

植物学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 56 ›› Issue (3): 262-274.DOI: 10.11983/CBB20163 cstr: 32102.14.CBB20163
王婷, 羊欢欢, 赵弘巍, JosefVoglmeir, 刘丽*( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-29
接受日期:2020-12-25
出版日期:2021-05-01
发布日期:2021-04-30
通讯作者:
刘丽
作者简介:* E-mail: lichen.liu@njau.edu.cn† 共同第一作者
基金资助:
Ting Wang, Huanhuan Yang, Hongwei Zhao, Josef Voglmeir, Li Liu*( )
)
Received:2020-09-29
Accepted:2020-12-25
Online:2021-05-01
Published:2021-04-30
Contact:
Li Liu
About author:First author contact:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 蛋白质N-糖基化修饰在植物生长发育中发挥重要作用。为探究蛋白质N-糖基化在拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)整个生长周期中的变化规律以及去N-糖基化对拟南芥生根发育的影响, 通过N-糖链酶解和HPLC与MALDI-TOF-MS分析解析了不同生长时期的拟南芥Col-0植株的N-糖链组成(结构和含量)变化。以BSA溶液为阴性对照, 无菌去离子水为空白对照, 用N-糖酰胺酶(PNGase Rz)溶液处理拟南芥幼苗8小时; 然后继续在MS培养基中培养5天、10天, 测量主根长度并检测N-糖链组成的变化。结果显示, 从拟南芥中解析出12种N-糖链结构, 其中包括4个高甘露糖型和8个复杂型。在拟南芥整个生长周期中, 复杂型N-糖链含量始终高于高甘露糖型, 其中含木糖和岩藻糖的复杂型结构是N-糖链的主要组成, 而Man3XylFucGlcNAc2含量最高。高甘露糖型N-糖链含量由幼苗期的13.87%缓慢上升至抽薹期的19.02%, 盛花期回落至17.98%, 而在长角果成熟期快速下降至最低点2.36%, 衰老期再度小幅回升至5.23%。用高浓度糖酰胺酶液PNGase Rz处理后, 可观察到幼苗主根生长受到显著抑制, 且培养10天后仍然无法恢复正常; 而低浓度酶液处理组与阴性对照组差异不显著, 根长和生长状态基本正常。糖链分析结果显示, 与对照组相比, 高、低浓度酶液处理组的N-糖链组成均发生显著变化, 主要表现为高甘露糖型含量显著低于空白对照组, 同时随生长时间的延长该差异逐渐减小, 最终消失。研究表明, 拟南芥N-糖基化组成随着生长发育发生周期性变化, 且去糖基化酶处理能够瞬时影响拟南芥蛋白质N-糖基化修饰, 进而抑制根的发育。
王婷, 羊欢欢, 赵弘巍, JosefVoglmeir, 刘丽. 蛋白质N-糖基化在拟南芥生长周期中的变化规律及去糖基化对根发育的影响. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 262-274.
Ting Wang, Huanhuan Yang, Hongwei Zhao, Josef Voglmeir, Li Liu. Changes of Protein N-glycosylation in the Growth of Arabidopsis thaliana and Effects of Enzymatic Deglycosylation on Root Development. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2021, 56(3): 262-274.
| Number | Retention time (min) | GU value | The theoretical electron charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Detection value of charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.2 | 4.86 | 1185.43 | 1185.51 | Man3XylGlcNAc2 | MMXF |
| 2 | 17.9 | 5.03 | - | 806.99 | Unknown | - |
| 3 | 19.4 | 5.39 | 1388.51 | - | GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | GnMXF |
| 4 | 20.1 | 5.56 | 1331.49 | 1331.39 | Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | MMX |
| 5 | 21.4 | 5.90 | 1591.558 | 1591.74 | GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | GnGnX |
| 6 | 22.3 | 6.10 | 1534.57 | 1534.70 | GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnMX |
| 7 | 23.2 | 6.35 | 1493.53 | 1494.16 | Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | M4XF |
| 8 | 24.0 | 6.58 | 1737.64 | 1737.93 | GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnGnXF |
| 9 | 24.9 | 6.82 | 1696.62 | 1697.37 | GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GGnXF |
| 10 | 25.5 | 6.97 | 1539.54 | 1540.16 | Man6GlcNAc2 | M6 |
| 11 | 27.3 | 7.47 | - | 1620.53 | Unknown | - |
| 12 | 28.6 | 7.86 | 1701.89 | 1701.74 | Man7GlcNAc2 | M7 |
| 13 | 31.4 | 8.73 | 1863.65 | 1863.86 | Man8GlcNAc2 | M8 |
| 14 | 33.4 | 9.44 | 2025.70 | 2025.88 | Man9GlcNAc2 | M9 |
表1 拟南芥糖蛋白N-糖链结构
Table 1 The summary of N-glycan structures from glycoprotein in Arabidopsis thaliana
| Number | Retention time (min) | GU value | The theoretical electron charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Detection value of charge-mass ratio (m/z) | Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.2 | 4.86 | 1185.43 | 1185.51 | Man3XylGlcNAc2 | MMXF |
| 2 | 17.9 | 5.03 | - | 806.99 | Unknown | - |
| 3 | 19.4 | 5.39 | 1388.51 | - | GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | GnMXF |
| 4 | 20.1 | 5.56 | 1331.49 | 1331.39 | Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | MMX |
| 5 | 21.4 | 5.90 | 1591.558 | 1591.74 | GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | GnGnX |
| 6 | 22.3 | 6.10 | 1534.57 | 1534.70 | GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnMX |
| 7 | 23.2 | 6.35 | 1493.53 | 1494.16 | Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | M4XF |
| 8 | 24.0 | 6.58 | 1737.64 | 1737.93 | GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GnGnXF |
| 9 | 24.9 | 6.82 | 1696.62 | 1697.37 | GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | GGnXF |
| 10 | 25.5 | 6.97 | 1539.54 | 1540.16 | Man6GlcNAc2 | M6 |
| 11 | 27.3 | 7.47 | - | 1620.53 | Unknown | - |
| 12 | 28.6 | 7.86 | 1701.89 | 1701.74 | Man7GlcNAc2 | M7 |
| 13 | 31.4 | 8.73 | 1863.65 | 1863.86 | Man8GlcNAc2 | M8 |
| 14 | 33.4 | 9.44 | 2025.70 | 2025.88 | Man9GlcNAc2 | M9 |
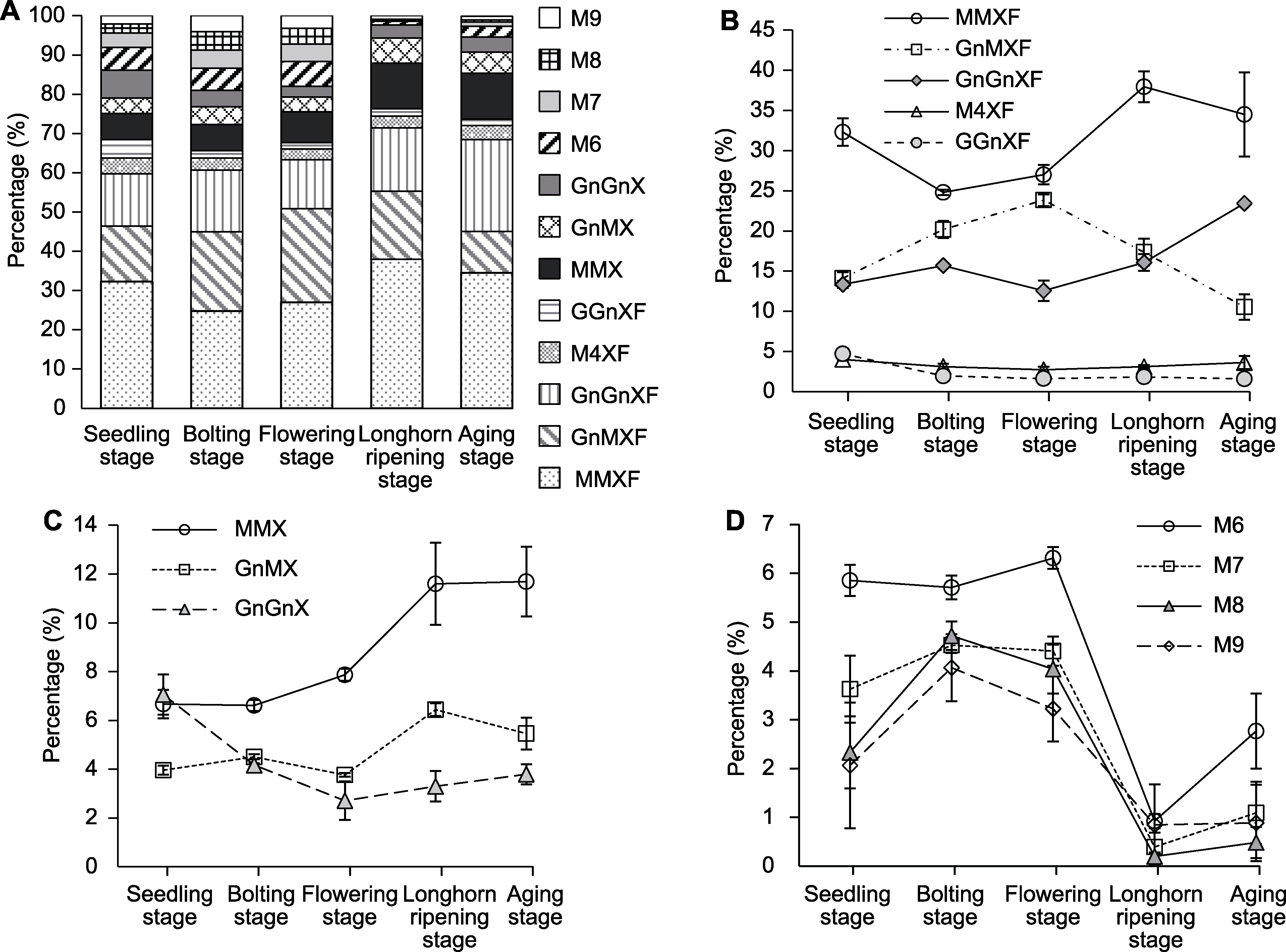
图2 不同生长时期拟南芥N-糖链中不同糖型相对含量的变化 (A) N-糖链不同糖型的比例变化趋势; (B) 含木糖和岩藻糖复杂型N-糖链的比例变化趋势; (C) 仅含木糖复杂型N-糖链的比例变化趋势; (D) 高甘露糖型N-糖链的比例变化趋势。不同糖型缩写同表1。
Figure 2 The relative proportion of different N-glycans from Arabidopsis thaliana at different growth stages (A) The changes of the proportions for each N-glycan structure; (B) The changes of the proportions of complex N-glycans with Xyl and Fuc; (C) The changes of the proportions of complex N-glycans only with Xyl; (D) The changes of the proportions of high-mannose N-glycans. The abbreviations of different N-glycans are the same as Table 1.
| N-glycans | Relative content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling stage | Bolting stage | Flowering stage | Longhorn ripening stage | Aging stage | |
| Complex type with Xyl and Fuc | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (MMXF) | 32.31±1.71 b | 24.79±0.33 c | 27.00±1.21 c | 37.96±1.92 a | 34.51±5.23 ab |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnMXF) | 14.11±0.75 d | 20.18±1.05 b | 23.83±0.74 a | 17.37±1.67 c | 10.53±1.58 e |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 (M4XF) | 3.99±0.15 a | 3.11±0.36 ab | 2.70±0.40 b | 3.10±0.21 ab | 3.61±0.80 ab |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnGnXF) | 13.33±0.42 b | 15.68±0.15 b | 12.55±1.26 b | 16.06±1.03 b | 23.44±0.12 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GGnXF) | 4.69±0.36 a | 1.93±0.20 b | 1.61±0.29 b | 1.82±0.09 b | 1.58±0.36 b |
| Sum | 68.44±1.51 b | 65.69±0.98 b | 67.68±2.33 b | 76.31±3.13 a | 73.84±2.79 a |
| Complex type only with Xyl | |||||
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 (MMX) | 6.67±0.58 b | 6.62±0.23 b | 7.87±0.25 b | 11.59±1.68 a | 10.69±1.43 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 (GnMX) | 3.96±0.18 cd | 4.51±0.10 c | 3.77±0.08 d | 6.44±0.26 a | 5.46±0.65 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 (GnGnX) | 7.06±0.82 a | 4.17±0.08 b | 2.71±0.79 bc | 3.30±0.62 bc | 3.80±0.41 c |
| Sum | 17.69±1.57 b | 15.29±0.41 bc | 14.34±0.70 c | 21.33±2.39 a | 20.94±2.79 a |
| Sum of complex | 86.13±2.95 b | 80.98±0.92 c | 82.02±1.65 c | 97.64±0.78 a | 94.77±0.94 a |
| High-mannose type | |||||
| Man6GlcNAc2 (M6) | 5.85±0.32 a | 5.71±0.24 a | 6.31±0.22 a | 0.92±0.15 c | 2.77±0.77 b |
| Man7GlcNAc2 (M7) | 3.63±0.69 b | 4.53±0.16 a | 4.41±0.30 ab | 0.39±0.30 c | 1.09±0.64 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 (M8) | 2.33±0.74 b | 4.72±0.29 a | 4.04±0.50 a | 0.20±0.09 c | 0.48±0.32 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 (M9) | 2.06±1.29 bc | 4.06±0.69 a | 3.23±0.67 ab | 0.84±0.83 c | 0.88±0.78 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 13.87±2.95 b | 19.02±0.92 a | 17.98±1.65 a | 2.36±0.78 c | 5.23±0.94 c |
表2 拟南芥不同生长时期N-糖链中各类糖型的相对含量
Table 2 The relative content of different N-glycans from Arabidopsis thaliana at different growth stages
| N-glycans | Relative content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seedling stage | Bolting stage | Flowering stage | Longhorn ripening stage | Aging stage | |
| Complex type with Xyl and Fuc | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (MMXF) | 32.31±1.71 b | 24.79±0.33 c | 27.00±1.21 c | 37.96±1.92 a | 34.51±5.23 ab |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnMXF) | 14.11±0.75 d | 20.18±1.05 b | 23.83±0.74 a | 17.37±1.67 c | 10.53±1.58 e |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 (M4XF) | 3.99±0.15 a | 3.11±0.36 ab | 2.70±0.40 b | 3.10±0.21 ab | 3.61±0.80 ab |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GnGnXF) | 13.33±0.42 b | 15.68±0.15 b | 12.55±1.26 b | 16.06±1.03 b | 23.44±0.12 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 (GGnXF) | 4.69±0.36 a | 1.93±0.20 b | 1.61±0.29 b | 1.82±0.09 b | 1.58±0.36 b |
| Sum | 68.44±1.51 b | 65.69±0.98 b | 67.68±2.33 b | 76.31±3.13 a | 73.84±2.79 a |
| Complex type only with Xyl | |||||
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 (MMX) | 6.67±0.58 b | 6.62±0.23 b | 7.87±0.25 b | 11.59±1.68 a | 10.69±1.43 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 (GnMX) | 3.96±0.18 cd | 4.51±0.10 c | 3.77±0.08 d | 6.44±0.26 a | 5.46±0.65 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 (GnGnX) | 7.06±0.82 a | 4.17±0.08 b | 2.71±0.79 bc | 3.30±0.62 bc | 3.80±0.41 c |
| Sum | 17.69±1.57 b | 15.29±0.41 bc | 14.34±0.70 c | 21.33±2.39 a | 20.94±2.79 a |
| Sum of complex | 86.13±2.95 b | 80.98±0.92 c | 82.02±1.65 c | 97.64±0.78 a | 94.77±0.94 a |
| High-mannose type | |||||
| Man6GlcNAc2 (M6) | 5.85±0.32 a | 5.71±0.24 a | 6.31±0.22 a | 0.92±0.15 c | 2.77±0.77 b |
| Man7GlcNAc2 (M7) | 3.63±0.69 b | 4.53±0.16 a | 4.41±0.30 ab | 0.39±0.30 c | 1.09±0.64 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 (M8) | 2.33±0.74 b | 4.72±0.29 a | 4.04±0.50 a | 0.20±0.09 c | 0.48±0.32 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 (M9) | 2.06±1.29 bc | 4.06±0.69 a | 3.23±0.67 ab | 0.84±0.83 c | 0.88±0.78 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 13.87±2.95 b | 19.02±0.92 a | 17.98±1.65 a | 2.36±0.78 c | 5.23±0.94 c |
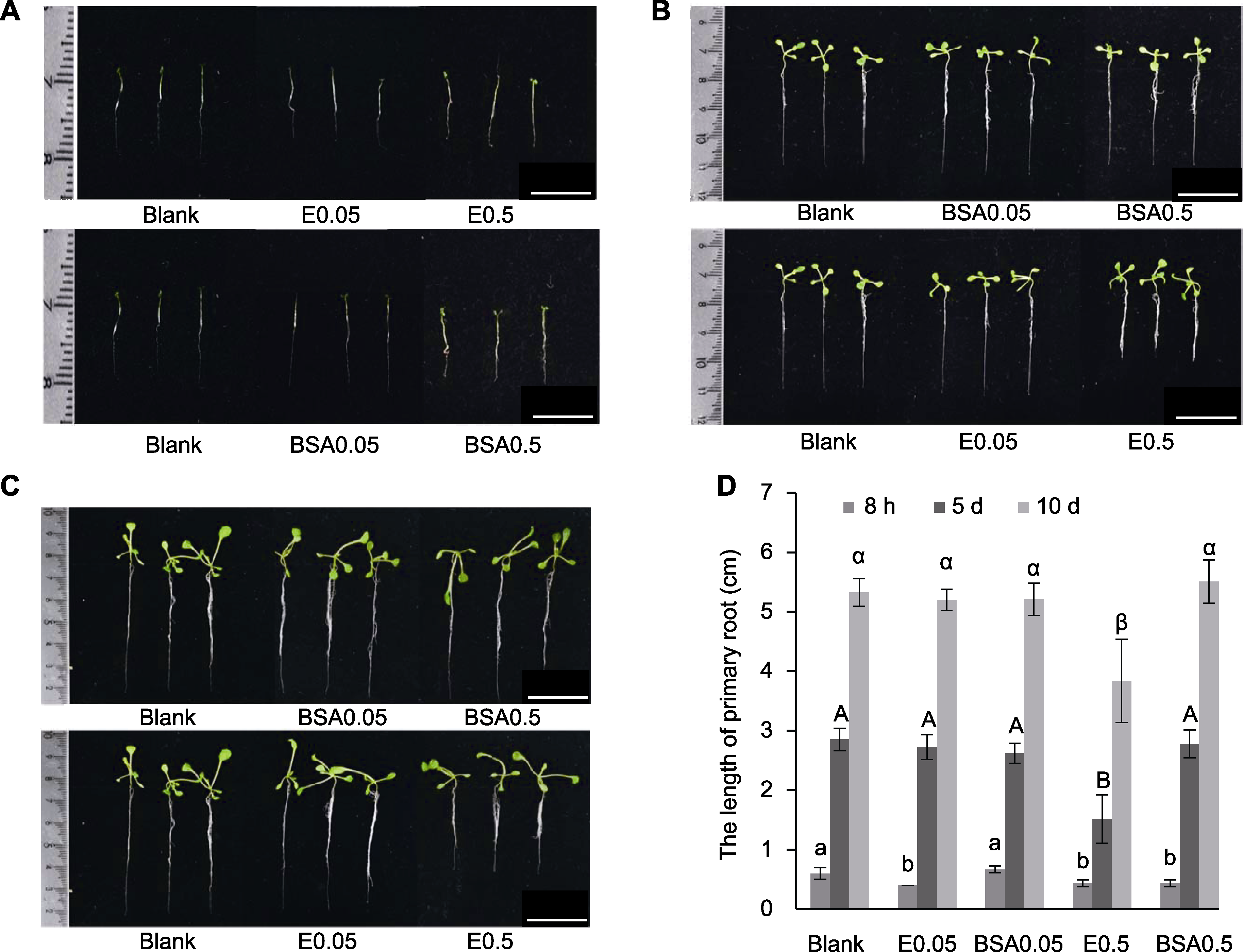
图3 不同浓度PNGase Rz处理对拟南芥主根生长的影响 (A) 处理8小时的幼苗; (B) 第5天的幼苗; (C) 第10天的幼苗; (D) 用不同浓度PNGase RZ处理拟南芥8小时, 不同处理组各时间点主根长度的统计分析(不同字母表示差异显著)。Blank: 无菌去离子水; BSA0.05: 0.05 mg·mL-1 BSA溶液; BSA0.5: 0.5 mg·mL-1 BSA溶液; E0.05: 0.05 mg·mL-1 PNGase Rz溶液; E0.5: 0.5 mg·mL-1 PNGase Rz溶液。Bars=1 cm
Figure 3 The influence of PNGase Rz with different concentrations on the growth of Arabidopsis primary root (A) Seedlings cultured for 8 hours; (B) Seedlings in the fifth day of growth; (C) Seedlings in the tenth day of growth; (D) Statistical analysis of primary root length of Arabidopsis seedlings treated with different concentrations of PNGase Rz for 8 hours at different time points (different letters indicate significant dfferences). Blank: Sterile deionized water; BSA0.05: 0.05 mg·mL-1 BSA; BSA0.5: 0.5 mg·mL-1 BSA; E0.05: 0.05 mg·mL-1 PNGase Rz; E0.5: 0.5 mg·mL-1 PNGase Rz. Bars=1 cm
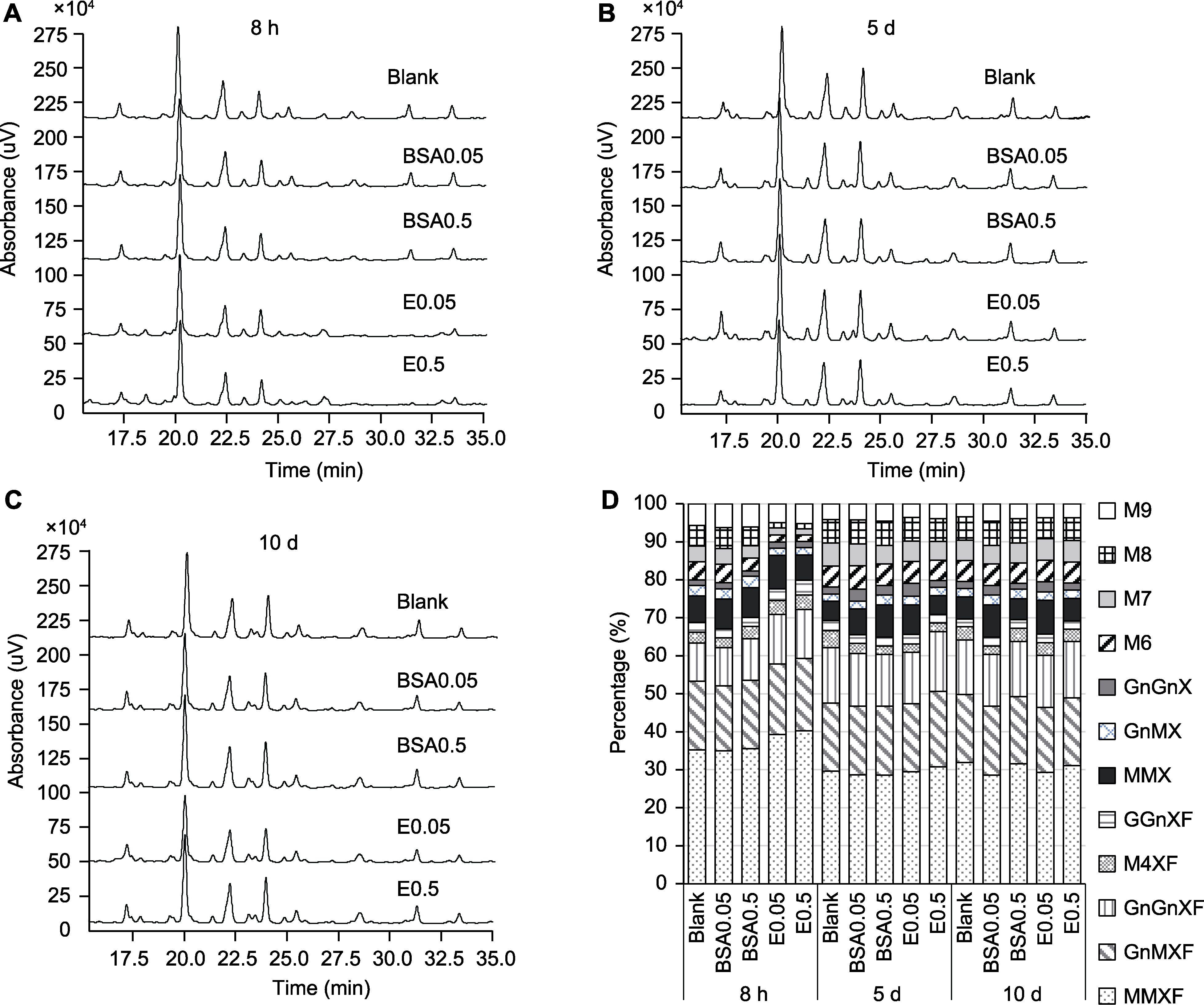
图4 拟南芥不同处理组在3个生长点N-糖链液相色谱图和相对含量 (A) 8小时N-糖链HPLC色谱图; (B) 第5天N-糖链HPLC色谱图; (C) 第10天N-糖链HPLC色谱图; (D) N-糖链相对含量。不同糖型缩写同表1。Blank、BSA0.05、BSA0.5、E0.05和E0.5同图3。
Figure 4 HPLC spectra of N-glycans from different groups at three growth points and the relative content of each N-glycan of Arabidopsis (A) HPLC spectra of N-glycans at 8 h; (B) HPLC spectra of N-glycans at 5 d; (C) HPLC spectra of N-glycans at 10 d; (D) The relative content of different N-glycans. The abbreviations of dfferent N-glycans are the same as Table 1. Blank, BSA0.05, BSA0.5, E0.05, and E0.5 are the same as Figure 3.
| N-glycans | The relative content of each N-glycan (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | BSA0.05 | BSA0.5 | E0.05 | E0.5 | |
| Culture for 8 hours | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 35.22±0.42 b | 35.00±0.07 b | 35.57±0.99 b | 39.29±0.14 a | 40.25±0.62 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 18.12±0.07 bc | 17.10±0.07 b | 18.00±0.55 c | 18.51±0.05 b | 19.03±0.20 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.83±0.20 c | 2.61±0.10 c | 3.24±0.16 b | 3.63±0.14 a | 3.86±0.18 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 9.98±0.13 c | 10.02±0.08 c | 10.95±0.79 b | 13.09±0.13 a | 12.89±0.55 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.63±0.09 c | 2.35±0.11 d | 2.35±0.16 d | 3.06±0.05 b | 3.83±0.12 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 6.98±0.16 c | 7.89±0.15 b | 7.86±0.19 b | 8.83±0.15 a | 6.66±0.32 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.77±0.14 a | 2.60±0.16 a | 2.95±0.22 a | 1.88±0.24 b | 1.94±0.21 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.44±0.14 b | 1.69±0.10 a | 1.40±0.13 b | 1.67±0.21 ab | 1.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of complex | 79.97±0.52 c | 79.26±0.48 d | 82.31±0.22 b | 89.95±0.12 a | 90.10±0.29 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 4.78±0.10 a | 4.81±0.05 a | 3.41±0.27 b | 1.86±0.09 c | 1.70±0.16 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 4.16±0.13 a | 4.16±0.11 a | 3.25±0.11 b | 1.87±0.11 c | 1.58±0.29 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 5.37±0.10 a | 5.52±0.11 a | 4.90±0.20 b | 1.39±0.21 c | 1.44±0.18 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 5.71±0.28 b | 6.25±0.29 a | 6.12±0.13 a | 4.93±0.30 c | 5.18±0.13 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.03±0.52 b | 20.74±0.48 a | 17.69±0.22 c | 10.05±0.12 d | 9.90±0.29 d |
| Culture for 5 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 29.60±0.18 b | 28.68±0.15 c | 28.60±0.87 c | 29.51±0.24 b | 30.74±0.36 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.97±0.10 b | 18.06±0.12 b | 18.15±0.61 b | 17.84±0.10 b | 19.85±0.28 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 4.46±0.08 a | 2.71±0.12 b | 2.24±0.15 c | 2.23±0.12 c | 2.34±0.11 c |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.58±0.11 b | 13.80±0.15 c | 13.56±0.27 c | 13.54±0.18 c | 15.72±0.14 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.62±0.13 a | 2.29±0.10 b | 2.29±0.12 b | 2.46±0.11 ab | 2.22±0.18 b |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.17±0.07 d | 6.80±0.11 c | 8.56±0.26 a | 7.77±0.30 b | 5.00±0.16 d |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.81±0.17 d | 2.02±0.10 cd | 2.58±0.11 a | 2.33±0.11 b | 2.19±0.07 bc |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.89±0.10 c | 3.14±0.05 a | 2.54±0.17 b | 3.36±0.25 a | 1.75±0.21 c |
| Sum of complex | 78.10±0.10 c | 77.51±0.15 d | 78.52±0.26 c | 79.05±0.18 b | 79.80±0.52 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.46±0.09 c | 6.16±0.05 a | 5.64±0.15 bc | 5.81±0.30 ab | 5.38±0.32 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 6.09±0.13 a | 5.78±0.15 b | 4.90±0.13 d | 5.33±0.22 c | 4.87±0.11 d |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.22±0.15 b | 6.35±0.04 a | 6.41±0.09 a | 6.27±0.17 ab | 6.04±0.10 b |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 4.12±0.11 b | 4.20±0.15 ab | 4.53±0.26 a | 3.55±0.25 c | 3.90±0.20 bc |
| Sum of high-mannose | 21.90±0.10 b | 22.49±0.15 a | 21.48±0.26 b | 20.95±0.18 c | 20.20±0.52 d |
| Culture for 10 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 31.88±0.19 a | 31.64±0.09 ab | 31.58±0.08 ab | 29.30±0.12 c | 31.11±0.12 b |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.96±0.09 a | 17.66±0.10 a | 17.70±0.37 a | 17.07±0.09 b | 17.77±0.13 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 3.46±0.57 a | 3.57±0.11 a | 3.43±0.13 a | 3.32±0.12 a | 3.28±0.12 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.34±0.07 ab | 13.88±0.10 bc | 14.50±0.58 a | 13.73±0.05 c | 14.85±0.16 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.05±0.09 a | 2.21±0.17 a | 2.30±0.20 a | 2.25±0.09 a | 2.20±0.23 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.81±0.23 c | 6.62±0.10 b | 5.48±0.38 c | 8.96±0.03 a | 5.86±0.14 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.20±0.15 a | 2.27±0.12 a | 2.51±0.42 a | 2.20±0.07 a | 2.19±0.11 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.87±0.10 c | 2.23±0.13 b | 1.56±0.19 d | 2.64±0.07 a | 1.88±0.05 c |
| Sum of complex | 79.57±0.47 ab | 80.08±0.30 a | 79.06±0.64 b | 79.47±0.07 ab | 79.15±0.15 b |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.47±0.09 a | 5.59±0.08 a | 5.39±0.32 a | 5.68±0.17 a | 5.52±0.10 a |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 5.36±0.16 b | 5.27±0.09 b | 5.24±0.10 b | 5.69±0.17 a | 5.66±0.17 a |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.20±0.07 a | 5.71±0.13 bc | 6.42±0.40 a | 5.52±0.21 c | 6.04±0.10 ab |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 3.41±0.22 b | 3.35±0.23 b | 3.89±0.15 a | 3.64±0.22 ab | 3.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.43±0.47 ab | 19.92±0.30 b | 20.94±0.64 a | 20.53±0.07 a | 20.85±0.15 a |
表3 不同时间点拟南芥各处理N-糖链相对含量
Table 3 The relative content of each N-glycan of Arabidopsis from different groups at different time points
| N-glycans | The relative content of each N-glycan (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | BSA0.05 | BSA0.5 | E0.05 | E0.5 | |
| Culture for 8 hours | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 35.22±0.42 b | 35.00±0.07 b | 35.57±0.99 b | 39.29±0.14 a | 40.25±0.62 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 18.12±0.07 bc | 17.10±0.07 b | 18.00±0.55 c | 18.51±0.05 b | 19.03±0.20 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.83±0.20 c | 2.61±0.10 c | 3.24±0.16 b | 3.63±0.14 a | 3.86±0.18 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 9.98±0.13 c | 10.02±0.08 c | 10.95±0.79 b | 13.09±0.13 a | 12.89±0.55 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.63±0.09 c | 2.35±0.11 d | 2.35±0.16 d | 3.06±0.05 b | 3.83±0.12 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 6.98±0.16 c | 7.89±0.15 b | 7.86±0.19 b | 8.83±0.15 a | 6.66±0.32 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.77±0.14 a | 2.60±0.16 a | 2.95±0.22 a | 1.88±0.24 b | 1.94±0.21 b |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.44±0.14 b | 1.69±0.10 a | 1.40±0.13 b | 1.67±0.21 ab | 1.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of complex | 79.97±0.52 c | 79.26±0.48 d | 82.31±0.22 b | 89.95±0.12 a | 90.10±0.29 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 4.78±0.10 a | 4.81±0.05 a | 3.41±0.27 b | 1.86±0.09 c | 1.70±0.16 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 4.16±0.13 a | 4.16±0.11 a | 3.25±0.11 b | 1.87±0.11 c | 1.58±0.29 c |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 5.37±0.10 a | 5.52±0.11 a | 4.90±0.20 b | 1.39±0.21 c | 1.44±0.18 c |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 5.71±0.28 b | 6.25±0.29 a | 6.12±0.13 a | 4.93±0.30 c | 5.18±0.13 c |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.03±0.52 b | 20.74±0.48 a | 17.69±0.22 c | 10.05±0.12 d | 9.90±0.29 d |
| Culture for 5 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 29.60±0.18 b | 28.68±0.15 c | 28.60±0.87 c | 29.51±0.24 b | 30.74±0.36 a |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.97±0.10 b | 18.06±0.12 b | 18.15±0.61 b | 17.84±0.10 b | 19.85±0.28 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 4.46±0.08 a | 2.71±0.12 b | 2.24±0.15 c | 2.23±0.12 c | 2.34±0.11 c |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.58±0.11 b | 13.80±0.15 c | 13.56±0.27 c | 13.54±0.18 c | 15.72±0.14 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.62±0.13 a | 2.29±0.10 b | 2.29±0.12 b | 2.46±0.11 ab | 2.22±0.18 b |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.17±0.07 d | 6.80±0.11 c | 8.56±0.26 a | 7.77±0.30 b | 5.00±0.16 d |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.81±0.17 d | 2.02±0.10 cd | 2.58±0.11 a | 2.33±0.11 b | 2.19±0.07 bc |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.89±0.10 c | 3.14±0.05 a | 2.54±0.17 b | 3.36±0.25 a | 1.75±0.21 c |
| Sum of complex | 78.10±0.10 c | 77.51±0.15 d | 78.52±0.26 c | 79.05±0.18 b | 79.80±0.52 a |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.46±0.09 c | 6.16±0.05 a | 5.64±0.15 bc | 5.81±0.30 ab | 5.38±0.32 c |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 6.09±0.13 a | 5.78±0.15 b | 4.90±0.13 d | 5.33±0.22 c | 4.87±0.11 d |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.22±0.15 b | 6.35±0.04 a | 6.41±0.09 a | 6.27±0.17 ab | 6.04±0.10 b |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 4.12±0.11 b | 4.20±0.15 ab | 4.53±0.26 a | 3.55±0.25 c | 3.90±0.20 bc |
| Sum of high-mannose | 21.90±0.10 b | 22.49±0.15 a | 21.48±0.26 b | 20.95±0.18 c | 20.20±0.52 d |
| Culture for 10 days | |||||
| Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 31.88±0.19 a | 31.64±0.09 ab | 31.58±0.08 ab | 29.30±0.12 c | 31.11±0.12 b |
| GlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 17.96±0.09 a | 17.66±0.10 a | 17.70±0.37 a | 17.07±0.09 b | 17.77±0.13 a |
| Man4XylFucGlcNAc2 | 3.46±0.57 a | 3.57±0.11 a | 3.43±0.13 a | 3.32±0.12 a | 3.28±0.12 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 14.34±0.07 ab | 13.88±0.10 bc | 14.50±0.58 a | 13.73±0.05 c | 14.85±0.16 a |
| GalGlcNAcMan3XylFucGlcNAc2 | 2.05±0.09 a | 2.21±0.17 a | 2.30±0.20 a | 2.25±0.09 a | 2.20±0.23 a |
| Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 5.81±0.23 c | 6.62±0.10 b | 5.48±0.38 c | 8.96±0.03 a | 5.86±0.14 c |
| GlcNAcMan3XylGlcNAc2 | 2.20±0.15 a | 2.27±0.12 a | 2.51±0.42 a | 2.20±0.07 a | 2.19±0.11 a |
| GlcNAc2Man3XylGlcNAc2 | 1.87±0.10 c | 2.23±0.13 b | 1.56±0.19 d | 2.64±0.07 a | 1.88±0.05 c |
| Sum of complex | 79.57±0.47 ab | 80.08±0.30 a | 79.06±0.64 b | 79.47±0.07 ab | 79.15±0.15 b |
| Man6GlcNAc2 | 5.47±0.09 a | 5.59±0.08 a | 5.39±0.32 a | 5.68±0.17 a | 5.52±0.10 a |
| Man7GlcNAc2 | 5.36±0.16 b | 5.27±0.09 b | 5.24±0.10 b | 5.69±0.17 a | 5.66±0.17 a |
| Man8GlcNAc2 | 6.20±0.07 a | 5.71±0.13 bc | 6.42±0.40 a | 5.52±0.21 c | 6.04±0.10 ab |
| Man9GlcNAc2 | 3.41±0.22 b | 3.35±0.23 b | 3.89±0.15 a | 3.64±0.22 ab | 3.64±0.11 ab |
| Sum of high-mannose | 20.43±0.47 ab | 19.92±0.30 b | 20.94±0.64 a | 20.53±0.07 a | 20.85±0.15 a |
| 1 | 王梦, 危双, 王婷, Voglmeir J, 刘丽 (2017). Solitalea canadensis源β-N-乙酰氨基己糖苷酶的基因克隆、异源表达和酶学特性. 微生物学报 57, 1270-1282. |
| 2 |
Altmann F (2007). The role of protein glycosylation in allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 142, 99-115.
DOI URL |
| 3 |
Bao LG, Ma SW, van Huystee RB (2001). The effects of the site-directed removal of N-glycosylation from cationic peanut peroxidase on its function. Arch Biochem Biophys 386, 17-24.
DOI URL |
| 4 |
Dam S, Thaysen-Andersen M, Stenkjær E, Lorentzen A, Roepstorff P, Packer NH, Stougaard J (2013). Combined N-glycome and N-glycoproteome analysis of the Lotus japonicus seed globulin fraction shows conservation of protein structure and glycosylation in legumes. J Proteome Res 12, 3383-3392.
DOI URL |
| 5 |
Du YM, Xia T, Gu XQ, Wang T, Ma HY, Voglmeir J, Liu L (2015). Rapid sample preparation methodology for plant N-glycan analysis using acid-stable PNGase H+. J Agric Food Chem 63, 10550-10555.
DOI URL |
| 6 |
Ghazarian H, Idoni B, Oppenheimer SB (2011). A glycobiology review: carbohydrates, lectins and implications in cancer therapeutics. Acta Histochem 113, 236-247.
DOI URL |
| 7 |
Horiuchi R, Hirotsu N, Miyanishi N (2015). Comparative analysis of N-glycans in the ungerminated and germinated stages of Oryza sativa. Carbohydr Res 418, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| 8 | Ihara Y, Ikezaki M, Takatani M, Ito Y (2020). Calnexin/calreticulin and assays related to N-glycoprotein folding in vitro. In: Hirabayashi J, ed. Lectin Purification and Analysis: Methods and Protocols. Humana: Springer. pp. 295-308. |
| 9 |
Kajiura H, Koiwa H, Nakazawa Y, Okazawa A, Kobayashi A, Seki T, Fujiyama K (2010). Two Arabidopsis thaliana Golgi, α-mannosidase I enzymes are responsible for plant N-glycan maturation. Glycobiology 20, 235-247.
DOI URL |
| 10 |
Kang JS, Frank J, Kang CH, Kajiura H, Vikram M, Ueda A, Kim S, Bahk JD, Triplett B, Fujiyama K, Lee SY, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2008). Salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana requires maturation of N-glycosylated proteins in the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 5933-5938.
DOI URL |
| 11 |
Kato S, Hayashi M, Kitagawa M, Kajiura H, Maeda M, Kimura Y, Igarashi K, Kasahara M, Ishimizu T (2018). Degradation pathway of plant complex-type N-glycans: identification and characterization of a key α1,3-fucosidase from glycoside hydrolase family 29. Biochem J 475, 305-317.
DOI URL |
| 12 |
Kimura Y, Matsuo S (2000). Changes in N-linked oligosaccharides during seed development of Ginkgo biloba. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64, 562-568.
DOI URL |
| 13 |
Kimura Y, Takeoka Y, Inoue M, Maeda M, Fujiyama K (2011). Double-knockout of putative endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENGase) genes in Arabidopsis thaliana: loss of ENGase activity induced accumulation of high- mannose type free N-glycans bearing N,N'-acetylchitobiosyl unit. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75, 1019-1021.
DOI URL |
| 14 |
Koiwa H, Li F, McCully MG, Mendoza I, Koizumi N, Manabe Y, Nakagawa Y, Zhu JH, Rus A, Pardo JM, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (2003). The STT3a subunit isoform of the Arabidopsis oligosaccharyltransferase controls adaptive responses to salt/osmotic stress. Plant Cell 15, 2273-2284.
DOI URL |
| 15 |
Liebminger E, Hüttner S, Vavra U, Fischl R, Schoberer J, Grass J, Blaukopf C, Seifert GJ, Altmann F, Mach L, Strasser R (2009). Class I α-mannosidases are required for N-glycan processing and root development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21, 3850-3867.
DOI URL |
| 16 |
Liebminger E, Veit C, Pabst M, Batoux M, Zipfel C, Altmann F, Mach L, Strasser R (2011). β-N-acetylhexosaminidases HEXO1 and HEXO3 are responsible for the formation of paucimannosidic N-glycans in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Biol Chem 286, 10793-10802.
DOI URL |
| 17 |
Lindner H, Kessler SA, Müller LM, Shimosato-Asano H, Boisson-Dernier A, Grossniklaus U (2015). TURAN and EVAN mediate pollen tube reception in Arabidopsis Synergids through protein glycosylation. PLoS Biol 13, e1002139.
DOI URL |
| 18 | Maeda M, Kimura Y (2014). Structural features of free N-glycans occurring in plants and functional features of de-N-glycosylation enzymes, ENGase, and PNGase: the presence of unusual plant complex type N-glycans. Front Plant Sci 5, 429. |
| 19 |
Misaki R, Kimura Y, Fujiyama K, Seki T (2001). Glycoproteins secreted from suspension -cultured tobacco BY2 cells have distinct glycan structures from intracellular glycoproteins. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65, 2482-2488.
DOI URL |
| 20 |
Nagashima Y, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2018). Function of N-glycosylation in plants. Plant Sci 274, 70-79.
DOI URL |
| 21 |
Nakamura K, Inoue M, Yoshiie T, Hosoi K, Kimura Y (2008). Changes in structural features of free N-glycan and endoglycosidase activity during tomato fruit ripening. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72, 2936-2945.
DOI URL |
| 22 |
Rips S, Bentley N, Jeong IS, Welch JL, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H (2014). Multiple N-glycans cooperate in the subcellular targeting and functioning of Arabidopsis KORRIGAN1. Plant Cell 26, 3792-3808.
DOI URL |
| 23 |
Saijo Y (2010). ER quality control of immune receptors and regulators in plants. Cell Microbiol 12, 716-724.
DOI URL |
| 24 |
Shen JB, Ding Y, Gao CJ, Rojo E, Jiang LW (2014). N-linked glycosylation of AtVSR1 is important for vacuolar protein sorting in Arabidopsis. Plant J 80, 977-992.
DOI URL |
| 25 |
Strasser R, Schoberer J, Jin CS, Glössl J, Mach L, Steinkellner H (2006). Molecular cloning and characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana Golgi α-mannosidase II, a key enzyme in the formation of complex N-glycans in plants. Plant J 45, 789-803.
PMID |
| 26 |
Viëtor R, Loutelier-Bourhis C, Fitchette AC, Margerie P, Gonneau M, Faye L, Lerouge P (2003). Protein N-glycosylation is similar in the moss Physcomitrella patens and in higher plants. Planta 218, 269-275.
PMID |
| 27 |
Wang T, Hu XC, Cai ZP, Voglmeir J, Liu L (2017a). Qualitative and quantitative analysis of carbohydrate modification on glycoproteins from seeds of Ginkgo biloba. J Agric Food Chem 65, 7669-7679.
DOI URL |
| 28 |
Wang T, Voglmeir J (2014). PNGases as valuable tools in glycoprotein analysis. Protein Pept Lett 21, 976-985.
DOI URL |
| 29 |
Wang WL, Wang W, Du YM, Wu H, Yu XB, Ye KP, Li CB, Jung YS, Qian YJ, Voglmeir J, Liu L (2017b). Comparison of anti-pathogenic activities of the human and bovine milk N-glycome: fucosylation is a key factor. Food Chem 235, 167-174.
DOI URL |
| 30 |
Wang ZY, Gehring C, Zhu JH, Li FM, Zhu JK, Xiong LM (2015). The Arabidopsis Vacuolar Sorting Receptor 1 is required for osmotic stress-induced abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 167, 137-152.
DOI URL |
| 31 |
Wei S, Henquet MGL, Mentink RA, van Dijk AJ, Cordewener JHG, Bosch D, America AHP, van der Krol AR (2011). N-glycoproteomics in plants: perspectives and challenges. J Proteomics 74, 1463-1474.
DOI URL |
| 32 |
Wilson IBH, Zeleny R, Kolarich D, Staudacher E, Stroop CJM, Kamerling JP, Altmann F (2001). Analysis of Asn -linked glycans from vegetable foodstuffs: widespread occurrence of Lewis a, core α1,3-linked fucose and xylose substitutions. Glycobiology 11, 261-274.
PMID |
| 33 |
Xu SL, Medzihradszky KF, Wang ZY, Burlingame AL, Chalkley RJ (2016). N-glycopeptide profiling in Arabidopsis inflorescence. Mol Cell Proteomics 15, 2048-2054.
DOI URL |
| 34 |
Zeng W, Ford KL, Bacic A, Heazlewood JL (2018). N- linked glycan micro-heterogeneity in glycoproteins of Arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 17, 413-421.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘雨函, 曹启江, 张诗晗, 李益慧, 王菁, 谭晓萌, 刘筱儒, 王显玲. 拟南芥AtFTCD-L参与根系响应土壤紧实度的机制研究[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 景艳军, 林荣呈. 蓝光受体CRY2化身“暗黑舞者”[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 878-882. |
| [3] | 罗燕, 刘奇源, 吕元兵, 吴越, 田耀宇, 安田, 李振华. 拟南芥光敏色素突变体种子萌发的光温敏感性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 752-762. |
| [4] | 陈艳晓, 李亚萍, 周晋军, 解丽霞, 彭永彬, 孙伟, 和亚男, 蒋聪慧, 王增兰, 郑崇珂, 谢先芝. 拟南芥光敏色素B氨基酸位点突变对其结构与功能的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [5] | 杨继轩, 王雪霏, 顾红雅. 西藏野生拟南芥开花时间变异的遗传基础[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 373-382. |
| [6] | 王钢, 王二涛. “卫青不败由天幸”——WeiTsing的广谱抗根肿病机理被揭示[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [7] | 杨永青, 郭岩. 植物细胞质外体pH感受机制的解析[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 409-411. |
| [8] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [9] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [10] | 车永梅, 孙艳君, 卢松冲, 侯丽霞, 范欣欣, 刘新. AtMYB77促进NO合成参与调控干旱胁迫下拟南芥侧根发育[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 404-413. |
| [11] | 李秋信, 迟伟, 季代丽. CURT1调控类囊体膜弯曲的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 462-469. |
| [12] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华. 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| [13] | 黄荣峰, 徐通达. 生长素通过MAPK介导的超长链脂肪酸合成调控侧根发育[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 6-9. |
| [14] | 杜斐, 焦雨铃. WUSCHEL介导的固有免疫: 植物干细胞抵御病毒侵害的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 537-540. |
| [15] | 马龙, 李桂林, 李师鹏, 蒋苏. 根尖整体透明技术改良[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(5): 596-604. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||