

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 300-315.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18217 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18217
张静,侯岁稳
收稿日期:2018-10-18
接受日期:2019-01-02
出版日期:2019-05-01
发布日期:2019-11-24
通讯作者:
侯岁稳
基金资助:Jing Zhang,Suiwen Hou
Received:2018-10-18
Accepted:2019-01-02
Online:2019-05-01
Published:2019-11-24
Contact:
Suiwen Hou
摘要: 脱落酸(ABA)是植物生长发育和逆境适应过程中非常关键的植物激素。植物响应ABA信号转导过程由信号识别、转导及响应级联完成, 其中心转导途径由ABA受体RCAR/PYR/PYLs、磷酸酶PP2Cs、激酶SnRK2s、转录因子和离子通道蛋白构成。蛋白磷酸化、泛素化、类泛素化和氧化还原等翻译后修饰在ABA转导途径中起重要作用。该文综述了翻译后修饰在ABA信号转导中的作用。
张静,侯岁稳. 蛋白质翻译后修饰在ABA信号转导中的作用. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 300-315.
Jing Zhang,Suiwen Hou. Role of Post-translational Modification of Proteins in ABA Signaling Transduction. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(3): 300-315.
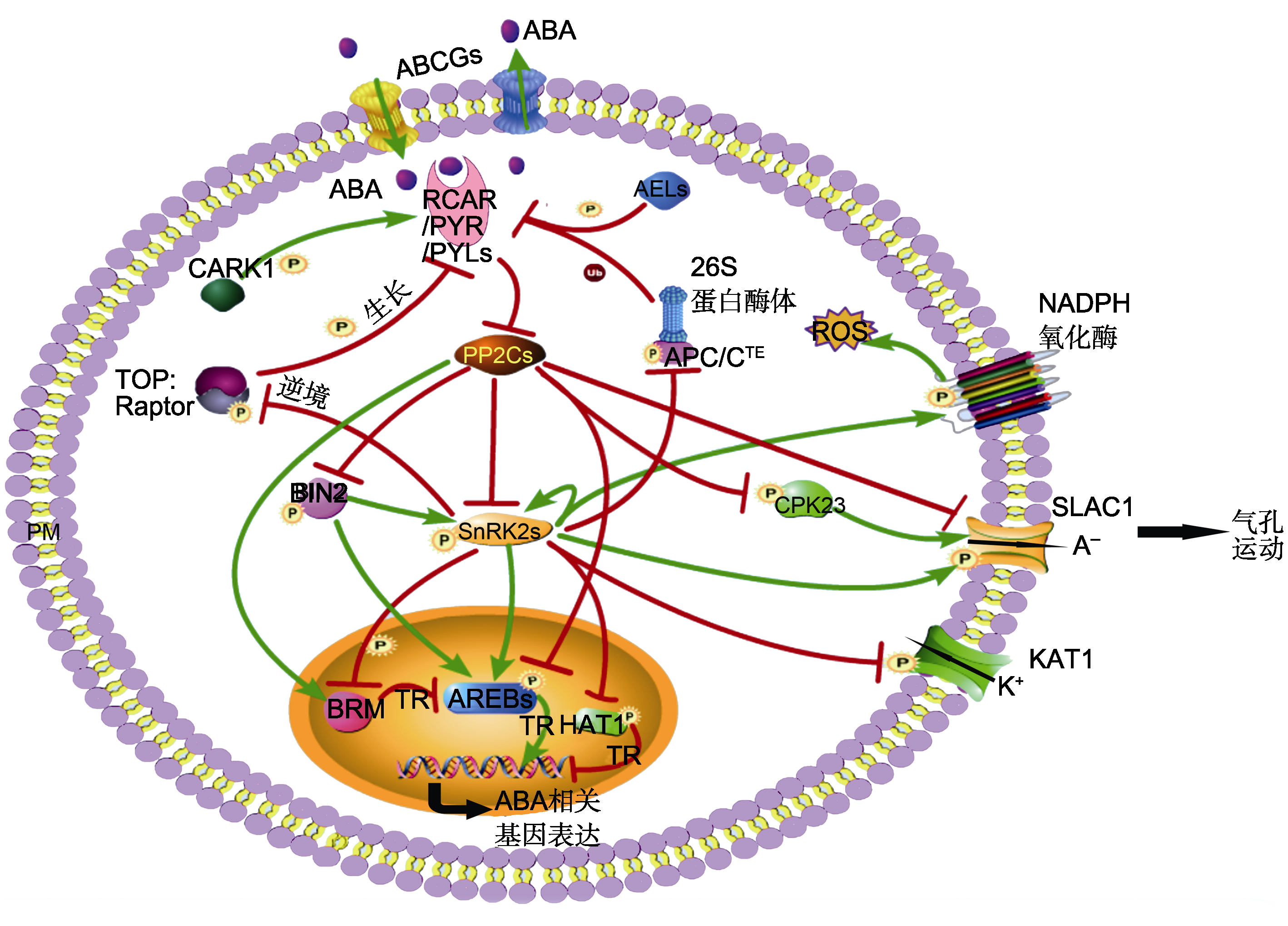
图1 磷酸化修饰在ABA信号中的作用 ABA的转运由运输载体如AtABCGs完成, 其转导途径由受体RCAR/PYR/PYLs、磷酸酶PP2Cs、激酶SnRK2s以及SnRK2s的底物等组成。转录因子(AREBs和HAT1)、膜蛋白(SLAC1、KAT1和NADPH氧化酶)、DNA解旋酶BRM、TOR激酶复合体和APC/C泛素复合体被SnRK2s磷酸化, 其中AREBs、BRM和SLAC1被PP2Cs去磷酸化。激酶BIN2是整合BR信号通路和ABA信号通路的关键因子。TOR激酶复合体与ABA信号相互拮抗调节植物生长与逆境响应。钙调激酶CPK23独立于SnRK2s参与气孔运动。激酶CARK1和AEL1磷酸化ABA受体PYR1的不同位点引起相反结果。绿色箭头表示促进作用; 红色T型线表示抑制作用。PM: 细胞膜; P: 磷酸化; Ub: 泛素化; A-: 阴离子; ROS: 活性氧; TR: 转录调控
Figure 1 The regulatory roles of protein phosphorylation in coreABA signaling ABA transport is performed by transporters, such as AtABCGs. The core ABA signaling pathway is composed of RCAR/PYR/PYLs, PP2Cs, SnRK2s, and the substrates of SnRK2s. The substrates of SnRK2s include AREBs, HAT1, SLAC1, KAT1, NADPH oxidases, BRM, TOR complex, and APC/C complex. AREBs, BRM and SLAC1 can be dephosphorylated by PP2Cs. BIN2 is a key factor that integrates BR and ABA signaling pathway. The TOR complex and ABA signaling antagonistically regulates plant growth and stress response. CPK23 is independent of SnRK2s in stomatal movement. Different phosphorylation sites of ABA receptor PYR1 by CARK1 and AEL1 give opposite results. Green arrows represent promotion; Red T-shaped bars represent repression. PM: Plasma membrane; P: Phosphorylation; Ub: Ubiquitination; A-: Negative ions; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TR: Transcriptional regulation
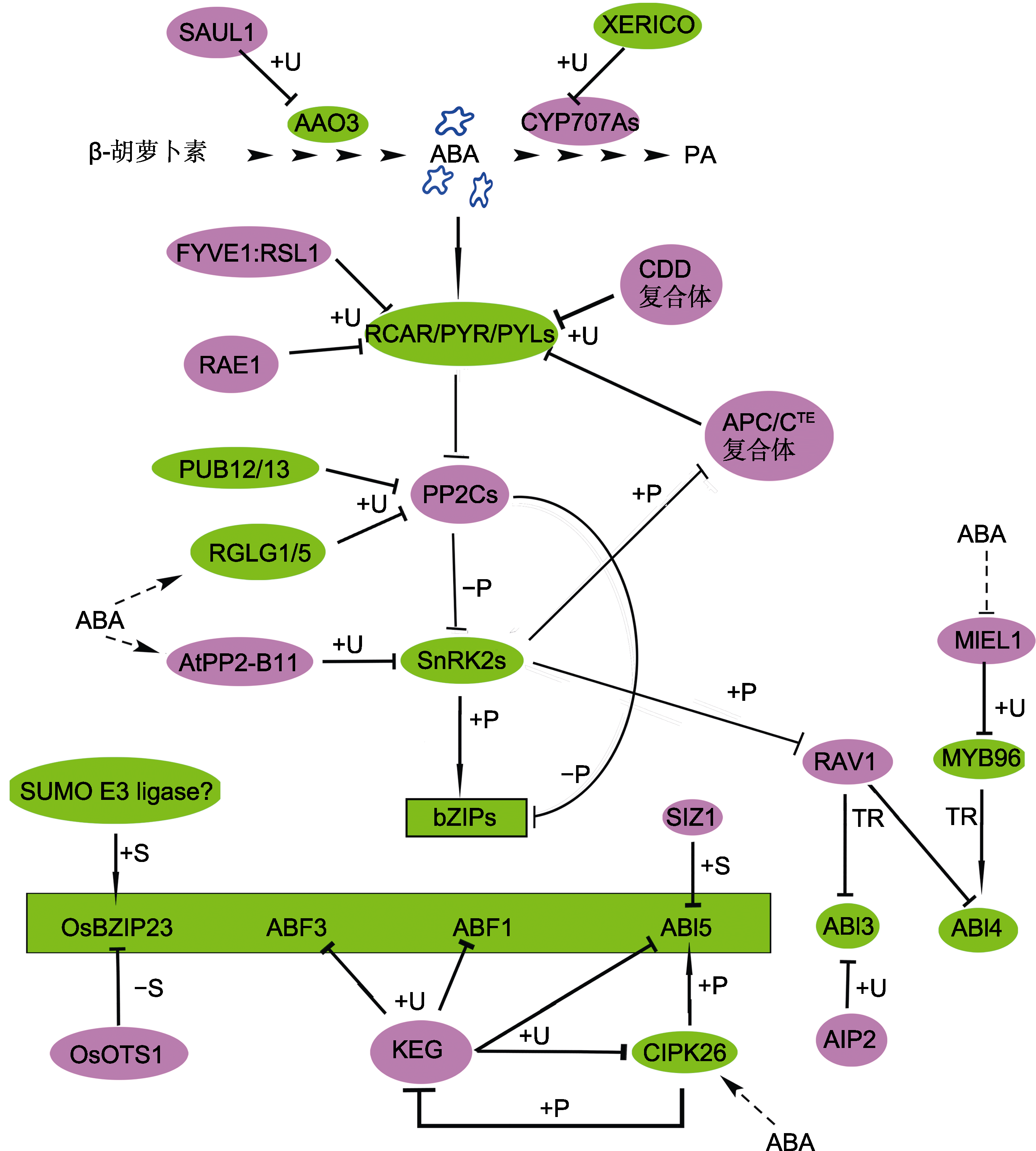
图2 蛋白泛素化和SUMO化修饰调节ABA合成代谢、识别、转导和响应AAO3和CYP707A分别是ABA的合成酶和氧化酶。ABA中心转导途径由RCAR/PYR/PYLs-PP2Cs-SnRK2s-bZIPs组成。图中bZIPs代表OsBZIP23、ABF3、ABF1和ABI5 (绿色背景方框内)。红色背景中蛋白是ABA信号的负调节因子; 绿色背景中蛋白是ABA信号的正调节因子。箭头表示促进作用; T型线表示抑制作用; 实线表示有直接的互作关系; 虚线和?表示具体过程未知。+/-P: 磷酸化/去磷酸化; +U: 泛素化; +/-S: SUMO/去SUMO化; TR: 转录调控
Figure 2 Protein ubiquitination and sumoylation regulate ABA biosynthesis and catabolism, ABA perception, signal transduction and responsesAAO3 and CYP707A are ABA synthase and oxidase enzyme, respectively. The core ABA signaling pathway is composed of RCAR/PYR/PYLs-PP2Cs-SnRK2s-bZIPs. In this figure, bZIPs represent OsBZIP23, ABF3, ABF1 and ABI5 (inside the box on the green background). The proteins in the red (green) background are negative (positive) factors in ABA signaling. Arrows represent promotion; T-shaped bars represent repression; The solid line indicates direct interaction; Dotted lines and ? represent uncon?rmed. +/-P: Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation; +U: Ubiquitination; +/-S: SUMOylation/de-SUMOylation; TR: Transcriptional regulation
| [1] | 韩丹璐, 赖建彬, 阳成伟 ( 2018). SUMO E3连接酶在植物生长发育中的功能研究进展. 植物学报 53, 175-184. |
| [2] |
王宇, 何奕騉 ( 2017). 一氧化氮介导蛋白质亚硝基化与甲基化协调植物非生物胁迫的分子机制. 植物学报 52, 681-684.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
伍静辉, 谢楚萍, 田长恩, 周玉萍 ( 2018). 脱落酸调控种子休眠和萌发的分子机制. 植物学报 53, 542-555.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Albertos P, Romero-Puertas MC, Tatematsu K, Mateos I, Sánchez-Vicente I, Nambara E, Lorenzo O ( 2015). S-nitrosylation triggers ABI5 degradation to promote seed germination and seedling growth. Nat Commun 6, 8669.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
Antoni R, Gonzalez-Guzman M, Rodriguez L, Rodrigues A, Pizzio GA, Rodriguez PL ( 2012). Selective inhibition of clade A phosphatases type 2C by PYR/PYL/RCAR abscisic acid receptors. Plant Physiol 158, 970-980.
DOI URL PMID |
| [6] |
Arc E, Sechet J, Corbineau F, Rajjou L, Marion-Poll A ( 2013). ABA crosstalk with ethylene and nitric oxide in seed dormancy and germination. Front Plant Sci 4, 63.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Augustine RC, Vierstra RD ( 2018). SUMOylation: re-wiring the plant nucleus during stress and development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 45, 143-154.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Batistič O, Rehers M, Akerman A, Schlücking K, Steinhorst L, Yalovsky S, Kudla J ( 2012). S-acylation- dependent association of the calcium sensor CBL2 with the vacuolar membrane is essential for proper abscisic acid responses. Cell Res 22, 1155-1168.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Begara-Morales JC, Chaki M, Valderrama R, Sanchez- Calvo B, Mata-Pérez C, Padilla MN, Corpas FJ, Barroso JB ( 2018). Nitric oxide buffering and conditional nitric oxide release in stress response. J Exp Bot 69, 3425-3438.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Belda-Palazon B, Rodriguez L, Fernandez MA, Castillo MC, Anderson EM, Gao C, Gonzalez-Guzman M, Peirats-Llobet M, Zhao Q, De Winne N, Gevaert K, De Jaeger G, Jiang L, León J, Mullen RT, Rodriguez PL ( 2016). FYVE1/FREE1 interacts with the PYL4 ABA receptor and mediates its delivery to the vacuolar degradation pathway. Plant Cell 28, 2291-2311.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Belin C, de Franco PO, Bourbousse C, Chaignepain S, Schmitter JM, Vavasseur A, Giraudat J, Barbier- Brygoo H, Thomine S ( 2006). Identification of features regulating OST1 kinase activity and OST1 function in guard cells. Plant Physiol 141, 1316-1327.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Belkhadir Y, Jaillais Y ( 2015). The molecular circuitry of brassinosteroid signaling. New Phytol 206, 522-540.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Bhatnagar N, Min MK, Choi EH, Kim N, Moon SJ, Yoon I, Kwon T, Jung KH, Kim BG ( 2017). The protein phosphatase 2C clade A protein OsPP2C51 positively regulates seed germination by directly inactivating OsbZIP10. Plant Mol Biol 93, 389-401.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] | Brady SM, Sarkar SF, Bonetta D, McCourt P ( 2003). The ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 3 (ABI3) gene is modulated by farnesylation and is involved in auxin signaling and lateral root development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 34, 67-75. |
| [15] |
Brandt B, Brodsky DE, Xue S, Negi J, Iba K, Kangasjarvi J, Ghassemian M, Stephan AB, Hu H, Schroeder JI ( 2012). Reconstitution of abscisic acid activation of SLAC1 anion channel by CPK6 and OST1 kinases and branched ABI1 PP2C phosphatase action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 10593-10598.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
Brugiére N, Zhang W, Xu Q, Scolaro EJ, Lu C, Kahsay RY, Kise R, Trecker L, Williams RW, Hakimi S, Niu X, Lafitte R, Habben JE ( 2017). Overexpression of RING domain E3 ligase ZmXERICO1 confers drought tolerance through regulation of ABA homeostasis. Plant Physiol 175, 1350-1369.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Bueso E, Rodriguez L, Lorenzo-Orts L, Gonzalez- Guzman M, Sayas E, Munoz-Bertomeu J, Ibañez C, Serrano R, Rodriguez PL ( 2014). The single-subunit RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase RSL1 targets PYL4 and PYR1 ABA receptors in plasma membrane to modulate abscisic acid signaling. Plant J 80, 1057-1071.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Cai Z, Liu J, Wang H, Yang C, Chen Y, Li Y, Pan S, Dong R, Tang G, Barajas-Lopez JDD, Fujii H, Wang X ( 2014). GSK3-like kinases positively modulate abscisic acid signaling through phosphorylating subgroup III SnRK2s in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 9651-9656.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Castillo MC, Lozano-Juste J, González-Guzmán M, Rodriguez L, Rodriguez PL, León J ( 2015). Inactivation of PYR/PYL/RCAR ABA receptors by tyrosine nitration may enable rapid inhibition of ABA signaling by nitric oxide in plants. Sci Signal 8, ra89.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Castro PH, Couto D, Freitas S, Verde N, Macho AP, Huguet S, Botella MA, Ruiz-Albert J, Tavares RM, Bejarano ER, Azevedo H ( 2016). SUMO proteases ULP1c and ULP1d are required for development and osmotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 92, 143-159.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
Castro PH, Tavares RM, Bejarano ER, Azevedo H ( 2012). SUMO, a heavyweight player in plant abiotic stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 69, 3269-3283.
DOI URL PMID |
| [22] |
Catala R, Ouyang J, Abreu IA, Hu Y, Seo H, Zhang X, Chua NH ( 2007). The Arabidopsis E3 SUMO ligase SIZ1 regulates plant growth and drought responses. Plant Cell 19, 2952-2966.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Chen HH, Qu L, Xu ZH, Zhu JK, Xue HW ( 2018). EL1-like casein kinases suppress ABA signaling and responses by phosphorylating and destabilizing the ABA receptors PYR/PYLs in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 11, 706-719.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
Chen L, Lee JH, Weber H, Tohge T, Witt S, Roje S, Fernie AR, Hellmann H ( 2013a) . Arabidopsis BPM proteins function as substrate adaptors to a cullin3-based E3 ligase to affect fatty acid metabolism in plants. Plant Cell 25, 2253-2264.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] |
Chen YT, Liu H, Stone S, Callis J ( 2013b) . ABA and the ubiquitin E3 ligase KEEP ON GOING affect proteolysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factors ABF1 and ABF3. Plant J 75, 965-976.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Cheng C, Wang Z, Ren Z, Zhi L, Yao B, Su C, Liu L, Li X ( 2017). SCFAtPP2-B11 modulates ABA signaling by facilitating SnRK2.3 degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 13, e1006947. |
| [27] |
Cheng MC, Hsieh EJ, Chen JH, Chen HY, Lin TP ( 2012). Arabidopsis RGLG2, functioning as a RING E3 ligase, interacts with AtERF53 and negatively regulates the plant drought stress response. Plant Physiol 158, 363-375.
DOI URL PMID |
| [28] |
Choi HI, Park HJ, Park JH, Kim S, Im MY, Seo HH, Kim YW, Hwang I, Kim SY ( 2005). Arabidopsis calcium- dependent protein kinase AtCPK32 interacts with ABF4, a transcriptional regulator of abscisic acid-responsive gene expression, and modulates its activity. Plant Physiol 139, 1750-1761.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Cohen P ( 2002). The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 4, E127-E130.
DOI URL PMID |
| [30] |
Dai M, Xue Q, McCray T, Margavage K, Chen F, Lee JH, Nezames CD, Guo L, Terzaghi W, Wan J, Deng XW, Wang H ( 2013). The PP6 phosphatase regulates ABI5 phosphorylation and abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 517-534.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
Dong T, Park Y, Hwang I ( 2015). Abscisic acid: biosynthesis, inactivation, homoeostasis and signaling. Essays Biochem 58, 29-48.
DOI URL PMID |
| [32] |
Feng CZ, Chen Y, Wang C, Kong YH, Wu WH, Chen YF ( 2014). Arabidopsis RAV1 transcription factor, phosphory- lated by SnRK2 kinases, regulates the expression of ABI3, ABI4, and ABI5 during seed germination and early seedling development. Plant J 80, 654-668.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Finkelstein R ( 2013). Abscisic acid synthesis and response. Arabidopsis Book 11, e0166.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Fujii H, Verslues PE, Zhu JK ( 2007). Identification of two protein kinases required for abscisic acid regulation of seed germination, root growth, and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 485-494.
DOI URL PMID |
| [35] |
Fujii H, Zhu JK ( 2009). Arabidopsis mutant deficient in 3 abscisic acid-activated protein kinases reveals critical roles in growth, reproduction, and stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 8380-8385.
DOI URL PMID |
| [36] |
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2011). ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. J Plant Res 124, 509-525.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Fujita Y, Nakashima K, Yoshida T, Katagiri T, Kidokoro S, Kanamori N, Umezawa T, Fujita M, Maruyama K, Ishiyama K, Kobayashi M, Nakasone S, Yamada K, Ito T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2009). Three SnRK2 protein kinases are the main positive regulators of abscisic acid signaling in response to water stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 50, 2123-2132.
DOI URL PMID |
| [38] |
Fujita Y, Yoshida T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2013). Pivotal role of the AREB/ABF-SnRK2 pathway in ABRE-mediated transcription in response to osmotic stress in plants. Physiol Plant 147, 15-27.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Garcia ME, Lynch T, Peeters J, Snowden C, Finkelstein R ( 2008). A small plant-specific protein family of ABI five binding proteins (AFPs) regulates stress response in germinating Arabidopsis seeds and seedlings. Plant Mol Biol 67, 643-658.
DOI URL PMID |
| [40] |
Geiger D, Scherzer S, Mumm P, Marten I, Ache P, Matschi S, Liese A, Wellmann C, Al-Rasheid KAS, Grill E, Romeis T, Hedrich R ( 2010). Guard cell anion channel SLAC1 is regulated by CDPK protein kinases with distinct Ca 2+ affinities . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 8023-8028.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] |
Geiger D, Scherzer S, Mumm P, Stange A, Marten I, Bauer H, Ache P, Matschi S, Liese A, Al-Rasheid KA, Romeis T, Hedrich R ( 2009). Activity of guard cell anion channel SLAC1 is controlled by drought-stress signaling kinase-phosphatase pair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 21425-21430.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Han SK, Sang Y, Rodrigues A, Biol F, Wu MF, Rodriguez PL, Wagner D ( 2012). The SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPase BRAHMA represses abscisic acid responses in the absence of the stress stimulus in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 4892-4906.
DOI URL PMID |
| [43] |
He JX, Gendron JM, Yang Y, Li J, Wang ZY ( 2002). The GSK3-like kinase BIN2 phosphorylates and destabilizes BZR1, a positive regulator of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99, 10185-10190.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Himmelbach A, Hoffmann T, Leube M, Höhener B, Grill E ( 2002). Homeodomain protein ATHB6 is a target of the protein phosphatase ABI1 and regulates hormone responses in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21, 3029-3038. |
| [45] |
Hõrak H, Sierla M, Tõldsepp K, Wang C, Wang YS, Nuhkat M, Valk E, Pechter P, Merilo E, Salojärvi J, Overmyer K, Loog M, Brosché M, Schroeder JI, Kangasjärvi J, Kollist H ( 2016). A dominant mutation in the HT1 kinase uncovers roles of MAP kinases and GHR1 in CO2-induced stomatal closure. Plant Cell 28, 2493-2509.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Hou YJ, Zhu Y, Wang P, Zhao Y, Xie S, Batelli G, Wang B, Duan CG, Wang X, Xing L, Lei M, Yan J, Zhu X, Zhu JK ( 2016). Type one protein phosphatase 1 and its regulatory protein inhibitor 2 negatively regulate ABA signaling. PLoS Genet 12, e1005835.
DOI URL PMID |
| [47] | Hu R, Zhu Y, Shen G, Zhang H ( 2014). TAP46 plays a positive role in the ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 5-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 164, 721-734. |
| [48] |
Hu Y, Yu D ( 2014). BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 2 interacts with ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 5 to mediate the antagonism of brassinosteroids to abscisic acid during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 4394-4408.
DOI URL PMID |
| [49] |
Hua D, Wang C, He J, Liao H, Duan Y, Zhu Z, Guo Y, Chen Z, Gong Z ( 2012). A plasma membrane receptor kinase, GHR1, mediates abscisic acid- and hydrogen peroxide-regulated stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 2546-2561.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] |
Hua Z, Vierstra RD ( 2011). The cullin-RING ubiquitin- protein ligases. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62, 299-334.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Huizinga DH, Denton R, Koehler KG, Tomasello A, Wood L, Sen SE, Crowell DN ( 2010). Farnesylcysteine lyase is involved in negative regulation of abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 3, 143-155.
DOI URL PMID |
| [52] |
Humphrey SJ, James DE, Mann M ( 2015). Protein phosphorylation: a major switch mechanism for metabolic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26, 676-687.
DOI URL |
| [53] | Irigoyen ML, Iniesto E, Rodriguez L, Puga MI, Yanagawa Y, Pick E, Strickland E, Paz-Ares J, Wei N, De Jaeger G, Rodriguez PL, Deng XW, Rubio V ( 2014). Targeted degradation of abscisic acid receptors is mediated by the ubiquitin ligase substrate adaptor DDA1 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 712-728. |
| [54] |
Jensen ON ( 2006). Interpreting the protein language using proteomics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7, 391-403.
DOI URL PMID |
| [55] |
Jin D, Wu M, Li B, Bücker B, Keil P, Zhang S, Li J, Kang D, Liu J, Dong J, Deng XW, Irish V, Wei N ( 2018). The COP9 signalosome regulates seed germination by facilitating protein degradation of RGL2 and ABI5. PLoS Genet 14, e1007237.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Kim H, Hwang H, Hong JW, Lee YN, Ahn IP, Yoon IS, Yoo SD, Lee S, Lee SC, Kim BG ( 2012a). A rice orthologue of the ABA receptor, OsPYL/RCAR5, is a positive regulator of the ABA signal transduction pathway in seed germination and early seedling growth. J Exp Bot 63, 1013-1024.
DOI URL PMID |
| [57] |
Kim JH, Kim WT ( 2013). The Arabidopsis RING E3 ubiquitin ligase AtAIRP3/LOG2 participates in positive regulation of high-salt and drought stress responses. Plant Physiol 162, 1733-1749.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Kim TH, Böhmer M, Hu H, Nishimura N, Schroeder JI ( 2010). Guard cell signal transduction network: advances in understanding abscisic acid, CO2, and Ca 2+ signaling . Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 561-591.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Kim TW, Michniewicz M, Bergmann DC, Wang ZY ( 2012b). Brassinosteroid regulates stomatal development by GSK3-mediated inhibition of a MAPK pathway. Nature 482, 419-422.
DOI URL PMID |
| [60] |
Ko JH, Yang SH, Han KH ( 2006). Upregulation of an Arabidopsis RING-H2 gene, XERICO, confers drought tolerance through increased abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 47, 343-355.
DOI URL PMID |
| [61] |
Kong L, Cheng J, Zhu Y, Ding Y, Meng J, Chen Z, Xie Q, Guo Y, Li J, Yang S, Gong Z ( 2015). Degradation of the ABA co-receptor ABI1 by PUB12/13 U-box E3 ligases. Nat Commun 6, 8630.
DOI URL PMID |
| [62] |
Kulich I, Pečenková T, Sekereš J, Smetana O, Fendrych M, Foissner I, Höftberger M, Žarský V ( 2013). Arabidopsis exocyst subcomplex containing subunit EXO70B1 is involved in autophagy-related transport to the vacuole. Traffic 14, 1155-1165.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] | Kuromori T, Fujita M, Urano K, Tanabata T, Sugimoto E, Shinozaki K ( 2016). Overexpression of AtABCG25 enhan-ces the abscisic acid signal in guard cells and improves plant water use efficiency. Plant Sci 251, 75-81. |
| [64] | Kurup S, Jones HD, Holdsworth MJ ( 2000). Interactions of the developmental regulator ABI3 with proteins identified from developing Arabidopsis seeds. Plant J 21, 143-155. |
| [65] |
Lechner E, Leonhardt N, Eisler H, Parmentier Y, Alioua M, Jacquet H, Leung J, Genschik P ( 2011). MATH/BTB CRL3 receptors target the homeodomain-leucine zipper ATHB6 to modulate abscisic acid signaling. Dev Cell 21, 1116-1128.
DOI URL PMID |
| [66] |
Lee HG, Seo PJ ( 2016). The Arabidopsis MIEL1 E3 ligase negatively regulates ABA signaling by promoting protein turnover of MYB96. Nat Commun 7, 12525.
DOI URL PMID |
| [67] | Lee JH, Yoon HJ, Terzaghi W, Martinez C, Dai M, Li J, Byun MO, Deng XW ( 2010). DWA1 and DWA2, two Arabidopsis DWD protein components of CUL4-based E3 ligases, act together as negative regulators in ABA signal transduction. Plant Cell 22, 1716-1732. |
| [68] | Lee K, Lee HG, Yoon S, Kim HU, Seo PJ ( 2015). The Arabidopsis MYB96 transcription factor is a positive regulator of ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 4 in the control of seed germination. Plant Physiol 168, 677-689. |
| [69] |
Lee KH, Piao HL, Kim HY, Choi SM, Jiang F, Hartung W, Hwang I, Kwak JM, Lee IJ, Hwang I ( 2006). Activation of glucosidase via stress-induced polymerization rapidly increases active pools of abscisic acid. Cell 126, 1109-1120.
DOI URL PMID |
| [70] |
Li D, Zhang L, Li X, Kong X, Wang X, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang J, Li X, Yang Y ( 2018). AtRAE1 is involved in degradation of ABA receptor RCAR1 and negatively regulates ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 41, 231-244.
DOI URL PMID |
| [71] |
Li F, Li M, Wang P, Cox JrKL, Duan L, Dever JK, Shan L, Li Z, He P ( 2017). Regulation of cotton ( Gossypium hirsutum) drought responses by mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade-mediated phosphorylation of GhWRKY59. New Phytol 215, 1462-1475.
DOI URL PMID |
| [72] |
Li Y, Zhang L, Li D, Liu Z, Wang J, Li X, Yang Y ( 2016). The Arabidopsis F-box E3 ligase RIFP1 plays a negative role in abscisic acid signaling by facilitating ABA receptor RCAR3 degradation. Plant Cell Environ 39, 571-582.
DOI URL PMID |
| [73] |
Liang S, Lu K, Wu Z, Jiang SC, Yu YT, Bi C, Xin Q, Wang XF, Zhang DP ( 2015). A link between magnesium-chelatase H subunit and sucrose nonfermenting 1 (SNF1)related protein kinase SnRK2.6/OST1 in Arabidopsis guard cell signaling in response to abscisic acid. J Exp Bot 66, 6355-6369.
DOI URL PMID |
| [74] |
Lim CW, Baek W, Lee SC ( 2017). The pepper RING-type E3 ligase CaAIRF1 regulates ABA and drought signaling via CaADIP1 protein phosphatase degradation. Plant Phy-siol 173, 2323-2339.
DOI URL PMID |
| [75] |
Lin Q, Wang D, Dong H, Gu S, Cheng Z, Gong J, Qin R, Jiang L, Li G, Wang JL, Wu F, Guo X, Zhang X, Lei C, Wang H, Wan J ( 2012). Rice APC/C(TE) controls tillering by mediating the degradation of MONOCULM 1. Nat Com-mun 3, 752.
DOI URL PMID |
| [76] |
Lin Q, Wu F, Sheng P, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Guo X, Wang J, Cheng Z, Wang J, Wang H, Wan J ( 2015). The SnRK2-APC/C (TE) regulatory module mediates the antagonistic action of gibberellic acid and abscisic acid pathways. Nat Commun 6, 7981.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Linster E, Stephan I, Bienvenut WV, Maple-Grødem J, Myklebust LM, Huber M, Reichelt M, Sticht C, Møller SG, Meinnel T, Arnesen T, Giglione C, Hell R, Wirtz M ( 2015). Downregulation of N-terminal acetylation triggers ABA-mediated drought responses in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 6, 7640.
DOI URL PMID |
| [78] |
Liu F, Wang X, Su M, Yu M, Zhang S, Lai J, Yang C, Wang Y ( 2015). Functional characterization of DnSIZ1, a SIZ/PIAS-type SUMO E3 ligase from Dendrobium. BMC Plant Biol 15, 225.
DOI URL PMID |
| [79] | Liu H, Stone SL ( 2010). Abscisic acid increases Arabidopsis ABI5 transcription factor levels by promoting KEG E3 ligase self-ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Plant Cell 22, 2630-2641. |
| [80] | Lois LM, Lima CD, Chua NH ( 2003). Small ubiquitin-like modifier modulates abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15, 1347-1359. |
| [81] |
Lopez-Molina L, Mongrand S, Kinoshita N, Chua NH ( 2003). AFP is a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling that promotes ABI5 protein degradation. Genes Dev 17, 410-418.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Lozano-Juste J, León J ( 2010). Enhanced abscisic acid-mediated responses in nia1nia2noa1-2 triple mutant impaired in NIA/NR- and AtNOA1-dependent nitric oxide biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152, 891-903.
DOI URL PMID |
| [83] |
Luo J, Shen G, Yan J, He C, Zhang H ( 2006). AtCHIP functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase of protein phosphatase 2A subunits and alters plant response to abscisic acid treatment. Plant J 46, 649-657.
DOI URL PMID |
| [84] |
Lyapina S, Cope G, Shevchenko A, Serino G, Tsuge T, Zhou C, Wolf DA, Wei N, Shevchenko A, Deshaies RJ ( 2001). Promotion of NEDD8-CUL1 conjugate cleavage by COP9 signalosome. Science 292, 1382-1385.
DOI URL PMID |
| [85] |
Lyzenga WJ, Liu H, Schofield A, Muise-Hennessey A, Stone SL ( 2013). Arabidopsis CIPK26 interacts with KEG, components of the ABA signaling network and is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Exp Bot 64, 2779-2791.
DOI URL PMID |
| [86] |
Lyzenga WJ, Sullivan V, Liu H, Stone SL ( 2017). The kinase activity of calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase 26 (CIPK26) influences its own stability and that of the ABA-regulated ubiquitin ligase, keep on going (KEG). Front Plant Sci 8, 502.
DOI URL PMID |
| [87] |
Ma QJ, Sun MH, Lu J, Liu YJ, You CX, Hao YJ ( 2017). An apple CIPK protein kinase targets a novel residue of AREB transcription factor for ABA-dependent phosphorylation. Plant Cell Environ 40, 2207-2219.
DOI URL PMID |
| [88] | Ma T, Yoo MJ, Zhang T, Liu L, Koh J, Song WY, Harmon AC, Sha W, Chen S ( 2018). Characterization of thiol-based redox modifications of Brassica napus SNF1-related protein kinase 2.6-2C. FEBS Open Biol 8, 628-645. |
| [89] | Ma Y, Szostkiewicz I, Korte A, Moes D, Yang Y, Christmann A, Grill E ( 2009). Regulators of PP2C phosphatase activity function as abscisic acid sensors. Science 324, 1064-1068. |
| [90] |
Merilo E, Jalakas P, Laanemets K, Mohammadi O, Hõrak H, Kollist H, Brosché M ( 2015). Abscisic acid transport and homeostasis in the context of stomatal regulation. Mol Plant 8, 1321-1333.
DOI URL PMID |
| [91] |
Miao Y, Lv D, Wang P, Wang XC, Chen J, Miao C, Song CP ( 2006). An Arabidopsis glutathione peroxidase functions as both a redox transducer and a scavenger in abscisic acid and drought stress responses. Plant Cell 18, 2749-2766.
DOI URL PMID |
| [92] |
Miricescu A, Goslin K, Graciet E ( 2018). Ubiquitylation in plants: signaling hub for the integration of environmental signals. J Exp Bot 69, 4511-4527.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Miura K, Lee J, Jin JB, Yoo CY, Miura T, Hasegawa PM ( 2009). Sumoylation of ABI5 by the Arabidopsis SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 5418-5423.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
Mulekar JJ, Huq E ( 2014). Expanding roles of protein kinase CK2 in regulating plant growth and development. J Exp Bot 65, 2883-2893.
DOI URL PMID |
| [95] |
Mur LAJ, Mandon J, Persijn S, Cristescu SM, Moshkov IE, Novikova GV, Hall MA, Harren FJM, Hebelstrup KH, Gupta KJ ( 2013). Nitric oxide in plants: an assessment of the current state of knowledge. AOB Plants 5, pls052.
DOI URL PMID |
| [96] |
Nagashima Y, von Schaewen A, Koiwa H ( 2018). Function of N-glycosylation in plants. Plant Sci 274, 70-79.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Ng LM, Soon FF, Zhou XE, West GM, Kovach A, Suino-Powell KM, Chalmers MJ, Li J, Yong EL, Zhu JK, Griffin PR, Melcher K, Xu HE ( 2011). Structural basis for basal activity and autoactivation of abscisic acid (ABA) signaling SnRK2 kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 21259-21264.
DOI URL PMID |
| [98] |
Pandey S, Nelson DC, Assmann SM ( 2009). Two novel GPCR-type G proteins are abscisic acid receptors in Arabidopsis. Cell 136, 136-148.
DOI URL PMID |
| [99] |
Park HC, Kim H, Koo SC, Park HJ, Cheong MS, Hong H, Baek D, Chung WS, Kim DH, Bressan RA, Lee SY, Bohnert HJ, Yun DJ ( 2010). Functional characterization of the SIZ/PIAS-type SUMO E3 ligases, OsSIZ1 and OsSIZ2 in rice. Plant Cell Environ 33, 1923-1934.
DOI URL PMID |
| [100] | Park SY, Fung P, Nishimura N, Jensen DR, Fujii H, Zhao Y, Lumba S, Santiago J, Rodrigues A, Chow TFF, Alfred SE, Bonetta D, Finkelstein R, Provart NJ, Desveaux D, Rodriguez PL, McCourt P, Zhu JK, Sch-roeder JI, Volkman BF, Cutler SR ( 2009). Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins. Science 324, 1068-1071. |
| [101] |
Peirats-Llobet M, Han SK, Gonzalez-Guzman M, Jeong CW, Rodriguez L, Belda-Palazon B, Wagner D, Rodriguez PL ( 2016). A direct link between abscisic acid sensing and the chromatin-remodeling ATPase BRAHMA via core ABA signaling pathway components. Mol Plant 9, 136-147.
DOI URL PMID |
| [102] |
Qi J, Song CP, Wang B, Zhou J, Kangasjärvi J, Zhu JK, Gong Z ( 2018). Reactive oxygen species signaling and stomatal movement in plant responses to drought stress and pathogen attack. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 805-826.
DOI URL PMID |
| [103] |
Raab S, Drechsel G, Zarepour M, Hartung W, Koshiba T, Bittner F, Hoth S ( 2009). Identification of a novel E3 ubiquitin ligase that is required for suppression of pre mature senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 59, 39-51.
DOI URL PMID |
| [104] |
Rosenberger CL, Chen J ( 2018). To grow or not to grow: TOR and SnRK2 coordinate growth and stress response in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 69, 3-4.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
Saruhashi M, Ghosh TK, Arai K, Ishizaki Y, Hagiwara K, Komatsu K, Shiwa Y, Izumikawa K, Yoshikawa H, Umezawa T, Sakata Y, Takezawa D ( 2015). Plant Raf-like kinase integrates abscisic acid and hyperosmotic stress signaling upstream of SNF1-related protein kinase2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, E6388-E6396.
DOI URL PMID |
| [106] |
Sato A, Sato Y, Fukao Y, Fujiwara M, Umezawa T, Shinozaki K, Hibi T, Taniguchi M, Miyake H, Goto DB, Uozumi N ( 2009). Threonine at position 306 of the KAT1 potassium channel is essential for channel activity and is a target site for ABA-activated SnRK2/OST1/SnRK2.6 protein kinase. Biochem J 424, 439-448.
DOI URL |
| [107] | Seo DH, Ahn MY, Park KY, Kim EY, Kim WT ( 2016). The N-terminal UND motif of the Arabidopsis U-box E3 ligase PUB18 is critical for the negative regulation of ABA- mediated stomatal movement and determines its ubiquitination specificity for exocyst subunit Exo70B1. Plant Cell 28, 2952-2973. |
| [108] |
Seo KI, Lee JH, Nezames CD, Zhong S, Song E, Byun MO, Deng XW ( 2014). ABD1 is an Arabidopsis DCAF substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1-based E3 ligases that acts as a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 26, 695-711.
DOI URL PMID |
| [109] |
Shang Y, Dai C, Lee MM, Kwak JM, Nam KH ( 2016). BRI1-associated receptor kinase 1 regulates guard cell ABA signaling mediated by open stomata 1 in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 9, 447-460.
DOI URL PMID |
| [110] |
Shen YY, Wang XF, Wu FQ, Du SY, Cao Z, Shang Y, Wang XL, Peng CC, Yu XC, Zhu SY, Fan RC, Xu YH, Zhang DP ( 2006). The Mg-chelatase H subunit is an abscisic acid receptor. Nature 443, 823-826.
DOI URL PMID |
| [111] |
Singh D, Laxmi A ( 2015). Transcriptional regulation of drought response: a tortuous network of transcriptional factors. Front Plant Sci 6, 895.
DOI URL PMID |
| [112] |
Sirichandra C, Gu D, Hu HC, Davanture M, Lee S, Djaoui M, Valot B, Zivy M, Leung J, Merlot S, Kwak JM ( 2009). Phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis AtrbohF NADPH oxidase by OST1 protein kinase. FEBS Lett 583, 2982-2986.
DOI URL PMID |
| [113] |
Srivastava AK, Zhang C, Caine RS, Gray J, Sadanandom A ( 2017). Rice SUMO protease Overly Tolerant to Salt 1 targets the transcription factor, OsbZIP23 to promote drought tolerance in rice. Plant J 92, 1031-1043.
DOI URL PMID |
| [114] |
Srivastava AK, Zhang C, Yates G, Bailey M, Brown A, Sadanandom A ( 2016). SUMO is a critical regulator of salt stress responses in rice. Plant Physiol 170, 2378-2391.
DOI URL PMID |
| [115] |
Stone SL, Williams LA, Farmer LM, Vierstra RD, Callis J ( 2006). KEEP ON GOING, a RING E3 ligase essential for Arabidopsis growth and development, is involved in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 18, 3415-3428.
DOI URL PMID |
| [116] |
Takahashi S, Monda K, Higaki T, Hashimoto-Sugimoto M, Negi J, Hasezawa S, Iba K ( 2017a). Differential effects of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (PI4K) and 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors on stomatal responses to environmental signals. Front Plant Sci 8, 677.
DOI URL PMID |
| [117] |
Takahashi Y, Ebisu Y, Shimazaki KI ( 2017b). Reconstitution of abscisic acid signaling from the receptor to DNA via bHLH transcription factors. Plant Physiol 174, 815-822.
DOI URL PMID |
| [118] |
Takahashi Y, Kinoshita T, Matsumoto M, Shimazaki KI ( 2016). Inhibition of the Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factor by monomerization through abscisic acid-induced phosphorylation. Plant J 87, 559-567.
DOI URL PMID |
| [119] |
Tan W, Zhang D, Zhou H, Zheng T, Yin Y, Lin H ( 2018). Transcription factor HAT1 is a substrate of SnRK2.3 kinase and negatively regulates ABA synthesis and signaling in Arabidopsis responding to drought. PLoS Genet 14, e1007336.
DOI URL PMID |
| [120] |
Tang N, Ma S, Zong W, Yang N, Lv Y, Yan C, Guo Z, Li J, Li X, Xiang Y, Song H, Xiao J, Li X, Xiong L ( 2016). MODD mediates deactivation and degradation of OsbZIP46 to negatively regulate ABA signaling and drought resistance in rice. Plant Cell 28, 2161-2177.
DOI URL PMID |
| [121] | Tian W, Hou C, Ren Z, Pan Y, Jia J, Zhang H, Bai F, Zhang P, Zhu H, He Y, Luo S, Li L, Luan S ( 2015). A molecular pathway for CO2 response in Arabidopsis guard cells. Nat Commun 6, 6057. |
| [122] |
Umezawa T, Nakashima K, Miyakawa T, Kuromori T, Tanokura M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2010). Molecular basis of the core regulatory network in ABA responses: sensing, signaling and transport. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1821-1839.
DOI URL PMID |
| [123] | Umezawa T, Sugiyama N, Mizoguchi M, Hayashi S, Myouga F, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Ishihama Y, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K ( 2009). Type 2C protein phosphatases directly regulate abscisic acid-activated pro-tein kinases in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 17588-17593. |
| [124] |
Umezawa T, Takahashi F, Shinozaki K ( 2014). Phosphory- lation networks in the abscisic acid signaling pathway. Enzymes 35, 27-56.
DOI URL |
| [125] |
Vandelle E, Delledonne M ( 2011). Peroxynitrite formation and function in plants. Plant Sci 181, 534-539.
DOI URL PMID |
| [126] |
Vert G, Walcher CL, Chory J, Nemhauser JL ( 2008). Integration of auxin and brassinosteroid pathways by Auxin Response Factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 9829-9834.
DOI URL PMID |
| [127] |
Vilela B, Nájar E, Lumbreras V, Leung J, Pagès M ( 2015). Casein kinase 2 negatively regulates abscisic acid-activated SnRK2s in the core abscisic acid-signaling module. Mol Plant 8, 709-721.
DOI URL PMID |
| [128] |
Vishwakarma K, Upadhyay N, Kumar N, Yadav G, Singh J, Mishra RK, Kumar V, Verma R, Upadhyay RG, Pandey M, Sharma S ( 2017). Abscisic acid signaling and abiotic stress tolerance in plants: a review on current knowledge and future prospects. Front Plant Sci 8, 161.
DOI URL PMID |
| [129] |
Waadt R, Manalansan B, Rauniyar N, Munemasa S, Booker MA, Brandt B, Waadt C, Nusinow DA, Kay SA, Kunz HH, Schumacher K, DeLong A, Yates III JR, Schroeder JI ( 2015). Identification of open stomata1- interacting proteins reveals interactions with sucrose non- fermenting1-related protein kinases 2 and with type 2A protein phosphatases that function in abscisic acid responses. Plant Physiol 169, 760-779.
DOI URL PMID |
| [130] |
Wang H, Tang J, Liu J, Hu J, Liu J, Chen Y, Cai Z, Wang X ( 2018a). Abscisic acid signaling inhibits brassinosteroid signaling through dampening the dephosphorylation of BIN2 by ABI1 and ABI2. Mol Plant 11, 315-325.
DOI URL PMID |
| [131] |
Wang H, Wang X ( 2018). GSK3-like kinases are a class of positive components in the core ABA signaling pathway. Mol Plant 11, 761-763.
DOI URL PMID |
| [132] |
Wang P, Du Y, Hou YJ, Zhao Y, Hsu CC, Yuan F, Zhu X, Tao WA, Song CP, Zhu JK ( 2015). Nitric oxide negatively regulates abscisic acid signaling in guard cells by S- nitrosylation of OST1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 613-618.
DOI URL PMID |
| [133] |
Wang P, Du Y, Li Y, Ren D, Song CP ( 2010a). Hydrogen peroxide-mediated activation of MAP kinase 6 modulates nitric oxide biosynthesis and signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22, 2981-2998.
DOI URL PMID |
| [134] |
Wang P, Zhao Y, Li Z, Hsu CC, Liu X, Fu L, Hou YJ, Du Y, Xie S, Zhang C, Gao J, Cao M, Huang X, Zhu Y, Tang K, Wang X, Tao WA, Xiong Y, Zhu JK ( 2018b). Reciprocal regulation of the TOR kinase and ABA receptor balances plant growth and stress response. Mol Cell 69, 100-112.
DOI URL PMID |
| [135] | Wang Q, Qu GP, Kong X, Yan Y, Li J, Jin JB ( 2018c). Arabidopsis small ubiquitin-related modifier protease ASP1 positively regulates abscisic acid signaling during early seedling development. J Integr Plant Biol 60, 924-937. |
| [136] |
Wang X, Guo C, Peng J, Li C, Wan F, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Yan Y, Qi L, Sun K, Yang S, Gong Z, Li J ( 2018d). ABRE-BINDING FACTORS play a role in the feedback regulation of ABA signaling by mediating rapid ABA induction of ABA co-receptor genes. New Phytol 221, 341-355.
DOI URL |
| [137] |
Wang XJ, Zhu SY, Lu YF, Zhao R, Xin Q, Wang XF, Zhang DP ( 2010b). Two coupled components of the mitogen- activated protein kinase cascade MdMPK1 and MdMKK1 from apple function in ABA signal transduction. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 754-766.
DOI URL PMID |
| [138] |
Weng JK, Ye M, Li B, Noel JP ( 2016). Co-evolution of hormone metabolism and signaling networks expands plant adaptive plasticity. Cell 166, 881-893.
DOI URL PMID |
| [139] |
Withers J, Dong X ( 2017). Post-translational regulation of plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 38, 124-132.
DOI URL PMID |
| [140] |
Wu Q, Zhang X, Peirats-Llobet M, Belda-Palazon B, Wang X, Cui S, Yu X, Rodriguez PL, An C ( 2016). Ubiquitin ligases RGLG1 and RGLG5 regulate abscisic acid signaling by controlling the turnover of phosphatase PP2CA. Plant Cell 28, 2178-2196.
DOI URL PMID |
| [141] |
Wurzinger B, Mair A, Fischer-Schrader K, Nukarinen E, Roustan V, Weckwerth W, Teige M ( 2017). Redox state-dependent modulation of plant SnRK1 kinase activity differs from AMPK regulation in animals. FEBS Lett 591, 3625-3636.
DOI URL PMID |
| [142] |
Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Mogami J, Todaka D, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K ( 2015). Four Arabidopsis AREB/ABF transcription factors function predominantly in gene expression downstream of SnRK2 ki- nases in abscisic acid signaling in response to osmotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 38, 35-49.
DOI URL PMID |
| [143] |
Youn JH, Kim TW ( 2015). Functional insights of plant GSK3-like kinases: multi-taskers in diverse cellular signal transduction pathways. Mol Plant 8, 552-565.
DOI URL PMID |
| [144] |
Yu F, Lou L, Tian M, Li Q, Ding Y, Cao X, Wu Y, Belda-Palazon B, Rodriguez PL, Yang S, Xie Q ( 2016a). ESCRT-I component VPS23A affects ABA signaling by recognizing ABA receptors for endosomal degradation. Mol Plant 9, 1570-1582.
DOI URL PMID |
| [145] |
Yu F, Wu Y, Xie Q ( 2015). Precise protein post-translational modifications modulate ABI5 activity. Trends Plant Sci 20, 569-575.
DOI URL PMID |
| [146] |
Yu F, Wu Y, Xie Q ( 2016b). Ubiquitin-proteasome system in ABA signaling: from perception to action. Mol Plant 9, 21-33.
DOI URL PMID |
| [147] |
Yu F, Xie Q ( 2017). Non-26S proteasome endomembrane trafficking pathways in ABA signaling. Trends Plant Sci 22, 976-985.
DOI URL PMID |
| [148] |
Zhang H, Cui F, Wu Y, Lou L, Liu L, Tian M, Ning Y, Shu K, Tang S, Xie Q ( 2015a). The RING finger ubiquitin E3 ligase SDIR1 targets SDIR1-INTERACTING PROTEIN 1 for degradation to modulate the salt stress response and ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27, 214-227.
DOI URL PMID |
| [149] |
Zhang L, Li X, Li D, Sun Y, Li Y, Luo Q, Liu Z, Wang J, Li X, Zhang H, Lou Z, Yang Y ( 2018). CARK1 mediates ABA signaling by phosphorylation of ABA receptors. Cell Discov 4, 30.
DOI URL PMID |
| [150] |
Zhang RF, Guo Y, Li YY, Zhou LJ, Hao YJ, You CX ( 2016). Functional identification of MdSIZ1 as a SUMO E3 ligase in apple. J Plant Physiol 198, 69-80.
DOI URL PMID |
| [151] | Zhang S, Qi Y, Liu M, Yang C ( 2013). SUMO E3 ligase AtMMS21 regulates drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Integr Plant Biol 55, 83-95. |
| [152] |
Zhang S, Zhuang K, Wang S, Lv J, Ma N, Meng Q ( 2017). A novel tomato SUMO E3 ligase, SlSIZ1, confers drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco. J Integr Plant Biol 59, 102-117.
DOI URL PMID |
| [153] |
Zhang T, Zhu M, Song WY, Harmon AC, Chen S ( 2015b). Oxidation and phosphorylation of MAP kinase 4 cause protein aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1854, 156-165.
DOI URL PMID |
| [154] |
Zhang X, Garreton V, Chua NH ( 2005). The AIP2 E3 ligase acts as a novel negative regulator of ABA signaling by promoting ABI3 degradation. Genes Dev 19, 1532-1543.
DOI URL PMID |
| [155] |
Zhao J, Zhao L, Zhang M, Zafar SA, Fang J, Li M, Zhang W, Li X ( 2017). Arabidopsis E3 ubiquitin ligases PUB22 and PUB23 negatively regulate drought tolerance by targeting ABA receptor PYL9 for degradation. Int J Mol Sci 18, 1841.
DOI URL PMID |
| [156] |
Zheng Y, Schumaker KS, Guo Y ( 2012). Sumoylation of transcription factor MYB30 by the small ubiquitin-like modifier E3 ligase SIZ1 mediates abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 12822-12827.
DOI URL |
| [157] | Zhou X, Hao H, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Zhu W, Qin Y, Yuan F, Zhao F, Wang M, Hu J, Xu H, Guo A, Zhao H, Zhao Y, Cao C, Yang Y, Schumaker KS, Guo Y, Xie CG ( 2015). SOS2-LIKE PROTEIN KINASE 5, an SNF1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE 3-type protein kinase, is important for abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis through phosphorylation of ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 5. Plant Physiol 168, 659-676. |
| [158] |
Zhuang X, Cui Y, Gao C, Jiang L ( 2015). Endocytic and autophagic pathways crosstalk in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 28, 39-47.
DOI URL PMID |
| [159] |
Zong W, Tang N, Yang J, Peng L, Ma S, Xu Y, Li G, Xiong L ( 2016). Feedback regulation of ABA signaling and biosynthesis by a bZIP transcription factor targets drought resistance related genes. Plant Physiol 171, 2810-2825.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [2] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [3] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [4] | 王文广, 王永红. 百年假说终获解析: 穿梭的LAZY蛋白“唤醒”植物对重力的感应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 677-681. |
| [5] | 周玉萍, 颜嘉豪, 田长恩. 保卫细胞中ABA信号调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 684-696. |
| [6] | 刘晓龙, 季平, 杨洪涛, 丁永电, 付佳玲, 梁江霞, 余聪聪. 脱落酸对水稻抽穗开花期高温胁迫的诱抗效应[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 596-610. |
| [7] | 谢玲玲, 王金龙, 伍国强. 植物CBL-CIPK信号系统响应非生物胁迫的调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 614-626. |
| [8] | 赵晓亭, 毛凯涛, 徐佳慧, 郑钏, 罗晓峰, 舒凯. 蛋白质磷酸化修饰与种子休眠及萌发调控[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 488-499. |
| [9] | 张一弓, 张怡, 阿依白合热木·木台力甫, 张道远. 异源过表达齿肋赤藓ScABI3基因改变拟南芥气孔表型并提高抗旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 414-421. |
| [10] | 温兴, 晋莲, 郭红卫. 甜蜜的相遇—营养与激素信号协同调节植物生长的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 138-141. |
| [11] | 朱丹,曹汉威,李媛,任东涛. 植物蛋白磷酸化的检测方法[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(1): 76-82. |
| [12] | 赵庆臻,刘利静,谢旗,于菲菲. 植物蛋白的体外泛素化检测方法[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 764-772. |
| [13] | 刘利静,赵庆臻,谢旗,于菲菲. 快速高效检测植物体内蛋白泛素化修饰研究方法[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 753-763. |
| [14] | 陈唯,曾晓贤,谢楚萍,田长恩,周玉萍. 植物内源ABA水平的动态调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 677-687. |
| [15] | 刘雅琼,侯岁稳. 蛋白磷酸化修饰在植物-病原微生物互作中的作用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(2): 168-184. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||