

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (5): 547-549.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19166 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19166
• 热点评 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2019-08-27
接受日期:2019-09-17
出版日期:2019-09-01
发布日期:2019-01-01
通讯作者:
陈学伟
Weitao Li,Min He,Xuewei Chen( )
)
Received:2019-08-27
Accepted:2019-09-17
Online:2019-09-01
Published:2019-01-01
Contact:
Xuewei Chen
摘要: 由真菌Rhizoctonia solani引起的纹枯病严重危害玉米(Zea mays)和水稻(Oryza sativa)等作物的安全生产。R. solani的宿主范围广且抗源少, 加之相关的抗性机制研究有限, 导致纹枯病的危害长期得不到有效控制。近期, 中国科学家通过对318份玉米自交系进行全基因组关联分析, 筛选到1个与纹枯病抗性相关的、编码F-box结构域蛋白的候选基因ZmFBL41 (GRMZM2G109140)。ZmFBL41蛋白是SCF (SKP1-Cullin-F-box) E3泛素连接酶复合体的一员, 能介导复合体对肉桂醇脱氢酶ZmCAD的降解, 从而降低木质素的积累, 使玉米易感纹枯病。玉米抗病自交系Chang7-2中, 蛋白ZmFBL41 Chang7-2因2个关键氨基酸的变异, 不能结合并降解底物ZmCAD, 使木质素含量增加, 从而提高玉米对纹枯病的抗性。该研究率先揭示了SCF复合体可通过降解肉桂醇脱氢酶来调控植物免疫反应的新型分子机制, 为提高玉米及其它作物对纹枯病的抗性提供了重要理论依据和基因资源。
李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549.
Weitao Li, Min He, Xuewei Chen. Discovery of ZmFBL41 Chang7-2 as A Key Weapon against Banded Leaf and Sheath Blight Resistance in Maize. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(5): 547-549.
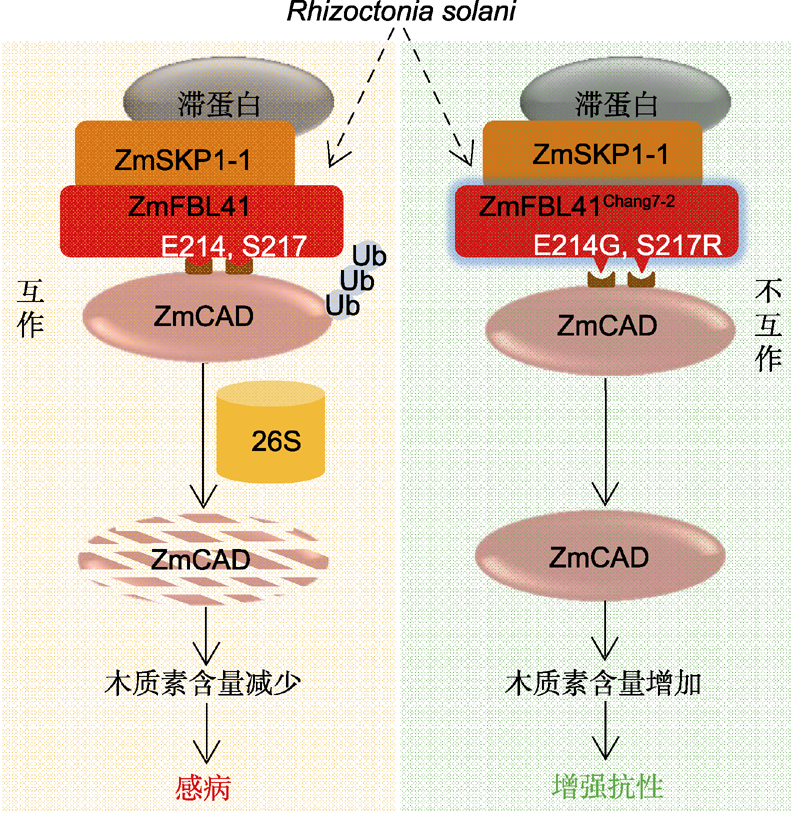
图1 ZmFBL41介导的纹枯病抗性 ZmFBL41与ZmSKP1-1互作形成SCF复合体, 通过26S蛋白酶体降解底物ZmCAD, 减少木质素的积累, 从而使玉米易感纹枯病。而ZmFBL41Chang7-2因其中2个关键氨基酸位点变异(E214G, S217R), 不能结合并降解底物ZmCAD, 从而引起木质素积累, 使玉米对纹枯病的抗性增强。
Figure 1 A model for ZmFBL41-mediated banded leaf and sheath blight (BLSB) resistance ZmFBL41 interacts with ZmSKP1-1 to form the SCF complex, and recruits ZmCAD for 26S proteasome-mediated degradation, resulting in reduced lignin synthesis and increased susceptibility of maize to R. solani. However, in the natural maize resource Chang7-2, the protein ZmFBL41Chang7-2 with two amino acid variations (E214G and S217R) is not able to interact with ZmCAD, leading to failure in degradation of ZmCAD and resulting in accumulation of lignin, which consequently enhances resistance to R. solani.
| 1 | Baruah P, Lal S (1981). Hostrange of Rhizoctonia solani f. sp. sasakii, then incitant of banded sclerotial disease of maize. Indian Phytopath 34, 494-496. |
| 2 | Hooda KS, Khokhar MK, Parmar H, Gogoi R, Joshi D, Sharma SS, Yadav OP (2017). Banded leaf and sheath blight of maize: historical perspectives, current status and future directions. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 87, 1041-1052. |
| 3 | Li N, Lin B, Wang H, Li X, Yang F, Ding X, Yan J, Chu Z (2019). Natural variation in ZmFBL41 confers banded leaf and sheath blight resistance in maize. Nat Genet 51, 1540-1548. |
| 4 | Li Z, Pinson SRM, Marchetti MA, Stansel JW, Park WD (1995). Characterization of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in cultivated rice contributing to field resistance to sheath blight ( Rhizoctonia solani). Theor Appl Genet 91, 382-388. |
| 5 | Maeda S, Dubouzet JG, Kondou Y, Jikumaru Y, Seo S, Oda K, Matsui M, Hirochika H, Mori M (2019) The rice CYP78A gene BSR2 confers resistance to Rhizoctonia solani and affects seed size and growth in Arabidopsis and rice. Sci Rep 9, 587. |
| 6 | Ogoshi A (1987). Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and interspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Ann Rev Phytopathol 25, 125-143. |
| 7 | Peng X, Wang H, Jang JC, Xiao T, He H, Jiang D, Tang X (2016). OsWRKY80-OsWRKY4 module as a positive regulatory circuit in rice resistance against Rhizoctonia solani. Rice 9, 63. |
| 8 | Richa K, Tiwari IM, Devanna BN, Botella JR, Sharma V, Sharma TR (2017). Novel chitinase gene LOC_Os 11g47510 from indica rice Tetep provides enhanced resistance against sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia solani in rice. Front Plant Sci 8, 596. |
| 9 | Sharma RC, Srinivas P, Batsa BK (2002). Banded leaf and sheath blight of maize its epidemiology and management. In: Rajbhandari NP, Ransom JK, Adhikari K, Palmer AFE, eds. Proceedings of a Maize Symposium Held. Kathmandu: NARC and CIMMYT. pp. 108-112. |
| 10 | Sharma RR, Gour HN, Rathore RS (2004). Etiology of banded leaf and sheath blight symptoms on maize. J Mycol Plant Pathol 34, 56-59. |
| 11 | Singh BM, Sharma YR (1976). Evaluation of maize germplasm to banded sclerotial disease and assessment of yield loss. Indian Phytopath 29, 129-132. |
| 12 | Wang H, Meng J, Peng X, Tang X, Zhou P, Xiang J, Deng X (2015). Rice WRKY4 acts as a transcriptional activator mediating defense responses toward Rhizoctonia solani, the causing agent of rice sheath blight. Plant Mol Biol 89, 157-171. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [5] | 杜淑辉, 褚建民, 段俊光, 薛建国, 徐磊, 徐晓庆, 王其兵, 黄建辉, 张倩. 木质素酚类物质对内蒙古退化草地土壤有机碳的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 30-41. |
| [6] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [7] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [8] | 郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊. 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 999-1006. |
| [9] | 李园, 范开建, 安泰, 李聪, 蒋俊霞, 牛皓, 曾伟伟, 衡燕芳, 李虎, 付俊杰, 李慧慧, 黎亮. 玉米自然群体自交系农艺性状的多环境全基因组预测初探[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1041-1053. |
| [10] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [11] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [12] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [13] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [14] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [15] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||