

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (1): 75-88.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23016 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23016
刘寅笃, 脱军康, 李成举, 张锋, 张春利, 张莹, 王云姣, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 孙超, 刘玉汇, 刘震, 毕真真*( ), 白江平*(
), 白江平*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-02-09
接受日期:2023-03-15
出版日期:2024-01-10
发布日期:2024-01-10
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Yindu Liu, Junkang Tuo, Chengju Li, Feng Zhang, Chunli Zhang, Ying Zhang, Yunjiao Wang, Youfang Fan, Panfeng Yao, Chao Sun, Yuhui Liu, Zhen Liu, Zhenzhen Bi*( ), Jiangping Bai*(
), Jiangping Bai*( )
)
Received:2023-02-09
Accepted:2023-03-15
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2024-01-10
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要: 土壤缺钾严重降低了我国马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum)的产量。而不同品种马铃薯对低钾的响应差异较大。因此, 采用耐低钾马铃薯品种可通过提高钾素利用效率减少钾肥施用量, 成为我国农业可持续发展和绿色发展的重要途径。该研究对30个马铃薯品种在正常钾处理(202.5 kg∙hm-2 K2O)和低钾处理(0 kg∙hm-2 K2O)下的17个指标进行测定, 并对9个代表性指标, 包括叶面积指数、根冠比、茎叶干质量、根干质量、单株产量、单株大薯产量、单株小薯产量、块茎干质量和块茎钾积累量进行后续分析。结果表明, 在低钾条件下, 各项指标均有不同程度的下降。主成分分析表明, 这9个指标可转换为4个独立的综合指标, 累计贡献率达87.1%。根据综合评价值(D值)和聚类分析, 将30个品种分为6类, 其中第1类为高度耐低钾品种, 包括Lucinda、Favorita、Kexin1、Xisen6、Xingjia2、Helan15和Chuanyin2, 第2类为中度耐低钾品种, 包括Longshu20、Dingshu3、Jizhang12(W)、Jiuen1、Longshu19和Jizhang12(Y)。此外还建立了耐低钾性评价回归模型Y= -0.595+0.247X5+0.155X4+0.138X3+0.167X8+0.088X1+0.081X6+0.097X9+0.053X2 (R2=0.999, P=0.000), 利用回归方程对30个品种的估计精度均在90%以上。在低钾条件下, 可利用单株产量、根干质量、茎叶干质量、块茎干质量、叶面积指数、单株大薯产量、块茎钾积累量和根冠比快速鉴定耐低钾马铃薯品种。
刘寅笃, 脱军康, 李成举, 张锋, 张春利, 张莹, 王云姣, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 孙超, 刘玉汇, 刘震, 毕真真, 白江平. 耐低钾马铃薯品种的筛选与评价. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 75-88.
Yindu Liu, Junkang Tuo, Chengju Li, Feng Zhang, Chunli Zhang, Ying Zhang, Yunjiao Wang, Youfang Fan, Panfeng Yao, Chao Sun, Yuhui Liu, Zhen Liu, Zhenzhen Bi, Jiangping Bai. Screening and Evaluation of Low-potassium Tolerance Potato Varieties. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(1): 75-88.
| No. | Cultivars | Main planting area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helan15 | Shandong |
| 2 | Favorita | Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, Guangdong |
| 3 | Xingjia2 | Guangdong, Guangxi, Jiangxi, Fujian, Sichuan |
| 4 | Xuechuan8 | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi |
| 5 | Longshu20 | Gansu |
| 6 | Xisen6 | Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Shandong, Sichuan |
| 7 | Lucinda | Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Gansu, Xinjiang |
| 8 | Atlantic | Guangxi, Shanxi, Tianjin, Inner Mongolia, Gansu |
| 9 | Chuanyin2 | Hebei, Inner Mongolia |
| 10 | Jizhang12(Y) | Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia, Tianjin, Gansu |
| 11 | Lishu6 | Yunnan |
| 12 | Dingshu4 | Gansu |
| 13 | Xindaping | Gansu |
| 14 | Longshu7 | Guangdong, Qinghai, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Gansu, Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi |
| 15 | Huasong7 | Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia, Yunnan, Guizhou, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Xizang, Guangdong, Fujian, Guangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Shandong |
| 16 | Longshu14 | Gansu, Inner Mongolia |
| 17 | Dingshu6 | Gansu, Inner Mongolia |
| 18 | Longshu22 | Gansu |
| 19 | Qingshu9 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Gansu |
| 20 | L0109-4 | Gansu |
| 21 | Jizhang12(W) | Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia, Tianjin, Gansu |
| 22 | Longshu10 | Gansu |
| 23 | Heijingang | Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Gansu, Xinjiang, Sichuan, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Shandong, Henan |
| 24 | Jiuen1 | Hebei, Henan, Shandong, Inner Mongolia, Guangdong, Fujian |
| 25 | Longshu19 | Gansu |
| 26 | Qingshu10 | Qinghai |
| 27 | Kexin1 | Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu |
| 28 | Dingshu3 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Gansu |
| 29 | Zhuangshu3 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Gansu |
| 30 | Longshu3 | Gansu, Ningxia, Shanxi, Qinghai, Xinjiang, Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang |
表1 马铃薯品种及主栽地区
Table 1 The potato cultivars and main planting area
| No. | Cultivars | Main planting area |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helan15 | Shandong |
| 2 | Favorita | Heilongjiang, Liaoning, Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, Guangdong |
| 3 | Xingjia2 | Guangdong, Guangxi, Jiangxi, Fujian, Sichuan |
| 4 | Xuechuan8 | Inner Mongolia, Shanxi |
| 5 | Longshu20 | Gansu |
| 6 | Xisen6 | Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Shandong, Sichuan |
| 7 | Lucinda | Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Gansu, Xinjiang |
| 8 | Atlantic | Guangxi, Shanxi, Tianjin, Inner Mongolia, Gansu |
| 9 | Chuanyin2 | Hebei, Inner Mongolia |
| 10 | Jizhang12(Y) | Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia, Tianjin, Gansu |
| 11 | Lishu6 | Yunnan |
| 12 | Dingshu4 | Gansu |
| 13 | Xindaping | Gansu |
| 14 | Longshu7 | Guangdong, Qinghai, Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Gansu, Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi |
| 15 | Huasong7 | Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu, Ningxia, Yunnan, Guizhou, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Xizang, Guangdong, Fujian, Guangxi, Hubei, Hunan, Shandong |
| 16 | Longshu14 | Gansu, Inner Mongolia |
| 17 | Dingshu6 | Gansu, Inner Mongolia |
| 18 | Longshu22 | Gansu |
| 19 | Qingshu9 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Gansu |
| 20 | L0109-4 | Gansu |
| 21 | Jizhang12(W) | Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Inner Mongolia, Tianjin, Gansu |
| 22 | Longshu10 | Gansu |
| 23 | Heijingang | Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Gansu, Xinjiang, Sichuan, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Ningxia, Shandong, Henan |
| 24 | Jiuen1 | Hebei, Henan, Shandong, Inner Mongolia, Guangdong, Fujian |
| 25 | Longshu19 | Gansu |
| 26 | Qingshu10 | Qinghai |
| 27 | Kexin1 | Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu |
| 28 | Dingshu3 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Gansu |
| 29 | Zhuangshu3 | Qinghai, Ningxia, Gansu |
| 30 | Longshu3 | Gansu, Ningxia, Shanxi, Qinghai, Xinjiang, Hebei, Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang |
| Item | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPK | Mean value | 2.72 | 0.06 | 70.94 | 7.33 | 0.99 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 2.73 |
| Maximum | 4.45 | 0.10 | 193.06 | 27.13 | 1.60 | 1.14 | 0.92 | 0.31 | 4.59 | |
| Minimum | 1.48 | 0.04 | 15.70 | 1.85 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 1.54 | |
| Range | 2.97 | 0.06 | 177.36 | 25.27 | 1.01 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.18 | 3.05 | |
| Variation of coefficient (%) | 25.3 | 22.3 | 55.3 | 68.9 | 23.8 | 35.7 | 41.5 | 24.2 | 29.0 | |
| NP | Mean value | 3.50 | 0.06 | 86.21 | 8.41 | 0.91 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 2.52 |
| Maximum | 5.20 | 0.10 | 161.21 | 38.54 | 1.45 | 1.08 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 4.32 | |
| Minimum | 2.15 | 0.03 | 24.24 | 1.80 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 1.18 | |
| Range | 3.05 | 0.07 | 136.97 | 36.74 | 1.08 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.24 | 3.13 | |
| Variation of coefficient (%) | 21.1 | 29.4 | 48.5 | 80.2 | 27.8 | 45.0 | 36.7 | 24.7 | 28.1 | |
| LPTC | Mean value | 1.33 | 0.94 | 1.28 | 1.16 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 1.05 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| Maximum | 1.66 | 1.42 | 1.66 | 1.76 | 1.35 | 1.51 | 2.18 | 1.31 | 1.37 | |
| Minimum | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.52 | |
| Range | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 1.28 | 0.83 | 1.18 | 1.57 | 0.72 | 0.85 | |
| Variation of coefficient (%) | 20.5 | 24.6 | 23.8 | 28.4 | 23.5 | 30.1 | 30.9 | 21.8 | 24.4 | |
表2 正常钾处理和低钾处理下马铃薯各指标的变异及耐低钾系数的变异
Table 2 Variation of potato indexes under normal potassium treatment, low potassium treatment and variation of low potassium tolerance coefficient
| Item | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPK | Mean value | 2.72 | 0.06 | 70.94 | 7.33 | 0.99 | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.22 | 2.73 |
| Maximum | 4.45 | 0.10 | 193.06 | 27.13 | 1.60 | 1.14 | 0.92 | 0.31 | 4.59 | |
| Minimum | 1.48 | 0.04 | 15.70 | 1.85 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 1.54 | |
| Range | 2.97 | 0.06 | 177.36 | 25.27 | 1.01 | 0.82 | 0.76 | 0.18 | 3.05 | |
| Variation of coefficient (%) | 25.3 | 22.3 | 55.3 | 68.9 | 23.8 | 35.7 | 41.5 | 24.2 | 29.0 | |
| NP | Mean value | 3.50 | 0.06 | 86.21 | 8.41 | 0.91 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.20 | 2.52 |
| Maximum | 5.20 | 0.10 | 161.21 | 38.54 | 1.45 | 1.08 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 4.32 | |
| Minimum | 2.15 | 0.03 | 24.24 | 1.80 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 1.18 | |
| Range | 3.05 | 0.07 | 136.97 | 36.74 | 1.08 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 0.24 | 3.13 | |
| Variation of coefficient (%) | 21.1 | 29.4 | 48.5 | 80.2 | 27.8 | 45.0 | 36.7 | 24.7 | 28.1 | |
| LPTC | Mean value | 1.33 | 0.94 | 1.28 | 1.16 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 1.05 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| Maximum | 1.66 | 1.42 | 1.66 | 1.76 | 1.35 | 1.51 | 2.18 | 1.31 | 1.37 | |
| Minimum | 0.68 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.52 | |
| Range | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 1.28 | 0.83 | 1.18 | 1.57 | 0.72 | 0.85 | |
| Variation of coefficient (%) | 20.5 | 24.6 | 23.8 | 28.4 | 23.5 | 30.1 | 30.9 | 21.8 | 24.4 | |
| Cultivars | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helan15 | 0.68 | 1.10 | 1.66 | 1.76 | 1.10 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 1.10 |
| Favorita | 1.55 | 0.76 | 1.54 | 1.34 | 1.22 | 1.19 | 1.26 | 1.17 | 1.10 |
| Xingjia2 | 1.29 | 0.94 | 1.55 | 1.07 | 1.22 | 1.39 | 0.98 | 1.25 | 1.21 |
| Xuechuan8 | 1.43 | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.77 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 1.45 | 1.14 | 1.23 |
| Longshu20 | 1.60 | 1.11 | 1.50 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 1.06 | 1.13 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Xisen6 | 1.55 | 0.67 | 1.64 | 1.38 | 1.12 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 1.14 |
| Lucinda | 1.61 | 0.99 | 1.57 | 1.55 | 1.19 | 0.97 | 1.64 | 1.19 | 1.14 |
| Atlantic | 1.60 | 1.34 | 0.96 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.61 |
| Chuanyin2 | 1.63 | 1.42 | 0.72 | 1.42 | 1.24 | 0.96 | 1.49 | 1.31 | 1.16 |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.07 | 1.32 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.24 |
| Lishu6 | 1.66 | 1.04 | 1.21 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.89 |
| Dingshu4 | 1.18 | 0.85 | 1.44 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 1.19 | 0.91 | 1.37 |
| Xindaping | 0.81 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 1.03 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
| Longshu7 | 1.05 | 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 1.02 |
| Huasong7 | 0.82 | 1.38 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.64 |
| Longshu14 | 1.11 | 1.27 | 0.98 | 1.37 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Dingshu6 | 1.05 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 1.19 | 0.63 | 0.67 |
| Longshu22 | 1.20 | 0.74 | 1.08 | 1.33 | 0.68 | 0.54 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.83 |
| Qingshu9 | 1.03 | 1.03 | 1.11 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 1.12 | 0.64 | 0.94 | 1.03 |
| L0109-4 | 1.53 | 0.97 | 1.30 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.53 | 0.94 | 0.74 | 0.60 |
| Jizhang12(W) | 1.50 | 1.15 | 1.54 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.17 | 1.24 |
| Longshu10 | 1.43 | 0.93 | 1.17 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 1.05 | 0.94 | 0.76 |
| Heijingang | 1.64 | 0.87 | 1.59 | 1.22 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| Jiuen1 | 1.24 | 0.73 | 1.60 | 1.72 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.85 |
| Longshu19 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 0.91 | 0.81 | 1.35 | 1.51 | 1.19 | 1.21 | 1.24 |
| Qingshu10 | 1.61 | 0.90 | 1.57 | 1.45 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.52 |
| Kexin1 | 1.64 | 0.64 | 1.65 | 1.27 | 1.28 | 0.91 | 2.18 | 1.11 | 1.05 |
| Dingshu3 | 1.39 | 0.95 | 1.53 | 1.44 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 1.37 | 1.09 | 0.95 |
| Zhuangshu3 | 1.45 | 1.01 | 1.22 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.72 |
| Longshu3 | 1.22 | 0.71 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.60 |
表3 低钾胁迫下马铃薯品种各单项指标的耐低钾系数(LPTC)
Table 3 Low potassium tolerance coefficient (LPTC) of each single index of potato cultivars under low potassium stress
| Cultivars | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helan15 | 0.68 | 1.10 | 1.66 | 1.76 | 1.10 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 1.10 |
| Favorita | 1.55 | 0.76 | 1.54 | 1.34 | 1.22 | 1.19 | 1.26 | 1.17 | 1.10 |
| Xingjia2 | 1.29 | 0.94 | 1.55 | 1.07 | 1.22 | 1.39 | 0.98 | 1.25 | 1.21 |
| Xuechuan8 | 1.43 | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.77 | 1.03 | 0.88 | 1.45 | 1.14 | 1.23 |
| Longshu20 | 1.60 | 1.11 | 1.50 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 1.06 | 1.13 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Xisen6 | 1.55 | 0.67 | 1.64 | 1.38 | 1.12 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 1.14 | 1.14 |
| Lucinda | 1.61 | 0.99 | 1.57 | 1.55 | 1.19 | 0.97 | 1.64 | 1.19 | 1.14 |
| Atlantic | 1.60 | 1.34 | 0.96 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.61 |
| Chuanyin2 | 1.63 | 1.42 | 0.72 | 1.42 | 1.24 | 0.96 | 1.49 | 1.31 | 1.16 |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.07 | 1.32 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.24 |
| Lishu6 | 1.66 | 1.04 | 1.21 | 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.92 | 0.76 | 0.89 |
| Dingshu4 | 1.18 | 0.85 | 1.44 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 1.19 | 0.91 | 1.37 |
| Xindaping | 0.81 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 1.03 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
| Longshu7 | 1.05 | 0.70 | 0.96 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 1.02 |
| Huasong7 | 0.82 | 1.38 | 0.72 | 0.92 | 0.70 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.64 |
| Longshu14 | 1.11 | 1.27 | 0.98 | 1.37 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 0.61 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| Dingshu6 | 1.05 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 1.19 | 0.63 | 0.67 |
| Longshu22 | 1.20 | 0.74 | 1.08 | 1.33 | 0.68 | 0.54 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.83 |
| Qingshu9 | 1.03 | 1.03 | 1.11 | 0.87 | 0.77 | 1.12 | 0.64 | 0.94 | 1.03 |
| L0109-4 | 1.53 | 0.97 | 1.30 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.53 | 0.94 | 0.74 | 0.60 |
| Jizhang12(W) | 1.50 | 1.15 | 1.54 | 1.06 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.17 | 1.24 |
| Longshu10 | 1.43 | 0.93 | 1.17 | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 1.05 | 0.94 | 0.76 |
| Heijingang | 1.64 | 0.87 | 1.59 | 1.22 | 0.81 | 0.74 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| Jiuen1 | 1.24 | 0.73 | 1.60 | 1.72 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.85 |
| Longshu19 | 1.27 | 0.56 | 0.91 | 0.81 | 1.35 | 1.51 | 1.19 | 1.21 | 1.24 |
| Qingshu10 | 1.61 | 0.90 | 1.57 | 1.45 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.59 | 0.52 |
| Kexin1 | 1.64 | 0.64 | 1.65 | 1.27 | 1.28 | 0.91 | 2.18 | 1.11 | 1.05 |
| Dingshu3 | 1.39 | 0.95 | 1.53 | 1.44 | 1.13 | 0.82 | 1.37 | 1.09 | 0.95 |
| Zhuangshu3 | 1.45 | 1.01 | 1.22 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.72 |
| Longshu3 | 1.22 | 0.71 | 1.66 | 1.66 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.60 |
| Index | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X2 | -0.018 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X3 | 0.305* | -0.309* | 1.000 | ||||||
| X4 | 0.121 | 0.053 | 0.611** | 1.000 | |||||
| X5 | 0.225 | -0.193 | 0.271 | 0.275 | 1.000 | ||||
| X6 | 0.017 | -0.146 | 0.264 | 0.209 | 0.814** | 1.000 | |||
| X7 | 0.364* | -0.255 | 0.107 | 0.066 | 0.634** | 0.143 | 1.000 | ||
| X8 | 0.196 | -0.138 | 0.165 | 0.193 | 0.910** | 0.779** | 0.557** | 1.000 | |
| X9 | -0.038 | -0.154 | 0.068 | 0.032 | 0.777** | 0.748** | 0.416** | 0.830** | 1.000 |
表4 低钾胁迫下马铃薯各单项指标的相关系数矩阵
Table 4 Correlation coefficient matrix of each single index of potato under low potassium stress
| Index | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1.000 | ||||||||
| X2 | -0.018 | 1.000 | |||||||
| X3 | 0.305* | -0.309* | 1.000 | ||||||
| X4 | 0.121 | 0.053 | 0.611** | 1.000 | |||||
| X5 | 0.225 | -0.193 | 0.271 | 0.275 | 1.000 | ||||
| X6 | 0.017 | -0.146 | 0.264 | 0.209 | 0.814** | 1.000 | |||
| X7 | 0.364* | -0.255 | 0.107 | 0.066 | 0.634** | 0.143 | 1.000 | ||
| X8 | 0.196 | -0.138 | 0.165 | 0.193 | 0.910** | 0.779** | 0.557** | 1.000 | |
| X9 | -0.038 | -0.154 | 0.068 | 0.032 | 0.777** | 0.748** | 0.416** | 0.830** | 1.000 |
| Item | CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | CI4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.130 | 0.375 | -0.528 | 0.392 |
| X2 | -0.140 | -0.129 | 0.274 | 0.862 |
| X3 | 0.189 | 0.635 | 0.160 | -0.205 |
| X4 | 0.159 | 0.552 | 0.398 | 0.175 |
| X5 | 0.486 | -0.056 | -0.009 | 0.077 |
| X6 | 0.415 | -0.129 | 0.351 | -0.046 |
| X7 | 0.310 | 0.015 | -0.571 | 0.079 |
| X8 | 0.471 | -0.150 | 0.006 | 0.116 |
| X9 | 0.420 | -0.305 | 0.112 | -0.039 |
| Eigen values | 3.961 | 1.628 | 1.217 | 1.032 |
| Contributive rate (%) | 44.0 | 18.1 | 13.5 | 11.5 |
| Cumulative contributive rate (%) | 44.0 | 62.1 | 75.6 | 87.1 |
表5 各综合指标的系数及贡献率
Table 5 Coefficient and contributive rate of each comprehensive index
| Item | CI1 | CI2 | CI3 | CI4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.130 | 0.375 | -0.528 | 0.392 |
| X2 | -0.140 | -0.129 | 0.274 | 0.862 |
| X3 | 0.189 | 0.635 | 0.160 | -0.205 |
| X4 | 0.159 | 0.552 | 0.398 | 0.175 |
| X5 | 0.486 | -0.056 | -0.009 | 0.077 |
| X6 | 0.415 | -0.129 | 0.351 | -0.046 |
| X7 | 0.310 | 0.015 | -0.571 | 0.079 |
| X8 | 0.471 | -0.150 | 0.006 | 0.116 |
| X9 | 0.420 | -0.305 | 0.112 | -0.039 |
| Eigen values | 3.961 | 1.628 | 1.217 | 1.032 |
| Contributive rate (%) | 44.0 | 18.1 | 13.5 | 11.5 |
| Cumulative contributive rate (%) | 44.0 | 62.1 | 75.6 | 87.1 |
| Cultivars | F(X1) | F(X2) | F(X3) | F(X4) | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | U(X4) | D value | Comprehensive valuation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lucinda | 2.683 | 1.108 | -0.681 | 0.936 | 0.936 | 0.710 | 0.317 | 0.557 | 0.743 | 1 |
| Favorita | 2.604 | 0.673 | -0.169 | -0.224 | 0.924 | 0.617 | 0.404 | 0.321 | 0.700 | 2 |
| Kexin1 | 3.097 | 1.249 | -2.530 | -0.386 | 1.000 | 0.740 | 0.000 | 0.289 | 0.697 | 3 |
| Xisen6 | 2.318 | 0.951 | 0.473 | -0.751 | 0.880 | 0.676 | 0.514 | 0.214 | 0.693 | 4 |
| Xingjia2 | 2.677 | -0.531 | 1.039 | -0.153 | 0.935 | 0.359 | 0.611 | 0.336 | 0.686 | 5 |
| Helan15 | 1.131 | 0.389 | 3.311 | -0.328 | 0.696 | 0.556 | 1.000 | 0.300 | 0.662 | 6 |
| Chuanyin2 | 2.107 | -1.227 | -0.553 | 3.118 | 0.847 | 0.211 | 0.338 | 1.000 | 0.656 | 7 |
| Longshu20 | 0.883 | 1.181 | 0.242 | 1.069 | 0.658 | 0.725 | 0.475 | 0.584 | 0.634 | 8 |
| Dingshu3 | 1.322 | 0.959 | -0.274 | 0.353 | 0.726 | 0.678 | 0.386 | 0.439 | 0.625 | 9 |
| Jizhang12(W) | 1.337 | -0.122 | 0.373 | 0.864 | 0.728 | 0.447 | 0.497 | 0.542 | 0.609 | 10 |
| Jiuen1 | 0.269 | 1.737 | 0.933 | -0.845 | 0.563 | 0.844 | 0.593 | 0.195 | 0.578 | 11 |
| Longshu19 | 3.014 | -2.212 | -0.226 | -1.257 | 0.987 | 0.000 | 0.394 | 0.112 | 0.575 | 12 |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 0.831 | -1.045 | 1.140 | 0.903 | 0.650 | 0.249 | 0.628 | 0.550 | 0.550 | 13 |
| Dingshu4 | 0.946 | -0.660 | 0.036 | -0.793 | 0.667 | 0.332 | 0.439 | 0.206 | 0.502 | 14 |
| Heijingang | -0.730 | 1.577 | -0.411 | -0.084 | 0.408 | 0.810 | 0.363 | 0.350 | 0.477 | 15 |
| Xuechuan8 | 1.427 | -1.589 | -1.830 | -0.922 | 0.742 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.180 | 0.445 | 16 |
| Longshu14 | -1.025 | -0.753 | 1.786 | 1.063 | 0.363 | 0.312 | 0.739 | 0.583 | 0.440 | 17 |
| Longshu3 | -1.866 | 2.430 | 0.765 | -1.197 | 0.233 | 0.992 | 0.564 | 0.124 | 0.428 | 18 |
| Qingshu10 | -2.239 | 2.466 | 0.059 | -0.041 | 0.175 | 1.000 | 0.443 | 0.358 | 0.412 | 19 |
| Qingshu9 | -0.664 | -1.497 | 1.337 | -0.342 | 0.419 | 0.153 | 0.662 | 0.297 | 0.385 | 20 |
| Lishu6 | -1.236 | 0.151 | -0.852 | 0.621 | 0.330 | 0.505 | 0.287 | 0.493 | 0.381 | 21 |
| Longshu10 | -0.945 | -0.256 | -0.906 | 0.041 | 0.375 | 0.418 | 0.278 | 0.375 | 0.369 | 22 |
| Zhuangshu3 | -1.778 | 0.132 | -0.054 | 0.142 | 0.247 | 0.501 | 0.424 | 0.396 | 0.347 | 23 |
| L0109-4 | -2.156 | 0.860 | -0.966 | 0.217 | 0.188 | 0.657 | 0.268 | 0.411 | 0.327 | 24 |
| Longshu22 | -1.953 | 0.325 | 0.040 | -0.877 | 0.219 | 0.542 | 0.440 | 0.189 | 0.317 | 25 |
| Longshu7 | -0.981 | -1.460 | -0.329 | -1.376 | 0.370 | 0.161 | 0.377 | 0.087 | 0.290 | 26 |
| Xindaping | -1.065 | -2.187 | -0.346 | -1.806 | 0.357 | 0.005 | 0.374 | 0.000 | 0.239 | 27 |
| Atlantic | -3.373 | -0.497 | -1.103 | 1.584 | 0.000 | 0.367 | 0.244 | 0.688 | 0.205 | 28 |
| Huasong7 | -3.358 | -1.698 | 0.708 | 0.986 | 0.002 | 0.110 | 0.554 | 0.567 | 0.185 | 29 |
| Dingshu6 | -3.259 | -0.472 | -1.019 | -0.515 | 0.018 | 0.372 | 0.259 | 0.262 | 0.161 | 30 |
| Index weight | 0.505 | 0.208 | 0.155 | 0.132 |
表6 各品种马铃薯的综合指标值F(Xj)、权重Wj、隶属函数值U(Xj)、D值及综合评价
Table 6 The value of each potato cultivar’s comprehensive index F(Xj), index weight Wj, subordinate function value U(Xj), D value and comprehensive valuation
| Cultivars | F(X1) | F(X2) | F(X3) | F(X4) | U(X1) | U(X2) | U(X3) | U(X4) | D value | Comprehensive valuation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lucinda | 2.683 | 1.108 | -0.681 | 0.936 | 0.936 | 0.710 | 0.317 | 0.557 | 0.743 | 1 |
| Favorita | 2.604 | 0.673 | -0.169 | -0.224 | 0.924 | 0.617 | 0.404 | 0.321 | 0.700 | 2 |
| Kexin1 | 3.097 | 1.249 | -2.530 | -0.386 | 1.000 | 0.740 | 0.000 | 0.289 | 0.697 | 3 |
| Xisen6 | 2.318 | 0.951 | 0.473 | -0.751 | 0.880 | 0.676 | 0.514 | 0.214 | 0.693 | 4 |
| Xingjia2 | 2.677 | -0.531 | 1.039 | -0.153 | 0.935 | 0.359 | 0.611 | 0.336 | 0.686 | 5 |
| Helan15 | 1.131 | 0.389 | 3.311 | -0.328 | 0.696 | 0.556 | 1.000 | 0.300 | 0.662 | 6 |
| Chuanyin2 | 2.107 | -1.227 | -0.553 | 3.118 | 0.847 | 0.211 | 0.338 | 1.000 | 0.656 | 7 |
| Longshu20 | 0.883 | 1.181 | 0.242 | 1.069 | 0.658 | 0.725 | 0.475 | 0.584 | 0.634 | 8 |
| Dingshu3 | 1.322 | 0.959 | -0.274 | 0.353 | 0.726 | 0.678 | 0.386 | 0.439 | 0.625 | 9 |
| Jizhang12(W) | 1.337 | -0.122 | 0.373 | 0.864 | 0.728 | 0.447 | 0.497 | 0.542 | 0.609 | 10 |
| Jiuen1 | 0.269 | 1.737 | 0.933 | -0.845 | 0.563 | 0.844 | 0.593 | 0.195 | 0.578 | 11 |
| Longshu19 | 3.014 | -2.212 | -0.226 | -1.257 | 0.987 | 0.000 | 0.394 | 0.112 | 0.575 | 12 |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 0.831 | -1.045 | 1.140 | 0.903 | 0.650 | 0.249 | 0.628 | 0.550 | 0.550 | 13 |
| Dingshu4 | 0.946 | -0.660 | 0.036 | -0.793 | 0.667 | 0.332 | 0.439 | 0.206 | 0.502 | 14 |
| Heijingang | -0.730 | 1.577 | -0.411 | -0.084 | 0.408 | 0.810 | 0.363 | 0.350 | 0.477 | 15 |
| Xuechuan8 | 1.427 | -1.589 | -1.830 | -0.922 | 0.742 | 0.133 | 0.120 | 0.180 | 0.445 | 16 |
| Longshu14 | -1.025 | -0.753 | 1.786 | 1.063 | 0.363 | 0.312 | 0.739 | 0.583 | 0.440 | 17 |
| Longshu3 | -1.866 | 2.430 | 0.765 | -1.197 | 0.233 | 0.992 | 0.564 | 0.124 | 0.428 | 18 |
| Qingshu10 | -2.239 | 2.466 | 0.059 | -0.041 | 0.175 | 1.000 | 0.443 | 0.358 | 0.412 | 19 |
| Qingshu9 | -0.664 | -1.497 | 1.337 | -0.342 | 0.419 | 0.153 | 0.662 | 0.297 | 0.385 | 20 |
| Lishu6 | -1.236 | 0.151 | -0.852 | 0.621 | 0.330 | 0.505 | 0.287 | 0.493 | 0.381 | 21 |
| Longshu10 | -0.945 | -0.256 | -0.906 | 0.041 | 0.375 | 0.418 | 0.278 | 0.375 | 0.369 | 22 |
| Zhuangshu3 | -1.778 | 0.132 | -0.054 | 0.142 | 0.247 | 0.501 | 0.424 | 0.396 | 0.347 | 23 |
| L0109-4 | -2.156 | 0.860 | -0.966 | 0.217 | 0.188 | 0.657 | 0.268 | 0.411 | 0.327 | 24 |
| Longshu22 | -1.953 | 0.325 | 0.040 | -0.877 | 0.219 | 0.542 | 0.440 | 0.189 | 0.317 | 25 |
| Longshu7 | -0.981 | -1.460 | -0.329 | -1.376 | 0.370 | 0.161 | 0.377 | 0.087 | 0.290 | 26 |
| Xindaping | -1.065 | -2.187 | -0.346 | -1.806 | 0.357 | 0.005 | 0.374 | 0.000 | 0.239 | 27 |
| Atlantic | -3.373 | -0.497 | -1.103 | 1.584 | 0.000 | 0.367 | 0.244 | 0.688 | 0.205 | 28 |
| Huasong7 | -3.358 | -1.698 | 0.708 | 0.986 | 0.002 | 0.110 | 0.554 | 0.567 | 0.185 | 29 |
| Dingshu6 | -3.259 | -0.472 | -1.019 | -0.515 | 0.018 | 0.372 | 0.259 | 0.262 | 0.161 | 30 |
| Index weight | 0.505 | 0.208 | 0.155 | 0.132 |
| Cluster | Cultivars | Treatments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPK (202.5 kg·hm-2 K2O) | NP (0 kg·hm-2 K2O) | ||
| First cluster | Lucinda | 0.81±0.04 a | 0.97±0.05 a |
| Favorita | 0.79±0.05 b | 0.97±0.02 a | |
| Kexin1 | 0.69±0.05 a | 0.89±0.10 a | |
| Xisen6 | 0.81±0.06 a | 0.90±0.01 a | |
| Xingjia2 | 0.95±0.01 a | 1.16±0.06 a | |
| Helan15 | 1.19±0.01 a | 1.31±0.04 a | |
| Chuanyin2 | 1.17±0.11 a | 1.45±0.08 a | |
| Second cluster | Longshu20 | 1.25±0.07 a | 1.34±0.04 a |
| Dingshu3 | 0.84±0.03 a | 0.95±0.03 a | |
| Jizhang12(W) | 1.04±0.00 a | 1.02±0.09 a | |
| Jiuen1 | 0.95±0.10 a | 0.88±0.03 a | |
| Longshu19 | 0.64±0.02 a | 0.87±0.04 a | |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 0.99±0.04 a | 1.03±0.09 a | |
| Third cluster | Dingshu4 | 1.15±0.08 a | 1.12±0.07 a |
| Heijingang | 0.70±0.03 a | 0.57±0.02 b | |
| Fourth cluster | Xuechuan8 | 0.81±0.02 a | 0.84±0.02 a |
| Longshu14 | 0.92±0.05 a | 0.73±0.02 b | |
| Longshu3 | 1.23±0.01 a | 0.82±0.05 b | |
| Qingshu10 | 1.20±0.03 a | 0.85±0.02 b | |
| Qingshu9 | 1.25±0.03 a | 0.96±0.08 b | |
| Lishu6 | 1.35±0.07 a | 1.07±0.04 b | |
| Longshu10 | 1.60±0.01 a | 1.33±0.10 a | |
| Fifth cluster | Zhuangshu3 | 1.08±0.13 a | 0.83±0.07 a |
| L0109-4 | 1.25±0.09 a | 0.92±0.04 b | |
| Longshu22 | 1.01±0.02 a | 0.69±0.06 b | |
| Longshu7 | 0.89±0.01 a | 0.75±0.03 a | |
| Sixth cluster | Xindaping | 0.80±0.07 a | 0.70±0.10 a |
| Atlantic | 0.59±0.03 a | 0.37±0.02 b | |
| Huasong7 | 0.92±0.04 a | 0.64±0.03 b | |
| Dingshu6 | 0.73±0.07 a | 0.38±0.03 b | |
表7 不同品种马铃薯单株产量在正常钾(NPK)与低钾(NP)处理下的差异
Table 7 Difference of tuber yield per plant of different potato varieties under normal potassium (NPK) and low potassium (NP) treatments
| Cluster | Cultivars | Treatments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPK (202.5 kg·hm-2 K2O) | NP (0 kg·hm-2 K2O) | ||
| First cluster | Lucinda | 0.81±0.04 a | 0.97±0.05 a |
| Favorita | 0.79±0.05 b | 0.97±0.02 a | |
| Kexin1 | 0.69±0.05 a | 0.89±0.10 a | |
| Xisen6 | 0.81±0.06 a | 0.90±0.01 a | |
| Xingjia2 | 0.95±0.01 a | 1.16±0.06 a | |
| Helan15 | 1.19±0.01 a | 1.31±0.04 a | |
| Chuanyin2 | 1.17±0.11 a | 1.45±0.08 a | |
| Second cluster | Longshu20 | 1.25±0.07 a | 1.34±0.04 a |
| Dingshu3 | 0.84±0.03 a | 0.95±0.03 a | |
| Jizhang12(W) | 1.04±0.00 a | 1.02±0.09 a | |
| Jiuen1 | 0.95±0.10 a | 0.88±0.03 a | |
| Longshu19 | 0.64±0.02 a | 0.87±0.04 a | |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 0.99±0.04 a | 1.03±0.09 a | |
| Third cluster | Dingshu4 | 1.15±0.08 a | 1.12±0.07 a |
| Heijingang | 0.70±0.03 a | 0.57±0.02 b | |
| Fourth cluster | Xuechuan8 | 0.81±0.02 a | 0.84±0.02 a |
| Longshu14 | 0.92±0.05 a | 0.73±0.02 b | |
| Longshu3 | 1.23±0.01 a | 0.82±0.05 b | |
| Qingshu10 | 1.20±0.03 a | 0.85±0.02 b | |
| Qingshu9 | 1.25±0.03 a | 0.96±0.08 b | |
| Lishu6 | 1.35±0.07 a | 1.07±0.04 b | |
| Longshu10 | 1.60±0.01 a | 1.33±0.10 a | |
| Fifth cluster | Zhuangshu3 | 1.08±0.13 a | 0.83±0.07 a |
| L0109-4 | 1.25±0.09 a | 0.92±0.04 b | |
| Longshu22 | 1.01±0.02 a | 0.69±0.06 b | |
| Longshu7 | 0.89±0.01 a | 0.75±0.03 a | |
| Sixth cluster | Xindaping | 0.80±0.07 a | 0.70±0.10 a |
| Atlantic | 0.59±0.03 a | 0.37±0.02 b | |
| Huasong7 | 0.92±0.04 a | 0.64±0.03 b | |
| Dingshu6 | 0.73±0.07 a | 0.38±0.03 b | |
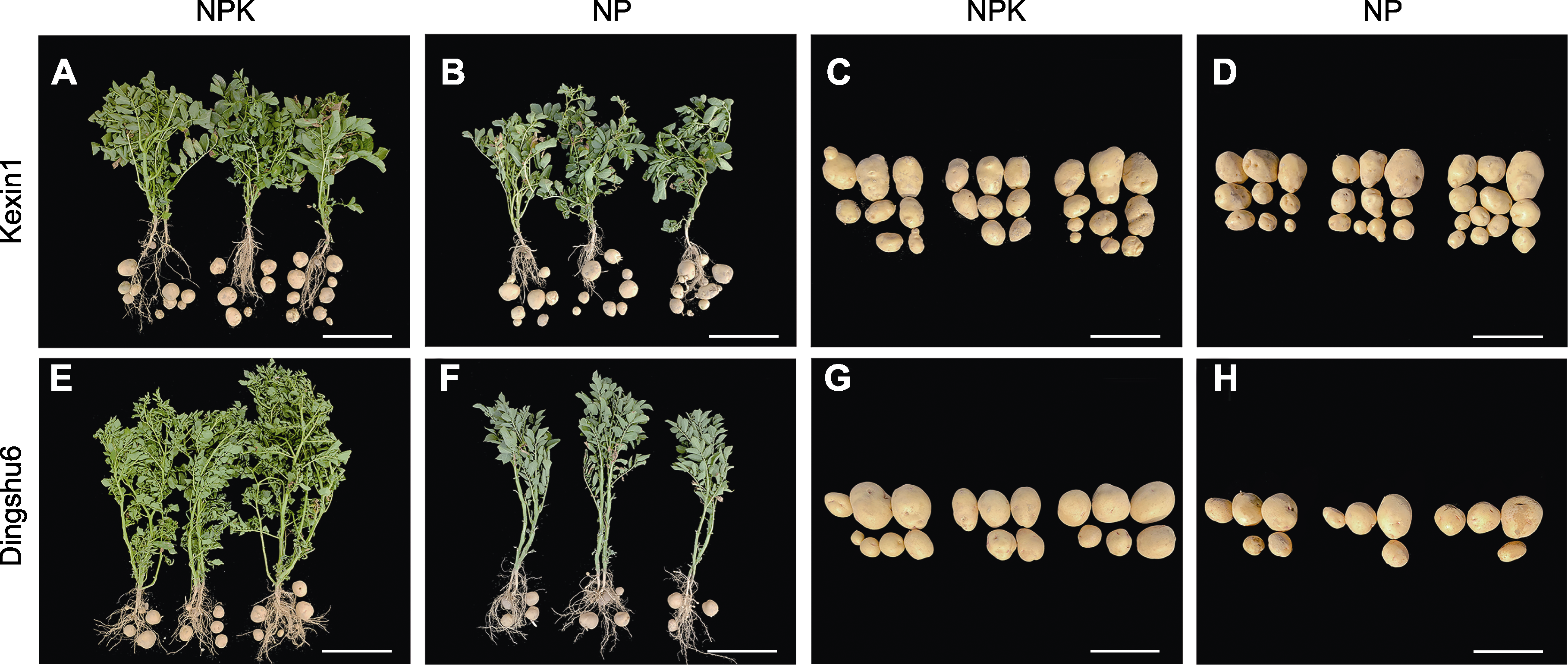
图2 Kexin1和Dingshu6的生长状况与产量表现 (A), (B), (E), (F) Kexin1和Dingshu6播后80天时的生长状况(bars=26.5 cm); (C), (D), (G), (H) Kexin1和Dingshu6收获时的产量表现(bars=15 cm)。NPK: 正常钾处理; NP: 低钾处理
Figure 2 Growth status and yield performance of Kexin1 and Dingshu6 (A), (B), (E), (F) Growth conditions of Kexin1 and Dingshu6 at 80 days after sowing (bars=26.5 cm); (C), (D), (G), (H) Yield performance of Kexin1 and Dingshu6 (bars=15 cm). NPK: Normal potassium treatment; NP: Low potassium treatment
| Cultivars | Primary value | Regression | Differen- ce | Evaluation accuracy (%) | Cultivars | Primary value | Regression | Differen- ce | Evaluation accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helan15 | 0.662 | 0.664 | -0.002 | 100.26 | Longshu14 | 0.440 | 0.439 | 0.001 | 99.73 |
| Favorita | 0.700 | 0.701 | -0.001 | 100.18 | Dingshu6 | 0.161 | 0.150 | 0.011 | 93.11 |
| Xingjia2 | 0.686 | 0.688 | -0.001 | 100.21 | Longshu22 | 0.317 | 0.322 | -0.005 | 101.70 |
| Xuechuan8 | 0.445 | 0.443 | 0.001 | 99.68 | Qingshu9 | 0.385 | 0.376 | 0.009 | 97.54 |
| Longshu20 | 0.634 | 0.631 | 0.003 | 99.54 | L0109-4 | 0.327 | 0.333 | -0.005 | 101.66 |
| Xisen6 | 0.693 | 0.696 | -0.002 | 100.36 | Jizhang12(W) | 0.609 | 0.612 | -0.003 | 100.49 |
| Lucinda | 0.743 | 0.737 | 0.005 | 99.26 | Longshu10 | 0.369 | 0.369 | 0.000 | 99.89 |
| Atlantic | 0.205 | 0.204 | 0.001 | 99.69 | Heijingang | 0.477 | 0.481 | -0.004 | 100.77 |
| Chuanyin2 | 0.656 | 0.658 | -0.002 | 100.37 | Jiuen1 | 0.578 | 0.578 | 0.000 | 100.01 |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 0.550 | 0.551 | 0.000 | 100.08 | Longshu19 | 0.575 | 0.575 | -0.001 | 100.10 |
| Lishu6 | 0.381 | 0.384 | -0.003 | 100.69 | Qingshu10 | 0.412 | 0.413 | -0.001 | 100.23 |
| Dingshu4 | 0.502 | 0.501 | 0.000 | 99.96 | Kexin1 | 0.697 | 0.684 | 0.013 | 98.17 |
| Xindaping | 0.239 | 0.243 | -0.003 | 101.44 | Dingshu3 | 0.625 | 0.631 | -0.006 | 100.95 |
| Longshu7 | 0.290 | 0.296 | -0.006 | 102.15 | Zhuangshu3 | 0.347 | 0.347 | 0.000 | 100.05 |
| Huasong7 | 0.185 | 0.184 | 0.000 | 99.83 | Longshu3 | 0.428 | 0.428 | 0.000 | 99.95 |
表8 回归方程的估计精度分析
Table 8 Analysis of evaluation accuracy of equation
| Cultivars | Primary value | Regression | Differen- ce | Evaluation accuracy (%) | Cultivars | Primary value | Regression | Differen- ce | Evaluation accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helan15 | 0.662 | 0.664 | -0.002 | 100.26 | Longshu14 | 0.440 | 0.439 | 0.001 | 99.73 |
| Favorita | 0.700 | 0.701 | -0.001 | 100.18 | Dingshu6 | 0.161 | 0.150 | 0.011 | 93.11 |
| Xingjia2 | 0.686 | 0.688 | -0.001 | 100.21 | Longshu22 | 0.317 | 0.322 | -0.005 | 101.70 |
| Xuechuan8 | 0.445 | 0.443 | 0.001 | 99.68 | Qingshu9 | 0.385 | 0.376 | 0.009 | 97.54 |
| Longshu20 | 0.634 | 0.631 | 0.003 | 99.54 | L0109-4 | 0.327 | 0.333 | -0.005 | 101.66 |
| Xisen6 | 0.693 | 0.696 | -0.002 | 100.36 | Jizhang12(W) | 0.609 | 0.612 | -0.003 | 100.49 |
| Lucinda | 0.743 | 0.737 | 0.005 | 99.26 | Longshu10 | 0.369 | 0.369 | 0.000 | 99.89 |
| Atlantic | 0.205 | 0.204 | 0.001 | 99.69 | Heijingang | 0.477 | 0.481 | -0.004 | 100.77 |
| Chuanyin2 | 0.656 | 0.658 | -0.002 | 100.37 | Jiuen1 | 0.578 | 0.578 | 0.000 | 100.01 |
| Jizhang12(Y) | 0.550 | 0.551 | 0.000 | 100.08 | Longshu19 | 0.575 | 0.575 | -0.001 | 100.10 |
| Lishu6 | 0.381 | 0.384 | -0.003 | 100.69 | Qingshu10 | 0.412 | 0.413 | -0.001 | 100.23 |
| Dingshu4 | 0.502 | 0.501 | 0.000 | 99.96 | Kexin1 | 0.697 | 0.684 | 0.013 | 98.17 |
| Xindaping | 0.239 | 0.243 | -0.003 | 101.44 | Dingshu3 | 0.625 | 0.631 | -0.006 | 100.95 |
| Longshu7 | 0.290 | 0.296 | -0.006 | 102.15 | Zhuangshu3 | 0.347 | 0.347 | 0.000 | 100.05 |
| Huasong7 | 0.185 | 0.184 | 0.000 | 99.83 | Longshu3 | 0.428 | 0.428 | 0.000 | 99.95 |
| Cluster | Average of low potassium tolerance coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X5 | X4 | X3 | X8 | X1 | X6 | X9 | X2 | |
| First cluster | 1.20±0.02 a | 1.40±0.08 a | 1.48±0.13 a | 1.16±0.04 a | 1.42±0.13 a | 1.13±0.07 a | 1.13±0.02 a | 0.93±0.10 a |
| Second cluster | 1.08±0.06 a | 1.30±0.13 a | 1.36±0.12 a | 1.05±0.05 ab | 1.36±0.07 a | 1.06±0.10 ab | 1.07±0.07 ab | 0.95±0.10 a |
| Third cluster | 0.89±0.08 b | 1.10±0.12 ab | 1.52±0.08 a | 0.87±0.04 bc | 1.41±0.23 a | 0.82±0.08 bc | 1.09±0.20 a | 0.86±0.01 a |
| Fourth cluster | 0.80±0.04 bc | 1.10±0.12 ab | 1.20±0.09 ab | 0.86±0.06 c | 1.36±0.08 a | 0.82±0.06 bc | 0.85±0.09 abc | 0.92±0.08 a |
| Fifth cluster | 0.70±0.05 bc | 1.00±0.16 ab | 1.14±0.10 ab | 0.76±0.03 c | 1.31±0.14 a | 0.66±0.07 c | 0.79±0.08 bc | 0.86±0.07 a |
| Sixth cluster | 0.68±0.07 c | 0.74±0.11 b | 0.91±0.06 b | 0.70±0.06 c | 1.07±0.19 a | 0.55±0.09 c | 0.72±0.06 c | 1.09±0.14 a |
表9 聚类结果中各类别的特征描述
Table 9 Characteristic description of each cluster in hierarchical cluster result
| Cluster | Average of low potassium tolerance coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X5 | X4 | X3 | X8 | X1 | X6 | X9 | X2 | |
| First cluster | 1.20±0.02 a | 1.40±0.08 a | 1.48±0.13 a | 1.16±0.04 a | 1.42±0.13 a | 1.13±0.07 a | 1.13±0.02 a | 0.93±0.10 a |
| Second cluster | 1.08±0.06 a | 1.30±0.13 a | 1.36±0.12 a | 1.05±0.05 ab | 1.36±0.07 a | 1.06±0.10 ab | 1.07±0.07 ab | 0.95±0.10 a |
| Third cluster | 0.89±0.08 b | 1.10±0.12 ab | 1.52±0.08 a | 0.87±0.04 bc | 1.41±0.23 a | 0.82±0.08 bc | 1.09±0.20 a | 0.86±0.01 a |
| Fourth cluster | 0.80±0.04 bc | 1.10±0.12 ab | 1.20±0.09 ab | 0.86±0.06 c | 1.36±0.08 a | 0.82±0.06 bc | 0.85±0.09 abc | 0.92±0.08 a |
| Fifth cluster | 0.70±0.05 bc | 1.00±0.16 ab | 1.14±0.10 ab | 0.76±0.03 c | 1.31±0.14 a | 0.66±0.07 c | 0.79±0.08 bc | 0.86±0.07 a |
| Sixth cluster | 0.68±0.07 c | 0.74±0.11 b | 0.91±0.06 b | 0.70±0.06 c | 1.07±0.19 a | 0.55±0.09 c | 0.72±0.06 c | 1.09±0.14 a |
| [1] | 杜培兵, 张永福, 白小东, 范向斌, 杨春, 齐海英, 王兴涛, 毛向红, 朱智慧 (2019). 主成分分析和隶属函数法对马铃薯品种抗旱性的评价. 种子 38(8), 120-126. |
| [2] |
段惠敏, 王郁, 程李香, 撒刚, 夏露露, 张峰 (2023). 马铃薯块茎末端糖化适应性、稳定性及薯条加工型品种(系)筛选. 作物学报 49, 262-276.
DOI |
| [3] | 国家统计局 (2021). 中国统计年鉴. 北京: 中国统计出版社. |
| [4] |
郭书亚, 艾金祥, 陈虹宇, 邵烨瑶, 汪妍, 王倩, 叶怡彤, 张雅婷, 丁哲晓, 吴昊辰, 吴玉环, 张建新, 饶米德, 刘鹏 (2022). 基于主成分-聚类-逐步回归分析构建番茄苗期耐铝性综合评价体系. 植物学报 57, 479-489.
DOI |
| [5] | 韩新爱, 杨先泉, 杨世民, 王西瑶 (2007). 不同马铃薯品种(系)钾营养特性的差异. 四川农业大学学报 25, 392-396. |
| [6] | 颉瑞霞, 张小川, 吴林科, 郭志乾, 张国辉, 余帮强 (2020). 马铃薯种质资源主要品质性状分析与评价. 分子植物育种 18, 6828-6836. |
| [7] |
李登高, 林睿, 穆青慧, 周娜, 张焱如, 白薇 (2022). 马铃薯StCRKs基因家族的鉴定分析及响应逆境信号的表达. 植物研究 42, 1033-1043.
DOI |
| [8] | 李晓云, 赵勇, 王杰, 杨学芳, 张树华, 杨学举 (2014). 不同小麦品系耐低钾性的综合评价. 麦类作物学报 34, 842-846. |
| [9] | 李忠旺, 陈玉梁, 罗俊杰, 石有太, 冯克云, 陈子萱 (2017). 棉花抗旱品种筛选鉴定及抗旱性综合评价方法. 干旱地区农业研究 35, 240-247. |
| [10] | 刘翠霞 (2006). 不同品种小麦耐低钾能力差异及筛选指标研究. 硕士论文. 郑州: 河南农业大学. pp. 12-36. |
| [11] | 鲁如坤 (1989). 我国土壤氮、磷、钾的基本状况. 土壤学报 26, 280-286. |
| [12] | 禄兴丽, 段雅欣, 李闪闪, 岳衡, 吴佳瑞, 刘继虎, 康建宏 (2021). 覆膜对半干旱地区马铃薯生长生理性状及作物产量的影响. 植物生理学报 57, 1582-1594. |
| [13] | 罗兰, 邓振鹏, 吕长文 (2021). 不同基因型马铃薯钾素吸收与利用效率的差异. 中国马铃薯 35, 424-431. |
| [14] |
罗曦, 吴方喜, 林强, 连玲, 何炜, 谢鸿光, 陈丽萍, 朱永生, 魏毅东, 蒋家焕, 谢华安, 张建福 (2019). 水稻苗期耐低钾品种筛选及相关性状的QTL定位. 植物遗传资源学报 20, 1262-1270.
DOI |
| [15] | 穆俊祥, 曹兴明, 弓建国, 梁建功, 郭美兰 (2009). 氮磷钾和有机肥配合施用对马铃薯淀粉含量和产量的影响. 土壤 41, 844-848. |
| [16] |
权月伟, 李喜焕, 常文锁, 张彩英 (2011). 大豆耐低钾种质资源筛选研究. 华北农学报 26(S1), 51-55.
DOI |
| [17] |
史佳文, 潘峰, 陈若男, 石瑛 (2019). 不同马铃薯品种块茎钾含量与相关生理特性的钾素响应度差异. 华北农学报 34 (S1), 78-84.
DOI |
| [18] | 孙慧, 王亚玲, 刘易, 李江涛, 邢斌德, 罗正乾, 冯怀章 (2021). 新疆地区马铃薯品种抗旱性比较及筛选. 西北农业学报 30, 1787-1796. |
| [19] |
唐忠厚, 张允刚, 魏猛, 陈晓光, 史新敏, 张爱君, 李洪民, 丁艳锋 (2014). 耐低钾和钾高效型甘薯品种(系)的筛选及评价指标. 作物学报 40, 542-549.
DOI |
| [20] | 万凯旋 (2020). 谷子耐低钾品种筛选及其生理生化研究. 硕士论文. 晋中: 山西农业大学. pp. 11-48. |
| [21] |
王吉祥, 宫焕宇, 屠祥建, 郭侲洐, 赵嘉楠, 沈健, 栗振义, 孙娟 (2021). 耐亚磷酸盐紫花苜蓿品种筛选及评价指标的鉴定. 草业学报 30, 186-199.
DOI |
| [22] |
王晓斌, 王瀚, 胡开明, 李亚杰, 秦天元, 曾文婕, 李鑫, 张楷露, 张俊莲, 白江平 (2017). 基于层次分析法和GGE双标图对引进马铃薯种质资源的综合评价. 植物遗传资源学报 18, 1067-1078.
DOI |
| [23] | 王旭东, 于振文, 王东 (2003). 钾对小麦茎和叶鞘碳水化合物含量及籽粒淀粉积累的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报 9, 57-62. |
| [24] | 王燕, 杨克俭, 龚学臣, 祁利潘, 冯琰, 王磊, 刘畅, 尹江 (2016). 全国主栽马铃薯品种的抗旱性评价. 种子 35(9), 82-85. |
| [25] | 王毅, 武维华 (2009). 植物钾营养高效分子遗传机制. 植物学报 44, 27-36. |
| [26] | 熊增华, 王兴富, 王石军, 薛红魁 (2021). 我国硝酸钾产业发展现状与展望. 化工矿物与加工 50(5), 49-53. |
| [27] |
许国春, 罗文彬, 李华伟, 许泳清, 纪荣昌, 张鸿, 邱思鑫, 汤浩 (2021). 马铃薯叶片光合效率遗传变异分析及高光效种质筛选. 园艺学报 48, 2239-2250.
DOI |
| [28] | 徐丽娟, 王倩, 郑春花, 隋炯明, 刘光亮, 刘贯山 (2015). 烟草幼苗期耐低钾突变体的筛选及验证. 植物生理学报 51, 977-982. |
| [29] |
杨春婷, 张永清, 马星星, 陈伟, 董璐, 张楚, 路之娟 (2018). 苦荞耐低磷基因型筛选及评价指标的鉴定. 应用生态学报 29, 2997-3007.
DOI |
| [30] |
于国红, 刘朋程, 李磊, 李明哲, 崔海英, 郝洪波, 郭安强 (2022). 不同基因型马铃薯对干旱胁迫的生理响应. 生物技术通报 38(5), 56-63.
DOI |
| [31] | 岳晓甜, 曲峻岭, 郭燕枝 (2016). 中国马铃薯产业现状、影响因素及对策初探. 农业展望 12(11), 55-58. |
| [32] | 张福锁, 王激清, 张卫峰, 崔振岭, 马文奇, 陈新平, 江荣风 (2008). 中国主要粮食作物肥料利用率现状与提高途径. 土壤学报 45, 915-924. |
| [33] | 张婷婷, 于崧, 于立河, 李琳, 金珊珊, 郭建华, 张静 (2016). 松嫩平原春小麦耐盐碱性鉴定及品种(系)筛选. 麦类作物学报 36, 1008-1019. |
| [34] | 张晓玲, 吕慧峰, 王菲, 唐静, 王正银, 毛国庆, 卢祥言, 沈云树, 许良兵, 朱斌 (2012). 重庆马铃薯土壤养分分级研究. 中国农学通报 28(21), 70-75. |
| [35] |
张正社, 牛娜, 宋瑜龙, 马守才, 张改生, 王军卫 (2017). 耐低钾山羊草基因型的筛选与鉴定. 草地学报 25, 832-838.
DOI |
| [36] | 赵霞, 杨豫龙, 王浩然, 穆心愿, 马智艳, 唐保军, 刘天学, 李潮海 (2019). 玉米苗期氮、磷、钾养分吸收利用效率研究. 玉米科学 27(4), 154-161, 166. |
| [37] | 赵媛媛, 石瑛, 张丽莉 (2018). 马铃薯抗旱种质资源的评价. 分子植物育种 16, 633-642. |
| [38] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局 (2017a). 食品安全国家标准食品中淀粉的测定(GB 5009.9-2016). 北京: 中国标准出版社. pp. 1-5. |
| [39] | 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局 (2017b). 食品安全国家标准食品中蛋白质的测定(GB 5009.5-2016). 北京: 中国标准出版社. pp. 1-3. |
| [40] | 邹春琴, 李振声, 李继云 (2002). 钾利用效率不同的小麦品种各生育期钾营养特点. 中国农业科学 35, 340-344. |
| [41] |
Busse JS, Wiberley-Bradford AE, Bethke PC (2019). Transient heat stress during tuber development alters post-harvest carbohydrate composition and decreases processing quality of chipping potatoes. J Sci Food Agric 99, 2579-2588.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Cai J, Chen L, Qu HY, Lian J, Liu W, Hu YB, Xu GH (2012). Alteration of nutrient allocation and transporter genes expression in rice under N, P, K, and Mg deficiencies. Acta Physiol Plant 34, 939-946.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Deng ZP, Yang J, Chen YY, Han HH, Liu X, Yi XP, Wang JC, Lyu CW (2021). Screening high potassium efficiency potato genotypes and physiological responses at different potassium levels. Not Bot Horti Agrobo 49, 12190.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Grudzińska M, Boguszewska Mańkowska D, Zarzyńska K (2022). Drought stress during the growing season: changes in reducing sugars, starch content and respiration rate during storage of two potato cultivars differing in drought sensitivity. J Agron Crop Sci 208, 609-620.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Kanai S, Ohkura K, Adu-Gyamfi JJ, Mohapatra PK, Nguyen NT, Saneoka H, Fujita K (2007). Depression of sink activity precedes the inhibition of biomass production in tomato plants subjected to potassium deficiency stress. J Exp Bot 58, 2917-2928.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Liu X, Chen L, Shi WL, Xu X, Li ZJ, Liu TF, He Q, Xie CH, Nie BH, Song BT (2021). Comparative transcriptome reveals distinct starch-sugar interconversion patterns in potato genotypes contrasting for cold-induced sweetening capacity. Food Chem 334, 127550.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Qin JH, Bian CS, Liu JG, Zhang JJ, Jin LP (2019). An efficient greenhouse method to screen potato genotypes for drought tolerance. Sci Hortic 253, 61-69.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张琨, 钱敏, 汪阳, 李志华, 孔令娜, 李明洋, 马瑾煜, 努尔艾合麦提•玉苏普, 陈乙一, 成沂芮, 张焕仕, 覃凤飞, 渠晖. 紫花苜蓿耐阴性综合评价及其鉴定指标的筛选[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 773-787. |
| [2] | 范惠玲, 路妍, 金文海, 王慧, 彭小星, 武学霞, 刘玉皎. 基于根系表型性状的蚕豆耐盐碱性鉴定与综合评价(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 204-217. |
| [3] | 张锋, Richard Dormatey, 刘寅笃, 李成举, 王云姣, 张春利, 张莹, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 毕真真, 刘玉汇, 白江平, 孙超. 耐亚磷酸盐马铃薯的筛选与评价[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 544-557. |
| [4] | 廖美哲, 张宗文, 白可喻. 中国农业生态系统多样性保护研究现状与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31(7): 23017-. |
| [5] | 郭书亚, 艾金祥, 陈虹宇, 邵烨瑶, 汪妍, 王倩, 叶怡彤, 张雅婷, 丁哲晓, 吴昊辰, 吴玉环, 张建新, 饶米德, 刘鹏. 基于主成分-聚类-逐步回归分析构建番茄苗期耐铝性综合评价体系[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 479-489. |
| [6] | 翟琼, 陈容钦, 梁晓华, 曾楚淳, 胡博, 李玲, 李晓云. 一种花生快速遗传转化方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 327-339. |
| [7] | 何雨龙, 王佳歌, 赵珊珊, 高锦, 常英英, 赵喜亭, 聂碧华, 杨清香, 张江利, 李明军. 马铃薯Y病毒RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a检测技术体系的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 308-319. |
| [8] | 许操. 而今迈步从头越: 马铃薯育种跨入“有种”时代[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 516-519. |
| [9] | 刘勋,张娇,沈昱辰,谢德斌,李宏利,李春明,易小平,赵勇,唐道彬,吕长文,王季春. 基于光合系统参数建立马铃薯耐荫性综合评价体系[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 360-370. |
| [10] | 刘国红, 刘波, 车建美, 陈倩倩, 林乃铨, 崔卫东. 新疆伊犁马铃薯根际芽胞杆菌纯培养多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(8): 856-863. |
| [11] | 方琦, 董家红, 郑宽瑜, 张仲凯. 番茄环纹斑点病毒与马铃薯Y病毒复合侵染烟草的细胞病理特征[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(6): 704-709. |
| [12] | 刘成刚, 薛建辉. 喀斯特石漠化山地不同类型人工林土壤的基本性质和综合评价[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(10): 1050-1060. |
| [13] | 张智猛, 万书波, 戴良香, 宋文武, 陈静, 石运庆. 花生抗旱性鉴定指标的筛选与评价[J]. 植物生态学报, 2011, 35(1): 100-109. |
| [14] | 许自成, 黎妍妍, 肖汉乾, 王林. 湘南烟区生态因素与烤烟质量的综合评价[J]. 植物生态学报, 2008, 32(1): 226-234. |
| [15] | 高清竹, 何立环, 江源, 杨劼, 康慕谊, 赵云龙. 黄河中游砒砂岩地区土地利用对生物多样性的影响评价[J]. 生物多样性, 2006, 14(1): 41-47. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||