

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (3): 440-448.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22221 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22221
刘叶飞1,2, 赵海霞2, 姜希萍2, 邱锐1,2, 周昕越1, 赵彦1( ), 付春祥2(
), 付春祥2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-13
接受日期:2022-11-15
出版日期:2023-05-01
发布日期:2023-05-17
通讯作者:
*E-mail: zhaoyannmg@163.com; fucx@qibebt.ac.cn
基金资助:
Yefei Liu1,2, Haixia Zhao2, Xiping Jiang2, Rui Qiu1,2, Xinyue Zhou1, Yan Zhao1( ), Chunxiang Fu2(
), Chunxiang Fu2( )
)
Received:2022-09-13
Accepted:2022-11-15
Online:2023-05-01
Published:2023-05-17
Contact:
*E-mail: zhaoyannmg@163.com; fucx@qibebt.ac.cn
摘要: 野大麦(Hordeum brevisubulatum)为禾本科大麦属多年生草本植物, 具有较强的抗寒和耐盐碱能力, 是挖掘抗逆基因的优良种质资源。但目前尚未见野大麦遗传转化体系的报道。该研究以蒙农1号杂交野大麦成熟胚为外植体诱导愈伤组织, 建立了野大麦高效组培快繁体系, 分化率达70%, 快繁系数为35。在此基础上, 利用根癌农杆菌(Agrobacterium tumefaciens) EHA105菌株侵染筛选获得的高质量愈伤系YZ101, 通过优化侵染条件使侵染率接近30%。该体系的建立为野大麦功能基因组研究与分子设计育种奠定了基础。
刘叶飞, 赵海霞, 姜希萍, 邱锐, 周昕越, 赵彦, 付春祥. 野大麦高效组培快繁及农杆菌介导的愈伤侵染体系建立. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 440-448.
Yefei Liu, Haixia Zhao, Xiping Jiang, Rui Qiu, Xinyue Zhou, Yan Zhao, Chunxiang Fu. Establishment of Highly Efficient Tissue Culture and Agrobacterium-mediated Callus Infection Systems for Hordeum brevisubulatum. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 440-448.
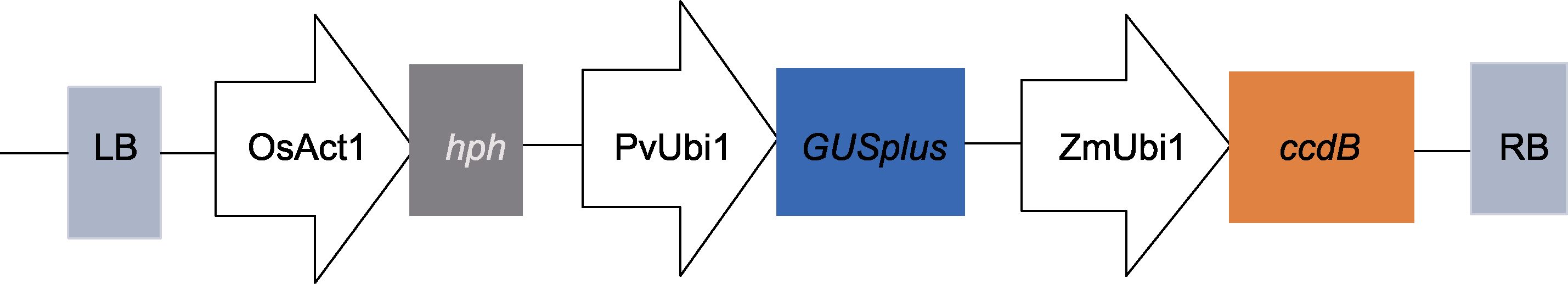
图1 PANIC6D(B)载体示意图 LB: T-DNA区段左边界; OsAct1: 水稻启动子; hph: 潮霉素抗性筛选标记基因; PvUbi1: 柳枝稷启动子; GUSplus: 葡萄糖苷酸酶报告基因; ZmUbi1: 玉米启动子; ccdB: 致死基因; RB: T-DNA区段右边界
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of PANIC6D(B) carrier LB: Left border of T-DNA; OsAct1: Rice promoter; hph: Screening marker gene for hygromycin resistance; PvUbi1: Switchgrass promoter; GUSplus: Glucosidase reporter gene; ZmUbi1: Maize promoter; ccdB: Lethal gene; RB: Right border of T-DNA
| Disinfection method | Disinfection time | Seed germination induction rate | Pollution rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (HgCl2) | 15 min | (61.3±4.0)%ab | (4.0±3.6)%b | |
| B (NaClO) | 15 min | (65.7±3.1)%a | (5.3±1.5)%b | |
| C (H2O2) | C-1 | 4 h | (52.3±4.0)%b | (33.3±1.5)%a |
| C-2 | 8 h | (34.0±2.7)%bc | (4.3±1.5)%b | |
| C-3 | 12 h | (20.1±3.1)%d | (1.3±1.5)%b | |
表1 不同消毒方法对野大麦种子诱导率的影响(平均值±标准误)
Table 1 Effect of different sterilization methods on seed induction rate of Hordeum brevisubulatum (means±SE)
| Disinfection method | Disinfection time | Seed germination induction rate | Pollution rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (HgCl2) | 15 min | (61.3±4.0)%ab | (4.0±3.6)%b | |
| B (NaClO) | 15 min | (65.7±3.1)%a | (5.3±1.5)%b | |
| C (H2O2) | C-1 | 4 h | (52.3±4.0)%b | (33.3±1.5)%a |
| C-2 | 8 h | (34.0±2.7)%bc | (4.3±1.5)%b | |
| C-3 | 12 h | (20.1±3.1)%d | (1.3±1.5)%b | |
| 2,4-D concen- tration (mg·L-1) | Seed induction rate | Callus status |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | (74.4±5.4)%a | Loose and transparent vitrification callus |
| 5 | (65.0±3.6)%b | Friable embryogenic callus with watery outer layer |
| 7 | (31.1±6.6)%c | Compact and translucent watery callus |
表2 不同浓度2,4-D对野大麦种子愈伤组织诱导率的影响(平均值±标准误)
Table 2 Effect of different 2,4-D concentrations on seed callus induction rate of Hordeum brevisubulatum (means±SE)
| 2,4-D concen- tration (mg·L-1) | Seed induction rate | Callus status |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | (74.4±5.4)%a | Loose and transparent vitrification callus |
| 5 | (65.0±3.6)%b | Friable embryogenic callus with watery outer layer |
| 7 | (31.1±6.6)%c | Compact and translucent watery callus |
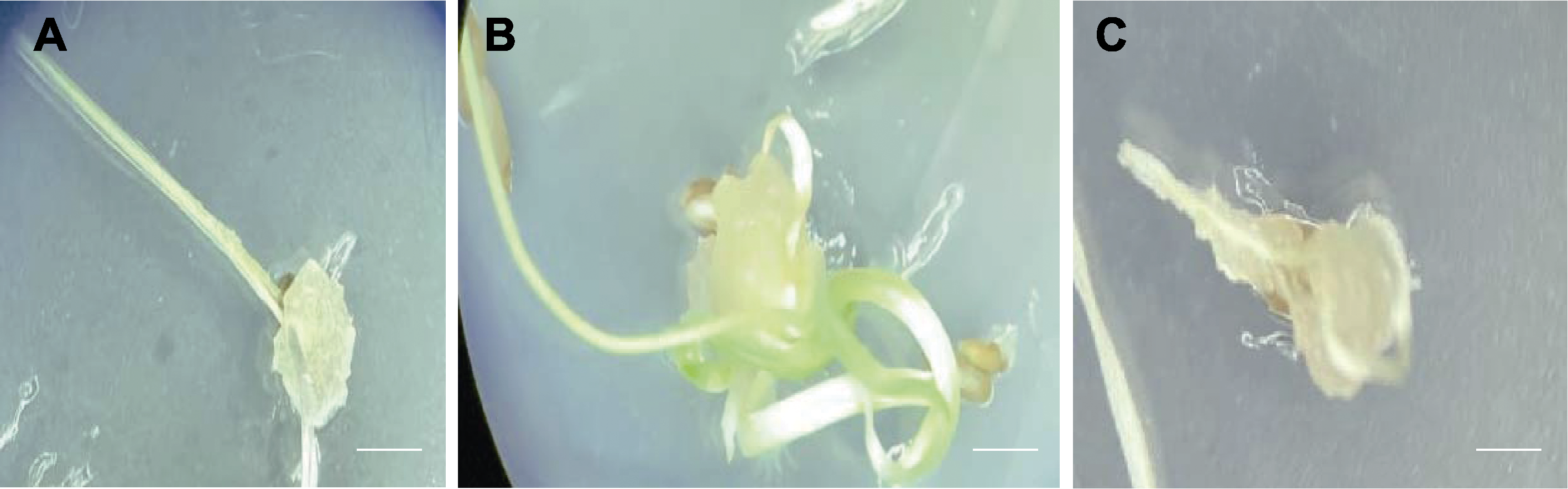

图2 不同浓度2,4-D (2 mg·L-1 (A)、5 mg·L-1 (B)和7 mg·L-1 (C))诱导的野大麦种子愈伤组织状态 (Bars=5 mm)
Figure 2 Seed callus status of Hordeum brevisubulatum induced by different concentrations of 2,4-D (2 mg·L-1 (A), 5 mg·L-1 (B) and 7 mg·L-1 (C)) (Bars=5 mm)
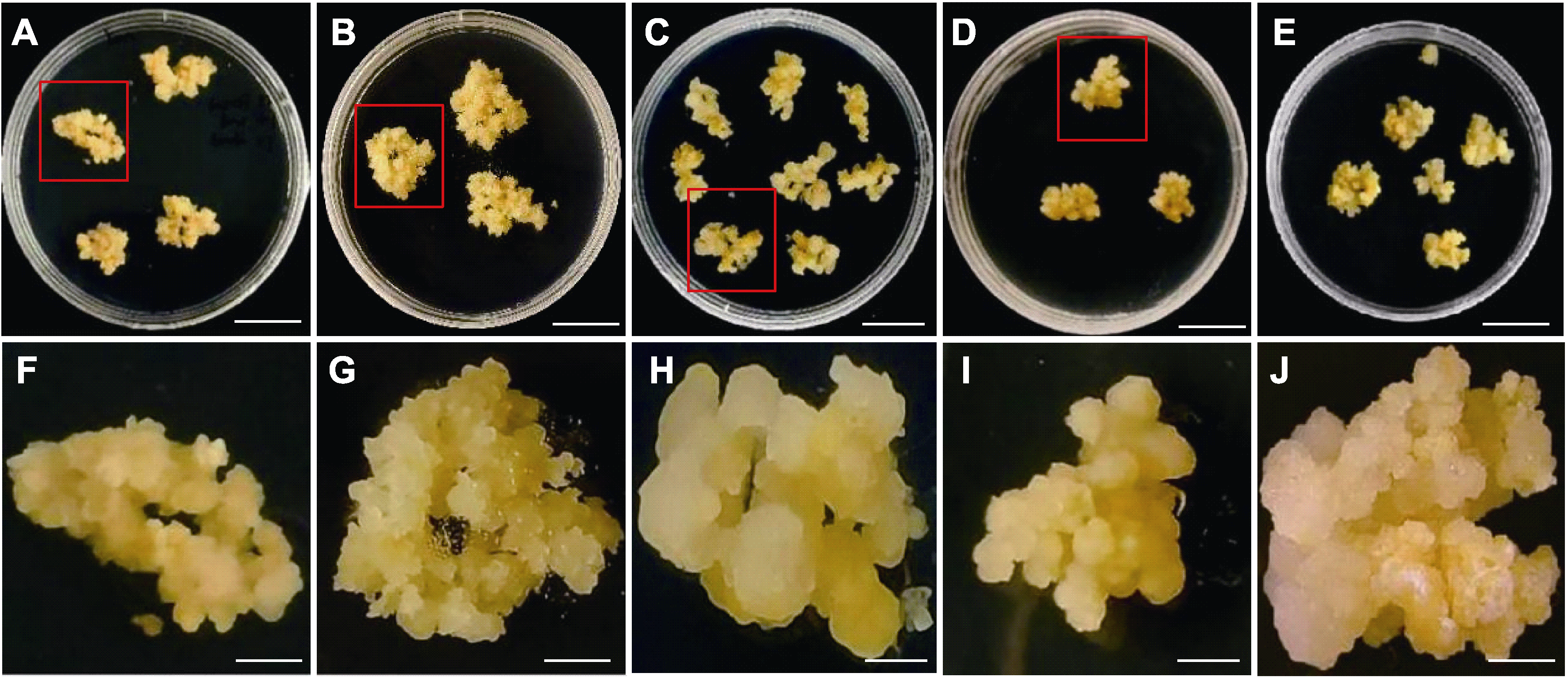

图3 野大麦种子愈伤组织系的筛选 (A)-(E) 不同愈伤组织系; (F)-(J) (A)-(E)对应放大图。Bars=5 mm
Figure 3 Selection of Hordeum brevisubulatum seed callus (A)-(E) Different calli; (F)-(J) Enlarged view of (A)-(E). Bars=5 mm
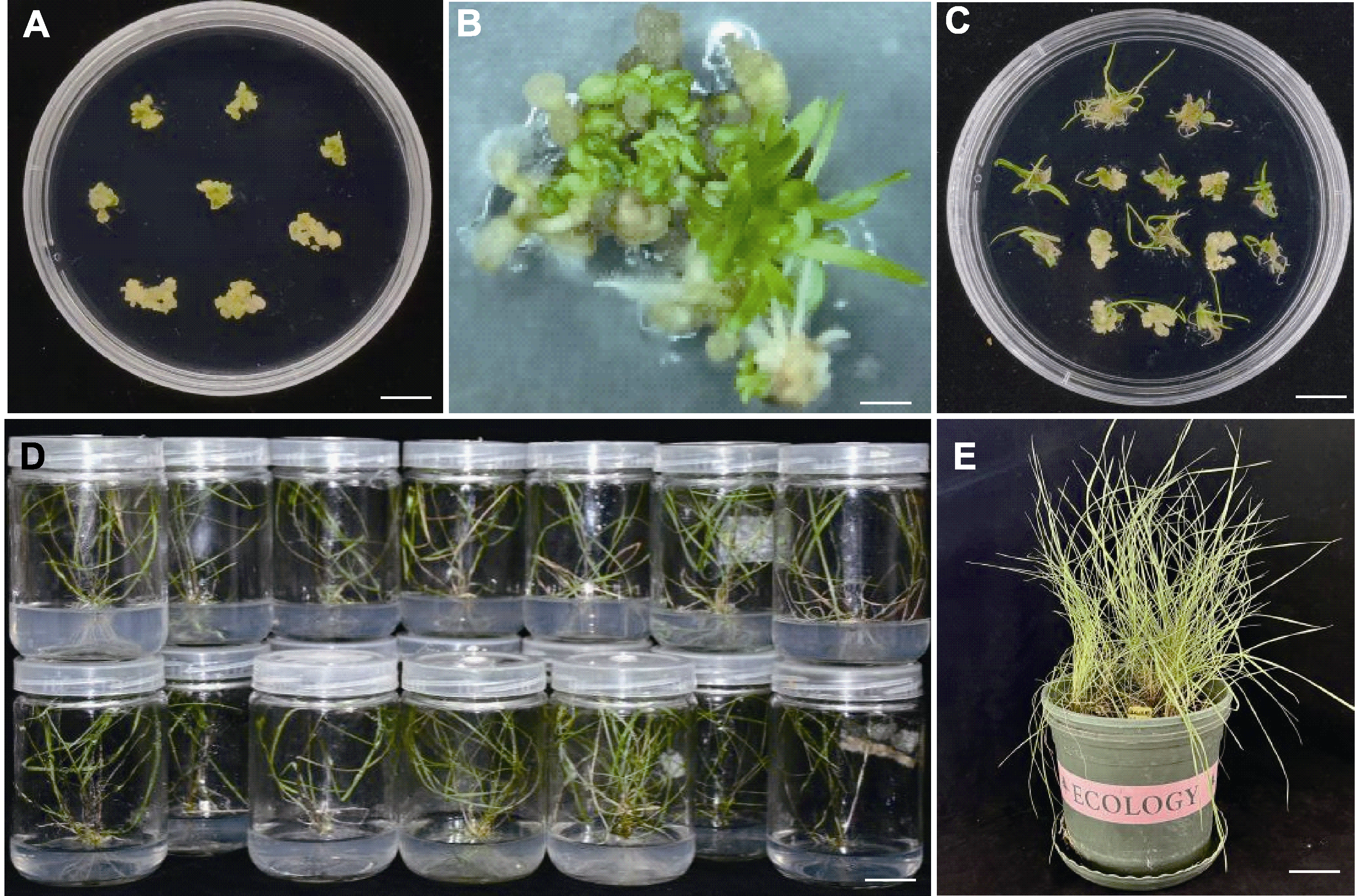
图4 野大麦胚性愈伤组织系的分化与生根 (A) 光照培养15天; (B) 光照培养25天; (C) 光照培养40天; (D) 生根; (E) 移栽
Figure 4 Differentiation and rooting of embryogenic callus of Hordeum brevisubulatum (A) 15 days’ culture in light; (B) 25 days’ culture in light; (C) 40 days’ culture in light; (D) Rooting; (E) Transplanting
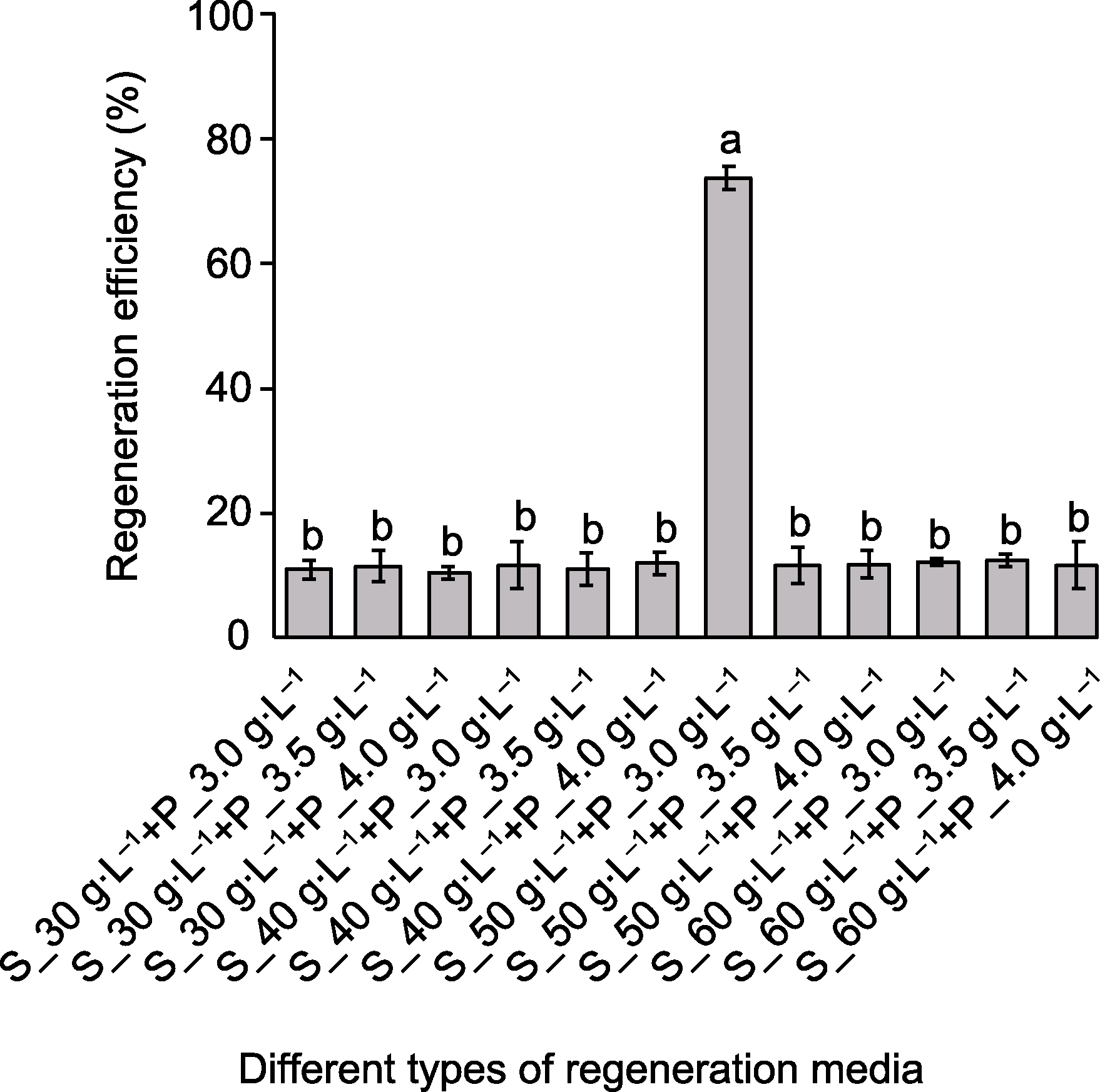
图5 野大麦不同类型分化培养基的筛选 横坐标代表不同类型的分化培养基, 其基础培养基为MS+ 2 mg·L-1 2,4-D+0.05 mg·L-1 KT, 在此基础上添加不同浓度梯度的蔗糖(30、40、50和60 g·L-1)以及phytagel (3.0、3.5和4.0 g·L-1)。S: 蔗糖; P: Phytagel。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(单因素方差分析, Duncan’s检验, P<0.05)。
Figure 5 Screening of regeneration medium for Hordeum brevisubulatum The horizontal axis represents different types of regeneration medium. The medium composition includes MS+2 mg·L-1 2,4-D+0.05 mg·L-1 KT, and supplemented with different levels of sucrose (30, 40, 50 and 60 g·L-1) and phytagel (3.0, 3.5 and 4.0 g·L-1). S: Sucrose; P: Phytagel. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (One-way ANOVA, Duncan’s test, P<0.05).
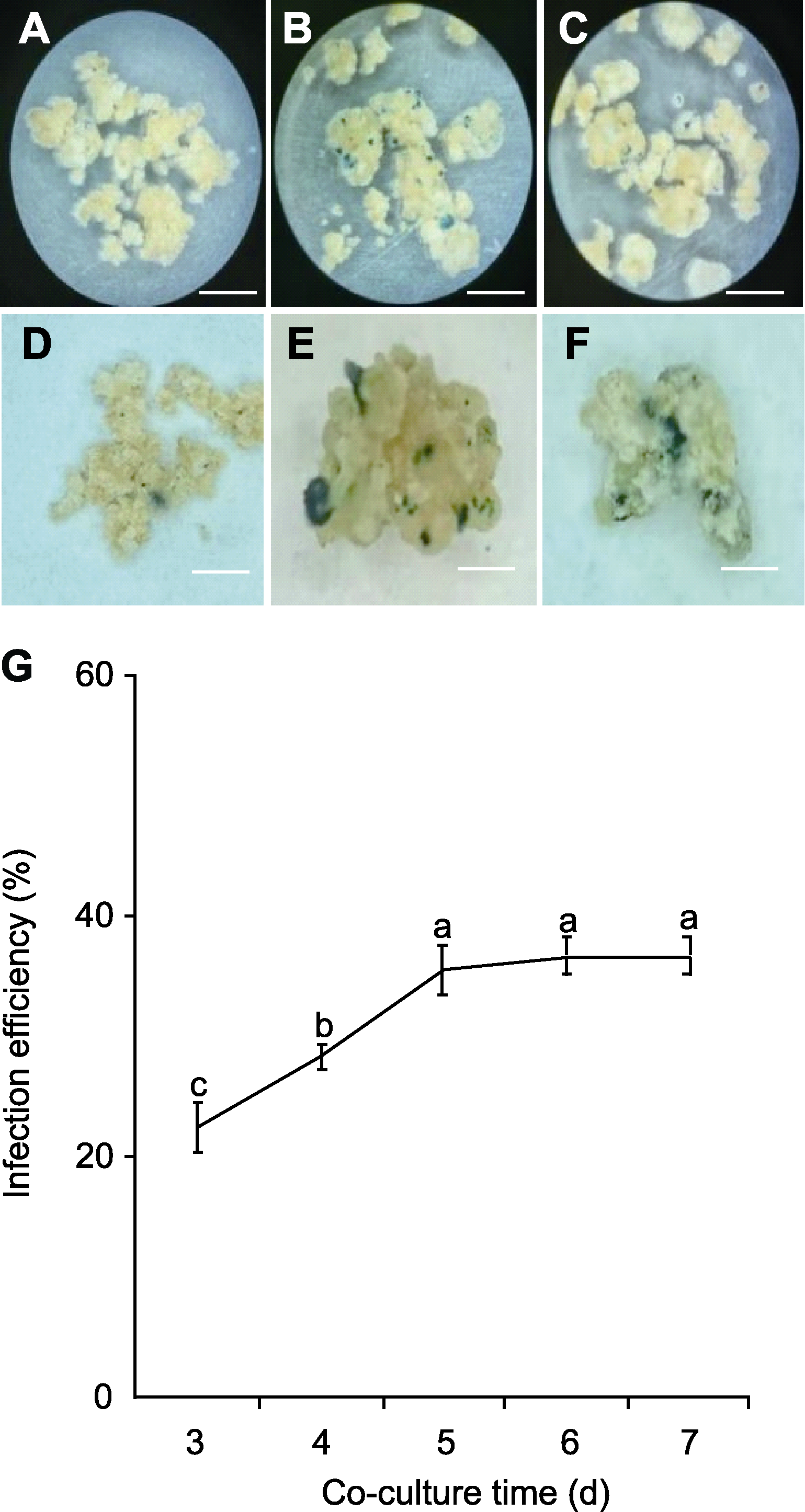
图6 根癌农杆菌共培养时间对侵染效率的影响 (A)-(C) 共培养3、4和5天的GUS染色情况; (D)-(F) (A)、(B)和(C)中GUS染色阳性愈伤组织的对应放大图; (G) 侵染效率与共培养时间的关系。不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(单因素方差分析, Duncan’s检验, P<0.05)。Bars=100 μm
Figure 6 Effect of co-culture time of Agrobacterium tumefaciens on infection efficiency (A)-(C) GUS staining of co-culture for 3, 4 and 5 days; (D)- (F) Enlarged view of GUS staining positive calli in (A), (B) and (C); (G) The relationship between infection efficiency and co-culture time. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (One-way ANOVA, Duncan’s test, P<0.05). Bars=100 μm
| [1] | 蔡联炳, 郭本兆 (1988). 中国大麦属的演化与地理分布的探讨. 西北植物学报 (02), 73-84. |
| [2] | 程肖蕊, 张亚兰, 杨松涛, 李彦舫 (1997). 野大麦幼根的愈伤组织诱导及植株再生. 吉林农业科学 (02), 94-96. |
| [3] | 丁雪梅, 何汉琼, 张英, 李玉梅, 赵云, 成军, 饶家辉, 王宏娟, 沈景林 (2010). 野大麦种子萌发条件的研究. 东北农业大学学报 41, 11-16. |
| [4] | 杜雪玲 (2004). 多年生黑麦草和结缕草再生体系及以农杆菌为介导的抗草甘瞵遗传转化体系建立的研究. 硕士论文. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. pp. 11-17. |
| [5] | 付凤玲, 李晚忱, 刘玉贞 (1999). 玉米幼穗培养及植株再生. 四川农业大学学报 (3), 278-281. |
| [6] | 李红, 杨允菲, 张成武 (2000). 松嫩平原碱化草甸野大麦无性系构建的定量分析. 草业学报 (4), 13-19. |
| [7] | 李庆华 (2021). 裸燕麦转基因体系的建立与优化. 硕士论文. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学. pp. 4-7. |
| [8] |
梁流芳, 佘建明, 吴瑛瑛 (2008). 海雀稗幼穗离体培养植株再生. 草地学报 (6), 590-593.
DOI |
| [9] | 罗雪梅, 金晓玲, 王征, 刘雪梅 (2012). 组培微环境对再生苗生长的影响. 经济林研究 30, 141-144. |
| [10] | 权军利, 刘正全, 陈耀锋, 韩德俊, 李春莲, 任慧莉 (1999). 蔗糖与激素对小麦幼穗体细胞无性系形成及生长特性的影响研究. 西北植物学报 19(6), 87-91. |
| [11] | 石德成, 奚惕 (1988). 野大麦幼叶组织培养及植株再生. 四川草原 (3), 13-15. |
| [12] | 唐静仪 (2010). 蔗糖和ABA对铁皮石斛体细胞胚胎发生的影响. 硕士论文. 成都: 西南交通大学. pp. 3-5. |
| [13] | 王春梅, 张茜, 张怀山, 汪晓斌, 朱新强, 夏曾润, 王晓力 (2013). 野大麦耐盐性研究进展. 中国草食动物科学 33, 48-52. |
| [14] | 王伟 (2020). 玉米高效遗传转化受体材料的筛选. 硕士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 8-20. |
| [15] | 杨海营 (2016). 玉米芽再生能力调控基因的全基因组关联分析. 硕士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 7-10. |
| [16] | 云玲格, 李造哲, 马青枝, 谢菲, 李月强 (2016). 披碱草×野大麦杂种F1幼穗培养再生体系的建立. 中国草地学报 38, 14-18. |
| [17] | 张立营, 李喜文, 许红力, 庞晓斌, 李彦舫 (2004). 野大麦组织培养及植株再生的研究. 内蒙古民族大学学报(自然科学版) (3), 290-292. |
| [18] | 张亚兰, 程肖蕊, 李彦舫 (1997). 野大麦幼叶组织培养. 植物生理学通讯 (5), 359. |
| [19] | 赵智燕, 潘俊松, 何亚丽, 王琛, 闫军辉 (2009). 两个高羊茅无性系的营养器官组织培养及再生体系的建立. 草业学报 18, 168-175. |
| [20] | 朱志国, 黄承钧, 陶陶, 郭丽 (2006). 红叶石楠组培增殖技术研究. 安徽农业科学 (15), 3668, 3691. |
| [21] |
Feng ZY, Zhang BT, Ding WN, Liu XD, Yang DL, Wei PL, Cao FQ, Zhu SH, Zhang F, Mao YF, Zhu JK (2013). Ef-ficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system. Cell Res 23, 1229-1232.
DOI |
| [22] |
Mann DG, Lafayette PR, Abercrombie LL, King ZR, Maza-rei M, Halter MC, Poovaiah CR, Baxter H, Shen H, Dixon RA, Parrott WA, Neal Stewart C Jr (2012). Gate-way-compatible vectors for high-throughput gene functio-nal analysis in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) and other monocot species. Plant Biotechnol J 10, 226-236.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Mao YF, Zhang H, Xu NF, Zhang BT, Gao F, Zhu JK (2013). Application of the CRISPR-Cas system for efficient genome engineering in plants. Mol Plant 6, 2008-2011.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Vasil IK (1994). Molecular improvement of cereals. Plant Mol Biol 25, 925-937.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 张尚文, 黄诗宇, 杨天为, 李婷, 张向军, 高曼熔. 基于正交实验的赤苍藤组培快繁体系建立[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 99-109. |
| [2] | 杜鹏飞, 王玉, 曹英萍, 杨松, 孙志超, 毛德才, 鄢家俊, 李达旭, 孙美贞, 付春祥, 白史且. 基因枪介导的老芒麦遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(1): 62-70. |
| [3] | 肖燕,王振兴,李东明,齐艳华,恩和巴雅尔. 羊草成熟胚诱导愈伤组织及植株再生系统的优化[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(2): 192-198. |
| [4] | 王燕, 汪一婷, 吕永平, 牟豪杰, 李海营, 陈剑平. 组培增殖方式对网纹草嵌合性状稳定性的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(3): 337-338. |
| [5] | 尚娅佳;申家恒*;郭德栋;丁常宏;李伟;陆俊萍. 甜菜无融合生殖单体附加系M14 成熟胚囊的超微结构特征[J]. 植物学报, 2009, 44(06): 682-693. |
| [6] | 赵利铭;刘树君;宋松泉;. 甜高粱再生体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2008, 25(04): 465-468. |
| [7] | 陈惠;赵原;种康. 一种改进的水稻成熟胚愈伤组织高效基因转化系统[J]. 植物学报, 2008, 25(03): 322-331. |
| [8] | 由继红. 中华芦荟组培苗与正常苗某些理化特性的比较研究[J]. 植物学报, 2001, 18(05): 623-626. |
| [9] | 廖祥儒 郭中伟 杜建芳 宋陆铧 王俊丽 陈丕铃. 低温和PEG预处理对小麦愈伤组织形成及IAA氧化的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2000, 17(03): 257-259. |
| [10] | 李彦舫 程肖蕊 张亚兰 庞劲松. 野大麦幼穗原生质体的分离和培养[J]. 植物学报, 1999, 16(01): 67-71. |
| [11] | 范光年 王培 方仁 王海波. 小麦成熟胚无性系后代的性状表现[J]. 植物学报, 1991, 8(02): 39-42. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||