

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (2): 231-244.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23065 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23065
段政勇1, 丁敏1, 王宇卓1, 丁艺冰2, 陈凌3, 王瑞云1,3,*( ), 乔治军3,*(
), 乔治军3,*( )
)
收稿日期:2023-05-21
接受日期:2023-12-25
出版日期:2024-03-10
发布日期:2024-03-10
通讯作者:
* 王瑞云, 山西农业大学农学院教授, 博士生导师, 山西省杂粮产业技术体系岗位专家, 中国作物学会粟类作物专业委员会委员。长期从事糜子种质资源遗传多样性研究。以通讯作者和第一作者身份发表学术论文80篇(其中SCI收录期刊8篇, 国家一级学术期刊11篇); 独著1部, 参编合著论著2部。E-mail: 基金资助:
Zhengyong Duan1, Min Ding1, Yuzhuo Wang1, Yibing Ding2, Ling Chen3, Ruiyun Wang1,3,*( ), Zhijun Qiao3,*(
), Zhijun Qiao3,*( )
)
Received:2023-05-21
Accepted:2023-12-25
Online:2024-03-10
Published:2024-03-10
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要: SBP (squamosa promoter binding protein)家族广泛参与植物生长发育、信号转导及多种生理生化过程。从糜子(Panicum miliaceum)全基因组中筛选并鉴定到25个SBP基因。系统发育分析表明, PmSBP家族成员分为6个亚家族。同一亚家族成员具有相似的基因结构和保守基序。共线性分析表明, PmSBP与拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana) AtSBP和水稻(Oryza sativa) OsSBP分别形成7对和31对直系同源基因。顺式作用元件分析表明, PmSBP启动子区富含逆境胁迫、光反应及激素信号响应元件。基因表达模式分析表明, PmSBP基因表达具有明显的组织特异性、品种特异性及发育阶段特异性, 表明SBP基因在糜子生长发育中发挥重要作用。研究结果为揭示SBP基因在糜子生长发育中的生物学功能奠定了基础, 也为其它作物SBP基因研究提供了借鉴参考。
段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244.
Zhengyong Duan, Min Ding, Yuzhuo Wang, Yibing Ding, Ling Chen, Ruiyun Wang, Zhijun Qiao. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Analysis of SBP Genes in Panicum miliaceum. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(2): 231-244.
| Gene name | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PM13G22100 | CTCATATGGCAGCCAGGGTA | CAGGCATTGACGCAGCAC |
| PM10G18000 | AGTTCGACGAGGCCAAGAG | TGGTGTAGGAGCCCGTCAT |
| PM07G33040 | GCTTCCCTTTCCTGACCAAT | ACAGTTGCCGTTGCTATGCT |
| PM03G01570 | GGTCACAATGAGCGTCGG | CCAGGCTCTTGAAATGATGC |
| Actin | CGAAGCCCCTCTTAACCC | GTATGGCTGACACCATCACC |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
| Gene name | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| PM13G22100 | CTCATATGGCAGCCAGGGTA | CAGGCATTGACGCAGCAC |
| PM10G18000 | AGTTCGACGAGGCCAAGAG | TGGTGTAGGAGCCCGTCAT |
| PM07G33040 | GCTTCCCTTTCCTGACCAAT | ACAGTTGCCGTTGCTATGCT |
| PM03G01570 | GGTCACAATGAGCGTCGG | CCAGGCTCTTGAAATGATGC |
| Actin | CGAAGCCCCTCTTAACCC | GTATGGCTGACACCATCACC |
| Gene name | Gene ID | Number of amino acids | Molecular weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | Grand average of hydropathicity | Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PmSBP1 | PM13G22100 | 389 | 40425.64 | 9.02 | 59.42 | 53.57 | -0.554 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP2 | PM15G18460 | 391 | 40589.82 | 9.03 | 59.36 | 51.79 | -0.586 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP3 | PM04G19860 | 351 | 36740.87 | 9.15 | 50.66 | 54.27 | -0.508 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP4 | PM03G01570 | 373 | 38851.28 | 9.11 | 51.60 | 55.01 | -0.454 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP5 | PM07G33040 | 378 | 39705.20 | 9.41 | 50.71 | 58.47 | -0.470 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP6 | PM16G15940 | 405 | 40953.59 | 9.61 | 58.23 | 55.11 | -0.442 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP7 | PM15G16820 | 398 | 40086.69 | 9.43 | 59.47 | 53.39 | -0.441 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP8 | PM10G18000 | 416 | 43996.51 | 9.18 | 63.21 | 57.09 | -0.528 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP9 | PM09G20570 | 423 | 45069.55 | 9.14 | 65.80 | 57.07 | -0.590 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP10 | PM03G07850 | 181 | 18864.75 | 9.80 | 70.12 | 49.34 | -0.796 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP11 | PM11G14200 | 475 | 51028.91 | 9.10 | 45.90 | 60.06 | -0.577 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP12 | PM12G02720 | 474 | 51043.79 | 9.10 | 47.15 | 61.22 | -0.573 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP13 | PM03G07830 | 195 | 20090.95 | 9.71 | 65.22 | 40.77 | -0.962 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP14 | PM12G04460 | 439 | 46205.92 | 6.84 | 59.02 | 61.07 | -0.423 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP15 | PM11G16250 | 249 | 27804.58 | 9.66 | 58.67 | 57.27 | -0.726 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP16 | PM01G25080 | 953 | 104207.41 | 5.74 | 46.12 | 78.91 | -0.310 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP17 | PM12G04270 | 331 | 36135.41 | 8.90 | 58.10 | 58.76 | -0.670 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP18 | PM13G22370 | 1107 | 121234.39 | 6.64 | 55.79 | 75.46 | -0.482 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP19 | PM15G18240 | 1109 | 121513.62 | 6.55 | 55.94 | 74.96 | -0.491 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP20 | PM06G21970 | 855 | 94067.89 | 5.78 | 53.45 | 82.02 | -0.327 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP21 | PM05G24780 | 857 | 94363.22 | 5.74 | 54.80 | 82.07 | -0.336 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP22 | PM07G07420 | 540 | 60348.18 | 5.60 | 56.90 | 82.19 | -0.396 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP23 | PM04G25580 | 105 | 11903.20 | 11.92 | 86.68 | 33.52 | -1.624 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP24 | PM11G02690 | 403 | 42276.93 | 6.22 | 57.12 | 61.64 | -0.481 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP25 | PM13G17660 | 255 | 27293.16 | 7.92 | 46.21 | 58.31 | -0.555 | Nucleus |
表2 糜子SBP转录因子家族成员理化性质及其亚细胞定位
Table 2 Physicochemical properties and subcellular localization of SBP transcription factor family members in Panicum miliaceum
| Gene name | Gene ID | Number of amino acids | Molecular weight (Da) | Theoretical pI | Instability index | Aliphatic index | Grand average of hydropathicity | Subcellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PmSBP1 | PM13G22100 | 389 | 40425.64 | 9.02 | 59.42 | 53.57 | -0.554 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP2 | PM15G18460 | 391 | 40589.82 | 9.03 | 59.36 | 51.79 | -0.586 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP3 | PM04G19860 | 351 | 36740.87 | 9.15 | 50.66 | 54.27 | -0.508 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP4 | PM03G01570 | 373 | 38851.28 | 9.11 | 51.60 | 55.01 | -0.454 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP5 | PM07G33040 | 378 | 39705.20 | 9.41 | 50.71 | 58.47 | -0.470 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP6 | PM16G15940 | 405 | 40953.59 | 9.61 | 58.23 | 55.11 | -0.442 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP7 | PM15G16820 | 398 | 40086.69 | 9.43 | 59.47 | 53.39 | -0.441 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP8 | PM10G18000 | 416 | 43996.51 | 9.18 | 63.21 | 57.09 | -0.528 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP9 | PM09G20570 | 423 | 45069.55 | 9.14 | 65.80 | 57.07 | -0.590 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP10 | PM03G07850 | 181 | 18864.75 | 9.80 | 70.12 | 49.34 | -0.796 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP11 | PM11G14200 | 475 | 51028.91 | 9.10 | 45.90 | 60.06 | -0.577 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP12 | PM12G02720 | 474 | 51043.79 | 9.10 | 47.15 | 61.22 | -0.573 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP13 | PM03G07830 | 195 | 20090.95 | 9.71 | 65.22 | 40.77 | -0.962 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP14 | PM12G04460 | 439 | 46205.92 | 6.84 | 59.02 | 61.07 | -0.423 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP15 | PM11G16250 | 249 | 27804.58 | 9.66 | 58.67 | 57.27 | -0.726 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP16 | PM01G25080 | 953 | 104207.41 | 5.74 | 46.12 | 78.91 | -0.310 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP17 | PM12G04270 | 331 | 36135.41 | 8.90 | 58.10 | 58.76 | -0.670 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP18 | PM13G22370 | 1107 | 121234.39 | 6.64 | 55.79 | 75.46 | -0.482 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP19 | PM15G18240 | 1109 | 121513.62 | 6.55 | 55.94 | 74.96 | -0.491 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP20 | PM06G21970 | 855 | 94067.89 | 5.78 | 53.45 | 82.02 | -0.327 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP21 | PM05G24780 | 857 | 94363.22 | 5.74 | 54.80 | 82.07 | -0.336 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP22 | PM07G07420 | 540 | 60348.18 | 5.60 | 56.90 | 82.19 | -0.396 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP23 | PM04G25580 | 105 | 11903.20 | 11.92 | 86.68 | 33.52 | -1.624 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP24 | PM11G02690 | 403 | 42276.93 | 6.22 | 57.12 | 61.64 | -0.481 | Nucleus |
| PmSBP25 | PM13G17660 | 255 | 27293.16 | 7.92 | 46.21 | 58.31 | -0.555 | Nucleus |
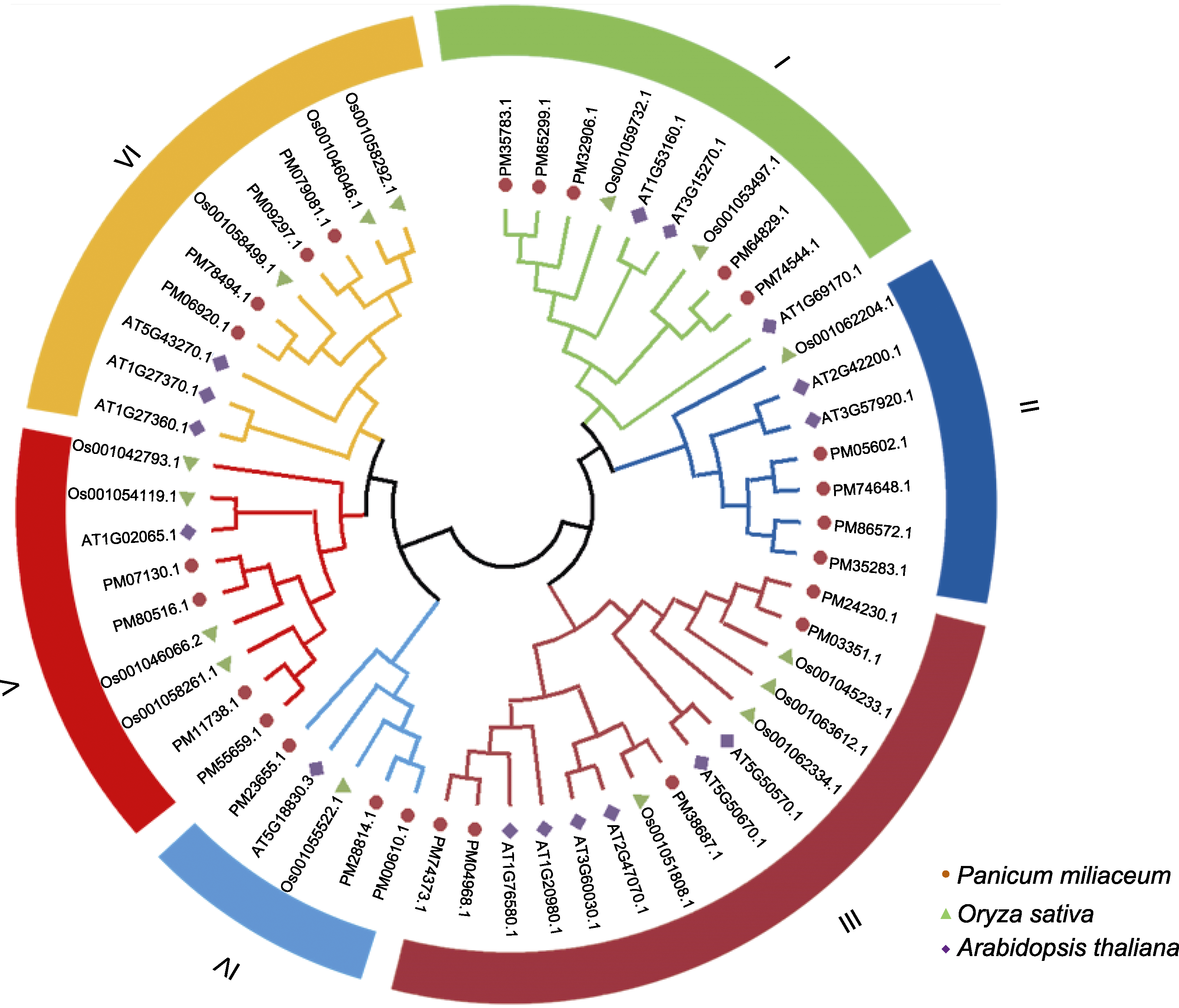
图1 糜子、水稻和拟南芥SBP家族蛋白系统进化树 系统进化树的分支颜色及填充底色表示不同的SBP亚家族, 分支颜色一致的为同一亚家族。
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree of SBP family proteins in Panicum miliaceum, Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana The branch color and the filling base color of the phylogenetic tree distinguish the subfamilies of the SBP family, and the proteins with the same branch color are represented as the same subfamily.
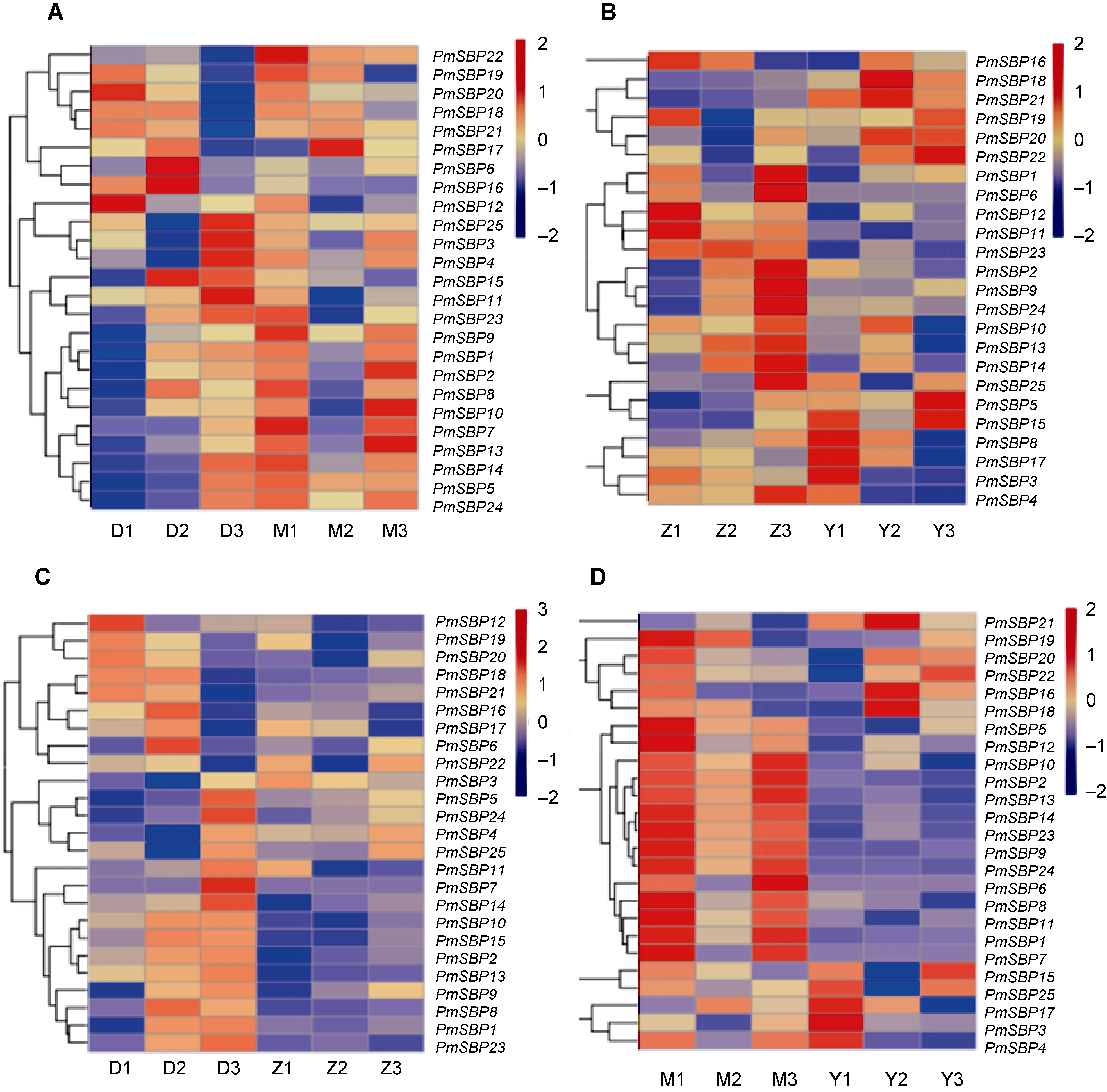
图8 SBP基因在不同时期不同品种糜子中的表达模式 (A) 抽穗期; (B) 开花期; (C) 单粒品种; (D) 双粒品种。D1-D3/Z1-Z3: 抽穗期/开花期的单粒品种; M1-M3/Y1-Y3: 抽穗期/开花期的双粒品种
Figure 8 Expression patterns of SBP genes in different stages and varieties of Panicum miliaceum (A) Heading stage; (B) Flowering stage; (C) Single grain varieties; (D) Double grain varieties. D1-D3/Z1-Z3: Single grain varieties at heading/flowering stage; M1-M3/Y1-Y3: Double grain varieties at heading/flowering stage
| [1] |
Arshad M, Feyissa BA, Amyot L, Aung B, Hannoufa A (2017). MicroRNA 156 improves drought stress tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) by silencing SPL13. Plant Sci 258, 122-136.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
Cardon GH, Höhmann S, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P (1997). Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana SBP-box gene SPL3: a novel gene involved in the floral transition. Plant J 12, 367-377.
PMID |
| [3] |
Chen XB, Zhang ZL, Liu DM, Zhang K, Li AL, Mao L (2010). SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein-like transcription factors: star players for plant growth and development. J Integr Plant Biol 52, 946-951.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Chen XH, Lin YX, Wang Q, Ding M, Wang HG, Chen L, Gao ZJ, Wang RY, Qiao ZJ (2022). Development of DNA molecular lD card in hog millet germplasm based on high motif SSR. Acta Agron Sin 48, 908-919. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
陈小红, 林元香, 王倩, 丁敏, 王海岗, 陈凌, 高志军, 王瑞云, 乔治军 (2022). 基于高基元SSR构建黍稷种质资源的分子身份证. 作物学报 48, 908-919.
DOI |
|
| [5] |
Chuck G, Whipple C, Jackson D, Hake S (2010). The maize SBP-box transcription factor encoded by tasselsheath4 regulates bract development and the establishment of meristem boundaries. Development 137, 1243-1250.
DOI PMID |
| [6] |
Devi PB, Vijayabharathi R, Sathyabama S, Malleshi NG, Priyadarisini VB (2014). Health benefits of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) polyphenols and dietary fiber: a review. J Food Sci Technol 51, 1021-1040.
DOI PMID |
| [7] | Ding M, Duan ZY, Wang YZ, Xue YP, Wang HG, Chen L, Wang RY, Qiao ZJ (2023). Development and validation of functional markers of GBSSI gene in proso millet. Acta Agron Sin 49, 703-718. (in Chinese) |
|
丁敏, 段政勇, 王宇卓, 薛亚鹏, 王海岗, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军 (2023). 糜子GBSSI基因功能标记的开发与验证. 作物学报 49, 703-718.
DOI |
|
| [8] | Gao RM, Wang Y, Gruber MY, Hannoufa A (2018). miR156/SPL10 modulates lateral root development, branching and leaf morphology in Arabidopsis by silencing AGAMOUS-LIKE 79. Front Plant Sci 8, 2226. |
| [9] |
Gou JQ, Tang CR, Chen NC, Wang H, Debnath S, Sun L, Flanagan A, Tang YH, Jiang QZ, Allen RD, Wang ZY (2019). SPL7 and SPL8 represent a novel flowering regulation mechanism in switchgrass. New Phytol 222, 1610-1623.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Gupta S, Shrivastava SK, Shrivastava M (2014). Proximate composition of seeds of hybrid varieties of minor millets. Int J Res Eng Technol 3, 687-693. |
| [11] | He JL, Shi TT, Chen L, Wang HG, Gao ZJ, Yang MH, Wang RY, Qiao ZJ (2019). The genetic diversity of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) germplasm resources based on the EST-SSR markers. Chin Bull Bot 54, 723-732. (in Chinese) |
|
何杰丽, 石甜甜, 陈凌, 王海岗, 高志军, 杨美红, 王瑞云, 乔治军 (2019). 糜子EST-SSR分子标记的开发及种质资源遗传多样性分析. 植物学报 54, 723-732.
DOI |
|
| [12] | Hou HM, Jia H, Yan Q, Wang XP (2018). Overexpression of a SBP-box gene (VpSBP16) from Chinese wild Vitis species in Arabidopsis improves salinity and drought stress tolerance. Int J Mol Sci 19, 940. |
| [13] |
Jung JH, Ju Y, Seo PJ, Lee JH, Park CM (2012). The SOC1-SPL module integrates photoperiod and gibberellic acid signals to control flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69, 577-588.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Li M, Li CS, Zhao CZ, Li AQ, Wang XJ (2013). Research advances in plant SPL transcription factors. Chin Bull Bot 48, 107-116. (in Chinese) |
|
李明, 李长生, 赵传志, 李爱芹, 王兴军 (2013). 植物SPL转录因子研究进展. 植物学报 48, 107-116.
DOI |
|
| [15] | Liu HJ, Yang XR, Liao XH, Zuo T, Qin C, Cao SL, Dong L, Zhou HK, Zhang YZ, Liu SS, Shen Y, Lin HJ, Lübberstedt T, Zhang ZM, Pan GT (2015). Genome-wide comparative analysis of digital gene expression tag profiles during maize ear development. Genomics 106, 52-60. |
| [16] | Liu MX, Xu Y, Lu P (2020). Advances in germplasm collection and genetic diversity research of wild broomcorn millet in China. J Plant Genet Resour 21, 1435-1445. (in Chinese) |
|
刘敏轩, 许月, 陆平 (2020). 中国野生黍稷资源收集保存与遗传多样性研究进展. 植物遗传资源学报 21, 1435-1445.
DOI |
|
| [17] | Lu BS, Zhu YJ, Zhang ST, Lü YM, Li XF, Song YY, Lai ZX, Lin YL (2020). Whole-genome identification and expression analysis of SPL gene family in Dimocarpus longan. Sci Agric Sin 53, 4259-4270. (in Chinese) |
|
路保顺, 朱永静, 张舒婷, 吕煜梦, 李晓斐, 宋雨洋, 赖钟雄, 林玉玲 (2020). 龙眼SPL基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析. 中国农业科学 53, 4259-4270.
DOI |
|
| [18] |
Lu HY, Zhang JP, Liu KB, Wu NQ, Li YM, Zhou KS, Ye ML, Zhang TY, Zhang HJ, Yang XY, Shen LC, Xu DK, Li Q (2009). Earliest domestication of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) in East Asia extended to 10, 000 years ago. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 7367-7372.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Ma JQ, Jian HJ, Yang B, Lu K, Zhang AX, Liu P, Li JN (2017). Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the GRF gene family in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Gene 620, 36-45.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Manning K, Tör M, Poole M, Hong YG, Thompson AJ, King GJ, Giovannoni JJ, Seymour GB (2006). A naturally occurring epigenetic mutation in a gene encoding an SBP-box transcription factor inhibits tomato fruit ripening. Nat Genet 38, 948-952. |
| [21] |
Martin RC, Asahina M, Liu PP, Kristof JR, Coppersmith JL, Pluskota WE, Bassel GW, Goloviznina NA, Nguyen TT, Martínez-Andújar CC, Kumar MBA, Pupel P, Nonogaki H (2010). The microRNA156 and microRNA172 gene regulation cascades at post-germinative stages in Arabidopsis. Seed Sci Res 20, 79-87.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Nielsen DC, Vigil MF (2017). Water use and environmental parameters influence proso millet yield. Field Crops Res 212, 34-44. |
| [23] |
Shao YL, Zhou HZ, Wu YR, Zhang H, Lin J, Jiang XY, He QJ, Zhu JS, Li Y, Yu H, Mao CZ (2019). OsSPL3, an SBP-domain protein, regulates crown root development in rice. Plant Cell 31, 1257-1275.
DOI |
| [24] | Shao ZW, Zeng ZP, Chen YZ, He MH, Zhang Y, Chen RL, Zhu HB (2021). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the SBP-box gene family in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). Mol Plant Breed 10, 1-20. (in Chinese) |
| 邵正伟, 曾志鹏, 陈彦竹, 何敏红, 张毅, 陈善兰, 朱宏波 (2021). 甘薯全基因组SBP-box基因家族鉴定及表达分析. 分子植物育种 10, 1-20. | |
| [25] |
Tripathi RK, Bregitzer P, Singh J (2018). Genome-wide analysis of the SPL/miR156 module and its interaction with the AP2/miR172 unit in barley. Sci Rep 8, 7085.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Wang Q, Zhang LY, Xu Y, Li H, Liu SX, Xue YP, Lu P, Wang RY, Liu MX (2022). High motif EST-SSR markers development and genetic diversity evaluation for 200 core germplasms in proso millet. Acta Agron Sin 49, 2308-2318. (in Chinese) |
|
王倩, 张立媛, 许月, 李海, 刘少雄, 薛亚鹏, 陆平, 王瑞云, 刘敏轩 (2023). 黍稷高基元EST-SSR标记开发及200份核心种质资源遗传多样性分析. 作物学报 49, 2308-2318.
DOI |
|
| [27] |
Wang SK, Li S, Liu Q, Wu K, Zhang JQ, Wang SS, Wang Y, Chen XB, Zhang Y, Gao CA, Wang F, Huang HX, Fu XD (2015). The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat Genet 47, 949-954.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Wang YZ, Lin YX, Xue YP, Duan ZY, Wang XD, Chen L, Cao XN, Wang RY, Qiao ZJ (2023). Construction of molecular ID card of core germplasm of hog millet (Panicum miliaceum) in Shanxi. Chin Bull Bot 58, 159-168. (in Chinese) |
| 王宇卓, 林元香, 薛亚鹏, 段政勇, 王晓丹, 陈凌, 曹晓宁, 王瑞云, 乔治军 (2023). 山西糜子核心种质分子身份证构建. 植物学报 58, 159-168. | |
| [29] | Wei XX, Lan HY (2022). Advances in the regulation of plant MYB transcription factors in secondary metabolism and stress response. Biotechnol Bull 38(8), 12-23. (in Chinese) |
|
位欣欣, 兰海燕 (2022). 植物MYB转录因子调控次生代谢及逆境响应的研究进展. 生物技术通报 38(8), 12-23.
DOI |
|
| [30] |
Xue YP, Ding YB, Wang YZ, Wang XD, Cao XN, Santra DK, Chen L, Qiao ZJ, Wang RY (2023). Construction of DNA molecular identity card of core germplasm of broomcorn millet in China based on fluorescence SSR. Sci Agric Sin 56, 2249-2261. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
薛亚鹏, 丁艺冰, 王宇卓, 王晓丹, 曹晓宁, Santra DK, 陈凌, 乔治军, 王瑞云 (2023). 基于荧光SSR构建中国糜子核心种质DNA分子身份证. 中国农业科学 56, 2249-2261.
DOI |
|
| [31] | Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Inoue M, Tateno M, Yamasaki T, Yabuki T, Aoki M, Seki E, Matsuda T, Nunokawa E, Ishizuka Y, Terada T, Shirouzu M, Osanai T, Tanaka A, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yokoyama S (2004). A novel zinc-binding motif revealed by solution structures of DNA- binding domains of Arabidopsis SBP-family transcription factors. J Mol Biol 337, 49-63. |
| [32] | Yang L (2018). Cloning and Functional Analysis of Arabidopsis SPL8 Homologous Gene. Master’s thesis. Taiyuan: Shanxi University. pp. 102-119. (in Chinese) |
| 杨柳 (2018). 拟南芥SPL8同源基因的克隆和功能分析. 硕士论文. 太原: 山西大学. pp. 102-119. | |
| [33] |
Yao T, Park BS, Mao HZ, Seo JS, Ohama N, Li Y, Yu N, Mustafa NFB, Huang CH, Chua NH (2019). Regulation of flowering time by SPL10/MED25 module in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 224, 493-504.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Yu N, Cai WJ, Wang SC, Shan CM, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2010). Temporal control of trichome distribution by microRNA156-targeted SPL genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 22, 2322-2335.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Yu ZX, Wang LJ, Zhao B, Shan CM, Zhang YH, Chen DF, Chen XY (2015). Progressive regulation of sesquiterpene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis and patchouli (Pogostemon cablin) by the miR156-targeted SPL transcription factors. Mol Plant 8, 98-110. |
| [36] | Zhang DY, Han ZL, Li JQ, Qin H, Zhou L, Wang YH, Zhu XJ, Ma YC, Fang WP (2020). Genome-wide analysis of the SBP-box gene family transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in tea (Camellia sinensis). Genomics 112, 2194-2202. |
| [37] | Zhang L (2022). Research progress on SPL transcription factors. Agric Technol 42(8), 25-27. (in Chinese) |
| 张磊 (2022). SPL转录因子研究进展. 农业与技术 42(8), 25-27. | |
| [38] |
Zhang Y, Schwarz S, Saedler H, Huijser P (2007). SPL8, a local regulator in a subset of gibberellin-mediated developmental processes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 63, 429-439.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Zhao YD (2021). Genetic Transformation of miR156e in Alfalfa Mediated by Short Tandem Target Simulation Technique. Master’s thesis. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University. pp. 100-121. (in Chinese) |
| 赵耀东 (2021). 短串联靶标模拟技术介导的miR156e在紫花苜蓿中的遗传转化. 硕士论文. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. pp. 100-121. |
| [1] | 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| [2] | 杨清华, 王洪露, 冯佰利. 糜子品质研究进展与展望[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 22-33. |
| [3] | 刘佳佳, 张大众, 张渊博, 张楚楚, 周佳玥, 熊亚红, 卓振生, 饶煜健, 冯佰利. 硒和碲对缓解糜子镉毒害及减少籽粒镉积累的调控效应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 62-76. |
| [4] | 王宇卓, 林元香, 薛亚鹏, 段政勇, 王晓丹, 陈凌, 曹晓宁, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 山西糜子核心种质分子身份证构建[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 159-168. |
| [5] | 何杰丽,石甜甜,陈凌,王海岗,高志军,杨美红,王瑞云,乔治军. 糜子EST-SSR分子标记的开发及种质资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 723-732. |
| [6] | 范业赓,丘立杭,黄杏,周慧文,甘崇琨,李杨瑞,杨荣仲,吴建明,陈荣发. 甘蔗节间伸长过程赤霉素生物合成关键基因的表达及相关植物激素动态变化[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(4): 486-496. |
| [7] | 刘宝玲, 张莉, 孙岩, 薛金爱, 高昌勇, 苑丽霞, 王计平, 贾小云, 李润植. 谷子bZIP转录因子的全基因组鉴定及其在干旱和盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(4): 473-487. |
| [8] | 袁伟, 万红建, 杨悦俭. 植物实时荧光定量PCR内参基因的特点及选择[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47(4): 427-436. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||