

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (6): 932-949.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24078 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24078
所属专题: 大食物观; 玉米生物学与分子设计(2024年59卷6期)
收稿日期:2024-05-24
接受日期:2024-07-23
出版日期:2024-11-10
发布日期:2024-07-29
通讯作者:
*万向元, 博士, 二级教授, 博导, 北京科技大学生物农业研究院院长, 北京中智生物农业国际研究院院长, 教育部“长江学者”特岗教授, 国家“万人计划”领军人才, 北京市特聘专家, “十四五”国家重点研发计划项目首席科学家, 中国作物学会常务理事、中国生物工程学会常务理事。主要从事玉米雄性不育机制解析及工程核不育技术、玉米绿色高效育种与遗传基础研究。E-mail: wanxiangyuan@ustb.edu.cn
基金资助:
Suowei Wu1,2, Xueli An1,2, Xiangyuan Wan1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-05-24
Accepted:2024-07-23
Online:2024-11-10
Published:2024-07-29
Contact:
*E-mail: wanxiangyuan@ustb.edu.cn
摘要: 玉米(Zea mays)是我国种植面积最大和总产量最高的第一大粮食作物, 同时也是杂种优势利用的典范。但与发达国家相比, 我国玉米生产仍然存在着平均单产偏低、突破性品种缺乏和杂交种生产成本高等突出问题。雄性不育系的应用可进一步提高玉米杂种优势的利用效率并最终提高单产。该文综述了玉米雄性不育的分类、基因克隆与机理解析以及分子调控网络构建最新研究进展, 系统介绍了已建立的玉米新型工程核不育技术体系及其应用前景, 为推动玉米雄性发育生物学研究与开展玉米雄性不育杂交育种和制种提供重要参考。
吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949.
Suowei Wu, Xueli An, Xiangyuan Wan. Molecular Mechanisms of Male Sterility and their Applications in Biotechnology-based Male-sterility Hybrid Seed Production in Maize. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(6): 932-949.
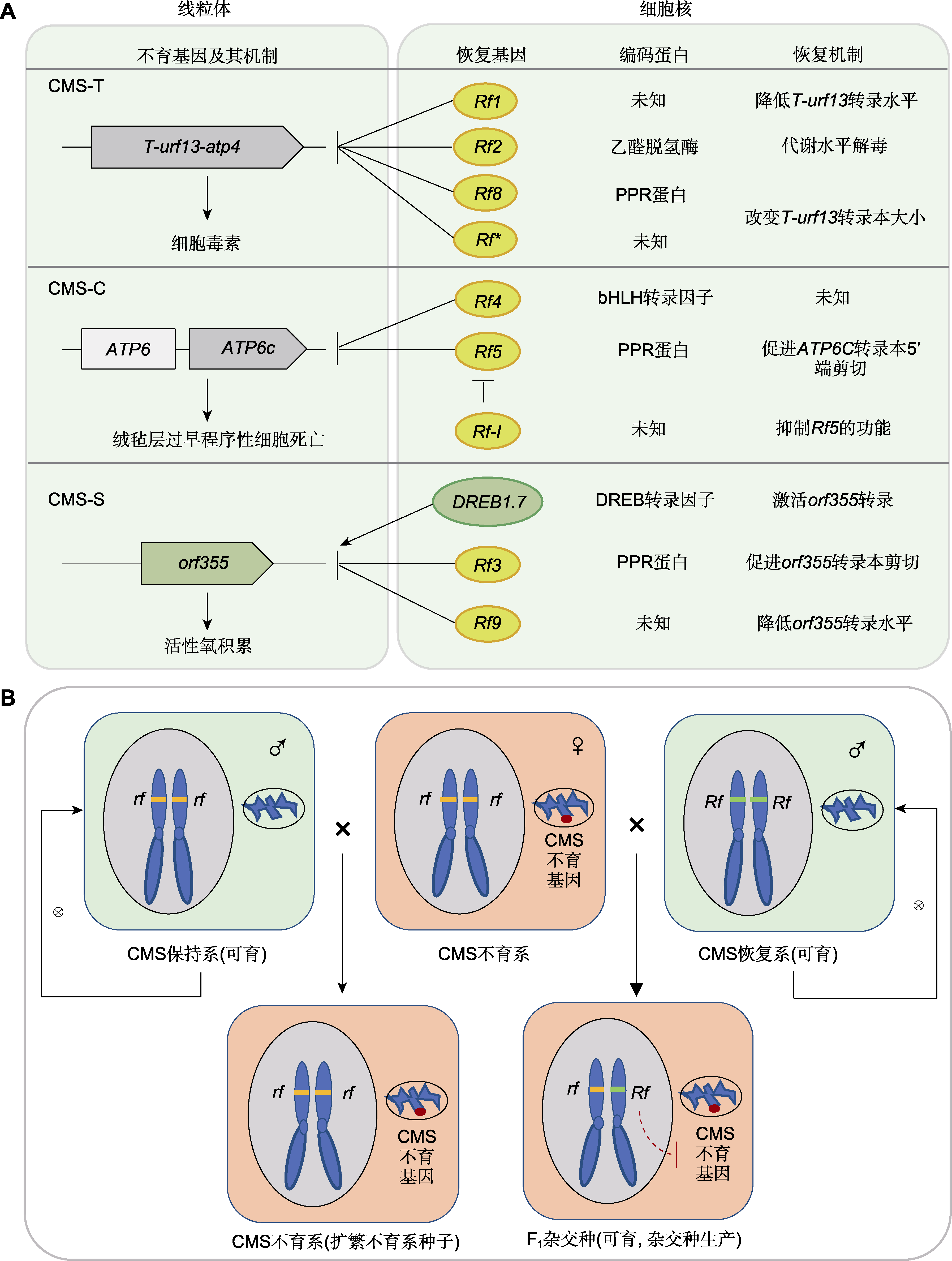
图1 玉米细胞质不育(CMS)和三系法杂交制种 (A) 三种类型细胞质不育及其育性恢复机制(箭头表示激活作用, T型线表示抑制作用); (B) 三系法杂交制种原理
Figure 1 Maize cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) and three-line hybrid seed production (A) Mechanism of male sterility and restoration of three types of CMS (arrow means activation, T type line means suppression); (B) The roadmap of three-line hybrid seed production
| 序号 | 不育基因 | 基因ID | 编码蛋白 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I 转录因子类 | ||||
| 1 | ZmMs1/ZmLBD30 | Zm00001d036435 | LBD转录因子 | Hou et al., |
| 2 | ZmIG1 | Zm00001d042560 | LBD转录因子 | Evans, |
| 3 | ZmLBD10 | Zm00001d033335 | LBD转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 4 | ZmLBD27 | Zm00001d013732 | LBD转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 5 | ZmMs7 | Zm00001d020680 | PHD-finger转录因子 | Zhang et al., |
| 6 | ZmPHD11 | Zm00001d013416 | PHD-finger转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 7 | ZmMs9 | Zm00001d028777 | MYB转录因子 | Albertsen et al., |
| 8 | ZmMYB33-1 | Zm00001d012544 | MYB转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 9 | ZmMYB33-2 | Zm00001d043131 | MYB转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 10 | ZmMYB84 | Zm00001d025664 | MYB转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 11 | ZmMs23 | Zm00001d008174 | bHLH转录因子 | Nan et al., |
| 12 | ZmMs32 | Zm00001d006564 | bHLH转录因子 | Moon et al., |
| 13 | ZmbHLH51 | Zm00001d053895 | bHLH转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 14 | ZmbHLH122 | Zm00001d017724 | bHLH转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 15 | ZmOCL4 | Zm00001d030069 | HD-ZIP转录因子 | Vernoud et al., |
| 16 | ZmTGA9-1 | Zm00001d052543 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 17 | ZmTGA9-2 | Zm00001d042777 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 18 | ZmTGA9-3 | Zm00001d012294 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 19 | ZmTGA10 | Zm00001d020938 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 20 | ZmMs53 | Zm00001d053890 | SBP转录因子 | Liu et al., |
| II 脂代谢类 | ||||
| 21 | ZmMs26 | Zm00001d027837 | 细胞色素P450单加氧酶, CYP704B1 | Djukanovic et al., |
| 22 | ZmMs10/APV1 | Zm00001d024712 | 细胞色素P450单加氧酶, CYP703A2 | Somaratne et al., |
| 23 | ZmMs30 | Zm00001d052403 | GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶 | An et al., |
| 24 | ZmMs5/IPE2 | Zm00001d015960 | GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶 | Huo et al., |
| 25 | ZmMs33/GPAT6 | Zm00001d007714 | 甘油-3-磷酸酰基转移酶 | Xie et al., |
| 26 | ZmMs45 | Zm00001d047859 | 异胡豆苷合成酶 | Cigan et al., |
| 27 | ZmMs20/IPE1* | Zm00001d029683 | GMC氧化还原酶 | Chen et al., |
| 28 | ZmMs25/ZmMs6021 | Zm00001d048337 | 脂肪酰还原酶 | Tian et al., |
| 29 | ZmMs44 | Zm00001d052736 | 非特异性脂质转移蛋白 | Fox et al., |
| 30 | ZmABCG26 | Zm00001d046537 | ABCG转运蛋白 | Jiang et al., |
| 31 | ZmMs13 | Zm00001d013960 | ABCG转运蛋白 | Fang et al., |
| 32 | ZmPKSB | Zm00001d019478 | 聚酮合酶B | Liu et al., |
| 33 | ZmTKPR1-1 | Zm00001d031488 | 四肽α-吡咯酮还原酶 | An et al., |
| 34 | ZmTKPR1-2 | Zm00001d020970 | 四肽α-吡咯酮还原酶 | An et al., |
| III 糖代谢类 | ||||
| 35 | ZmMs8 | Zm00001d012234 | β-1,3-半乳糖基转移酶 | Wang et al., |
| 36 | ZmMs39 | Zm00001d043909 | 胼胝质合成酶 | Zhu et al., |
| 37 | ZmSTK1 | Zm00001d045056 | 丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶1 | Fan et al., |
| 38 | ZmSTK2 | Zm00001d052067 | 丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶2 | Fan et al., |
| 39 | ZmINVAN6/Mei025 | Zm00001d015094 | 胞质转化酶 | Huang et al., |
| IV 其它途径类 | ||||
| 40 | ZmMs22/MSCA1 | Zm00001d018802 | 谷氧还蛋白 | Kelliher and Walbot, |
| 41 | ZmMAC1 | Zm00001d023681 | 小分泌蛋白配体 | Wang et al., |
| 42 | ZmMSP1 | Zm00001d042362 | 富亮氨酸重复受体激酶 | van der Linde et al., |
| 43 | ZmDRP1 | Zm00001d035791 | 干燥相关蛋白 | Hu et al., |
| 44 | ZmCOI2a | Zm00001d042833 | 茉莉酸受体 | Qi et al., |
| 45 | ZmCOI2b | Zm00001d010082 | 茉莉酸受体 | Qi et al., |
| 46 | ZmMs28/AGO5c | Zm00001d013063 | ARGONAUTE蛋白 | Li et al., |
| 47 | ZmMs42/HSP101 | Zm00001d038806 | 热激蛋白 | Li et al., |
| 48 | ZmTMS5 | Zm00001d053351 | RNA酶ZS1 | Li et al., |
| 49 | ZmDCL5 | Zm00001d032655 | Dicer类似蛋白 | Teng et al., |
表1 克隆鉴定的玉米核雄性不育(GMS)基因
Table 1 The cloned genic male-sterility (GMS) genes in maize
| 序号 | 不育基因 | 基因ID | 编码蛋白 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I 转录因子类 | ||||
| 1 | ZmMs1/ZmLBD30 | Zm00001d036435 | LBD转录因子 | Hou et al., |
| 2 | ZmIG1 | Zm00001d042560 | LBD转录因子 | Evans, |
| 3 | ZmLBD10 | Zm00001d033335 | LBD转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 4 | ZmLBD27 | Zm00001d013732 | LBD转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 5 | ZmMs7 | Zm00001d020680 | PHD-finger转录因子 | Zhang et al., |
| 6 | ZmPHD11 | Zm00001d013416 | PHD-finger转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 7 | ZmMs9 | Zm00001d028777 | MYB转录因子 | Albertsen et al., |
| 8 | ZmMYB33-1 | Zm00001d012544 | MYB转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 9 | ZmMYB33-2 | Zm00001d043131 | MYB转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 10 | ZmMYB84 | Zm00001d025664 | MYB转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 11 | ZmMs23 | Zm00001d008174 | bHLH转录因子 | Nan et al., |
| 12 | ZmMs32 | Zm00001d006564 | bHLH转录因子 | Moon et al., |
| 13 | ZmbHLH51 | Zm00001d053895 | bHLH转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 14 | ZmbHLH122 | Zm00001d017724 | bHLH转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 15 | ZmOCL4 | Zm00001d030069 | HD-ZIP转录因子 | Vernoud et al., |
| 16 | ZmTGA9-1 | Zm00001d052543 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 17 | ZmTGA9-2 | Zm00001d042777 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 18 | ZmTGA9-3 | Zm00001d012294 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 19 | ZmTGA10 | Zm00001d020938 | bZIP转录因子 | Jiang et al., |
| 20 | ZmMs53 | Zm00001d053890 | SBP转录因子 | Liu et al., |
| II 脂代谢类 | ||||
| 21 | ZmMs26 | Zm00001d027837 | 细胞色素P450单加氧酶, CYP704B1 | Djukanovic et al., |
| 22 | ZmMs10/APV1 | Zm00001d024712 | 细胞色素P450单加氧酶, CYP703A2 | Somaratne et al., |
| 23 | ZmMs30 | Zm00001d052403 | GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶 | An et al., |
| 24 | ZmMs5/IPE2 | Zm00001d015960 | GDSL酯酶/脂肪酶 | Huo et al., |
| 25 | ZmMs33/GPAT6 | Zm00001d007714 | 甘油-3-磷酸酰基转移酶 | Xie et al., |
| 26 | ZmMs45 | Zm00001d047859 | 异胡豆苷合成酶 | Cigan et al., |
| 27 | ZmMs20/IPE1* | Zm00001d029683 | GMC氧化还原酶 | Chen et al., |
| 28 | ZmMs25/ZmMs6021 | Zm00001d048337 | 脂肪酰还原酶 | Tian et al., |
| 29 | ZmMs44 | Zm00001d052736 | 非特异性脂质转移蛋白 | Fox et al., |
| 30 | ZmABCG26 | Zm00001d046537 | ABCG转运蛋白 | Jiang et al., |
| 31 | ZmMs13 | Zm00001d013960 | ABCG转运蛋白 | Fang et al., |
| 32 | ZmPKSB | Zm00001d019478 | 聚酮合酶B | Liu et al., |
| 33 | ZmTKPR1-1 | Zm00001d031488 | 四肽α-吡咯酮还原酶 | An et al., |
| 34 | ZmTKPR1-2 | Zm00001d020970 | 四肽α-吡咯酮还原酶 | An et al., |
| III 糖代谢类 | ||||
| 35 | ZmMs8 | Zm00001d012234 | β-1,3-半乳糖基转移酶 | Wang et al., |
| 36 | ZmMs39 | Zm00001d043909 | 胼胝质合成酶 | Zhu et al., |
| 37 | ZmSTK1 | Zm00001d045056 | 丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶1 | Fan et al., |
| 38 | ZmSTK2 | Zm00001d052067 | 丝氨酸苏氨酸激酶2 | Fan et al., |
| 39 | ZmINVAN6/Mei025 | Zm00001d015094 | 胞质转化酶 | Huang et al., |
| IV 其它途径类 | ||||
| 40 | ZmMs22/MSCA1 | Zm00001d018802 | 谷氧还蛋白 | Kelliher and Walbot, |
| 41 | ZmMAC1 | Zm00001d023681 | 小分泌蛋白配体 | Wang et al., |
| 42 | ZmMSP1 | Zm00001d042362 | 富亮氨酸重复受体激酶 | van der Linde et al., |
| 43 | ZmDRP1 | Zm00001d035791 | 干燥相关蛋白 | Hu et al., |
| 44 | ZmCOI2a | Zm00001d042833 | 茉莉酸受体 | Qi et al., |
| 45 | ZmCOI2b | Zm00001d010082 | 茉莉酸受体 | Qi et al., |
| 46 | ZmMs28/AGO5c | Zm00001d013063 | ARGONAUTE蛋白 | Li et al., |
| 47 | ZmMs42/HSP101 | Zm00001d038806 | 热激蛋白 | Li et al., |
| 48 | ZmTMS5 | Zm00001d053351 | RNA酶ZS1 | Li et al., |
| 49 | ZmDCL5 | Zm00001d032655 | Dicer类似蛋白 | Teng et al., |
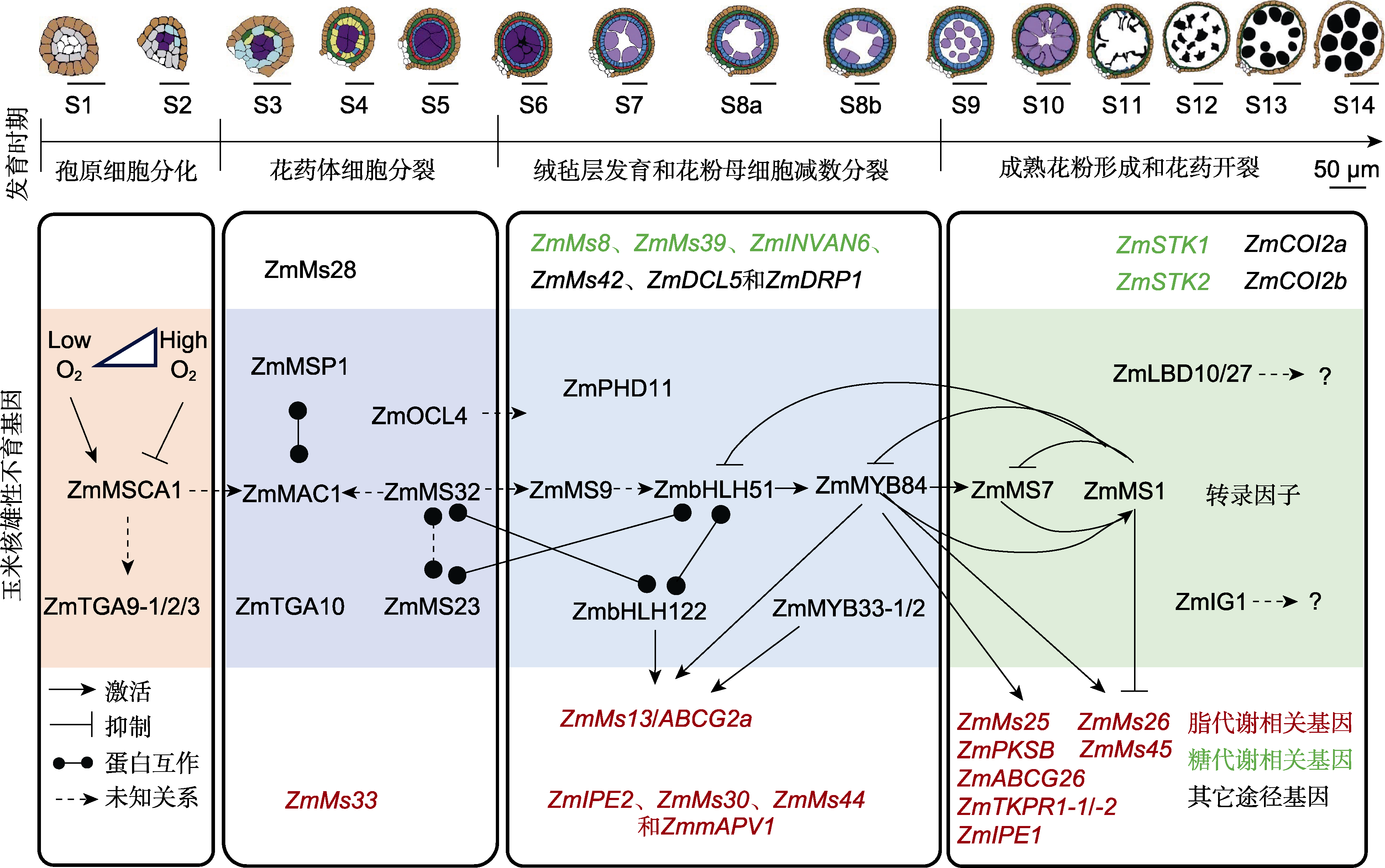
图2 已克隆的玉米核不育(GMS)基因及其调控花药和花粉发育的分子网络
Figure 2 The cloned genic male sterility (GMS) genes and the molecular regulation network of anther and pollen development in maize
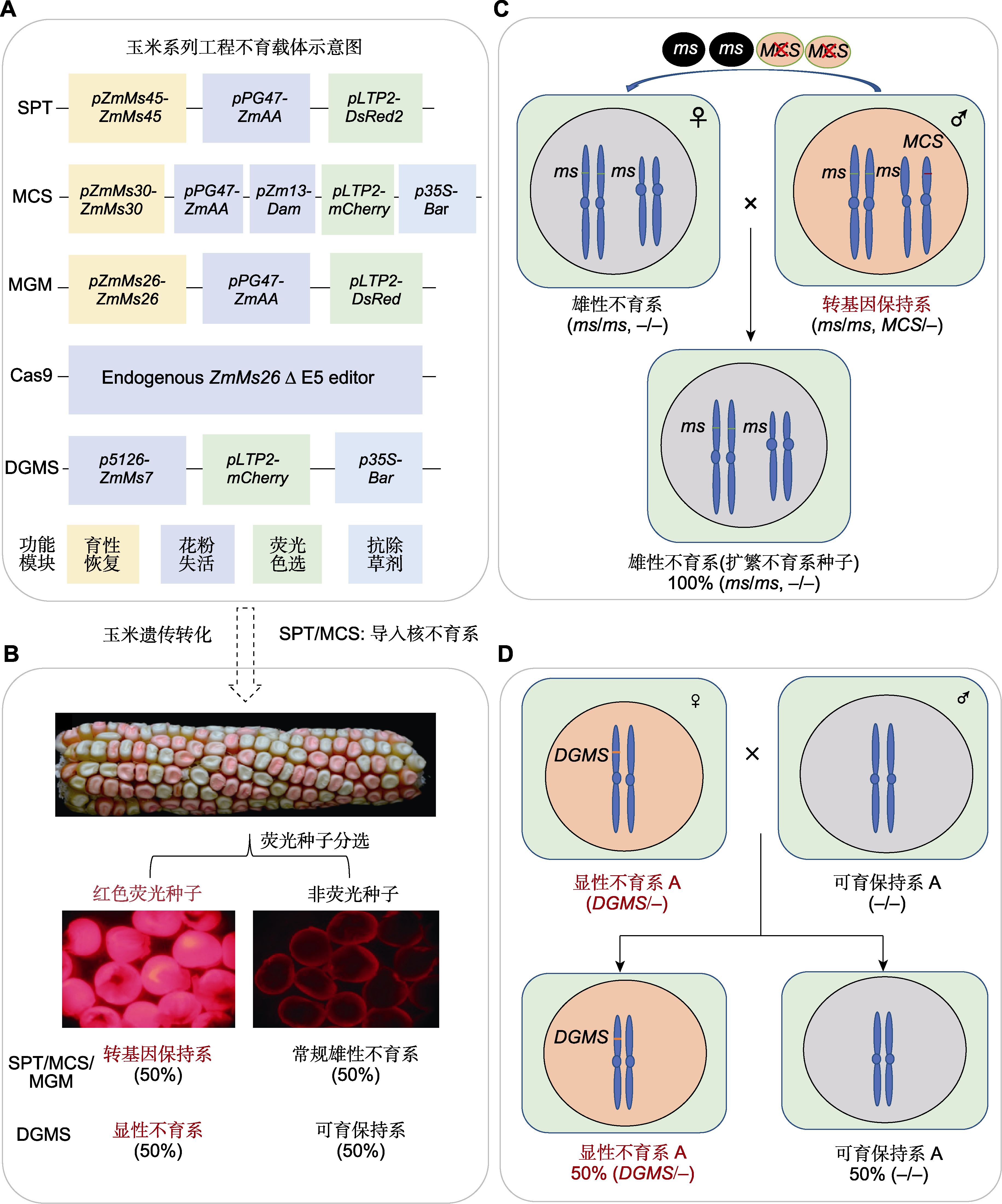
图3 基于生物技术的玉米工程核不育技术体系 (A) 玉米系列工程不育载体(SPT、MCS、MGM+Cas9和DGMS); (B) 玉米工程核不育系及其保持系的分离; (C), (D) 玉米多控不育系(MCS)和显性不育系(DGMS)的繁殖
Figure 3 Biotechnology-based genic male sterility systems in maize (A) Diagram of the expression constructs of SPT, MCS, MGM+Cas9 and DGMS systems in maize; (B) The segregation of male-sterility lines and maintainers in different systems; (C), (D) Propagation roadmap of maize multi-control sterility (MCS) lines and dominant genic male sterility (DGMS) lines
| [1] | Albertsen M, Fox T, Leonard A, Li B, Loveland B, Trimnell M (2016). Cloning and use of the ms9 gene from maize. US patent, US 20160024520A1. 2016-01-28. |
| [2] | An XL, Dong ZY, Tian YH, Xie K, Wu SW, Zhu TT, Zhang DF, Zhou Y, Niu CF, Ma B, Hou QC, Bao JX, Zhang SM, Li ZW, Wang YB, Yan TW, Sun XJ, Zhang YW, Li JP, Wan XY (2019). ZmMs30 encoding a novel GDSL lipase is essential for male fertility and valuable for hybrid breeding in maize. Mol Plant 12, 343-359. |
| [3] | An XL, Ma B, Duan MJ, Dong ZY, Liu RG, Yuan DY, Hou QC, Wu SW, Zhang DF, Liu DC, Yu D, Zhang YW, Xie K, Zhu TT, Li ZW, Zhang SM, Tian YH, Liu C, Li JP, Yuan LP, Wan XY (2020). Molecular regulation of ZmMs7 required for maize male fertility and development of a dominant male-sterility system in multiple species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 23499-23509. |
| [4] | An XL, Zhang SW, Jiang YL, Liu XZ, Fang CW, Wang J, Zhao LN, Hou QC, Zhang J, Wan XY (2024). CRISPR/ Cas9-based genome editing of 14 lipid metabolic genes reveals a sporopollenin metabolon ZmPKSB-ZmTKPR1- 1/-2 required for pollen exine formation in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 216-232. |
| [5] | Beckett JB (1971). Classification of male-sterile cytoplasms in maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci 11, 724-727. |
| [6] | Cai CF, Zhu J, Lou Y, Guo ZL, Xiong SX, Wang K, Yang ZN (2015). The functional analysis of OsTDF1 reveals a conserved genetic pathway for tapetal development between rice and Arabidopsis. Sci Bull 60, 1073-1082. |
| [7] |
Chaubal R, Anderson JR, Trimnell MR, Fox TW, Albertsen MC, Bedinger P (2003). The transformation of anthers in the msca1 mutant of maize. Planta 216, 778-788.
PMID |
| [8] |
Chen XY, Zhang H, Sun HY, Luo HB, Zhao L, Dong ZB, Yan SS, Zhao C, Liu RY, Xu CY, Li S, Chen HB, Jin WW (2017). IRREGULAR POLLEN EXINE1 is a novel factor in anther cuticle and pollen exine formation. Plant Physiol 173, 307-325.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Cheng JH, Li YC, Mei DS, Hu Q (2006). Molecular mapping and markers for fertility restorer genes of cytoplasmic male sterility in major crops. Chin Bull Bot 23, 613-624. (in Chinese) |
| 程计华, 李云昌, 梅德圣, 胡琼 (2006). 几种农作物细胞质雄性不育恢复基因的定位和分子标记研究进展. 植物学报 23, 613-624. | |
| [10] | Cigan AM, Unger E, Xu RJ, Kendall T, Fox TW (2001). Phenotypic complementation of ms45 maize requires tapetal expression of MS45. Sex Plant Reprod 14, 135-142. |
| [11] |
Collinson S, Hamdziripi E, De Groote H, Ndegwa M, Cairns JE, Albertsen M, Ligeyo D, Mashingaidze K, Olsen MS (2022). Incorporating male sterility increases hybrid maize yield in low input African farming systems. Commun Biol 5, 729.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Cui X, Wise RP, Schnable PS (1996). The rf2 nuclear restorer gene of male-sterile T-cytoplasm maize. Science 272, 1334-1336.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Dill CL, Wise RP, Schnable PS (1997). Rf8 and Rf* mediate unique T-urf13-transcript accumulation, revealing a conserved motif associated with RNA processing and restoration of pollen fertility in T-cytoplasm maize. Genetics 147, 1367-1379.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Djukanovic V, Smith J, Lowe K, Yang MZ, Gao HR, Jones S, Nicholson MG, West A, Lape J, Bidney D, Carl Falco S, Jantz D, Alexander Lyznik L (2013). Male- sterile maize plants produced by targeted mutagenesis of the cytochrome P450-like gene (MS26) using a re-designed I-CreI homing endonuclease. Plant J 76, 888-899. |
| [15] | Evans MMS (2007). The indeterminate gamethophyte1gene of maize encodes a LOB domain protein required for embryo sac and leaf development. Plant Cell 19, 46-62. |
| [16] | Fan MX, Zhang CY, Shi L, Liu C, Ma WJ, Chen MM, Liu KC, Cai FC, Wang GH, Wei ZY, Jiang M, Liu ZC, Javeed A, Lin F (2018). ZmSTK1 and ZmSTK2, encoding receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase, are involved in maize pollen development with additive effect. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 1402-1414. |
| [17] | Fang CW, Wu SW, Li ZW, Pan SS, Wu YR, An XL, Long Y, Wei X, Wan XY (2023a). A systematic investigation of lipid transfer proteins involved in male fertility and other biological processes in maize. Int J Mol Sci 24, 1660. |
| [18] | Fang CW, Wu SW, Niu CF, Hou QC, An XL, Wei X, Zhao LN, Jiang YL, Liu XZ, Wan XY (2023b). Triphasic regulation of ZmMs13 encoding an ABCG transporter is sequentially required for callose dissolution, pollen exine and anther cuticle formation in maize. J Adv Res 49, 15-30. |
| [19] |
Feng PCC, Qi YL, Chiu T, Stoecker MA, Schuster CL, Johnson SC, Fonseca AE, Huang JT (2014). Improving hybrid seed production in corn with glyphosate-mediated male sterility. Pest Manag Sci 70, 212-218.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Fox T, DeBruin J, Haug Collet K, Trimnell M, Clapp J, Leonard A, Li BL, Scolaro E, Collinson S, Glassman K, Miller M, Schussler J, Dolan D, Liu L, Gho C, Albertsen M, Loussaert D, Shen B (2017). A single point mutation in Ms44 results in dominant male sterility and improves nitrogen use efficiency in maize. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 942-952. |
| [21] | Fu ZY, Qin YT, Tang JH (2018). Reviews of photo-or/and thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene in major crops. China Biotechnol 38, 115-125. (in Chinese) |
| 付志远, 秦永田, 汤继华 (2018). 主要作物光温敏核雄性不育基因的研究进展与应用. 中国生物工程杂志 38, 115-125. | |
| [22] |
Gabay-Laughnan S, Kuzmin EV, Monroe J, Roark L, Newton KJ (2009). Characterization of a novel thermosensitive restorer of fertility for cytoplasmic male sterility in maize. Genetics 182, 91-103.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Han YJ, Hu MJ, Ma XX, Yan G, Wang CY, Jiang SQ, Lai JS, Zhang M (2022). Exploring key developmental phases and phase-specific genes across the entirety of anther development in maize. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 1394-1410.
DOI |
| [24] | Hou QC, An XL, Ma B, Wu SW, Wei X, Yan TW, Zhou Y, Zhu TT, Xie K, Zhang DF, Li ZW, Zhao LN, Niu CF, Long Y, Liu C, Zhao W, Ni F, Li JP, Fu DL, Yang ZN, Wan XY (2023). ZmMS1/ZmLBD30-orchestrated transcriptional regulatory networks precisely control pollen exine development. Mol Plant 16, 1321-1338. |
| [25] | Hu MJ, Li YF, Zhang XB, Song WB, Jin WW, Huang W, Zhao HM (2022). Maize sterility gene DRP1encodes a desiccation-related protein that is critical for Ubisch bodies and pollen exine development. J Exp Bot 73, 6800-6815. |
| [26] |
Hu YM, Tang JH, Yang H, Xie HL, Lu XM, Niu JH, Chen WC (2006). Identification and mapping of Rf-I an inhibitor of the Rf5restorer gene for CMS-C in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 113, 357-360.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Huang W, Li YF, Du Y, Pan LL, Huang YM, Liu HB, Zhao Y, Shi YL, Ruan YL, Dong ZB, Jin WW (2022). Maize cytosolic invertase INVAN6 ensures faithful meiotic progression under heat stress. New Phytol 236, 2172-2188.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Huo YQ, Pei YR, Tian YH, Zhang ZG, Li K, Liu J, Xiao SL, Chen HB, Liu J (2020). IRREGULAR POLLEN EXINE2 encodes a GDSL lipase essential for male fertility in maize. Plant Physiol 184, 1438-1454. |
| [29] | Jaqueth JS, Hou ZL, Zheng PZ, Ren RH, Nagel BA, Cutter G, Niu XM, Vollbrecht E, Greene TW, Kumpatla SP (2020). Fertility restoration of maize CMS-C altered by a single amino acid substitution within the Rf4 bHLH transcription factor. Plant J 101, 101-111. |
| [30] |
Jiang YL, An XL, Li ZW, Yan TW, Zhu TT, Xie K, Liu SS, Hou QC, Zhao LN, Wu SW, Liu XZ, Zhang SW, He W, Li F, Li JP, Wan XY (2021). CRISPR/Cas9-based discovery of maize transcription factors regulating male sterility and their functional conservation in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 1769-1784.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Kelliher T, Walbot V (2012). Hypoxia triggers meiotic fate acquisition in maize. Science 337, 345-348.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Levings III CS (1990). The Texas cytoplasm of maize: cytoplasmic male sterility and disease susceptibility. Science 250, 942-947.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Li J, Zhang HW, Si XM, Tian YH, Chen KL, Liu JX, Chen HB, Gao CX (2017). Generation of thermosensitive male-sterile maize by targeted knockout of the ZmTMS5gene. J Genet Genomics 44, 465-468. |
| [34] | Li YF, Huang YM, Pan LL, Zhao Y, Huang W, Jin WW (2021). Male sterile 28 encodes an ARGONAUTE family protein essential for male fertility in maize. Chromosome Res 29, 189-201. |
| [35] | Li YF, Huang YM, Sun HY, Wang TY, Ru W, Pan LL, Zhao XM, Dong ZB, Huang W, Jin WW (2022). Heat shock protein 101 contributes to the thermotolerance of male meiosis in maize. Plant Cell 34, 3702-3717. |
| [36] | Lin YA, Yang HL, Liu HM, Lu XY, Cao HF, Li B, Chang YY, Guo ZY, Ding D, Hu YM, Xue YD, Liu ZH, Tang JH (2024). A P-type pentatricopeptide repeat protein ZmRF5 promotes 5′ region partial cleavages of atp6c transcripts to restore the fertility of CMS-C maize by recruiting a splicing factor. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 1269-1281. |
| [37] | Liu CX, Wang GQ, Gao J, Li CY, Zhang ZR, Yu TT, Wang JG, Zhou L, Cai YL (2018). Characterization, fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of novel, dominant, nuclear male-sterile gene Ms53 in maize. Euphytica 214, 52. |
| [38] | Liu SS, Wu SW, Rao LQ, Wan XY (2018). Molecular mechanism and application analysis of genic male sterility in maize. China Biotechnol 38, 100-107. (in Chinese) |
| 柳双双, 吴锁伟, 饶力群, 万向元 (2018). 玉米核雄性不育的分子机制研究与应用分析. 中国生物工程杂志 38, 100-107. | |
| [39] | Liu XZ, Jiang YL, Wu SW, Wang J, Fang CW, Zhang SW, Xie RR, Zhao LN, An XL, Wan XY (2022a). The ZmMYB84-ZmPKSB regulatory module controls male fertility through modulating anther cuticle-pollen exine trade- off in maize anthers. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 2342-2356. |
| [40] | Liu XZ, Zhang SW, Jiang YL, Yan TW, Fang CW, Hou QC, Wu SW, Xie K, An XL, Wan XY (2022b). Use of CRISPR/Cas9-based gene editing to simultaneously mutate multiple homologous genes required for pollen development and male fertility in maize. Cells 11, 439. |
| [41] | Lou Y, Zhou HS, Han Y, Zeng QY, Zhu J, Yang ZN (2018). Positive regulation of AMS by TDF1 and the formation of a TDF1-AMS complex are required for anther development in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 217, 378-391. |
| [42] |
Lu XD, Liu JS, Ren W, Yang Q, Chai ZG, Chen RM, Wang L, Zhao J, Lang ZH, Wang HY, Fan YL, Zhao JR, Zhang CY (2018). Gene-indexed mutations in maize. Mol Plant 11, 496-504.
DOI PMID |
| [43] | Marchant DB, Walbot V (2022). Anther development—the long road to making pollen. Plant Cell 34, 4677-4695. |
| [44] | Moon J, Skibbe D, Timofejeva L, Wang CJR, Kelliher T, Kremling K, Walbot V, Cande WZ (2013). Regulation of cell divisions and differentiation by MALE STERILITY32 is required for anther development in maize. Plant J 76, 592-602. |
| [45] | Nan GL, Teng C, Fernandes J, O'Connor L, Meyers BC, Walbot V (2022). A cascade of bHLH-regulated pathways programs maize anther development. Plant Cell 34, 1207-1225. |
| [46] | Nan GL, Zhai JX, Arikit S, Morrow D, Fernandes J, Mai L, Nguyen N, Meyers BC, Walbot V (2017). MS23, a master basic helix-loop-helix factor, regulates the specification and development of tapetum in maize. Development 144, 163-172. |
| [47] | Qi XL, Guo SW, Wang D, Zhong Y, Chen M, Chen C, Cheng DH, Liu ZK, An T, Li JL, Jiao YY, Wang YW, Liu JC, Zhang YL, Chen SJ, Liu CX (2022). ZmCOI2a and ZmCOI2b redundantly regulate anther dehiscence and gametophytic male fertility in maize. Plant J 110, 849-862. |
| [48] |
Qi XT, Zhang CS, Zhu JJ, Liu CL, Huang CL, Li XH, Xie CX (2020). Genome editing enables next-generation hybrid seed production technology. Mol Plant 13, 1262-1269.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Qin XE, Tian SK, Zhang WL, Zheng Q, Wang H, Feng Y, Lin YN, Tang JH, Wang Y, Yan JB, Dai MQ, Zheng YL, Yue B (2021). The main restorer Rf3 of maize S type cytoplasmic male sterility encodes a PPR protein that functions in reduction of the transcripts of orf355. Mol Plant 14, 1961-1964. |
| [50] | Shi Z, Ren W, Zhao YX, Wang XQ, Zhang RY, Su AG, Wang S, Li CH, Wang JR, Wang SS, Zhang YX, Ji YL, Song W, Zhao JR (2020). Identification of a locus associated with genic male sterility in maize via EMS mutagenesis and bulked-segregant RNA-seq. Crop J 9, 1263-1269. |
| [51] | Somaratne Y, Tian YH, Zhang H, Wang MM, Huo YQ, Cao FG, Zhao L, Chen HB (2017). ABNORMAL POLLEN VACUOLATION1 (APV1) is required for male fertility by contributing to anther cuticle and pollen exine formation in maize. Plant J 90, 96-110. |
| [52] | Su AG, Song W, Wang SS, Zhao JR (2018). Advance on cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration genes in maize. China Biotechnol 38, 108-114. (in Chinese) |
| 苏爱国, 宋伟, 王帅帅, 赵久然 (2018). 玉米细胞质雄性不育及其育性恢复基因的研究进展. 中国生物工程杂志 38, 108-114. | |
| [53] | Sun QQ, Rong TZ (2003). Study on genic male sterility in maize and use in molecular breeding. Chin Bull Bot 20, 248-253. (in Chinese) |
| 孙庆泉, 荣廷昭 (2003). 玉米核雄性不育材料的研究及其在分子育种中的利用. 植物学通报 20, 248-253. | |
| [54] | Teng C, Zhang H, Hammond R, Huang K, Meyers BC, Walbot V (2020). Dicer-like 5 deficiency confers temperature-sensitive male sterility in maize. Nat Commun 11, 2912. |
| [55] | Tian YH, Xiao SL, Liu J, Somaratne Y, Zhang H, Wang MM, Zhang HR, Zhao L, Chen HB (2017). MALE STERILE6021 (MS6021) is required for the development of anther cuticle and pollen exine in maize. Sci Rep 7, 16736. |
| [56] | Van Der Linde K, Timofejeva L, Egger RL, Ilau B, Hammond R, Teng C, Meyers BC, Doehlemann G, Walbot V (2018). Pathogen Trojan horse delivers bioactive host protein to alter maize anther cell behavior in situ. Plant Cell 30, 528-542. |
| [57] | Vernoud V, Laigle G, Rozier F, Meeley RB, Perez P, Rogowsky PM (2009). The HD-ZIP IV transcription factor OCL4 is necessary for trichome patterning and anther development in maize. Plant J 59, 883-894. |
| [58] |
Wan XY, Wu SW, Li X (2021). Breeding with dominant genic male-sterility genes to boost crop grain yield in the post-heterosis utilization era. Mol Plant 14, 531-534.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Wan XY, Wu SW, Li ZW, An XL, Tian YH (2020). Lipid metabolism: critical roles in male fertility and other aspects of reproductive development in plants. Mol Plant 13, 955-983.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Wan XY, Wu SW, Li ZW, Dong ZY, An XL, Ma B, Tian YH, Li JP (2019). Maize genic male-sterility genes and their applications in hybrid breeding: progress and perspectives. Mol Plant 12, 321-342.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Wang CJR, Nan GL, Kelliher T, Timofejeva L, Vernoud V, Golubovskaya IN, Harper L, Egger R, Walbot V, Cande WZ (2012). Maize multiple archesporial cells 1 (mac1), an ortholog of rice TDL1A, modulates cell proliferation and identity in early anther development. Development 139, 2594-2603. |
| [62] | Wang DX, Skibbe DS, Walbot V (2013). Maize Male sterile 8 (Ms8), a putative β-1,3-galactosyltransferase, modulates cell division, expansion, and differentiation during early maize anther development. Plant Reprod 26, 329-338. |
| [63] | Wang YB, Liu DC, Tian YH, Wu SW, An XL, Dong ZY, Zhang SM, Bao JX, Li ZW, Li JP, Wan XY (2019). Map- based cloning, phylogenetic, and microsynteny analyses of ZmMs20 gene regulating male fertility in maize. Int J Mol Sci 20, 1411. |
| [64] | Wu H, Xu H, Liu ZL, Liu YG (2007). Molecular basis of plant cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration. Chin Bull Bot 24, 399-413. (in Chinese) |
| 吴豪, 徐虹, 刘振兰, 刘耀光 (2007). 植物细胞质雄性不育及其育性恢复的分子基础. 植物学通报 24, 399-413. | |
| [65] | Wu SW, Wan XY (2018). Construction of male-sterility system using biotechnology and application in crop breeding and hybrid seed production. China Biotechnol 38, 78-87. (in Chinese) |
| 吴锁伟, 万向元 (2018). 利用生物技术创建主要作物雄性不育杂交育种和制种的技术体系. 中国生物工程杂志 38, 78-87. | |
| [66] |
Wu YZ, Fox TW, Trimnell MR, Wang LJ, Xu RJ, Cigan AM, Huffman GA, Garnaat CW, Hershey H, Albertsen MC (2016). Development of a novel recessive genetic male sterility system for hybrid seed production in maize and other cross-pollinating crops. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 1046-1054.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Xiao SL, Zang J, Pei YR, Liu J, Liu J, Song W, Shi Z, Su AG, Zhao JR, Chen HB (2020). Activation of mitochondrial orf355 gene expression by a nuclear-encoded DREB transcription factor causes cytoplasmic male sterility in maize. Mol Plant 13, 1270-1283. |
| [68] |
Xie K, Wu SW, Li ZW, Zhou Y, Zhang DF, Dong ZY, An XL, Zhu TT, Zhang SM, Liu SS, Li JP, Wan XY (2018). Map-based cloning and characterization of Zea mays male sterility33 (ZmMs33) gene, encoding a glycerol-3- phosphate acyltransferase. Theor Appl Genet 131, 1363-1378.
DOI PMID |
| [69] | Xu QL, Yang L, Kang D, Ren ZJ, Liu YJ (2021). Maize MS2 encodes an ATP-binding cassette transporter that is essential for anther development. Crop J 9, 1301-1308. |
| [70] | Yang HL, Xue YD, Li B, Lin YN, Li HC, Guo ZY, Li WH, Fu ZY, Ding D, Tang JH (2022). The chimeric gene atp6c confers cytoplasmic male sterility in maize by impairing the assembly of the mitochondrial ATP synthase complex. Mol Plant 15, 872-886. |
| [71] | Yang HP, Qi YL, Goley ME, Huang JT, Ivashuta S, Zhang YJ, Sparks OC, Ma JY, Van Scoyoc BM, Caruano-Yze- rmans AL, King-Sitzes J, Li X, Pan AH, Stoecker MA, Wiggins BE, Varagona MJ (2018). Endogenous tassel-specific small RNAs-mediated RNA interference enables a novel glyphosate-inducible male sterility system for commercial production of hybrid seed in Zea mays L. PLoS One 13, e0202921. |
| [72] | Zhang DF, Wu SW, An XL, Xie K, Dong ZY, Zhou Y, Xu LW, Fang W, Liu SS, Liu SS, Zhu TT, Li JP, Rao LQ, Zhao JR, Wan XY (2018a). Construction of a multicontrol sterility system for a maize male-sterile line and hybrid seed production based on the ZmMs7 gene encoding a PHD-finger transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 459-471. |
| [73] | Zhang L, Luo HB, Zhao Y, Chen XY, Huang YM, Yan SS, Li SX, Liu MS, Huang W, Zhang XL, Jin WW (2018b). Maize male sterile 33 encodes a putative glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase that mediates anther cuticle formation and microspore development. BMC Plant Biol 18, 318. |
| [74] | Zhang SM, Wu SW, Niu CF, Liu DC, Yan TW, Tian YH, Liu SS, Xie K, Li ZW, Wang YB, Zhao W, Dong ZY, Zhu TT, Hou QC, Ma B, An XL, Li JP, Wan XY (2021). ZmMs25encoding a plastid-localized fatty acyl reductase is critical for anther and pollen development in maize. J Exp Bot 72, 4298-4318. |
| [75] | Zheng MM, Huang Q, Zhang P, Liu XW, Zhao ZF, Yi HY, Rong TZ, Cao MJ (2024). Research progress on cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in maize. Chin Bull Bot 59, 999-1006. (in Chinese) |
|
郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊 (2024). 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展. 植物学报 59, 999-1006.
DOI |
|
| [76] | Zheng YL (1982). Study on the mechanism of the fertility about several types of cytoplasmic male-sterility in maize (Zea mays L.). J Huazhong Agri Coll (1), 44-68. (in Chinese) |
| 郑用琏 (1982). 若干玉米细胞质雄性不育类型(CMS)育性机理的研究. 华中农学院学报 (1), 44-68. | |
| [77] |
Zhu TT, Li ZW, An XL, Long Y, Xue XF, Xie K, Ma B, Zhang DF, Guan YJ, Niu CF, Dong ZY, Hou QC, Zhao LN, Wu SW, Li JP, Jin WW, Wan XY (2020). Normal structure and function of endothecium chloroplasts maintained by ZmMs33-mediated lipid biosynthesis in Tapetal cells are critical for anther development in maize. Mol Plant 13, 1624-1643.
DOI PMID |
| [78] | Zhu TT, Wu SW, Zhang DF, Li ZW, Xie K, An XL, Ma B, Hou QC, Dong ZY, Tian YH, Li JP, Wan XY (2019). Genome-wide analysis of maize GPAT gene family and cytological characterization and breeding application of ZmMs33/ZmGPAT6 gene. Theor Appl Genet 132, 2137-2154. |
| [79] | Zhu YH, Shi ZW, Li SZ, Liu HY, Liu FX, Niu QK, Li C, Wang J, Rong TZ, Yi HY, Cao MJ (2018). Fine mapping of the novel male-sterile mutant gene ms39in maize originated from outer space flight. Mol Breed 38, 125. |
| [1] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [2] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [3] | 张强, 赵振宇, 李平华. 基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 978-998. |
| [4] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [5] | 郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊. 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 999-1006. |
| [6] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [7] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [8] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [9] | 李园, 范开建, 安泰, 李聪, 蒋俊霞, 牛皓, 曾伟伟, 衡燕芳, 李虎, 付俊杰, 李慧慧, 黎亮. 玉米自然群体自交系农艺性状的多环境全基因组预测初探[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1041-1053. |
| [10] | 程可心, 杜尧, 李凯航, 王浩臣, 杨艳, 金一, 何晓青. 玉米与叶际微生物组的互作遗传机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [11] | 周文期, 周玉乾, 李永生, 何海军, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 胡筑兵. 玉米ZmICE2基因调控气孔发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 866-881. |
| [12] | 于熙婷, 黄学辉. 现代玉米起源新见解——两类大刍草的混血[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 857-860. |
| [13] | 郭丽, 王雪涵, 田丰. 多组学整合网络: 一把精准解码玉米功能基因组的钥匙[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 1-5. |
| [14] | 余泓, 李家洋. 是金子无论在何处都发光: 玉米和水稻驯化中的趋同选择[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 153-156. |
| [15] | 孙佳欢, 刘冬, 朱家祺, 张书宁, 高梅香. 小麦-玉米轮作农田土壤螨多样性空间分布格局[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(12): 22292-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||