

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 548-559.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22147 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22147
收稿日期:2022-07-05
接受日期:2022-10-09
出版日期:2023-07-01
发布日期:2022-11-02
通讯作者:
*E-mail: xukai_li@sxau.edu.cn基金资助:
Rong Sun1, Yulu Yang2, Yajun Li2, Hui Zhang1, Xukai Li1( )
)
Received:2022-07-05
Accepted:2022-10-09
Online:2023-07-01
Published:2022-11-02
Contact:
*E-mail: xukai_li@sxau.edu.cn摘要: PLATZ转录因子家族是一类植物特异性锌依赖DNA结合蛋白, 在植物生长发育和抗逆过程中发挥不可或缺的作用。然而, 对于谷子(Setaria italica) PLATZ家族基因尚未进行系统研究。在谷子基因组中鉴定出17个PLATZ基因并对其进行系统命名。通过系统发育分析将SiPLATZ基因划分为5个亚家族, 同一亚家族成员具有相似的基因结构和保守基序。顺式作用元件分析表明, SiPLATZ基因可能在籽粒胚乳发育和多种抗逆反应中发挥作用。Ka/Ks分析表明, 重复基因受到纯化选择。SiPLATZ基因在不同组织和发育阶段的表达存在显著差异, 主要包括在根、叶和茎中高表达, 以及在穗和籽粒中高表达两类, 这体现出SiPLATZ基因生理功能的复杂性, 其可能参与调节籽粒生长和多种抗逆反应。此外, 结合WGCNA分析构建的共表达网络, 发现SiPLATZ6、SiPLATZ8、SiPLATZ9和SiPLATZ11可能是谷子产量遗传改良和功能基因研究的候选基因。研究结果为深入揭示PLATZ转录因子在谷子生长发育中的生物学功能奠定了基础。
孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559.
Rong Sun, Yulu Yang, Yajun Li, Hui Zhang, Xukai Li. Genome-wide Identification and Analysis of PLATZ Transcription Factor Gene Family in Foxtail Millet. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 548-559.
| Gene name | Locus ID | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Isoelectric point | Instability index | Predicted sub-cellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiPLATZ1 | Si1g06060 | 210 | 22.98 | 6.65 | 45.46 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ2 | Si1g06070 | 182 | 19.81 | 9.32 | 43.97 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ3 | Si1g06080 | 248 | 26.72 | 5.45 | 45.38 | Nucleus, mitochondrion |
| SiPLATZ4 | Si1g06100 | 143 | 15.56 | 9.05 | 42.96 | Nucleus, chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ5 | Si1g06720 | 237 | 27.18 | 8.75 | 54.77 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ6 | Si1g07690 | 257 | 27.79 | 8.63 | 45.93 | Chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ7 | Si1g26800 | 198 | 21.94 | 9.05 | 69.15 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ8 | Si1g28470 | 247 | 27.37 | 9.07 | 56.56 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ9 | Si4g17460 | 242 | 26.07 | 8.65 | 47.57 | Nucleus, cell membrane, chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ10 | Si4g20160 | 243 | 26.84 | 9.47 | 60.37 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ11 | Si5g17000 | 214 | 24.38 | 7.90 | 63.39 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ12 | Si5g19690 | 209 | 23.92 | 6.50 | 66.21 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ13 | Si6g24710 | 207 | 22.35 | 9.15 | 47.83 | Nucleus, chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ14 | Si7g22910 | 251 | 27.42 | 9.23 | 51.67 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ15 | Si9g30780 | 246 | 26.90 | 9.16 | 56.51 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ16 | Si9g36990 | 256 | 29.23 | 6.02 | 70.27 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ17 | Si9g47270 | 239 | 26.34 | 9.37 | 52.33 | Nucleus |
表1 谷子SiPLATZ基因家族编码蛋白理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of the proteins encoded by SiPLATZ gene family in foxtail millet
| Gene name | Locus ID | Protein length (aa) | Molecular weight (kDa) | Isoelectric point | Instability index | Predicted sub-cellular localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiPLATZ1 | Si1g06060 | 210 | 22.98 | 6.65 | 45.46 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ2 | Si1g06070 | 182 | 19.81 | 9.32 | 43.97 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ3 | Si1g06080 | 248 | 26.72 | 5.45 | 45.38 | Nucleus, mitochondrion |
| SiPLATZ4 | Si1g06100 | 143 | 15.56 | 9.05 | 42.96 | Nucleus, chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ5 | Si1g06720 | 237 | 27.18 | 8.75 | 54.77 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ6 | Si1g07690 | 257 | 27.79 | 8.63 | 45.93 | Chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ7 | Si1g26800 | 198 | 21.94 | 9.05 | 69.15 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ8 | Si1g28470 | 247 | 27.37 | 9.07 | 56.56 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ9 | Si4g17460 | 242 | 26.07 | 8.65 | 47.57 | Nucleus, cell membrane, chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ10 | Si4g20160 | 243 | 26.84 | 9.47 | 60.37 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ11 | Si5g17000 | 214 | 24.38 | 7.90 | 63.39 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ12 | Si5g19690 | 209 | 23.92 | 6.50 | 66.21 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ13 | Si6g24710 | 207 | 22.35 | 9.15 | 47.83 | Nucleus, chloroplast |
| SiPLATZ14 | Si7g22910 | 251 | 27.42 | 9.23 | 51.67 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ15 | Si9g30780 | 246 | 26.90 | 9.16 | 56.51 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ16 | Si9g36990 | 256 | 29.23 | 6.02 | 70.27 | Nucleus |
| SiPLATZ17 | Si9g47270 | 239 | 26.34 | 9.37 | 52.33 | Nucleus |
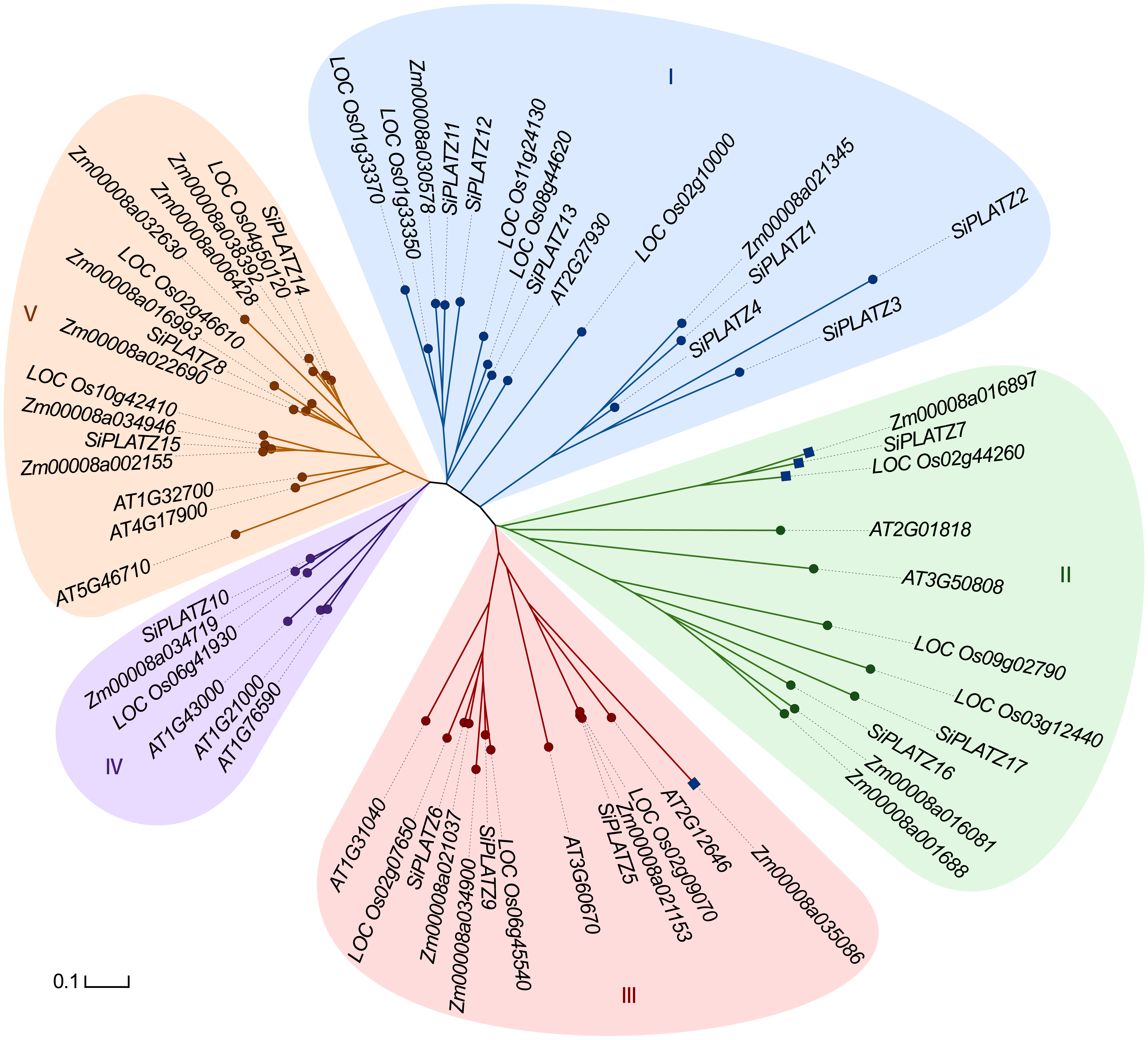
图1 谷子、水稻、玉米和拟南芥PLATZ家族蛋白系统发育关系 PLATZ基因家族的亚组通过系统发育树的分支颜色及填充底色区分, 分支长度表示基因的遗传距离。圆形节点的基因与Wang等(2018)的研究分组一致, 方形节点的基因(4个)则与其不同, 节点颜色一致的基因表示在Wang等(2018)的研究中为同一亚组。
Figure 1 Phylogenetic relationships of PLATZ family proteins in foxtail millet, rice, maize and Arabidopsis The branch color and filled base color on the phylogenetic tree distinguish subgroups of the PLATZ gene family, and the branch length indicates the genetic distance of the gene. Genes in round nodes are consistent with the grouping of Wang et al. (2018), genes in square nodes (4 genes) are different from that, and genes with the same node colors indicate in the same subgroup of the Wang et al. (2018).
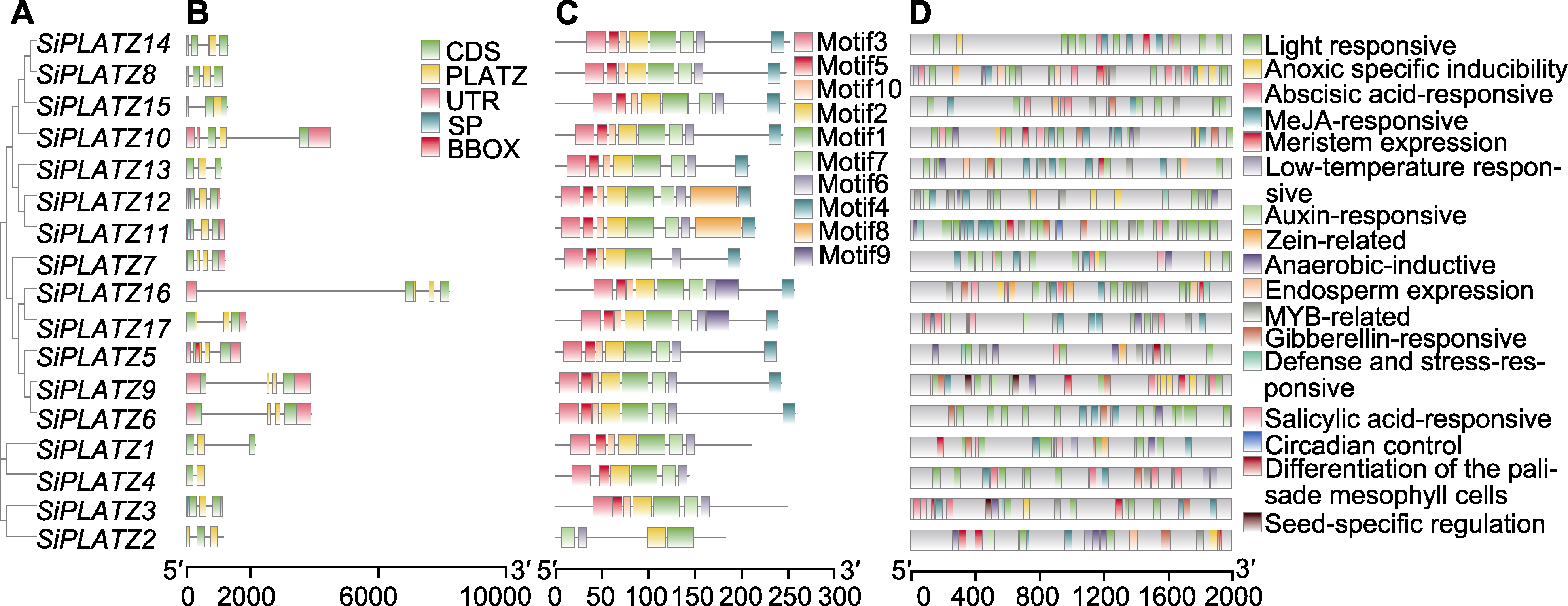
图2 谷子PLATZ家族基因结构分析 (A) 谷子PLATZ家族进化树; (B) 谷子PLATZ家族基因结构(CDS: 蛋白质编码区; PLATZ: Plant AT-rich sequence and zinc-bind- ing proteins结构域; UTR: 非翻译区; SP: 信号肽; BBOX: B-Box-type zinc finger结构域); (C) 谷子PLATZ家族保守基序; (D) 谷子PLATZ家族基因启动子顺式作用元件分析
Figure 2 Structural analysis of PLATZ family genes in foxtail millet (A) Evolutionary tree of PLATZ family in foxtail millet; (B) The gene structure of PLATZ family in foxtail millet (CDS: Coding sequences; PLATZ: Plant AT-rich sequence and zinc-binding protein domains; UTR: Untranslated regions; SP: Signal peptide; BBOX: B-Box-type zinc finger domains); (C) The conserved motif of PLATZ family in foxtail millet; (D) Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoter of PLATZ family gene in foxtail millet
| Homologous gene | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiPLATZ10-SiPLATZ4 segmental duplication | 0.434473 | 0.577238 | 0.752677 |
| SiPLATZ14-SiPLATZ8 segmental duplication | 0.164238 | 0.394477 | 0.416344 |
| SiPLATZ1-SiPLATZ2 tandem repeats | 0.471405 | 1.482013 | 0.318084 |
| SiPLATZ1-SiPLATZ3 tandem repeats | 0.415490 | 0.958245 | 0.433595 |
| SiPLATZ1-SiPLATZ4 tandem repeats | 0.173058 | 0.550660 | 0.314274 |
| SiPLATZ2-SiPLATZ3 tandem repeats | 0.516098 | 0.872575 | 0.591465 |
| SiPLATZ2-SiPLATZ4 tandem repeats | 0.614008 | 1.027812 | 0.597393 |
| SiPLATZ3-SiPLATZ4 tandem repeats | 0.352090 | 0.772969 | 0.455503 |
表2 NG法计算谷子基因组内SiPLATZ共线性基因对Ka/Ks值
Table 2 Calculation of Ka/Ks value of SiPLATZ collinear gene pair in foxtail millet genome by NG method
| Homologous gene | Ka | Ks | Ka/Ks |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiPLATZ10-SiPLATZ4 segmental duplication | 0.434473 | 0.577238 | 0.752677 |
| SiPLATZ14-SiPLATZ8 segmental duplication | 0.164238 | 0.394477 | 0.416344 |
| SiPLATZ1-SiPLATZ2 tandem repeats | 0.471405 | 1.482013 | 0.318084 |
| SiPLATZ1-SiPLATZ3 tandem repeats | 0.415490 | 0.958245 | 0.433595 |
| SiPLATZ1-SiPLATZ4 tandem repeats | 0.173058 | 0.550660 | 0.314274 |
| SiPLATZ2-SiPLATZ3 tandem repeats | 0.516098 | 0.872575 | 0.591465 |
| SiPLATZ2-SiPLATZ4 tandem repeats | 0.614008 | 1.027812 | 0.597393 |
| SiPLATZ3-SiPLATZ4 tandem repeats | 0.352090 | 0.772969 | 0.455503 |
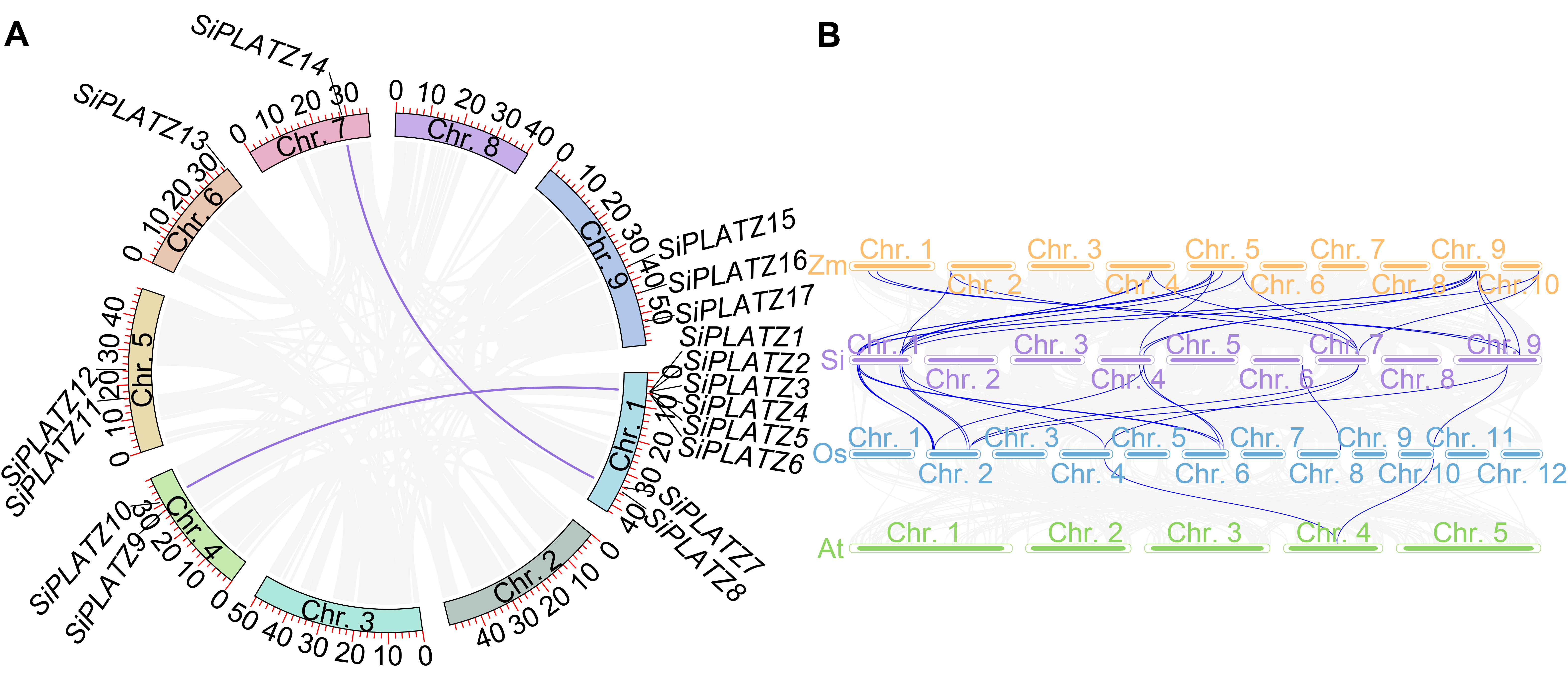
图3 PLATZ家族基因共线性分析 (A) 谷子PLATZ家族内部共线性关系; (B) 玉米、谷子、水稻和拟南芥PLATZ家族共线性关系
Figure 3 Collinear analysis of PLATZ family genes (A) The internal collinearity of the PLATZ family in foxtail millet; (B) The collinearity of the PLATZ family in maize, foxtail millet, rice and Arabidopsis
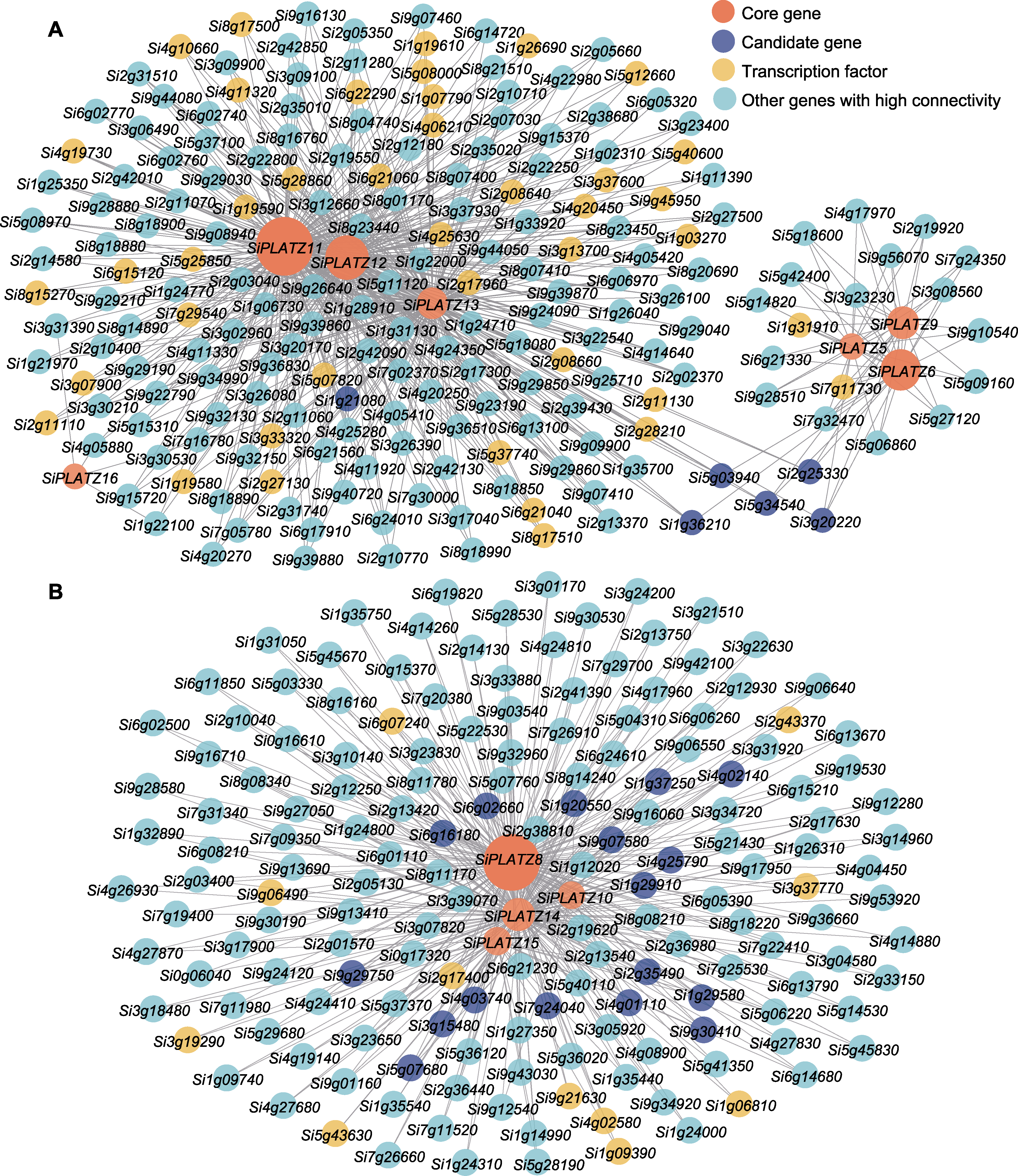
图4 谷子PLATZ家族相关基因局部网络图 (A) Blue模块中谷子PLATZ家族相关基因网络图; (B) Turquoise模块中谷子PLATZ家族相关基因网络图。红色表示核心基因, 蓝色表示候选基因, 黄色表示转录因子, 绿色表示其它连通度较高的共表达基因。圆圈的大小代表基因连通度的高低。圆圈越大连通度越高, 反之越低。
Figure 4 Local network of genes related to the PLATZ family of foxtail millet (A) The related gene network diagram of the foxtail millet PLATZ family in the blue module; (B) The related gene network diagram of the foxtail millet PLATZ family in the turquoise module. Red indicates the core gene, blue indicates the candidate gene, yellow indicates the transcription factor, and green indicates other co-expressed genes with high connectivity. The size of the circle represented the level of gene connectivity. The larger the circle, the higher the connectivity, and vice versa.
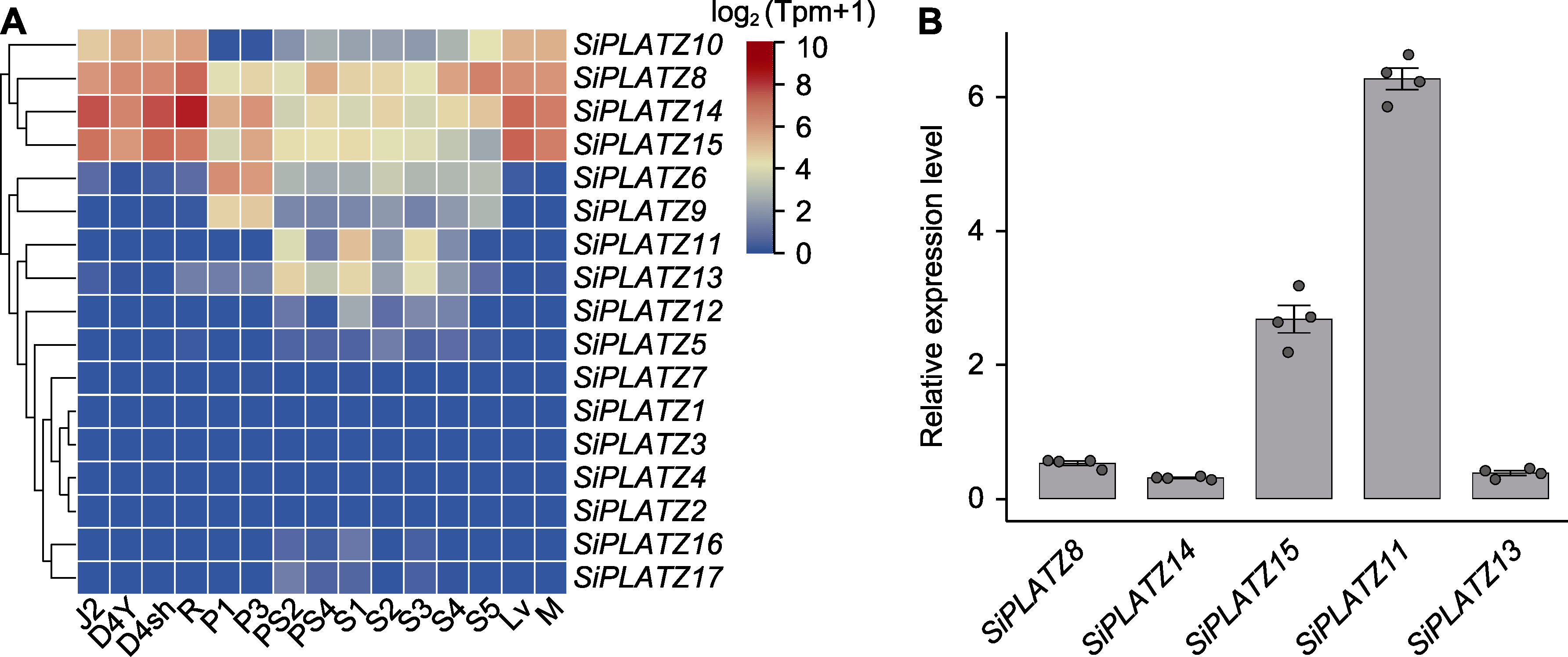
图5 SiPLATZ家族成员在谷子不同组织和发育时期的表达模式 (A) SiPLATZ家族成员在谷子不同组织和发育时期的表达谱(共包括15个组织时期, J2: 谷子灌浆期S3的倒2节茎秆; D4Y: 灌浆期倒4叶; D4sh: 灌浆期倒4叶叶鞘; R: 灌浆期根; P1: 初生分枝分化期小穗; P3: 第3级分枝分化期小穗; PS2: 灌浆期S2小穗; PS4: 灌浆期S4小穗; S1-S5: 灌浆期S1-S5籽粒; Lv: S3期叶脉; M: S3期叶肉); (B) 部分SiPLATZ基因籽粒灌浆S3时期的qPCR验证。
Figure 5 Expression patterns of SiPLATZ family members in different tissue and development stages of foxtail millet (A) The expression levels of SiPLATZ family members in different tissue stages of foxtail millet (it consists of 15 tissue stages, J2: Stem-top-second_filling-stage; D4Y: Leaf-top-fourth_filling-stage; D4sh: Leaf-sheath-top-fourth_filling-stage; R: Root_filling- stage; P1: Panicle_primary-panicle-branch-differentiation-stage; P3: Panicle_third-panicle-branch-differentiation-stage; PS2: Immature-spikelet_S2; PS4: Immature-spikelet_S4; S1-S5: Immature-seed_S1-S5; Lv: Leaf-veins_S3; M: Mesophyll_S3); (B) qPCR verification of part of the SiPLATZ genes.
| [1] | 陈睿, 陈建民, 吴明基, 杨绍华, 胡昌泉 (2019). 水稻OsPLATZ14基因启动子的克隆及表达分析. 福建农业学报 34, 1137-1143. |
| [2] |
刘宝玲, 张莉, 孙岩, 薛金爱, 高昌勇, 苑丽霞, 王计平, 贾小云, 李润植 (2016). 谷子bZIP转录因子的全基因组鉴定及其在干旱和盐胁迫下的表达分析. 植物学报 51, 473-487.
DOI |
| [3] |
王海岗, 贾冠清, 智慧, 温琪汾, 董俊丽, 陈凌, 王君杰, 曹晓宁, 刘思辰, 王纶, 乔治军, 刁现民 (2016). 谷子核心种质表型遗传多样性分析及综合评价. 作物学报 42, 19-30.
DOI |
| [4] | 杨瑞 (2017). 拟南芥锌指转录因子PLATZ5在盐胁迫响应中的功能研究. 硕士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 1-66. |
| [5] | 张亚 (2018). 锌依赖的DNA结合蛋白家族基因OsPLATZ的功能研究. 硕士论文. 广州: 华南农业大学. pp. 1-69. |
| [6] |
赵娟, 尹艺臻, 王晓璐, 马春英, 尹美强, 温银元, 宋喜娥, 董淑琦, 杨雪芳, 原向阳 (2020). 不同品种谷子愈伤组织对拿捕净胁迫的生理响应. 中国农业科学 53, 917-928.
DOI |
| [7] | Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE, Noble WS (2015). The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res 43, W39-W49. |
| [8] |
Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13, 1194-1202.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | Chou KC, Shen HB (2010). Cell-PLoc 2.0: an improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat Sci 2, 1090-1103. |
| [10] | Diao XM, Schnable J, Bennetzen JL, Li JY (2014). Initiation of Setaria as a model plant. Front Agric Sci Eng 1, 16-20. |
| [11] | Duvaud S, Gabella C, Lisacek F, Stockinger H, Ioannidis V, Durinx C (2021). Expasy, the Swiss bioinformatics resource portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res 49, W216-W227. |
| [12] |
Fu YX, Cheng MP, Li ML, Guo XJ, Wu YR, Wang JR (2020). Identification and characterization of PLATZ transcription factors in wheat. Int J Mol Sci 21, 8934.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Goodstein DM, Shu SQ, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Rokhsar DS (2012). Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40, D1178-D1186. |
| [14] |
Huangfu YG, Pan JW, Li Z, Wang QG, Mastouri F, Li Y, Yang S, Liu M, Dai SJ, Liu W (2021). Genome-wide identification of PTI1 family in Setaria italica and salinity-responsive functional analysis of SiPTI1-5. BMC Plant Biol 21, 319.
DOI |
| [15] |
Jones MK, Liu XY (2009). Origins of agriculture in East Asia. Science 324, 730-731.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Kim JH, Kim J, Jun SE, Park S, Timilsina R, Kwon DS, Kim Y, Park SJ, Hwang JY, Nam HG, Kim GT, Woo HR (2018). ORESARA15, a PLATZ transcription factor, mediates leaf growth and senescence in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 220, 609-623.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008). WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9, 559.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Lee GA, Crawford GW, Liu L, Chen XC (2007). Plants and people from the Early Neolithic to Shang periods in North China. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 1087-1092.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [20] | Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P (2021). SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res 49, D458-D460. |
| [21] |
Li Q, Wang JC, Ye JW, Zheng XX, Xiang XL, Li CS, Fu MM, Wang Q, Zhang ZY, Wu YR (2017). The maize imprinted gene Floury3 encodes a PLATZ protein required for tRNA and 5S rRNA transcription through interaction with RNA polymerase III. Plant Cell 29, 2661-2675.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, Tosatto SCE, Paladin L, Raj S, Richardson LJ, Finn RD, Bateman A (2021). Pfam: the protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 49, D412-D419. |
| [24] |
Nagano Y, Furuhashi H, Inaba T, Sasaki Y (2001). A novel class of plant-specific zinc-dependent DNA-binding protein that binds to A/T-rich DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 29, 4097-4105.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdóttir H, Turner D, Mesirov JP (2020). igv.js: an embeddable JavaScript implementation of the integrative genomics viewer (IGV). BioRxiv. [2020-05-05]. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.03.075499. |
| [26] |
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13, 2498-2504.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021). MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38, 3022-3027.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Wang AH, Hou QQ, Si LZ, Huang XH, Luo JH, Lu DF, Zhu JJ, Shangguan YY, Miao JS, Xie YF, Wang YC, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhou CC, Li Y, Fan DL, Lu YQ, Tian QL, Wang ZX, Han B (2019). The PLATZ transcription factor GL6 affects grain length and number in rice. Plant Physiol 180, 2077-2090.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Wang J, Li SM, Lan L, Xie MS, Cheng S, Gan XL, Huang G, Du GH, Yu K, Ni XM, Liu BL, Peng GX (2021). De novo genome assembly of a foxtail millet cultivar Huagu11 uncovered the genetic difference to the cultivar Yugu1, and the genetic mechanism of imazethapyr tolerance. BMC Plant Biol 21, 271.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Wang JC, Ji C, Li Q, Zhou Y, Wu YR (2018). Genome-wide analysis of the plant-specific PLATZ proteins in maize and identification of their general role in interaction with RNA polymerase III complex. BMC Plant Biol 18, 221.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Wu JD, Jiang CP, Zhu HS, Jiang HY, Cheng BJ, Zhu SW (2015). Cloning and functional analysis of the promoter of a maize starch synthase III gene (ZmDULL1). Genet Mol Res 14, 5468-5479.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Xu WY, Tang WS, Wang CX, Ge LH, Sun JC, Qi X, He Z, Zhou YB, Chen J, Xu ZS, Ma YZ, Chen M (2020). SiMYB56 confers drought stress tolerance in transgenic rice by regulating lignin biosynthesis and ABA signaling pathway. Front Plant Sci 11, 785.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Yamada M, Han XW, Benfey PN (2020). RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signaling. Nature 577, 85-88.
DOI |
| [34] |
Yang ZR, Zhang HS, Li XK, Shen HM, Gao JH, Hou SY, Zhang B, Mayes S, Bennett M, Ma JX, Wu CY, Sui Y, Han YH, Wang XC (2020). A mini foxtail millet with an Arabidopsis-like life cycle as a C4 model system. Nat Plants 6, 1167-1178.
DOI |
| [35] |
Zhou SR, Xue HW (2020). The rice PLATZ protein SHORT GRAIN6 determines grain size by regulating spikelet hull cell division. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 847-864.
DOI |
| [1] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [2] | 张慧, 梁红凯, 智慧, 张林林, 刁现民, 贾冠清. 谷子β-胡萝卜素异构酶家族基因的表达与变异分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 34-50. |
| [3] | 王琦, 许艳丽, 闫鹏, 董好胜, 张薇, 卢霖, 董志强. PAC对谷子花后土壤氮素供应和叶片抗氧化特性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 90-107. |
| [4] | 杨澜, 刘雅, 项阳, 孙秀娟, 颜景畏, 张阿英. 谷子茎尖体外遗传转化体系的建立与优化[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 71-79. |
| [5] | 刘宝玲, 张莉, 孙岩, 薛金爱, 高昌勇, 苑丽霞, 王计平, 贾小云, 李润植. 谷子bZIP转录因子的全基因组鉴定及其在干旱和盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(4): 473-487. |
| [6] | 陈青青, 李德志. 根系隔离条件下的谷子亲缘识别[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(12): 1188-1197. |
| [7] | 李园莉 江元清 赵武玲 阎隆飞. 谷子肌动蛋白基因的克隆及序列分析[J]. 植物学报, 2002, 19(03): 310-316. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||