

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (5): 720-732.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22202 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22202
收稿日期:2022-08-26
接受日期:2022-12-01
出版日期:2023-09-01
发布日期:2023-09-21
通讯作者:
*E-mail: csyyoukeer@126.com
基金资助:
Cai Shuyu( ), Liu Jianxin, Wang Guofu, Wu Liyuan, Song Jiangping
), Liu Jianxin, Wang Guofu, Wu Liyuan, Song Jiangping
Received:2022-08-26
Accepted:2022-12-01
Online:2023-09-01
Published:2023-09-21
Contact:
*E-mail: csyyoukeer@126.com
摘要: 土壤镉(Cd2+)污染严重制约设施蔬菜的产量和品质。褪黑素(MT)可以增强植株对多种逆境的抗性, 然而Cd2+胁迫下MT调控番茄(Solanum lycopersicum)种子萌发的下游信号尚不清楚。该研究以番茄野生型Alisa Craig种子为材料, 探究不同浓度Cd2+处理及外源MT对番茄种子萌发的调控效应。结果表明, 0.5 mmol·L-1以上的Cd2+处理显著抑制番茄种子的萌发和幼苗生长。用0.15 mmol·L-1 MT浸种可降低种子萌发后地下部和地上部的Cd2+含量, 有效缓解Cd2+胁迫对番茄种子萌发和幼苗生长的抑制作用。MT上调了番茄胚根中植物螯合肽和转运蛋白基因(PCS、NRAMP1、ABCC3、HMA3与ABCG5)的表达, 促进Cd2+的跨膜转运以及液泡隔离。此外, MT减轻了Cd2+诱导的氧化损伤, 除褪黑素自身的抗氧化作用外, 也与抗氧化酶(CAT、APX与ALDH)活性的增强相关。进一步分析表明, MT显著下调了Cd2+胁迫下脱落酸(ABA)合成基因(NCED1和NCED2)的表达, 并上调了ABA分解基因ABA8ox1的表达, 降低ABA含量, 从而有效调节赤霉素/脱落酸(GA/ABA)的比值, 促进Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子的萌发。
蔡淑钰, 刘建新, 王国夫, 吴丽元, 宋江平. 褪黑素促进镉胁迫下番茄种子萌发的调控机理. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 720-732.
Cai Shuyu, Liu Jianxin, Wang Guofu, Wu Liyuan, Song Jiangping. Regulatory Mechanism of Melatonin on Tomato Seed Germination Under Cd2+ Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(5): 720-732.
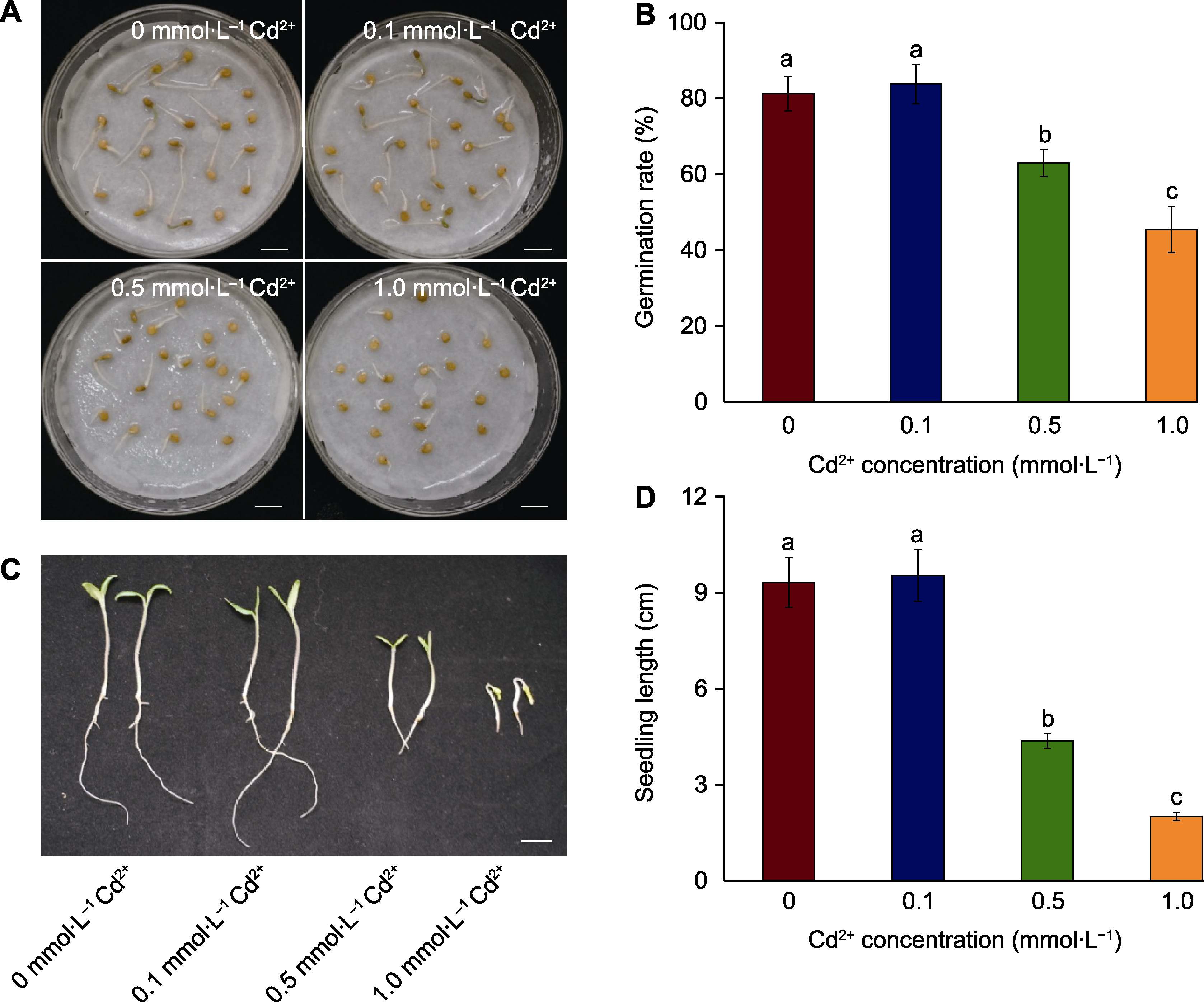
图1 Cd2+浓度梯度对番茄种子萌发与幼苗质量的影响 (A) 发芽3天番茄种子的萌发情况(bars=1 cm); (B) 发芽3天番茄种子的发芽率; (C) 发芽5天番茄幼苗表型(bar=1 cm); (D) 发芽5天番茄幼苗长度。不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure1 Effect of cadmium concentrations on seed germination and seedling growth of tomato (A) Germination phenotypes of tomato seeds 3 days after germination(bars=1 cm); (B) Germination rate of tomato seeds 3 days after germination; (C) Phenotypes of tomato seedlings 5 days after germination (bar=1 cm); (D) Seedling length of tomato 5 days after germination. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
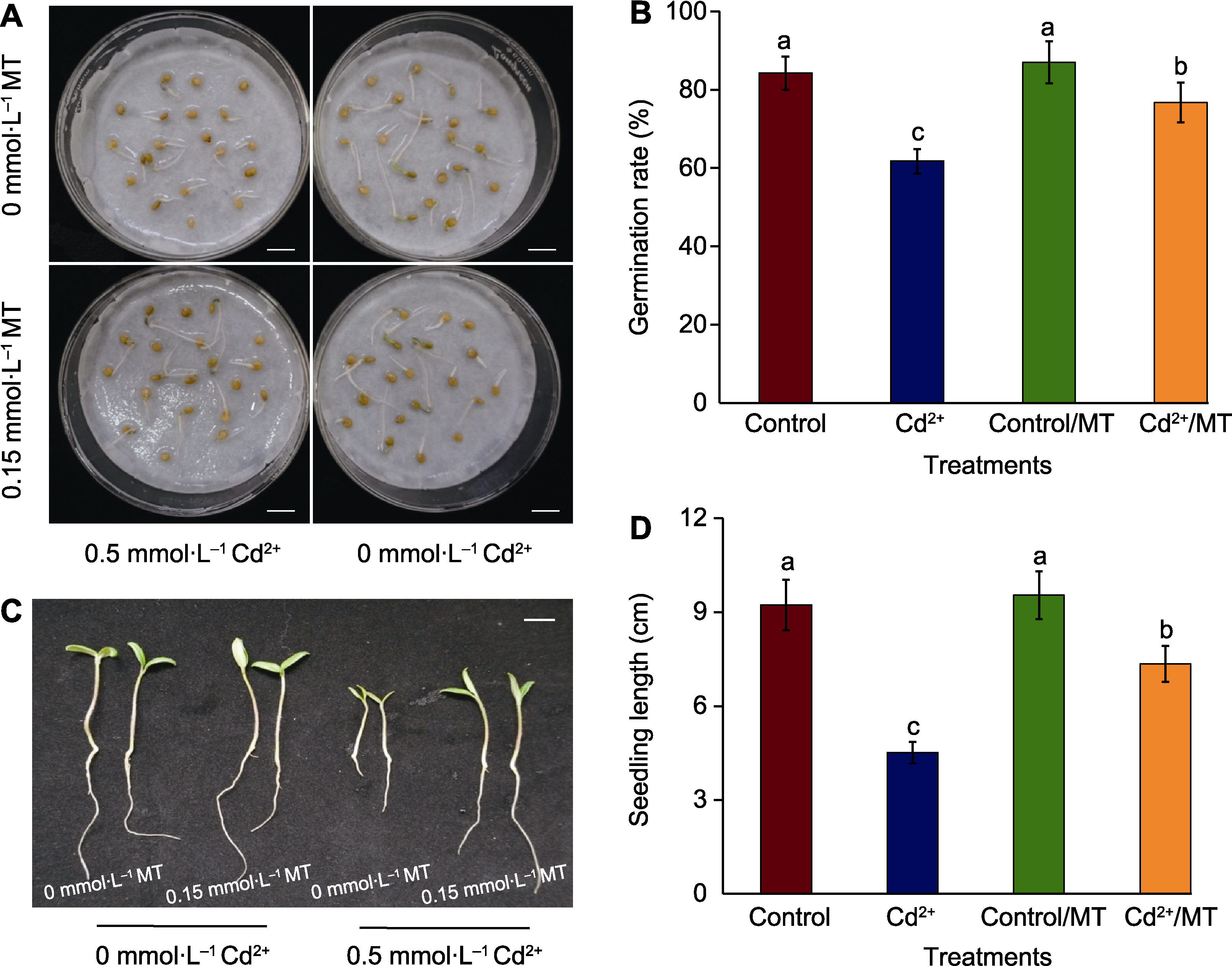
图2 褪黑素(MT)对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发的影响 (A) 发芽3天种子的萌发情况(bars=1 cm); (B) 发芽率; (C) 发芽5天番茄幼苗的表型(bar=1 cm); (D) 幼苗长度。不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Control: 0 mmol·L-1 Cd2+; Cd2+: 0.5 mmol·L-1 Cd2+; Control/MT: 0 mmol·L-1 Cd2++0.15 mmol·L-1 MT; Cd2+/MT: 0.5 mmol·L-1 Cd2++0.15 mmol·L-1 MT
Figure 2 Effects of melatonin (MT) on tomato seed germination under Cd2+ stress (A) Germination phenotypes of seeds 3 days after germination(bars=1 cm); (B) Germination rate; (C) Phenotypes of tomato seedlings 5 days after germination (bar=1 cm); (D) Seedling length. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
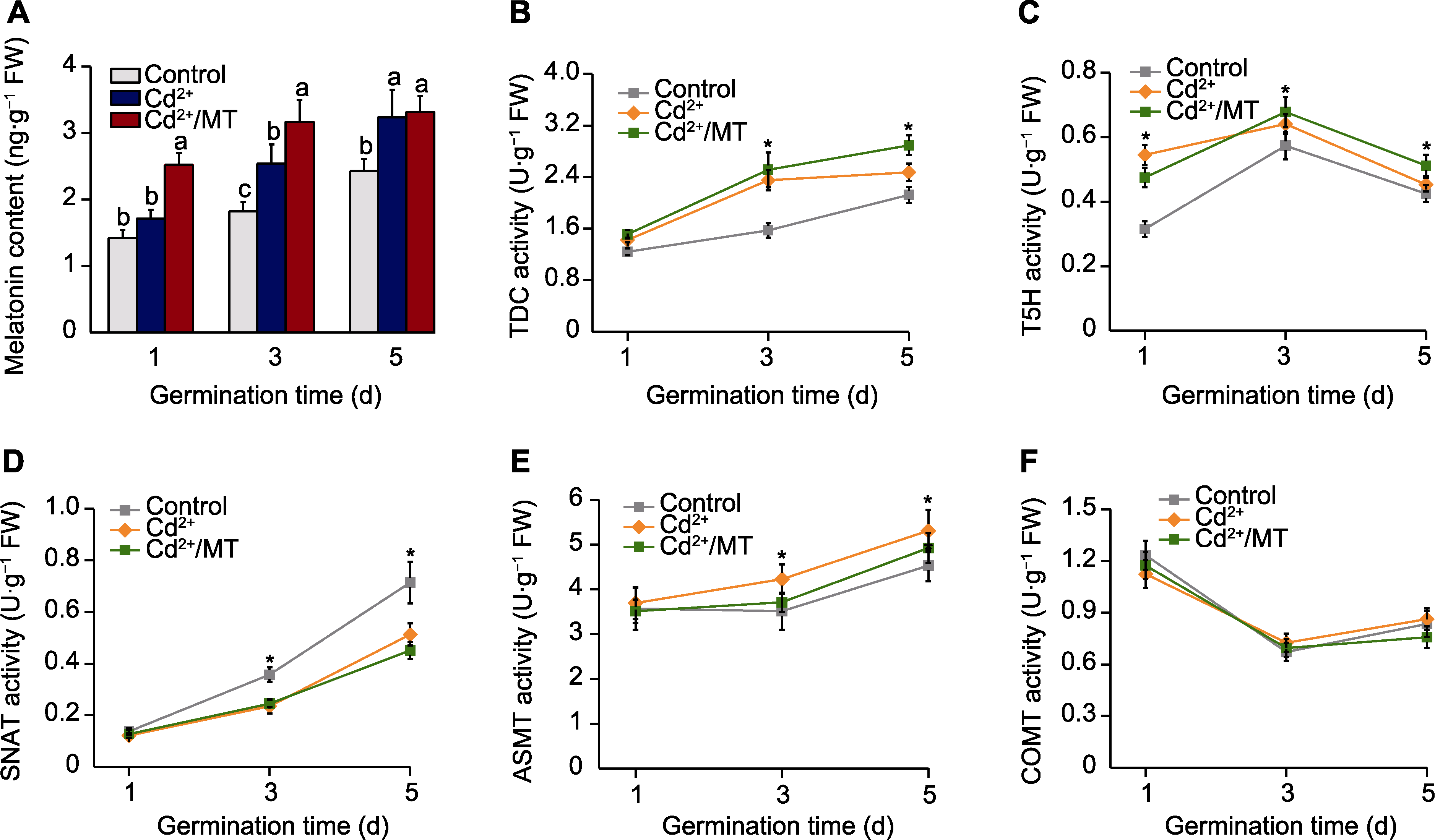
图3 褪黑素(MT)处理对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中内源褪黑素代谢的影响 (A) MT含量; (B) 氨酸脱羧酶(TDC)活性; (C) 色胺-5-羟化酶(T5H)活性; (D) 5-羟色胺-N-乙酰基转移酶(SNAT)活性; (E) N-乙酰基- 5-羟色胺-甲基转移酶(ASMT)活性; (F) 咖啡酸-O-甲基转移酶(COMT)活性。不同小写字母和*表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。Control、Cd2+和Cd2+/MT同图2。
Figure 3 Effects of melatonin (MT) treatment on endogenous melatonin metabolism during tomato seed germination under Cd2+ stress (A) MT content; (B) Tryptophan decarboxylase (TDC) activity; (C) Tryptamine-5-hydroxylase (T5H) activity; (D) 5-serotonin-N-acetyltransferae (SNAT) activity; (E) N-acetyl-5-serotonin-methyltransferase (ASMT) activity; (F) Caffeicacid-O-me- thyltransferase (COMT) activity. Different lowercase letters and * indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05). Control, Cd2+, and Cd2+/MT are the same as shown in Figure 2.
| Treatment | Cd2+ content in underground parts (mg·kg-1 DW) | Cd2+ content in above-ground parts (mg·kg-1 DW) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 5 d | 3 d | 5d | |
| Control | 0.074±0.004 c | 0.098±0.012 c | 0.034±0.005 b | 0.047±0.003 c |
| Cd2+ | 0.138±0.011 a | 0.176±0.009 a | 0.041±0.006 a | 0.068±0.004 a |
| Cd2+/MT | 0.097±0.007 b | 0.126±0.007 b | 0.042±0.005 a | 0.054±0.007 b |
表1 Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中Cd2+积累情况
Table 1 Cd2+ accumulation of tomato seeds during germination under Cd2+ stress
| Treatment | Cd2+ content in underground parts (mg·kg-1 DW) | Cd2+ content in above-ground parts (mg·kg-1 DW) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 5 d | 3 d | 5d | |
| Control | 0.074±0.004 c | 0.098±0.012 c | 0.034±0.005 b | 0.047±0.003 c |
| Cd2+ | 0.138±0.011 a | 0.176±0.009 a | 0.041±0.006 a | 0.068±0.004 a |
| Cd2+/MT | 0.097±0.007 b | 0.126±0.007 b | 0.042±0.005 a | 0.054±0.007 b |
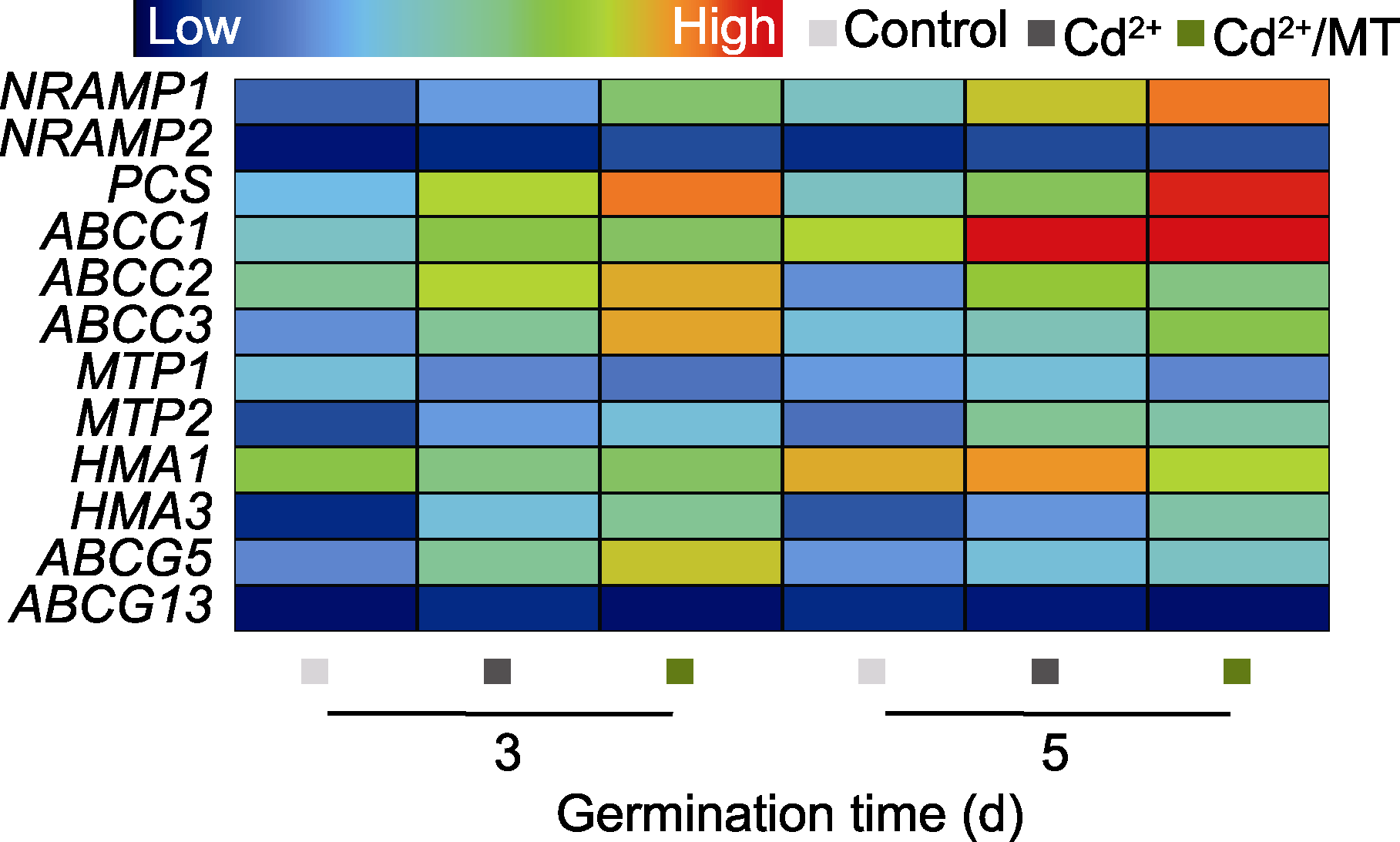
图4 褪黑素(MT)处理对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中Cd2+吸收、转运以及螯合代谢酶基因表达的影响 Control、Cd2+和Cd2+/MT同图2。
Figure 4 Effects of melatonin (MT) on the gene expression of Cd2+ uptake, transport and chelating metabolic enzymes in tomato seed germination under Cd2+ stress Control, Cd2+, and Cd2+/MT are the same as shown in Figure 2.
| Treatment | H2O2 (μmol·g-1 FW) | O2-. (μmol·g-1 FW) | MDA (μmol·g-1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 13.24±0.714 c | 2.43±0.154 b | 6.26±0.514 c |
| Cd2+ | 25.37±1.325 a | 4.79±0.328 a | 10.13±0.758 a |
| Cd2+/MT | 20.13±1.628 b | 4.13±0.376 a | 8.24±0.811 b |
表2 褪黑素(MT)处理对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中过氧化氢(H2O2)、超氧阴离子(O2-. )与丙二醛(MDA)积累的影响
Table 2 Effects of melatonin (MT) on the accumulation of H2O2, O2-. and malonaldehyde (MDA) in tomato seed germination under Cd2+ stress
| Treatment | H2O2 (μmol·g-1 FW) | O2-. (μmol·g-1 FW) | MDA (μmol·g-1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 13.24±0.714 c | 2.43±0.154 b | 6.26±0.514 c |
| Cd2+ | 25.37±1.325 a | 4.79±0.328 a | 10.13±0.758 a |
| Cd2+/MT | 20.13±1.628 b | 4.13±0.376 a | 8.24±0.811 b |
| Treatment | SOD (U·g-1 FW) | POD (U·g-1 FW) | CAT (U·g-1 FW) | APX (U·g-1 FW) | ALDH (U·g-1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.13±0.175 b | 0.105±0.078 b | 3.57±0.295 c | 0.274±0.037 c | 1.37±0.116 c |
| Cd2+ | 2.74±0.213 a | 0.157±0.024 a | 4.19±0.182 b | 0.357±0.042 b | 2.17±0.133 b |
| Cd2+/MT | 2.63±0.146 a | 0.142±0.021 a | 5.12±0.411 a | 0.408±0.026 a | 2.58±0.179 a |
表3 褪黑素(MT)处理对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中抗氧化酶活性的影响
Table 3 Effects of melatonin (MT) on antioxidant enzyme activities during tomato seed germination under Cd2+ stress
| Treatment | SOD (U·g-1 FW) | POD (U·g-1 FW) | CAT (U·g-1 FW) | APX (U·g-1 FW) | ALDH (U·g-1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 2.13±0.175 b | 0.105±0.078 b | 3.57±0.295 c | 0.274±0.037 c | 1.37±0.116 c |
| Cd2+ | 2.74±0.213 a | 0.157±0.024 a | 4.19±0.182 b | 0.357±0.042 b | 2.17±0.133 b |
| Cd2+/MT | 2.63±0.146 a | 0.142±0.021 a | 5.12±0.411 a | 0.408±0.026 a | 2.58±0.179 a |
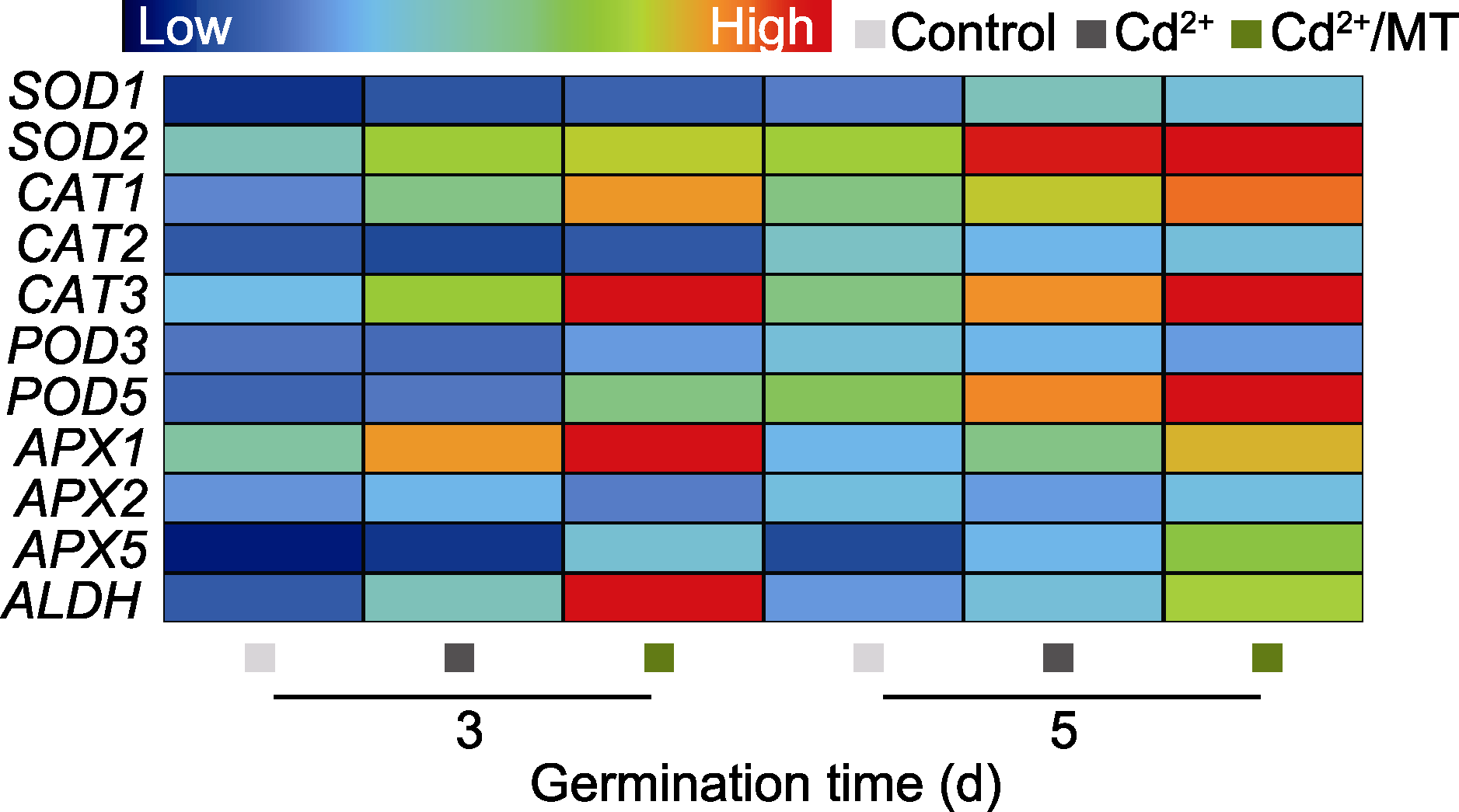
图5 褪黑素(MT)对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中抗氧化酶基因表达的影响 Control、Cd2+和Cd2+/MT同图2。
Figure 5 Effects of melatonin (MT) on the expression of antioxidant enzyme genes in tomato seed germination under Cd2+ stress Control, Cd2+, and Cd2+/MT are the same as shown in Figure 2.
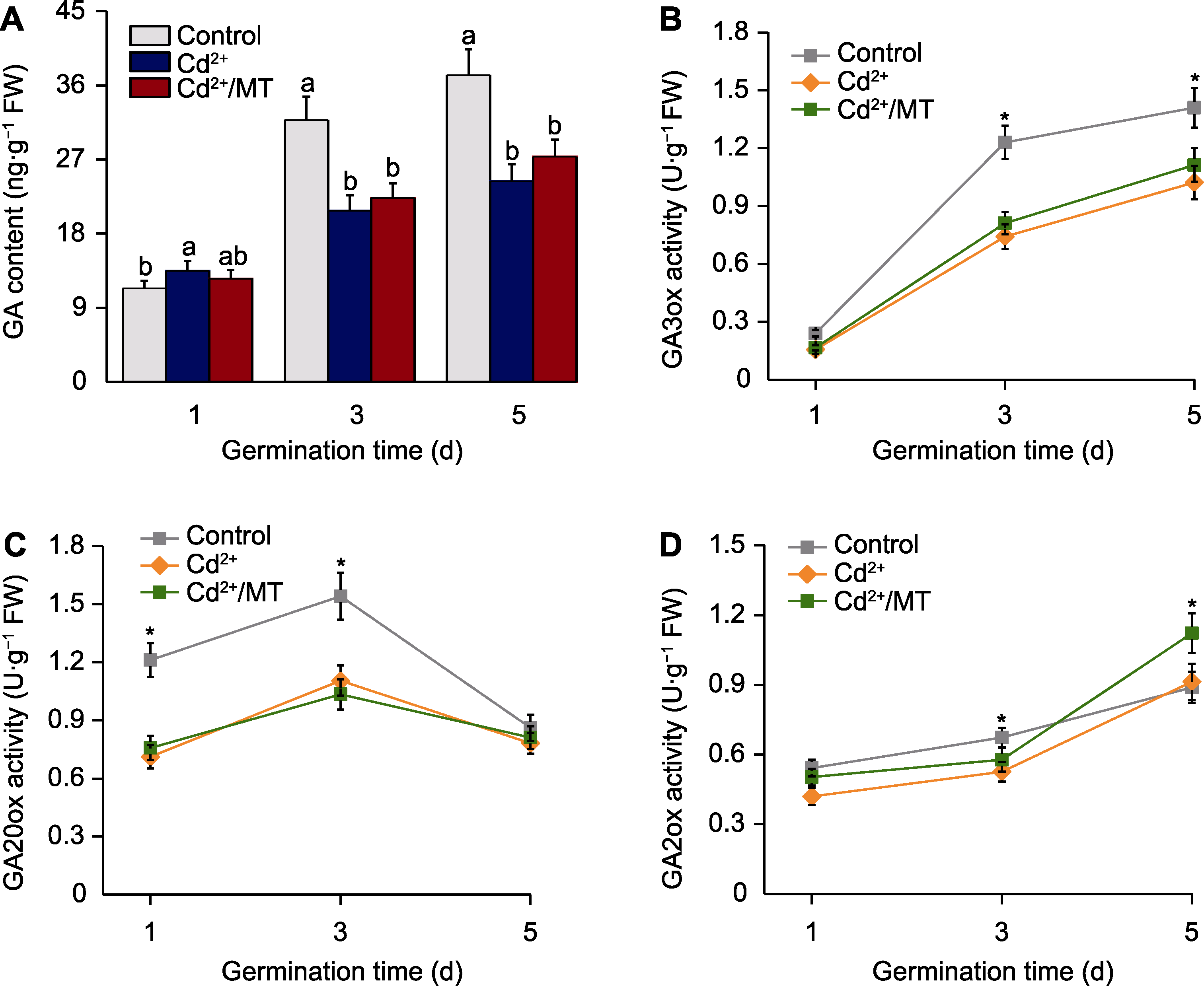
图6 褪黑素(MT)处理对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中赤霉素(GA)代谢的影响 (A) 赤霉素含量; (B) 赤霉素-3-氧化酶(GA3ox)活性; (C) 赤霉素-20-氧化酶(GA20ox)活性; (D) 赤霉素-2-氧化酶(GA2ox)活性。不同小写字母和*表示在0.05水平差异显著。Control、Cd2+和Cd2+/MT同图2。
Figure 6 Effects of melatonin (MT) on gibberellin acid (GA) metabolism during tomato seed germination under Cd2+stress (A) GA content; (B) GA-3-oxidase (GA3ox) activity; (C) GA-20-oxidase (GA20ox) activity; (D) GA-2-oxidase (GA2ox) activity. Different lowercase letters and * indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. Control, Cd2+, and Cd2+/MT are the same as shown in Figure 2.
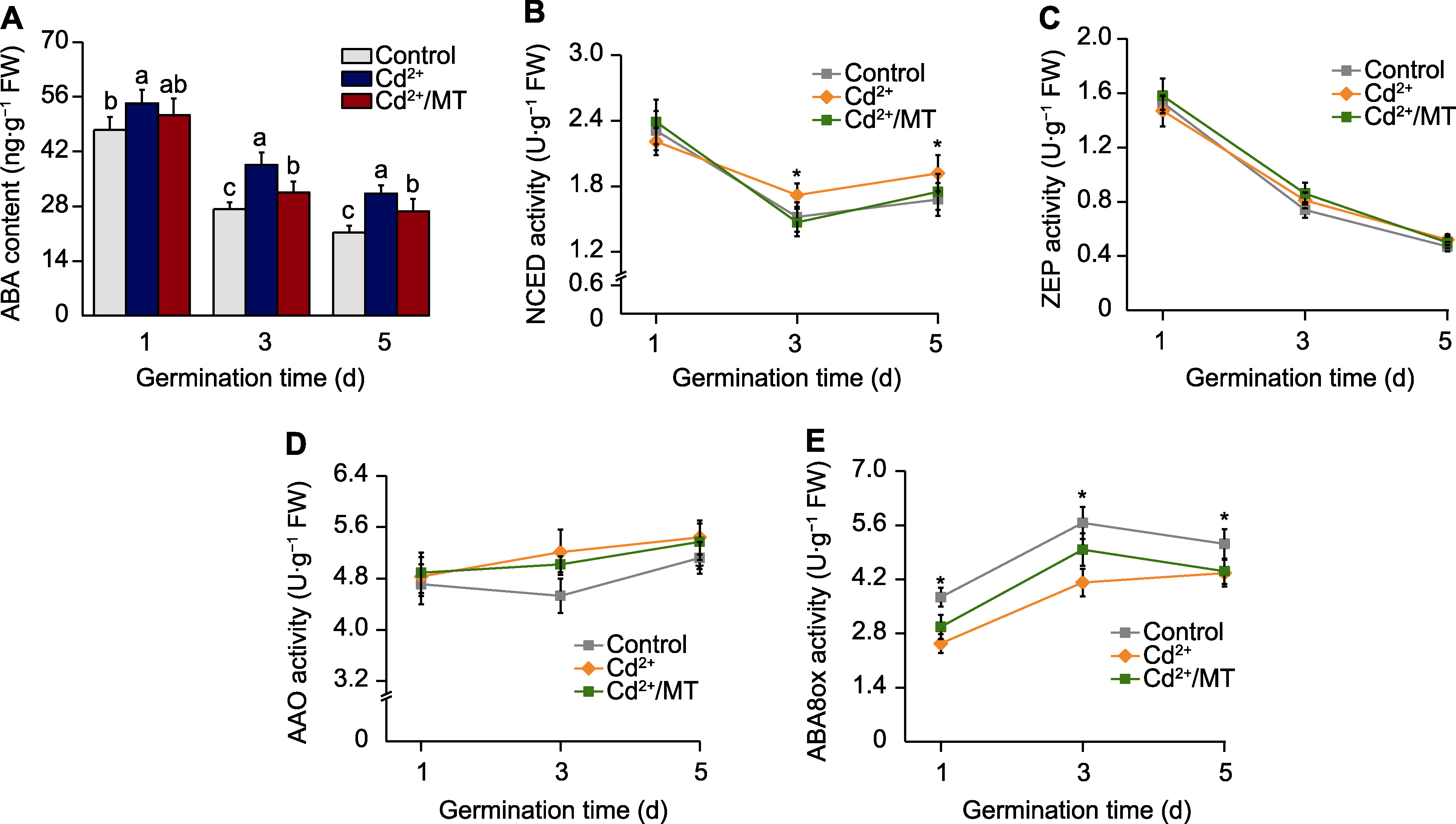
图7 褪黑素(MT)处理对Cd2+胁迫下番茄种子萌发过程中脱落酸(ABA)代谢的影响 (A) ABA含量; (B) 9-顺式-环氧类胡萝卜素二加氧酶(NCED)活性; (C) 玉米黄质环氧化酶(ZEP)活性; (D) 脱落酸醛氧化酶(AAO)活性; (E) 脱落酸-8-羟化酶(ABA8ox)活性。不同小写字母和*表示在0.05水平差异显著。Control、Cd2+和Cd2+/MT同图2。
Figure 7 Effects of melatonin (MT) on abscisic acid (ABA) metabolism during tomato seed germination under Cd2+stress (A) Abscisic acid content; (B) 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED) activity; (C) Zeaxanthin epoxidase (ZEP) activity; (D) ABA-aldehyde oxidase (AAO) activity; (E) ABA-8-hydroxylase (ABA8ox) activity. Different lowercase letters and * indicate significant differences at 0.05 level. Control, Cd2+, and Cd2+/MT are the same as shown in Figure 2.
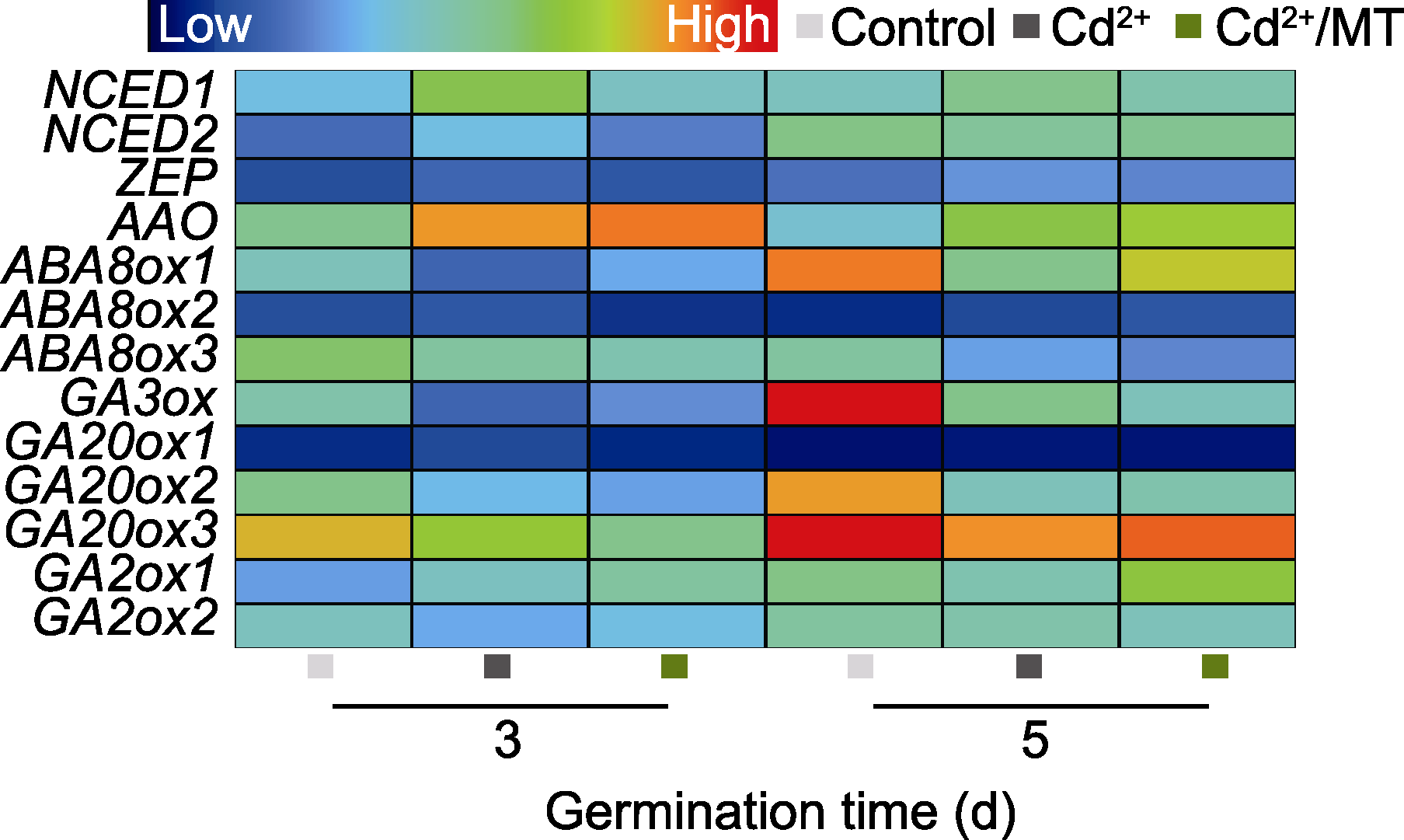
图8 褪黑素(MT)处理对赤霉素(GA)与脱落酸(ABA)代谢基因表达的影响 Control、Cd2+和Cd2+/MT同图2。
Figure 8 Effects of melatonin (MT) on gene expression of gibberellin (GA) and abscisic acid (ABA) metabolism Control, Cd2+, and Cd2+/MT are the same as shown in Figure 2.
| [1] | 安婷婷, 黄帝, 王浩, 张一, 陈应龙 (2021). 植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展. 植物学报 56, 347-362. |
| [2] | 陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 武晓娟, 李永涛 (2019). 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展. 农业环境科学学报 38, 2219-2238. |
| [3] |
李冬, 王艳芳, 王悦华, 温烜琳, 蔡慧英, 郑晓蕾, 陈彤彤, 刘领 (2019). 外源褪黑素对镉胁迫下豌豆种子萌发、幼苗抗性生理及镉含量的影响. 核农学报 33, 2271-2279.
DOI |
| [4] |
刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔 (2022). 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展. 植物学报 57, 111-126.
DOI |
| [5] | 刘仕翔, 黄益宗, 罗泽娇, 黄永春, 保琼莉, 王培培, 袁彪, 李文华 (2016). 外源褪黑素处理对镉胁迫下水稻种子萌发的影响. 农业环境科学学报 35, 1034-1041. |
| [6] | 刘茵, 梁峰 (2021). 不同重金属离子影响下番茄种子的萌发及幼苗生长研究. 安徽农学通报 27(17), 99-101. |
| [7] | 孙淑珍 (2020). 不同小麦品种耐铬(Cr6+)性差异及褪黑素缓解效应. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 22-37. |
| [8] |
王璐瑶, 陈謇, 赵守清, 闫慧莉, 许文秀, 刘若溪, 麻密, 虞轶俊, 何振艳 (2022). 水稻镉积累特性的生理和分子机制研究概述. 植物学报 57, 236-249.
DOI |
| [9] | 张星雨, 叶志彪, 张余洋 (2021). 植物响应镉胁迫的生理与分子机制研究进展. 植物生理学报 57, 1437-1450. |
| [10] | 周明, 李常保 (2022). 我国番茄种业发展现状及展望. 蔬菜 (5), 6-10. |
| [11] |
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2015). Functions of melatonin in plants: a review. J Pineal Res 59, 133-150.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Back K (2021). Melatonin metabolism, signaling and possible roles in plants. Plant J 105, 376-391.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Chen L, Lu B, Liu LT, Duan WJ, Jiang D, Li J, Zhang K, Sun HC, Zhang YJ, Li CD, Bai ZY (2021). Melatonin promotes seed germination under salt stress by regulating ABA and GA3 in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 162, 506-516.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
DalCorso G, Farinati S, Furini A (2010). Regulatory networks of cadmium stress in plants. Plant Signal Behav 5, 663-667.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012). Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83, 33-46. |
| [16] |
Gu Q, Chen ZP, Yu XL, Cui WT, Pan JC, Zhao G, Xu S, Wang R, Shen WB (2017). Melatonin confers plant tolerance against cadmium stress via the decrease of cadmium accumulation and reestablishment of microRNA- mediated redox homeostasis. Plant Sci 261, 28-37.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Hardeland R (2016). Melatonin in plants—diversity of levels and multiplicity of functions. Front Plant Sci 7, 198.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Hasan MK, Ahammed GJ, Yin LL, Shi K, Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Yu JQ, Zhou J (2015). Melatonin mitigates cadmium phytotoxicity through modulation of phytochelatins biosynthesis, vacuolar sequestration, and antioxidant potential in Solanum lycopersicum L. Front Plant Sci 6, 601. |
| [19] |
He JL, Zhuang XL, Zhou JT, Sun LY, Wan HX, Li HF, Lyu DG (2020). Exogenous melatonin alleviates cadmium uptake and toxicity in apple rootstocks. Tree Physiol 40, 746-761.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Huang XY, Deng FL, Yamaji N, Pinson SRM, Fujii-Kashino M, Danku J, Douglas A, Guerinot ML, Salt DE, Ma JF (2016). A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain. Nat Commun 7, 12138.
DOI |
| [21] |
Khan N, You FM, Datla R, Ravichandran S, Jia BS, Cloutier S (2020). Genome-wide identification of ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter and heavy metal associated (HMA) gene families in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). BMC Genomics 21, 722.
DOI |
| [22] |
Li C, Tan DX, Liang D, Chang C, Jia DF, Ma FW (2015). Melatonin mediates the regulation of ABA metabolism, free-radical scavenging, and stomatal behaviour in two Malus species under drought stress. J Exp Bot 66, 669-680.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Li H, Guo YL, Lan ZX, Zhang ZX, Ahammed GJ, Chang JJ, Zhang Y, Wei CH, Zhang X (2021). Melatonin antagonizes ABA action to promote seed germination by regulating Ca2+ efflux and H2O2 accumulation. Plant Sci 303, 110761.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Li MQ, Hasan MK, Li CX, Ahammed GJ, Xia XJ, Shi K, Zhou YH, Reiter RJ, Yu JQ, Xu MX, Zhou J (2016a). Melatonin mediates selenium-induced tolerance to cadmium stress in tomato plants. J Pineal Res 61, 291-302.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Li XN, Tan DX, Jiang D, Liu FL (2016b). Melatonin enhances cold tolerance in drought-primed wild-type and abscisic acid-deficient mutant barley. J Pineal Res 61, 328-339.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Liang CZ, Zheng GY, Li WZ, Wang YQ, Hu B, Wang HR, Wu HK, Qian YW, Zhu XG, Tan DX, Chen SY, Chu CC (2015). Melatonin delays leaf senescence and enhances salt stress tolerance in rice. J Pineal Res 59, 91-101.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆Ct methods. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Lv Y, Pan JJ, Wang HP, Reiter RJ, Li X, Mou ZM, Zhang JM, Yao ZP, Zhao DK, Yu DQ (2021). Melatonin inhibits seed germination by crosstalk with abscisic acid, gibberellin, and auxin in Arabidopsis. J Pineal Res 70, e12736. |
| [29] |
Moustafa-Farag M, Elkelish A, Dafea M, Khan M, Arnao MB, Abdelhamid MT, Abu El-Ezz A, Almoneafy A, Mahmoud A, Awad M, Li LF, Wang YH, Hasanuzzaman M, Ai SY (2020). Role of melatonin in plant tolerance to soil stressors: salinity, pH and heavy metals. Molecules 25, 5359.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Ni J, Wang QJ, Shah FA, Liu WB, Wang DD, Huang SW, Fu SL, Wu LF (2018). Exogenous melatonin confers cadmium tolerance by counterbalancing the hydrogen peroxide homeostasis in wheat seedlings. Molecules 23, 799.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral S, Tan DX, Jou MJ, Galano A, Xu B (2017). Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: one of evolution’s best ideas. Cell Mol Life Sci 74, 3863-3881.
DOI |
| [32] |
Sharma A, Sidhu GPS, Araniti F, Bali AS, Shahzad B, Tripathi DK, Brestic M, Skalicky M, Landi M (2020). The role of salicylic acid in plants exposed to heavy metals. Molecules 25, 540.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Sheteiwy MS, Shao HB, Qi WC, Hamoud YA, Shaghaleh H, Khan NU, Yang RP, Tang BP (2019). GABA-alleviated oxidative injury induced by salinity, osmotic stress and their combination by regulating cellular and molecular signals in rice. Int J Mol Sci 20, 5709.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Tousi S, Zoufan P, Ghahfarrokhie AR (2020). Alleviation of cadmium-induced phytotoxicity and growth improvement by exogenous melatonin pretreatment in mallow (Malva parviflora) plants. Ecotox Environ Saf 206, 111403.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Wang L, Feng C, Zheng XD, Guo Y, Zhou FF, Shan DQ, Liu X, Kong J (2017). Plant mitochondria synthesize melatonin and enhance the tolerance of plants to drought stress. J Pineal Res 63, e12429. |
| [36] |
Wang L, Zhao Y, Reiter RJ, He CJ, Liu GS, Lei Q, Zuo BX, Zheng XD, Li QT, Kong J (2014). Changes in melatonin levels in transgenic ‘Micro-Tom’ tomato overexpressing ovine AANAT and ovine HIOMT genes. J Pineal Res 56, 134-142.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Wang YP, Reiter RJ, Chan Z (2018). Phytomelatonin: a universal abiotic stress regulator. J Exp Bot 69, 963-974.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Wang YS, Yang ZM (2005). Nitric oxide reduces aluminum toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in the roots of Cassia tora L. Plant Cell Physiol 46, 1915-1923.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Wei W, Li QT, Chu YN, Reiter RJ, Yu XM, Zhu DH, Zhang WK, Ma B, Lin Q, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2015). Melatonin enhances plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance in soybean plants. J Exp Bot 66, 695-707.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Yadav SK (2010). Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S Afr J Bot 76, 167-179.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Zhang HJ, Qiu YH, Ji YH, Wu X, Xu XL, Wu P (2023). Melatonin promotes seed germination via regulation of ABA signaling under low temperature stress in cucumber. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 2232-2245.
DOI |
| [42] | Zhang HJ, Zhang N, Yang RC, Wang L, Sun QQ, Li DB, Cao YY, Weeda S, Zhao B, Ren SX, Guo YD (2014). Melatonin promotes seed germination under high salinity by regulating antioxidant systems, ABA and GA4 interaction in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J Pineal Res 57, 269-279. |
| [43] |
Zhang Y, Zhou XJ, Dong YT, Zhang F, He QL, Chen JH, Zhu SJ, Zhao TL (2021). Seed priming with melatonin improves salt tolerance in cotton through regulating photosynthesis, scavenging reactive oxygen species and coordinating with phytohormone signal pathways. Ind Crop Prod 169, 113671.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 周鑫宇, 刘会良, 高贝, 卢妤婷, 陶玲庆, 文晓虎, 张岚, 张元明. 新疆特有濒危植物雪白睡莲繁殖生物学研究[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [2] | 樊蓓, 任敏, 王延峰, 党峰峰, 陈国梁, 程国亭, 杨金雨, 孙会茹. 番茄SlWRKY45转录因子在响应低温和干旱胁迫中的功能(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 186-203. |
| [3] | 孙龙, 李文博, 娄虎, 于澄, 韩宇, 胡同欣. 火干扰对兴安落叶松种子萌发的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(6): 770-779. |
| [4] | 袁涵, 钟爱文, 刘送平, 彭焱松, 徐磊. 水毛花种子萌发特性的差异及休眠解除方法[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(5): 638-650. |
| [5] | 罗燕, 刘奇源, 吕元兵, 吴越, 田耀宇, 安田, 李振华. 拟南芥光敏色素突变体种子萌发的光温敏感性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 752-762. |
| [6] | 赵来鹏, 王柏柯, 杨涛, 李宁, 杨海涛, 王娟, 闫会转. SlHVA22l基因调节番茄耐旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 558-573. |
| [7] | 杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [8] | 朱晓博, 董张, 祝梦瑾, 胡晋, 林程, 陈敏, 关亚静. 重要的种子储存物质长寿命mRNA[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 355-372. |
| [9] | 廖人玉, 王佳伟. 从损伤到重生——REF1小肽如何激发植物的内在再生潜能[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 347-350. |
| [10] | 张琦, 张文静, 袁宪凯, 李明, 赵强, 杜艳丽, 杜吉到. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下普通菜豆芽期核酸修复的调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 108-121. |
| [11] | 郭书亚, 艾金祥, 陈虹宇, 邵烨瑶, 汪妍, 王倩, 叶怡彤, 张雅婷, 丁哲晓, 吴昊辰, 吴玉环, 张建新, 饶米德, 刘鹏. 基于主成分-聚类-逐步回归分析构建番茄苗期耐铝性综合评价体系[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 479-489. |
| [12] | 徐海霞, 何静, 易航, 王丽. 镉胁迫下地钱转录组的性别特异性响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 182-196. |
| [13] | 艾金祥, 宋嘉怡, 严浙楠, 王志超, 陈文倩, 吴玉环, 王燕燕, 潘蕾蕾, 许俞韬, 刘鹏. 褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 171-181. |
| [14] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [15] | 王晓敏, 李洪磊, 王林, 周鹏泽, 白圣懿, 李国花, 郑福顺, 陶小荣, 程国新, 高艳明, 李建设. 银川番茄斑萎病毒的分子鉴定[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(6): 715-721. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||