

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 62-76.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22172 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22172
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
刘佳佳, 张大众, 张渊博, 张楚楚, 周佳玥, 熊亚红, 卓振生, 饶煜健, 冯佰利*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-29
接受日期:2022-11-15
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: fengbaili@nwafu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jiajia Liu, Dazhong Zhang, Yuanbo Zhang, Chuchu Zhang, Jiayue Zhou, Yahong Xiong, Zhensheng Zhuo, Yujian Rao, Baili Feng*( )
)
Received:2022-07-29
Accepted:2022-11-15
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: fengbaili@nwafu.edu.cn
摘要: 提高糜子(Panicum miliaceum)镉耐受性与低积累能力对镉污染地区糜子的安全生产具有重要意义。该研究以镉耐受和镉敏感糜子品种为材料, 通过苗期水培和全生育期盆栽试验, 分析不同形态硒和四价碲对镉胁迫下糜子生长、根系形态、镉吸收转运和籽粒矿质营养含量的影响。结果表明, 外源添加硒和碲能缓解镉毒害, 其中有机硒缓解效果较好。与单独镉处理相比, 硒和碲能够促进根系直径增加并抑制镉吸收, 最高可使根系镉含量降低33%。此外, 硒和碲能够增加细胞壁和液泡中镉的占比, 提高镉耐受性。叶面喷施硒提高了糜子籽粒中锌、锰和钼等矿质营养元素含量。无机四价硒能更有效地抑制镉从营养器官向籽粒的转运, 在5 mg·kg-1镉处理下, 可使镉敏感和镉耐受品种籽粒镉含量分别降低11.3%和20.3%。综上, 外源添加硒能够显著提高糜子镉耐受性并减少籽粒镉积累。研究结果可为镉污染地区糜子的安全生产提供参考。
刘佳佳, 张大众, 张渊博, 张楚楚, 周佳玥, 熊亚红, 卓振生, 饶煜健, 冯佰利. 硒和碲对缓解糜子镉毒害及减少籽粒镉积累的调控效应. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 62-76.
Jiajia Liu, Dazhong Zhang, Yuanbo Zhang, Chuchu Zhang, Jiayue Zhou, Yahong Xiong, Zhensheng Zhuo, Yujian Rao, Baili Feng. Regulatory Effects of Selenium and Tellurium on Alleviating Cadmium Toxicity and Reducing Grain Cadmium Accumulation in Broomcorn Millet (Panicum miliaceum). Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 62-76.
| Treatment | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Control | CK |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2 | Cd |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 Na2SeO3 | SeIV |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 SeMet | SeMet |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 Na2TeO3 | Te |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 Na2SeO3+ 5 μmol?L-1 Na2TeO3 | SeIV+Te |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 SeMet+ 5 μmol?L-1 Na2TeO3 | SeMet+Te |
表1 试验设计
Table 1 Experimental design
| Treatment | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Control | CK |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2 | Cd |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 Na2SeO3 | SeIV |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 SeMet | SeMet |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 Na2TeO3 | Te |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 Na2SeO3+ 5 μmol?L-1 Na2TeO3 | SeIV+Te |
| 15 μmol?L-1 CdCl2+5 μmol?L-1 SeMet+ 5 μmol?L-1 Na2TeO3 | SeMet+Te |
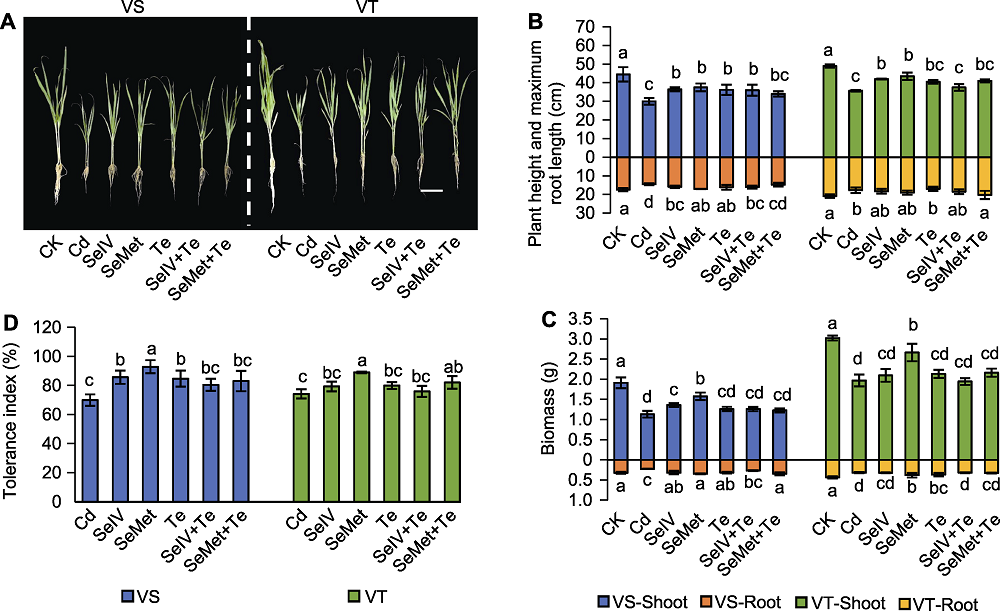
图1 Se和Te对Cd胁迫下Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种生长参数的影响 (A) 生长情况(bar=10 cm); (B) 株高和最大根长; (C) 地上部和根系生物量; (D) Cd耐受指数。CK、Cd、SeIV、SeMet、Te、SeIV+Te和SeMet+Te同表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 1 Effects of Se and Te on growth parameters of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties under Cd stress (A) Growth (bar=10 cm); (B) Plant height and maximum root length; (C) Shoot and root biomass; (D) Cd tolerance index. CK, Cd, SeIV, SeMet, Te, SeIV+Te, and SeMet+Te are the same as shown in Table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among differerent treatments (P<0.05).
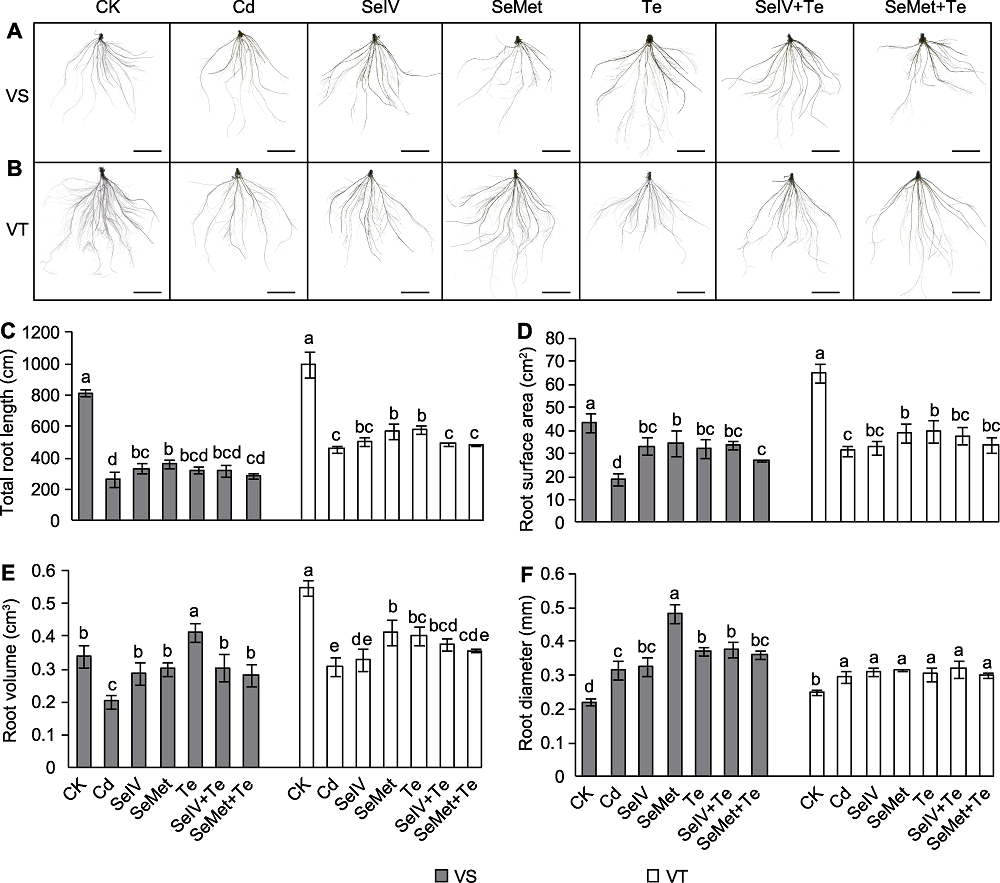
图2 Se和Te对Cd胁迫下Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种根系性状的影响 (A) Cd敏感品种(VS)根系扫描图(bars=5 cm); (B) Cd耐受品种(VT)根系扫描图(bars=5 cm); (C) 总根长; (D) 根系表面积; (E) 根系体积; (F) 根系直径。CK、Cd、SeIV、SeMet、Te、SeIV+Te和SeMet+Te同表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 2 Effects of Se and Te on root traits of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties under Cd stress (A) Root scanned picture of Cd-sensitive variety (VS) (bars=5 cm); (B) Root scanned picture of Cd-tolerant variety (VT) (bars=5 cm); (C) Total root length; (D) Root surface area; (E) Root volume; (F) Root diameter. CK, Cd, SeIV, SeMet, Te, SeIV+Te, and SeMet+Te are the same as shown in Table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
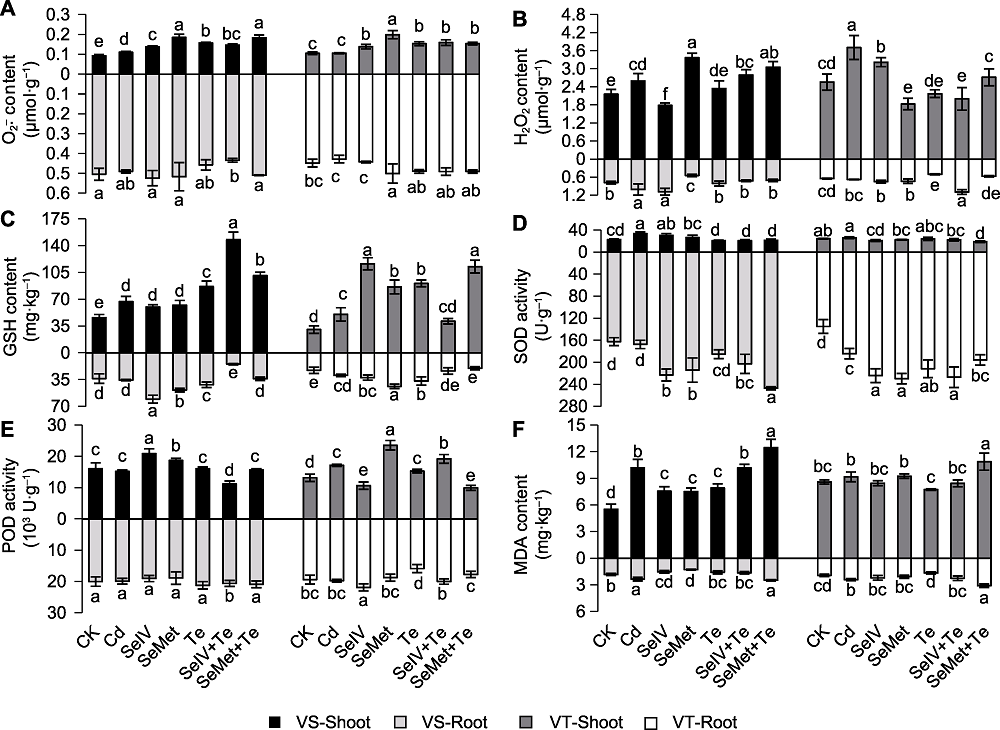
图3 Se和Te对Cd胁迫下Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种生理指标的影响 (A) 超氧阴离子(O2-.)含量; (B) 过氧化氢(H2O2)含量; (C) 还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)含量; (D) 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性; (E) 过氧化物酶(POD)活性; (F) 丙二醛(MDA)含量。CK、Cd、SeIV、SeMet、Te、SeIV+Te和SeMet+Te含义同表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 3 Effects of Se and Te on physiological indexes of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties under Cd stress (A) Superoxide anion (O2-.) content; (B) Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content; (C) Reduced glutathione (GSH) content; (D) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity; (E) Peroxidase (POD) activity; (F) Malondialdehyde (MDA) content. CK, Cd, SeIV, SeMet, Te, SeIV+Te, and SeMet+Te are the same as shown in Table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
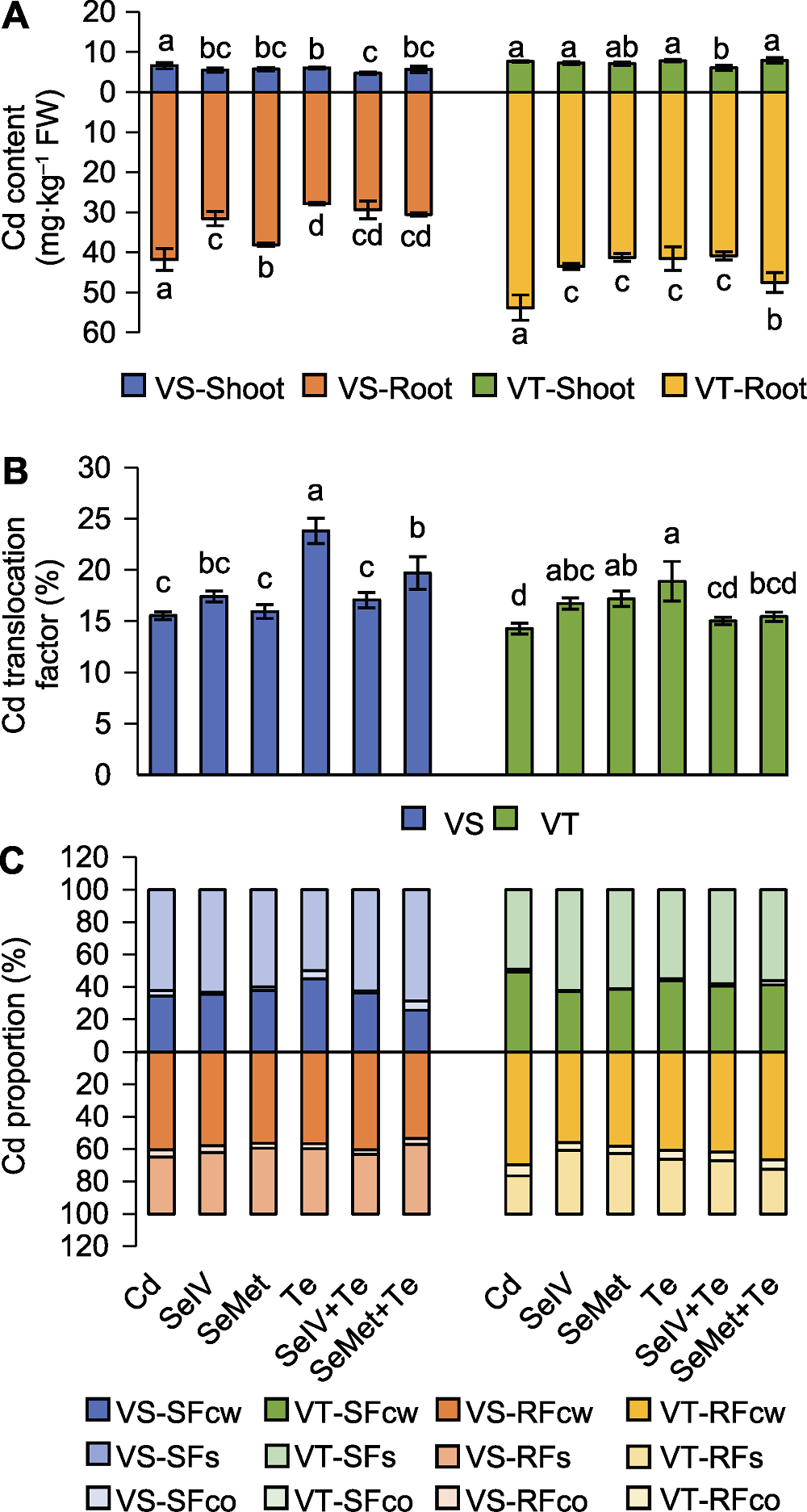
图4 Se和Te对Cd胁迫下Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种幼苗Cd吸收转运和亚细胞分布的影响 (A) Cd含量; (B) Cd转运系数; (C) 地上部(S)和根部(R)细胞壁组分(Fcw)、细胞器组分(Fco)和细胞质组分(Fs) Cd占比。CK、Cd、SeIV、SeMet、Te、SeIV+Te和SeMet+Te含义同表1。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 4 Effects of Se and Te on Cd uptake and translocation and Cd subcellular distribution in seedlings of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties under Cd stress (A) Cd content; (B) Cd translocation factor; (C) Cd percentage in cell wall fraction (Fcw), organelle fraction (Fco) and solubility fraction (Fs) of shoot (S) and root (R). CK, Cd, SeIV, SeMet, Te, SeIV+Te, and SeMet+Te are the same as shown in Table 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
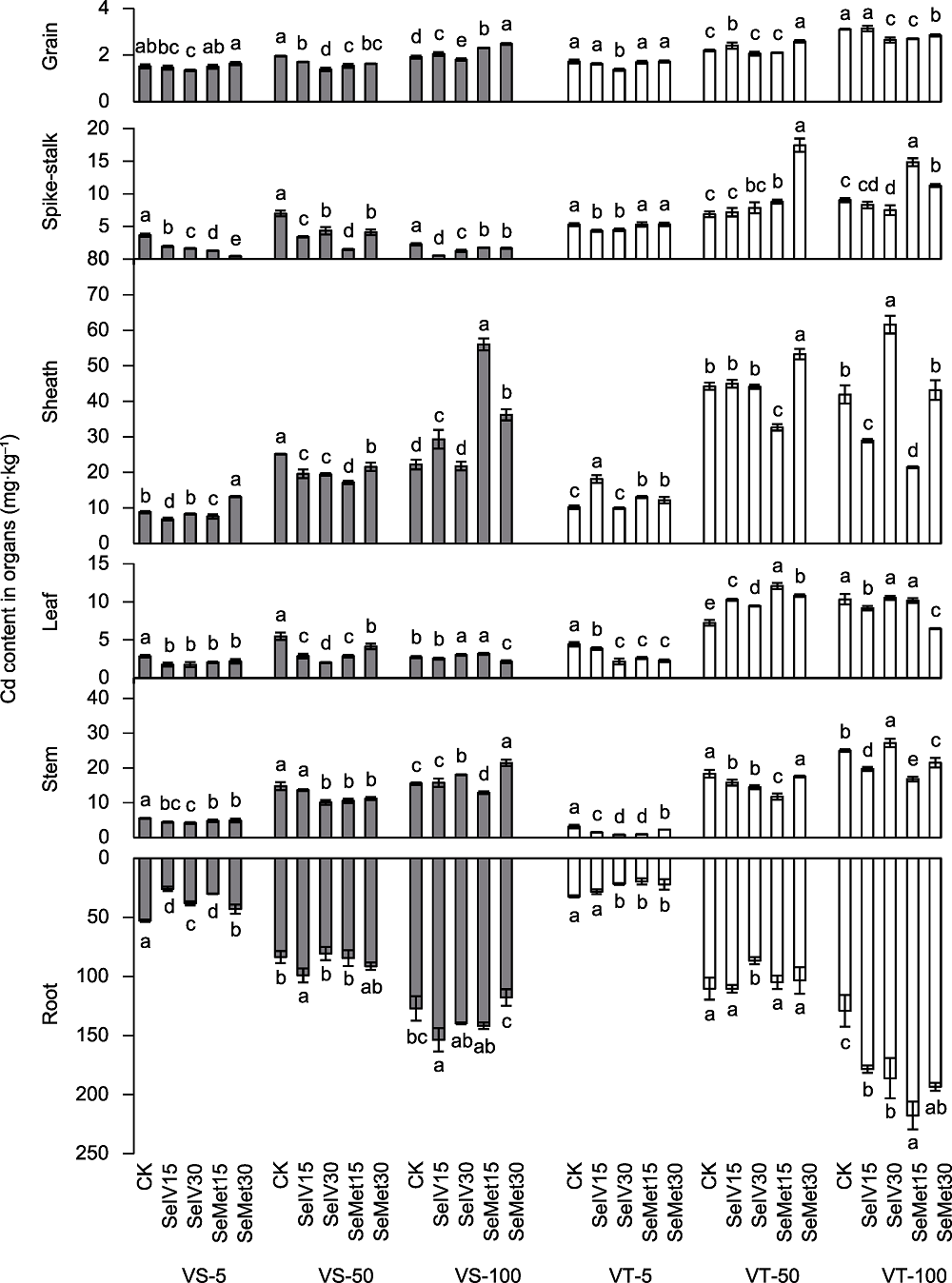
图5 Se对Cd胁迫下成熟期Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种各器官Cd含量的影响 -5、-50和-100分别表示5、50和100 mg·kg-1 Cd处理。CK、SeIV15、SeIV30、SeMet15和SeMet30分别表示0、15 mg?L-1 Na2SeO3、30 mg?L-1 Na2SeO3、15 mg?L-1硒代蛋氨酸和30 mg?L-1硒代蛋氨酸处理。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 5 Effects of Se on Cd content of various organs of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties at maturity under Cd stress -5, -50, and -100 indicate 5, 50, and 100 mg·kg-1 Cd treatments, respectively. CK, SeIV15, SeIV30, SeMet15, and SeMet30 represented the 0, 15 mg?L-1 Na2SeO3, 30 mg?L-1 Na2SeO3, 15 mg?L-1 selenomethionine, and 30 mg?L-1 selenomethionine treatments, respectively. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
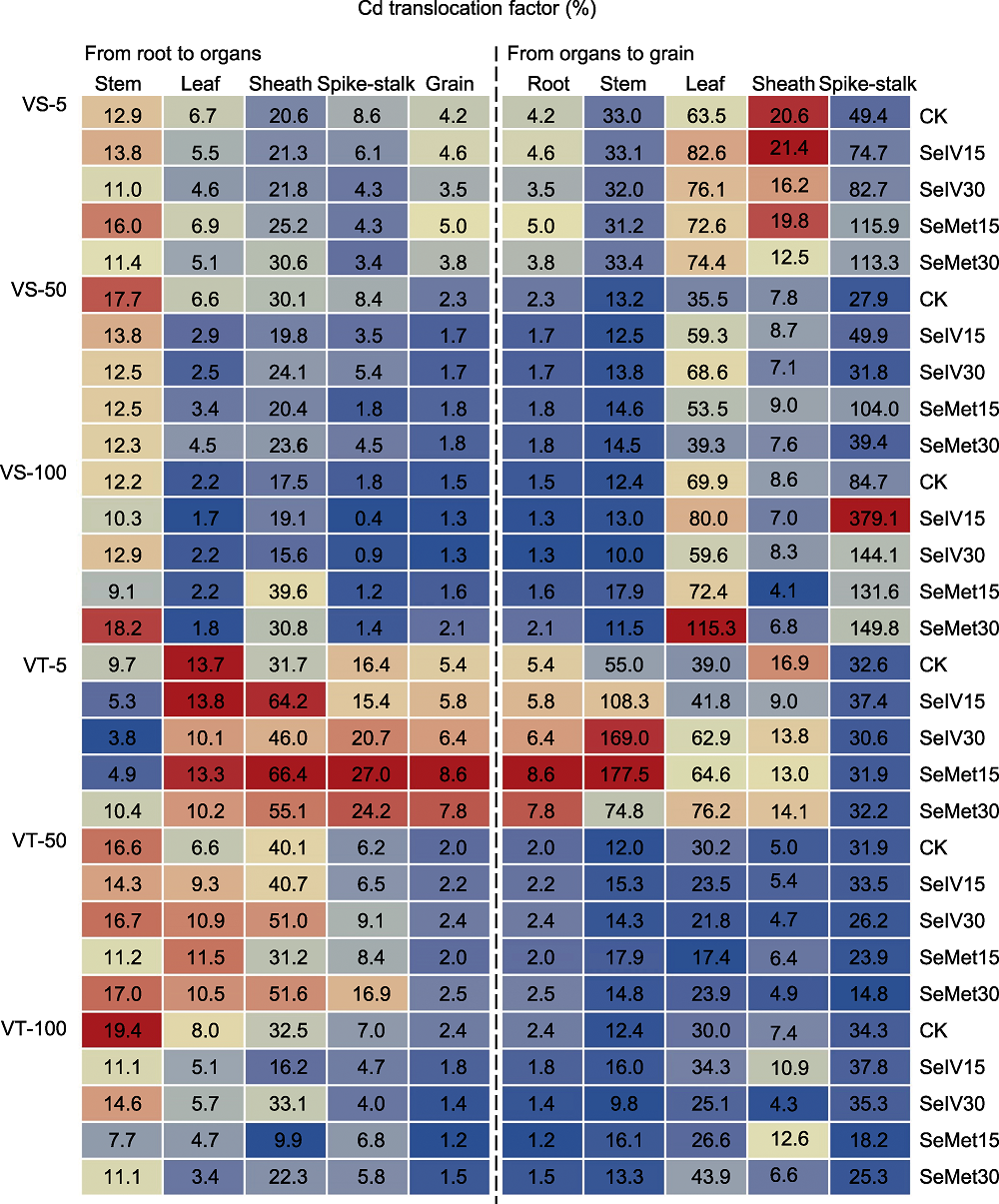
图6 Se对Cd胁迫下Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种根到地上部各器官和各器官到籽粒Cd转运系数的影响 -5、-50、-100、CK、SeIV15、SeIV30、SeMet15和SeMet30同图5。不同颜色表示Cd转运系数在不同处理间存在差异, 颜色越红表示转运系数越大, 颜色越蓝表示转运系数越小。
Figure 6 Effect of Se on Cd translocation factor from root to shoot and from each organ to grains of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties under Cd stress -5, -50, -100, CK, SeIV15, SeIV30, SeMet15, and SeMet30 are the same as shown in Figure 5. Different colors indicate that Cd translocation factor is different among treatments. The redder the color is, the greater Cd translocation factor is, and the bluer the color is, the smaller Cd translocation factor is.
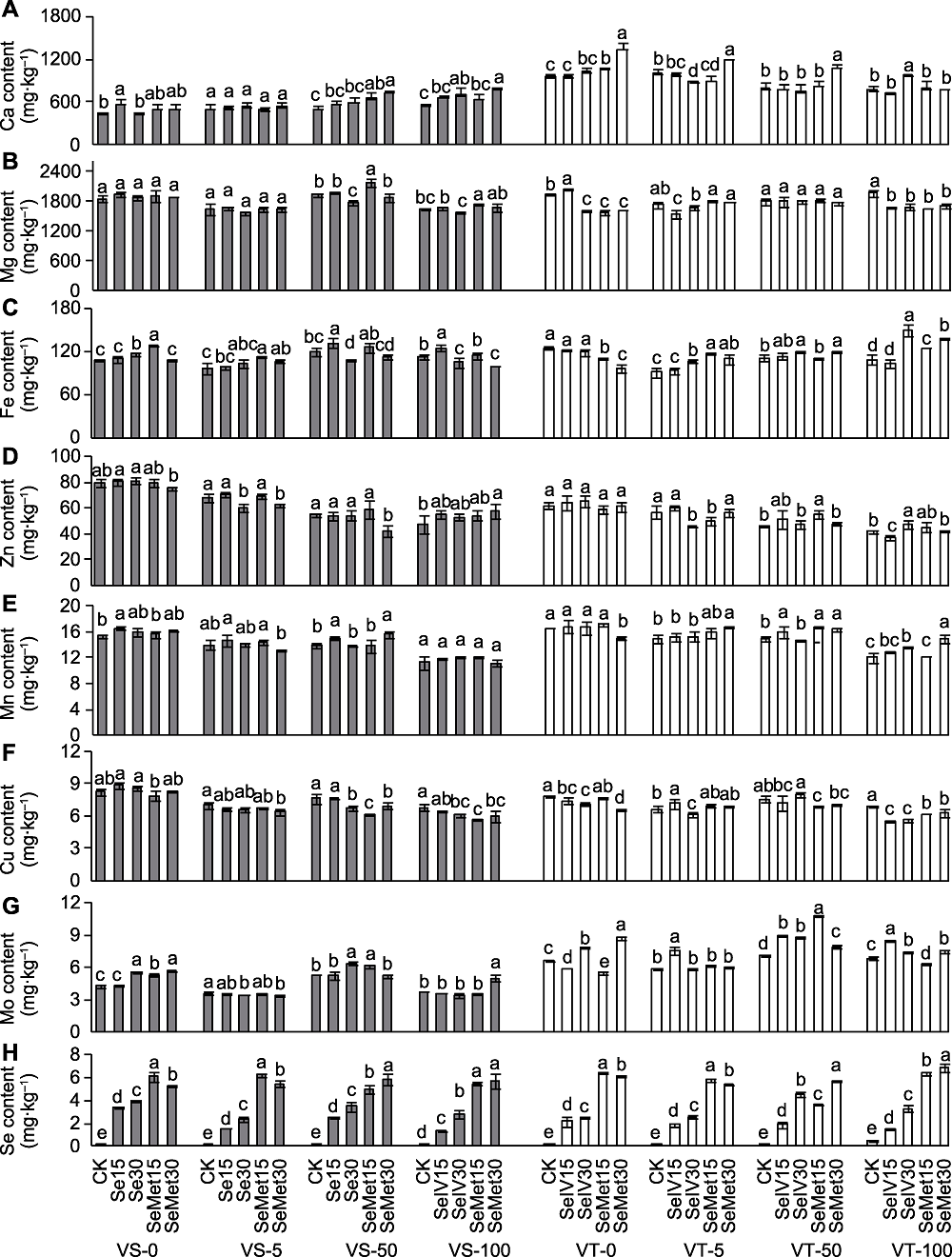
图7 Se对Cd胁迫下Cd敏感(VS)和Cd耐受(VT)糜子品种籽粒中矿质元素含量的影响 (A) 钙含量; (B) 镁含量; (C) 铁含量; (D) 锌含量; (E) 锰含量; (F) 铜含量; (G) 钼含量; (H) 硒含量。-0、-5、-50和-100分别表示0、5、50和100 mg·kg-1 Cd处理。CK、SeIV15、SeIV30、SeMet15和SeMet30的含义同图5。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 7 Effect of Se on mineral element content in the grains of Cd-sensitive (VS) and Cd-tolerant (VT) broomcorn millet varieties under Cd stress (A) Calcium content; (B) Magnesium content; (C) Iron content; (D) Zinc content; (E) Manganese content; (F) Copper content; (G) Molybdenum content; (H) Selenium content. -0, -5, -50, and -100 indicate 0, 5, 50, and 100 mg·kg-1 Cd treatments, respectively. CK, SeIV15, SeIV30, SeMet15, and SeMet30 are the same as shown in Figure 5. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (P<0.05).
| [1] | 安婷婷, 黄帝, 王浩, 张一, 陈应龙 (2021). 植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展. 植物学报 56, 347-362. |
| [2] | 陈建信, 孙燕英, 刘鑫, 李元杰, 李永林 (2018). 内蒙古东部两个有色金属集中开采区土壤重金属污染健康风险评估的对比研究. 干旱区资源与环境 32, 140-146. |
| [3] | 陈文轩, 李茜, 王珍, 孙兆军 (2020). 中国农田土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价. 环境科学 41, 2822-2833. |
| [4] | 邓坤 (2015). 水稻根系吸收和转运硒代蛋氨酸的机制研究. 硕士论文. 洛阳: 河南科技大学. pp. 1-37. |
| [5] |
董萌, 赵运林, 库文珍, 周小梅, 李燕子 (2013). 蒌蒿对镉的富集特征及亚细胞分布特点. 植物学报 48, 381-388.
DOI |
| [6] | 龚继明 (2014). 重金属污染的缓与急. 植物生理学报 50, 567-568. |
| [7] |
王璐瑶, 陈謇, 赵守清, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 刘若溪, 麻密, 虞轶俊, 何振艳 (2022). 水稻镉积累特性的生理和分子机制研究概述. 植物学报 57, 236-249.
DOI |
| [8] | 袁文淼 (2015). 陕北能源化工基地土壤中重金属与多环芳烃污染现状及其污染风险分析. 硕士论文. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学. pp. 19-27. |
| [9] | 赵晓光, 张亦扬, 杜华栋 (2019). 陕北矿区不同土地类型下土壤重金属污染评价. 环境工程 37(9), 188-193. |
| [10] | 周鑫斌, 赖凡, 张城铭, 高阿祥, 徐卫红 (2017). 不同形态硒向水稻籽粒转运途径及品种差异. 土壤学报 54(5), 1251-1258. |
| [11] |
Anan Y, Yoshida M, Hasegawa S, Katai R, Tokumoto M, Ouerdane L, Łobiński R, Ogra Y (2013). Speciation and identification of tellurium-containing metabolites in garlic,Allium sativum. Metallomics 5, 1215-1224.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Berenguel O, Arruda MAZ (2018). Total content and in vitro bioaccessibility of tellurium in brazil nuts. J Trace Elem Med Biol 48, 46-51.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Cheng YR, Bao YJ, Chen X, Yao Q, Wang C, Chai SY, Zeng J, Fan X, Kang HY, Sha LN, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH, Wang Y (2020). Different nitrogen forms differentially affect Cd uptake and accumulation in dwarf Polish wheat (Triticum polonicum L.) seedlings. J Hazard Mater 400, 123209.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Ding YZ, Feng RW, Wang RG, Guo JK, Zheng XQ (2014). A dual effect of Se on Cd toxicity: evidence from plant growth, root morphology and responses of the antioxidative systems of paddy rice. Plant Soil 375, 289-301.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Farooq MA, Gill RA, Faisal I, Ali B, Liu HB, Xu JX, He SP, Zhou WJ (2016). Methyl jasmonate regulates antioxidant defense and suppresses arsenic uptake in Brassica napus L. Front Plant Sci 7, 468. |
| [16] |
Feng RW, Wang LZ, Yang JG, Zhao PP, Zhu YM, Li YP, Yu YS, Liu H, Rensing C, Wu ZY, Ni RX, Zheng SA (2021). Underlying mechanisms responsible for restriction of uptake and translocation of heavy metals (metalloids) by selenium via root application in plants. J Hazard Mater 402, 123570.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Feng RW, Wei CY, Tu SX (2013). The roles of selenium in protecting plants against abiotic stresses. Environ Exp Bot 87, 58-68.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Habiyaremye C, Matanguihan JB, D'Alpoim Guedes J, Ganjyal GM, Whiteman MR, Kidwell KK, Murphy KM (2017). Proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) and its potential for cultivation in the Pacific Northwest, U.S: a review. Front Plant Sci 7, 1961. |
| [19] |
Haider FU, Cai LQ, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Wu J, Zhang RZ, Ma WJ, Farooq M (2021). Cadmium toxicity in plants: impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211, 111887.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Huang BF, Xin JL, Dai HW, Zhou WJ (2017). Effects of interaction between cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) on grain yield and Cd and Se accumulation in a hybrid rice (Oryza sativa) system. J Agric Food Chem 65, 9537-9546.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Huang HL, Li M, Rizwan M, Dai ZH, Yuan Y, Hossain M, Cao MH, Xiong SL, Tu SX (2021). Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. J Hazard Mater 401, 123393.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Jia WT, Lv SL, Feng JJ, Li JH, Li YX, Li SZ (2016). Morphophysiological characteristic analysis demonstrated the potential of sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) in the phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23, 18823-18831.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Li HF, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008). Selenium uptake, translocation and speciation in wheat supplied with selenate or selenite. New Phytol 178, 92-102.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Li J, Liang DL, Qin SY, Feng PY, Wu XP (2015). Effects of selenite and selenate application on growth and shoot selenium accumulation of pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) during successive planting conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22, 11076-11086.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Li XZ, Yu H, Sun XW, Yang JT, Wang DC, Shen LF, Pan YS, Wu YC, Wang Q, Zhao Y (2019). Effects of sulfur application on cadmium bioaccumulation in tobacco and its possible mechanisms of rhizospheric microorganisms. J Hazard Mater 368, 308-315.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Lin L, Zhou WH, Dai HX, Cao FB, Zhang GP, Wu FB (2012). Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. J Hazard Mater 235-236, 343-351.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Liu JH, Hou H, Zhao L, Sun ZJ, Li H (2020). Protective effect of foliar application of sulfur on photosynthesis and antioxidative defense system of rice under the stress of Cd. Sci Total Environ 710, 136230.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Liu JJ, Zhang DZ, Yuan YH, Chen PL, Zhang PP, Jin F, Yang QH, Feng BL (2021). A promising crop for cadmium-contamination remediation: broomcorn millet. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 224, 112669.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Liu JJ, Zhang DZ, Zhang YB, Zhou H, Chen PL, Yuan YH, Yang QH, Zhao L, Feng BL (2022). Dynamic and comparative transcriptome analyses reveal key factors contributing to cadmium tolerance in broomcorn millet. Int J Mol Sci 23, 6148.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Lu HY, Zhang JP, Liu KB, Wu NQ, Li YM, Zhou KS, Ye ML, Zhang TY, Zhang HJ, Yang XY, Shen LC, Xu DK, Li Q (2009). Earliest domestication of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) in East Asia extended to 10, 000 years ago. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 7367-7372.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Lu M, Yu S, Lian JP, Wang Q, He ZL, Feng Y, Yang XE (2021). Physiological and metabolomics responses of two wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes differing in grain cadmium accumulation. Sci Total Environ 769, 145345.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Mabhaudhi T, Chimonyo VGP, Hlahla S, Massawe F, Mayes S, Nhamo L, Modi AT (2019). Prospects of orphan crops in climate change. Planta 250, 695-708.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Mendoza-Cózatl DG, Butko E, Springer F, Torpey JW, Komives EA, Kehr J, Schroeder JI (2008). Identification of high levels of phytochelatins, glutathione and cadmium in the phloem sap of Brassica napus. A role for thiol-peptides in the long-distance transport of cadmium and the effect of cadmium on iron translocation. Plant J 54, 249-259. |
| [34] |
Muthamilarasan M, Prasad M (2021). Small millets for enduring food security amidst pandemics. Trends Plant Sci 26, 33-40.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Paciolla C, De Leonardis S, Dipierro S (2011). Effects of selenite and selenate on the antioxidant systems in Senecio scandens L. Plant Biosyst-Int J Deal Aspects Plant Biol 145, 253-259. |
| [36] |
Qin XM, Nie ZJ, Liu HE, Zhao P, Qin SY, Shi ZW (2018). Influence of selenium on root morphology and photosynthetic characteristics of winter wheat under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 150, 232-239.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Wan YN, Yu Y, Wang Q, Qiao YH, Li HF (2016). Cadmium uptake dynamics and translocation in rice seedling: influence of different forms of selenium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 133, 127-134.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Wang KJ, Yu HY, Zhang XZ, Ye DH, Huang HG, Wang YD, Zheng ZC, Li TX (2021). A transcriptomic view of cadmium retention in roots of cadmium-safe rice line (Oryza sativa L.). J Hazard Mater 418, 126379.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Wang YD, Wang X, Wong YS (2012). Proteomics analysis reveals multiple regulatory mechanisms in response to selenium in rice. J Proteomics 75, 1849-1866.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Wu C, Dun Y, Zhang ZJ, Li ML, Wu GQ (2020). Foliar application of selenium and zinc to alleviate wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cadmium toxicity and uptake from cadmium- contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190, 110091.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Yang XR, Wang CR, Huang YC, Liu B, Liu ZQ, Huang YZ, Cheng LL, Huang YF, Zhang CB (2021). Foliar application of the sulfhydryl compound 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid inhibits cadmium, lead, and arsenic accumulation in rice grains by promoting heavy metal immobilization in flag leaves. Environ Pollut 285, 117355.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Yang Z, Yang F, Liu JL, Wu HT, Yang H, Shi Y, Liu J, Zhang YF, Luo YR, Chen KM (2022). Heavy metal transporters: functional mechanisms, regulation, and application in phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ 809, 151099.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Yu Y, Yuan SL, Zhuang J, Wan YN, Wang Q, Zhang JS, Li HF (2018). Effect of selenium on the uptake kinetics and accumulation of and oxidative stress induced by cadmium in Brassica chinensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162, 571-580.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Zandi P, Yang JJ, Xia X, Tian Y, Li Q, Możdżeń K, Barabasz-Krasny B, Wang YS (2020). Do sulfur addition and rhizoplane iron plaque affect chromium uptake by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings in solution culture? J Hazard Mater 388, 121803.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Zhang DX, Du GH, Chen D, Shi GL, Rao W, Li X, Jiang Y, Liu SL, Wang DC (2019a). Effect of elemental sulfur and gypsum application on the bioavailability and redistribution of cadmium during rice growth. Sci Total Environ 657, 1460-1467.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Zhang DZ, Panhwar RB, Liu JJ, Gong XW, Liang JB, Liu MX, Lu P, Gao XL, Feng BL (2019b). Morphological diversity and correlation analysis of phenotypes and quality traits of proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) core collections. J Integr Agric 18, 958-969.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Zhang DZ, Zhang YB, Zhou H, Wang HR, Gao YJ, Shao LL, Ding Q, Ma LJ (2022a). Chalcogens reduce grain Cd accumulation by enhancing Cd root efflux and upper organ retention in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ Exp Bot 201, 104975.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Zhang DZ, Zhou H, Shao LL, Wang HR, Zhang YB, Zhu T, Ma LT, Ding Q, Ma LJ (2022b). Root characteristics critical for cadmium tolerance and reduced accumulation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Environ Manage 305, 114365.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Zhang YL, He SR, Zhang Z, Xu HJ, Wang JJ, Chen HY, Liu YL, Wang XL, Li YT (2019c). Glycine transformation induces repartition of cadmium and lead in soil constituents. Environ Pollut 251, 930-937.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Zhao YY, Hu CX, Wang X, Qing XJ, Wang P, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Zhao XH (2019a). Selenium alleviated chromium stress in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Pekinensis) by regulating root morphology and metal element uptake. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 173, 314-321.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Zhao YY, Hu CX, Wu ZC, Liu XW, Cai MM, Jia W, Zhao XH (2019b). Selenium reduces cadmium accumulation in seed by increasing cadmium retention in root of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Environ Exp Bot 158, 161-170.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Zhu HH, Ai HL, Cao LW, Sui R, Ye HP, Du DY, Sun J, Yao J, Chen K, Chen L (2018). Transcriptome analysis providing novel insights for Cd-resistant tall fescue responses to Cd stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 160, 349-356.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Zhu JJ, Zhao P, Nie ZJ, Shi HZ, Li C, Wang Y, Qin SY, Qin XM, Liu HE (2020). Selenium supply alters the subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium and the expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum). BMC Plant Biol 20, 550.
DOI PMID |
| [54] |
Zou CS, Li LT, Miki D, Li DL, Tang QM, Xiao LH, Rajput S, Deng P, Peng L, Jia W, Huang R, Zhang ML, Sun YD, Hu JM, Fu X, Schnable PS, Chang YX, Li F, Zhang H, Feng BL, Zhu XG, Liu RY, Schnable JC, Zhu JK, Zhang H (2019). The genome of broomcorn millet. Nat Commun 10, 436.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [2] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [3] | 李柳, 刘庆华, 尹春英. 植物硒生物强化及微生物在其中的应用潜力[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(6): 756-769. |
| [4] | 蔡淑钰, 刘建新, 王国夫, 吴丽元, 宋江平. 褪黑素促进镉胁迫下番茄种子萌发的调控机理[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 720-732. |
| [5] | 杨清华, 王洪露, 冯佰利. 糜子品质研究进展与展望[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 22-33. |
| [6] | 王宇卓, 林元香, 薛亚鹏, 段政勇, 王晓丹, 陈凌, 曹晓宁, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 山西糜子核心种质分子身份证构建[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 159-168. |
| [7] | 王璐瑶, 陈謇, 赵守清, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 刘若溪, 麻密, 虞轶俊, 何振艳. 水稻镉积累特性的生理和分子机制研究概述[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 236-249. |
| [8] | 徐海霞, 何静, 易航, 王丽. 镉胁迫下地钱转录组的性别特异性响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 182-196. |
| [9] | 安婷婷, 黄帝, 王浩, 张一, 陈应龙. 植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 347-362. |
| [10] | 潘晨阳, 叶涵斐, 周维永, 王盛, 李梦佳, 路梅, 李三峰, 朱旭东, 王跃星, 饶玉春, 戴高兴. 水稻籽粒镉积累QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 25-32. |
| [11] | 陈欢欢, 李竹梅, 唐利洲. 榕小蜂温度耐受性及其对种间共存关系的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(10): 1222-1228. |
| [12] | 何杰丽,石甜甜,陈凌,王海岗,高志军,杨美红,王瑞云,乔治军. 糜子EST-SSR分子标记的开发及种质资源遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 723-732. |
| [13] | 黄新元, 赵方杰. 植物防御素调控水稻镉积累的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 451-455. |
| [14] | 陈良华, 赖娟, 胡相伟, 杨万勤, 张健, 王小军, 谭灵杰. 接种丛枝菌根真菌对受镉胁迫美洲黑杨雌、雄株光合生理的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(4): 480-488. |
| [15] | 康菊清, 张岱鹏. 低温条件下中国野生拟南芥种群中CBF3与ROS浓度的相关性[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 577-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||