

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (3): 481-494.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23074 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23074
陈艳晓1,2, 李亚萍2, 周晋军3, 解丽霞2, 彭永彬2, 孙伟2, 和亚男2, 蒋聪慧2, 王增兰1, 郑崇珂2,*( ), 谢先芝2,*(
), 谢先芝2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-05
接受日期:2023-12-19
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-05-10
通讯作者:
E-mail: 基金资助:
Yanxiao Chen1,2, Yaping Li2, Jinjun Zhou3, Lixia Xie2, Yongbin Peng2, Wei Sun2, Yanan He2, onghui Jiang2, Zenglan Wang1, Chongke Zheng2,*( ), Xianzhi Xie2,*(
), Xianzhi Xie2,*( )
)
Received:2023-06-05
Accepted:2023-12-19
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-05-10
Contact:
E-mail: 摘要: 生物体为适应外界不断变化的光环境, 进化出不同的光受体, 其中光敏色素是一类经典的植物感受红光和远红光的受体蛋白, 其通过暗适应的Pr状态和光激活的Pfr状态之间的光转换来检测红光和远红光。植物光敏色素具有1个保守的N端感光区域和1个C端调节区域, 其中N端部分包括NTE、PAS、GAF和PHY亚结构域, C端部分包括2个PAS结构域和1个组氨酸激酶相关结构域(HKRD)。为深入了解光敏色素的结构及功能, 已获得许多光敏色素功能缺失或氨基酸位点突变体, 并对其进行功能研究, 发现N端结构域在光敏色素的光谱特性、光信号感知和光信号转导等方面均具有重要作用; 而C端结构域是光敏色素的二聚化与核定位所必需。该文综述了拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中光敏色素B (phyB)各亚结构域中氨基酸位点突变对其功能的影响, 以期深入理解phyB的结构及功能, 为未来通过基因编辑手段进行作物农艺性状的遗传改良奠定基础。
陈艳晓, 李亚萍, 周晋军, 解丽霞, 彭永彬, 孙伟, 和亚男, 蒋聪慧, 王增兰, 郑崇珂, 谢先芝. 拟南芥光敏色素B氨基酸位点突变对其结构与功能的影响. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 481-494.
Yanxiao Chen, Yaping Li, Jinjun Zhou, Lixia Xie, Yongbin Peng, Wei Sun, Yanan He, onghui Jiang, Zenglan Wang, Chongke Zheng, Xianzhi Xie. Effect of Amino Acid Point Mutations on the Structure and Function of Phytochrome B in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(3): 481-494.
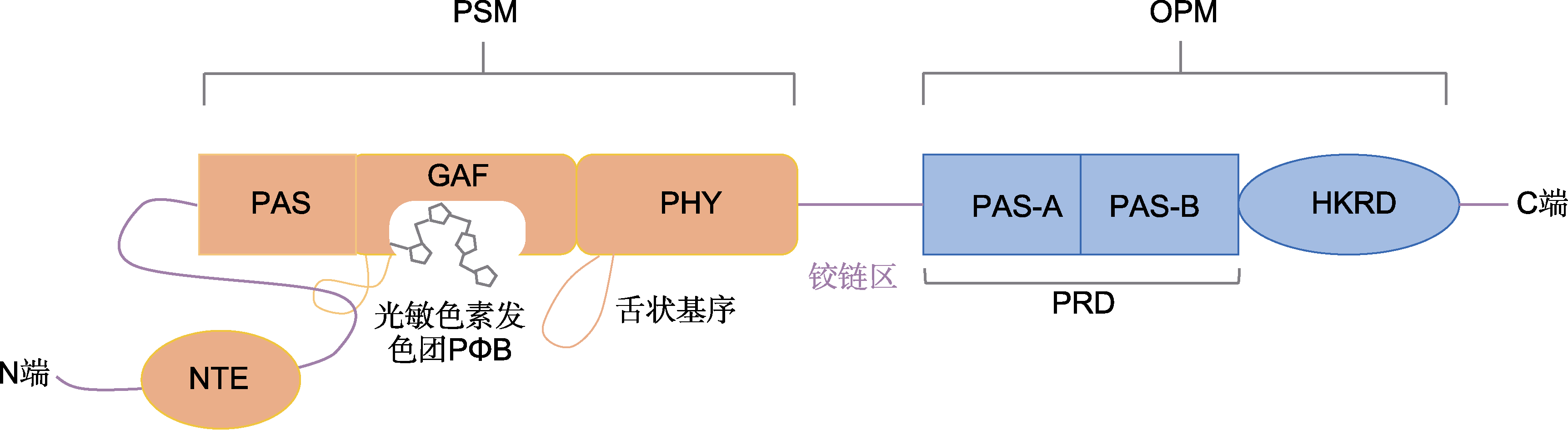
图1 拟南芥phyB结构域示意图 PSM: 感光模块; OPM: 输出模块; NTE: N端延伸区; PAS: Per(昼夜节律蛋白)-Arnt(芳香烃受体核转位蛋白)-Sim(Sim蛋白); GAF: cGMP激活的磷酸二酯酶, 鱼腥藻腺苷酸环化酶, 大肠杆菌FhlA; PHY: 光敏色素; PRD: PAS相关结构域; HKRD: 组氨酸激酶相关结构域
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of phyB domain in Arabidopsis thaliana PSM: Photosensory module; OPM: Output module; NTE: N-terminal extension; PAS: Per (period circadian protein)-Arnt (Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein)-Sim (single-minded protein); GAF: cGMP-stimulated phosphodiesterase, anabaena adenylate cyclases, Escherichia coli FhlA; PHY: Phytochrome; PRD: PAS-related domain; HKRD: Histidine kinase-related domain
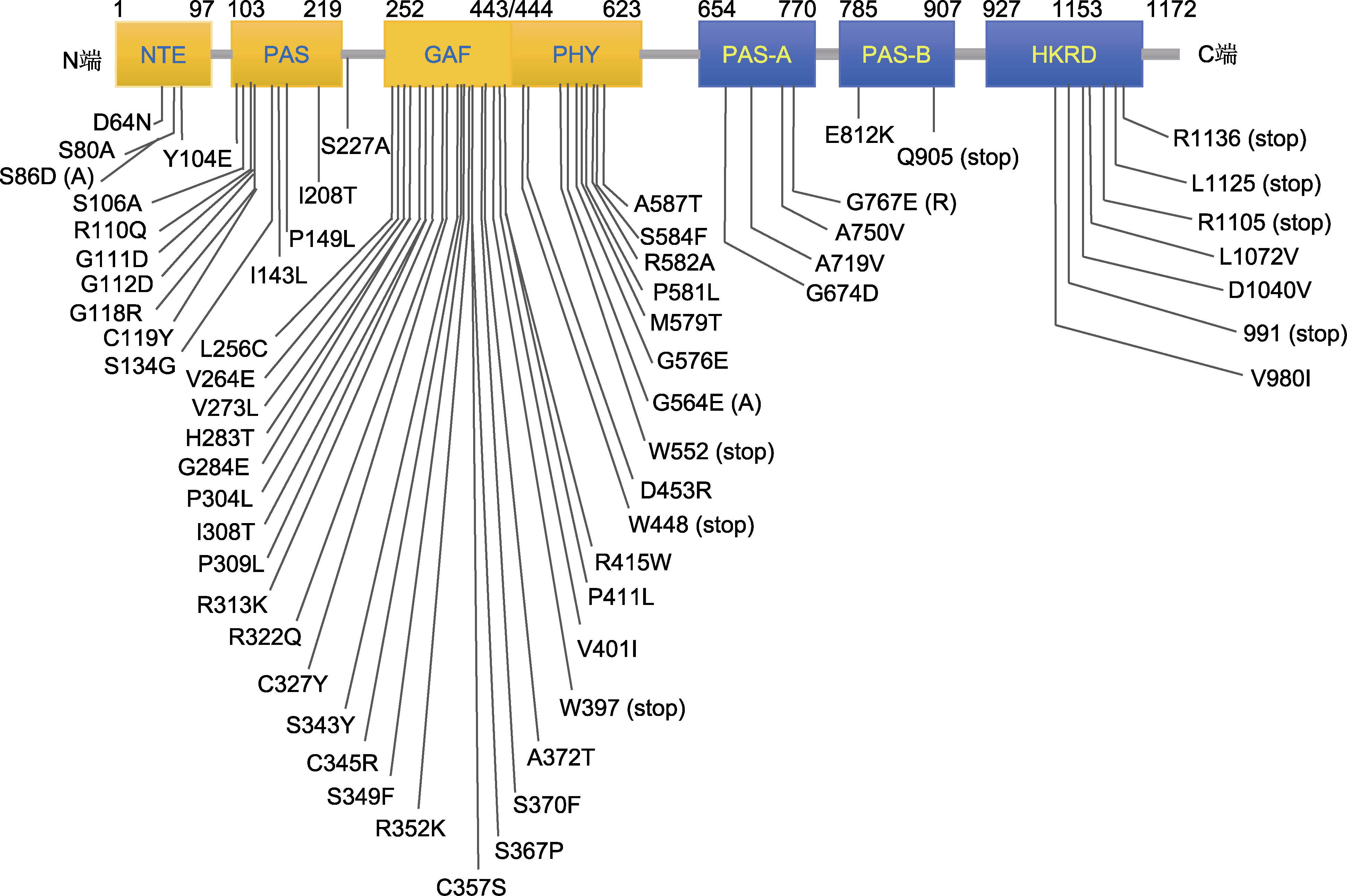
图2 携带错义突变拟南芥phyB蛋白结构域示意图 各结构域简称同图1。
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the phyB protein domain in Arabidopsis thaliana carrying a missense mutation The alphabet abbreviation of each domain is explained in Figure 1.
| 结构域 | 突变位点 | 光敏感性 | 发色团组 装及结合 | 光敏色素 稳定性 | 光小体 形成 | 光敏色素 核定位 | 光信号 传递 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTE | D64N | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| S80A | - | Zhao et al., | ||||||
| S86D(A) | -(+) | o(o) | - | Medzihradszky et al., | ||||
| PAS | Y104E | - | - | Nito et al., | ||||
| S106A | - | - | Zhao et al., | |||||
| R110Q | - | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| G111D | - | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| G112D | - | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| G118R | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| C119Y | - | - | Kikis et al., | |||||
| S134G | - | - | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| I143L | + | Ruiz-Diaz et al., | ||||||
| PAS | P149L | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| I208T | - | o | Oka et al., | |||||
| S227A | + | - | Liu et al., | |||||
| GAF | L256C | - | Kikis et al., | |||||
| V264E | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| V273L | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| Y276H | + | + | Su and Lagarias, | |||||
| H283T | - | Reed et al., | ||||||
| G284E | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| P304L | o | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| I308T | o | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| P309L | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| R313K | - | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| R322Q | - | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| C327Y | - | Chen et al., | ||||||
| S343Y | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| C345R | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| R352K | o | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| C357S | - | Wagner et al., | ||||||
| S367P | o | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| S370F | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| A372T | - | - | Chen et al., | |||||
| V401I | - | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| P411L | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| R415W | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| PHY | D453R | + | + | Viczian et al., | ||||
| G564E(A) | + | o | + | +(-) | Kretsch et al., | |||
| M579T | - | Maloof et al., | ||||||
| R582A | + | + | Burgie et al., | |||||
| S584F | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| A587T | - | - | Chen et al., | |||||
| PRD | G674D | - | - | Chen et al., | ||||
| A719V | - | - | Chen et al., | |||||
| A750V | - | - | Wagner and Quail, | |||||
| G767E(R) | -(-) | -(-) | Wagner and Quail, | |||||
| E812K | - | - | - | Wagner and Quail, | ||||
| HKRD | V980I | - | Ruiz-Diaz et al., | |||||
| D1040V | - | - | - | Qiu et al., | ||||
| L1072V | - | Ruiz-Diaz et al., |
表1 phyB突变体中氨基酸突变位点及其对光敏感性、发色团组装与结合、光敏色素稳定性、光小体形成、光敏色素核定位及光信号传递的影响
Table 1 Overview of amino acid point mutation in phyB mutants and their effects on photosensitivity, chromophore assembly and binding, phytochrome stability, photobodies formation, phytochrome nuclear localization and light signaling
| 结构域 | 突变位点 | 光敏感性 | 发色团组 装及结合 | 光敏色素 稳定性 | 光小体 形成 | 光敏色素 核定位 | 光信号 传递 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTE | D64N | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| S80A | - | Zhao et al., | ||||||
| S86D(A) | -(+) | o(o) | - | Medzihradszky et al., | ||||
| PAS | Y104E | - | - | Nito et al., | ||||
| S106A | - | - | Zhao et al., | |||||
| R110Q | - | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| G111D | - | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| G112D | - | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| G118R | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| C119Y | - | - | Kikis et al., | |||||
| S134G | - | - | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| I143L | + | Ruiz-Diaz et al., | ||||||
| PAS | P149L | - | Oka et al., | |||||
| I208T | - | o | Oka et al., | |||||
| S227A | + | - | Liu et al., | |||||
| GAF | L256C | - | Kikis et al., | |||||
| V264E | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| V273L | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| Y276H | + | + | Su and Lagarias, | |||||
| H283T | - | Reed et al., | ||||||
| G284E | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| P304L | o | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| I308T | o | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| P309L | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| R313K | - | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| R322Q | - | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| C327Y | - | Chen et al., | ||||||
| S343Y | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| C345R | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| R352K | o | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| C357S | - | Wagner et al., | ||||||
| S367P | o | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| S370F | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| A372T | - | - | Chen et al., | |||||
| V401I | - | o | - | Oka et al., | ||||
| P411L | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| R415W | - | Kikis et al., | ||||||
| PHY | D453R | + | + | Viczian et al., | ||||
| G564E(A) | + | o | + | +(-) | Kretsch et al., | |||
| M579T | - | Maloof et al., | ||||||
| R582A | + | + | Burgie et al., | |||||
| S584F | - | Oka et al., | ||||||
| A587T | - | - | Chen et al., | |||||
| PRD | G674D | - | - | Chen et al., | ||||
| A719V | - | - | Chen et al., | |||||
| A750V | - | - | Wagner and Quail, | |||||
| G767E(R) | -(-) | -(-) | Wagner and Quail, | |||||
| E812K | - | - | - | Wagner and Quail, | ||||
| HKRD | V980I | - | Ruiz-Diaz et al., | |||||
| D1040V | - | - | - | Qiu et al., | ||||
| L1072V | - | Ruiz-Diaz et al., |
| 模块 | 亚结构域 | 功能 | 主要作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSM | NTE | 调控光敏色素Pfr形式的稳定性, 如影响光敏色素的热逆转反应; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB与下游转录因子PIF结合及通过光-钙调控环促进phyB入核 | 光信号感知及传递 |
| PAS | 调控发色团的组装; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB与下游转录因子PIF3的结合能力 | ||
| GAF | 负责发色团的组装, 感应光信号; 维持phyB Pr/Pfr形式正常的可逆转换; 保持光敏色素Pfr形式的数量或整体结构, 如影响phyB的暗逆转率; 负责光信号传递, 如感光结可能直接与PIF相互作用 | ||
| PHY | 调控光敏色素Pfr形式的稳定性, 如影响phyB的暗逆转率以及热逆转反应; 维持phyB Pr/Pfr形式正常的可逆转换; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB与下游成分的相互作用及phyB的核定位 | ||
| OPM | PRD | 调控光敏色素Pfr形式的稳定性, 如影响phyB的暗逆转反应; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB的核定位 | 光信号传递 |
| HKRD | 介导光敏色素的二聚化, 从而影响phyB在核内积累和光小体定位中的早期信号传递 |
表2 拟南芥光敏色素结构域功能
Table 2 Summary on the function of phytochrome domains in Arabidopsis
| 模块 | 亚结构域 | 功能 | 主要作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSM | NTE | 调控光敏色素Pfr形式的稳定性, 如影响光敏色素的热逆转反应; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB与下游转录因子PIF结合及通过光-钙调控环促进phyB入核 | 光信号感知及传递 |
| PAS | 调控发色团的组装; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB与下游转录因子PIF3的结合能力 | ||
| GAF | 负责发色团的组装, 感应光信号; 维持phyB Pr/Pfr形式正常的可逆转换; 保持光敏色素Pfr形式的数量或整体结构, 如影响phyB的暗逆转率; 负责光信号传递, 如感光结可能直接与PIF相互作用 | ||
| PHY | 调控光敏色素Pfr形式的稳定性, 如影响phyB的暗逆转率以及热逆转反应; 维持phyB Pr/Pfr形式正常的可逆转换; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB与下游成分的相互作用及phyB的核定位 | ||
| OPM | PRD | 调控光敏色素Pfr形式的稳定性, 如影响phyB的暗逆转反应; 负责光信号传递, 如影响phyB的核定位 | 光信号传递 |
| HKRD | 介导光敏色素的二聚化, 从而影响phyB在核内积累和光小体定位中的早期信号传递 |
| [1] |
顾建伟, 刘婧, 薛彦久, 臧新, 谢先芝 (2011). 光敏色素在水稻生长发育中的作用. 中国水稻科学 25, 130-135.
DOI |
| [2] |
刘莎, 郑晓明, 冯雳, 乔卫华, 王君瑞, 公婷婷, 梁新霞, 齐兰, 苏龙, 丁膺宾, 许睿, 张丽芳, 程云连, 杨庆文 (2017). 水稻长日抑制基因PhyB的多样性及区域适应性初探. 植物遗传资源学报 18, 283-289.
DOI |
| [3] | 童哲, 赵玉锦, 王台, 李念华, 毛居代·亚力 (2000). 植物的光受体和光控发育研究. 植物学报 42, 111-115. |
| [4] | 张芳, 张晓枫, 王进征, 胡勇, 刘祥林 (2011). 植物光敏色素PHYA、PHYB研究进展. 生物学通报 46, 11-14. |
| [5] |
赵翔, 赵青平, 杨煦, 慕世超, 张骁 (2015). 向光素调节植物向光性及其与光敏色素/隐花色素的相互关系. 植物学报 50, 122-132.
DOI |
| [6] | Ádám É, Hussong A, Bindics J, Wüst F, Viczián A, Essing M, Medzihradszky M, Kircher S, Schäfer E, Nagy F (2011). Altered dark- and photo-conversion of phytochrome B mediate extreme light sensitivity and loss of photoreversibility of the phyB-401 mutant. PLoS One 6, e27250. |
| [7] |
Anders K, Daminelli-Widany G, Mroginski MA, von Stetten D, Essen LO (2013). Structure of the cyanobacterial phytochrome 2 photosensor implies a tryptophan switch for phytochrome signaling. J Biol Chem 288, 35714-35725.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Auldridge ME, Forest KT (2011). Bacterial phytochromes: more than meets the light. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 46, 67-88. |
| [9] |
Bae G, Choi G (2008). Decoding of light signals by plant phytochromes and their interacting proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59, 281-311.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Bellini D, Papiz MZ (2012). Structure of a bacteriophytochrome and light-stimulated protomer swapping with a gene repressor. Structure 20, 1436-1446.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Burgie ES, Bussell AN, Walker JM, Dubiel K, Vierstra RD (2014). Crystal structure of the photosensing module from a red/far-red light-absorbing plant phytochrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 10179-10184.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Burgie ES, Vierstra RD (2014). Phytochromes: an atomic perspective on photoactivation and signaling. Plant Cell 26, 4568-4583. |
| [13] |
Chen D, Lyu M, Kou XX, Li J, Yang ZX, Gao LL, Li Y, Fan LM, Shi H, Zhong SW (2022). Integration of light and temperature sensing by liquid-liquid phase separation of phytochrome B. Mol Cell 82, 3015-3029.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Chen M, Chory J, Fankhauser C (2004). Light signal transduction in higher plants. Annu Rev Genet 38, 87-117.
PMID |
| [15] |
Chen M, Schwab R, Chory J (2003). Characterization of the requirements for localization of phytochrome B to nuclear bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 14493-14498.
PMID |
| [16] |
Chen M, Tao Y, Lim J, Shaw A, Chory J (2005). Regulation of phytochrome B nuclear localization through light-dependent unmasking of nuclear-localization signals. Curr Biol 15, 637-642.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Cheng MC, Kathare PK, Paik I, Huq E (2021). Phytochrome signaling networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 217-244. |
| [18] | Cheng YL, Tu SL (2018). Alternative splicing and cross-talk with light signaling. Plant Cell Physiol 59, 1104-1110. |
| [19] |
Cherry JR, Hondred D, Walker JM, Keller JM, Hershey HP, Vierstra RD (1993). Carboxy-terminal deletion analysis of oat phytochrome A reveals the presence of separate domains required for structure and biological activity. Plant Cell 5, 565-575.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Cherry JR, Hondred D, Walker JM, Vierstra RD (1992). Phytochrome requires the 6 kDa N-terminal domain for full biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89, 5039-5043.
PMID |
| [21] |
Clack T, Mathews S, Sharrock RA (1994). The phytochrome apoprotein family in Arabidopsis is encoded by five genes: the sequences and expression of PHYD and PHYE. Plant Mol Biol 25, 413-427.
PMID |
| [22] |
Clack T, Shokry A, Moffet M, Liu P, Faul M, Sharrock RA (2009). Obligate heterodimerization of Arabidopsis phytochromes C and E and interaction with the PIF3 basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor. Plant Cell 21, 786-799.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Dash L, McEwan RE, Montes C, Mejia L, Walley JW, Dilkes BP, Kelley DR (2021). Slim shady is a novel allele of PHYTOCHROME B present in the T-DNA line SALK_ 015201. Plant Direct 5, e00326. |
| [24] |
Edgerton MD, Jones AM (1992). Localization of protein- protein interactions between subunits of phytochrome. Plant Cell 4, 161-171.
PMID |
| [25] |
Elich TD, Chory J (1997). Biochemical characterization of Arabidopsis wild-type and mutant phytochrome B holoproteins. Plant Cell 9, 2271-2280.
PMID |
| [26] | Essen LO, Mailliet J, Hughes J (2008). The structure of a complete phytochrome sensory module in the Pr ground state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 14709-14714. |
| [27] |
Franklin KA, Quail PH (2010). Phytochrome functions in Arabidopsis development. J Exp Bot 61, 11-24.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | He YN, Li YP, Cui LX, Xie LX, Zheng CK, Zhou GH, Zhou JJ, Xie XZ (2016). Phytochrome B negatively affects cold tolerance by regulating OsDREB1 gene expression through phytochrome interacting factor-like protein OsPIL16 in rice. Front Plant Sci 7, 1963. |
| [29] |
Hernando CE, Murcia MG, Pereyra ME, Sellaro R, Casal JJ (2021). Phytochrome B links the environment to transcription. J Exp Bot 72, 4068-4084.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Hu W, Su YS, Lagarias JC (2009). A light-independent allele of phytochrome B faithfully recapitulates photomorphogenic transcriptional networks. Mol Plant 2, 166-182.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Jung JH, Li Z, Chen H, Yang S, Li DD, Priatama RA, Kumar V, Xuan YH (2023). Mutation of phytochrome B promotes resistance to sheath blight and saline-alkaline stress via increasing ammonium uptake in rice. Plant J 113, 277-290. |
| [32] | Kikis EA, Oka Y, Hudson ME, Nagatani A, Quail PH (2009). Residues clustered in the light-sensing knot of phytochrome B are necessary for conformer-specific binding to signaling partner PIF3. PLoS Genet 5, e1000352. |
| [33] |
Kim C, Kwon Y, Jeong J, Kang MJ, Lee GS, Moon JH, Lee HJ, Park YI, Choi G (2023). Phytochrome B photobodies are comprised of phytochrome B and its primary and secondary interacting proteins. Nat Commun 14, 1708.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Kircher S, Gil P, Kozma-Bognár L, Fejes E, Speth V, Husselstein-Muller T, Bauer D, Ádám É, Schäfer E, Nagy F (2002). Nucleocytoplasmic partitioning of the plant photoreceptors phytochrome A, B, C, D, and E is regulated differentially by light and exhibits a diurnal rhythm. Plant Cell 14, 1541-1555.
PMID |
| [35] |
Klose C, Venezia F, Hussong A, Kircher S, Schäfer E, Fleck C (2015). Systematic analysis of how phytochrome B dimerization determines its specificity. Nat Plants 1, 15090.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Krall L, Reed JW (2000). The histidine kinase-related domain participates in phytochrome B function but is dispensable. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 8169-8174.
PMID |
| [37] |
Kretsch T, Poppe C, Schäfer E (2000). A new type of mutation in the plant photoreceptor phytochrome B causes loss of photoreversibility and an extremely enhanced light sensitivity. Plant J 22, 177-186.
PMID |
| [38] | Kwon CT, Song G, Kim SH, Han J, Yoo SC, An G, Kang K, Paek NC (2018). Functional deficiency of phytochrome B improves salt tolerance in rice. Environ Exp Bot 148, 100-108. |
| [39] |
Legris M, Ince YÇ, Fankhauser C (2019). Molecular mechanisms underlying phytochrome-controlled morphogenesis in plants. Nat Commun 10, 5219.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Li H, Burgie ES, Gannam ZTK, Li HL, Vierstra RD (2022). Plant phytochrome B is an asymmetric dimer with unique signaling potential. Nature 604, 127-133. |
| [41] |
Liu J, Zhang F, Zhou JJ, Chen F, Wang BS, Xie XZ (2012). Phytochrome B control of total leaf area and stomatal density affects drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 78, 289-300.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Liu X, Jiang W, Li YL, Nie HZ, Cui LN, Li RX, Tan L, Peng L, Li C, Luo JY, Li M, Wang HX, Yang J, Zhou B, Wang PC, Liu HT, Zhu JK, Zhao CZ (2023). FERONIA coordinates plant growth and salt tolerance via the phosphorylation of phyB. Nat Plants 9, 645-660.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Maloof JN, Borevitz JO, Dabi T, Lutes J, Nehring RB, Redfern JL, Trainer GT, Wilson JM, Asami T, Berry CC, Weigel D, Chory J (2001). Natural variation in light sensitivity of Arabidopsis. Nat Genet 29, 441-446.
PMID |
| [44] |
Mathews S (2006). Phytochrome-mediated development in land plants: red light sensing evolves to meet the challenges of changing light environments. Mol Ecol 15, 3483-3503.
PMID |
| [45] | Matsushita T, Mochizuki N, Nagatani A (2003). Dimers of the N-terminal domain of phytochrome B are functional in the nucleus. Nature 424, 571-574. |
| [46] | Medzihradszky M, Bindics J, Ádám É, Viczián A, Klement É, Lorrain S, Gyula P, Mérai Z, Fankhauser C, Medzihradszky KF, Kunkel T, Schäfer E, Nagy F (2013). Phosphorylation of phytochrome B inhibits light-induced signaling via accelerated dark reversion in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 535-544. |
| [47] |
Nagano S (2016). From photon to signal in phytochromes: similarities and differences between prokaryotic and plant phytochromes. J Plant Res 129, 123-135.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Nito K, Wong CCL, Yates III JR, Chory J (2013). Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the activity of phytochrome photoreceptors. Cell Rep 3, 1970-1979.
DOI PMID |
| [49] | Oka Y, Matsushita T, Mochizuki N, Quail PH, Nagatani A (2008). Mutant screen distinguishes between residues necessary for light-signal perception and signal transfer by phytochrome B. PLoS Genet 4, e1000158. |
| [50] | Oka Y, Matsushita T, Mochizuki N, Suzuki T, Tokutomi S, Nagatani A (2004). Functional analysis of a 450-amino acid N-terminal fragment of phytochrome B in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 2104-2116. |
| [51] |
Paik I, Huq E (2019). Plant photoreceptors: multi-functional sensory proteins and their signaling networks. Semin Cell Dev Biol 92, 114-121.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Qiu YJ, Pasoreck EK, Reddy AK, Nagatani A, Ma WX, Chory J, Chen M (2017). Mechanism of early light signaling by the carboxy-terminal output module of Arabidopsis phytochrome B. Nat Commun 8, 1905. |
| [53] | Quail PH (2002). Phytochrome photosensory signaling networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3, 85-93. |
| [54] |
Reed JW, Nagpal P, Poole DS, Furuya M, Chory J (1993). Mutations in the gene for the red/far-red light receptor phytochrome B alter cell elongation and physiological responses throughout Arabidopsis development. Plant Cell 5, 147-157.
PMID |
| [55] |
Rockwell NC, Lagarias JC (2006). The structure of phytochrome: a picture is worth a thousand spectra. Plant Cell 18, 4-14.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Rockwell NC, Su YS, Lagarias JC (2006). Phytochrome structure and signaling mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57, 837-858.
PMID |
| [57] | Ruiz-Diaz MJ, Matsusaka D, Cascales J, Sánchez DH, Sánchez-Lamas M, Cerdán PD, Botto JF (2022). Functional analysis of PHYB polymorphisms in Arabidopsis thaliana collected in Patagonia. Front Plant Sci 13, 952214. |
| [58] | Sharrock RA, Quail PH (1989). Novel phytochrome sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana: structure, evolution, and differential expression of a plant regulatory photoreceptor family. Genes Dev 3, 1745-1757. |
| [59] | Su YS, Lagarias JC (2007). Light-independent phytochrome signaling mediated by dominant GAF domain tyrosine mutants of Arabidopsis phytochromes in transgenic plants. Plant Cell 19, 2124-2139. |
| [60] | Sun W, Xu XH, Lu XB, Xie LX, Bai B, Zheng CK, Sun HW, He YN, Xie XZ (2017). The rice phytochrome genes, PHYA and PHYB, have synergistic effects on anther development and pollen viability. Sci Rep 7, 6439. |
| [61] |
Velázquez Escobar F, Buhrke D, Fernandez Lopez M, Shenkutie SM, von Horsten S, Essen LO, Hughes J, Hildebrandt P (2017). Structural communication between the chromophore-binding pocket and the N-terminal extension in plant phytochrome phyB. FEBS Lett 591, 1258-1265.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Viczián A, Ádám É, Staudt AM, Lambert D, Klement E, Romero Montepaone S, Hiltbrunner A, Casal J, Schäfer E, Nagy F, Klose C (2020). Differential phosphorylation of the N-terminal extension regulates phytochrome B signaling. New Phytol 225, 1635-1650.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Viczián A, Nagy F (2024). Phytochrome B phosphorylation expanded: site-specific kinases are identified. New Phytol 241, 65-72. |
| [64] |
Vierstra RD (1993). Illuminating phytochrome functions (There is light at the end of the tunnel). Plant Physiol 103, 679-684.
PMID |
| [65] | Wagner D, Koloszvari M, Quail PH (1996). Two small spatially distinct regions of phytochrome B are required for efficient signaling rates. Plant Cell 8, 859-871. |
| [66] |
Wagner D, Quail PH (1995). Mutational analysis of phytochrome B identifies a small COOH-terminal-domain region critical for regulatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92, 8596-8600.
PMID |
| [67] | Wagner JR, Brunzelle JS, Forest KT, Vierstra RD (2005). A light-sensing knot revealed by the structure of the chromophore-binding domain of phytochrome. Nature 438, 325-331. |
| [68] | Wagner JR, Zhang JR, Brunzelle JS, Vierstra RD, Forest KT (2007). High resolution structure of Deinococcus bacteriophytochrome yields new insights into phytochrome architecture and evolution. J Biol Chem 282, 12298-12309. |
| [69] | Wies G, Mantese AI, Casal JJ, Maddonni GÁ (2019). Phytochrome B enhances plant growth, biomass and grain yield in field-grown maize. Ann Bot 123, 1079-1088. |
| [70] |
Xie XZ, Shinomura T, Inagaki N, Kiyota S, Takano M (2007). Phytochrome-mediated inhibition of coleoptile growth in rice: age-dependency and action spectra. Photochem Photobiol 83, 131-138.
PMID |
| [71] | Xie XZ, Xue YJ, Zhou JJ, Zhang B, Chang H, Takano M (2011). Phytochromes regulate SA and JA signaling pathways in rice and are required for developmentally controlled resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant 4, 688-696. |
| [72] |
Xu Y, Parks BM, Short TW, Quail PH (1995). Missense mutations define a restricted segment in the C-terminal domain of phytochrome A critical to its regulatory activity. Plant Cell 7, 1433-1443.
PMID |
| [73] |
Yamaguchi R, Nakamura M, Mochizuki N, Kay SA, Nagatani A (1999). Light-dependent translocation of a phytochrome B-GFP fusion protein to the nucleus in transgenic Arabidopsis. J Cell Biol 145, 437-445.
DOI PMID |
| [74] | Yang XJ, Kuk J, Moffat K (2008). Crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophytochrome: photoconversion and signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 14715-14720. |
| [75] | Yang XJ, Kuk J, Moffat K (2009). Conformational differences between the Pfr and Pr states in Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophytochrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 15639-15644. |
| [76] | Zhang JR, Stankey RJ, Vierstra RD (2013). Structure- guided engineering of plant phytochrome B with altered photochemistry and light signaling. Plant Physiol 161, 1445-1457. |
| [77] |
Zhao Y, Shi H, Pan Y, Lyu M, Yang ZX, Kou XX, Deng XW, Zhong SW (2023). Sensory circuitry controls cytosolic calcium-mediated phytochrome B phototransduction. Cell 186, 1230-1243.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 邱丹妮, 彭清清, 张慧玲, 温辉辉, 吴福忠. 中亚热带常绿阔叶林典型乔木树种对蚂蚁群落季节性动态的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [2] | 童金莲, 张博纳, 汤璐瑶, 叶琳峰, 李姝雯, 谢江波, 李彦, 王忠媛. C4植物狗尾草功能性状网络沿降水梯度带的区域分异规律[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [3] | 张静 陈洁 李艳朋 盘李军 许涵 李意德 何海生. 南亚热带针阔混交人工林植物生物量比较及其影响因子分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 0-0. |
| [4] | 戴丽君, 向玲艺, 蹇陈, 王晓锋. 三峡回水扰动增强了入库小流域河岸带典型草本植物功能性状的局域分化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 1-. |
| [5] | 赵珮杉 高广磊 丁国栋 张英. 林龄和生态位对樟子松人工林地下真菌群落构建的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 1-0. |
| [6] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [7] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [8] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [9] | 杜英杰, 范爱连, 王雪, 闫晓俊, 陈廷廷, 贾林巧, 姜琦, 陈光水. 亚热带天然常绿阔叶林乔木树种与林下灌木树种根-叶功能性状协调性及差异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 585-595. |
| [10] | 李梦琦, 苗灵凤, 李大东, 龙奕帆, 叶冰冰, 杨帆. 海南东寨港红树林植物细根功能性状对不同潮位沉积物养分变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 552-561. |
| [11] | 刘雨函, 曹启江, 张诗晗, 李益慧, 王菁, 谭晓萌, 刘筱儒, 王显玲. 拟南芥AtFTCD-L参与根系响应土壤紧实度的机制研究[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [12] | 刘茹, 李阳, 唐兆成, 郝婷婷, 张保龙. 甘蓝中催化NMN降解生成NR的5′-核苷酸酶基因克隆和功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 363-376. |
| [13] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 江智诚, 刘江慧, 闫江超. 短期氮、水添加和刈割减弱了苦豆子型退化草地土壤生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的联系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24305-. |
| [14] | 刘志祥, 谢华, 张慧, 黄晓磊. 表皮碳氢化合物在社会性昆虫中的功能多样性及其调控[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24302-. |
| [15] | 吴闫宁, 郝珉辉, 何怀江, 张春雨, 赵秀海. 长白山森林功能多样性与地上碳汇功能的关系及其随演替的变化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 232-243. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||