

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 533-550.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24196 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24196
崔娟†, 于晓玉†, 于跃娇, 梁铖玮, 孙健*( ), 陈温福*(
), 陈温福*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-20
接受日期:2025-03-18
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2025-03-18
通讯作者:
*孙健, 沈阳农业大学教授, 博士生导师。入选首批国家“神农青年英才”计划, 获“辽宁青年科技奖”等奖励或荣誉。主要研究方向为水稻种质资源创新。主持“国家自然科学基金面上项目”等多项国家与省部级项目。围绕杂草稻种质创新开展了系统性研究工作, 阐明了杂草稻的分类学地位, 提出起源演化新假说, 克隆了多个对栽培稻遗传改良具有重要价值的新基因。带领团队设计研发了粳稻种质资源芯片, 在粳稻资源评价、分子设计育种、全基因组选择等方面开展了广泛应用。研究成果在Nature Communications、Molecular Plant、New Phytologist等国际著名期刊上发表。E-mail: sunjian811119@syau.edu.cn;陈温福, 辽宁法库人, 我国著名水稻专家和生物炭专家, 中国工程院院士, 沈阳农业大学教授。第十一届、第十二届、第十三届全国人大代表, 第十四届全国政协委员。曾任国家重点学科“作物栽培学与耕作学”学科带头人, 国务院学位委员会第五届、第六届学科评议组成员和作物学科组召集人, 国家农作物品种审定委员会委员, 农业农村部第九届科技委常委、水稻专家组成员, 辽宁省科协副主席。曾获全国劳动模范和五一劳动奖章、全国模范教师、全国教学名师、创先争优奖、全国农业科技先进工作者、中华农业英才奖、辽宁省特等劳动模范、辽宁省科技功勋奖等多项荣誉。E-mail: wfchen@syau.edu.cn
作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Juan Cui†, Xiaoyu Yu†, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun*( ), Wenfu Chen*(
), Wenfu Chen*( )
)
Received:2024-12-20
Accepted:2025-03-18
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-03-18
Contact:
*E-mail: sunjian811119@syau.edu.cn;wfchen@syau.edu.cnAbout author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 由于育种目标的差异, 使得东北粳稻(Oryza sativa subsp. geng or japonica)在单产水平上比日本粳稻更具优势, 而日本粳米食味品质则明显优于中国粳米。明确中日粳米间食味品质差异的遗传基础, 对于培育高产优质兼顾的粳稻具有重要意义。以274份中日粳稻为研究材料, 应用质构参数量化食味品质, 并将诸多参数降维后结合全基因组关联分析揭示影响中日粳米食味差异的遗传基础。结果表明, 中日粳稻食味值的显著差异体现在粘力(adhesion force, ADF)、第一可恢复形变循环(first recoverable deformation cycle, FRDC)和弹性指数(elasticity index, EI)三个质构特征参数上。同时, 食味值与30个质构特性指标相关性分析表明, 24个指标与米饭食味之间呈显著或极显著相关性。将30个质构特性指标降维为4个可解释群体80%表型变异的主成分, 通过对其特征值进行全基因组关联分析挖掘到2个影响中日粳米质构特性的主效位点qFPC4.3与qFPC9.2。该研究从质构角度量化了食味品质参数, 由此解析了中日稻米食味品质特性差异的遗传基础, 为我国粳稻食味品质遗传改良提供了有价值的遗传信息和理论依据。
崔娟, 于晓玉, 于跃娇, 梁铖玮, 孙健, 陈温福. 影响中国东北和日本粳稻食味品质差异的质构因素及其遗传基础解析. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 533-550.
Juan Cui, Xiaoyu Yu, Yuejiao Yu, Chengwei Liang, Jian Sun, Wenfu Chen. Analysis of the Texture Factors and Genetic Basis Influencing the Differences in Eating Quality between Northeast China and Japanese Japonica Rice. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 533-550.
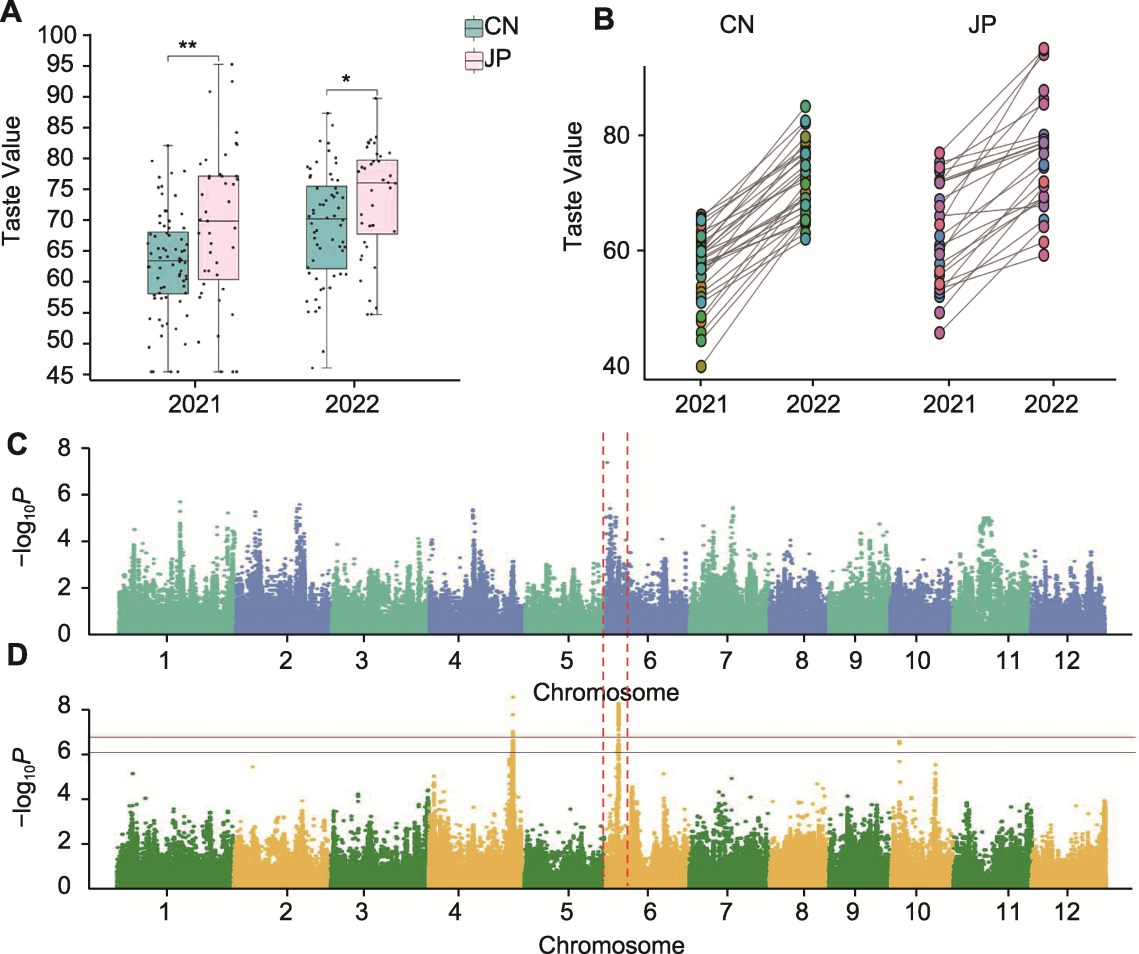
图1 两年间中日粳稻食味值差异以及基于食味值的全基因组关联分析 (A) 2021年和2022年中日粳米食味值差异; (B) 2022年中日粳米食味值相较于2021年变化幅度(CN: 中国粳稻; JP: 日本粳稻; * P<0.05; ** P<0.01); (C) 基于2021年食味值的全基因组关联分析; (D) 基于2022年食味值的全基因组关联分析。蓝线表示标记-性状关联的显著性阈值(0.05显著水平), 黄线表示标记-性状关联的极显著性阈值(0.01显著水平)。
Figure 1 Differences in taste values of japonica rice between China and Japan and genome-wide association studies based on taste value in two years (A) Differences in taste values of japonica rice between China and Japan in 2021 and 2022; (B) Changes in taste values of Chinese and Japanese japonica rice in 2022 compared with 2021 (CN: Chinese japonica rice; JP: Japanese japonica rice; * P<0.05; ** P<0.01); (C) Genome wide association studies based on taste value in 2021; (D) Genome-wide association studies based on taste value in 2022. The blue line represents the threshold for the significance of marker-trait association (0.05 significance level), and the yellow line represents the threshold for the extreme significance of marker-trait association (0.01 significance level).
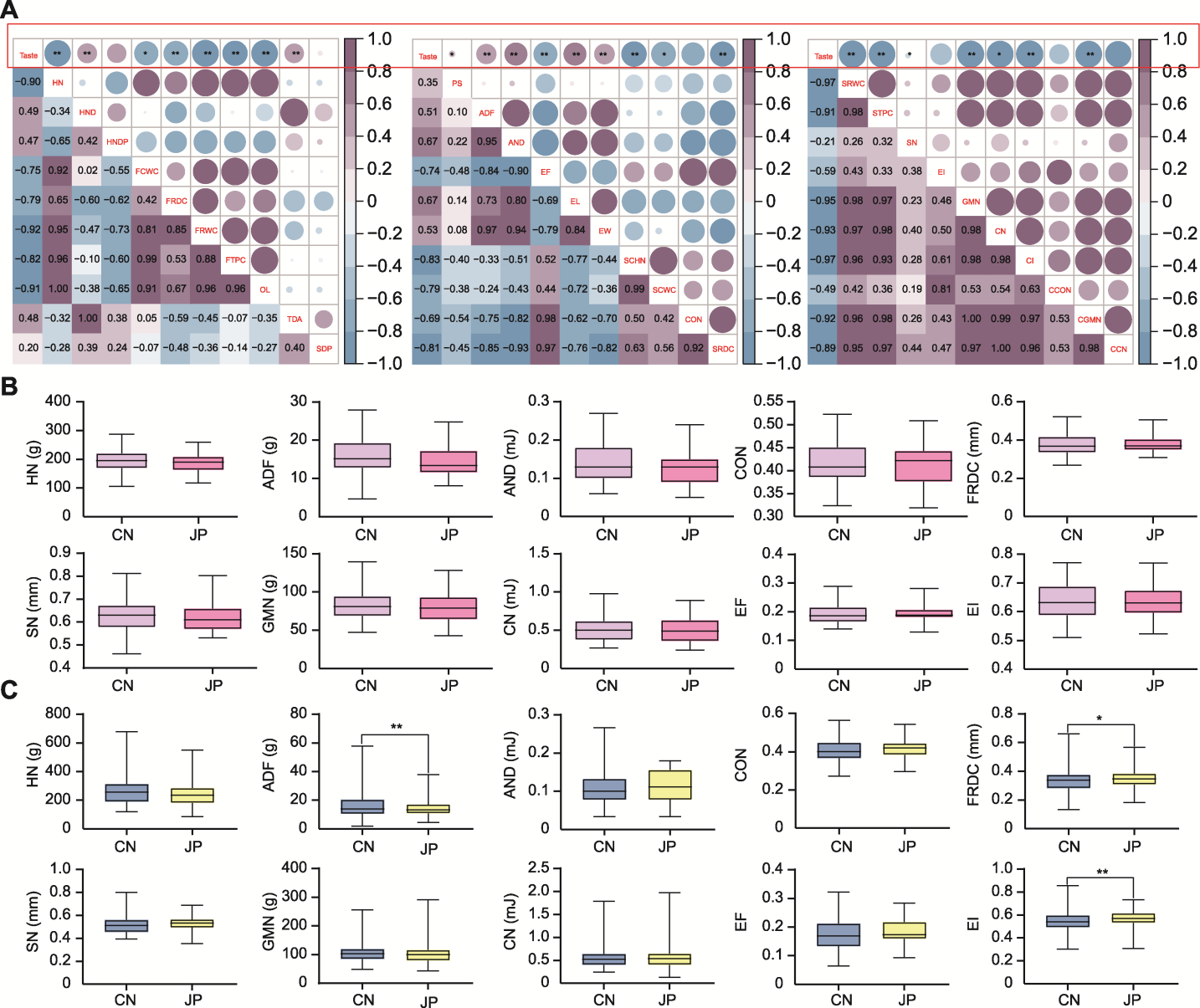
图2 两年间中日粳稻食味和质构相关性分析及其在质构特性上的差异 (A) 中日粳米食味值和质构特性指标的相关性分析(HN: 第一循环硬度; HND: 硬度形变量; HNDP: 硬度形变百分比; FCWC: 压缩功循环1; FRDC: 第一可恢复形变循环; FRWC: 可恢复功循环1; FTPC: 第一循环总功; OL: 目标负载; TDA: 目标变形量; SDP: 样品变形百分比; PS: 峰值应变; ADF: 粘力; AND: 粘性; EF: 弹力; EL: 弹性长度; EW: 弹性功; SCHN: 第二循环硬度; SCWC: 压缩功循环2; CON: 内聚性; SRDC: 可恢复形变循环2; SRWC: 可恢复功循环2; STPC: 总功循环2; SN: 弹性; EI: 弹性指数; GMN: 胶着性; CN: 咀嚼性; CI: 咀嚼指数; CCON: 校正内聚性; CGMN: 校正胶着性; CCN: 校正咀嚼性); (B) 2021年部分质构特性指标在中日粳米间的差异; (C) 2022年部分质构特性指标在中日粳米间的差异。CN和JP同图1; * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
Figure 2 Correlation analysis of the taste and texture of japonica rice and differences in some textural characteristics of japonica rice between China and Japan in two years (A) Correlation analysis of the taste and texture of japonica rice between China and Japan in two years (HN: Hardness; HND: Hardness deformation; HNDP: Hardness deformation percentage; FCWC: First compression work cycle; FRDC: First recoverable deformation cycle; FRWC: First recoverable work cycle; FTPC: First total power cycle; OL: Objective load; TDA: Target deformation amount; SDP: Sample deformation percentage; PS: Peak strain; ADF: Adhesion force; AND: Adhesion degree; EF: Elastic force; EL: Elastic length; EW: Elastic work; SCHN: Second cycle hardness; SCWC: Second compression work cycle; CON: Cohesiveness; SRDC: Second recoverable deformation cycle; SRWC: Second recoverable work cycle; STPC: Second total power cycle; SN: Springiness; EI: Elasticity index; GMN: Gumminess; CN: Chewiness; CI: Chewing index; CCON: Corrected cohesiveness; CGMN: Corrected gumminess; CCN: Corrected chewiness); (B) Differences in some textural characteristics of japonica rice between China and Japan in 2021; (C) Differences in some textural characteristics of japonica rice between China and Japan in 2022. CN and JP are the same as shown in Figure 1; * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
| Year | Variable | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | Year | Variable | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | HN | -0.238 | -0.077 | -0.139 | -0.153 | 2022 | HN | -0.250 | 0.110 | -0.126 | -0.050 |
| HND | -0.039 | -0.343 | -0.066 | 0.261 | HND | -0.076 | 0.285 | 0.210 | 0.002 | ||
| HNDP | 0.002 | -0.139 | 0.028 | 0.459 | HNDP | -0.037 | 0.069 | 0.430 | -0.448 | ||
| FCWC | -0.191 | -0.235 | -0.186 | -0.089 | FCWC | -0.215 | 0.198 | -0.071 | -0.028 | ||
| FRDC | -0.176 | 0.186 | -0.016 | 0.299 | FRDC | -0.144 | -0.236 | 0.245 | 0.049 | ||
| FRWC | -0.249 | 0.038 | -0.088 | 0.042 | FRWC | -0.264 | -0.042 | 0.019 | 0.020 | ||
| FTPC | -0.214 | -0.189 | -0.177 | -0.067 | FTPC | -0.231 | 0.169 | -0.064 | -0.022 | ||
| OL | -0.242 | -0.060 | -0.140 | -0.117 | OL | -0.253 | 0.097 | -0.116 | -0.048 | ||
| TDA | -0.040 | -0.344 | -0.071 | 0.243 | TDA | -0.076 | 0.287 | 0.196 | 0.021 | ||
| SDP | -0.025 | -0.186 | -0.076 | 0.196 | SDP | -0.059 | 0.184 | 0.212 | 0.096 | ||
| PS | -0.001 | -0.144 | 0.036 | 0.449 | PS | -0.033 | 0.068 | 0.443 | -0.420 | ||
| ADF | -0.039 | -0.267 | 0.296 | -0.211 | ADF | 0.010 | 0.284 | -0.125 | 0.078 | ||
| AND | 0.005 | -0.286 | 0.299 | -0.132 | AND | 0.061 | 0.186 | 0.034 | 0.311 | ||
| EF | -0.137 | 0.322 | 0.088 | 0.158 | EF | -0.031 | -0.323 | -0.012 | -0.090 | ||
| EL | 0.045 | -0.128 | 0.386 | 0.034 | EL | -0.012 | -0.082 | 0.302 | 0.381 | ||
| EW | -0.036 | -0.223 | 0.385 | -0.124 | EW | 0.039 | 0.206 | 0.081 | 0.418 | ||
| SCHN | -0.244 | -0.046 | -0.127 | -0.143 | SCHN | -0.252 | 0.100 | -0.139 | -0.051 | ||
| SCWC | -0.251 | -0.110 | -0.066 | -0.031 | SCWC | -0.264 | -0.081 | -0.050 | 0.008 | ||
| CON | -0.153 | 0.256 | 0.236 | 0.089 | CON | -0.058 | -0.315 | -0.077 | -0.052 | ||
| SRDC | -0.166 | 0.221 | 0.003 | 0.280 | SRDC | -0.128 | -0.245 | 0.243 | 0.050 | ||
| SRWC | -0.240 | 0.090 | -0.067 | 0.066 | SRWC | -0.263 | -0.055 | -0.004 | -0.013 | ||
| STPC | -0.258 | -0.050 | -0.071 | -0.010 | STPC | -0.269 | 0.043 | -0.038 | -0.003 | ||
| SN | -0.151 | -0.166 | 0.248 | 0.206 | SN | -0.141 | -0.060 | 0.378 | 0.329 | ||
| EI | -0.130 | 0.175 | 0.338 | -0.019 | EI | -0.039 | -0.296 | 0.096 | 0.212 | ||
| GMN | -0.256 | 0.047 | -0.012 | -0.080 | GMN | -0.265 | -0.032 | -0.100 | -0.027 | ||
| CN | -0.259 | -0.014 | 0.080 | 0.008 | CN | -0.264 | -0.056 | 0.047 | 0.065 | ||
| CI | -0.249 | 0.093 | 0.086 | -0.062 | CI | -0.241 | -0.140 | -0.025 | 0.054 | ||
| CCON | -0.152 | 0.129 | 0.321 | 0.029 | CCON | -0.073 | -0.284 | -0.104 | 0.004 | ||
| CGMN | -0.252 | -0.013 | 0.018 | -0.105 | CGMN | -0.264 | -0.006 | -0.109 | -0.016 | ||
| CCN | -0.252 | -0.069 | 0.102 | -0.009 | CCN | -0.265 | 0.037 | 0.070 | -0.092 | ||
| Eigenvalue | 14.250 | 5.510 | 3.588 | 2.393 | Eigenvalue | 13.354 | 8.352 | 2.513 | 1.728 | ||
| Contribution rate (%) | 53.28 | 14.80 | 8.69 | 6.32 | Contribution rate (%) | 44.49 | 27.81 | 8.35 | 5.80 | ||
| Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 53.28 | 68.08 | 76.77 | 83.09 | Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 44.49 | 72.30 | 80.65 | 86.45 |
表1 2021年和2022年质构特性指标因子主成分的荷载矩阵、特征值、贡献率和累积贡献率
Table 1 Factor load matrix, eigenvalues, contribution rates and cumulative contribution rates of the principal components of the qualitative and structural property indicators in 2021 and 2022
| Year | Variable | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | Year | Variable | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | HN | -0.238 | -0.077 | -0.139 | -0.153 | 2022 | HN | -0.250 | 0.110 | -0.126 | -0.050 |
| HND | -0.039 | -0.343 | -0.066 | 0.261 | HND | -0.076 | 0.285 | 0.210 | 0.002 | ||
| HNDP | 0.002 | -0.139 | 0.028 | 0.459 | HNDP | -0.037 | 0.069 | 0.430 | -0.448 | ||
| FCWC | -0.191 | -0.235 | -0.186 | -0.089 | FCWC | -0.215 | 0.198 | -0.071 | -0.028 | ||
| FRDC | -0.176 | 0.186 | -0.016 | 0.299 | FRDC | -0.144 | -0.236 | 0.245 | 0.049 | ||
| FRWC | -0.249 | 0.038 | -0.088 | 0.042 | FRWC | -0.264 | -0.042 | 0.019 | 0.020 | ||
| FTPC | -0.214 | -0.189 | -0.177 | -0.067 | FTPC | -0.231 | 0.169 | -0.064 | -0.022 | ||
| OL | -0.242 | -0.060 | -0.140 | -0.117 | OL | -0.253 | 0.097 | -0.116 | -0.048 | ||
| TDA | -0.040 | -0.344 | -0.071 | 0.243 | TDA | -0.076 | 0.287 | 0.196 | 0.021 | ||
| SDP | -0.025 | -0.186 | -0.076 | 0.196 | SDP | -0.059 | 0.184 | 0.212 | 0.096 | ||
| PS | -0.001 | -0.144 | 0.036 | 0.449 | PS | -0.033 | 0.068 | 0.443 | -0.420 | ||
| ADF | -0.039 | -0.267 | 0.296 | -0.211 | ADF | 0.010 | 0.284 | -0.125 | 0.078 | ||
| AND | 0.005 | -0.286 | 0.299 | -0.132 | AND | 0.061 | 0.186 | 0.034 | 0.311 | ||
| EF | -0.137 | 0.322 | 0.088 | 0.158 | EF | -0.031 | -0.323 | -0.012 | -0.090 | ||
| EL | 0.045 | -0.128 | 0.386 | 0.034 | EL | -0.012 | -0.082 | 0.302 | 0.381 | ||
| EW | -0.036 | -0.223 | 0.385 | -0.124 | EW | 0.039 | 0.206 | 0.081 | 0.418 | ||
| SCHN | -0.244 | -0.046 | -0.127 | -0.143 | SCHN | -0.252 | 0.100 | -0.139 | -0.051 | ||
| SCWC | -0.251 | -0.110 | -0.066 | -0.031 | SCWC | -0.264 | -0.081 | -0.050 | 0.008 | ||
| CON | -0.153 | 0.256 | 0.236 | 0.089 | CON | -0.058 | -0.315 | -0.077 | -0.052 | ||
| SRDC | -0.166 | 0.221 | 0.003 | 0.280 | SRDC | -0.128 | -0.245 | 0.243 | 0.050 | ||
| SRWC | -0.240 | 0.090 | -0.067 | 0.066 | SRWC | -0.263 | -0.055 | -0.004 | -0.013 | ||
| STPC | -0.258 | -0.050 | -0.071 | -0.010 | STPC | -0.269 | 0.043 | -0.038 | -0.003 | ||
| SN | -0.151 | -0.166 | 0.248 | 0.206 | SN | -0.141 | -0.060 | 0.378 | 0.329 | ||
| EI | -0.130 | 0.175 | 0.338 | -0.019 | EI | -0.039 | -0.296 | 0.096 | 0.212 | ||
| GMN | -0.256 | 0.047 | -0.012 | -0.080 | GMN | -0.265 | -0.032 | -0.100 | -0.027 | ||
| CN | -0.259 | -0.014 | 0.080 | 0.008 | CN | -0.264 | -0.056 | 0.047 | 0.065 | ||
| CI | -0.249 | 0.093 | 0.086 | -0.062 | CI | -0.241 | -0.140 | -0.025 | 0.054 | ||
| CCON | -0.152 | 0.129 | 0.321 | 0.029 | CCON | -0.073 | -0.284 | -0.104 | 0.004 | ||
| CGMN | -0.252 | -0.013 | 0.018 | -0.105 | CGMN | -0.264 | -0.006 | -0.109 | -0.016 | ||
| CCN | -0.252 | -0.069 | 0.102 | -0.009 | CCN | -0.265 | 0.037 | 0.070 | -0.092 | ||
| Eigenvalue | 14.250 | 5.510 | 3.588 | 2.393 | Eigenvalue | 13.354 | 8.352 | 2.513 | 1.728 | ||
| Contribution rate (%) | 53.28 | 14.80 | 8.69 | 6.32 | Contribution rate (%) | 44.49 | 27.81 | 8.35 | 5.80 | ||
| Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 53.28 | 68.08 | 76.77 | 83.09 | Cumulative contribution rate (%) | 44.49 | 72.30 | 80.65 | 86.45 |
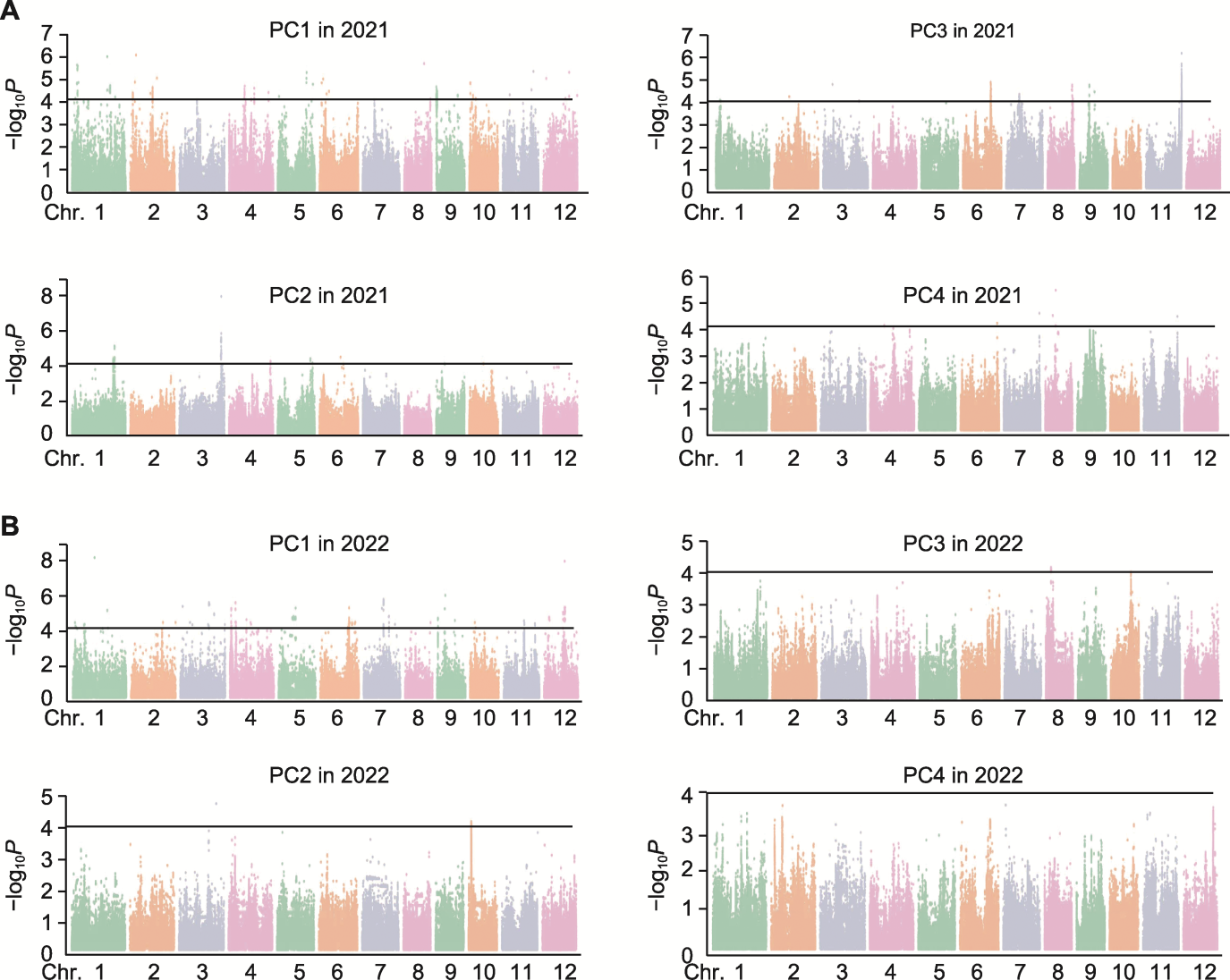
图3 基于自然群体质构特性指标主成分特征值的全基因组关联分析 (A) 2021年基于质构特性特征值的全基因组关联分析; (B) 2022年基于质构特性特征值的全基因组关联分析。黑线表示标记-性状关联的显著性阈值。
Figure 3 Genome-wide association studies based on principal component eigenvalues of natural population texture characteristic indicators (A) Genome-wide association studies based on texture characteristic feature values in 2021; (B) Genome-wide association studies based on texture characteristic feature values in 2022. The black lines represent the threshold for the significance of marker-trait association.
| Traits | Chromosome | Quanti- tative trait nucleo- tides | Year | Lead single nucleotide polymorphism | P value | Traits | Chro-moso-me | Quanti- tative trait nucleo- tides | Year | Lead single nucleotide polymorphism | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 1 | qFPC1.1 | 2021 | S01_4122448 | 1.77E-06 | 9 | qFPC9.2 | 2021 | S09_655033 | 2.84E-05 | |
| 2 | qFPC2.1 | 2021 | S02_2111625 | 3.54E-05 | 2022 | S09_707465 | 2.00E-05 | ||||
| 2 | qFPC2.2 | 2021 | S02_18008119 | 1.89E-05 | PC2 | 1 | qSPC1.1 | 2021 | S01_34361048 | 6.28E-06 | |
| 2 | qFPC2.3 | 2022 | S02_24989754 | 9.26E-05 | 3 | qSPC3.1 | 2021 | S03_33811087 | 1.07E-06 | ||
| 3 | qFPC3.1 | 2021 | S03_14095190 | 8.10E-05 | 4 | qSPC4.1 | 2021 | S04_33424615 | 4.92E-05 | ||
| 4 | qFPC4.1 | 2022 | S04_1115264 | 5.54E-06 | 10 | qSPC10.1 | 2022 | S10_2285014 | 5.95E-05 | ||
| 4 | qFPC4.2 | 2022 | S04_4490974 | 2.53E-06 | PC3 | 6 | qTPC6.1 | 2021 | S06_22391759 | 1.33E-05 | |
| 4 | qFPC4.3 | 2021 | S04_13268045 | 7.14E-05 | 7 | qTPC7.1 | 2021 | S07_10551451 | 4.89E-05 | ||
| 2022 | S04_13329698 | 2.47E-05 | 8 | qTPC8.1 | 2021 | S08_19868807 | 1.81E-05 | ||||
| 6 | qFPC6.1 | 2022 | S06_23235180 | 5.02E-06 | 9 | qTPC9.1 | 2021 | S09_7944917 | 1.80E-05 | ||
| 7 | qFPC7.1 | 2021 | S07_9324722 | 7.40E-05 | 10 | qTPC10.1 | 2022 | S10_16314058 | 7.08E-05 | ||
| 8 | qFPC8.1 | 2021 | S08_21150875 | 6.47E-05 | 11 | qTPC11.1 | 2021 | S11_28894771 | 6.28E-07 | ||
| 9 | qFPC9.1 | 2021 | S09_38586 | 1.82E-05 |
表2 自然群体质构特性重要指标显著位点
Table 2 Significant loci of important indicators of the texture characteristics of natural populations
| Traits | Chromosome | Quanti- tative trait nucleo- tides | Year | Lead single nucleotide polymorphism | P value | Traits | Chro-moso-me | Quanti- tative trait nucleo- tides | Year | Lead single nucleotide polymorphism | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 1 | qFPC1.1 | 2021 | S01_4122448 | 1.77E-06 | 9 | qFPC9.2 | 2021 | S09_655033 | 2.84E-05 | |
| 2 | qFPC2.1 | 2021 | S02_2111625 | 3.54E-05 | 2022 | S09_707465 | 2.00E-05 | ||||
| 2 | qFPC2.2 | 2021 | S02_18008119 | 1.89E-05 | PC2 | 1 | qSPC1.1 | 2021 | S01_34361048 | 6.28E-06 | |
| 2 | qFPC2.3 | 2022 | S02_24989754 | 9.26E-05 | 3 | qSPC3.1 | 2021 | S03_33811087 | 1.07E-06 | ||
| 3 | qFPC3.1 | 2021 | S03_14095190 | 8.10E-05 | 4 | qSPC4.1 | 2021 | S04_33424615 | 4.92E-05 | ||
| 4 | qFPC4.1 | 2022 | S04_1115264 | 5.54E-06 | 10 | qSPC10.1 | 2022 | S10_2285014 | 5.95E-05 | ||
| 4 | qFPC4.2 | 2022 | S04_4490974 | 2.53E-06 | PC3 | 6 | qTPC6.1 | 2021 | S06_22391759 | 1.33E-05 | |
| 4 | qFPC4.3 | 2021 | S04_13268045 | 7.14E-05 | 7 | qTPC7.1 | 2021 | S07_10551451 | 4.89E-05 | ||
| 2022 | S04_13329698 | 2.47E-05 | 8 | qTPC8.1 | 2021 | S08_19868807 | 1.81E-05 | ||||
| 6 | qFPC6.1 | 2022 | S06_23235180 | 5.02E-06 | 9 | qTPC9.1 | 2021 | S09_7944917 | 1.80E-05 | ||
| 7 | qFPC7.1 | 2021 | S07_9324722 | 7.40E-05 | 10 | qTPC10.1 | 2022 | S10_16314058 | 7.08E-05 | ||
| 8 | qFPC8.1 | 2021 | S08_21150875 | 6.47E-05 | 11 | qTPC11.1 | 2021 | S11_28894771 | 6.28E-07 | ||
| 9 | qFPC9.1 | 2021 | S09_38586 | 1.82E-05 |
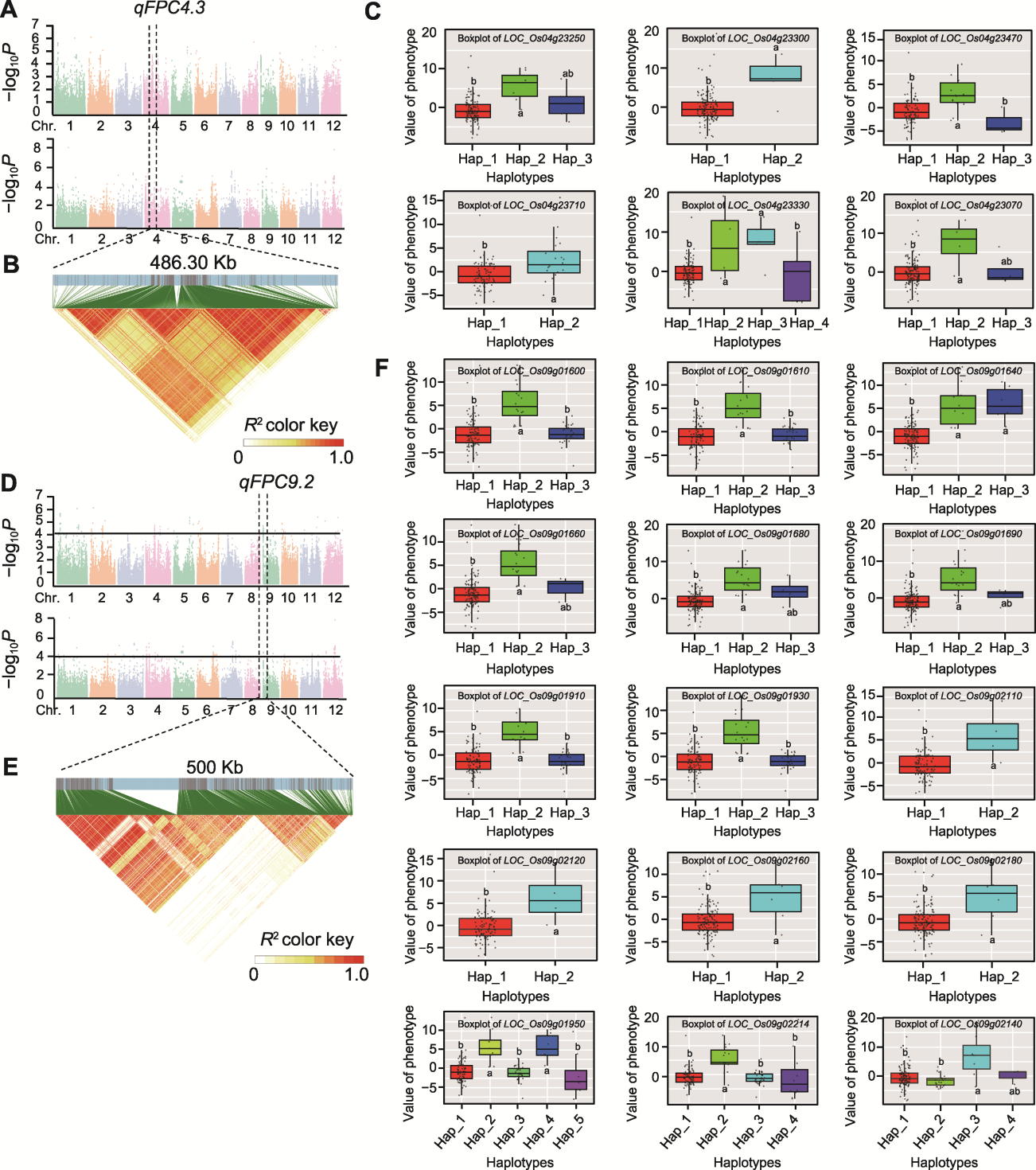
图4 qFPC4.3和qFPC9.2位点的候选基因单倍型分析 (A) 2021年和2022年基于质构特性特征值的全基因组关联分析; (B) qFPC4.3位点附近的LD black图; (C) qFPC4.3位点附近LD区间内与表型变异相关的基因, 纵坐标代表PC1的主成分特征值得分; (D) 2021年和2022年基于质构特性特征值的全基因组关联分析; (E) qFPC9.2位点附近的LD black图; (F) qFPC9.2位点附近LD区间内与表型变异相关的基因, 纵坐标代表PC1的主成分特征值得分。(C), (F) 不同小写字母表示差异显著。
Figure 4 Haplotype analysis of candidate genes for qFPC4.3 and qFPC9.2 (A) Genome-wide association studies based on eigenvalues of texture properties in 2021 and 2022; (B) LD black near the qFPC4.3 locus; (C) Genes associated with phenotypic variation in the LD interval near the qFPC4.3 locus, whose vertical coordinates represent the principal component eigenvalue scores of PC1; (D) Genome-wide association studies based on eigenvalues of texture properties in 2021 and 2022; (E) LD black near the qFPC9.2 locus; (F) Genes associated with phenotypic variation in the LD interval near the qFPC9.2 locus, whose vertical coordinates represent the principal component eigenvalue scores of PC1. (C), (F) Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences.
| Gene ID | Annotation | High expression site | Gene ID | Annotation | High expression site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os04g23070 | Retrotransposon protein | NA | LOC_Os04g23330 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os04g23250 | Transposon protein | NA | LOC_Os04g23470 | Transposon protein | Seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os04g23300 | Retrotransposon protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage | LOC_Os04g23710 | Transposon protein | NA |
表3 qFPC4.3的候选基因注释信息
Table 3 Candidate gene annotation information of qFPC4.3
| Gene ID | Annotation | High expression site | Gene ID | Annotation | High expression site |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os04g23070 | Retrotransposon protein | NA | LOC_Os04g23330 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os04g23250 | Transposon protein | NA | LOC_Os04g23470 | Transposon protein | Seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os04g23300 | Retrotransposon protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage | LOC_Os04g23710 | Transposon protein | NA |
| Gene ID | Annotation | High expression site |
|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os09g01600 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01610 | Clumping factor B | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01640 | CAX-interacting protein 4 | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01660 | Expressed protein | Leaf |
| LOC_Os09g01680 | DNA repair protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01690 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01910 | Transposon protein | NA |
| LOC_Os09g01930 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and mature seed |
| LOC_Os09g01950 | Expressed protein | NA |
| LOC_Os09g02120 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g02160 | DEFL47-defensin and Defensin-like DEFL family | Pistils |
| LOC_Os09g02180 | Oryza sativa drought and salt stress response-1 | Mature seed |
| LOC_Os09g02214 | Na+/H+ antiporter gene | Mature leaf and SAM |
| LOC_Os09g02110 | Retrotransposon protein | Seed of filling stage |
表4 qFPC9.2候选基因注释信息
Table 4 Candidate gene annotation information of qFPC9.2
| Gene ID | Annotation | High expression site |
|---|---|---|
| LOC_Os09g01600 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01610 | Clumping factor B | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01640 | CAX-interacting protein 4 | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01660 | Expressed protein | Leaf |
| LOC_Os09g01680 | DNA repair protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01690 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g01910 | Transposon protein | NA |
| LOC_Os09g01930 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and mature seed |
| LOC_Os09g01950 | Expressed protein | NA |
| LOC_Os09g02120 | Expressed protein | Young panicle and seed of filling stage |
| LOC_Os09g02160 | DEFL47-defensin and Defensin-like DEFL family | Pistils |
| LOC_Os09g02180 | Oryza sativa drought and salt stress response-1 | Mature seed |
| LOC_Os09g02214 | Na+/H+ antiporter gene | Mature leaf and SAM |
| LOC_Os09g02110 | Retrotransposon protein | Seed of filling stage |
| [1] | Bian JL, Xu FF, Liu GD, Xu D, Zhu Y, Hu Q, Zhang HC, Wei HY (2023). Study on comprehensive evaluation method of Japonica rice eating quality in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. J Yangzhou Univ Agric Life Sci Ed 44(5), 1-11. (in Chinese) |
| 卞金龙, 许方甫, 刘国栋, 徐栋, 朱盈, 胡群, 张洪程, 魏海燕 (2023). 长江中下游粳稻食味品质综合评价方法研究. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版) 44(5), 1-11. | |
| [2] |
Boomsma DI, Dolan CV (1998). A comparison of power to detect a QTL in sib-pair data using multivariate phenotypes, mean phenotypes, and factor scores. Behav Genet 28, 329-340.
PMID |
| [3] | Bu YP (2019). Identification of QTL for Vegetable Soybean Seed Hardness and Preliminary Functional Verification of Candidate Gene GmMFTL. PhD dissertation. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University. pp. 53-68. (in Chinese) |
| 卜远鹏 (2019). 菜用大豆籽粒硬度QTL的定位及候选基因GmMFTL的初步功能验证. 博士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 53-68. | |
| [4] |
Cantor RM, Lange K, Sinsheimer JS (2010). Prioritizing GWAS results: a review of statistical methods and recommendations for their application. Am J Hum Genet 86, 6-22.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chang JN, Jiao GA, Hui SZ, Guo W, Wang JL (2021). Research progress on influencing factors of rice texture properties. Mol Plant Breed 19, 2419-2426. (in Chinese) |
| 常俊楠, 焦桂爱, 惠索祯, 郭雯, 王建龙 (2021). 稻米质构特性影响因素的研究进展. 分子植物育种 19, 2419-2426. | |
| [6] | Chen HF, Hu SK, Tang SQ, Hu PS (2023). Current status and prospect of genetic improvement of rice grain quality. J Yangtze Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 20(5), 110-123. (in Chinese) |
| 陈宏法, 胡时开, 唐绍清, 胡培松 (2023). 稻米品质遗传改良现状及展望. 长江大学学报(自然科学版) 20(5), 110-123. | |
| [7] | Friendly M (2002). Corrgrams: exploratory displays for correlation matrices. Am Stat 56, 316-324. |
| [8] | Gao H, Jiang N, Lü GY, Xia YJ, Wang JY, Sun J, Tang L, Xu ZJ, Sui GM (2018). Dissection of grain yield differences between Japonica rice in Northeast China and in Japan. Chin J Rice Sci 32, 357-364. (in Chinese) |
|
高虹, 姜楠, 吕国依, 夏英俊, 王嘉宇, 孙健, 唐亮, 徐正进, 隋国民 (2018). 中国东北粳稻与日本粳稻产量差异及原因分析. 中国水稻科学 32, 357-364.
DOI |
|
| [9] |
Goh L, Yap VB (2009). Effects of normalization on quantitative traits in association test. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 415.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Gong JY, Miao JS, Zhao Y, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhan QL, Cheng BY, Xia JH, Huang XH, Yang SH, Han B (2017). Dissecting the genetic basis of grain shape and chalkiness traits in hybrid rice using multiple collaborative populations. Mol Plant 10, 1353-1356.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Guan B, Liu W, Liu CM, Su KM (2011). Effect of soaking treatment on pasting properties and textural properties of early indica rice. Food Mach 27(3), 13-15, 115. (in Chinese) |
| 官斌, 刘伟, 刘成梅, 苏坤明 (2011). 浸泡处理对早籼米糊化特性及质构特性的影响. 食品与机械 27(3), 13-15, 115. | |
| [12] |
He LN, Liu YJ, Xiao P, Zhang L, Guo Y, Yang TL, Zhao LJ, Drees B, Hamilton J, Deng HY, Recker RR, Deng HW (2008). Genomewide linkage scan for combined obesity phenotypes using principal component analysis. Ann Hum Genet 72, 319-326.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Holberg CJ, Halonen M, Solomon S, Graves PE, Baldini M, Erickson RP, Martinez FD (2001). Factor analysis of asthma and atopy traits shows 2 major components, one of which is linked to markers on chromosome 5q. J Allergy Clin Immunol 108, 772-780. |
| [14] |
Huang XH, Wei XH, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li CY, Zhu CR, Lu TT, Zhang ZW, Li M, Fan DL, Guo YL, Wang AH, Wang L, Deng LW, Li WJ, Lu YQ, Weng QJ, Liu KY, Huang T, Zhou TY, Jing YF, Li W, Lin Z, Buckler ES, Qian Q, Zhang QF, Li JY, Han B (2010). Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet 42, 961-967.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Isshiki M, Matsuda Y, Takasaki A, Wong HL, Satoh H, Shimamoto K (2008). Du3, a mRNA cap-binding protein gene, regulates amylose content in japonica rice seeds. Plant Biotechnol 25, 483-487. |
| [16] | Jiang JF (2020). Evaluation, QTL Analysis and Candidate Gene Prediction for Berry Texture in Vitis vinifera L. PhD dissertation. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. pp. 88-92. (in Chinese) |
| 姜建福 (2020). 葡萄果肉质地性状的评价、QTL定位及候选基因预测. 博士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 88-92. | |
| [17] | Jin LC, Geng ZM, Li JZ, Wang P, Chen F, Liu AM (2011). Correlation between components and molecule structure of rice starch and eating quality. Jiangsu J Agric Sci 27, 13-18. (in Chinese) |
| 金丽晨, 耿志明, 李金州, 王澎, 陈菲, 刘蔼民 (2011). 稻米淀粉组成及分子结构与食味品质的关系. 江苏农业学报 27, 13-18. | |
| [18] |
Li HY, Prakash S, Nicholson TM, Fitzgerald MA, Gilbert RG (2016). The importance of amylose and amylopectin fine structure for textural properties of cooked rice grains. Food Chem 196, 702-711.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | Li XH, Zhang RY, Meng QH, Gao F, Yao XM, Xu CJ (2007). Advantages of palatability evaluation methods for japonica rice variety. North Rice (5), 5-9. (in Chinese) |
| 李霞辉, 张瑞英, 孟庆虹, 高锋, 姚鑫淼, 许长军 (2007). 粳稻品种食味品质评价方法的研究进展. 北方水稻 (5), 5-9. | |
| [20] | Li XM, Wang LF, Tang YS, Chang YJ, Zhang JX, Wang SM, Wu J (2023). Genome-wide association analysis of resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in common bean. Chin Bull Bot 58, 77-89. (in Chinese) |
|
李晓明, 王兰芬, 唐永生, 常玉洁, 张菊香, 王述民, 武晶 (2023). 普通菜豆抗菜豆象性状的全基因组关联分析. 植物学报 58, 77-89.
DOI |
|
| [21] | Liao CY, Wu P, Hu B, Yi KK (2001). Effects of genetic background and environment on QTLs and epistasis for rice (Oryza sativa L.) panicle number. Theor Appl Genet 103, 104-111. |
| [22] |
Lin T, Zhu GT, Zhang JH, Xu XY, Yu QH, Zheng Z, Zhang ZH, Lun YY, Li S, Wang XX, Huang ZJ, Li JM, Zhang CZ, Wang TT, Zhang YY, Wang AX, Zhang YC, Lin K, Li CY, Xiong GS, Xue YB, Mazzucato A, Causse M, Fei ZJ, Giovannoni JJ, Chetelat RT, Zamir D, Städler T, Li JF, Ye ZB, Du YC, Huang SW (2014). Genomic analyses provide insights into the history of tomato breeding. Nat Genet 46, 1220-1226.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Lu H, Yuan YJ, Zhang SQ, Chen H, Chen D, Zhong XY, Li B, Deng F, Chen Y, Li GY, Ren WJ (2021). Evaluation of rice eating quality and optimization of varieties of southwest indica hybrid rice based on three taste evaluation methods. Sci Agric Sin 54, 1243-1257. (in Chinese) |
|
卢慧, 袁玉洁, 张丝琪, 陈虹, 陈多, 钟晓媛, 李博, 邓飞, 陈勇, 李贵勇, 任万军 (2021). 基于3种方法的西南杂交籼稻稻米食味评价及品种优选. 中国农业科学 54, 1243-1257.
DOI |
|
| [24] | Meng QH, Meng CL, Yan S, Zhang ZH, Wang LQ, Zhang YL, Zhang SW, Lu SW (2017). Optimization of rice texture properties determination by three grains method. Food Sci Technol 42(5), 157-164. (in Chinese) |
| 孟庆虹, 孟春玲, 严松, 张志宏, 王丽群, 张英蕾, 张守文, 卢淑雯 (2017). 三粒法米饭质构测定参数优化. 食品科技 42(5), 157-164. | |
| [25] |
Monna L, Lin H, Kojima S, Sasaki T, Yano M (2002). Genetic dissection of a genomic region for a quantitative trait locus, Hd3, into two loci, Hd3a and Hd3b, controlling heading date in rice. Theor Appl Genet 104, 772-778.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Shan ZC, Chen FZ (2023). Research progress on factors affecting the flavor quality of rice. Bull Agric Sci Technol (11), 140-143. (in Chinese) |
| 单智超, 陈富忠 (2023). 影响稻米食味品质因素的研究进展. 农业科技通讯 (11), 140-143. | |
| [27] | Shi SJ, Wang ET, Li CX, Cai ML, Cheng B, Cao CG, Jiang Y (2022). Use of protein content, amylose content, and RVA parameters to evaluate the taste quality of rice. Front Nutr 8, 758547. |
| [28] | Sreenivasulu N, Zhang CQ, Tiozon RN Jr, Liu QQ (2022). Post-genomics revolution in the design of premium quality rice in a high-yielding background to meet consumer demands in the 21st century. Plant Commun 3, 100271. |
| [29] | Sultana S, Faruque M, Islam R (2022). Rice grain quality parameters and determination tools: a review on the current developments and future prospects. Int J Food Prop 25, 1063-1078. |
| [30] | Sun L (2021). QTL Identification and Candidate Genes Analysis for Central Flesh Hardness of Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). PhD dissertation. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University. pp. 34-38. (in Chinese) |
| 孙蕾 (2021). 西瓜中心果肉硬度主效QTL及候选基因分析. 博士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. pp. 34-38. | |
| [31] | Tang ZW, Zhang DP (2023). Research progress on the molecular mechanism of starch accumulation in rice endosperm. Chin Bull Bot 58, 612-621. (in Chinese) |
|
唐子雯, 张冬平 (2023). 水稻胚乳淀粉积累过程的分子机理研究进展. 植物学报 58, 612-621.
DOI |
|
| [32] | Tu B, Zhang T, Liu P, Yang W, Zheng L, Dai Y, Wang H, Lin S, Zhang ZH, Zheng XH, Yuan MT, Chen Y, Zhu XB, Yuan H, Li T, Xiong JW, Zhong ZH, Chen WL, Ma BT, Qin P, Wang YP, Li SG (2025). The LCG1-OsBP5/ OsEBP89-Wx module regulates the grain chalkiness and taste quality in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 23, 36-50. |
| [33] | Wang CG, Ju RH, Ma CL, Liu XF, Duan LL (2015). Different cooking methods affect the quality of instant rice. Food Ind 36(2), 118-121. (in Chinese) |
| 汪长钢, 句荣辉, 马长路, 刘小飞, 段丽丽 (2015). 不同蒸煮方式对方便米饭品质影响研究. 食品工业 36(2), 118-121. | |
| [34] | Wang CL, Chang JN, Zhong KZ, Guo W, Hui SZ, Wang JL, Jiao GA (2022). QTL mapping of the traits for rice texture characteristics. Mol Plant Breed. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220216.1055.002.html. (inChinese) |
| 王翠丽, 常俊楠, 钟开珍, 郭雯, 惠索祯, 王建龙, 焦桂爱 (2022). 米饭质构特性QTL定位分析. 分子植物育种. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220216.1055.002.html. | |
| [35] | Wang LH, Zhang JN, Zhang XX, Sun HF, Zhou HL, Zhou S (2023). Research progress of rice taste quality and its influencing factors in China. Acta Agric Shanghai 39(3), 148-154. (in Chinese) |
| 王乐惠, 张继宁, 张鲜鲜, 孙会峰, 周化岚, 周胜 (2023). 我国稻米食味品质的研究进展及其影响因素. 上海农业学报 39(3), 148-154. | |
| [36] | Wang PY, Lu XH, Pang LJ (2016). Key physicochemical factors of rice affecting textural properties and sensory of cooked rice. Sci Technol Food Ind 37, 119-124. (in Chinese) |
| 王鹏跃, 路兴花, 庞林江 (2016). 影响米饭质构特性和感官的关键理化因素分析. 食品工业科技 37, 119-124. | |
| [37] | Wu BB, Hao YQ, Yang SB, Huang YX, Guan PF, Zheng XW, Zhao JJ, Qiao L, Li XH, Liu WZ, Zheng J (2023). Evaluation and genetic variation of grain lutein contents in common wheat from Shanxi. Chin Bull Bot 58, 535-547. (in Chinese) |
|
武棒棒, 郝宇琼, 杨淑斌, 黄雨茜, 关攀锋, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 乔玲, 李晓华, 刘维仲, 郑军 (2023). 山西小麦籽粒叶黄素含量变异及遗传特性分析. 植物学报 58, 535-547.
DOI |
|
| [38] | Wu CM, Sun CQ, Wang XK, Li ZC, Fu XL, Zhang Q (2003). Study on QTLs of grain eating quality characters in rice. J Jilin Agric Sci 28(2), 6-14. (in Chinese) |
| 吴长明, 孙传清, 王象坤, 李自超, 付秀林, 张强 (2003). 稻米食味品质性状的QTL分析. 吉林农业科学 28(2), 6-14. | |
| [39] |
Xi M, Ji YL, Wu WG, Xu YZ, Sun XY, Zhou YJ (2020). Research progress and prospects of factors affecting rice eating quality. Chin Agric Sci Bull 36(12), 159-164. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
习敏, 季雅岚, 吴文革, 许有尊, 孙雪原, 周永进 (2020). 水稻食味品质形成影响因素研究与展望. 中国农学通报 36(12), 159-164.
DOI |
|
| [40] | Xu H, Li XK, Lu JH, Jiang K, Ma Y, Xu ZJ, Xu Q (2023). The effect of Indica/xian pedigree introgression in Japonica/geng rice breeding in China. Sci Agric Sin 56, 4359-4370. (in Chinese) |
|
徐海, 李秀坤, 芦佳浩, 姜恺, 马玥, 徐正进, 徐铨 (2023). 籼型血缘渗入对北方粳稻产量和品质的影响. 中国农业科学 56, 4359-4370.
DOI |
|
| [41] | Xu Q, Tang L, Xu F, Fukushima A, Huang RD, Chen WF, Xu ZJ (2017). Research advances and prospects of eating quality improvement in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin 39, 961-968. (in Chinese) |
| 徐铨, 唐亮, 徐凡, 福嶌阳, 黄瑞冬, 陈温福, 徐正进 (2017). 粳稻食味品质改良研究现状与展望. 作物学报 39, 961-968. | |
| [42] | Xu R, Sui Y, Li SY, Zhu ZZ, Zhou L, Shi JB, Cai S, Xiong T, Cai F, Mei X (2024). Research progress on influencing factors of rice eating quality. J Food Saf Qual 15(7), 234-241. (in Chinese) |
| 许锐, 隋勇, 李书艺, 祝振洲, 周雷, 施建斌, 蔡沙, 熊添, 蔡芳, 梅新 (2024). 稻米食味品质影响因素研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报 15(7), 234-241. | |
| [43] | Xu SN, Li CP (2011). Dissection to three typical issues of principal component analysis. Math Theor Appl 31(4), 116-121. (in Chinese) |
| 许淑娜, 李长坡 (2011). 对主成分分析法三个问题的剖析. 数学理论与应用 31(4), 116-121. | |
| [44] | Xu ZJ, Chen WF, Ma DR, Wu XD, Zheng YY, Wang JY (2005). Relationship between eating quality and other quality characters of rice in Liaoning. Acta Agron Sin 31, 1092-1094. (in Chinese) |
| 徐正进, 陈温福, 马殿荣, 吴晓冬, 郑煜焱, 王嘉宇 (2005). 辽宁水稻食味值及其与品质性状的关系. 作物学报 31, 1092-1094. | |
| [45] | Xu ZJ, Han Y, Shao GJ, Zhang XJ, Quan CZ, Pan GJ, Yan P, Chen WF (2010). Comparison of rice quality characters in Northeast region of China. Chin J Rice Sci 24, 531-534. (in Chinese) |
|
徐正进, 韩勇, 邵国军, 张学军, 全成哲, 潘国君, 闫平, 陈温福 (2010). 东北三省水稻品质性状比较研究. 中国水稻科学 24, 531-534.
DOI |
|
| [46] |
Yang TT, Wei J, Zou JX, Wu LM, Bao XZ, Huang Q, Chen QC, Zhang B (2023). Difference in grain qualities of early and late season dual-use rice cultivars planted in early and late seasons. J Nucl Agric Sci 37, 1843-1851. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
杨陶陶, 韦佳, 邹积祥, 伍龙梅, 包晓哲, 黄庆, 陈青春, 张彬 (2023). 早晚兼用型水稻稻米品质在早、晚季的差异特征. 核农学报 37, 1843-1851.
DOI |
|
| [47] | Yang XH, Nong BX, Xia XZ, Zhang ZQ, Zeng Y, Liu KQ, Deng GF, Li DT (2016). Genome-wide association study of genes related to waxiness in Oryza sativa. Chin Bull Bot 51, 737-742. (in Chinese) |
|
杨行海, 农保选, 夏秀忠, 张宗琼, 曾宇, 刘开强, 邓国富, 李丹婷 (2016). 水稻糯性相关基因的全基因组关联分析. 植物学报 51, 737-742.
DOI |
|
| [48] |
Yano K, Morinaka Y, Wang FM, Huang P, Takehara S, Hirai T, Ito A, Koketsu E, Kawamura M, Kotake K, Yoshida S, Endo M, Tamiya G, Kitano H, Ueguchi- Tanaka M, Hirano K, Matsuoka M (2019). GWAS with principal component analysis identifies a gene comprehensively controlling rice architecture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 21262-21267.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Yao XY, Wang JY, Liu J, Wang Q, Jiang X, Jiang SK, Xu ZJ (2016). Dissection of quantitative trait loci for cooking and eating quality traits in Oryza sativa subsp. japonica. Chin Bull Bot 51, 757-763. (in Chinese) |
|
姚晓云, 王嘉宇, 刘进, 王棋, 姜鑫, 姜树坤, 徐正进 (2016). 粳稻蒸煮食味品质相关性状的QTL分析. 植物学报 51, 757-763.
DOI |
|
| [50] | Yu ZR (2007). Mapping Quantitative Trait Loci Underlying the Texture and Cooking Quality of Rice Using A RIL Population. Master’s thesis. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. pp. 2-3. (in Chinese) |
| 余峥嵘 (2007). 米饭蒸煮品质以及质构的QTL定位研究. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 2-3. | |
| [51] | Zhang X, Safdar LB, Tang MQ, Liu YY, Zhang YY, Liu SY (2021). Genetic dissection of plant architecture-related traits by GWAS with PCA in Brassica napus. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 43, 462-469. (in Chinese) |
| 张旭, Safdar LB, 唐敏强, 刘越英, 张园园, 刘胜毅 (2021). 结合PCA和GWAS解析甘蓝型油菜株型相关性状的遗传调控位点. 中国油料作物学报 43, 462-469. | |
| [52] | Zhao KY, Tung CW, Eizenga GC, Wright MH, Ali ML, Price AH, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Reynolds A, Mezey J, McClung AM, Bustamante CD, McCouch SR (2011). Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa. Nat Commun 2, 467. |
| [53] | Zhou XL, Wang H, Zhou YM, Zhang H, Hu YQ (2017). Influence of different cooking methods on eating quality of rice. Food Sci 38(11), 75-80. (in Chinese) |
|
周小理, 王惠, 周一鸣, 张欢, 胡业芹 (2017). 不同烹煮方式对米饭食味品质的影响. 食品科学 38(11), 75-80.
DOI |
|
| [54] | Zhou XQ, Ren HL, Zhang YR, Wang JF (2012). Correlation between texture property of cooked rice and main quality properties of rice. J Henan Univ Technol (Nat Sci Ed) 33(5), 21-24. (in Chinese) |
| 周显青, 任洪玲, 张玉荣, 王军锋 (2012). 大米主要品质指标与米饭质构的相关性分析. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版) 33(5), 21-24. | |
| [55] |
Zhu DW, Zhang LP, Chen MX, Fang CY, Yu YH, Zheng XL, Shao YF (2022). Characteristics of high-quality rice varieties and taste sensory evaluation values in China. Sci Agric Sin 55, 1271-1283. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
朱大伟, 章林平, 陈铭学, 方长云, 于永红, 郑小龙, 邵雅芳 (2022). 中国优质稻品种品质及食味感官评分值的特征. 中国农业科学 55, 1271-1283.
DOI |
| [1] | 张锋, Richard Dormatey, 刘寅笃, 李成举, 王云姣, 张春利, 张莹, 范又方, 姚攀锋, 毕真真, 刘玉汇, 白江平, 孙超. 耐亚磷酸盐马铃薯的筛选与评价[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 544-557. |
| [2] | 武棒棒, 郝宇琼, 杨淑斌, 黄雨茜, 关攀锋, 郑兴卫, 赵佳佳, 乔玲, 李晓华, 刘维仲, 郑军. 山西小麦籽粒叶黄素含量变异及遗传特性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 535-547. |
| [3] | 李晓明, 王兰芬, 唐永生, 常玉洁, 张菊香, 王述民, 武晶. 普通菜豆抗菜豆象性状的全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 77-89. |
| [4] | 李园, 常玉洁, 王兰芬, 王述民, 武晶. 普通菜豆镰孢菌枯萎病抗性种质资源筛选及全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 51-61. |
| [5] | 金京波, 梁承志. 饲草基因组学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(6): 732-741. |
| [6] | 宣伟, 徐国华. 植物适应土壤氮素环境的基因选择: 以水稻为例[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 1-5. |
| [7] | 赵宇慧, 李秀秀, 陈倬, 鲁宏伟, 刘羽诚, 张志方, 梁承志. 生物信息学分析方法I: 全基因组关联分析概述[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 715-732. |
| [8] | 何杰丽,石甜甜,陈凌,王海岗,高志军,杨美红,王瑞云,乔治军. 糜子EST-SSR分子标记的开发及种质资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 723-732. |
| [9] | 刘勋,张娇,沈昱辰,谢德斌,李宏利,李春明,易小平,赵勇,唐道彬,吕长文,王季春. 基于光合系统参数建立马铃薯耐荫性综合评价体系[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 360-370. |
| [10] | 周亚峰, 许彦宾, 王艳玲, 李琼, 胡建斌. 基于主成分-聚类分析构建甜瓜幼苗耐冷性综合评价体系[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(4): 520-529. |
| [11] | 汪鸿儒, 储成才. 组学技术揭示水稻杂种优势遗传机制[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(1): 4-9. |
| [12] | 杨行海, 农保选, 夏秀忠, 张宗琼, 曾宇, 刘开强, 邓国富, 李丹婷. 水稻糯性相关基因的全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(6): 737-742. |
| [13] | 厉新民, 林鸿宣. 全基因组关联分析实现水稻粒型自然变异的分子解析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(4): 411-415. |
| [14] | 严玫, 张新友, 韩锁义, 黄冰艳, 董文召, 刘华, 孙子淇, 张忠信, 汤丰收. 花生重要农艺及产量性状的全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(4): 460-472. |
| [15] | 王鹏飞, 王倩倩, 李先恩, 秦民坚. GC-MS技术在延胡索块茎代谢产物研究中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47(2): 149-154. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||