

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (6): 857-860.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23138 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23138
所属专题: 大食物观
• 热点评述 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-10-10
接受日期:2023-10-17
出版日期:2023-11-01
发布日期:2023-12-01
通讯作者:
* E-mail: xhhuang@shnu.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2023-10-10
Accepted:2023-10-17
Online:2023-11-01
Published:2023-12-01
Contact:
* E-mail: xhhuang@shnu.edu.cn
摘要: 农作物驯化推动了农业文明的出现和繁荣, 是人类历史上的重大事件。玉米(Zea mays)作为全球范围内的重要粮食作物, 其驯化起源一直备受生物学和历史学界的关注。之前, 现代玉米起源自小颖大刍草亚种(Z. mays subsp. parviglumis)的观点一直占主流地位。近期, 严建兵与其合作团队系统收集并梳理了玉米各种类型野生种和栽培种资源, 综合运用基因组学、群体遗传学和数量遗传学方法及考古学成果, 发现现代玉米也存在墨西哥高原亚种(Z. mays subsp. mexicana)的杂交渐渗, 并影响了诸多农艺性状, 进而提出现代玉米起源的新模型。
于熙婷, 黄学辉. 现代玉米起源新见解——两类大刍草的混血. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 857-860.
Xiting Yu, Xuehui Huang. New Insights Into the Origin of Modern Maize-hybridization of Two Teosintes. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(6): 857-860.
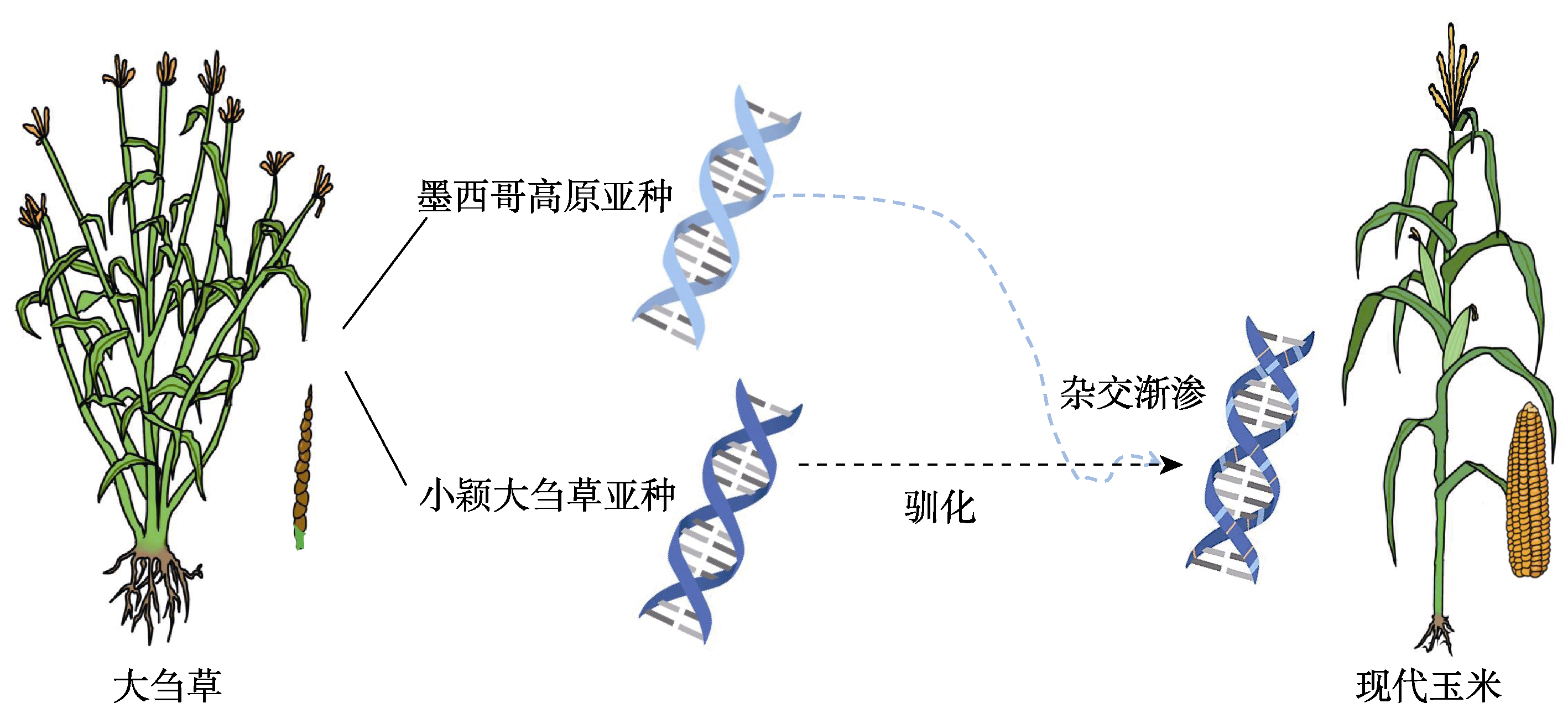
图1 现代玉米起源过程简图 研究人员推测, 现代玉米(Zea mays)首先起源于墨西哥平原地区的小颖大刍草亚种(Z. mays subsp. parviglumis), 而后与墨西哥高原地区的墨西哥高原亚种(Z. mays subsp. mexicana)发生杂交渐渗。DNA双螺旋中深蓝、浅蓝和橙色分别示意小颖大刍草亚种单倍型、墨西哥高原亚种单倍型和驯化改良产生的新变异。
Figure 1 A simplified diagram of the origin process of modern maize Researchers speculate that modern maize first originated from the parviglumis type of teosinte in the Mexican lowlands, and then introgression with the mexicana type of teosinte in the Mexican highlands occurred. The deep blue, light blue, and orange colors in the DNA double helix represent the haplotypes of parviglumis-type teosinte, mexicana-type teosinte, and new allelic variation during domestication, respectively.
| [1] |
Calfee E, Gates D, Lorant A, Perkins MT, Coop G, Ross-Ibarra J (2021). Selective sorting of ancestral introgression in maize and teosinte along an elevational cline. PLoS Genet 17, e1009810.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Doebley JF, Gaut BS, Smith BD (2006). The molecular genetics of crop domestication. Cell 127, 1309-1321.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Huang XH, Huang SW, Han B, Li JY (2022a). The integrated genomics of crop domestication and breeding. Cell 185, 2828-2839.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Huang XH, Kurata N, Wei XH, Wang ZX, Wang AH, Zhao Q, Zhao Y, Liu KY, Lu HY, Li WJ, Guo YL, Lu YQ, Zhou CC, Fan DL, Weng QJ, Zhu CR, Huang T, Zhang L, Wang YC, Feng L, Furuumi H, Kubo T, Miyabayashi T, Yuan XP, Xu Q, Dong GJ, Zhan QL, Li CY, Fujiyama A, Toyoda A, Lu TT, Feng Q, Qian Q, Li JY, Han B (2012). A map of rice genome variation reveals the origin of cultivated rice. Nature 490, 497-501.
DOI |
| [5] | Huang YC, Wang HH, Zhu YD, Huang X, Li S, Wu XG, Zhao Y, Bao ZG, Qin L, Jin YB, Cui YH, Ma GJ, Xiao Q, Wang Q, Wang JC, Yang XR, Liu HJ, Lu XD, Larkins BA, Wang WQ, Wu YR (2022b). THP9 enhances seed protein content and nitrogen-use efficiency in maize. Nature 612, 292-300. |
| [6] |
Hufford MB, Lubinksy P, Pyhäjärvi T, Devengenzo MT, Ellstrand NC, Ross-Ibarra J (2013). The genomic signature of crop-wild introgression in maize. PLoS Genet 9, e1003477.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Jing CY, Zhang FM, Wang XH, Wang MX, Zhou L, Cai Z, Han JD, Geng MF, Yu WH, Jiao ZH, Huang L, Liu R, Zheng XM, Meng QL, Ren NN, Zhang HX, Du YS, Wang X, Qiang CG, Zou XH, Gaut BS, Ge S (2023). Multiple domestications of Asian rice. Nat Plants 9, 1221-1235.
DOI |
| [8] |
Li CB, Zhou AL, Sang T (2006). Rice domestication by reducing shattering. Science 311, 1936-1939.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Matsuoka Y, Vigouroux Y, Goodman MM, Sanchez GJ, Buckler E, Doebley J (2002). A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 6080-6084.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Pääbo S (2015). The diverse origins of the human gene pool. Nat Rev Genet 16, 313-314.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Wang H, Studer AJ, Zhao Q, Meeley R, Doebley JF (2015). Evidence that the origin of naked kernels during maize domestication was caused by a single amino acid substitution in tga1. Genetics 200, 965-974.
DOI |
| [12] | Yang N, Wang YB, Liu XG, Jin ML, Vallebueno-Estrada M, Calfee E, Chen L, Dilkes BP, Gui ST, Fan XM, Harper TK, Kennett DJ, Li WQ, Lu YL, Luo JY, Mambak-kam S, Menon M, Snodgrass S, Veller C, Wu SS, Wu SY, Xiao YJ, Yang XH, Stitzer MC, Runcie D, Yan JB, Ross-Ibarra J (2023). Two teosintes made modern maize. Science doi: 10.1126/science.adg8940 |
| [13] |
Yu H, Lin T, Meng XB, Du HL, Zhang JK, Liu GF, Chen ML, Jing YH, Kou LQ, Li XX, Gao Q, Liang Y, Liu XD, Fan ZL, Liang YT, Cheng ZK, Chen MS, Tian ZX, Wang YH, Chu CC, Zuo JR, Wan JM, Qian Q, Han B, Zuccolo A, Wing RA, Gao CX, Liang CZ, Li JY (2021). A route to de novo domestication of wild allotetraploid rice. Cell 184, 1156-1170.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 逯子佳, 王天瑞, 郑斯斯, 孟宏虎, 曹建国, Gregor Kozlowski, 宋以刚. 孑遗植物湖北枫杨的环境适应性遗传变异与遗传脆弱性[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [2] | 崔娟, 于晓玉, 于跃娇, 梁铖玮, 孙健, 陈温福. 影响中国东北和日本粳稻食味品质差异的质构因素及其遗传基础解析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [3] | 王传永, 庄典, 宋正达, 翟恒华, 李乃伟, 张凡. 黑果腺肋花楸叶绿体全基因组的结构和比较分析及系统进化推断[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [4] | 卢晓强, 董姗姗, 马月, 徐徐, 邱凤, 臧明月, 万雅琼, 李孪鑫, 于赐刚, 刘燕. 前沿技术在生物多样性研究中的应用现状、挑战与展望[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24440-. |
| [5] | 张如礼, 李德铢, 张玉霄. 短穗竹居群遗传结构及气候适应性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 407-424. |
| [6] | 林珍, 向家宝, 蔡何佳奕, 高贝, 杨金涛, 李俊毅, 周青松, 黄晓磊, 邓鋆. 七种半翅目昆虫线粒体基因组数据[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24434-. |
| [7] | 夏琳凤, 李瑞, 王海政, 冯大领, 王春阳. 轮藻门植物基因组学研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 271-282. |
| [8] | 曹东, 李焕龙, 彭扬, 魏存争. 植物基因组大小与性状关系的研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24192-. |
| [9] | 邓洪, 钟占友, 寇春妮, 朱书礼, 李跃飞, 夏雨果, 武智, 李捷, 陈蔚涛. 基于线粒体全基因组揭示斑鳠的种群遗传结构与演化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(1): 24241-. |
| [10] | 姚祥坦, 张心怡, 陈阳, 袁晔, 程旺大, 王天瑞, 邱英雄. 基于基因组重测序揭示栽培欧菱遗传多样性及‘南湖菱’的起源驯化历史[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(9): 24212-. |
| [11] | 张强, 赵振宇, 李平华. 基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 978-998. |
| [12] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [13] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [14] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [15] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
