

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 519-534.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22086 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22086
张蕾1, 姜鹏飞1, 王一鸣2, 兰婷3, 刘妍婧1, 曾庆银1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-23
接受日期:2022-06-16
出版日期:2023-07-01
发布日期:2022-07-17
通讯作者:
*E-mail: qingyin.zeng@caf.ac.cn
基金资助:
Lei Zhang1, Pengfei Jiang1, Yiming Wang2, Ting Lan3, Yanjing Liu1, Qingyin Zeng1( )
)
Received:2022-04-23
Accepted:2022-06-16
Online:2023-07-01
Published:2022-07-17
Contact:
*E-mail: qingyin.zeng@caf.ac.cn
摘要: 创制抗旱林木新品种对维持我国干旱半干旱地区森林生产力, 应对全球气候变暖具有重要意义。苦杨(Populus laurifolia)是分布在新疆额尔齐斯河流域的我国乡土树种, 具有速生和耐寒等优良特性, 而小叶杨(P. simonii)具有抗旱和耐瘠薄特性。我们对苦杨×小叶杨杂交F1代幼苗的抗旱性进行全面分析和综合评价。测定了正常生长与干旱胁迫下亲本和杂交F1代的株高生长量和叶片相对含水量等7个生长指标, 净光合速率和胞间CO2浓度等6个光合参数, 以及SOD活性和MDA含量等5个抗旱生化指标。对18个性状指标进行抗旱系数和隶属函数分析, 将亲本及23个F1代幼苗划分为高、中和低3个抗旱类型。高度抗旱型幼苗的叶片、上表皮、下表皮和栅栏组织厚度较大, 叶片组织结构紧密度高, 且在干旱胁迫下抗旱关键基因的表达量显著高于其它抗旱类型幼苗。该研究为杨树抗旱育种提供了理论指导和基础材料。
张蕾, 姜鹏飞, 王一鸣, 兰婷, 刘妍婧, 曾庆银. 苦杨×小叶杨杂交F1代苗期抗旱性比较研究. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 519-534.
Lei Zhang, Pengfei Jiang, Yiming Wang, Ting Lan, Yanjing Liu, Qingyin Zeng. Comparative Study on the Drought Resistance of Young Seedling from Populus laurifolia × P. simonii F1 Progeny. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 519-534.
| Gene | Primer name | Primer sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | RT-Actin-F | TGTTGCCCTTGACTATGAGCAG- GA |
| RT-Actin-R | ACGGAATCTCTCAGCTCCAATG- GT | |
| NAC006 | RT-NAC006-F | AAGAACAGCATCTTAGCGTCAAG |
| RT-NAC006-R | TGGCGGCAGCAAAACAACCTG | |
| NAC007 | RT-NAC007-F | ATGAAAGGAAATAGATCAGCAG- AT |
| RT-NAC007-R | ATTGGCCTCCACATTTCTTAAGC | |
| NAC120 | RT-NAC120-F | TGTGCGCTAAGCTGCAGTCTG |
| RT-NAC120-R | ACCAGCAACTTTCCTGCACAAAT | |
| AREB1-2 | RT-AREB1-2-F | CCTAAGCAGCCTAATATGGGATA |
| RT-AREB1-2-R | GGCAAATTAGAAGATTGCAAAG- AT | |
| ABF3 | RT-ABF3-F | ACTGCCGAAGAGACTCAAGC |
| RT-ABF3-R | ACTCCCATCTTCAGCAGCAC | |
| AREB3 | RT-AREB3-F | AGGAGGCAGAAGAGGATGAT |
| RT-AREB3-R | GTTTCCTCAGCCTTTCATTTTC | |
| SHN1 | RT-SHN1-F | AGAGCCTACGATGAAGCAGC |
| RT-SHN1-R | ACGAGGAGGAGGGAGAGTTC | |
| NF-YA9 | RT-NA9-F | TCAAGTCTCGGAAGCCATACT |
| RT-NA9-R | TTGTCATCCAAGGAAGCAAT |
表1 qRT-PCR引物
Table 1 Primers for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Primer name | Primer sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Actin | RT-Actin-F | TGTTGCCCTTGACTATGAGCAG- GA |
| RT-Actin-R | ACGGAATCTCTCAGCTCCAATG- GT | |
| NAC006 | RT-NAC006-F | AAGAACAGCATCTTAGCGTCAAG |
| RT-NAC006-R | TGGCGGCAGCAAAACAACCTG | |
| NAC007 | RT-NAC007-F | ATGAAAGGAAATAGATCAGCAG- AT |
| RT-NAC007-R | ATTGGCCTCCACATTTCTTAAGC | |
| NAC120 | RT-NAC120-F | TGTGCGCTAAGCTGCAGTCTG |
| RT-NAC120-R | ACCAGCAACTTTCCTGCACAAAT | |
| AREB1-2 | RT-AREB1-2-F | CCTAAGCAGCCTAATATGGGATA |
| RT-AREB1-2-R | GGCAAATTAGAAGATTGCAAAG- AT | |
| ABF3 | RT-ABF3-F | ACTGCCGAAGAGACTCAAGC |
| RT-ABF3-R | ACTCCCATCTTCAGCAGCAC | |
| AREB3 | RT-AREB3-F | AGGAGGCAGAAGAGGATGAT |
| RT-AREB3-R | GTTTCCTCAGCCTTTCATTTTC | |
| SHN1 | RT-SHN1-F | AGAGCCTACGATGAAGCAGC |
| RT-SHN1-R | ACGAGGAGGAGGGAGAGTTC | |
| NF-YA9 | RT-NA9-F | TCAAGTCTCGGAAGCCATACT |
| RT-NA9-R | TTGTCATCCAAGGAAGCAAT |
| Drought stress time | Levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First level | Second level | Third level | Fourth level | |
| The 5th day | B13, B8 | |||
| The 6th day | B13, B8, B25 | |||
| The 7th day | B13, B25 | B8 | ||
| The 8th day | B25, B17 | B13, B8 | ||
| The 9th day | B12, C11, B25, B17 | B8, B13 | ||
| The 10th day | C10, B20, B12, C11, B25 | B8, B13, B17 | ||
| The 11th day | A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12 | B17, B25, B13 | B8 | |
| The 12th day | B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, Populus laurifolia | C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12 | B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 13th day | B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, P. laurifolia | C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12 | B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 14th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5, P. laurifolia | B19, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12 | C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 15th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, P. laurifolia | B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, C10 | B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8 | B25, B13 |
| The 16th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, P. laurifolia | A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5 | B19, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12 | C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 |
| The 17th day | A11, A15, B18 | B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, P. laurifolia | B11, B5, B19, A10, C10, B20, C6 | C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 |
| The 18th day | A11, A15 | B18, B15, A24, C7, P. laurifolia | A25, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10 | C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 |
| The 19th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, P. laurifolia | A25, A24, C7, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, B20, C25 | C10, C6, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 20th day | A11, A15, B15 | B18, A25, A24, C7, B16, B5, B19, P. laurifolia | B11, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 21th day | A11, A15 | B18, B15, A25, A24, C7, B16, P. laurifolia | B11, B5, B19, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
表2 干旱胁迫对亲本及F1代幼苗伤害程度的分级调查
Table 2 Investigation on damage grade of seedlings of parent and F1 progeny under drought stress
| Drought stress time | Levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First level | Second level | Third level | Fourth level | |
| The 5th day | B13, B8 | |||
| The 6th day | B13, B8, B25 | |||
| The 7th day | B13, B25 | B8 | ||
| The 8th day | B25, B17 | B13, B8 | ||
| The 9th day | B12, C11, B25, B17 | B8, B13 | ||
| The 10th day | C10, B20, B12, C11, B25 | B8, B13, B17 | ||
| The 11th day | A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12 | B17, B25, B13 | B8 | |
| The 12th day | B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, Populus laurifolia | C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12 | B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 13th day | B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, P. laurifolia | C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12 | B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 14th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5, P. laurifolia | B19, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12 | C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 15th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, A24, C7, A25, P. laurifolia | B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, C10 | B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8 | B25, B13 |
| The 16th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, P. laurifolia | A24, C7, A25, B16, B11, B5 | B19, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12 | C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 |
| The 17th day | A11, A15, B18 | B15, A24, C7, A25, B16, P. laurifolia | B11, B5, B19, A10, C10, B20, C6 | C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 |
| The 18th day | A11, A15 | B18, B15, A24, C7, P. laurifolia | A25, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10 | C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 |
| The 19th day | A11, A15, B18, B15, P. laurifolia | A25, A24, C7, B16, B11, B5, B19, A10, B20, C25 | C10, C6, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 20th day | A11, A15, B15 | B18, A25, A24, C7, B16, B5, B19, P. laurifolia | B11, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
| The 21th day | A11, A15 | B18, B15, A25, A24, C7, B16, P. laurifolia | B11, B5, B19, A10, C10, B20, C6, C25, B12, C11, A12, B17, B8, B25, B13 | |
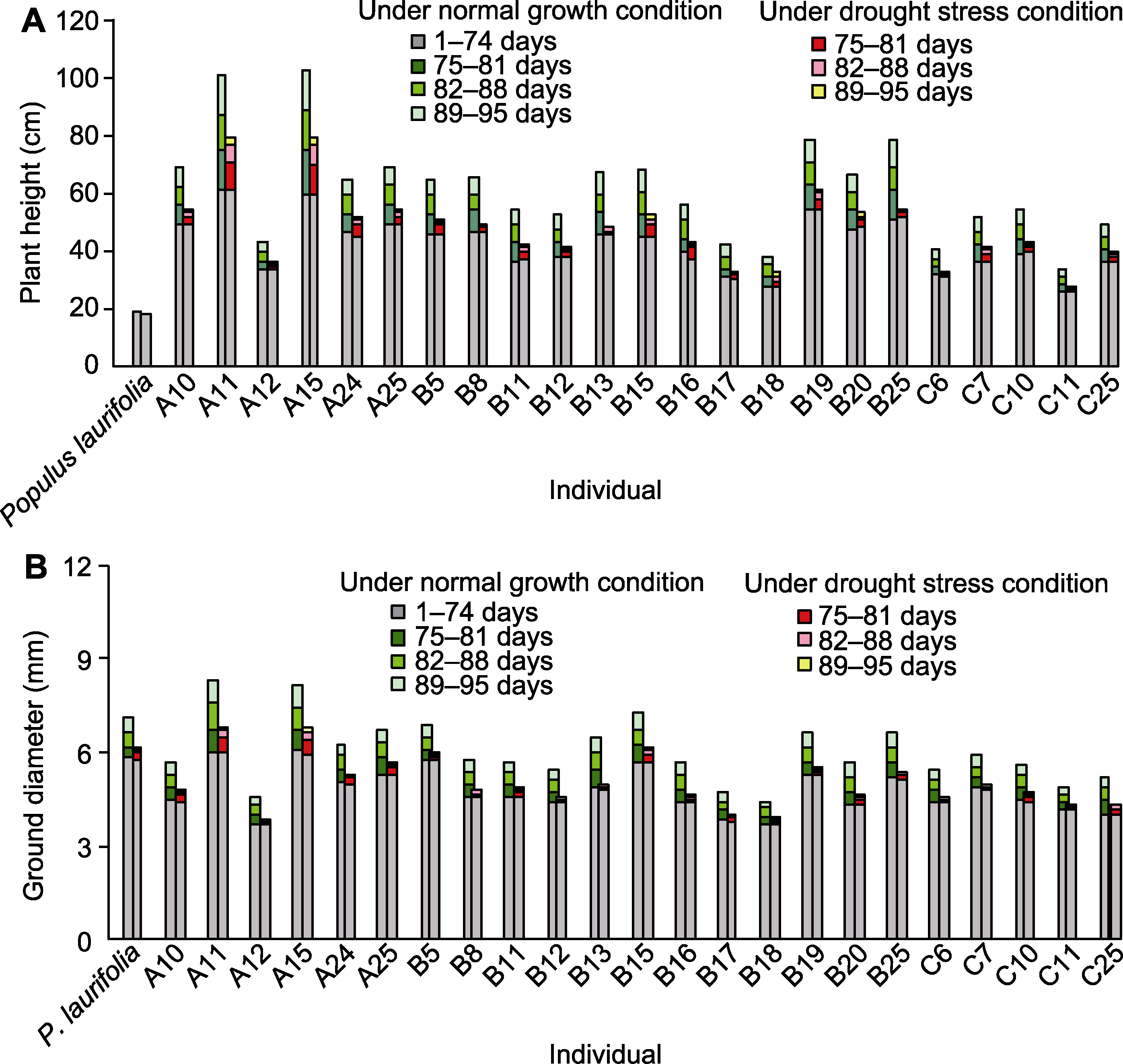
图3 正常生长和干旱胁迫条件下亲本及F1代幼苗的株高生长(A)与径向生长(B)
Figure 3 Plant height growth (A) and ground diameter growth (B) of seedlings of parent and F1 progeny under normal growth and drought stress conditions
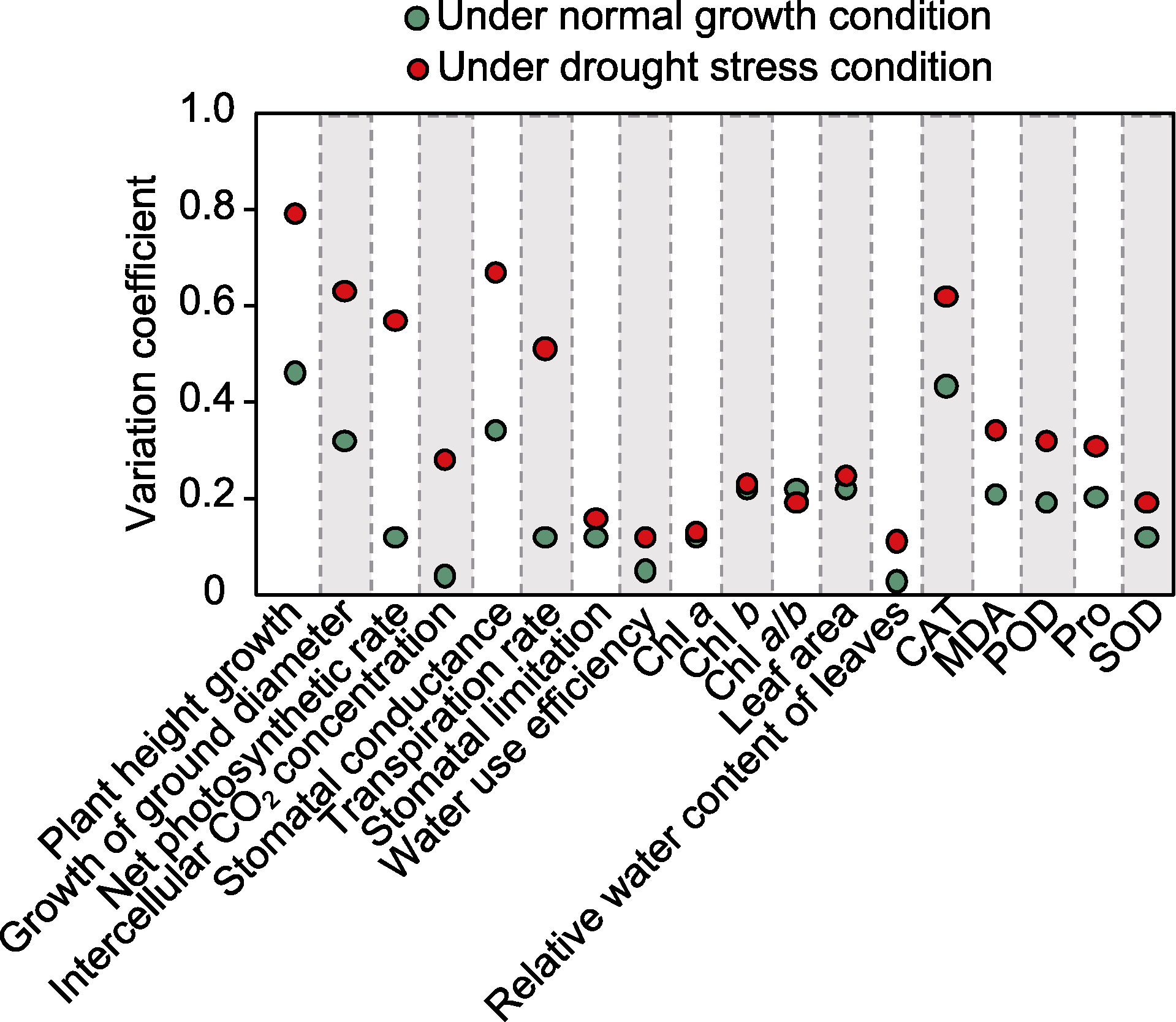
图4 F1代18个抗旱性状的变异系数 CAT: 过氧化氢酶; MDA: 丙二醛; POD: 过氧化物酶; Pro: 脯氨酸; SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶
Figure 4 Variation coefficient of 18 drought resistance traits in F1 progeny CAT: Catalase; MDA: Malondialdehyde; POD: Peroxidase; Pro: Proline; SOD: Superoxide dismutase
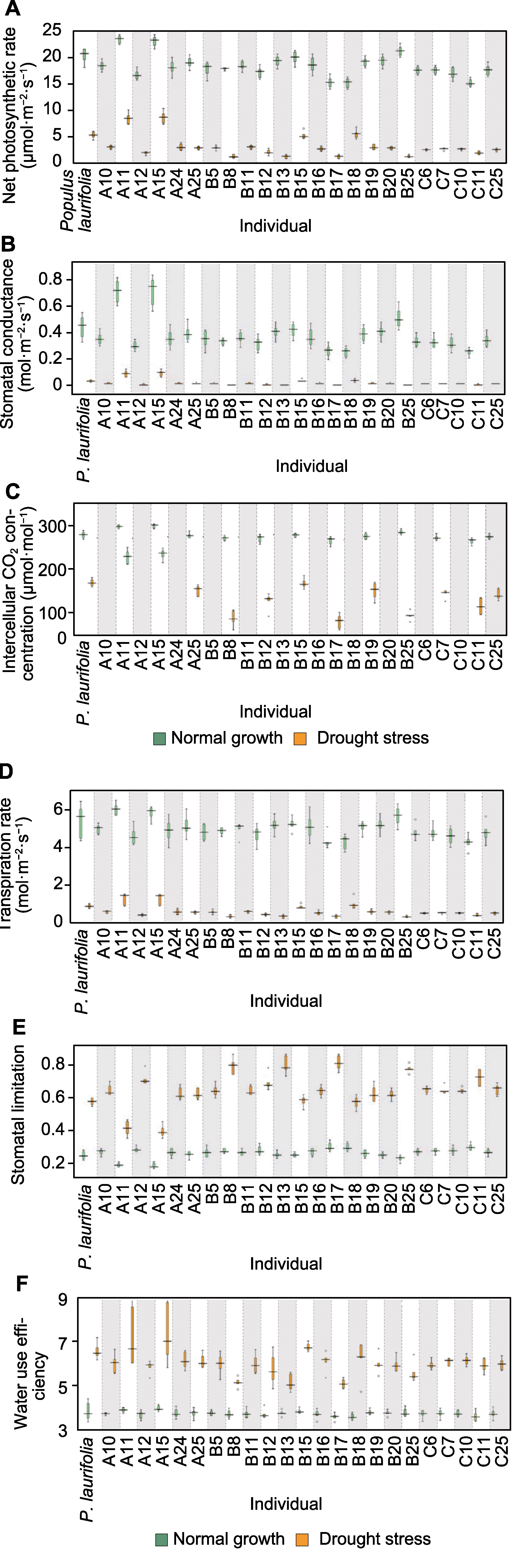
图5 正常生长和干旱胁迫下亲本与F1代的净光合速率(A)、气孔导度(B)、胞间CO2浓度(C)、蒸腾速率(D)、气孔限制值(E)和水分利用率(F)
Figure 5 Net photosynthetic rate (A), stomatal conductance (B), intercellular CO2 concentration (C), transpiration rate (D), stomatal limitation (E) and water use efficiency (F) of seedlings of parent and F1 progeny under normal growth and drought stress conditions
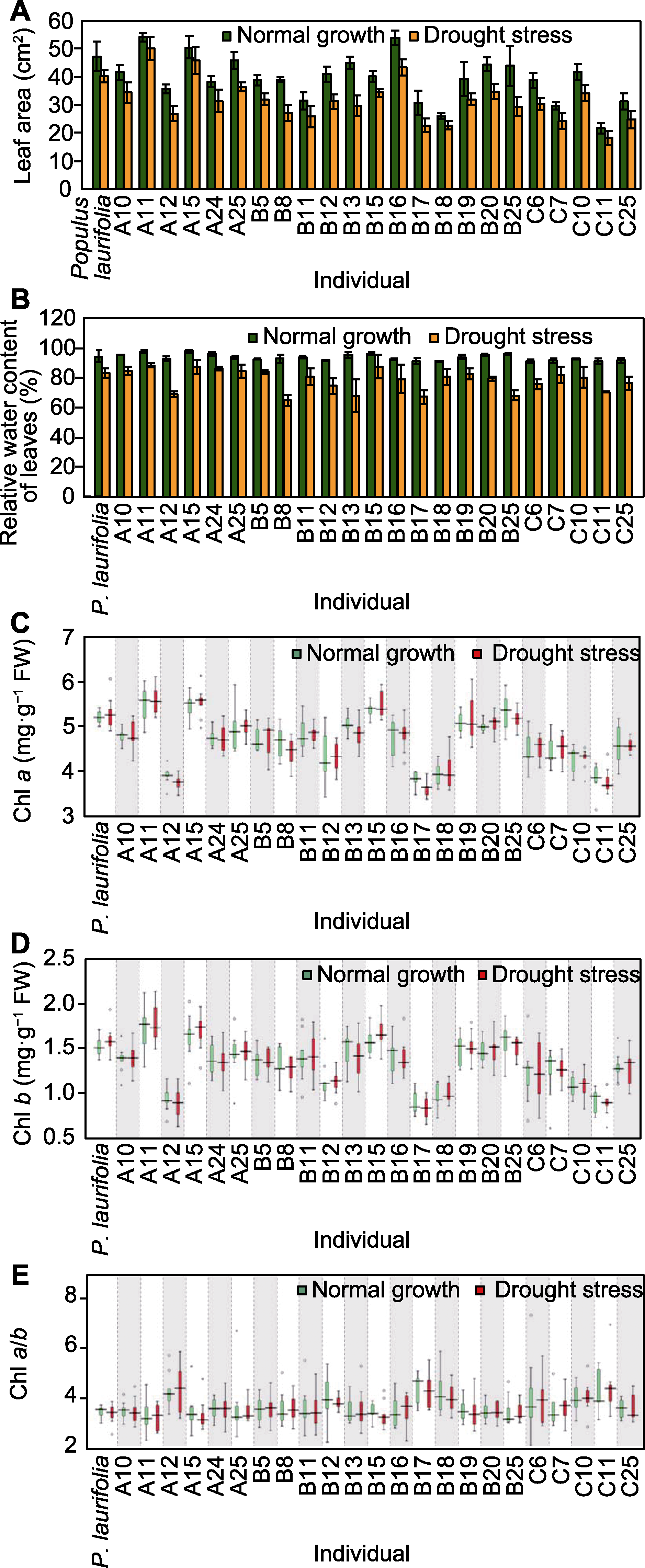
图6 正常生长和干旱胁迫条件下亲本与F1代的叶面积(A)、叶片相对含水量(B)、叶绿素a (C)和叶绿素b (D)含量及叶绿素a/b (E)分析
Figure 6 Leaf area (A), leaf relative water content (B), chlorophyll a (C), chlorophyll b (D) and chlorophyll a/b (E) of seedlings of parent and F1 progeny under normal growth and drought stress conditions
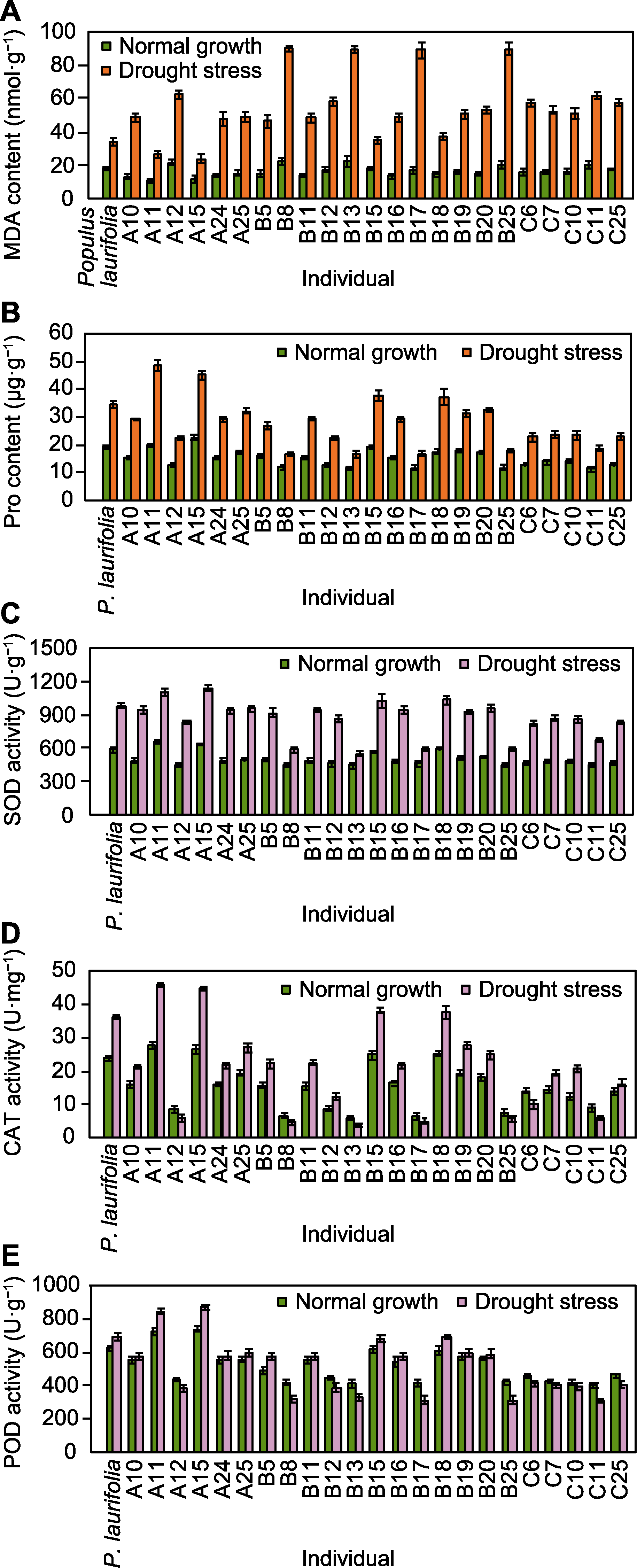
图7 正常生长和干旱胁迫下亲本与F1代的MDA (A)和Pro (B)含量及SOD (C)、CAT (D)和POD (E)酶活性 MDA、Pro、SOD、CAT和POD同图4。
Figure 7 MDA (A) and Pro (B) contents, SOD (C), CAT (D) and POD (E) activities of seedlings of parent and F1 progeny under normal growth and drought stress conditions MDA, Pro, SOD, CAT and POD are the same as shown in Figure 4.
| Traits | Drought resistance coefficient |
|---|---|
| Plant height growth (cm) | 0.27±0.11 |
| Growth of ground diameter (mm) | 0.24±0.07 |
| Net photosynthetic rate (μmol·m-2·s-1) | 0.19±0.09 |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (μmol·mol-1) | 0.52±0.12 |
| Stomatal conductance (mol·m-2·s-1) | 0.07±0.04 |
| Transpiration rate (mmol·m-2·s-1) | 0.12±0.05 |
| Stomatal limitation | 2.43±0.29 |
| Water use efficiency | 1.61±0.12 |
| Chl a (mg·g-1) | 1.00±0.02 |
| Chl b (mg·g-1) | 1.00±0.04 |
| Chl a/b | 0.99±0.03 |
| Leaf area (cm2) | 0.80±0.07 |
| Relative water content of leaves (%) | 0.84±0.07 |
| Catalase (U·mg-1) | 1.23±0.36 |
| Malondialdehyde (nmol·g-1) | 3.24±0.76 |
| Peroxidase (U·g-1) | 0.98±0.14 |
| Proline (μg·g-1) | 1.79±0.23 |
| Superoxide dismutase (U·g-1) | 1.72±0.22 |
表3 亲本和杂交F1代18个性状的抗旱系数(平均值±标准差)
Table 3 Drought resistance coefficient of 18 traits of seedlings of parent and F1 progeny (means ± SD)
| Traits | Drought resistance coefficient |
|---|---|
| Plant height growth (cm) | 0.27±0.11 |
| Growth of ground diameter (mm) | 0.24±0.07 |
| Net photosynthetic rate (μmol·m-2·s-1) | 0.19±0.09 |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (μmol·mol-1) | 0.52±0.12 |
| Stomatal conductance (mol·m-2·s-1) | 0.07±0.04 |
| Transpiration rate (mmol·m-2·s-1) | 0.12±0.05 |
| Stomatal limitation | 2.43±0.29 |
| Water use efficiency | 1.61±0.12 |
| Chl a (mg·g-1) | 1.00±0.02 |
| Chl b (mg·g-1) | 1.00±0.04 |
| Chl a/b | 0.99±0.03 |
| Leaf area (cm2) | 0.80±0.07 |
| Relative water content of leaves (%) | 0.84±0.07 |
| Catalase (U·mg-1) | 1.23±0.36 |
| Malondialdehyde (nmol·g-1) | 3.24±0.76 |
| Peroxidase (U·g-1) | 0.98±0.14 |
| Proline (μg·g-1) | 1.79±0.23 |
| Superoxide dismutase (U·g-1) | 1.72±0.22 |
| H | D | Pn | Ga | Ci | Tr | Ls | WUE | Chl a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height growth (H) | 1 | 0.569** | 0.626** | 0.658** | 0.651** | 0.633** | -0.694** | 0.635** | 0.529** |
| Growth of ground diameter (D) | 1 | 0.826** | 0.785** | 0.799** | 0.816** | -0.701** | 0.786** | 0.581** | |
| Net photosynthetic rate (Pn) | 1 | 0.980** | 0.908** | 0.998** | -0.782** | 0.893** | 0.726** | ||
| Stomatal conductance (Ga) | 1 | 0.845** | 0.987** | -0.786** | 0.839** | 0.690** | |||
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) | 1 | 0.896** | -0.838** | 0.946** | 0.884** | ||||
| Transpiration rate (Tr) | 1 | -0.785** | 0.871** | 0.722** | |||||
| Stomatal limitation (Ls) | 1 | -0.847** | -0.809** | ||||||
| Water use efficiency (WUE) | 1 | 0.821** | |||||||
| Chl a | 1 | ||||||||
| Chl b | |||||||||
| Chl a/b | |||||||||
| Leaf area (LA) | |||||||||
| Relative water content of leaves (LRWC) | |||||||||
| Catalase (CAT) | |||||||||
| Malondialdehyde (MDA) | |||||||||
| Peroxidase (POD) | |||||||||
| Proline (Pro) | |||||||||
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD) | |||||||||
| Chl b | Chl a/b | LA | LRWC | CAT | MDA | POD | Pro | SOD | |
| Plant height growth (H) | 0.540** | -0.415* | 0.696** | 0.569** | 0.509** | -0.318 | 0.538** | 0.721** | 0.481** |
| Growth of ground diameter (D) | 0.681** | -0.512** | 0.762** | 0.619** | 0.650** | -0.572** | 0.715** | 0.722** | 0.422* |
| Net photosynthetic rate (Pn) | 0.847** | -0.642** | 0.883** | 0.686** | 0.698** | -0.783** | 0.785** | 0.838** | 0.373* |
| Stomatal conductance (Ga) | 0.824** | -0.637** | 0.846** | 0.643** | 0.640** | -0.725** | 0.741** | 0.807** | 0.337 |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) | 0.915** | -0.645** | 0.917** | 0.851** | 0.824** | -0.802** | 0.873** | 0.899** | 0.645** |
| Transpiration rate (Tr) | 0.845** | -0.643** | 0.875** | 0.683** | 0.695** | -0.764** | 0.788** | 0.833** | 0.369* |
| Stomatal limitation (Ls) | -0.820** | 0.563** | -0.917** | -0.815** | -0.708** | 0.714** | -0.739** | -0.778** | -0.716** |
| Water use efficiency (WUE) | 0.868** | -0.593** | 0.940** | 0.793** | 0.733** | -0.847** | 0.776** | 0.871** | 0.605** |
| Chl a | 0.964** | -0.714** | 0.815** | 0.881** | 0.833** | -0.716** | 0.830** | 0.783** | 0.741** |
| Chl b | 1 | -0.761* | 0.853** | 0.881** | 0.820** | -0.768** | 0.861** | 0.843** | 0.637** |
| Chl a/b | 1 | -0.566** | -0.640** | -0.627** | 0.460* | -0.577** | -0.588** | -0.378* | |
| Leaf area (LA) | 1 | 0.834** | 0.760** | -0.768** | 0.797** | 0.839** | 0.582** | ||
| Relative water content of leaves (LRWC) | 1 | 0.867** | -0.665** | 0.887** | 0.751** | 0.775** | |||
| Catalase (CAT) | 1 | -0.622** | 0.837** | 0.714** | 0.677** | ||||
| Malondialdehyde (MDA) | 1 | -0.688** | -0.665** | -0.514* | |||||
| Peroxidase (POD) | 1 | 0.810** | 0.678** | ||||||
| Proline (Pro) | 1 | 0.641** | |||||||
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD) | 1 |
表4 抗旱系数的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of drought resistance coefficient
| H | D | Pn | Ga | Ci | Tr | Ls | WUE | Chl a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height growth (H) | 1 | 0.569** | 0.626** | 0.658** | 0.651** | 0.633** | -0.694** | 0.635** | 0.529** |
| Growth of ground diameter (D) | 1 | 0.826** | 0.785** | 0.799** | 0.816** | -0.701** | 0.786** | 0.581** | |
| Net photosynthetic rate (Pn) | 1 | 0.980** | 0.908** | 0.998** | -0.782** | 0.893** | 0.726** | ||
| Stomatal conductance (Ga) | 1 | 0.845** | 0.987** | -0.786** | 0.839** | 0.690** | |||
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) | 1 | 0.896** | -0.838** | 0.946** | 0.884** | ||||
| Transpiration rate (Tr) | 1 | -0.785** | 0.871** | 0.722** | |||||
| Stomatal limitation (Ls) | 1 | -0.847** | -0.809** | ||||||
| Water use efficiency (WUE) | 1 | 0.821** | |||||||
| Chl a | 1 | ||||||||
| Chl b | |||||||||
| Chl a/b | |||||||||
| Leaf area (LA) | |||||||||
| Relative water content of leaves (LRWC) | |||||||||
| Catalase (CAT) | |||||||||
| Malondialdehyde (MDA) | |||||||||
| Peroxidase (POD) | |||||||||
| Proline (Pro) | |||||||||
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD) | |||||||||
| Chl b | Chl a/b | LA | LRWC | CAT | MDA | POD | Pro | SOD | |
| Plant height growth (H) | 0.540** | -0.415* | 0.696** | 0.569** | 0.509** | -0.318 | 0.538** | 0.721** | 0.481** |
| Growth of ground diameter (D) | 0.681** | -0.512** | 0.762** | 0.619** | 0.650** | -0.572** | 0.715** | 0.722** | 0.422* |
| Net photosynthetic rate (Pn) | 0.847** | -0.642** | 0.883** | 0.686** | 0.698** | -0.783** | 0.785** | 0.838** | 0.373* |
| Stomatal conductance (Ga) | 0.824** | -0.637** | 0.846** | 0.643** | 0.640** | -0.725** | 0.741** | 0.807** | 0.337 |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) | 0.915** | -0.645** | 0.917** | 0.851** | 0.824** | -0.802** | 0.873** | 0.899** | 0.645** |
| Transpiration rate (Tr) | 0.845** | -0.643** | 0.875** | 0.683** | 0.695** | -0.764** | 0.788** | 0.833** | 0.369* |
| Stomatal limitation (Ls) | -0.820** | 0.563** | -0.917** | -0.815** | -0.708** | 0.714** | -0.739** | -0.778** | -0.716** |
| Water use efficiency (WUE) | 0.868** | -0.593** | 0.940** | 0.793** | 0.733** | -0.847** | 0.776** | 0.871** | 0.605** |
| Chl a | 0.964** | -0.714** | 0.815** | 0.881** | 0.833** | -0.716** | 0.830** | 0.783** | 0.741** |
| Chl b | 1 | -0.761* | 0.853** | 0.881** | 0.820** | -0.768** | 0.861** | 0.843** | 0.637** |
| Chl a/b | 1 | -0.566** | -0.640** | -0.627** | 0.460* | -0.577** | -0.588** | -0.378* | |
| Leaf area (LA) | 1 | 0.834** | 0.760** | -0.768** | 0.797** | 0.839** | 0.582** | ||
| Relative water content of leaves (LRWC) | 1 | 0.867** | -0.665** | 0.887** | 0.751** | 0.775** | |||
| Catalase (CAT) | 1 | -0.622** | 0.837** | 0.714** | 0.677** | ||||
| Malondialdehyde (MDA) | 1 | -0.688** | -0.665** | -0.514* | |||||
| Peroxidase (POD) | 1 | 0.810** | 0.678** | ||||||
| Proline (Pro) | 1 | 0.641** | |||||||
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD) | 1 |
| Principal component | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 13.58 | 1.30 | 0.81 |
| Contribution rate | 75.45% | 7.24% | 4.52% |
| Weight | 86.52% | 8.30% | 5.19% |
| Plant height growth | 0.687 | -0.111 | 0.628 |
| Growth of ground diameter | 0.806 | -0.279 | 0.104 |
| Net photosynthetic rate | 0.922 | -0.369 | -0.073 |
| Stomatal conductance | 0.889 | -0.408 | -0.025 |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration | 0.975 | -0.013 | -0.012 |
| Transpiration rate | 0.917 | -0.371 | -0.064 |
| Stomatal limitation | -0.899 | -0.070 | -0.190 |
| Water use efficiency | 0.945 | -0.088 | 0.015 |
| Chl a | 0.904 | 0.309 | -0.149 |
| Chl b | 0.948 | 0.101 | -0.200 |
| Chl a/b | -0.701 | -0.021 | 0.337 |
| Leaf area | 0.944 | -0.074 | 0.109 |
| Relative water content of leaves | 0.890 | 0.366 | -0.026 |
| Catalase | 0.848 | 0.276 | -0.097 |
| Malondialdehyde | -0.801 | 0.054 | 0.288 |
| Peroxidase | 0.895 | 0.160 | -0.056 |
| Proline | 0.906 | -0.034 | 0.169 |
| Superoxide dismutase | 0.672 | 0.638 | 0.224 |
表5 亲本及F1代18个抗旱性状的主成分分析
Table 5 Principal component of 18 drought resistance traits in parent and F1 progeny
| Principal component | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | 13.58 | 1.30 | 0.81 |
| Contribution rate | 75.45% | 7.24% | 4.52% |
| Weight | 86.52% | 8.30% | 5.19% |
| Plant height growth | 0.687 | -0.111 | 0.628 |
| Growth of ground diameter | 0.806 | -0.279 | 0.104 |
| Net photosynthetic rate | 0.922 | -0.369 | -0.073 |
| Stomatal conductance | 0.889 | -0.408 | -0.025 |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration | 0.975 | -0.013 | -0.012 |
| Transpiration rate | 0.917 | -0.371 | -0.064 |
| Stomatal limitation | -0.899 | -0.070 | -0.190 |
| Water use efficiency | 0.945 | -0.088 | 0.015 |
| Chl a | 0.904 | 0.309 | -0.149 |
| Chl b | 0.948 | 0.101 | -0.200 |
| Chl a/b | -0.701 | -0.021 | 0.337 |
| Leaf area | 0.944 | -0.074 | 0.109 |
| Relative water content of leaves | 0.890 | 0.366 | -0.026 |
| Catalase | 0.848 | 0.276 | -0.097 |
| Malondialdehyde | -0.801 | 0.054 | 0.288 |
| Peroxidase | 0.895 | 0.160 | -0.056 |
| Proline | 0.906 | -0.034 | 0.169 |
| Superoxide dismutase | 0.672 | 0.638 | 0.224 |
| Individual | D value | Individual | D value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A11 | 0.91 | B19 | 0.61 |
| A15 | 0.90 | C10 | 0.60 |
| B18 | 0.87 | B20 | 0.59 |
| B15 | 0.77 | C25 | 0.52 |
| Populus laurifolia | 0.66 | C6 | 0.51 |
| A24 | 0.64 | B12 | 0.49 |
| A25 | 0.64 | A12 | 0.38 |
| B16 | 0.63 | C11 | 0.38 |
| A10 | 0.63 | B17 | 0.17 |
| B11 | 0.63 | B8 | 0.12 |
| B5 | 0.62 | B25 | 0.12 |
| C7 | 0.61 | B13 | 0.06 |
表6 亲本及F1代抗旱性综合评价
Table 6 Comprehensive evaluation of drought resistance of parent and F1 progeny
| Individual | D value | Individual | D value |
|---|---|---|---|
| A11 | 0.91 | B19 | 0.61 |
| A15 | 0.90 | C10 | 0.60 |
| B18 | 0.87 | B20 | 0.59 |
| B15 | 0.77 | C25 | 0.52 |
| Populus laurifolia | 0.66 | C6 | 0.51 |
| A24 | 0.64 | B12 | 0.49 |
| A25 | 0.64 | A12 | 0.38 |
| B16 | 0.63 | C11 | 0.38 |
| A10 | 0.63 | B17 | 0.17 |
| B11 | 0.63 | B8 | 0.12 |
| B5 | 0.62 | B25 | 0.12 |
| C7 | 0.61 | B13 | 0.06 |
| [1] | 陈章水 (2014). 东北华北关中地区杨树栽培新技术. 北京: 金盾出版社. pp. 57-58. |
| [2] | 冯冬霞, 施生锦 (2005). 叶面积测定方法的研究效果初报. 中国农学通报 21(6), 4. |
| [3] | 付士磊, 周永斌, 何兴元, 陈玮 (2006). 干旱胁迫对杨树光合生理指标的影响. 应用生态学报 17, 2016-2019. |
| [4] | 姬慧娟 (2015). 丹红杨与小叶杨杂交子代苗期抗旱相关性状遗传分析. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院. pp. 20-21. |
| [5] | 刘增兵, 姜景彬, 杨欢欢, 姜秀明, 李景富 (2019). 植物杂种优势的研究进展. 分子植物育种 17, 4127-4134. |
| [6] | 潘静, 韩蕾 (2017). 葡萄叶片叶绿素含量测定方法比较. 西北园艺 (6), 58-60. |
| [7] | 山仑, 邓西平, 康绍忠 (2002). 我国半干旱地区农业用水现状及发展方向. 水利学报 33(9), 27-31. |
| [8] |
孙佩, 姬慧娟, 张亚红, 贾会霞, 胡建军 (2019). 丹红杨×通辽1号杨杂交子代苗期抗旱性初步评价. 植物遗传资源学报 20, 297-308.
DOI |
| [9] | 《新疆植物志》编写委员会 (2019). 新疆植物志(第1卷). 乌鲁木齐: 新疆科学技术出版社. pp. 170. |
| [10] | 徐虎智, 孟丙南, 李云, 王先保, 吕保聚, 程新林, 梁润峰 (2006). 影响林木扦插成活率的因素分析. 河南林业科技 26(3), 26-27. |
| [11] |
张龙进, 李桂双, 白成科, 文苗苗, 张志勤 (2012). 山茱萸种质资源数量性状评价及相关性分析. 植物遗传资源学报 13, 655-659.
DOI |
| [12] |
Ennajeh M, Vadel AM, Cochard H, Khemira H (2010). Comparative impacts of water stress on the leaf anatomy of a drought-resistant and a drought-sensitive olive cultivar. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 85, 289-294.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Farooq M, Hussain M, Wahid A, Siddique KHM (2012). Drought stress in plants:an overview. In: Aroca R, ed. Plant Responses to Drought Stress: From Morphological to Molecular Features. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 1-8. |
| [14] |
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, Fujita D, Basra SMA (2009). Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29, 185-212.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Farquhar GD, Sharkey TD (1982). Stomatal conductance and photosynthesis. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 33, 317-345.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Fathi A, Tari DB (2016). Effect of drought stress and its mechanism in plants. Int J Life Sci 10, 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Li S, Lin YCJ, Wang PY, Zhang BF, Li M, Chen S, Shi R, Tunlaya-Anukit S, Liu XY, Wang ZF, Dai XF, Yu J, Zhou CG, Liu BG, Wang JP, Chiang VL, Li W (2019). The AREB1 transcription factor influences histone acetylation to regulate drought responses and tolerance in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Cell 31, 663-686.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Lian CL, Li Q, Yao K, Zhang Y, Meng S, Yin WL, Xia XL (2018). Populus trichocarpa PtNF-YA9, a multifunctional transcription factor, regulates seed germination, abiotic stress, plant growth and development in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 9, 954.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Meng S, Cao Y, Li HG, Bian Z, Wang DL, Lian CL, Yin WL, Xia XL (2019). PeSHN1 regulates water-use efficiency and drought tolerance by modulating wax biosynthesis in poplar. Tree Physiol 39, 1371-1386.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Orchard KA, Cernusak LA, Hutley LB (2010). Photosynthesis and water-use efficiency of seedlings from northern Australian monsoon forest, savanna and swamp habitats grown in a common garden. Funct Plant Biol 37, 1050-1060.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Ulrich K, Ewald D (2014). Breeding triploid aspen and poplar clones for biomass production. Silvae Genet 63, 47-58. |
| [22] |
Vanlerberghe GC, Martyn GD, Dahal K (2016). Alternative oxidase: a respiratory electron transport chain pathway essential for maintaining photosynthetic performance during drought stress. Physiol Plant 157, 322-337.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Walter J, Nagy L, Hein R, Rascher U, Beierkuhnlein C, Willner E, Jentsch A (2011). Do plants remember drought? Hints towards a drought-memory in grasses. En- viron Exp Bot 71, 34-40. |
| [24] |
Yang YL, Li HG, Wang J, Wang HL, He F, Su YY, Zhang Y, Feng CH, Niu MX, Li ZH, Liu C, Yin WL, Xia XL (2020). ABF3 enhances drought tolerance via promoting ABA- induced stomatal closure by directly regulating ADF5 in Populus euphratica. J Exp Bot 71, 7270-7285.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Yu DD, Wildhagen H, Tylewicz S, Miskolczi PC, Bhalerao RP, Polle A (2019). Abscisic acid signaling mediates biomass trade-off and allocation in poplar. New Phytol 223, 1192-1203.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Zhu JK (2016). Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 167, 313-324.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张琨, 钱敏, 汪阳, 李志华, 孔令娜, 李明洋, 马瑾煜, 努尔艾合麦提•玉苏普, 陈乙一, 成沂芮, 张焕仕, 覃凤飞, 渠晖. 紫花苜蓿耐阴性综合评价及其鉴定指标的筛选[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 773-787. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 范惠玲, 路妍, 金文海, 王慧, 彭小星, 武学霞, 刘玉皎. 基于根系表型性状的蚕豆耐盐碱性鉴定与综合评价(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 204-217. |
| [4] | 张舒欣, 贾紫璇, 方涛, 刘一凡, 赵微, 王荣, 昌海超, 罗芳丽, 朱耀军, 于飞海. 植物抗逆能力评价方法研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24168-. |
| [5] | 吴昱萱, 王平, 胡晓生, 丁一, 彭甜恬, 植秋滢, 巴德木其其格, 李文杰, 关潇, 李俊生. 呼伦贝尔草地退化现状评估与植被特征变化[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24118-. |
| [6] | 尚华丹, 张楚晴, 王梅, 裴文娅, 李国宏, 王鸿斌. 中国杨树害虫物种多样性及其地理分布[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24370-. |
| [7] | 顾燚芸, 薛嘉祈, 高金会, 谢心仪, 韦铭, 雷进宇, 闻丞. 一种基于公众科学数据的区域性鸟类多样性评价方法[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(7): 24080-. |
| [8] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [9] | 张锋, Richard Dormatey, 刘寅笃, 李成举, 王云姣, 张春利, 张莹, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 毕真真, 刘玉汇, 白江平, 孙超. 耐亚磷酸盐马铃薯的筛选与评价[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 544-557. |
| [10] | 王淏, 钦鹏, 李仕贵. 水稻“混血杂交”群体揭示遗传互作奥秘[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 529-532. |
| [11] | 杨尚锦, 范云翔, 章毓文, 韩巧玲, 赵玥, 段劼, 邸楠, 席本野. 树木夜间液流组分划分方法对比——以毛白杨为例[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(4): 496-507. |
| [12] | 廖星鑫, 牛祎, 多兴武, 阿克也得力·居玛哈孜, 买热哈巴·阿不都克尤木, 热孜瓦尼姑丽·胡甫尔, 兰海燕, 曹婧. 异源表达异子蓬SaPEPC2基因提高烟草抗旱性和光合特性(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 585-599. |
| [13] | 倪艳梅, 陈莉, 董志远, 孙德斌, 李宝泉, 王绪敏, 陈琳琳. 黄河三角洲湿地生态修复区大型底栖动物群落结构与生态健康评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(3): 23303-. |
| [14] | 王贺萍, 孙震, 刘雨辰, 苏彦龙, 杜锦瑜, 赵彦, 赵竑博, 王召明, 苑峰, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草肉桂醇脱氢酶基因序列鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 204-216. |
| [15] | 刘寅笃, 脱军康, 李成举, 张锋, 张春利, 张莹, 王云姣, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 孙超, 刘玉汇, 刘震, 毕真真, 白江平. 耐低钾马铃薯品种的筛选与评价[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 75-88. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||