

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 108-121.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22155 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22155
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
张琦1, 张文静1, 袁宪凯1, 李明1, 赵强1, 杜艳丽1, 杜吉到1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-15
接受日期:2022-10-17
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: djdbynd@163.com
基金资助:
Qi Zhang1, Wenjing Zhang1, Xiankai Yuan1, Ming Li1, Qiang Zhao1, Yanli Du1, Jidao Du1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-07-15
Accepted:2022-10-17
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: djdbynd@163.com
摘要: 普通菜豆(Phaseolus vulgaris)是重要的食用豆作物, 然而其极易受盐胁迫危害, 导致产量下降。褪黑素能提高植物耐盐能力。为探明外源褪黑素调控普通菜豆耐盐能力的机制, 以普通菜豆品种奶花芸豆(GZ-YD014)为实验材料, 设置水(W, 对照)、盐胁迫(S)和盐胁迫+100 µmol∙L-1褪黑素(M+S) 3个处理。结果发现, 盐胁迫抑制了普通菜豆胚根的生长, 使其长度、表面积、体积以及直径显著降低, 外源褪黑素可缓解盐胁迫对普通菜豆胚根生长的抑制。外施褪黑素显著降低盐胁迫下活性氧积累和丙二醛(MDA)含量, 提高保护酶(过氧化物酶、超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶以及抗坏血酸过氧化物酶)活性, 增加渗透调节物质(可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白)以及生长素(IAA)、赤霉素(GA)和玉米素(ZT)的含量, 降低脱落酸(ABA)含量。通过转录组分析挖掘出217个差异表达基因(DEGs), DEGs在GO富集中显著(P-value<0.05)富集到核酸相关条目上, 在KEGG富集中显著(P-value<0.05)富集到核酸损伤修复(包括碱基切除修复、错配修复以及核苷酸切除修复)通路。qRT-PCR以及RAPD分析结果表明, 核酸损伤修复通路为外源褪黑素调控普通菜豆耐盐能力的一种机制。该研究揭示了外源褪黑素对普通菜豆芽期耐盐能力的调控机制, 可为褪黑素应用于盐胁迫下普通菜豆增产提供理论依据。
张琦, 张文静, 袁宪凯, 李明, 赵强, 杜艳丽, 杜吉到. 褪黑素对盐胁迫下普通菜豆芽期核酸修复的调控机制. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 108-121.
Qi Zhang, Wenjing Zhang, Xiankai Yuan, Ming Li, Qiang Zhao, Yanli Du, Jidao Du. The Regulatory Mechanism of Melatonin on Nucleic Acid Repairing of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) at the Sprout Stage Under Salt Stress. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 108-121.
| ID | Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pvactin11-qF | TGCATACGTTGGTGATGAGG |
| 2 | Pvactin11-qR | AGCCTTGGGGTTAAGAGGAG |
| 3 | Phvul.005G021100F | CGTTCTTCCAGTCTTCGTTC |
| 4 | Phvul.005G021100R | TCTCACTTCCCACACCTCAC |
| 5 | Phvul.005G021200F | TGGAGATGGAGAAGCAAGTG |
| 6 | Phvul.005G021200R | AGGCGAGAAAGAGAAACGG |
| 7 | Phvul.005G045900F | TGACTGTAGGCATAGAGGGT |
| 8 | Phvul.005G045900R | GGTCTTGCTAGAAAGAGGTG |
| 9 | Phvul.006G137800F | ACTATGATTGATATGAACGA |
| 10 | Phvul.006G137800R | TTTGACAGACTAATGGAGAC |
表1 qRT-PCR所用引物
Table 1 qRT-PCR primers used in this study
| ID | Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pvactin11-qF | TGCATACGTTGGTGATGAGG |
| 2 | Pvactin11-qR | AGCCTTGGGGTTAAGAGGAG |
| 3 | Phvul.005G021100F | CGTTCTTCCAGTCTTCGTTC |
| 4 | Phvul.005G021100R | TCTCACTTCCCACACCTCAC |
| 5 | Phvul.005G021200F | TGGAGATGGAGAAGCAAGTG |
| 6 | Phvul.005G021200R | AGGCGAGAAAGAGAAACGG |
| 7 | Phvul.005G045900F | TGACTGTAGGCATAGAGGGT |
| 8 | Phvul.005G045900R | GGTCTTGCTAGAAAGAGGTG |
| 9 | Phvul.006G137800F | ACTATGATTGATATGAACGA |
| 10 | Phvul.006G137800R | TTTGACAGACTAATGGAGAC |
| ID | Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Random primer 1 | GGTGCGGGAA |
| 2 | Random primer 2 | GAGAGCCACC |
| 3 | Random primer 3 | GGGATATCGG |
| 4 | Random primer 4 | TGAGCGGACA |
表2 随机扩增多态性DNA (RAPD)引物
Table 2 Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers in this study
| ID | Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Random primer 1 | GGTGCGGGAA |
| 2 | Random primer 2 | GAGAGCCACC |
| 3 | Random primer 3 | GGGATATCGG |
| 4 | Random primer 4 | TGAGCGGACA |
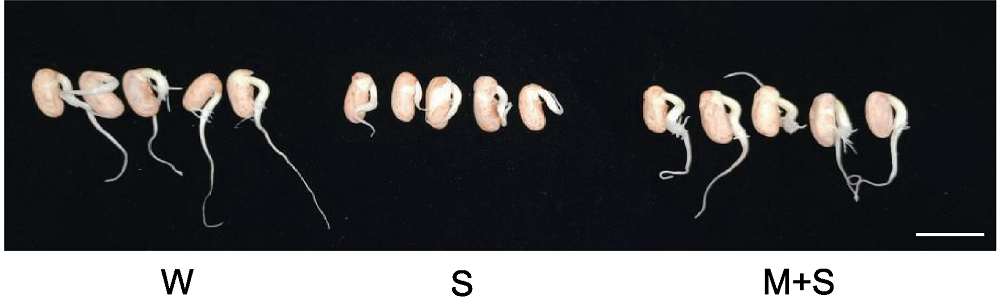
图1 3种处理下普通菜豆芽的表型 W: 对照; S: 盐胁迫; M+S: 褪黑素+盐胁迫。Bar=5 cm
Figure 1 The phenotypes on the sprouts of common bean under three treatments W: Control; S: Salt stress; M+S: Melatonin+salt stress. Bar=5 cm
| Treatments | Length (cm) | Surface area (cm2) | Volume (cm3) | Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 11.917±0.776 a | 2.945±0.283 b | 0.113±0.007 b | 1.266±0.033 a |
| S | 6.122±0.510 b | 1.652±0.244 c | 0.077±0.013 c | 1.013±0.066 b |
| M+S | 12.096±0.975 a | 3.896±0.212 a | 0.138±0.011 a | 1.293±0.051 a |
表3 不同处理下普通菜豆芽的表型分析
Table 3 The phenotypical analysis of common bean sprouts under different treatments
| Treatments | Length (cm) | Surface area (cm2) | Volume (cm3) | Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 11.917±0.776 a | 2.945±0.283 b | 0.113±0.007 b | 1.266±0.033 a |
| S | 6.122±0.510 b | 1.652±0.244 c | 0.077±0.013 c | 1.013±0.066 b |
| M+S | 12.096±0.975 a | 3.896±0.212 a | 0.138±0.011 a | 1.293±0.051 a |
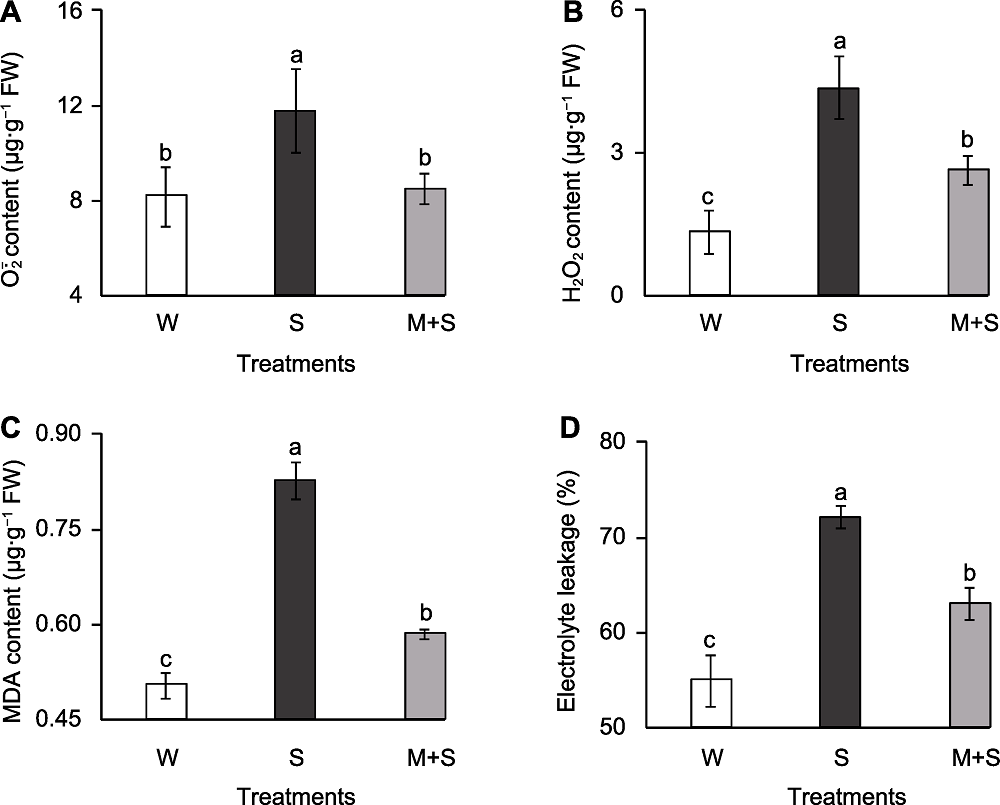
图2 普通菜豆芽膜脂过氧化指标 (A) 超氧阴离子(O2- . )含量; (B) 过氧化氢(H2O2)含量; (C) 丙二醛(MDA)含量; (D) 电导率。W、S和M+S同图1。不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 2 The membrane peroxidation indicators of common bean sprouts (A) O2- . content; (B) H2O2 content; (C) Malondialdehyde (MDA) content; (D) Electrolyte leakage. W, S, and M+S are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
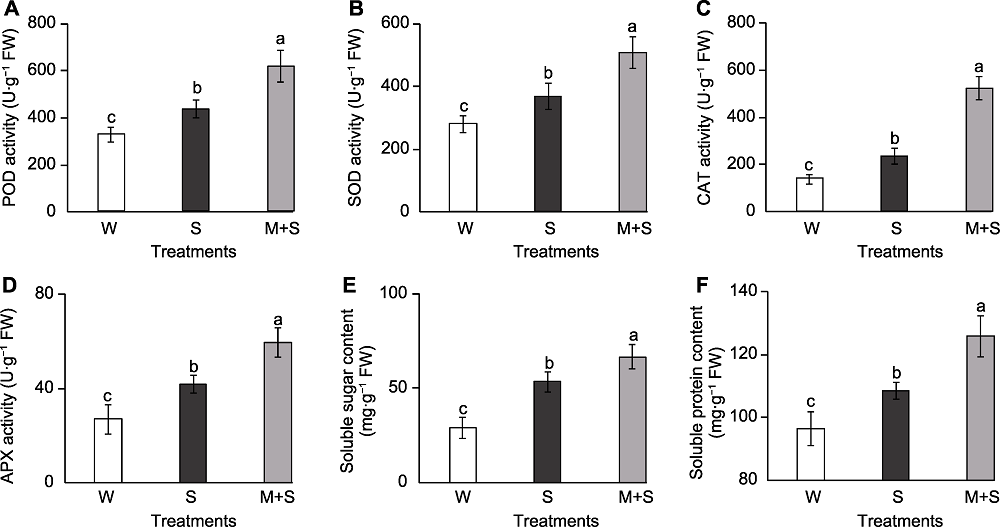
图3 普通菜豆芽抗氧化酶活性和渗透调节物质含量 (A) 过氧化物酶(POD)活性; (B) 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性; (C) 过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性; (D) 抗坏血酸过氧化物酶(APX)活性; (E) 可溶性糖含量; (F) 可溶性蛋白含量。W、S和M+S同图1。不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 3 The antioxidant enzyme activity and osmolyte content of common bean sprouts (A) Peroxidase (POD) activity; (B) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity; (C) Catalase (CAT) activity; (D) Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity; (E) Soluble sugar content; (F) Soluble protein content. W, S, and M+S are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
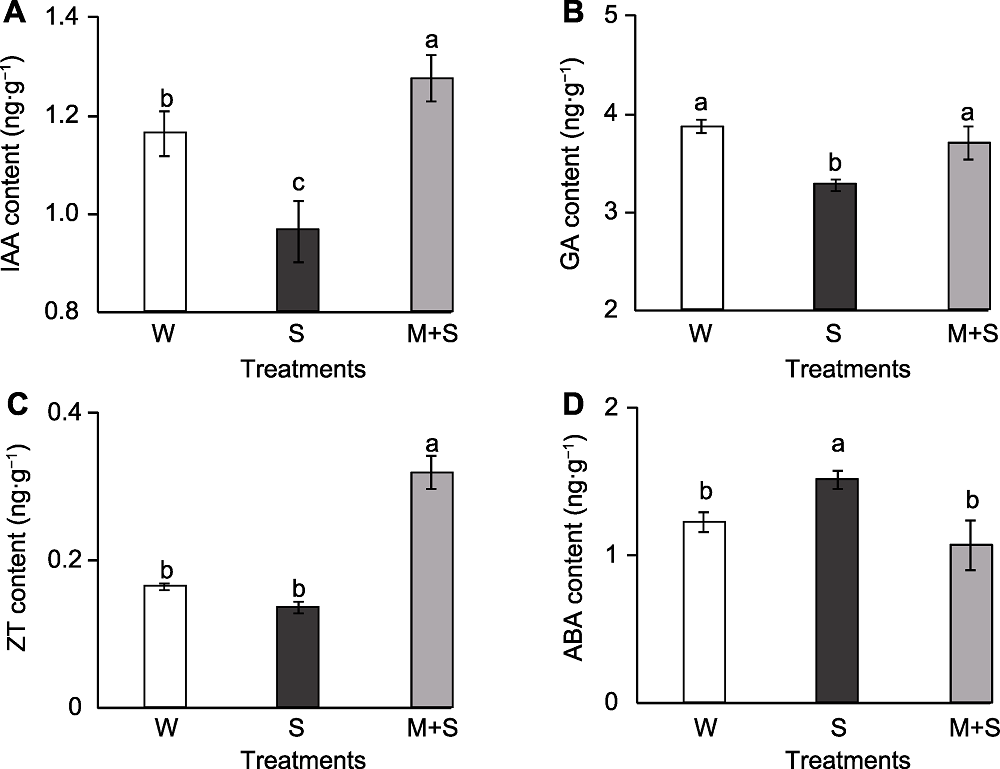
图4 普通菜豆芽内源激素含量 (A) 生长素(IAA)含量; (B) 赤霉素(GA)含量; (C) 玉米素(ZT)含量; (D) 脱落酸(ABA)含量。W、S和M+S同图1。不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 4 The endogenous hormone content of common bean sprouts (A) Auxin (IAA) content; (B) Gibberellin (GA) content; (C) Zeatin (ZT) content; (D) Abscisic acid (ABA) content. W, S, and M+S are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
| ID | Sample name | Raw reads | Clean reads | Error rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | W1 | 55633866 | 53026610 | 0.01 | 96.84 | 92.16 |
| 2 | W2 | 50577884 | 48331946 | 0.02 | 96.69 | 91.84 |
| 3 | W3 | 52446224 | 50061634 | 0.02 | 96.68 | 91.86 |
| 4 | S1 | 41534300 | 40199494 | 0.02 | 94.93 | 88.25 |
| 5 | S2 | 50772136 | 49248286 | 0.02 | 95.10 | 88.47 |
| 6 | S3 | 48326882 | 46935654 | 0.02 | 95.13 | 88.53 |
| 7 | (M+S)1 | 51502046 | 49958064 | 0.02 | 95.08 | 88.43 |
| 8 | (M+S)2 | 51946416 | 50411968 | 0.02 | 94.93 | 88.21 |
| 9 | (M+S)3 | 45445652 | 44010506 | 0.02 | 95.30 | 88.83 |
表4 转录组数据质量评估
Table 4 The assessment of data quality in RNA-Seq
| ID | Sample name | Raw reads | Clean reads | Error rate (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | W1 | 55633866 | 53026610 | 0.01 | 96.84 | 92.16 |
| 2 | W2 | 50577884 | 48331946 | 0.02 | 96.69 | 91.84 |
| 3 | W3 | 52446224 | 50061634 | 0.02 | 96.68 | 91.86 |
| 4 | S1 | 41534300 | 40199494 | 0.02 | 94.93 | 88.25 |
| 5 | S2 | 50772136 | 49248286 | 0.02 | 95.10 | 88.47 |
| 6 | S3 | 48326882 | 46935654 | 0.02 | 95.13 | 88.53 |
| 7 | (M+S)1 | 51502046 | 49958064 | 0.02 | 95.08 | 88.43 |
| 8 | (M+S)2 | 51946416 | 50411968 | 0.02 | 94.93 | 88.21 |
| 9 | (M+S)3 | 45445652 | 44010506 | 0.02 | 95.30 | 88.83 |
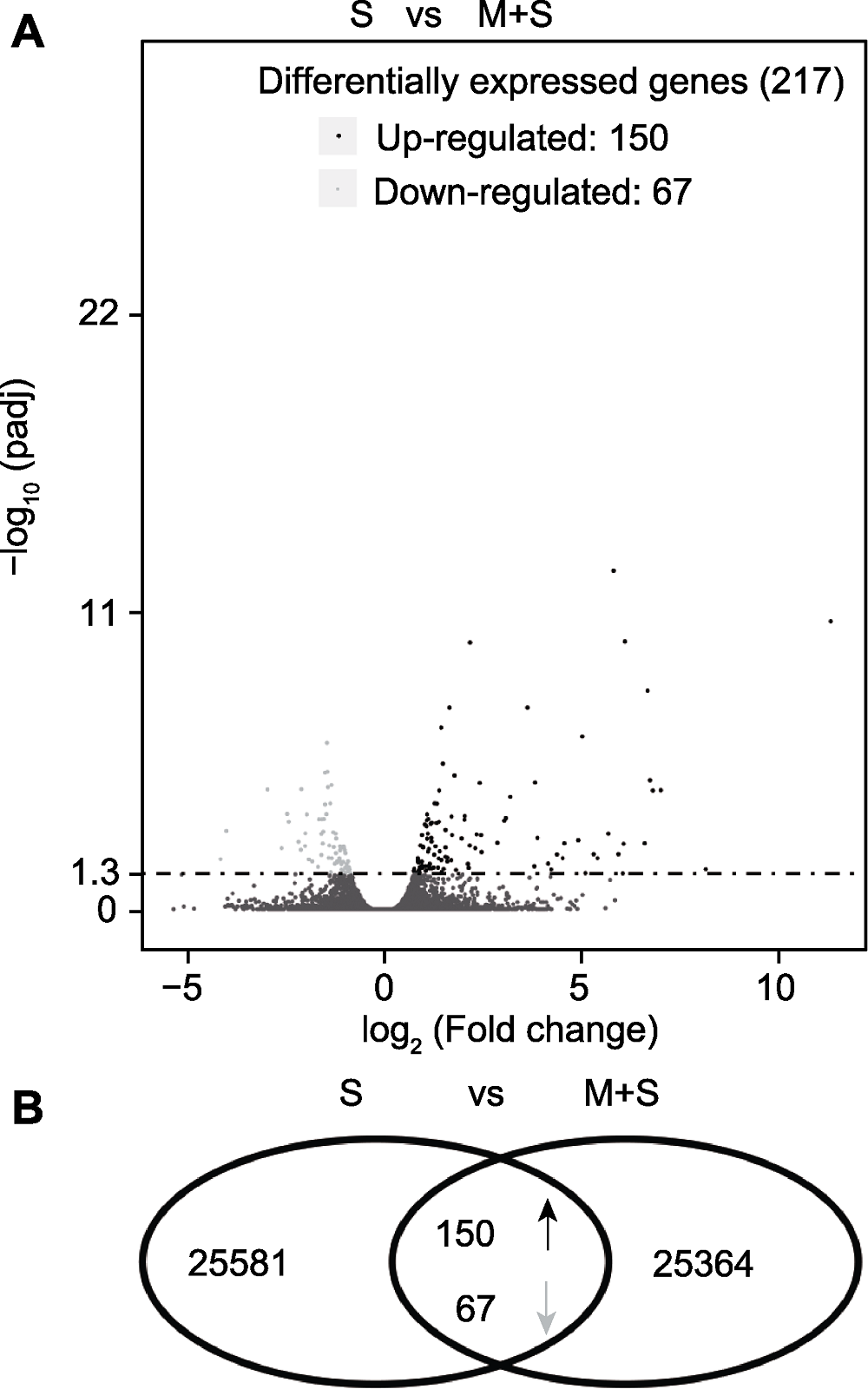
图5 差异表达基因分析 (A) 差异表达基因火山图; (B) 差异表达基因韦恩图。黑色的点和向上箭头代表基因表达上调, 浅灰色的点和向下箭头代表基因表达下调, 虚线下的点代表非差异表达基因。S和M+S同图1。
Figure 5 The analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (A) The volcano plot of DEGs in RNA-Seq; (B) The Venn diagram of DEGs in RNA-Seq. The black dots and up-arrow are up-regulated genes, the light gray dots and down-arrow are down-regulated genes while the dots under dotted line are non-differentially expressed genes. S and M+S are the same as shown in Figure 1.
| ID | GO ID | Enriched pathway | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GO:0009664 | Plant-type cell wall organization | 0.0000 |
| 2 | GO:0071669 | Plant-type cell wall organization or biogenesis | 0.0000 |
| 3 | GO:0005199 | Structural constituent of cell wall | 0.0000 |
| 4 | GO:0030623 | U5 snRNA binding | 0.0000 |
| 5 | GO:0017069 | SnRNA binding | 0.0000 |
| 6 | GO:0071555 | Cell wall organization | 0.0005 |
| 7 | GO:0045229 | External encapsulating structure organization | 0.0006 |
| 8 | GO:0003910 | DNA ligase (ATP) activity | 0.0028 |
| 9 | GO:0071554 | Cell wall organization or biogenesis | 0.0037 |
| 10 | GO:0004448 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase activity | 0.0068 |
| 11 | GO:0004450 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity | 0.0068 |
| 12 | GO:0003909 | DNA ligase activity | 0.0074 |
| 13 | GO:0001539 | Cilium or flagellum-dependent cell motility | 0.0075 |
| 14 | GO:0016886 | Ligase activity, forming phosphoric ester bonds | 0.0087 |
| 15 | GO:0030193 | Regulation of blood coagulation | 0.0096 |
表5 差异表达基因GO富集分析(前15条GO条目)
Table 5 GO enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes (Top15 GO terms)
| ID | GO ID | Enriched pathway | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GO:0009664 | Plant-type cell wall organization | 0.0000 |
| 2 | GO:0071669 | Plant-type cell wall organization or biogenesis | 0.0000 |
| 3 | GO:0005199 | Structural constituent of cell wall | 0.0000 |
| 4 | GO:0030623 | U5 snRNA binding | 0.0000 |
| 5 | GO:0017069 | SnRNA binding | 0.0000 |
| 6 | GO:0071555 | Cell wall organization | 0.0005 |
| 7 | GO:0045229 | External encapsulating structure organization | 0.0006 |
| 8 | GO:0003910 | DNA ligase (ATP) activity | 0.0028 |
| 9 | GO:0071554 | Cell wall organization or biogenesis | 0.0037 |
| 10 | GO:0004448 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase activity | 0.0068 |
| 11 | GO:0004450 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+) activity | 0.0068 |
| 12 | GO:0003909 | DNA ligase activity | 0.0074 |
| 13 | GO:0001539 | Cilium or flagellum-dependent cell motility | 0.0075 |
| 14 | GO:0016886 | Ligase activity, forming phosphoric ester bonds | 0.0087 |
| 15 | GO:0030193 | Regulation of blood coagulation | 0.0096 |
| ID | KEGG ID | Enriched pathway | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pvu04626 | Plant-pathogen interaction | 0.0001 |
| 2 | Pvu03410 | Base excision repair | 0.0020 |
| 3 | Pvu03030 | DNA replication | 0.0044 |
| 4 | Pvu03430 | Mismatch repair | 0.0181 |
| 5 | Pvu04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic re- ticulum | 0.0223 |
| 6 | Pvu00073 | Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | 0.0312 |
| 7 | Pvu03420 | Nucleotide excision repair | 0.0411 |
| 8 | Pvu02010 | ABC transporters | 0.0446 |
表6 差异表达基因KEGG富集分析
Table 6 KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes
| ID | KEGG ID | Enriched pathway | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pvu04626 | Plant-pathogen interaction | 0.0001 |
| 2 | Pvu03410 | Base excision repair | 0.0020 |
| 3 | Pvu03030 | DNA replication | 0.0044 |
| 4 | Pvu03430 | Mismatch repair | 0.0181 |
| 5 | Pvu04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic re- ticulum | 0.0223 |
| 6 | Pvu00073 | Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis | 0.0312 |
| 7 | Pvu03420 | Nucleotide excision repair | 0.0411 |
| 8 | Pvu02010 | ABC transporters | 0.0446 |
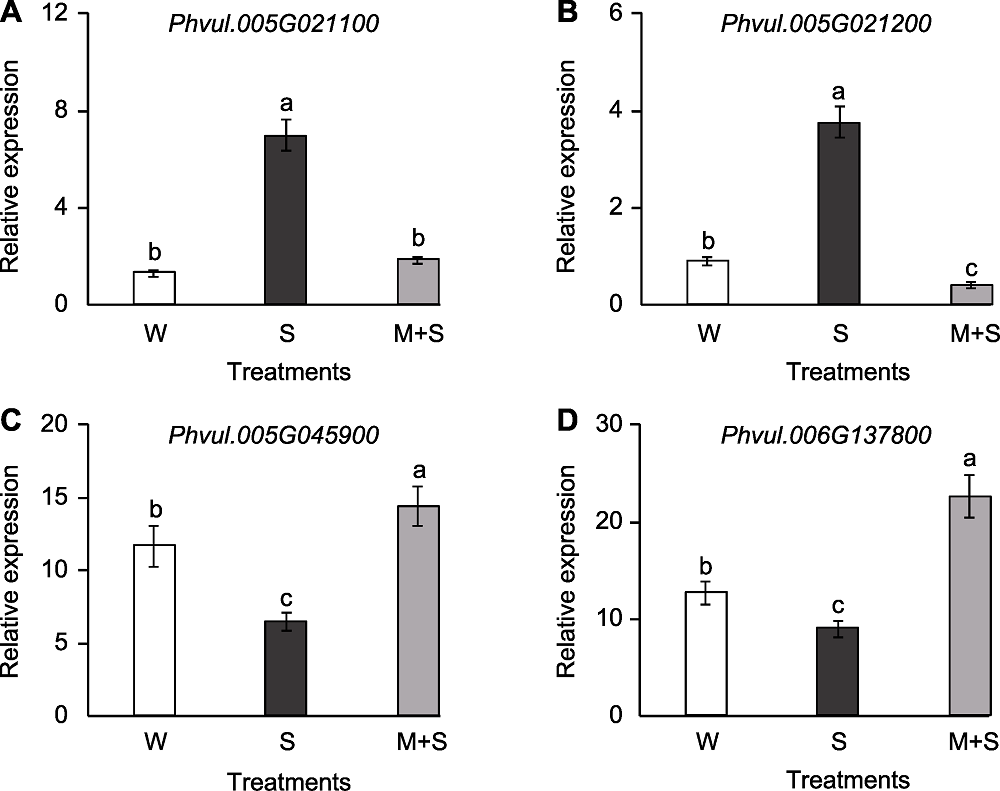
图6 普通菜豆芽期KEGG富集通路的基因表达分析 (A) Phvul.005G021100表达量; (B) Phvul.005G021200表达量; (C) Phvul.005G045900表达量; (D) Phvul.006G137800表达量。W、S和M+S同图1。不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 6 The gene expression analysis in KEGG enrichment pathway of common bean at sprout stage (A) The expression of Phvul.005G021100; (B) The expression of Phvul.005G021200; (C) The expression of Phvul.005G045900; (D) The expression of Phvul.006G137800. W, S, and M+S are the same as shown in Figure 1. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P<0.05).
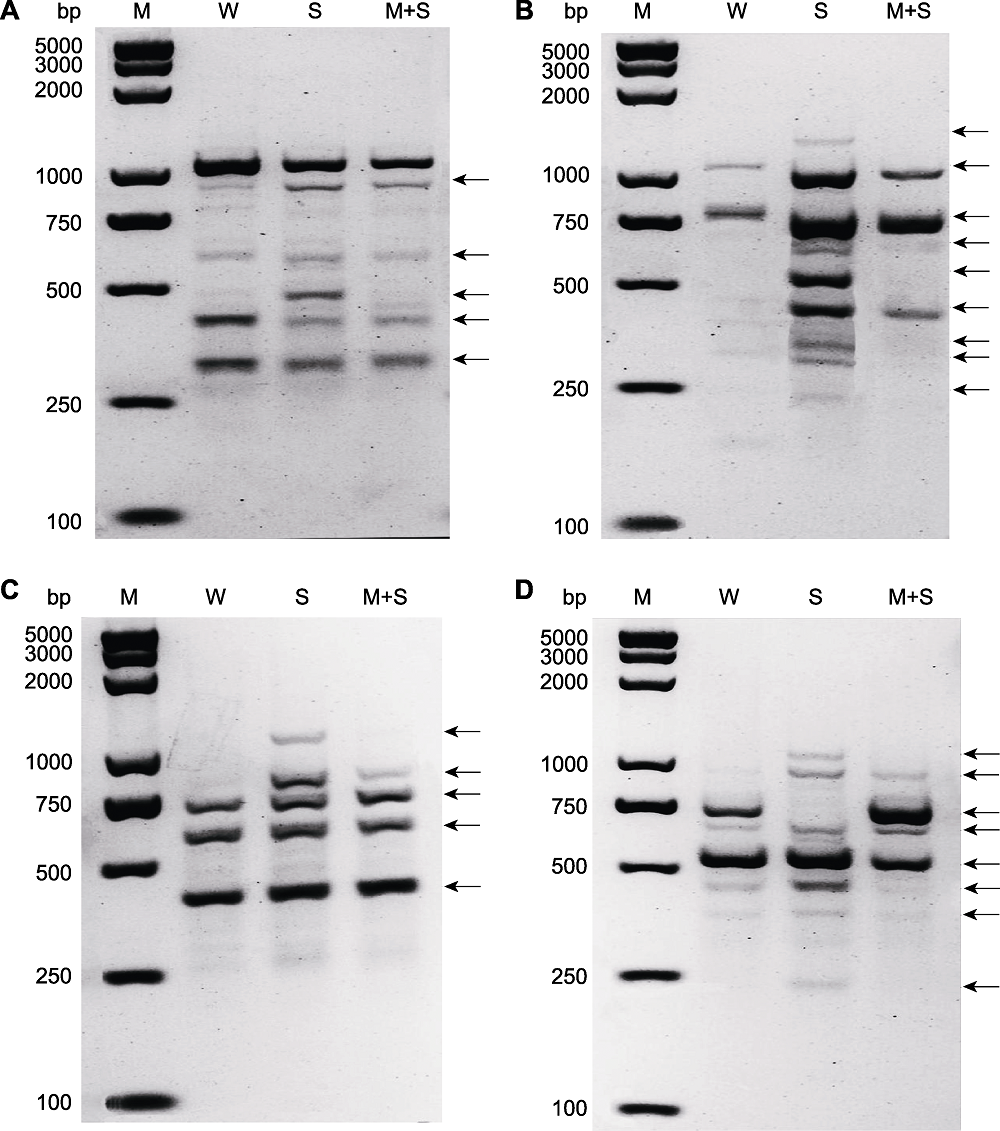
图7 普通菜豆芽期随机扩增多态性DNA (RAPD)分析 利用随机引物1 (A)、随机引物2 (B)、随机引物3 (C)和随机引物4 (D)扩增不同处理下普通菜豆芽的RAPD多态性。W、S和M+S同图1。M代表DL2K plusII, 黑色箭头表示与对照组相比, 处理组在此位点出现的RAPD多态性。
Figure 7 The random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis of common bean at sprout stage Random primer 1 (A), random primer 2 (B), random primer 3 (C) and random primer 4 (D) were used to amplify the RAPD polymorphisms of common bean sprouts in different treatments. W, S, and M+S are the same as shown in Figure 1. M was DL2K plusII marker, while black arrows indicate the RAPD appeared polymorphism at this site in the treatment group compared with the control.
| [1] |
艾金祥, 宋嘉怡, 严浙楠, 王志超, 陈文倩, 吴玉环, 王燕燕, 潘蕾蕾, 许俞韬, 刘鹏 (2022). 褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应. 植物学报 57, 171-181.
DOI |
| [2] | 曹亮 (2020). 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下鼓粒期大豆碳氮代谢及产量品质的调控效应. 博士论文. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学. pp. 21-28. |
| [3] | 陈莉, 刘连涛, 马彤彤, 江丹, 孙红春, 张永江, 张科, 白志英, 李存东 (2019). 褪黑素对盐胁迫下棉花种子抗氧化酶活性及萌发的影响. 棉花学报 31, 438-447. |
| [4] | 陈琼, 韩瑞玺, 唐浩, 刘明月, 黄科, 周义之 (2018). 我国菜豆新品种选育研究现状及展望. 中国种业 (10), 9-14. |
| [5] | 陈瑞, 唐秀梅, 张琪, 杨蓉, 黄蕾蕾, 任晴雯, 朱森林, 刘鹏 (2020). NaCl胁迫对黑小麦根系DNA损伤的影响. 南方农业学报 51, 299-304. |
| [6] | 陈素玉, 赵强, 于高波, 任春元, 张玉先 (2022). 基于RAPD技术分析盐胁迫对大豆幼苗根系DNA的损伤. 生态学杂志 41, 1441-1447. |
| [7] | 何松榆, 秦彬, 张明聪, 金喜军, 王孟雪, 任春元, 张玉先 (2019). 水分胁迫下外源褪黑素对大豆苗期抗氧化特性和产量的影响. 大豆科学 39, 407-412. |
| [8] | 胡涛, 张鸽香, 郑福超, 曹钰 (2018). 植物盐胁迫响应的研究进展. 分子植物育种 16, 3006-3015. |
| [9] |
姜超强, 祖朝龙 (2015). 褪黑素与植物抗逆性研究进展. 生物技术通报 31(4), 47-55.
DOI |
| [10] |
雷新慧, 万晨茜, 陶金才, 冷佳俊, 吴怡欣, 王家乐, 王鹏科, 杨清华, 冯佰利, 高金锋 (2022). 褪黑素与2,4-表油菜素内酯浸种对盐胁迫下荞麦发芽与幼苗生长的促进效应. 作物学报 48, 1210-1221.
DOI |
| [11] |
刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔 (2022). 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展. 植物学报 57, 111-126.
DOI |
| [12] | 栾非时, 祖元刚 (2002). 菜豆种质资源RAPD多样性的研究I. 植物研究 (4), 473-478. |
| [13] | 聂志刚, 王艳, 李韶山 (2009). 重金属诱导拟南芥原生质体DNA损伤的单细胞凝胶电泳检测. 植物学通报 44, 117-123. |
| [14] | 牛远, 杨修艳, 戴存凤, 王博文, 任高磊, 吴静磊, 王飞兵, 陈新红 (2018). 大豆芽期和苗期耐盐性评价指标筛选. 大豆科学 37, 215-223. |
| [15] | 孙浩月 (2021). 盐胁迫对普通菜豆(Phaseolus vulgaris L.)萌发期生长的影响及其耐盐性分子机制. 硕士论文. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学. pp. 9-10. |
| [16] |
孙莎莎, 巩彪, 温丹, 王秀峰, 魏珉, 杨凤娟, 李岩, 史庆华 (2016). 对羟基苯甲酸胁迫下褪黑素对黄瓜胚根生理生化特性的影响. 应用生态学报 27, 897-903.
DOI |
| [17] | 孙玉珺 (2019). 玉米芽期抗冷性筛选及低温胁迫下油菜素内酯对幼苗的调控效应研究. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. pp. 15-16. |
| [18] | 王斌, 张腾霄, 刘超群, 祖余洋, 李艳芳, 孟祥才 (2022). 非生物胁迫对药用植物活性氧代谢影响的研究进展. 现代中药研究与实践 36(3), 94-98. |
| [19] | 王鹤潼, 贾春云, 张延召, 赵强, 李晓军, 巩宗强, 刘宛 (2021). 植物DNA错配修复系统响应Cd胁迫的研究进展. 农业环境科学学报 40, 700-711. |
| [20] |
杨新元 (2019). 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下向日葵幼苗生长、光合及抗氧化系统的影响. 华北农学报 34(4), 113-121.
DOI |
| [21] | 钟鸣, 陈琢, 刘宛, 李培军, 台培东 (2012). 逆境胁迫下植物DNA损伤和DNA错配修复研究进展. 生态学杂志 31, 2404-2411. |
| [22] | 邹京南 (2019). 外源褪黑素对干旱胁迫下大豆光合及生长的影响. 硕士论文. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学. pp. 32-35. |
| [23] |
Arnao MB, Hernández-Ruiz J (2018). Melatonin and its relationship to plant hormones. Ann Bot 121, 195-207.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Beaver JS, Osorno JM (2009). Achievements and limitations of contemporary common bean breeding using conventional and molecular approaches. Euphytica 168, 145-175.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Bray CM, West CE (2005). DNA repair mechanisms in plants: crucial sensors and effectors for the maintenance of genome integrity. New Phytol 168, 511-528.
PMID |
| [26] |
Cakmak I, Marschner H (1992). Magnesium deficiency and high light intensity enhance activities of superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase in bean leaves. Plant Physiol 98, 1222-1227.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Chen K, Li GJ, Bressan RA, Song CP, Zhu JK, Zhao Y (2020). Abscisic acid dynamics, signaling, and functions in plants. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 25-54.
DOI |
| [28] |
Colebrook EH, Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P (2014). The role of gibberellin signaling in plant responses to abiotic stress. J Exp Biol 217, 67-75.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Djanaguiraman M, Sheeba JA, Durga DD, Bangarusamy U (2009). Cotton leaf senescence can be delayed by nitrophenolate spray through enhanced antioxidant defence system. J Agron Crop Sci 195, 213-224.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976). Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammonium chloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70, 616-620.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Farhangi-Abriz S, Torabian S (2017). Antioxidant enzyme and osmotic adjustment changes in bean seedlings as affected by biochar under salt stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137, 64-70.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Ganesan K, Xu BJ (2017). Polyphenol-rich dry common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and their health benefits. Int J Mol Sci 18, 2331.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Han YQ, Gao YM, Li M, Du YL, Zhang YX, Zhang WH, Du JD (2022). The molecular events underpinning cultivar differences in melatonin counteracting salt damage in Phaseolus vulgaris. Funct Plant Biol 49, 201-217.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Jan JE, Reiter RJ, Wasdell MB, Bax M (2009). The role of the thalamus in sleep, pineal melatonin production, and circadian rhythm sleep disorders. J Pineal Res 46, 1-7.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Kaya C, Okant M, Ugurlar F, Alyemeni MN, Ashraf M, Ahmad P (2019). Melatonin-mediated nitric oxide improves tolerance to cadmium toxicity by reducing oxidative stress in wheat plants. Chemosphere 225, 627-638.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Lei YB, Yin CY, Li CY (2006). Differences in some morphological, physiological, and biochemical responses to drought stress in two contrasting populations of Populus przewalskii. Physiol Plant 127, 182-191.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Lerner AB, Case JD, Takahashi Y, Lee TH, Mori W (1958). Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocytes. Am Chem Soc 80, 2587. |
| [38] |
Lin CC, Kao CH (1999). NaCl induced changes in ionically bound peroxidase activity in roots of rice seedlings. Plant Soil 216, 147-153.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Melis JPM, van Steeg H, Luijten M (2013). Oxidative DNA damage and nucleotide excision repair. Antioxid Redox Signal 18, 2409-2419.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Okant M, Kaya C (2019). The role of endogenous nitric oxide in melatonin-improved tolerance to lead toxicity in maize plants. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26, 11864-11874.
DOI |
| [41] |
Patterson BD, MacRae EA, Ferguson IB (1984). Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium (IV). Anal Biochem 139, 487-492.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Popelka JC, Terryn N, Higgins TJV (2004). Gene technology for grain legumes: can it contribute to the food challenge in developing countries? Plant Sci 167, 195-206.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Posmyk MM, Balabusta M, Wieczorek M, Sliwinska E, Janas KM (2009). Melatonin applied to cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seeds improves germination during chilling stress. J Pineal Res 46, 214-223.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antolín I, Herrera F, Martín V, Reiter RJ (2004). Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin. J Pineal Res 36, 1-9.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Scott TL, Rangaswamy S, Wicker CA, Izumi T (2014). Repair of oxidative DNA damage and cancer: recent progress in DNA base excision repair. Antioxid Redox Signal 20, 708-726.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Shabala S (2013). Learning from halophytes: physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Ann Bot 112, 1209-1221.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Sharif R, Xie C, Zhang HQ, Arnao MB, Ali M, Ali Q, Muhammad I, Shalmani A, Nawaz MA, Chen P, Li YH (2018). Melatonin and its effects on plant systems. Molecules 23, 2352.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Singh KP, Roy D (2001). Identification of novel breast tumor- specific mutation(s) in the q11.2 region of chromosome 17 by RAPD/AP-PCR fingerprinting. Gene 269, 33-43.
PMID |
| [49] |
Singh KP, Roy D (2004). Somatic mutations in stilbene estrogen-induced Syrian hamster kidney tumors identified by DNA fingerprinting. J Carcinog 3, 4.
PMID |
| [50] |
Strother S (1988). The role of free radicals in leaf senescence. Gerontology 34, 151-156.
PMID |
| [51] |
Sun CL, Liu LJ, Wang LX, Li BH, Jin CW, Lin XY (2021). Melatonin: a master regulator of plant development and stress responses. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 126-145.
DOI |
| [52] | Sun CL, Lv T, Huang L, Liu XX, Jin CW, Lin XY (2020). Melatonin ameliorates aluminum toxicity through enhancing aluminum exclusion and reestablishing redox homeo- stasis in roots of wheat. J Pineal Res 68, e12642. |
| [53] |
Sun YL, Li F, Su N, Sun XL, Zhao SJ, Meng QW (2010). The increase in unsaturation of fatty acids of phosphatidylglycerol in thylakoid membrane enhanced salt tolerance in tomato. Photosynthetica 48, 400-408.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Ubbens J, Cieslak M, Prusinkiewicz P, Stavness I (2018). The use of plant models in deep learning: an application to leaf counting in rosette plants. Plant Methods 14, 6.
DOI PMID |
| [55] |
Vafadar F, Amooaghaie R, Ehsanzadeh P, Ghanati F, Sajedi RH (2020). Crosstalk between melatonin and Ca2+/ CaM evokes systemic salt tolerance in Dracocephalum kotschyi. J Plant Physiol 252, 153237.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Wang H, Takano T, Liu SK (2018). Screening and evaluation of saline-alkaline tolerant germplasm of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in soda saline-alkali soil. Agronomy 8, 205.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Wang LQ, Li Z, Lu MZ, Wang YC (2017). ThNAC13, a NAC transcription factor from Tamarix hispida, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance to transgenic Tamarix and Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8, 635.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Yang YR, Cao YP, Li ZX, Zhukova A, Yang ST, Wang JL, Tang ZH, Cao YH, Zhang YF, Wang DL (2020). Interactive effects of exogenous melatonin and Rhizophagus intraradices on saline-alkaline stress tolerance in Leymus chinensis. Mycorrhiza 30, 357-371.
DOI |
| [59] |
Zahedi SM, Hosseini MS, Abadía J, Marjani M (2020). Melatonin foliar sprays elicit salinity stress tolerance and enhance fruit yield and quality in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.). Plant Physiol Biochem 149, 313-323.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Zhan HS, Nie XJ, Zhang T, Li S, Wang XY, Du XH, Tong W, Song WN (2019). Melatonin: a small molecule but important for salt stress tolerance in plants. Int J Mol Sci 20, 709.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Zhang JL, Wang P, Long HY, Su SS, Wu YG, Wang HR (2022). Metabolomics analysis reveals the physiological mechanism underlying growth restriction in maize roots under continuous negative pressure and stable water sup- ply. Agric Water Manag 263, 107452.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
Zhang Q, Li M, Xia CY, Zhang WJ, Yin ZG, Zhang YL (2021). Transcriptome-based analysis of salt-related genes during the sprout stage of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under salt stress conditions. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 35, 1086-1098.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
Zhang Q, Zhang WJ, Yin ZG, Li WJ, Zhao HH, Zhang S, Zhuang L, Wang YX, Zhang WH, Du JD (2020). Genome- and transcriptome-wide identification of C3Hs in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and structural and expression-based analyses of their functions during the sprout stage under salt-stress conditions. Front Genet 11, 564607.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Zhao Q, Chen SY, Wang GD, Du YL, Zhang ZN, Yu GB, Ren CY, Zhang YX, Du JD (2022). Exogenous melatonin enhances soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) seedling tolerance to saline-alkali stress by regulating antioxidant response and DNA damage repair. Physiol Plant 174, e13731. |
| [65] |
Zhao Q, Wang HT, Du YL, Rogers HJ, Wu ZX, Jia S, Yao XD, Xie FT, Liu W (2020). MSH2 and MSH6 in mismatch repair system account for soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) tolerance to cadmium toxicity by determining DNA damage response. J Agric Food Chem 68, 1974-1985.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 徐田甜, 杨培建, 周晓茜, 曹怡, 陈艳红, 刘国元, 张健, 魏辉. 紫薇GolS家族基因的理化特性与表达特征[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 393-406. |
| [2] | 杜锦瑜, 孙震, 苏彦龙, 王贺萍, 刘亚玲, 吴振映, 何峰, 赵彦, 付春祥. 蒙古冰草咖啡酸氧甲基转移酶基因AmCOMT1的鉴定及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 383-396. |
| [3] | 蔡淑钰, 刘建新, 王国夫, 吴丽元, 宋江平. 褪黑素促进镉胁迫下番茄种子萌发的调控机理[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 720-732. |
| [4] | 李晓明, 王兰芬, 唐永生, 常玉洁, 张菊香, 王述民, 武晶. 普通菜豆抗菜豆象性状的全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 77-89. |
| [5] | 王菲菲, 周振祥, 洪益, 谷洋洋, 吕超, 郭宝健, 朱娟, 许如根. 大麦NF-YC基因鉴定及在盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 140-149. |
| [6] | 李园, 常玉洁, 王兰芬, 王述民, 武晶. 普通菜豆镰孢菌枯萎病抗性种质资源筛选及全基因组关联分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 51-61. |
| [7] | 艾金祥, 宋嘉怡, 严浙楠, 王志超, 陈文倩, 吴玉环, 王燕燕, 潘蕾蕾, 许俞韬, 刘鹏. 褪黑素对铅胁迫下虎舌红和朱砂根生理响应及DNA损伤的调控效应[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 171-181. |
| [8] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| [9] | 王研, 贾博为, 孙明哲, 孙晓丽. 野生大豆耐逆分子调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 104-115. |
| [10] | 张春艳. P700氧化还原动力学的测量方法及原理[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 740-748. |
| [11] | 张楠,刘自广,孙世臣,刘圣怡,林建辉,彭疑芳,张晓旭,杨贺,岑曦,吴娟. 拟南芥AtR8 lncRNA对盐胁迫响应及其对种子萌发的调节作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 421-429. |
| [12] | 曹栋栋,陈珊宇,秦叶波,吴华平,阮关海,黄玉韬. 水杨酸调控盐胁迫下羽衣甘蓝种子萌发的机理[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 49-61. |
| [13] | 张静,侯岁稳. 蛋白质翻译后修饰在ABA信号转导中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 300-315. |
| [14] | 栗露露,殷文超,牛梅,孟文静,张晓星,童红宁. 油菜素甾醇调控水稻盐胁迫应答的作用研究[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 185-193. |
| [15] | 秦童,黄震,康振辉. 叶绿体硫氧还蛋白系统的调节机制[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 119-132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||