

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 1-5.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22271 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22271
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
• 热点评述 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2022-12-05
接受日期:2022-12-13
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: ft55@cau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Li Guo, Xuehan Wang, Feng Tian*( )
)
Received:2022-12-05
Accepted:2022-12-13
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: ft55@cau.edu.cn
摘要: 高通量组学技术的快速发展使生命科学进入大数据时代。科学家们从基因组、转录组、蛋白质组和代谢组等多组学数据中剥茧抽丝, 逐步揭示生物体内复杂而巧妙的调控网络。近日, 华中农业大学李林课题组联合杨芳课题组和严建兵课题组构建了玉米(Zea mays)首个多组学整合网络。该网络包括3万个玉米基因在三维基因组水平、转录水平、翻译水平和蛋白质互作水平的调控关系, 由280万个网络连接组成, 构成1 412个调控模块。利用该整合网络, 研究团队预测并证实了5个调控玉米分蘖、侧生器官发育和籽粒皱缩的新基因。进一步结合机器学习方法, 他们预测出2 651个影响玉米开花期的候选基因, 鉴定到8条可能参与玉米开花期的调控通路, 并利用基因编辑技术和EMS突变体证实了20个候选基因的生物学功能。此外, 通过对整合调控网络的进化分析, 他们发现玉米两套亚基因组在转录组、翻译组和蛋白互作组水平上存在渐进式的功能分化。这套集合多组学数据构建的整合网络图谱是玉米功能基因组学研究的重大进展, 为玉米重要性状新基因克隆、分子调控通路解析和玉米基因组进化分析提供了新工具, 是解锁玉米功能基因组学的一把新钥匙。
郭丽, 王雪涵, 田丰. 多组学整合网络: 一把精准解码玉米功能基因组的钥匙. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 1-5.
Li Guo, Xuehan Wang, Feng Tian. Multi-omics Integrative Network Map, a Key to Accurately Deco-ding the Maize Functional Genomics. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 1-5.
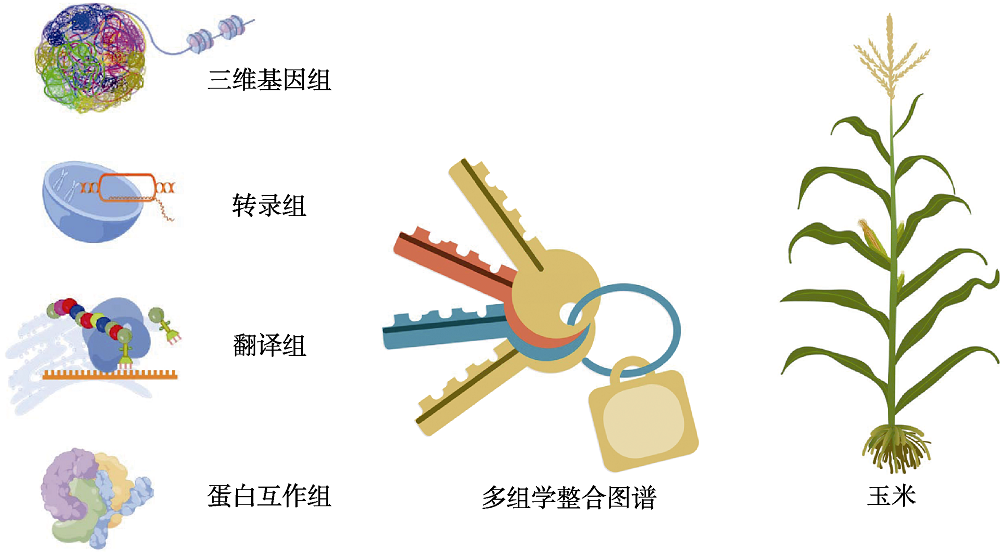
图1 多组学整合网络图谱是精准解锁玉米功能基因组学的新钥匙(本图由Figdraw绘制, 玉米植株图改自Chen等(2021))
Figure 1 Multi-omics integrative network map is a new key to accurately decode the maize functional genomics (this figure is drawn by figdraw and the plant picture is adapted from Chen et al., 2021)
| [1] |
汪海, 赖锦盛, 王海洋, 李新海 (2022). 作物智能设计育种——自然变异的智能组合和人工变异的智能创制. 中国农业科技导报 24(6), 1-8.
DOI |
| [2] | 王向峰, 才卓 (2019). 中国种业科技创新的智能时代——“玉米育种4.0”. 玉米科学 27, 1-9. |
| [3] |
Chen Q, Li W, Tan L, Tian F (2021). Harnessing knowledge from maize and rice domestication for new crop breeding. Mol Plant 14, 9-26.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Doebley J, Stec A, Hubbard L (1997). The evolution of apical dominance in maize. Nature 386, 485-488.
DOI |
| [5] | Dong ZB, Li W, Unger-Wallace E, Yang JL, Vollbrecht E, Chuck G (2017). Ideal crop plant architecture is mediated by tassels replace upper ears1, a BTB/POZ ankyrin repeat gene directly targeted by TEOSINTE BRANCHED1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E8656-E8664. |
| [6] |
Gallavotti A, Zhao Q, Kyozuka J, Meeley RB, Ritter MK, Doebley JF, Pè ME, Schmidt RJ (2004). The role of barren stalk1 in the architecture of maize. Nature 432, 630-635.
DOI |
| [7] |
Gälweiler L, Guan CH, Müller A, Wisman E, Mendgen K, Yephremov A, Palme K (1998). Regulation of polar auxin transport by AtPIN1 in Arabidopsis vascular tissue. Science 282, 2226-2230.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Gui ST, Wei WJ, Jiang CL, Luo JY, Chen L, Wu SS, Li WQ, Wang YB, Li SY, Yang N, Li Q, Fernie AR, Yan JB (2022). A pan-Zea genome map for enhancing maize improvement. Genome Biol 23, 178.
DOI |
| [9] | Han LQ, Zhong WS, Qian J, Jin ML, Tian P, Zhu WC, Zhang HW, Sun YH, Feng JW, Liu XG, Chen G, Farid B, Li RN, Xiong ZM, Tian ZH, Li J, Luo Z, Du DX, Chen SJ, Jin QX, Li JX, Li Z, Liang Y, Jin XM, Peng Y, Zheng C, Ye XN, Yin YJ, Chen H, Li WF, Chen LL, Li Q, Yan JB, Yang F, Li L (2022). A multi-omics integrative network map of maize. Nat Genet https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-022-01262-1 |
| [10] | Hufford MB, Seetharam AS, Woodhouse MR, Chougule KM, Ou SJ, Liu JN, Ricci WA, Guo TT, Olson A, Qiu YJ, Della Coletta R, Tittes S, Hudson AI, Marand AP, Wei S, Lu ZY, Wang B, Tello-Ruiz MK, Piri RD, Wang N, Kim DW, Zeng YB, O’Connor CH, Li XR, Gilbert AM, Baggs E, Krasileva KV, Portwood JL II, Cannon EKS, Andorf CM, Manchanda N, Snodgrass SJ, Hufnagel DE, Jiang QH, Pedersen S, Syring ML, Kudrna DA, Llaca V, Fengler K, Schmitz RJ, Ross-Ibarra J, Yu JM, Gent JI, Hirsch CN, Ware D, Dawe RK (2021). De novo assembly, annotation, and comparative analysis of 26 diverse maize genomes. Science 373, 655-662. |
| [11] |
Liang YM, Liu HJ, Yan JB, Tian F (2021). Natural variation in crops: realized understanding, continuing promise. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 357-385.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Matsuoka Y, Vigouroux Y, Goodman MM, Sanchez GJ, Buckler E, Doebley J (2002). A single domestication for maize shown by multilocus microsatellite genotyping. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 6080-6084.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Peng Y, Xiong D, Zhao L, Ouyang WZ, Wang SQ, Sun J, Zhang Q, Guan PP, Xie L, Li WQ, Li GL, Yan JB, Li XW (2019). Chromatin interaction maps reveal genetic regulation for quantitative traits in maize. Nat Commun 10, 2632.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Schnable JC, Springer NM, Freeling M (2011). Differentiation of the maize subgenomes by genome dominance and both ancient and ongoing gene loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 4069-4074. |
| [15] |
Tu XY, Mejía-Guerra MK, Valdes Franco JA, Tzeng D, Chu PY, Shen W, Wei YY, Dai XR, Li PH, Buckler ES, Zhong SL (2020). Reconstructing the maize leaf regulatory network using ChIP-seq data of 104 transcription factors. Nat Commun 11, 5089.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Walley JW, Sartor RC, Shen ZX, Schmitz RJ, Wu KJ, Urich MA, Nery JR, Smith LG, Schnable JC, Ecker JR, Briggs SP (2016). Integration of omic networks in a developmental atlas of maize. Science 353, 814-818.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Wen WW, Jin M, Li K, Liu HJ, Xiao YJ, Zhao MC, Alseekh S, Li WQ, de Abreu e Lima F, Brotman Y, Willmitzer L, Fernie AR, Yan JB (2018). An integrated multi-layered analysis of the metabolic networks of different tissues uncovers key genetic components of primary metabolism in maize. Plant J 93, 1116-1128.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Whipple CJ, Kebrom TH, Weber AL, Yang F, Hall D, Meeley R, Schmidt R, Doebley J, Brutnell TP, Jackson DP (2011). grassy tillers1 promotes apical dominance in maize and responds to shade signals in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, E506-E512. |
| [19] | Xiao YG, Guo JY, Dong ZB, Richardson A, Patterson E, Mangrum S, Bybee S, Bertolini E, Bartlett M, Chuck G, Eveland AL, Scanlon MJ, Whipple C (2022). Boundary domain genes were recruited to suppress bract growth and promote branching in maize. Sci Adv 8, m6835. |
| [20] |
Xu XS, Crow M, Rice BR, Li F, Harris B, Liu L, Demesa-Arevalo E, Lu ZF, Wang LY, Fox N, Wang XF, Drenkow J, Luo AD, Char SN, Yang B, Sylvester AW, Gingeras TR, Schmitz RJ, Ware D, Lipka AE, Gillis J, Jackson D (2021). Single-cell RNA sequencing of developing maize ears facilitates functional analysis and trait candidate gene discovery. Dev Cell 56, 557-568.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Yang F, Lei YY, Zhou ML, Yao QL, Han YC, Wu X, Zhong WS, Zhu CH, Xu WZ, Tao R, Chen X, Lin D, Rahman K, Tyagi R, Habib Z, Xiao SB, Wang D, Yu Y, Chen HC, Fu ZF, Cao G (2018). Development and application of a recombination-based library versus library high-throughput yeast two-hybrid (RLL-Y2H) screening system. Nucleic Acids Res 46, e17.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Zhu WC, Xu J, Chen SJ, Chen J, Liang Y, Zhang CJ, Li Q, Lai JS, Li L (2021). Large-scale translatome profiling annotates the functional genome and reveals the key role of genic 3' untranslated regions in translatomic variation in plants. Plant Commun 2, 100181.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 付照琦, 胡旭, 田沁瑞, 葛艳灵, 周红娟, 吴小云, 陈立欣. 晋西黄土区2种典型森林树种夜间液流特征及对环境因子的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(9): 1128-1142. |
| [2] | 杨文丽, 李钊, 刘志铭, 张志华, 杨今胜, 吕艳杰, 王永军. 不同熟期玉米叶片衰老特性及其对叶际细菌的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1024-1040. |
| [3] | 张强, 赵振宇, 李平华. 基因编辑技术在玉米中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 978-998. |
| [4] | 杨娟, 赵月磊, 陈晓远, 王宝宝, 王海洋. 玉米开花期调控机理及育种应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 912-931. |
| [5] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [6] | 吴锁伟, 安学丽, 万向元. 玉米雄性不育机理及其在工程核不育制种中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 932-949. |
| [7] | 郑名敏, 黄强, 张鹏, 刘孝伟, 赵卓凡, 易洪杨, 荣廷昭, 曹墨菊. 玉米细胞质雄性不育及育性恢复研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 999-1006. |
| [8] | 李园, 范开建, 安泰, 李聪, 蒋俊霞, 牛皓, 曾伟伟, 衡燕芳, 李虎, 付俊杰, 李慧慧, 黎亮. 玉米自然群体自交系农艺性状的多环境全基因组预测初探[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1041-1053. |
| [9] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [10] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [11] | 王子阳, 刘升学, 杨志蕊, 秦峰. 玉米抗旱性的遗传解析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 883-902. |
| [12] | 程可心, 杜尧, 李凯航, 王浩臣, 杨艳, 金一, 何晓青. 玉米与叶际微生物组的互作遗传机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(2): 215-228. |
| [13] | 王秀英, 陈奇, 杜华礼, 张睿, 马红璐. 基于机器学习的青藏高原高寒沼泽湿地蒸散发插补研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(7): 912-921. |
| [14] | 周文期, 周玉乾, 李永生, 何海军, 杨彦忠, 王晓娟, 连晓荣, 刘忠祥, 胡筑兵. 玉米ZmICE2基因调控气孔发育[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 866-881. |
| [15] | 于熙婷, 黄学辉. 现代玉米起源新见解——两类大刍草的混血[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 857-860. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||