

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 90-107.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22104 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22104
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
王琦, 许艳丽, 闫鹏, 董好胜, 张薇, 卢霖*( ), 董志强*(
), 董志强*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-05-12
接受日期:2022-09-26
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: dongzhiqiang@caas.cn;lulin@caas.cn
基金资助:
Qi Wang, Yanli Xu, Peng Yan, Haosheng Dong, Wei Zhang, Lin Lu*( ), Zhiqiang Dong*(
), Zhiqiang Dong*( )
)
Received:2022-05-12
Accepted:2022-09-26
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: dongzhiqiang@caas.cn;lulin@caas.cn
摘要: 全基施肥方式会造成作物全生育期内营养供应失衡, 导致生育后期缺氮早衰。为探究聚天门冬氨酸和壳聚糖复配剂(PAC)保障谷子(Setaria italica)花后氮素供应和调控叶片抗氧化特性的机制, 建立全基施肥背景下东北春谷防衰增产的生产技术, 于2020-2021年在中国农业科学院作物科学研究所公主岭试验站开展大田试验, 以谷子品种张杂谷13号和华优谷9号为材料, 设置常规氮素(CN)和PAC配合氮素(PN) 6个氮素水平(0、75、112.5、150、225和337.5 kg·hm-2)播种前进行全基施肥处理。结果表明, 与常规氮肥处理相比, 相同施氮量下, PAC处理后, 两品种谷子花期和灌浆中期0-20 cm和20-40 cm土层土壤硝态氮和铵态氮含量升高, 花后叶面积显著增大, 叶面积降幅减小; 花后0-40天旗叶超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化物酶及过氧化氢酶活性升高, 丙二醛含量降低。因此, PAC有效保障了谷子生育中、后期土壤氮素的供应, 提高了叶片抗氧化能力, 延缓了叶片衰老进程, 进而提高产量。2020年和2021年Z13的增产幅度分别为11.24%-21.55%和8.65%- 14.22%, H9的增产幅度分别为5.53%-15.75%和10.43%-16.17%。上述调控效应在低氮和中氮水平(75、112.5和150 kg·hm-2)下更为显著。综上, PAC配合氮肥全基施可作为一项防衰增产的栽培技术应用于我国东北春谷区。
王琦, 许艳丽, 闫鹏, 董好胜, 张薇, 卢霖, 董志强. PAC对谷子花后土壤氮素供应和叶片抗氧化特性的影响. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 90-107.
Qi Wang, Yanli Xu, Peng Yan, Haosheng Dong, Wei Zhang, Lin Lu, Zhiqiang Dong. Effects of PAC on Soil Nitrogen Supply and Leaf Antioxidant Properties in Foxtail Millet at Anthesis Stage. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 90-107.
| Treatments | Basic application amount of nitrogen (kg·hm-2) | PASP content (‰) | CTS content (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CN1 | 75 | 0 | 0 |
| CN2 | 112.5 | 0 | 0 |
| CN3 | 150 | 0 | 0 |
| CN4 | 225 | 0 | 0 |
| CN5 | 337.5 | 0 | 0 |
| PN0 | 0 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN1 | 75 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN2 | 112.5 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN3 | 150 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN4 | 225 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN5 | 337.5 | 3 | 0.45 |
表1 实验处理及编号
Table 1 Different treatments and their abbreviations
| Treatments | Basic application amount of nitrogen (kg·hm-2) | PASP content (‰) | CTS content (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CN1 | 75 | 0 | 0 |
| CN2 | 112.5 | 0 | 0 |
| CN3 | 150 | 0 | 0 |
| CN4 | 225 | 0 | 0 |
| CN5 | 337.5 | 0 | 0 |
| PN0 | 0 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN1 | 75 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN2 | 112.5 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN3 | 150 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN4 | 225 | 3 | 0.45 |
| PN5 | 337.5 | 3 | 0.45 |
| Year | PAC | Nitrogen | Replication | PAC*Nitrogen | Year*PAC*Nitrogen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD activity | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| POD activity | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| CAT activity | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| MDA content | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| NO3--N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | ns | * | ** | ns | * | ns |
| NO3--N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| NO3--N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | * | ns | ** | ns | * | ns |
| NO3--N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | * | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | ** | ** | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | * | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| Leaf area per plant | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| Leaf area reduction per plant | ns | ** | ** | ns | * | * |
| 1000-kernel weight | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Ears per hectare | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| Kernels per ear | * | * | ** | ns | ** | ** |
| Yield | ** | * | ** | ns | ** | ns |
表2 方差分析
Table 2 Analysis of variance
| Year | PAC | Nitrogen | Replication | PAC*Nitrogen | Year*PAC*Nitrogen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOD activity | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| POD activity | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| CAT activity | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| MDA content | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| NO3--N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | ns | * | ** | ns | * | ns |
| NO3--N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| NO3--N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | * | ns | ** | ns | * | ns |
| NO3--N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | * | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 0-20 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at anthesis stage | ** | ** | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| NH4+-N content in 20-40 cm soil layer at mid-filling stage | * | * | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| Leaf area per plant | ** | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns |
| Leaf area reduction per plant | ns | ** | ** | ns | * | * |
| 1000-kernel weight | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Ears per hectare | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | ns |
| Kernels per ear | * | * | ** | ns | ** | ** |
| Yield | ** | * | ** | ns | ** | ns |
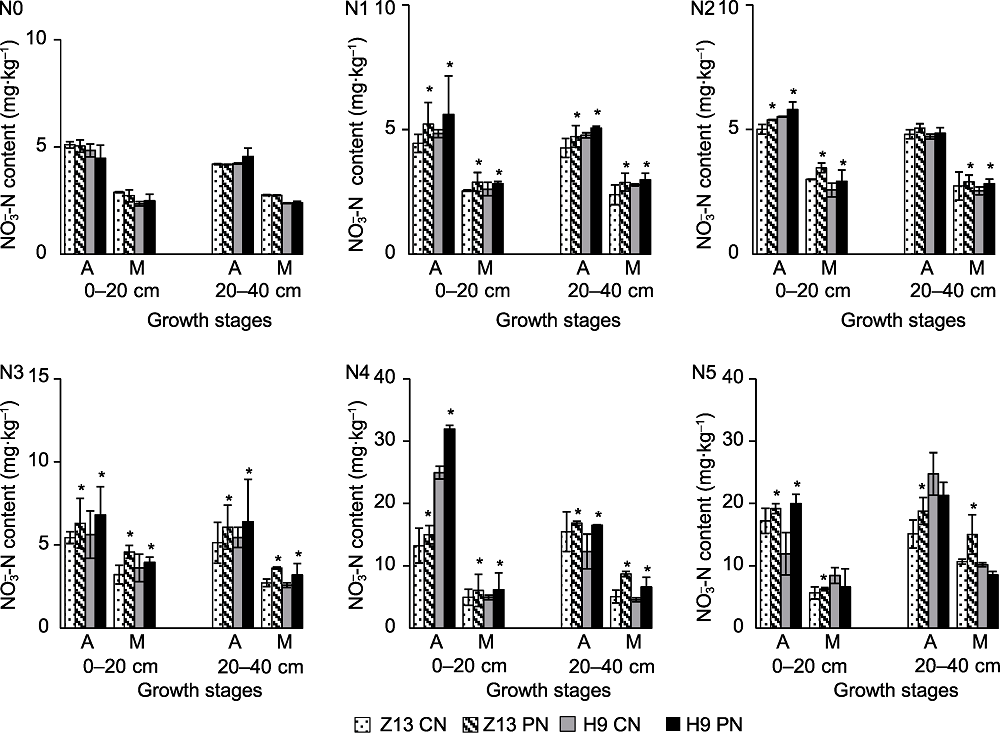
图2 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下两品种谷子0-20 cm和20-40 cm土层土壤硝态氮含量的影响 N0-N5分别代表施氮量为0、75、112.5、150、225和337.5 kg·hm-2。A: 花期; M: 灌浆中期; Z13: 张杂谷13号; H9: 华优谷9号; CN: 常规氮肥; PN: PAC配施氮肥。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 2 Effects of CN and PN treatments on NO3--N contents in 0-20 cm and 20-40 cm soil layers of two foxtail millet varieties under different nitrogen application levels N0-N5 represent nitrogen application levels of 0, 75, 112.5, 150, 225, and 337.5 kg·hm-2, respectively. A: Anthesis; M: Mid-filling; Z13: Zhangzagu 13; H9: Huayougu 9; CN: Conventional nitrogen fertilizer; PN: Polyaspartic acid-chitosan with nitrogen fertilizer. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
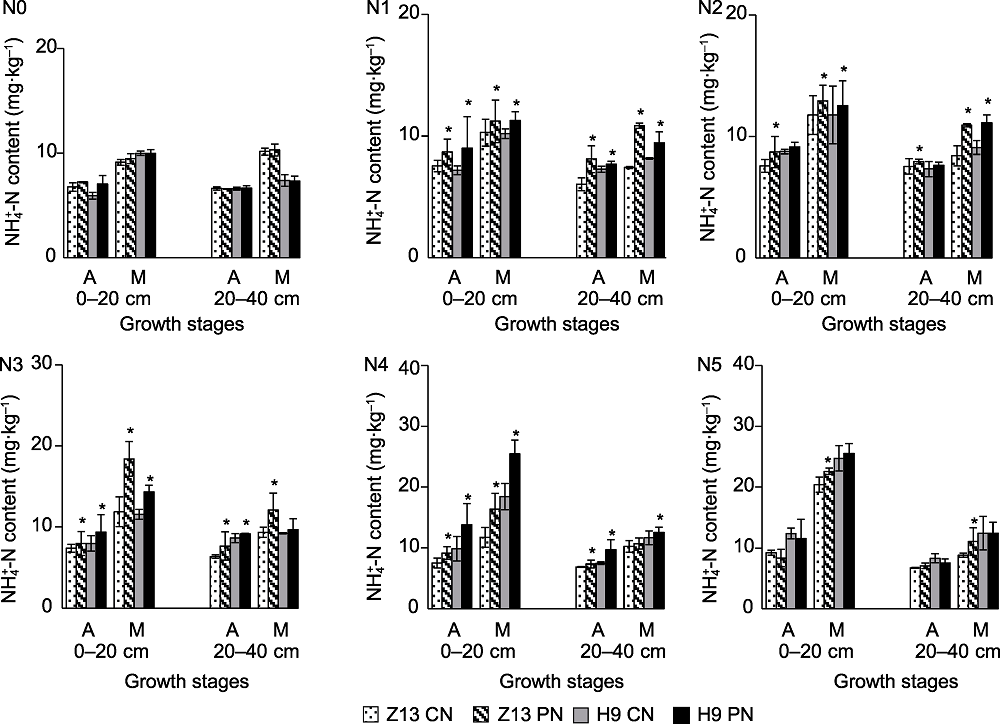
图3 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下两品种谷子0-20 cm和20-40 cm土层土壤铵态氮含量的影响 N0-N5、A、M、Z13、H9、CN和PN同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 3 Effects of CN and PN treatments on NH4+-N contents in 0-20 cm and 20-40 cm soil layers of two foxtail millet varieties under different nitrogen application levels N0-N5, A, M, Z13, H9, CN and PN see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
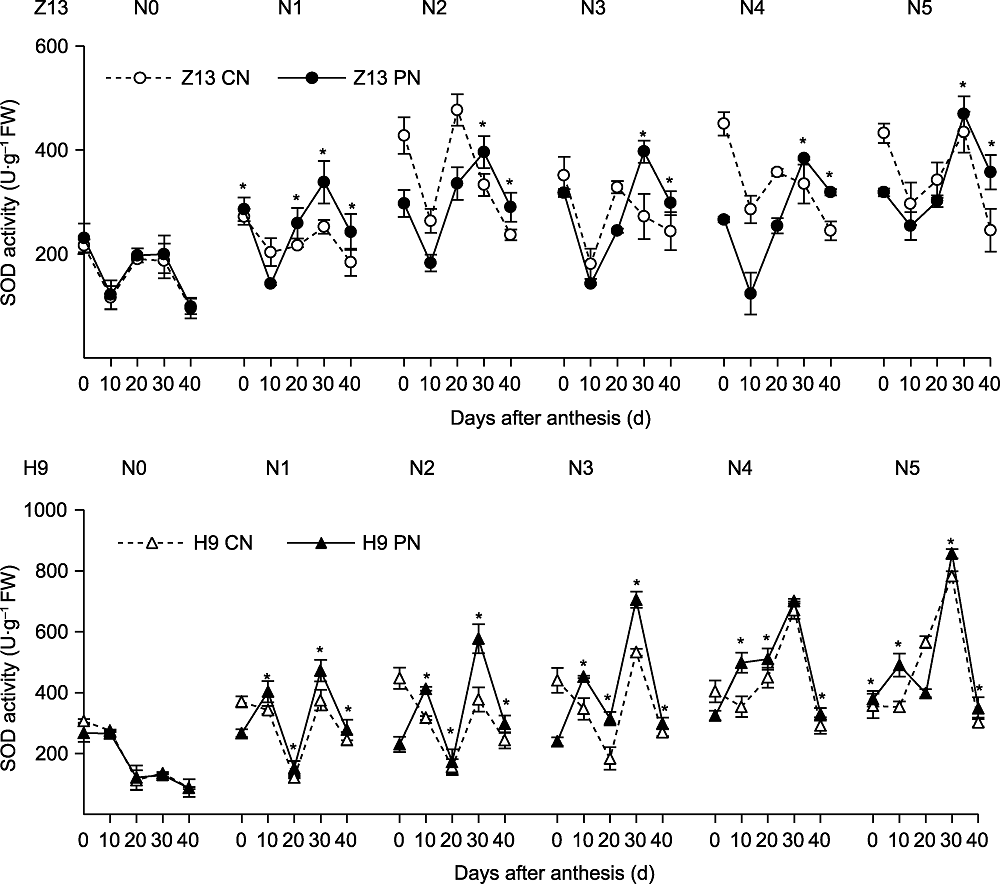
图4 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下两品种谷子(Z13和H9)旗叶SOD活性的影响 SOD: 超氧化物歧化酶。N0-N5、CN、PN、Z13和H9同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 4 Effects of CN and PN treatments on SOD activity in the flag leaf of two foxtail millet varieties (Z13 and H9) under different nitrogen application levels SOD: Superoxide dismutase. N0-N5, CN, PN, Z13 and H9 see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
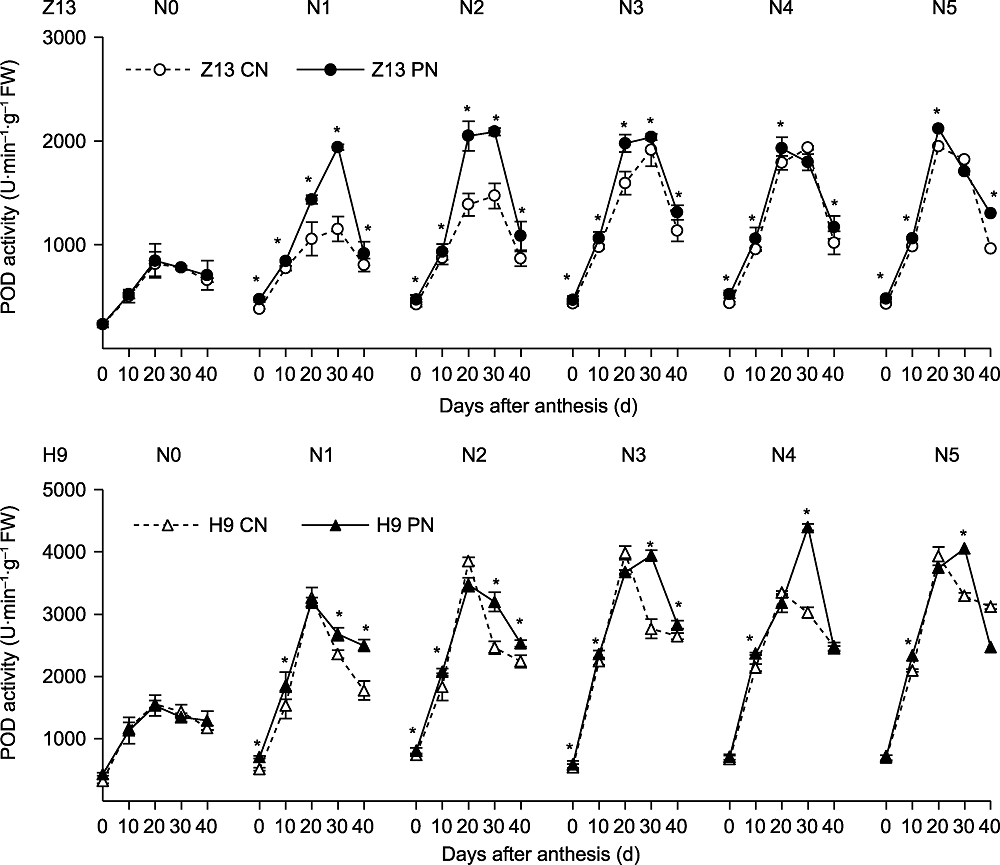
图5 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下两品种谷子(Z13和H9)旗叶POD活性的影响 POD: 过氧化物酶。N0-N5、CN、PN、Z13和H9同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 5 Effects of CN and PN treatments on POD activity in the flag leaf of two foxtail millet varieties (Z13 and H9) under different nitrogen application levels POD: Peroxidase. N0-N5, CN, PN, Z13 and H9 see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
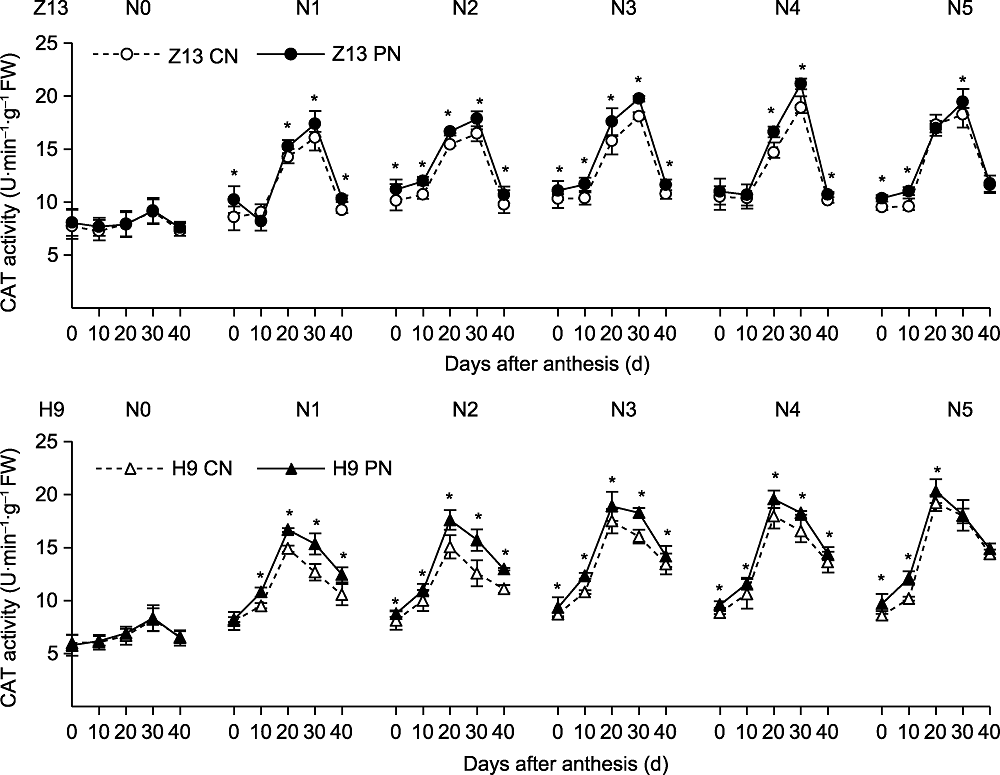
图6 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下两品种谷子(Z13和H9)旗叶CAT活性的影响 CAT: 过氧化氢酶。N0-N5、CN、PN、Z13和H9同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 6 Effects of CN and PN treatments on CAT activity in the flag leaf of two foxtail millet varieties (Z13 and H9) under different nitrogen application levels CAT: Catalase. N0-N5, CN, PN, Z13 and H9 see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
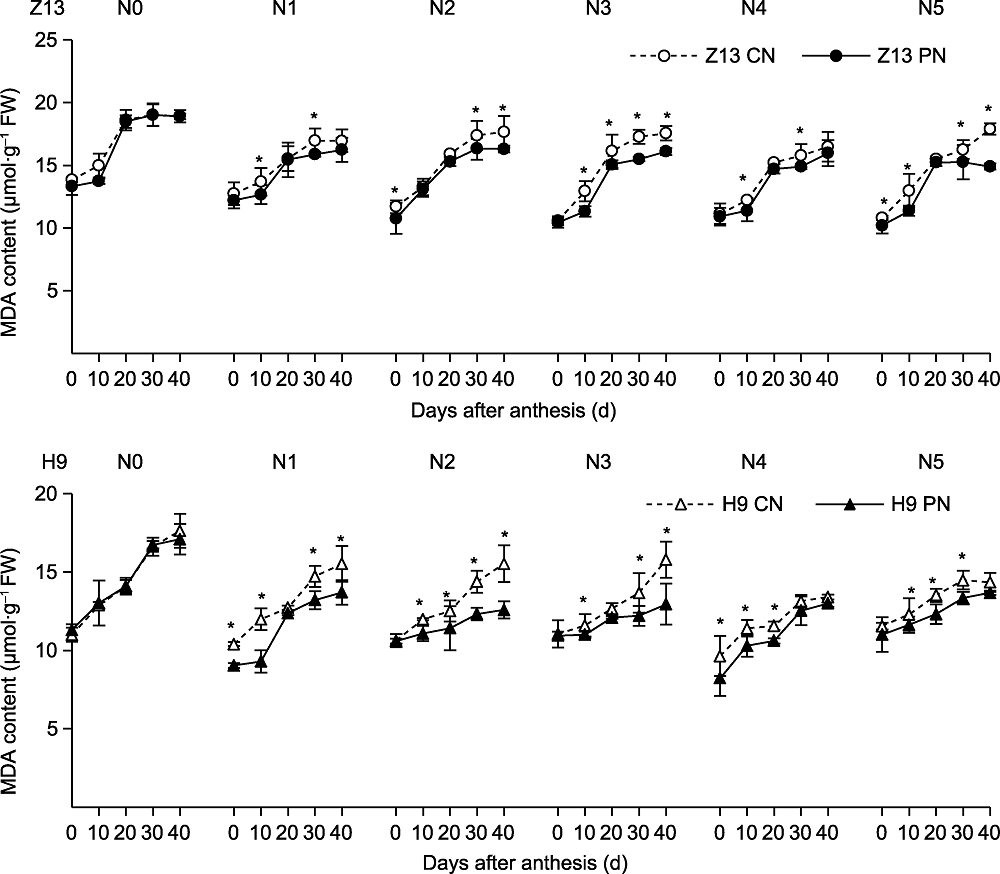
图7 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下两品种谷子(Z13和H9)旗叶MDA含量的影响 MDA: 丙二醛。N0-N5、CN、PN、Z13和H9同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 7 Effects of CN and PN treatments on MDA content in the flag leaf of two foxtail millet varieties (Z13 and H9) under different nitrogen application levels MDA: Malondialdehyde. N0-N5, CN, PN, Z13 and H9 see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
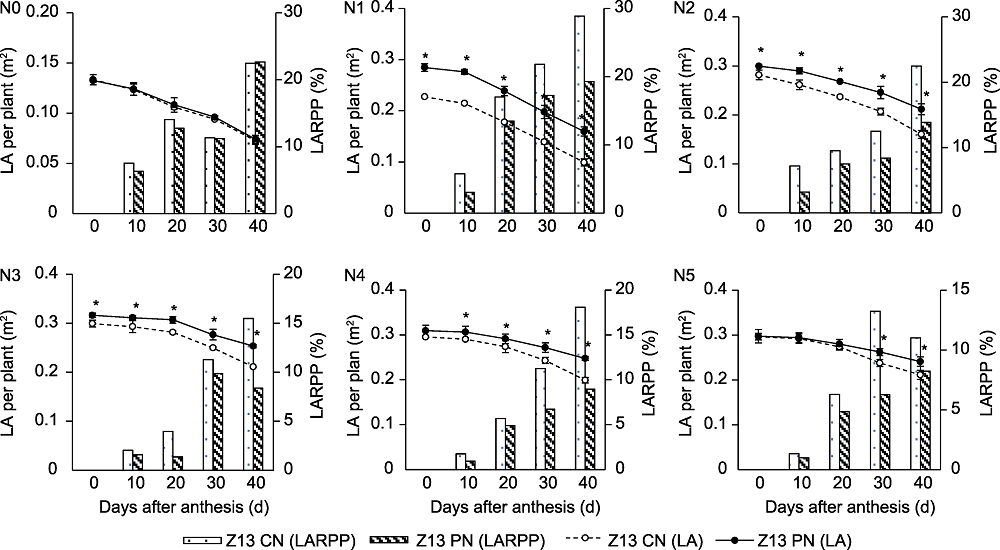
图8 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下张杂谷13号单株叶面积(LA)和叶面积降幅(LARPP)的影响 N0-N5、CN、PN和Z13同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 8 Effects of CN and PN treatments on the leaf area (LA) per plant and the leaf area reduction per plant (LARPP) of Zhangzagu 13 under different nitrogen application levels N0-N5, CN, PN and Z13 see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
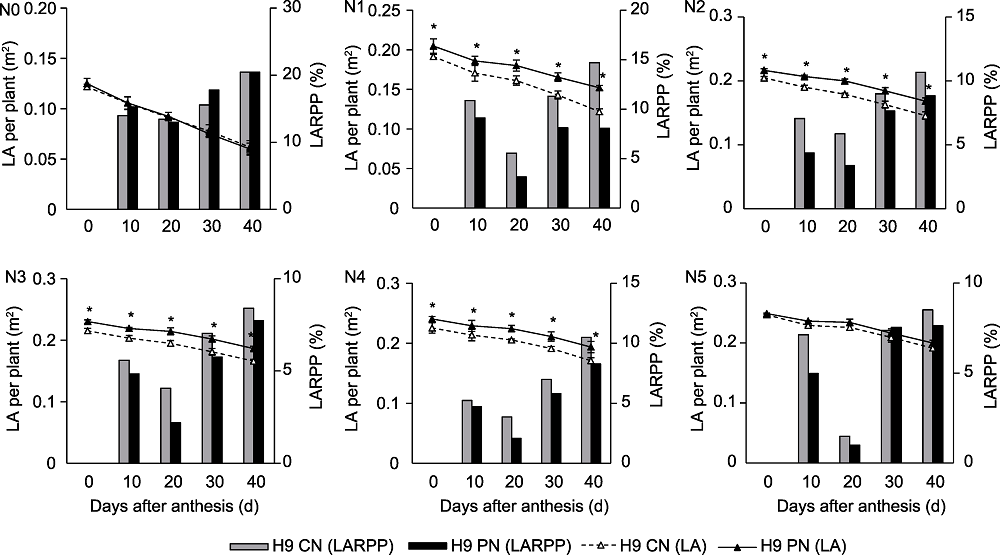
图9 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下华优谷9号单株叶面积(LA)和叶面积降幅(LARPP)的影响 N0-N5、CN、PN和H9同图2。*表示T检验结果在0.05水平差异显著。
Figure 9 Effects of CN and PN treatments on the leaf area (LA) per plant and the leaf area reduction per plant (LARPP) of Huayougu 9 under different nitrogen application levels N0-N5, CN, PN and H9 see Figure 2. *represent significant differences at the 0.05 level according to T test.
| Year | Variety | Nitrogen application level | Treatments | 1000-kernel weight (g) | Ears per hectare (×104) | Kernels per ear | Yield (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Z13 | N0 | CN | 3.01±0.01 a | 54.04±7.64 d | 2958.92±197.08 e | 3961.28±666.41 e |
| PN | 3.20±0.02 a | 49.73±11.39 d | 3120.26±717.45 e | 4492.38±47.10 e | |||
| N1 | CN | 3.10±0.07 a | 74.68±1.41 bcd | 3336.44±64.81 de | 5210.65±269.69 d | ||
| PN | 3.16±0.01 a | 82.64±6.94 abc | 4469.97±169.58 bc | 5833.84±115.27 cd | |||
| N2 | CN | 3.10±0.01 a | 72.20±4.62 bcd | 3219.22±139.57 de | 5086.68±154.24 d | ||
| PN | 3.19±0.05 a | 82.53±1.30 abc | 4348.85±324.25 bc | 6084.11±181.29 c | |||
| N3 | CN | 3.11±0.04 a | 88.94±0.05 ab | 3808.47±97.49 cd | 5704.99±228.11 cd | ||
| PN | 3.05±0.09 a | 101.18±9.35 a | 4149.58±300.65 bc | 6346.00±251.15 bc | |||
| N4 | CN | 3.08±0.05 a | 82.30±1.93 abc | 4352.51±289.94 bc | 6221.06±45.78 bc | ||
| PN | 3.03±0.03 a | 79.75±12.27 abc | 4764.54±276.44 ab | 7218.13±170.15 a | |||
| N5 | CN | 3.04±0.06 a | 61.31±2.88 cd | 5171.64±121.91 a | 5643.82±205.85 cd | ||
| PN | 3.14±0.02 a | 82.43±14.50 abc | 5337.16±278.97 a | 6859.80±54.30 ab | |||
| H9 | N0 | CN | 2.77±0.06 a | 42.90±2.77 c | 3259.58±294.10 f | 2841.87±266.10 e | |
| PN | 2.87±0.04 a | 44.07±1.39 c | 3179.86±397.05 f | 2665.03±576.40 e | |||
| Year | Variety | Nitrogen application level | Treatments | 1000-kernel weight (g) | Ears per hectare (×104) | Kernels per ear | Yield (kg·hm-2) |
| N1 | CN | 2.96±0.04 a | 48.45±5.47 bc | 3762.92±276.60 ef | 4819.18±162.46 cd | ||
| PN | 2.77±0.17 a | 47.30±1.45 bc | 5627.07±483.28 abc | 5102.19±41.82 bcd | |||
| N2 | CN | 2.90±0.06 a | 48.88±0.57 bc | 3704.04±110.08 ef | 4708.26±40.61 d | ||
| PN | 2.71±0.16 a | 54.23±5.33 ab | 5970.81±488.05 ab | 5449.61±182.03 ab | |||
| N3 | CN | 2.84±0.03 a | 54.30±0.03 ab | 4260.95±488.52 def | 5191.22±319.75 bcd | ||
| PN | 2.93±0.03 a | 61.75±0.00 a | 4655.47±346.73 cde | 5807.44±189.45 a | |||
| N4 | CN | 2.87±0.05 a | 49.42±0.35 bc | 4304.03±28.78 def | 5322.38±16.18 abc | ||
| PN | 2.71±0.05 a | 48.76±1.11 bc | 4989.91±134.54 bcd | 5573.23±114.46 ab | |||
| N5 | CN | 2.89±0.07 a | 44.44±1.54 c | 5634.94±224.43abc | 5358.65±90.55 abc | ||
| PN | 2.82±0.06 a | 47.29±1.36 bc | 6178.41±152.83 a | 5654.90±225.72 ab | |||
| 2021 | Z13 | N0 | CN | 2.99±0.01 a | 30.61±1.57 c | 2795.47±25.62 f | 4401.94±86.96 g |
| PN | 2.98±0.01 a | 33.04±3.44 c | 2804.69±30.94 f | 4703.18±43.57 g | |||
| N1 | CN | 2.98±0.01 a | 53.96±3.92 b | 3278.62±5.73 e | 6058.60±144.94 f | ||
| PN | 2.76±0.00 d | 61.47±1.48 ab | 3806.51±18.85 d | 6920.37±115.53 e | |||
| N2 | CN | 2.84±0.02 bcd | 54.09±0.17 b | 3968.71±135.66 cd | 6909.46±128.48 e | ||
| PN | 2.88±0.02 b | 62.08±0.24 ab | 4522.32±105.31 b | 7528.52±220.42 cd | |||
| N3 | CN | 2.80±0.05 cd | 53.93±0.94 b | 4405.35±315.60 bc | 7431.84±166.51 cde | ||
| PN | 2.92±0.01ab | 67.86±7.28 a | 5082.53±216.23 a | 8331.60±174.92 a | |||
| N4 | CN | 2.79±0.03 cd | 60.30±2.92 ab | 3861.02±123.59 d | 7554.17±154.64 cd | ||
| PN | 2.84±0.02 bcd | 67.82±1.00 a | 4373.39±92.35 bc | 8207.58±116.12 ab | |||
| N5 | CN | 2.84±0.05 bc | 54.36±1.99 b | 4448.14±100.82 b | 7014.04±189.48 de | ||
| PN | 2.88±0.03 bc | 53.83±2.00 b | 4804.27±215.53 ab | 7728.81±387.39 bc | |||
| H9 | N0 | CN | 2.78±0.04 a | 31.55±3.44 e | 2715.21±69.13 f | 3394.46±321.84 e | |
| PN | 2.77±0.05 ab | 33.33±1.11 cde | 2737.97±72.11 f | 3451.73±92.78 e | |||
| N1 | CN | 2.65±0.01 bc | 43.06±1.81 ab | 3253.50±14.89 e | 4435.98±47.33 d | ||
| PN | 2.65±0.03 bc | 47.33±3.67 a | 3924.53±69.32 d | 4900.02±42.41 bc | |||
| N2 | CN | 2.72±0.04 abc | 43.26±2.42 ab | 3228.59±43.95 e | 4582.70±157.50 cd | ||
| PN | 2.68±0.06 abc | 46.69±3.12 a | 3836.65±46.26 d | 5323.72±45.71 b | |||
| N3 | CN | 2.69±0.04 abc | 41.50±1.97 abc | 3701.82±56.01 d | 5204.25±17.00 b | ||
| PN | 2.74±0.01 ab | 44.32±0.50 ab | 4406.01±109.46 c | 5878.46±78.52 a | |||
| N4 | CN | 2.67±0.00 abc | 37.52±1.96 bcde | 3848.09±126.56 d | 4728.62±80.51 cd | ||
| PN | 2.72±0.03 abc | 40.64±1.25 abcd | 4575.28±86.38 c | 5221.79±154.69 b | |||
| N5 | CN | 2.62±0.05 c | 32.37±2.72 de | 5946.01±128.77 a | 4590.14±171.44 d | ||
| PN | 2.72±0.03 abc | 33.32±4.88 cde | 5452.32±240.20 b | 5244.53±216.27 b |
表3 CN和PN处理对不同施氮量下谷子产量及产量构成因素的影响
Table 3 Effects of CN and PN treatments on yield and yield components of two foxtail millet varieties under different nitrogen application levels
| Year | Variety | Nitrogen application level | Treatments | 1000-kernel weight (g) | Ears per hectare (×104) | Kernels per ear | Yield (kg·hm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Z13 | N0 | CN | 3.01±0.01 a | 54.04±7.64 d | 2958.92±197.08 e | 3961.28±666.41 e |
| PN | 3.20±0.02 a | 49.73±11.39 d | 3120.26±717.45 e | 4492.38±47.10 e | |||
| N1 | CN | 3.10±0.07 a | 74.68±1.41 bcd | 3336.44±64.81 de | 5210.65±269.69 d | ||
| PN | 3.16±0.01 a | 82.64±6.94 abc | 4469.97±169.58 bc | 5833.84±115.27 cd | |||
| N2 | CN | 3.10±0.01 a | 72.20±4.62 bcd | 3219.22±139.57 de | 5086.68±154.24 d | ||
| PN | 3.19±0.05 a | 82.53±1.30 abc | 4348.85±324.25 bc | 6084.11±181.29 c | |||
| N3 | CN | 3.11±0.04 a | 88.94±0.05 ab | 3808.47±97.49 cd | 5704.99±228.11 cd | ||
| PN | 3.05±0.09 a | 101.18±9.35 a | 4149.58±300.65 bc | 6346.00±251.15 bc | |||
| N4 | CN | 3.08±0.05 a | 82.30±1.93 abc | 4352.51±289.94 bc | 6221.06±45.78 bc | ||
| PN | 3.03±0.03 a | 79.75±12.27 abc | 4764.54±276.44 ab | 7218.13±170.15 a | |||
| N5 | CN | 3.04±0.06 a | 61.31±2.88 cd | 5171.64±121.91 a | 5643.82±205.85 cd | ||
| PN | 3.14±0.02 a | 82.43±14.50 abc | 5337.16±278.97 a | 6859.80±54.30 ab | |||
| H9 | N0 | CN | 2.77±0.06 a | 42.90±2.77 c | 3259.58±294.10 f | 2841.87±266.10 e | |
| PN | 2.87±0.04 a | 44.07±1.39 c | 3179.86±397.05 f | 2665.03±576.40 e | |||
| Year | Variety | Nitrogen application level | Treatments | 1000-kernel weight (g) | Ears per hectare (×104) | Kernels per ear | Yield (kg·hm-2) |
| N1 | CN | 2.96±0.04 a | 48.45±5.47 bc | 3762.92±276.60 ef | 4819.18±162.46 cd | ||
| PN | 2.77±0.17 a | 47.30±1.45 bc | 5627.07±483.28 abc | 5102.19±41.82 bcd | |||
| N2 | CN | 2.90±0.06 a | 48.88±0.57 bc | 3704.04±110.08 ef | 4708.26±40.61 d | ||
| PN | 2.71±0.16 a | 54.23±5.33 ab | 5970.81±488.05 ab | 5449.61±182.03 ab | |||
| N3 | CN | 2.84±0.03 a | 54.30±0.03 ab | 4260.95±488.52 def | 5191.22±319.75 bcd | ||
| PN | 2.93±0.03 a | 61.75±0.00 a | 4655.47±346.73 cde | 5807.44±189.45 a | |||
| N4 | CN | 2.87±0.05 a | 49.42±0.35 bc | 4304.03±28.78 def | 5322.38±16.18 abc | ||
| PN | 2.71±0.05 a | 48.76±1.11 bc | 4989.91±134.54 bcd | 5573.23±114.46 ab | |||
| N5 | CN | 2.89±0.07 a | 44.44±1.54 c | 5634.94±224.43abc | 5358.65±90.55 abc | ||
| PN | 2.82±0.06 a | 47.29±1.36 bc | 6178.41±152.83 a | 5654.90±225.72 ab | |||
| 2021 | Z13 | N0 | CN | 2.99±0.01 a | 30.61±1.57 c | 2795.47±25.62 f | 4401.94±86.96 g |
| PN | 2.98±0.01 a | 33.04±3.44 c | 2804.69±30.94 f | 4703.18±43.57 g | |||
| N1 | CN | 2.98±0.01 a | 53.96±3.92 b | 3278.62±5.73 e | 6058.60±144.94 f | ||
| PN | 2.76±0.00 d | 61.47±1.48 ab | 3806.51±18.85 d | 6920.37±115.53 e | |||
| N2 | CN | 2.84±0.02 bcd | 54.09±0.17 b | 3968.71±135.66 cd | 6909.46±128.48 e | ||
| PN | 2.88±0.02 b | 62.08±0.24 ab | 4522.32±105.31 b | 7528.52±220.42 cd | |||
| N3 | CN | 2.80±0.05 cd | 53.93±0.94 b | 4405.35±315.60 bc | 7431.84±166.51 cde | ||
| PN | 2.92±0.01ab | 67.86±7.28 a | 5082.53±216.23 a | 8331.60±174.92 a | |||
| N4 | CN | 2.79±0.03 cd | 60.30±2.92 ab | 3861.02±123.59 d | 7554.17±154.64 cd | ||
| PN | 2.84±0.02 bcd | 67.82±1.00 a | 4373.39±92.35 bc | 8207.58±116.12 ab | |||
| N5 | CN | 2.84±0.05 bc | 54.36±1.99 b | 4448.14±100.82 b | 7014.04±189.48 de | ||
| PN | 2.88±0.03 bc | 53.83±2.00 b | 4804.27±215.53 ab | 7728.81±387.39 bc | |||
| H9 | N0 | CN | 2.78±0.04 a | 31.55±3.44 e | 2715.21±69.13 f | 3394.46±321.84 e | |
| PN | 2.77±0.05 ab | 33.33±1.11 cde | 2737.97±72.11 f | 3451.73±92.78 e | |||
| N1 | CN | 2.65±0.01 bc | 43.06±1.81 ab | 3253.50±14.89 e | 4435.98±47.33 d | ||
| PN | 2.65±0.03 bc | 47.33±3.67 a | 3924.53±69.32 d | 4900.02±42.41 bc | |||
| N2 | CN | 2.72±0.04 abc | 43.26±2.42 ab | 3228.59±43.95 e | 4582.70±157.50 cd | ||
| PN | 2.68±0.06 abc | 46.69±3.12 a | 3836.65±46.26 d | 5323.72±45.71 b | |||
| N3 | CN | 2.69±0.04 abc | 41.50±1.97 abc | 3701.82±56.01 d | 5204.25±17.00 b | ||
| PN | 2.74±0.01 ab | 44.32±0.50 ab | 4406.01±109.46 c | 5878.46±78.52 a | |||
| N4 | CN | 2.67±0.00 abc | 37.52±1.96 bcde | 3848.09±126.56 d | 4728.62±80.51 cd | ||
| PN | 2.72±0.03 abc | 40.64±1.25 abcd | 4575.28±86.38 c | 5221.79±154.69 b | |||
| N5 | CN | 2.62±0.05 c | 32.37±2.72 de | 5946.01±128.77 a | 4590.14±171.44 d | ||
| PN | 2.72±0.03 abc | 33.32±4.88 cde | 5452.32±240.20 b | 5244.53±216.27 b |
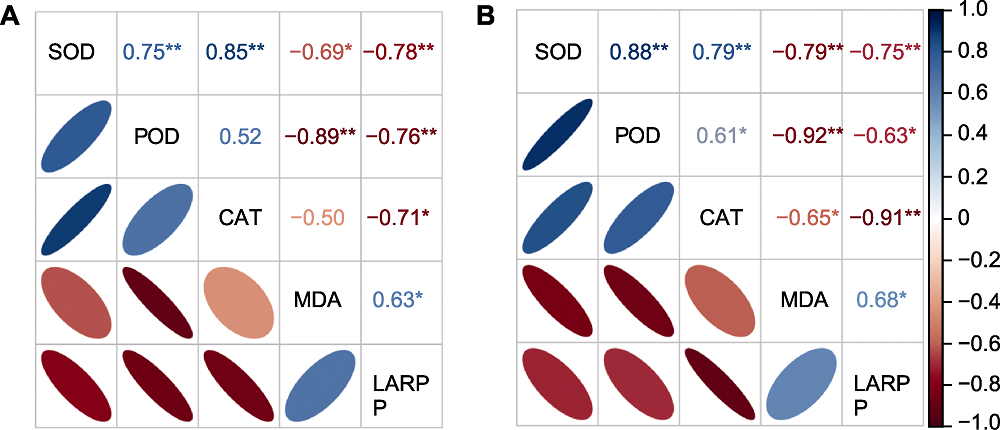
图10 不同施氮量下两品种谷子花后叶面积降幅(LARPP)与旗叶抗氧化酶(SOD、POD和CAT)活性及MDA含量的相关性 (A) 常规氮肥处理; (B) PAC配施氮肥处理。SOD、POD、CAT和MDA同表2。*P<0.05, **P<0.01
Figure 10 Correlation coefficients of the leaf area reduction per plant (LARPP) with the activity of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, POD and CAT) and MDA content in the flag leaf at anthesis stage in two foxtail millet varieties under different nitrogen application levels (A) Conventional nitrogen fertilizer treatments; (B) Polyaspartic acid-chitosan with nitrogen fertilizer treatments. SOD, POD, CAT and MDA see Table 2. *P<0.05, **P<0.01
| NO3--N content | NH4+-N content | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-20 cm soil layer | 20-40 cm soil layer | 0-20 cm soil layer | 20-40 cm soil layer | |||||
| Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | |
| SOD | 0.67** | 0.72** | 0.68** | 0.48* | 0.84** | 0.78** | 0.66** | 0.60** |
| POD | 0.40 | 0.41* | 0.37 | 0.16 | 0.72** | 0.51* | 0.72** | 0.43* |
| CAT | 0.50* | 0.64** | 0.54** | 0.46* | 0.66** | 0.66** | 0.58** | 0.62** |
| MDA | -0.48* | -0.34 | -0.32 | -0.18 | -0.64** | -0.48* | -0.67** | -0.39 |
| LARPP | -0.52** | -0.64** | -0.54** | -0.50* | -0.63** | -0.66** | -0.60** | -0.70** |
表4 不同施氮量下两品种谷子花后土壤含氮量与叶面积降幅及抗氧化指标的相关性
Table 4 Correlation coefficients of nitrogen content in soil with the leaf area reduction per plant and antioxidant items after anthesis stage in two foxtail millet varieties under different nitrogen application levels
| NO3--N content | NH4+-N content | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-20 cm soil layer | 20-40 cm soil layer | 0-20 cm soil layer | 20-40 cm soil layer | |||||
| Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | Anthesis stage | Mid-filling stage | |
| SOD | 0.67** | 0.72** | 0.68** | 0.48* | 0.84** | 0.78** | 0.66** | 0.60** |
| POD | 0.40 | 0.41* | 0.37 | 0.16 | 0.72** | 0.51* | 0.72** | 0.43* |
| CAT | 0.50* | 0.64** | 0.54** | 0.46* | 0.66** | 0.66** | 0.58** | 0.62** |
| MDA | -0.48* | -0.34 | -0.32 | -0.18 | -0.64** | -0.48* | -0.67** | -0.39 |
| LARPP | -0.52** | -0.64** | -0.54** | -0.50* | -0.63** | -0.66** | -0.60** | -0.70** |
| [1] | 常闻谦, 刘鹏, 赵世伟 (2018). 水氮耦合对谷子拔节后生长、产量和水氮利用效率的影响. 西北农业学报 27, 1313-1321. |
| [2] | 陈佳阳, 乐学义 (2011). 壳聚糖及其衍生物在农业上的应用. 化学研究与应用 23, 1-8. |
| [3] | 陈军, 高贵珍, 赵亮, 徐礼生, 张兴桃, 薛文 (2015). 干旱胁迫下壳聚糖浸种对小麦萌发期保护酶活性的影响. 基因组学与应用生物学 34, 2251-2254. |
| [4] | 段咏新, 宋松泉, 傅家瑞 (1997). 钙对延缓杂交水稻叶片衰老的作用机理. 杂交水稻 12(6), 23-25. |
| [5] | 高月亮 (2007). 聚天冬氨酸对尿素氮在土壤中运移影响的研究. 硕士论文. 北京: 首都师范大学. pp. 1-82. |
| [6] | 何萍, 金继运 (1999). 氮钾营养对春玉米叶片衰老过程中激素变化与活性氧代谢的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报 5, 289-296. |
| [7] | 侯彩霞, 汤章城 (1999). 细胞相容性物质的生理功能及其作用机制. 植物生理学通讯 35, 1-7. |
| [8] | 李红梅 (2018). 减量分期施氮对小麦产量和氮素利用效率的影响. 硕士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 1-166. |
| [9] |
李顺国, 刘斐, 刘猛, 程汝宏, 夏恩君, 刁现民 (2021). 中国谷子产业和种业发展现状与未来展望. 中国农业科学 54, 459-470.
DOI |
| [10] |
李宗新, 王庆成, 齐世军, 刘开昌, 刘霞, 张彗 (2007). 控释肥对玉米高产的应用效应研究进展. 华北农学报 22(S1), 127-130.
DOI |
| [11] | 林春梅 (2012). 壳聚糖在农业领域中的应用. 现代农业科技 (12), 331-332. |
| [12] | 刘光明, 赵灿, 蒋岩, 赵凌天, 廖平强, 王维领, 霍中洋 (2022). 施氮量对水稻源库协同衰老特征的影响. 植物生理学报 58, 173-185. |
| [13] | 刘红卫 (2010). 聚天门冬氨酸和多肽肥料应用展望. 黑龙江农业科学 (7), 162-164. |
| [14] | 刘连涛, 李存东, 孙红春, 张永江, 白志英, 冯丽肖 (2009). 氮素营养水平对棉花衰老的影响及其生理机制. 中国农业科学 42, 1575-1581. |
| [15] | 刘球, 李志辉, 吴际友, 陈彩霞, 李艳, 吴志华, 程勇, 黄明军 (2015). 红椿幼苗对干旱胁迫及复水生理响应的典型相关分析. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版) 43(10), 35-44. |
| [16] | 陆雯芸 (2016). 水稻OsVPE3转基因株系表型及其盐胁迫诱导的程序性细胞死亡研究. 硕士论文. 杭州: 浙江大学. pp. 1-70. |
| [17] | 马承, 罗庆熙 (2008). 壳聚糖在农业领域中的应用. 北方园艺 (9), 55-56. |
| [18] | 曲丹阳 (2018). 壳聚糖缓解玉米幼苗镉毒害的生理机制. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. pp. 1-62. |
| [19] | 孙海燕, 罗兵, 徐朗莱 (2006). 壳聚糖浸种对黄瓜幼苗生长和果实品质的影响. 安徽农业科学 34, 3329-3330. |
| [20] | 唐会会 (2019). 聚天门冬氨酸(PASP)对东北春玉米氮素代谢的调控效应及其节氮机理. 硕士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 1-57. |
| [21] |
唐会会, 许艳丽, 王庆燕, 马正波, 李光彦, 董会, 董志强 (2019). 聚天门冬氨酸螯合氮肥减量基施对东北春玉米的增效机制. 作物学报 45, 431-442.
DOI |
| [22] | 王琦, 许艳丽, 闫鹏, 董好胜, 张薇, 卢霖, 董志强 (2022). 聚天门冬氨酸和壳聚糖复配剂对谷子光合特性、氮素利用率及产量的影响. 生态学杂志. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/21.1148.Q.20220531.1713.013.html. 2022-06-01. |
| [23] | 王三根 (2000). 细胞分裂素在植物抗逆和延衰中的作用. 植物学通报 17, 121-126. |
| [24] | 王涛, 黄语燕, 陈永快, 廖水兰, 刘现, 康育鑫 (2019). 高温胁迫下外源壳聚糖对黄瓜幼苗生长的影响. 江苏农业科学 47(23), 142-146. |
| [25] | 王燚 (2019). 5-氨基乙酰丙酸(ALA)缓解玉米早春低温胁迫生理机制. 博士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. pp. 1-110. |
| [26] |
王永军, 杨今胜, 袁翠平, 柳京国, 李登海, 董树亭 (2013). 超高产夏玉米花粒期不同部位叶片衰老与抗氧化酶特性. 作物学报 39, 2183-2191.
DOI |
| [27] | 解振兴, 董志强, 兰宏亮, 高娇, 朱平, 彭畅 (2012). 磷酸胆碱合剂对不同种植密度玉米叶片衰老生理的影响. 核农学报 26, 157-163. |
| [28] |
徐娜, 徐江民, 蒋玲欢, 饶玉春 (2017). 水稻叶片早衰成因及分子机理研究进展. 植物学报 52, 102-112.
DOI |
| [29] | 薛盈文, 苗兴芬, 王玉凤 (2019). 施氮对谷子光合特性及产量和品质的影响. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报 31(4), 1-7, 39. |
| [30] | 杨俊刚, 高强, 曹兵, 陈新平 (2009). 一次性施肥对春玉米产量和环境效应的影响. 中国农学通报 25(19), 123-128. |
| [31] | 杨淑慎, 高俊凤, 李学俊 (2001). 高等植物叶片的衰老. 西北植物学报 21, 1271-1277. |
| [32] | 曾蓉 (2013). 氮肥运筹对谷子产量及品质的影响. 硕士论文. 晋中: 山西农业大学. pp. 1-46. |
| [33] | 张林, 武文明, 陈欢, 陈洪俭, 彭晨, 王世济, 曹承富 (2021). 氮肥运筹方式对土壤无机氮变化、玉米产量和氮素吸收利用的影响. 中国土壤与肥料 (4), 126-134. |
| [34] |
张盛春, 李清明, 阳成伟 (2017). 拟南芥金属蛋白酶FtSH4通过生长素与活性氧调控叶片衰老. 植物学报 52, 453-464.
DOI |
| [35] | 张文清, 吕伟娇, 陈强, 李辉信 (2006). 不同分子量壳聚糖对土壤碳、氮及呼吸的影响. 生态学报 26, 1280-1284. |
| [36] | 张亚琦, 李淑文, 付巍, 文宏达 (2014). 施氮对杂交谷子产量与光合特性及水分利用效率的影响. 植物营养与肥料学报 20, 1119-1126. |
| [37] | 张忠学, 尚文彬, 齐智娟, 郑恩楠, 刘明 (2019). 不同水氮管理下玉米叶片衰老对氮转移效率的影响. 农业机械学报 50 (12), 297-303, 267. |
| [38] | 朱云林, 顾大路, 王伟中, 杜小凤, 杨文飞, 孙爱侠 (2017). 壳聚糖对水稻幼苗抗冷性的影响. 江苏农业科学 45(8), 66-68. |
| [39] |
Attia MS, Osman MS, Mohamed AS, Mahgoub HA, Garada MO, Abdelmouty ES, Latef AAHA (2021). Impact of foliar application of chitosan dissolved in different organic acids on isozymes, protein patterns and physio-bio-chemical characteristics of tomato grown under salinity stress. Plants 10, 388.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Deng F, Wang L, Ren WJ, Mei XF (2014). Enhancing ni-trogen utilization and soil nitrogen balance in paddy fields by optimizing nitrogen management and using polyaspar-tic acid urea. Field Crops Res 169, 30-38.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Hidangmayum A, Dwivedi P, Katiyar D, Hemantaranjan A (2019). Application of chitosan on plant responses with special reference to abiotic stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25, 313-326.
DOI |
| [42] |
Ho SL, Tong WF, Yu SM (2000). Multiple mode regulation of a cysteine proteinase gene expression in rice. Plant Physiol 122, 57-66.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Lü SY, Feng C, Gao CM, Wang XG, Xu XB, Bai X, Gao NN, Liu MZ (2016). Multifunctional environmental smart fertilizer based on L-aspartic acid for sustained nutrient re-lease. J Agric Food Chem 64, 4965-4974.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Ma LJ, Li YY, Yu CM, Wang Y, Li XM, Li N, Chen Q, Bu N (2012). Alleviation of exogenous oligochitosan on wheat seedlings growth under salt stress. Protoplasma 249, 393-399.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Nkrumah M, Griffith SM, Ahmad N (1989). Lysimeter and field studies on 15N in a tropical soil. II. Transformation of (NH2)2CO-15N in a tropical loam in lysimeter and field plots. Plant Soil 114, 13-18.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Shen JB, Cui ZL, Miao YX, Mi GH, Zhang HY, Fan MS, Zhang CC, Jiang RF, Zhang WF, Li HG, Chen XP, Li XL, Zhang FS (2013). Transforming agriculture in China: from solely high yield to both high yield and high resource use efficiency. Glob Food Secur 2, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Tollenaar M, Daynard TB (1978). Leaf senescence in short- season maize hybrids. Can J Plant Sci 58, 869-874.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Van Der Graaff E, Schwacke R, Schneider A, Desimone M, Flügge UI, Kunze R (2006). Transcription analysis of Arabidopsis membrane transporters and hormone path-ways during developmental and induced leaf senescence. Plant Physiol 141, 776-792.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Yang F, Hu JJ, Li JL, Wu XL, Qian YR (2009). Chitosan enhances leaf membrane stability and antioxidant enzyme activities in apple seedlings under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul 58, 131-136.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 樊蓓, 任敏, 王延峰, 党峰峰, 陈国梁, 程国亭, 杨金雨, 孙会茹. 番茄SlWRKY45转录因子在响应低温和干旱胁迫中的功能(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 186-203. |
| [2] | 田建红, 刘燕, 尹梦琪, 王静, 陈婷, 汪燕, 姜孝成. 水稻OsWAK16通过调节抗氧化酶活性调控种子抗老化能力(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 17-32. |
| [3] | 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| [4] | 余玉蓉, 吴浩, 高娅菲, 赵媛博, 李小玲, 卜贵军, 薛丹, 刘正祥, 武海雯, 吴林. 模拟氮沉降对鄂西南湿地泥炭藓生理及形态特征的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(11): 1493-1506. |
| [5] | 张慧, 梁红凯, 智慧, 张林林, 刁现民, 贾冠清. 谷子β-胡萝卜素异构酶家族基因的表达与变异分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 34-50. |
| [6] | 杨澜, 刘雅, 项阳, 孙秀娟, 颜景畏, 张阿英. 谷子茎尖体外遗传转化体系的建立与优化[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 71-79. |
| [7] | 许馨露, 李丹丹, 马元丹, 翟建云, 孙建飞, 高岩, 张汝民. 四季桂抗氧化防御系统对干旱、高温及协同胁迫的响应[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(1): 72-81. |
| [8] | 许红梅, 李进, 张元明. 水分条件对人工培养齿肋赤藓光化学效率及生理特性的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(8): 882-893. |
| [9] | 刘盟盟, 贾丽, 程路芸, 张洪芹, 臧晓琳, 宝音陶格涛, 张汝民, 高岩. 冷蒿酚酸及其抗氧化防御酶活性对机械损伤的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(2): 219-230. |
| [10] | 刘宝玲, 张莉, 孙岩, 薛金爱, 高昌勇, 苑丽霞, 王计平, 贾小云, 李润植. 谷子bZIP转录因子的全基因组鉴定及其在干旱和盐胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(4): 473-487. |
| [11] | 陈思羽, 刘鹏, 朱末, 夏冬冬, 李亮, 徐克章, 陈展宇, 张治安. 大豆植株不同冠层种子活力及其萌发中抗氧化酶活性[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(1): 24-30. |
| [12] | 尹本丰, 张元明. 冻融过程对荒漠区不同微生境下齿肋赤藓渗透调节物含量和抗氧化酶活力的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(5): 517-529. |
| [13] | 陈青青, 李德志. 根系隔离条件下的谷子亲缘识别[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(12): 1188-1197. |
| [14] | 郭慧媛, 马元丹, 王丹, 左照江, 高岩, 张汝民, 王玉魁. 模拟酸雨对毛竹叶片抗氧化酶活性及释放绿叶挥发物的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2014, 38(8): 896-903. |
| [15] | 耿东梅, 单立山, 李毅, Жигунов Анатолий Васильевич. 土壤水分胁迫对红砂幼苗叶绿素荧光和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(3): 282-291. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||