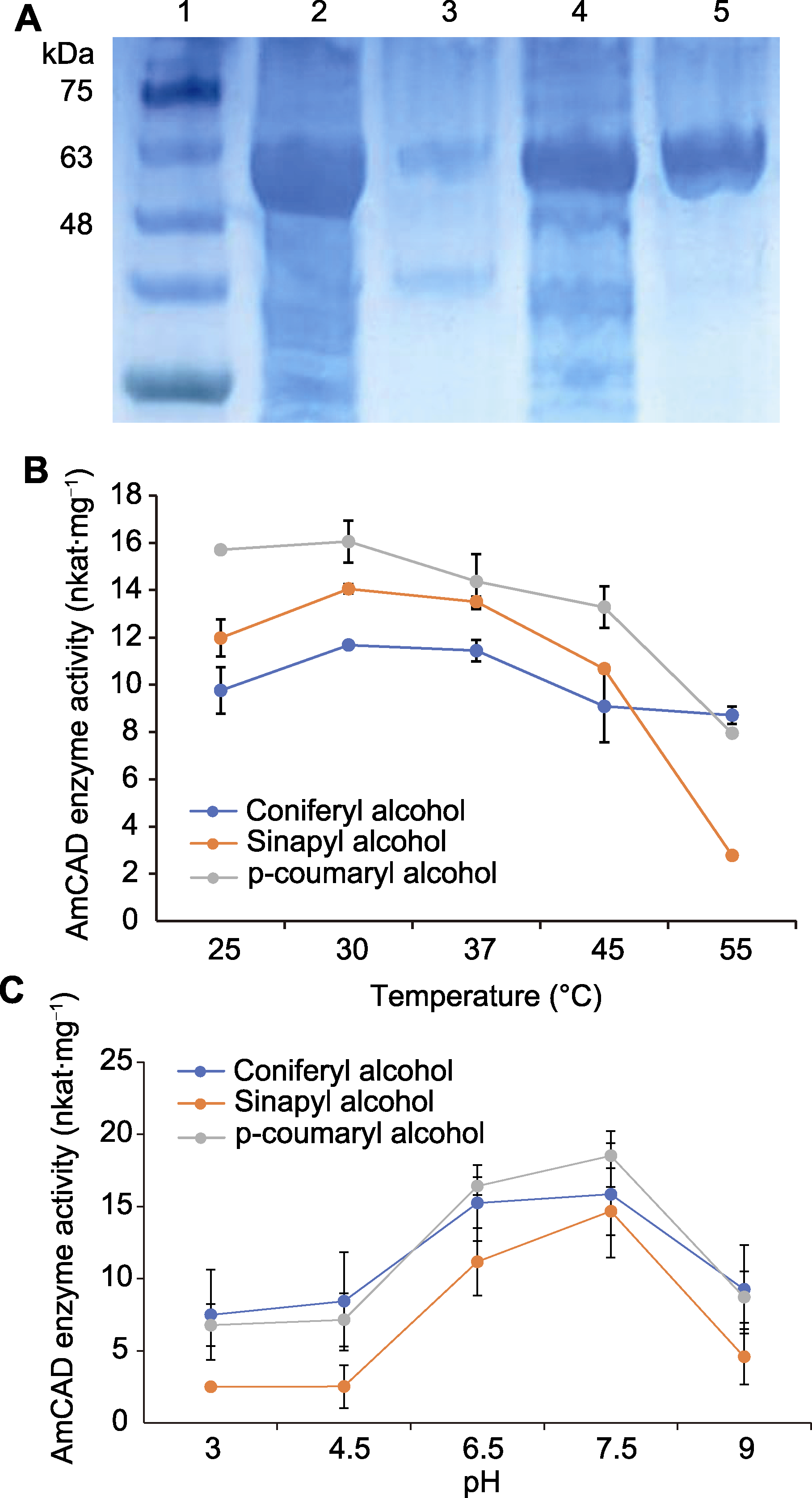
图4 AmCAD重组蛋白在大肠杆菌中的异源表达(A)及不同温度(B)和pH (C)下的酶学性质 1: 蛋白Marker; 2: 上清液; 3: 沉淀; 4: 流出液; 5: 纯化蛋白
Figure 4 Heterologous expression (A) and enzymatic properties of AmCAD recombinant protein in Escherichia coli at different temperatures (B) and pH (C) 1: Marker; 2: Supernatant; 3: Precipitant; 4: Effluent; 5: Purified protein
| Substract | Km (μmol·L-1) | Vmax (μmol·L-1·s-1) | Kcat (·s−1) | Kcat/Km (μmol·L-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferylaldehyde | 8.94±0.15 | 6.87±0.008 | 441.37±0.53 | 49.35±0.90 |
| Sinapaldehyde | 10.35±2.14 | 7.18±0.43 | 461.51±27.94 | 45.26±6.69 |
| p-coumaraldehyde | 35.35±3.74 | 15.21±1.60 | 977.60±102.97 | 27.65±0.01 |
表2 AmCAD重组蛋白催化不同底物的酶动力学特性
Table 2 Enzyme kinetic characteristics of different substrates catalyzed by recombinant AmCAD
| Substract | Km (μmol·L-1) | Vmax (μmol·L-1·s-1) | Kcat (·s−1) | Kcat/Km (μmol·L-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferylaldehyde | 8.94±0.15 | 6.87±0.008 | 441.37±0.53 | 49.35±0.90 |
| Sinapaldehyde | 10.35±2.14 | 7.18±0.43 | 461.51±27.94 | 45.26±6.69 |
| p-coumaraldehyde | 35.35±3.74 | 15.21±1.60 | 977.60±102.97 | 27.65±0.01 |
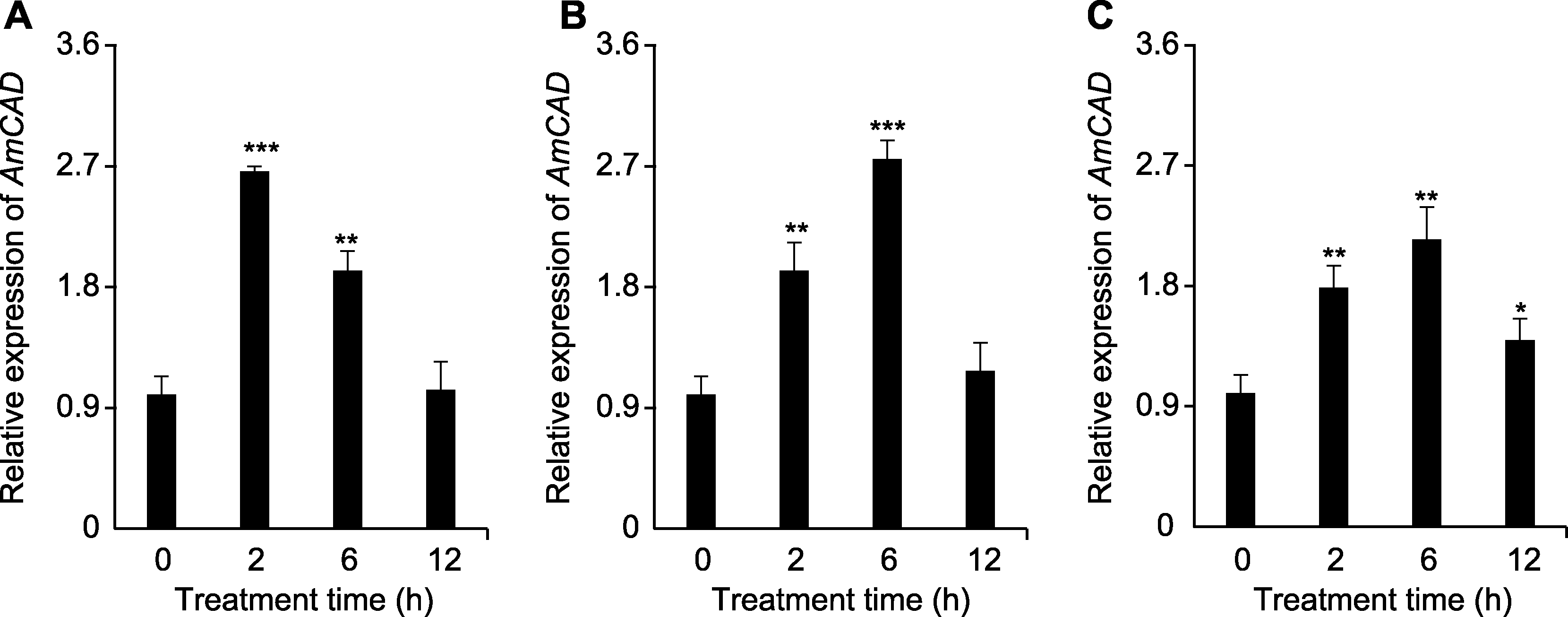
图6 AmCAD基因在不同处理时间及不同浓度甘露醇模拟干旱胁迫下的表达分析 (A) 75 mmol∙L-1甘露醇处理; (B) 150 mmol∙L-1甘露醇处理; (C) 250 mmol∙L-1甘露醇处理。* P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
Figure 6 Expression analysis of AmCAD gene under drought stress at different time points and mannitol concentrations (A) 75 mmol∙L-1 mannitol treatment; (B) 150 mmol∙L-1 mannitol treatment; (C) 250 mmol∙L-1 mannitol treatment. * P<0.05; ** P<0.01; *** P<0.001
| [1] |
Barakat A, Bagniewska-Zadworna A, Choi A, Plakkat U, DiLoreto DS, Yellanki P, Carlson JE (2009). The cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene family in Populus: phylogeny, organization, and expression. BMC Plant Biol 9, 26.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Bukh C, Nord-Larsen PH, Rasmussen SK (2012). Phylogeny and structure of the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene family in Brachypodium distachyon. J Exp Bot 63, 6223-6236.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Che YH, Li LH (2007). Genetic diversity of prolamines in Agropyron mongolicum Keng indigenous to northern China. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54, 1145-1151.
DOI URL |
| [4] | Cherney JH, Cherney DJR, Akin DE, Axtell JD (1991). Potential of brown-midrib, low-lignin mutants for improving forage quality. Adv Agron 46, 157-198. |
| [5] |
Eudes A, Pollet B, Sibout R, Do CT, Séguin A, Lapierre C, Jouanin L (2006). Evidence for a role of AtCAD 1 in lignification of elongating stems of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 225, 23-39.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Fan BB, Zhang XF, Yu Z, Zhao Y, Ma YH (2021). Bioinformatics and expression analysis of NAC transcription factors related to drought resistance of Agropyron mongolicum Keng. Acta Agre Sin 29, 1183-1192. (in Chinese) |
|
范菠菠, 张学峰, 于卓, 赵彦, 马艳红 (2021). 与蒙古冰草抗旱相关的NAC转录因子生物信息学及其表达分析. 草地学报 29, 1183-1192.
DOI |
|
| [7] | Fu CX, Xiao XR, Xi YJ, Ge YX, Chen F, Bouton J, Dixon RA, Wang ZY (2011). Downregulation of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) leads to improved saccharification efficiency in switchgrass. BioEnergy Res 4, 153-164. |
| [8] |
Halpin C, Holt K, Chojecki J, Oliver D, Chabbert B, Monties B, Edwards K, Barakate A, Foxon GA (1998). Brown-midrib maize (bm1)—a mutation affecting the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Plant J 14, 545-553.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Huang WH (2014). Selection of Control Gene in Quantitative PCR and Analysis of Differential Expression of P5CS Gene in Agropyron mongolicum Keng Under Drought Stress. Master’s thesis. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. pp. 11-17. (in Chinese) |
| 黄文华 (2014). 蒙古冰草干旱胁迫下内参基因的筛选及P5CS基因定量表达分析. 硕士论文. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. pp. 11-17. | |
| [10] | Ibrahim W, Zhu YM, Chen Y, Qiu CW, Zhu SJ, Wu FB (2019). Genotypic differences in leaf secondary metabolism, plant hormones and yield under alone and combined stress of drought and salinity in cotton genotypes. Physiol Plant 165, 343-355. |
| [11] |
Janiak A, Kwaśniewski M, Szarejko I (2016). Gene expression regulation in roots under drought. J Exp Bot 67, 1003-1014.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Jin YZ, Zhang C, Liu W, Qi HY, Chen H, Cao SX (2014). The cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene family in melon (Cucumis melo L.): bioinformatic analysis and expression patterns. PLoS One 9, e101730. |
| [13] | Kim SJ, Kim MR, Bedgar DL, Moinuddin SGA, Cardenas CL, Davin LB, Kang C, Lewis NG (2004). Functional reclassification of the putative cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase multigene family in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 1455-1460. |
| [14] | Lange BM, Lapierre C, Sandermann Jr H (1995). Elicitor-induced spruce stress lignin (structural similarity to early developmental lignins). Plant Physiol 108, 1277-1287. |
| [15] |
Lee CJ, Kim SE, Park SU, Lim YH, Choi HY, Kim WG, Ji CY, Kim HS, Kwak SS (2021). Tuberous roots of transgenic sweetpotato overexpressing IbCAD1 have enhanced low-temperature storage phenotypes. Plant Physiol Biochem 166, 549-557.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Li LG, Cheng XF, Leshkevich J, Umezawa T, Harding SA, Chiang VL (2001). The last step of syringyl monolignol biosynthesis in angiosperms is regulated by a novel gene encoding sinapyl alcohol dehydrogenase. Plant Cell 13, 1567-1586.
PMID |
| [17] | Li X, Ma DM, Chen JL, Pu GB, Ji YP, Lei CY, Du ZG, Liu BY, Ye HC, Wang H (2012). Biochemical characterization and identification of a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase from Artemisia annua. Plant Sci 193-194, 85-95. |
| [18] | Li Z, Wang HZ, Li RF, Wei JH (2009). Lignin biosynthesis and manipulation in plants and utilization of biomass energy. Chin Bull Bot 44, 262-272. (in Chinese) |
|
李桢, 王宏芝, 李瑞芬, 魏建华 (2009). 植物木质素合成调控与生物质能源利用. 植物学报 44, 262-272.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Lin KJ, Liu ZP, Luo D, Wu ZN (2023). The current status, problems and suggestions for the researchon forage germplasm resources. Chin Bull Bot 58, 241-247. (in Chinese) |
|
林克剑, 刘志鹏, 罗栋, 武自念 (2023). 饲草种质资源研究现状、存在问题与发展建议. 植物学报 58, 241-247.
DOI |
|
| [20] |
Liu W, Jiang Y, Wang CH, Zhao LL, Jin YZ, Xing QJ, Li M, Lv TH, Qi HY (2020). Lignin synthesized by CmCAD2 and CmCAD3 in oriental melon (Cucumis melo L.) seedlings contributes to drought tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 103, 689-704.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TDL (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Ma QH (2010). Functional analysis of a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase involved in lignin biosynthesis in wheat. J Exp Bot 61, 2735-2744.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Ma QH, Tian B (2005). Biochemical characterization of a cinnamoyl-CoA reductase from wheat. Biol Chem 386, 553-560. |
| [24] |
McKie JH, Jaouhari R, Douglas KT, Goffner D, Feuillet C, Grima-Pettenati J, Boudet AM, Baltas M, Gorrichon L (1993). A molecular model for cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, a plant aromatic alcohol dehydrogenase involved in lignification. Biochim Biophys Acta 1202, 61-69.
PMID |
| [25] |
Pan HY, Zhou R, Louie GV, Mühlemann JK, Bomati EK, Bowman ME, Dudareva N, Dixon RA, Noel JP, Wang XQ (2014). Structural studies of cinnamoyl-CoA reductase and cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase, key enzymes of monolignol biosynthesis. Plant Cell 26, 3709-3727.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Pandey B, Pandey VP, Dwivedi UN (2011). Cloning, expression, functional validation and modeling of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase isolated from xylem of Leucaena leucocephala. Protein Expres Purif 79, 197-203.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Park HL, Kim TL, Bhoo SH, Lee TH, Lee SW, Cho MH (2018). Biochemical characterization of the rice cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene family. Molecules 23, 2659.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Qi KJ, Song XF, Yuan YZ, Bao JP, Gong X, Huang XS, Khanizadeh S, Zhang SL, Tao ST (2021). CAD genes: genome-wide identification, evolution, and their contribution to lignin biosynthesis in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Plants 10, 1444. |
| [29] | Qiu R, He F, Li R, Wang YM, Xing SN, Cao YP, Liu YF, Zhou XY, Zhao Y, Fu CX (2023). Highly efficient gene editing of lignin gene F5H in switchgrass. Chin Bull Bot 58, 298-307. (in Chinese) |
| 邱锐, 何峰, 李瑞, 王亚梅, 邢思年, 曹英萍, 刘叶飞, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥 (2023). 柳枝稷木质素基因F5H的高效编辑. 植物学报 58, 298-307. | |
| [30] |
Rollins JA, Habte E, Templer SE, Colby T, Schmidt J, von Korff M (2013). Leaf proteome alterations in the context of physiological and morphological responses to drought and heat stress in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Exp Bot 64, 3201-3212.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Rong W, Luo MY, Shan TL, Wei XN, Du LP, Xu HJ, Zhang ZY (2016). A wheat cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase TaCAD12 contributes to host resistance to the sharp eyespot disease. Front Plant Sci 7, 1723. |
| [32] |
Saballos A, Ejeta G, Sanchez E, Kang C, Vermerris W (2009). A genomewide analysis of the cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase family in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] identifies SbCAD2 as the Brown midrib6 gene. Genetics 181, 783-795.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Sattler SE, Saathoff AJ, Haas EJ, Palmer NA, Funnell-Harris DL, Sarath G, Pedersen JF (2009). A nonsense mutation in a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase gene is responsible for the sorghum brown midrib6 phenotype. Plant Physiol 150, 584-595.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Shafiei R, Hooper M, McClellan C, Oakey H, Stephens J, Lapierre C, Tsuji Y, Goeminne G, Vanholme R, Boerjan W, Ralph J, Halpin C (2023). Downregulation of barley ferulate 5-hydroxylase dramatically alters straw lignin structure without impact on mechanical properties. Front Plant Sci 13, 1125003.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Sibout R, Eudes A, Pollet B, Goujon T, Mila I, Granier F, Séguin A, Lapierre C, Jouanin L (2003). Expression pattern of two paralogs encoding cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenases in Arabidopsis. Isolation and characterization of the corresponding mutants. Plant Physiol 132, 848-860.
PMID |
| [36] | Tobias CM, Chow EK (2005). Structure of the cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase gene family in rice and promoter activity of a member associated with lignification. Planta 220, 678-688. |
| [37] |
Tsuruta SI, Ebina M, Nakagawa H, Kawamura O, Akashi R (2007). Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). Grassl Sci 53, 103-109.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Vasupalli N, Hou D, Singh RM, Wei HT, Zou LH, Yrjälä K, Wu AM, Lin XC (2021). Homo- and hetero-dimers of CAD enzymes regulate lignification and abiotic stress response in moso bamboo. Int J Mol Sci 22, 12917.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Vermerris W, Thompson KJ, McIntyre LM (2002). The maize Brown midrib1 locus affects cell wall composition and plant development in a dose-dependent manner. Heredity 88, 450-457.
PMID |
| [40] | Wang RH, Shi L, Tang GG, Liang YC, Zhang CY (2003). Effect of osmotic stress on activities of protective enzymes system in Agropyron mongolicum seedling. Chin Bull Bot 20, 330-335. (in Chinese) |
| 王荣华, 石雷, 汤庚国, 梁寅初, 张称意 (2003). 渗透胁迫对蒙古冰草幼苗保护酶系统的影响. 植物学通报 20, 330-335. (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | Wang RH, Shi L, Tang GG, Liang YC, Zhang CY (2004). Effect of NaCl stress on growth and content of severalions of wheatgrass. Bull Botanical Res 24, 326-330. (in Chinese) |
| 王荣华, 石雷, 汤庚国, 梁寅初, 张称意 (2004). 盐胁迫下蒙古冰草幼苗生长和离子含量的变化. 植物研究 24, 326-330. | |
| [42] |
Xiao SH, Hu Q, Shen JL, Liu SM, Yang ZG, Chen K, Klosterman SJ, Javornik B, Zhang XL, Zhu LF (2021). GhMYB4 downregulates lignin biosynthesis and enhances cotton resistance to Verticillium dahliae. Plant Cell Rep 40, 735-751.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Xu L, Zhu LF, Tu LL, Liu LL, Yuan DJ, Jin L, Long L, Zhang XL (2011). Lignin metabolism has a central role in the resistance of cotton to the wilt fungus Verticillium dahliae as revealed by RNA-Seq-dependent transcriptional analysis and histochemistry. J Exp Bot 62, 5607-5621.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Youn B, Camacho R, Moinuddin SGA, Lee C, Davin LB, Lewis NG, Kang C (2006). Crystal structures and catalytic mechanism of the Arabidopsis cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenases AtCAD5 and AtCAD4. Org Biomol Chem 4, 1687-1697.
PMID |
| [45] |
Yusuf CYL, Nabilah NS, Taufik NAAM, Seman IA, Abdullah MP (2022). Genome-wide analysis of the CAD gene family reveals two bona fide CAD genes in oil palm. 3 Biotech 12, 149.
DOI |
| [46] |
Zeng JJ, Helms GL, Gao X, Chen SL (2013). Quantification of wheat straw lignin structure by comprehensive NMR analysis. J Agric Food Chem 61, 10848-10857.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Zhang KW, Qian Q, Huang ZJ, Wang YQ, Li M, Hong LL, Zeng DL, Gu MH, Chu CC, Cheng ZK (2006). GOLD HULL AND INTERNODE2 encodes a primarily multifunctional cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase in rice. Plant Physiol 140, 972-983.
DOI PMID |
| [48] | Zhao Y, Chen XY, Shi FM, Yun JF, Wang JJ (2015). Cloning and expression analysis of MwDREB3 from Mongolian wheatgrass. Acta Agre Sin 23, 377. (in Chinese) |
| 赵彦, 陈雪英, 石凤敏, 云锦凤, 王俊杰 (2015). 蒙古冰草MwDREB3基因的克隆及表达分析. 草地学报 23, 377. |
| [1] | 杜淑辉, 褚建民, 段俊光, 薛建国, 徐磊, 徐晓庆, 王其兵, 黄建辉, 张倩. 木质素酚类物质对内蒙古退化草地土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 30-41. |
| [2] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [3] | 李宇琛, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 黄馨田, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 赵彦, 付春祥. 根癌农杆菌介导的蒙古冰草稳定遗传转化体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 600-612. |
| [4] | 廖星鑫, 牛祎, 多兴武, 阿克也得力·居玛哈孜, 买热哈巴·阿不都克尤木, 热孜瓦尼姑丽·胡甫尔, 兰海燕, 曹婧. 异源表达异子蓬SaPEPC2基因提高烟草抗旱性和光合特性(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 585-599. |
| [5] | 杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [6] | 张蕾, 姜鹏飞, 王一鸣, 兰婷, 刘妍婧, 曾庆银. 苦杨×小叶杨杂交F1代苗期抗旱性比较研究[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 519-534. |
| [7] | 邱锐, 何峰, 李瑞, 王亚梅, 邢思年, 曹英萍, 刘叶飞, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥. 柳枝稷木质素基因F5H的高效编辑[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 298-307. |
| [8] | 罗丹丹, 王传宽, 金鹰. 木本植物水力系统对干旱胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2021, 45(9): 925-941. |
| [9] | 张一弓, 张怡, 阿依白合热木·木台力甫, 张道远. 异源过表达齿肋赤藓ScABI3基因改变拟南芥气孔表型并提高抗旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 414-421. |
| [10] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [11] | 郜怀峰,张亚飞,王国栋,孙希武,贺月,彭福田,肖元松. 钼在桃树干旱胁迫响应中的作用解析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 227-236. |
| [12] | 龙海涛, 李丽梅, 谢泽虹, 刘帅, 李晓云, 邓斌, 刘海燕, 李玲. 综合隶属函数法评价花生品种抗旱性与AhNCED1基因表达的关系[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(6): 706-712. |
| [13] | 安东升, 曹娟, 黄小华, 周娟, 窦美安. 基于Lake模型的叶绿素荧光参数在甘蔗苗期抗旱性研究中的应用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(4): 398-406. |
| [14] | 陈慧颖, 张景慧, 黄永梅, 龚吉蕊. 内蒙古大针茅草原常见植物在不同土地利用方式下的固碳相关属性[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(8): 821-832. |
| [15] | 邱权,潘昕,李吉跃,王军辉,马建伟,杜坤. 青藏高原20种灌木抗旱形态和生理特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(6): 562-575. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||