

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 535-547.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22081 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22081
武棒棒1, 郝宇琼2, 杨淑斌1, 黄雨茜1, 关攀锋3, 郑兴卫2, 赵佳佳2, 乔玲2, 李晓华2, 刘维仲1( ), 郑军2(
), 郑军2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-20
接受日期:2022-09-19
出版日期:2023-07-01
发布日期:2022-11-11
通讯作者:
*E-mail: liuwzh@sxnu.edu.cn;sxnkyzj@126.com
作者简介:† 共同第一作者。
基金资助:
Bangbang Wu1, Yuqiong Hao2, Shubin Yang1, Yuxi Huang1, Panfeng Guan3, Xingwei Zheng2, Jiajia Zhao2, Ling Qiao2, Xiaohua Li2, Weizhong Liu1( ), Jun Zheng2(
), Jun Zheng2( )
)
Received:2022-04-20
Accepted:2022-09-19
Online:2023-07-01
Published:2022-11-11
Contact:
*E-mail: liuwzh@sxnu.edu.cn;sxnkyzj@126.com
About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper.
摘要: 叶黄素在保护视力、预防糖尿病、心血管硬化和癌症等方面具有良好功效。利用小麦(Triticum aestivum)进行叶黄素的生物强化逐渐引起人们的重视。以3种环境下种植的194份山西小麦为材料, 采用有机溶剂浸提法提取叶黄素, 利用高效液相色谱法测定不同种质的叶黄素含量, 分析小麦叶黄素含量的广义遗传力, 及其与籽粒颜色、冬春性、地域分布、品种类型和主要农艺性状的关系, 并通过全基因组关联分析挖掘叶黄素含量相关的遗传位点。结果表明, 山西小麦品种间叶黄素含量变异范围较广, 变异系数为33.12%-48.57%, 基因型是影响叶黄素含量的主要因素, 3种环境下小麦叶黄素含量范围分别为0.67-4.03、0.16-5.05和0.16-3.63 μg·g-1; 冬性小麦品种的平均含量高于春性品种, 水地品种平均含量高于旱地品种, 籽粒颜色与育种年代对叶黄素含量无显著影响; 抽穗期、株高和千粒重与叶黄素含量呈显著负相关, 其它农艺性状对叶黄素均无明显影响; 全基因组关联分析在1B、3A和7A染色体上发现4个与叶黄素含量相关的主效位点, 其中QLuc.3A和QLuc.7A.1是影响叶黄素含量的新位点。研究结果可为小麦叶黄素生物强化品种的选育和栽培提供有价值的信息。
武棒棒, 郝宇琼, 杨淑斌, 黄雨茜, 关攀锋, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 乔玲, 李晓华, 刘维仲, 郑军. 山西小麦籽粒叶黄素含量变异及遗传特性分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 535-547.
Bangbang Wu, Yuqiong Hao, Shubin Yang, Yuxi Huang, Panfeng Guan, Xingwei Zheng, Jiajia Zhao, Ling Qiao, Xiaohua Li, Weizhong Liu, Jun Zheng. Evaluation and Genetic Variation of Grain Lutein Contents in Common Wheat From Shanxi. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 535-547.
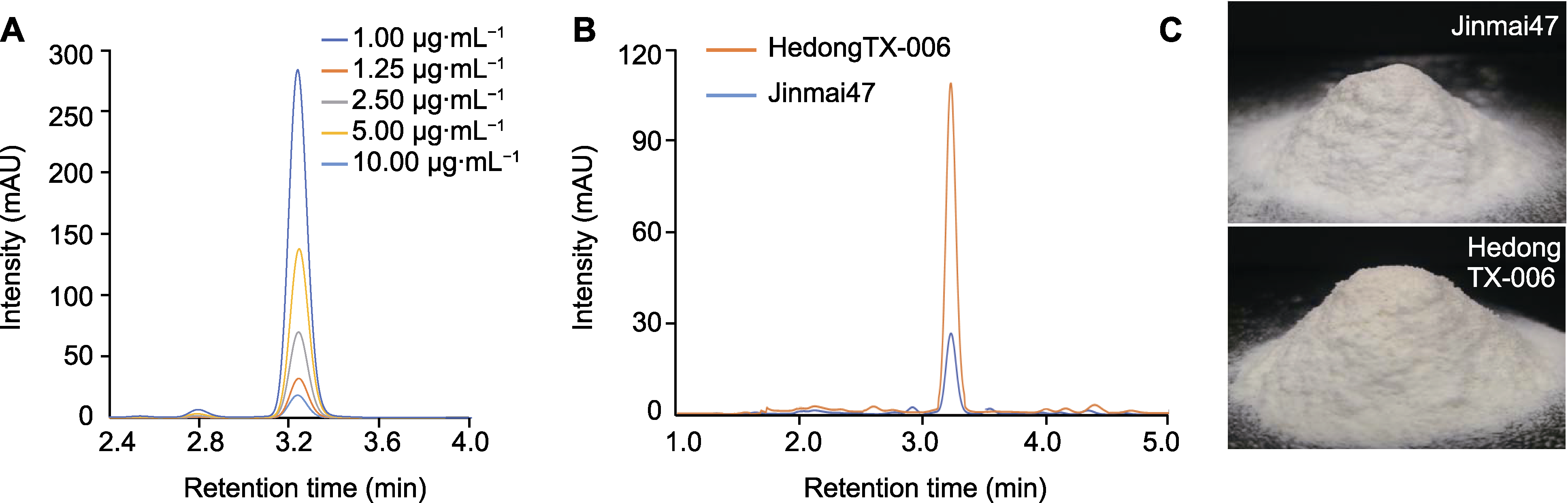
图1 HPLC色谱图及差异品种的面粉实物图 (A) 不同浓度标样的HPLC峰图; (B) 小麦样品HPLC峰图; (C) 面粉实物图
Figure 1 HPLC chromatogram of lutein from standards of different concentrations and flour of samples (A) HPLC peak plots of lutein from standards of different concentrations; (B) HPLC peak plots of lutein from tested wheat samples; (C) Flour of samples
| Accessions | Sample contents (μg·g-1) | Added (μg) | Detection (μg·g-1) | Recove- ries (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinmai47 | 1.22 | 3 | 4.06 | 96.33 |
| Jinmai98 | 2.36 | 5 | 7.27 | 98.76 |
| Jinmai84 | 1.85 | 4 | 5.72 | 97.81 |
| Jinmai919 | 2.38 | 5 | 7.25 | 98.24 |
表1 小麦样品叶黄素的加标回收率
Table 1 The spiked recoveries of lutein content with wheat genotypes
| Accessions | Sample contents (μg·g-1) | Added (μg) | Detection (μg·g-1) | Recove- ries (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinmai47 | 1.22 | 3 | 4.06 | 96.33 |
| Jinmai98 | 2.36 | 5 | 7.27 | 98.76 |
| Jinmai84 | 1.85 | 4 | 5.72 | 97.81 |
| Jinmai919 | 2.38 | 5 | 7.25 | 98.24 |
| Accessions | Samples contents (μg·g-1) | Average (μg·g-1) | RSD (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Jinmai47 | 1.34 | 1.37 | 1.32 | 1.25 | 1.28 | 1.31 | 3.25 |
| Jinmai98 | 2.76 | 2.64 | 2.93 | 2.99 | 2.85 | 2.83 | 4.38 |
| Jinmai84 | 1.89 | 1.97 | 1.95 | 1.74 | 1.85 | 1.88 | 4.36 |
| Jinmai919 | 2.53 | 2.66 | 2.37 | 2.49 | 2.59 | 2.53 | 3.86 |
表2 小麦样品叶黄素含量的相对标准偏差(n=5)
Table 2 Relative standard deviation of lutein content with wheat genotypes (n=5)
| Accessions | Samples contents (μg·g-1) | Average (μg·g-1) | RSD (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Jinmai47 | 1.34 | 1.37 | 1.32 | 1.25 | 1.28 | 1.31 | 3.25 |
| Jinmai98 | 2.76 | 2.64 | 2.93 | 2.99 | 2.85 | 2.83 | 4.38 |
| Jinmai84 | 1.89 | 1.97 | 1.95 | 1.74 | 1.85 | 1.88 | 4.36 |
| Jinmai919 | 2.53 | 2.66 | 2.37 | 2.49 | 2.59 | 2.53 | 3.86 |
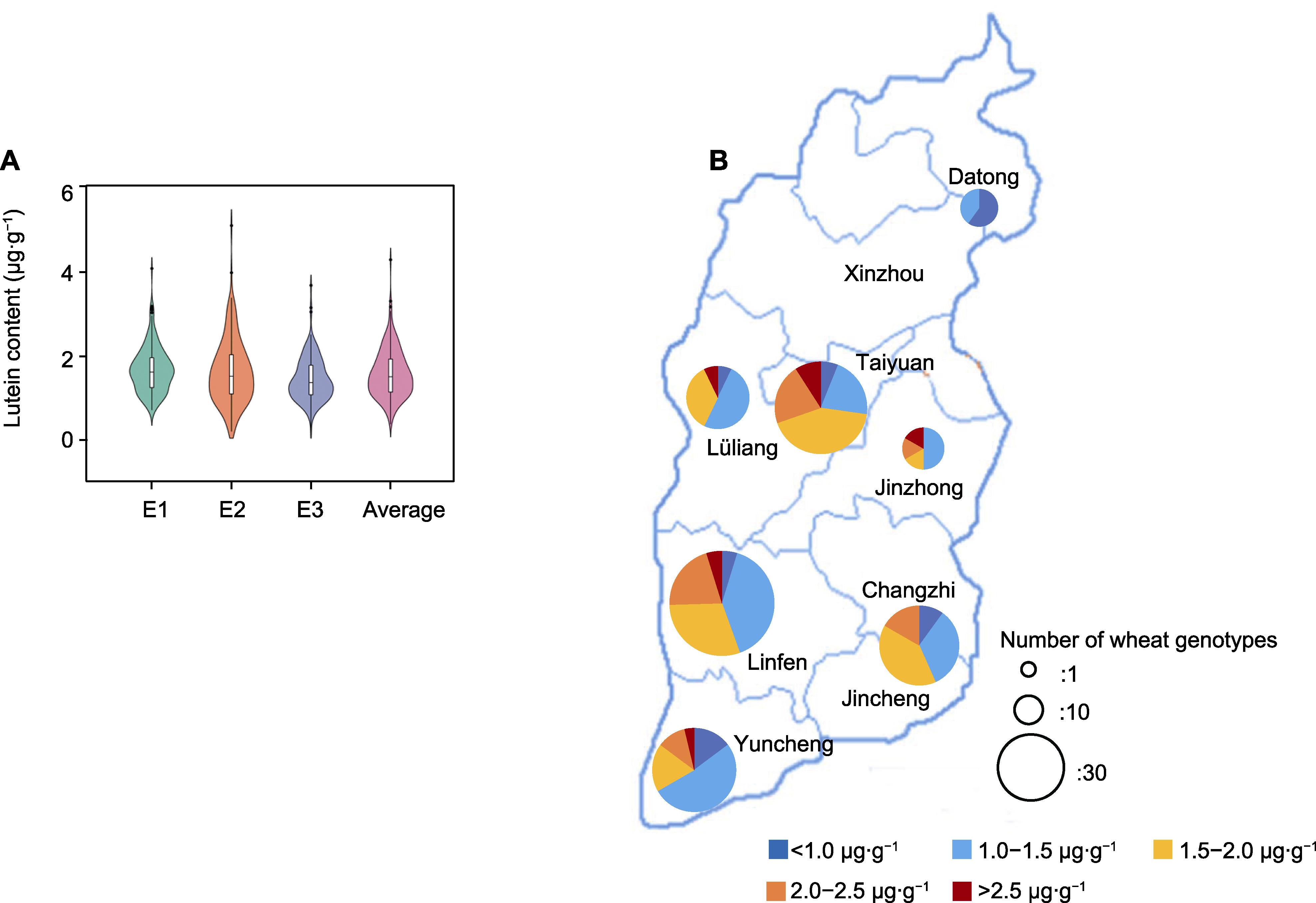
图2 不同环境小麦品种的叶黄素含量水平及地域分布 (A) 3种环境下小麦品种的叶黄素含量分布; (B) 不同地域品种的叶黄素含量分布。E1、E2和E3同表3。
Figure 2 The lutein contents and the effect of geographic distribution of wheat accessions from different environments (A) Lutein contents of wheat genotypes under different environments; (B) Effect of geographic distribution on lutein content. E1, E2 and E3 are the same as shown in Table 3.
| Environment | Number of wheat genotypes grouped by lutein contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1.0 (μg·g-1) | 1.0-1.5 (μg·g-1) | 1.5-2.0 (μg·g-1) | 2.0-2.5 (μg·g-1) | >2.5 (μg·g-1) | |
| E1 | 19 | 58 | 68 | 29 | 11 |
| E2 | 41 | 49 | 46 | 19 | 24 |
| E3 | 41 | 74 | 42 | 19 | 3 |
表3 不同环境下山西小麦叶黄素含量分组
Table 3 Wheat genotypes grouped by lutein content under different environments
| Environment | Number of wheat genotypes grouped by lutein contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1.0 (μg·g-1) | 1.0-1.5 (μg·g-1) | 1.5-2.0 (μg·g-1) | 2.0-2.5 (μg·g-1) | >2.5 (μg·g-1) | |
| E1 | 19 | 58 | 68 | 29 | 11 |
| E2 | 41 | 49 | 46 | 19 | 24 |
| E3 | 41 | 74 | 42 | 19 | 3 |
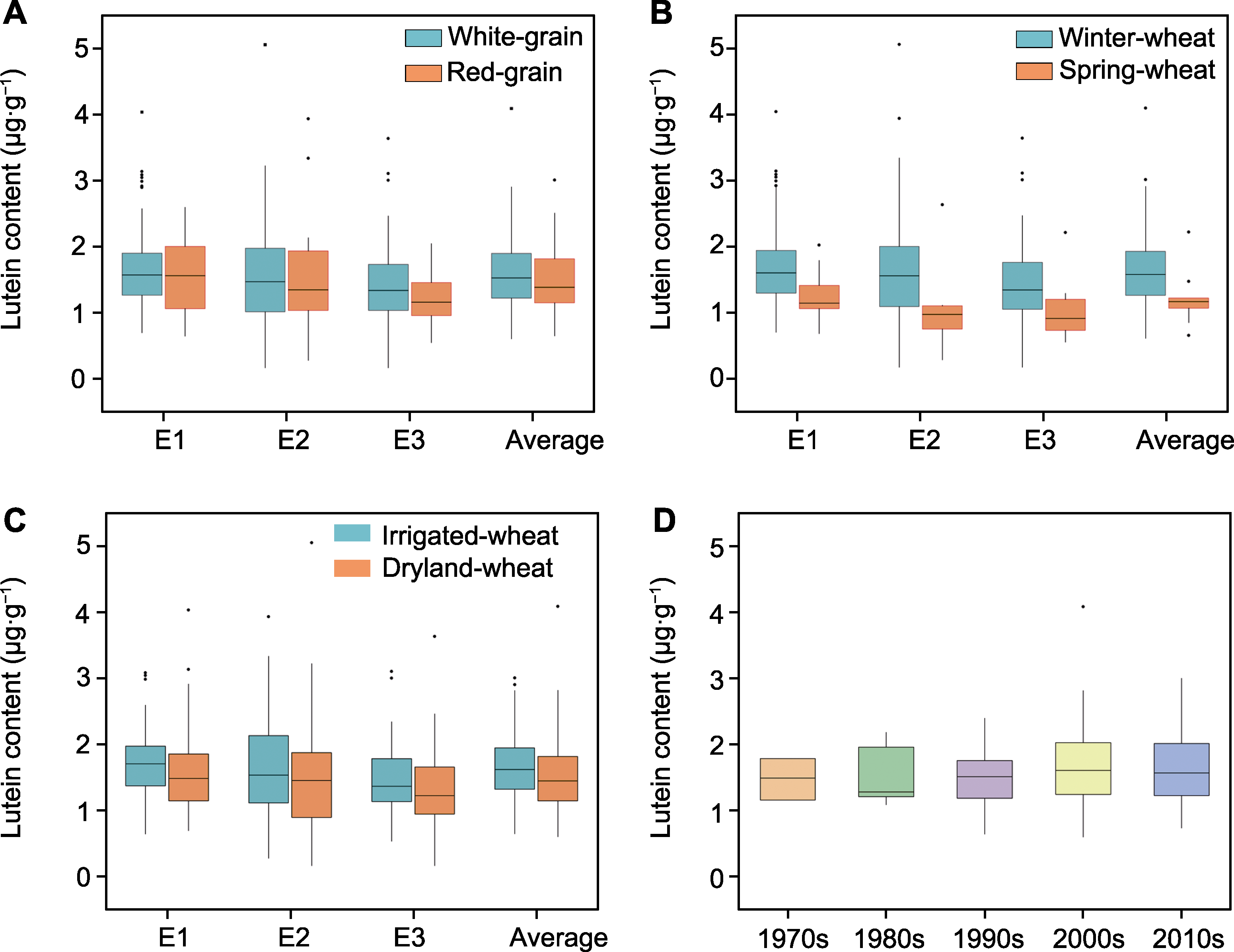
图3 不同因素(粒色(A)、冬春性(B)、水旱品种类型(C)和育成年代(D))对小麦叶黄素含量的影响 E1、E2和E3同表3. *P<0.05; **P<0.01
Figure 3 Lutein contents effected by grain color (A), winter/spring types (B), irrigated/dryland types (C) and released years (D) E1, E2 and E3 are the same as shown in Table 3. *P<0.05; **P<0.01
| Environment | pH | SL | NS | SIU | HD | FLL | FLW | SN | GNS | GL | GW | GT | TKW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | -0.21* | -0.12 | -0.12 | -0.14 | -0.07* | -0.43 | -0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.06 | -0.18* |
| E2 | -0.20* | -0.04 | -0.16* | -0.16* | -0.10* | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | -0.16* | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| E3 | -0.19* | -0.05 | -0.13 | -0.13 | -0.04* | -0.01 | 0.01 | -0.02 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| BLUP | -0.22* | -0.07 | -0.14 | -0.16* | -0.04* | -0.03 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.10 | -0.13* | 0.07 | -0.23* |
表4 叶黄素含量与重要农艺性状的相关性
Table 4 Correlation of lutein contents and important agronomic traits
| Environment | pH | SL | NS | SIU | HD | FLL | FLW | SN | GNS | GL | GW | GT | TKW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | -0.21* | -0.12 | -0.12 | -0.14 | -0.07* | -0.43 | -0.03 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.06 | -0.18* |
| E2 | -0.20* | -0.04 | -0.16* | -0.16* | -0.10* | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | -0.16* | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| E3 | -0.19* | -0.05 | -0.13 | -0.13 | -0.04* | -0.01 | 0.01 | -0.02 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| BLUP | -0.22* | -0.07 | -0.14 | -0.16* | -0.04* | -0.03 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.10 | -0.13* | 0.07 | -0.23* |
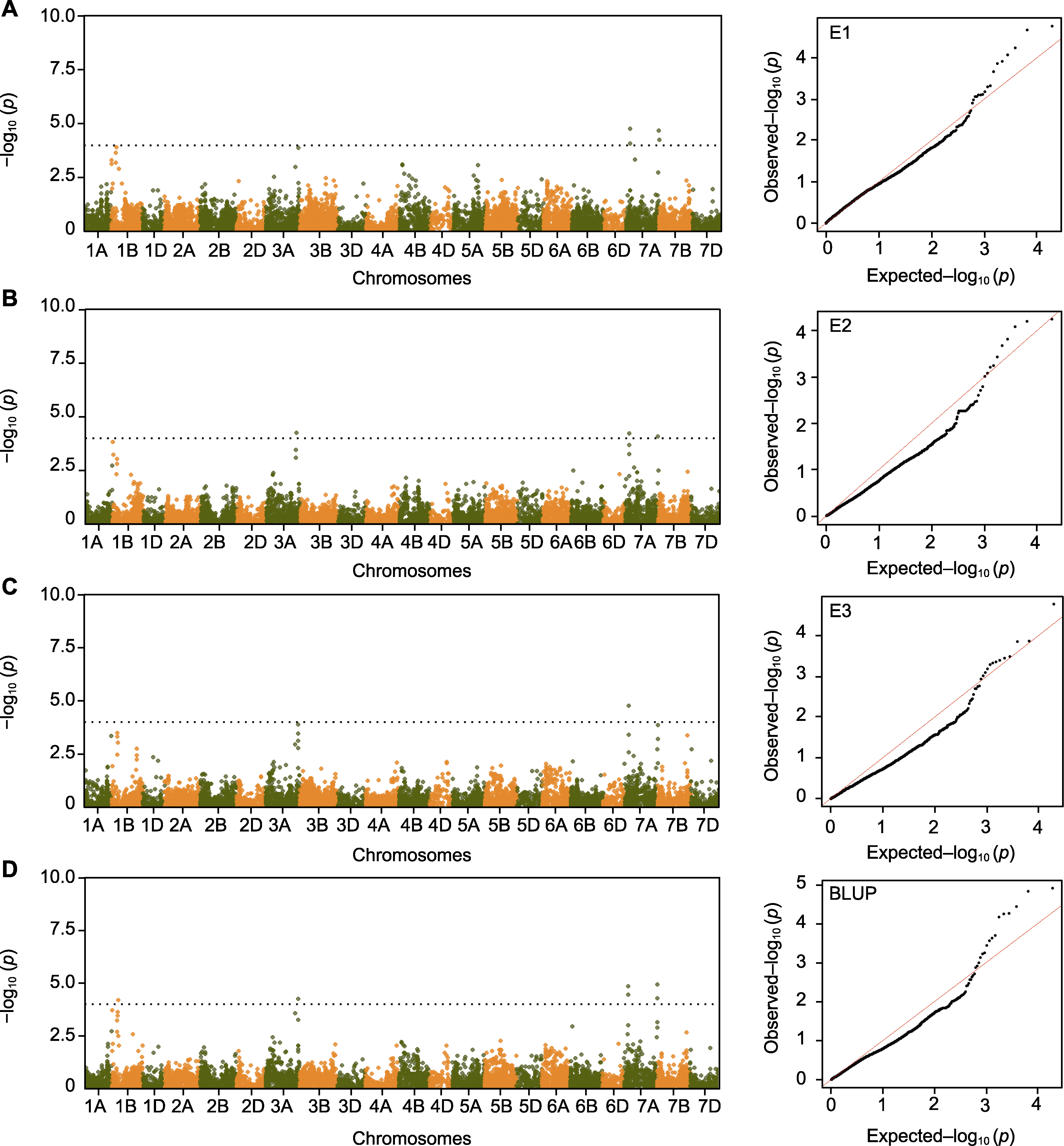
图4 不同环境中叶黄素含量的全基因组关联分析(GWAS) E1、E2和E3同表3; BLUP同表4。黑色虚线表示标记-性状关联的显著性阈值。
Figure 4 The genome-wide association study (GWAS) result of the lutein content from different environments E1, E2 and E3 are the same as shown in Table 3; BLUP is the same as shown in Table 4. The black dashed line represent the threshold for the significance of marker-trait association.
| Loci | Chr. | Interval (MB) | Environment | Peak SNP | P-value | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QLuc.1B | 1B | 135.25-158.25 | BLUP | 1B_146746777 | 6.70E-05 | 5.78 |
| QLuc.3A | 3A | 648.92-660.63 | BLUP | 3A_653919298 | 5.68E-05 | 8.47 |
| E2 | 3A_655632858 | 5.59E-05 | 7.74 | |||
| QLuc.7A.1 | 7A | 75.63-95.65 | E1, E2, BLUP | 7A_85627950 | 6.30E-05 | 6.32 |
| E1, E3, BLUP | 7A_85658392 | 4.84E-05 | 10.95 | |||
| QLuc.7A.2 | 7A | 729.71-765.19 | E2 | 7A_739708412 | 4.08E-05 | 12.28 |
| E1 | 7A_741083088 | 4.23E-05 | 10.03 | |||
| BLUP | 7A_741778749 | 4.92E-05 | 10.43 | |||
| BLUP | 7A_755187469 | 4.26E-05 | 11.21 |
表5 全基因组关联分析(GWAS)得到的性状关联位点汇总
Table 5 Summary of associated loci with traits by genome-wide association study (GWAS)
| Loci | Chr. | Interval (MB) | Environment | Peak SNP | P-value | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QLuc.1B | 1B | 135.25-158.25 | BLUP | 1B_146746777 | 6.70E-05 | 5.78 |
| QLuc.3A | 3A | 648.92-660.63 | BLUP | 3A_653919298 | 5.68E-05 | 8.47 |
| E2 | 3A_655632858 | 5.59E-05 | 7.74 | |||
| QLuc.7A.1 | 7A | 75.63-95.65 | E1, E2, BLUP | 7A_85627950 | 6.30E-05 | 6.32 |
| E1, E3, BLUP | 7A_85658392 | 4.84E-05 | 10.95 | |||
| QLuc.7A.2 | 7A | 729.71-765.19 | E2 | 7A_739708412 | 4.08E-05 | 12.28 |
| E1 | 7A_741083088 | 4.23E-05 | 10.03 | |||
| BLUP | 7A_741778749 | 4.92E-05 | 10.43 | |||
| BLUP | 7A_755187469 | 4.26E-05 | 11.21 |
| [1] |
何卿, 孙国峰, 林秦文, 李晓东, 张金政 (2018). 植物类胡萝卜素提取与分析技术研究进展. 植物学报 53, 700-709.
DOI |
| [2] | 胡瑞波, 田纪春, 吕建华 (2004). 小麦类胡萝卜素含量的稳定性及其与黄碱面条色泽性状的相关性分析. 作物学报 30, 597-601. |
| [3] |
刘敏轩, 陆平 (2013). 中国谷子育成品种维生素E含量分布规律及其与主要农艺性状和类胡萝卜素的相关性分析. 作物学报 39, 398-408.
DOI |
| [4] |
乔玲, 刘成, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 尚保华, 马小飞, 乔麟轶, 盖红梅, 姬虎太, 刘建军, 张建诚, 郑军 (2018). 小麦骨干亲本临汾5064单元型区段的遗传解析. 作物学报 44, 931-937.
DOI |
| [5] | 任得强, 吴媛媛, 周健, 姜艳, 郑文寅, 张文明, 姚大年 (2014). 小麦品种(系)籽粒类胡萝卜素含量及其与其他品质性状的相关性. 麦类作物学报 34, 868-873. |
| [6] | 孙善澄, 孙玉, 袁文业, 阎文泽, 裴自友, 张美荣, 白云凤 (1999). 优质黑粒小麦76的选育及品质分析. 作物学报 25, 50-54. |
| [7] | 汪帆, 郑文寅, 黄建华, 王冠球, 崔文礼, 张文明, 姚大年 (2012). 20个小麦品种(系)籽粒LOX活性和类胡萝卜素含量及全麦粉色泽的研究. 麦类作物学报 32, 68-73. |
| [8] | 王光瑞, 周桂英, 王瑞 (1997). 焙烤品质与面团形成和稳定时间相关分析. 中国粮油学报 12(3), 1-6. |
| [9] | 王亮, 穆培源, 徐红军, 庄丽, 桑伟, 聂迎彬, 韩新年, 邹波 (2009). 新疆小麦品种黄色素含量基因(Psy-A1) 等位变异的分子检测. 麦类作物学报 29, 782-786. |
| [10] | 王秋叶, 张建诚, 姚景珍 (1999). 河东乌麦526品种资源营养学评价. 山西农业科学 27(3), 18-21. |
| [11] | 徐兆飞 (2006). 山西小麦. 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 25-27. |
| [12] |
赵佳佳, 乔玲, 武棒棒, 葛川, 乔麟轶, 张树伟, 闫素仙, 郑兴卫, 郑军 (2021). 山西省小麦苗期根系性状及抗旱特性分析. 作物学报 47, 714-727.
DOI |
| [13] | 朱金宝, 刘广田, 张树榛 (1995). 基因型和环境对小麦烘烤品质的影响. 作物学报 21, 679-684. |
| [14] |
Abdel-Aal ESM, Young JC, Rabalski I, Hucl P, Fregeau- Reid J (2007). Identification and quantification of seed carotenoids in selected wheat species. J Agric Food Chem 55, 787-794.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Abdel-Aal ESM, Young JC, Wood PJ, Rabalski I, Hucl P, Falk D, Fregeau-Reid J (2002). Einkorn: a potential candidate for developing high lutein wheat. Cereal Chem 79, 455-457.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Ashokkumar K, Govindaraj M, Karthikeyan A, Shobhana VG, Warkentin TD (2020). Genomics-integrated breeding for carotenoids and folates in staple cereal grains to reduce malnutrition. Front Genet 11, 414.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Blanco A, Colasuonno P, Gadaleta A, Mangini G, Schiavulli A, Simeone R, Digesù AM, De Vita P, Mastrangelo AM, Cattivelli L (2011). Quantitative trait loci for yellow pigment concentration and individual carotenoid compounds in durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 54, 255-264.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Calvo MM (2005). Lutein: a valuable ingredient of fruit and vegetables. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45, 671-696.
PMID |
| [19] |
Colasuonno P, Gadaleta A, Giancaspro A, Nigro D, Giove S, Incerti O, Mangini G, Signorile A, Simeone R, Blanco A (2014). Development of a high-density SNP-based linkage map and detection of yellow pigment content QTLs in durum wheat. Mol Breed 34, 1563-1578.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Colasuonno P, Lozito ML, Marcotuli I, Nigro D, Giancaspro A, Mangini G, De Vita P, Mastrangelo AM, Pecchioni N, Houston K, Simeone R, Gadaleta A, Blanco A (2017). The carotenoid biosynthetic and catabolic genes in wheat and their association with yellow pigments. BMC Genomics 18, 122.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Colasuonno P, Marcotuli I, Blanco A, Maccaferri M, Condorelli GE, Tuberosa R, Parada R, De Camargo AC, Schwember AR, Gadaleta A (2019). Carotenoid pigment content in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum): an overview of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes. Front Plant Sci 10, 1347.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Crawford AC, Francki MG (2013). Lycopene-ε-cyclase (e-LCY3A) is functionally associated with quantitative trait loci for flour b* colour on chromosome 3A in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breed 31, 737-741.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Demmig-Adams B, Adams III WW (2002). Antioxidants in photosynthesis and human nutrition. Science 298, 2149-2153.
PMID |
| [24] |
Dibari B, Murat F, Chosson A, Gautier V, Poncet C, Lecomte P, Mercier I, Bergès H, Pont C, Blanco A, Salse J (2012). Deciphering the genomic structure, function and evolution of carotenogenesis related phytoene synthases in grasses. BMC Genomics 13, 221.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Digesù AM, Platani C, Cattivelli L, Mangini G, Blanco A (2009). Genetic variability in yellow pigment components in cultivated and wild tetraploid wheats. J Cereal Sci 50, 210-218.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Elouafi I, Nachit MM, Martin LM (2001). Identification of a microsatellite on chromosome 7B showing a strong linkage with yellow pigment in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum). Hereditas 135, 255-261.
PMID |
| [27] | FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP, WHO (2017). The state of food security and nutrition in the world 2017: building resilience for peace and food security. Roma: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. pp. 14-15. |
| [28] |
Farré G, Sanahuja G, Naqvi S, Bai C, Capell T, Zhu CF, Christou P (2010). Travel advice on the road to carotenoids in plants. Plant Sci 179, 28-48.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Gann PH, Khachik F (2003). Tomatoes or lycopene versus prostate cancer: is evolution anti-reductionist? J Natl Cancer Inst 95, 1563-1565.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Giambanelli E, Ferioli F, Koçaoglu B, Jorjadze M, Alexieva I, Darbinyan N, D'antuono LF (2013). A comparative study of bioactive compounds in primitive wheat populations from Italy, Turkey, Georgia, Bulgaria and Armenia. J Sci Food Agric 93, 3490-3501.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Groth S, Wittmann R, Longin CFH, Böhm V (2020). Influence of variety and growing location on carotenoid and vitamin E contents of 184 different durum wheat varieties (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) in Germany. Eur Food Res Technol 246, 2079-2092.
DOI |
| [32] |
Hadley CW, Clinton SK, Schwartz SJ (2003). The consumption of processed tomato products enhances plasma lycopene concentrations in association with a reduced lipoprotein sensitivity to oxidative damage. J Nutr 133, 727-732.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Harjes CE, Rocheford TR, Bai L, Brutnell TP, Kandianis CB, Sowinski SG, Stapleton AE, Vallabhaneni R, Williams M, Wurtzel ET, Yan JB, Buckler ES (2008). Natural genetic variation in lycopene epsilon cyclase tapped for maize biofortification. Science 319, 330-333.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Hidalgo A, Brandolini A (2014). Nutritional properties of einkorn wheat (Triticum monococcum L.). J Sci Food Agric 94, 601-612.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Howitt CA, Cavanagh CR, Bowerman AF, Cazzonelli C, Rampling L, Mimica JL, Pogson BJ (2009). Alternative splicing, activation of cryptic exons and amino acid substitutions in carotenoid biosynthetic genes are associated with lutein accumulation in wheat endosperm. Funct Integr Genomics 9, 363-376.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Institute of Medicine US Panel on Dietary Antioxidants and Related Compounds (2000). Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). pp. 143-151. |
| [37] |
Konopka I, Czaplicki S, Rotkiewicz D (2006). Differences in content and composition of free lipids and carotenoids in flour of spring and winter wheat cultivated in Poland. Food Chem 95, 290-300.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Li FQ, Vallabhaneni R, Wurtzel ET (2008). PSY3, a new member of the phytoene synthase gene family conserved in the Poaceae and regulator of abiotic stress-induced root carotenogenesis. Plant Physiol 146, 1333-1345.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Li LH, Lee JCY, Leung HH, Lam WC, Fu ZJ, Lo ACY (2020). Lutein supplementation for eye diseases. Nutrients 12, 1721.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Li WS, Zhai SN, Jin H, Wen WE, Liu JD, Xia XC, He ZH (2016). Genetic variation of carotenoids in Chinese bread wheat cultivars and the effect of the 1BL.1RS translocation. Front Agric Sci Eng 3, 124-130.
DOI |
| [41] |
Lv JL, Lu YJ, Niu YG, Whent M, Ramadan MF, Costa J, Yu LL (2013). Effect of genotype, environment, and their interaction on phytochemical compositions and antioxidant properties of soft winter wheat flour. Food Chem 138, 454-462.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Mares DJ, Campbell AW (2001). Mapping components of flour and noodle colour in Australian wheat. Aust J Agric Res 52, 1297-1309.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Moore J, Hao ZG, Zhou KQ, Luther M, Costa J, Yu LL (2005). Carotenoid, tocopherol, phenolic acid, and antioxidant properties of Maryland-grown soft wheat. J Agric Food Chem 53, 6649-6657.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Patil RM, Oak MD, Tamhankar SA, Sourdille P, Rao VS (2008). Mapping and validation of a major QTL for yellow pigment content on 7AL in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. ssp. durum). Mol Breed 21, 485-496.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Paznocht L, Kotíková Z, Šulc M, Lachman J, Orsák M, Eliášová M, Martinek P (2018). Free and esterified carotenoids in pigmented wheat, tritordeum and barley grains. Food Chem 240, 670-678.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Pozniak CJ, Knox RE, Clarke FR, Clarke JM (2007). Identification of QTL and association of a phytoene synthase gene with endosperm colour in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 114, 525-537.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
Reimer S, Pozniak CJ, Clarke FR, Clarke JM, Somers DJ, Knox RE, Singh AK (2008). Association mapping of yellow pigment in an elite collection of durum wheat cultivars and breeding lines. Genome 51, 1016-1025.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Ronen G, Carmel-Goren L, Zamir D, Hirschberg J (2000). An alternative pathway to β-carotene formation in plant chromoplasts discovered by map-based cloning of beta and old-gold color mutations in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 11102-11107.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Shewry PR, Sandra H (2015). Do “ancient” wheat species differ from modern bread wheat in their contents of bioactive components? J Cereal Sci 65, 236-243.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Singh A, Reimer S, Pozniak CJ, Clarke FR, Clarke JM, Knox RE, Singh AK (2009). Allelic variation at Psy1-A1 and association with yellow pigment in durum wheat grain. Theor Appl Genet 118, 1539-1548.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Tracewell CA, Vrettos JS, Bautista JA, Frank HA, Brudvig GW (2001). Carotenoid photooxidation in photosystem II. Arch Biochem Biophys 385, 61-69.
PMID |
| [52] |
Wang LF, Ge HM, Hao CY, Dong YS, Zhang XY (2012). Identifying loci influencing 1 000-kernel weight in wheat by microsatellite screening for evidence of selection during breeding. PLoS One 7, e29432.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Welsch R, Wüst F, Bär C, Al-Babili S, Beyer P (2008). A third phytoene synthase is devoted to abiotic stress-induced abscisic acid formation in rice and defines functional diversification of phytoene synthase genes. Plant Physiol 147, 367-380.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Zhai SN, He ZH, Wen WE, Jin H, Liu JD, Zhang Y, Liu ZY, Xia XC (2016). Genome-wide linkage mapping of flour color-related traits and polyphenol oxidase activity in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 129, 377-394.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Zhang W, Chao S, Manthey F, Chicaiza O, Brevis JC, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2008). QTL analysis of pasta quality using a composite microsatellite and SNP map of durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 117, 1361-1377.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Zhang YL, Wu YP, Xiao YG, He ZH, Zhang Y, Yan J, Zhang Y, Xia XC, Ma CX (2009). QTL mapping for flour and noodle colour components and yellow pigment content in common wheat. Euphytica 165, 435-444.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Zhao Y, Sun HY, Wang YY, Pu YY, Kong FM, Li SS (2013). QTL mapping for the color, carotenoids and polyphenol oxidase activity of flour in recombinant inbred lines of wheat. Aust J Crop Sci 7, 328-337. |
| [58] |
Zheng XW, Qiao L, Liu Y, Wei NC, Zhao JJ, Wu BB, Yang B, Wang JL, Zheng J (2022). Genome-wide association study of grain number in common wheat from Shanxi under different water regimes. Front Plant Sci 12, 806295.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 崔娟, 于晓玉, 于跃娇, 梁铖玮, 孙健, 陈温福. 影响中国东北和日本粳稻食味品质差异的质构因素及其遗传基础解析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 许庭旸, 刘雨辰, 王万鹏, 苏航, 苏昆龙, 吴振映, 吕明, 李福利, 王小山, 付春祥. 喷施不同植物生长调节剂对盐碱地小麦生长发育的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 354-362. |
| [3] | 刘笑, 杜琬莹, 张云秀, 唐成名, 李华伟, 夏海勇, 樊守金, 孔令安. NO3-缓解小麦根部NH4+毒性机理(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 397-413. |
| [4] | 白明义, 彭金荣, 傅向东. 赤霉素和油菜素内酯信号通路双重调控助力小麦新一轮“绿色革命”[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 194-198. |
| [5] | 李晓明, 王兰芬, 唐永生, 常玉洁, 张菊香, 王述民, 武晶. 普通菜豆抗菜豆象性状的全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 77-89. |
| [6] | 李园, 常玉洁, 王兰芬, 王述民, 武晶. 普通菜豆镰孢菌枯萎病抗性种质资源筛选及全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 51-61. |
| [7] | 金京波, 梁承志. 饲草基因组学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 732-741. |
| [8] | 孔令让. 另辟蹊径破解小麦条锈病的基因密码[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 405-408. |
| [9] | 熊淑萍, 曹文博, 曹锐, 张志勇, 付新露, 徐赛俊, 潘虎强, 王小纯, 马新明. 水平结构配置对冬小麦冠层垂直结构、微环境及产量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(2): 188-196. |
| [10] | 孙佳欢, 刘冬, 朱家祺, 张书宁, 高梅香. 小麦-玉米轮作农田土壤螨多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22292-. |
| [11] | 焦振彬, 罗毅波. 群体表型性状研究揭示环境与遗传因素对霍山石斛表型及物种分类的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2021, 29(8): 1073-1086. |
| [12] | 宣伟, 徐国华. 植物适应土壤氮素环境的基因选择: 以水稻为例[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 1-5. |
| [13] | 赵宇慧, 李秀秀, 陈倬, 鲁宏伟, 刘羽诚, 张志方, 梁承志. 生物信息学分析方法I: 全基因组关联分析概述[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 715-732. |
| [14] | 祝光涛,黄三文. 360度群体遗传变异扫描——大豆泛基因组研究[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 403-406. |
| [15] | 周俭民. 小麦抗赤霉病利器——他山之石[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 123-125. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||