

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (1): 34-50.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22171 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22171
所属专题: 杂粮生物学专辑 (2023年58卷1期)
张慧, 梁红凯, 智慧, 张林林, 刁现民*( ), 贾冠清*(
), 贾冠清*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-07-28
接受日期:2022-12-01
出版日期:2023-01-01
发布日期:2023-01-05
通讯作者:
*E-mail: diaoxianmin@caas.cn;jiaguanqing@caas.cn
基金资助:
Hui Zhang, Hongkai Liang, Hui Zhi, Linlin Zhang, Xianmin Diao*( ), Guanqing Jia*(
), Guanqing Jia*( )
)
Received:2022-07-28
Accepted:2022-12-01
Online:2023-01-01
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
*E-mail: diaoxianmin@caas.cn;jiaguanqing@caas.cn
摘要: 株型是影响谷类作物产量的重要性状, 株型改良对提高作物产量具有重要意义。独脚金内酯(strigolactones, SLs)作为一种最新被鉴定的植物激素, 其通过抑制腋芽的伸长调控分枝/分蘖的形成。β-胡萝卜素异构酶(D27s)是SLs合成途径的关键酶, 通过对谷子(Setaria italica) β-胡萝卜素异构酶典型结构域Pfam:DUF4033进行分析, 鉴定到3个谷子D27s基因家族成员(Seita.8G168400、Seita.6G088800和Seita.3G050900)。蛋白质特性分析显示, 谷子D27s蛋白由271-277个氨基酸残基组成, 分子量为30.1-30.4 kDa, 等电点为5.85-9.31, 不稳定系数介于38.48-74.47之间, 且均定位于叶绿体; 系统进化分析发现, 谷子D27s家族成员位于3个不同进化分支; 顺式作用元件预测显示, SiD27-1 (Seita.8G168400)可能参与调控生物节律、生长素介导的生长发育以及干旱和低温等胁迫应答过程。基因表达分析显示, SiD27-1在谷子多分蘖材料中表达下调, 在低磷胁迫处理下, D27s基因均能产生不同程度的响应, 并且SiD27-1的响应较其它成员更快速。单倍型分析结果表明, SiD27-1的H001单倍型为优异单倍型, 对谷子的株高、抽穗期和产量改良具有重要应用价值。综上, 推测SiD27-1极可能在SLs合成中发挥关键作用并对谷子株型产生影响。研究结果为深入揭示D27s对谷子分蘖形成的调控机制奠定了基础, 也为谷子株型分子设计育种提供了优异的等位变异位点。
张慧, 梁红凯, 智慧, 张林林, 刁现民, 贾冠清. 谷子β-胡萝卜素异构酶家族基因的表达与变异分析. 植物学报, 2023, 58(1): 34-50.
Hui Zhang, Hongkai Liang, Hui Zhi, Linlin Zhang, Xianmin Diao, Guanqing Jia. Analyses on the Transcription and Structure Variation of β-carotene Isomerase Gene Family in Foxtail Millet. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(1): 34-50.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| D27-8G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGAGGTC- GCGGCCACTTC |
| D27-8G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAATCAC- TTGACGATTCT |
| D27family-6G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCAGCA- GCCCTGCCCAT |
| D27family-6G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCCTATGTCTG-AAGTTTGGGGC |
| D27family-3G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCGACG- CCGCTCGCGAC |
| D27family-3G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAACTTG-GGGGCAACCGA |
| QRT-8G-F | ATGAAACGAAGCTACTACACGA |
| QRT-8G-R | CAGATTGTCGAACCAGTTGTC |
| QRT-6G-F | GATGGGGGAGAAGACGGAGTA |
| QRT-6G-R | TTCTTCTTCTTCTCCAACTCCG |
| QRT-3G-F | CGCCTCTATTGCTTGTCCTATA |
| QRT-3G-R | AACTGAACATGTGCCCATTAAC |
| Culin-F | TATGGGTCATCAACAGCTTGTC |
| Culin-R | GTAGTCCCTCGTGATGAGATCC |
表1 引物列表
Table 1 List of primers
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| D27-8G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGAGGTC- GCGGCCACTTC |
| D27-8G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAATCAC- TTGACGATTCT |
| D27family-6G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCAGCA- GCCCTGCCCAT |
| D27family-6G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCCTATGTCTG-AAGTTTGGGGC |
| D27family-3G-N-F | GCTGTACAAGACTAGTATGGCGACG- CCGCTCGCGAC |
| D27family-3G-N-R | GGGGAAATTCGAGCTCTCAAACTTG-GGGGCAACCGA |
| QRT-8G-F | ATGAAACGAAGCTACTACACGA |
| QRT-8G-R | CAGATTGTCGAACCAGTTGTC |
| QRT-6G-F | GATGGGGGAGAAGACGGAGTA |
| QRT-6G-R | TTCTTCTTCTTCTCCAACTCCG |
| QRT-3G-F | CGCCTCTATTGCTTGTCCTATA |
| QRT-3G-R | AACTGAACATGTGCCCATTAAC |
| Culin-F | TATGGGTCATCAACAGCTTGTC |
| Culin-R | GTAGTCCCTCGTGATGAGATCC |
| Gene ID | Species | Primary structure | GRAVY | Subcellular location | Secondary structure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of amino acids | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical PI | Instability index (II) | Alpha helix | Beta bridge | Exten- ded strand | Ran- dom coil | ||||
| AT4G01995 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 258.00 | 28636.56 | 7.97 | 38.48 | 0.030 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.49 |
| AT1G03055 | A. thaliana | 264.00 | 29795.14 | 8.94 | 53.39 | -0.358 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.46 |
| AT1G64680 | A. thaliana | 250.00 | 28162.63 | 8.52 | 51.89 | -0.333 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.52 |
| BdiBd21-2.2G0489400 | Brachypodium distachyon | 268.00 | 29298.93 | 8.28 | 56.92 | -0.093 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.51 |
| BdiBd21-4.4G0220000 | B. distachyon | 277.00 | 30715.66 | 8.76 | 52.53 | -0.091 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.54 |
| BdiBd21-3.3G0180800 | B. distachyon | 275.00 | 30152.06 | 9.16 | 58.90 | -0.147 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| Seita.6G088800 | Setaria italica | 271.00 | 30429.45 | 8.93 | 54.85 | -0.380 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.52 |
| Seita.3G050900 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Seita.8G168400 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| LOC_Os08g02210 | Oryza sativa | 261.00 | 28906.58 | 8.88 | 49.96 | -0.244 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| LOC_Os05g04090 | O. sativa | 118.00 | 13355.34 | 5.85 | 56.27 | -0.186 | Cytoplasm | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.56 |
| LOC_Os05g04070 | O. sativa | 270.00 | 29343.02 | 7.94 | 58.60 | -0.047 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.51 |
| LOC_Os11g37650 | O. sativa | 365.00 | 40864.68 | 8.52 | 55.08 | 0.024 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.45 |
| Sobic.009G030800 | Sorghum bicolor | 277.00 | 30225.93 | 8.51 | 64.68 | -0.182 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.55 |
| Sobic.005G168200 | So. bicolor | 292.00 | 32325.36 | 8.72 | 54.69 | -0.216 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 |
| Sobic.007G016600 | So. bicolor | 369.00 | 30202.19 | 8.79 | 62.57 | -0.383 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.54 |
| Sevir.6G087800 | Setaria viridis | 271.00 | 30483.49 | 8.83 | 55.49 | -0.403 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.49 |
| Sevir.8G177900 | Se. viridis | 289.00 | 32243.38 | 8.82 | 54.93 | -0.187 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| Sevir.3G051400 | Se. viridis | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Zm00008a034103 | Zea mays | 202.00 | 22824.65 | 9.31 | 65.45 | -0.249 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.44 |
| Zm00008a023158 | Z. mays | 155.00 | 17878.49 | 8.22 | 56.01 | -0.370 | Chloroplast | 0.46 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| Zm00008a023504 | Z. mays | 235.00 | 26224.37 | 8.93 | 67.47 | -0.340 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU1Hr1G015940 | Hordeum vulgare | 307.00 | 33309.59 | 9.29 | 65.88 | -0.191 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.52 |
| HORVU7Hr1G076030 | H. vulgare | 294.00 | 33156.27 | 8.63 | 65.27 | -0.413 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU7Hr1G096970 | H. vulgare | 275.00 | 30372.12 | 8.89 | 74.47 | -0.130 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 |
表2 不同物种D27s基因基本特征
Table 2 Characteristics of D27s genes from different plant species
| Gene ID | Species | Primary structure | GRAVY | Subcellular location | Secondary structure | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of amino acids | Molecular weight (kDa) | Theoretical PI | Instability index (II) | Alpha helix | Beta bridge | Exten- ded strand | Ran- dom coil | ||||
| AT4G01995 | Arabidopsis thaliana | 258.00 | 28636.56 | 7.97 | 38.48 | 0.030 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.49 |
| AT1G03055 | A. thaliana | 264.00 | 29795.14 | 8.94 | 53.39 | -0.358 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.46 |
| AT1G64680 | A. thaliana | 250.00 | 28162.63 | 8.52 | 51.89 | -0.333 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.52 |
| BdiBd21-2.2G0489400 | Brachypodium distachyon | 268.00 | 29298.93 | 8.28 | 56.92 | -0.093 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.51 |
| BdiBd21-4.4G0220000 | B. distachyon | 277.00 | 30715.66 | 8.76 | 52.53 | -0.091 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.54 |
| BdiBd21-3.3G0180800 | B. distachyon | 275.00 | 30152.06 | 9.16 | 58.90 | -0.147 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.53 |
| Seita.6G088800 | Setaria italica | 271.00 | 30429.45 | 8.93 | 54.85 | -0.380 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.52 |
| Seita.3G050900 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Seita.8G168400 | S. italica | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| LOC_Os08g02210 | Oryza sativa | 261.00 | 28906.58 | 8.88 | 49.96 | -0.244 | Chloroplast | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| LOC_Os05g04090 | O. sativa | 118.00 | 13355.34 | 5.85 | 56.27 | -0.186 | Cytoplasm | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.56 |
| LOC_Os05g04070 | O. sativa | 270.00 | 29343.02 | 7.94 | 58.60 | -0.047 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.51 |
| LOC_Os11g37650 | O. sativa | 365.00 | 40864.68 | 8.52 | 55.08 | 0.024 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.45 |
| Sobic.009G030800 | Sorghum bicolor | 277.00 | 30225.93 | 8.51 | 64.68 | -0.182 | Chloroplast | 0.31 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.55 |
| Sobic.005G168200 | So. bicolor | 292.00 | 32325.36 | 8.72 | 54.69 | -0.216 | Chloroplast | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 |
| Sobic.007G016600 | So. bicolor | 369.00 | 30202.19 | 8.79 | 62.57 | -0.383 | Chloroplast | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.54 |
| Sevir.6G087800 | Setaria viridis | 271.00 | 30483.49 | 8.83 | 55.49 | -0.403 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.49 |
| Sevir.8G177900 | Se. viridis | 289.00 | 32243.38 | 8.82 | 54.93 | -0.187 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.48 |
| Sevir.3G051400 | Se. viridis | 277.00 | 30185.83 | 8.66 | 58.84 | -0.170 | Chloroplast | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.51 |
| Zm00008a034103 | Zea mays | 202.00 | 22824.65 | 9.31 | 65.45 | -0.249 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.44 |
| Zm00008a023158 | Z. mays | 155.00 | 17878.49 | 8.22 | 56.01 | -0.370 | Chloroplast | 0.46 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.33 |
| Zm00008a023504 | Z. mays | 235.00 | 26224.37 | 8.93 | 67.47 | -0.340 | Chloroplast | 0.36 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU1Hr1G015940 | Hordeum vulgare | 307.00 | 33309.59 | 9.29 | 65.88 | -0.191 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.52 |
| HORVU7Hr1G076030 | H. vulgare | 294.00 | 33156.27 | 8.63 | 65.27 | -0.413 | Chloroplast | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.49 |
| HORVU7Hr1G096970 | H. vulgare | 275.00 | 30372.12 | 8.89 | 74.47 | -0.130 | Chloroplast | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 |
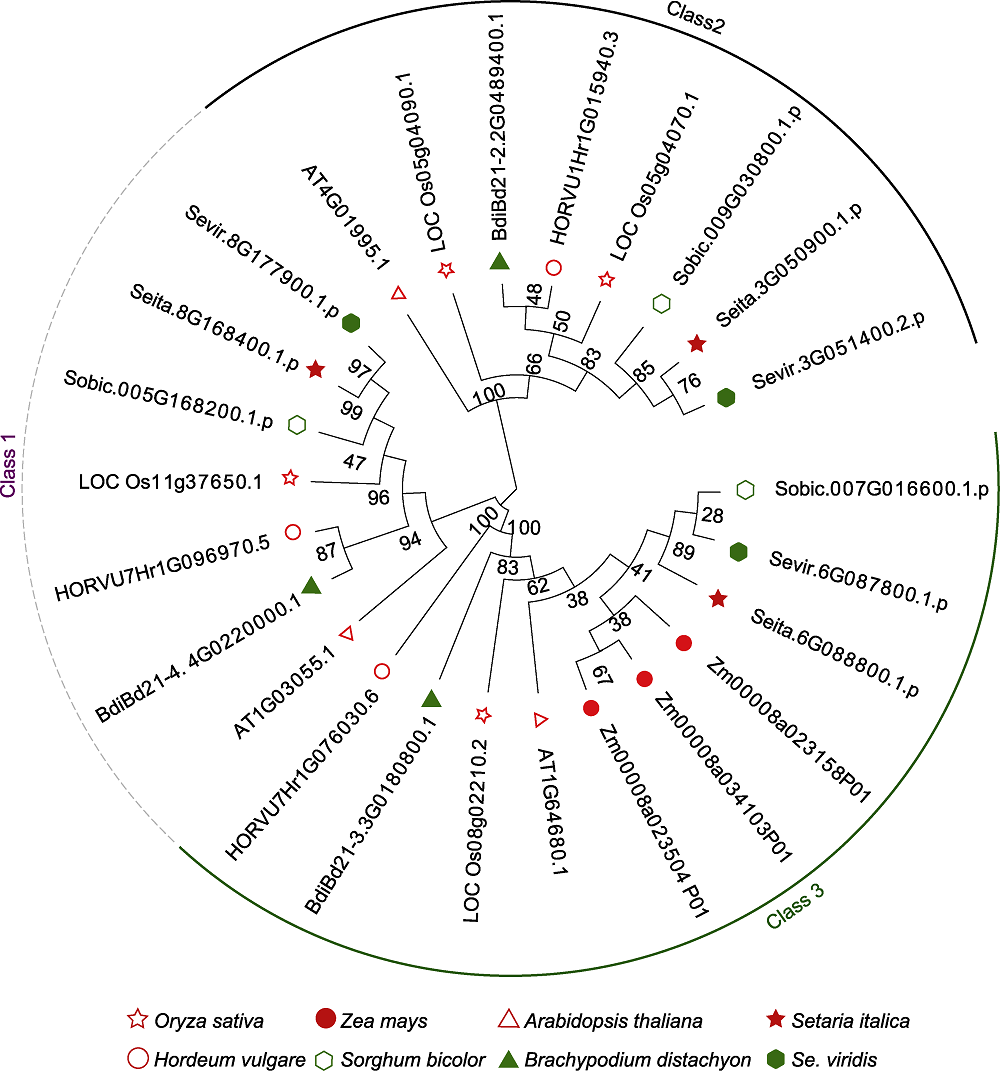
图1 不同作物D27s基因的系统进化树 使用邻接法, 利用8个物种中鉴定的D27s蛋白质的氨基酸序列构建系统进化树。
Figure 1 Phylogenetic trees of D27s genes in different crops The phylogenetic tree was constructed by using amino acid sequences of D27 proteins from 8 crop species, and the neighbor-joining method.
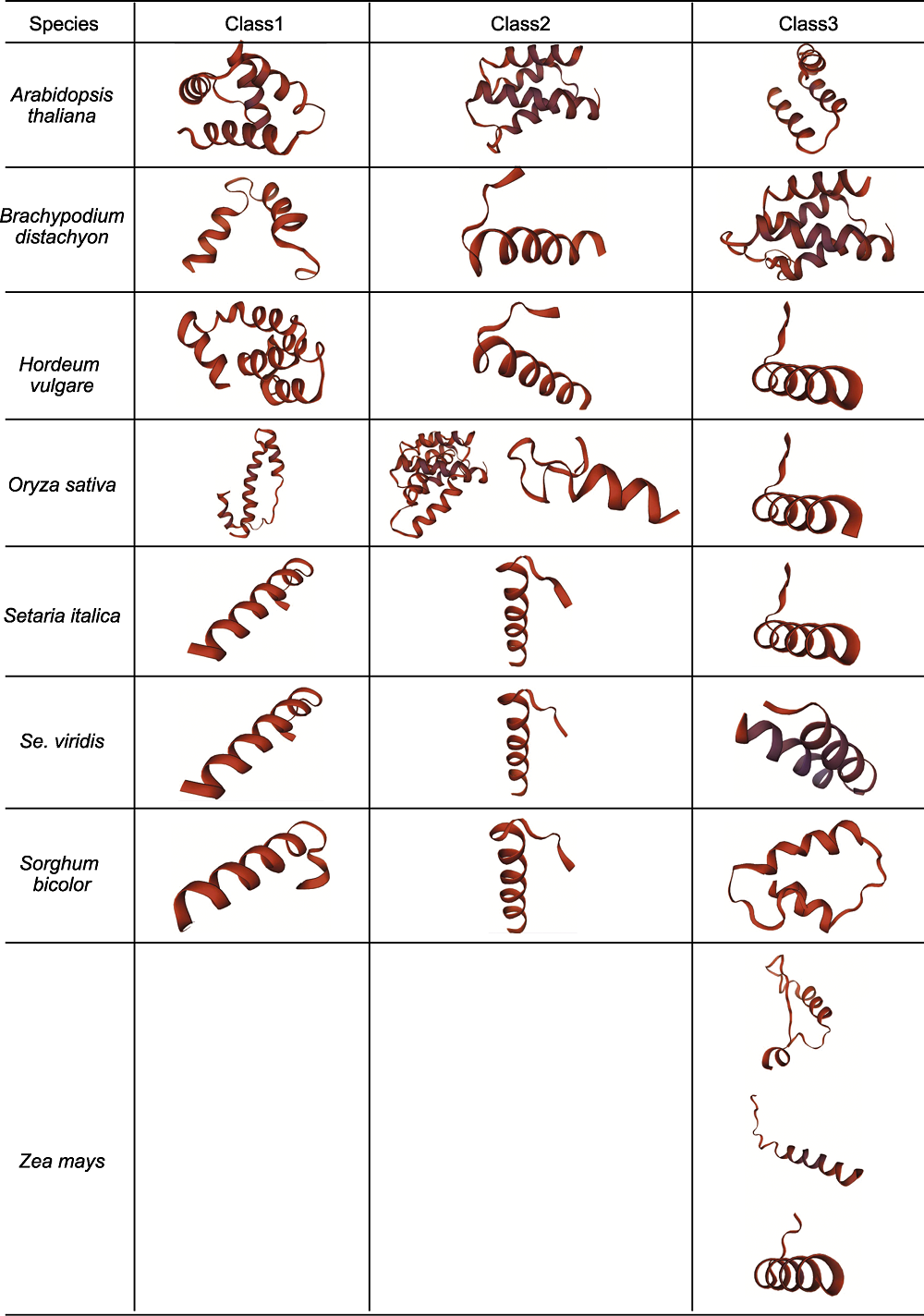
图2 不同物种D27s的三级结构 根据系统进化树对拟南芥、二穗短柄草、大麦、水稻、谷子、青狗尾草、高粱和玉米不同分支成员三级结构进行可视化, 其中Class1、Class2和Class3分别对应系统进化树中的第一、二和三分支。
Figure 2 Tertiary structure of D27s in different species The tertiary structure of D27s in Arabidopsis thaliana, Brachypodium distachyon, Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa, Setaria italica, Se. viridis, Sorghum bicolor and Zea mays are visualized according to the phylogenetic tree. Class1, Class2 and Class3 correspond to the first, second and third clades of the phylogenetic tree, respectively.
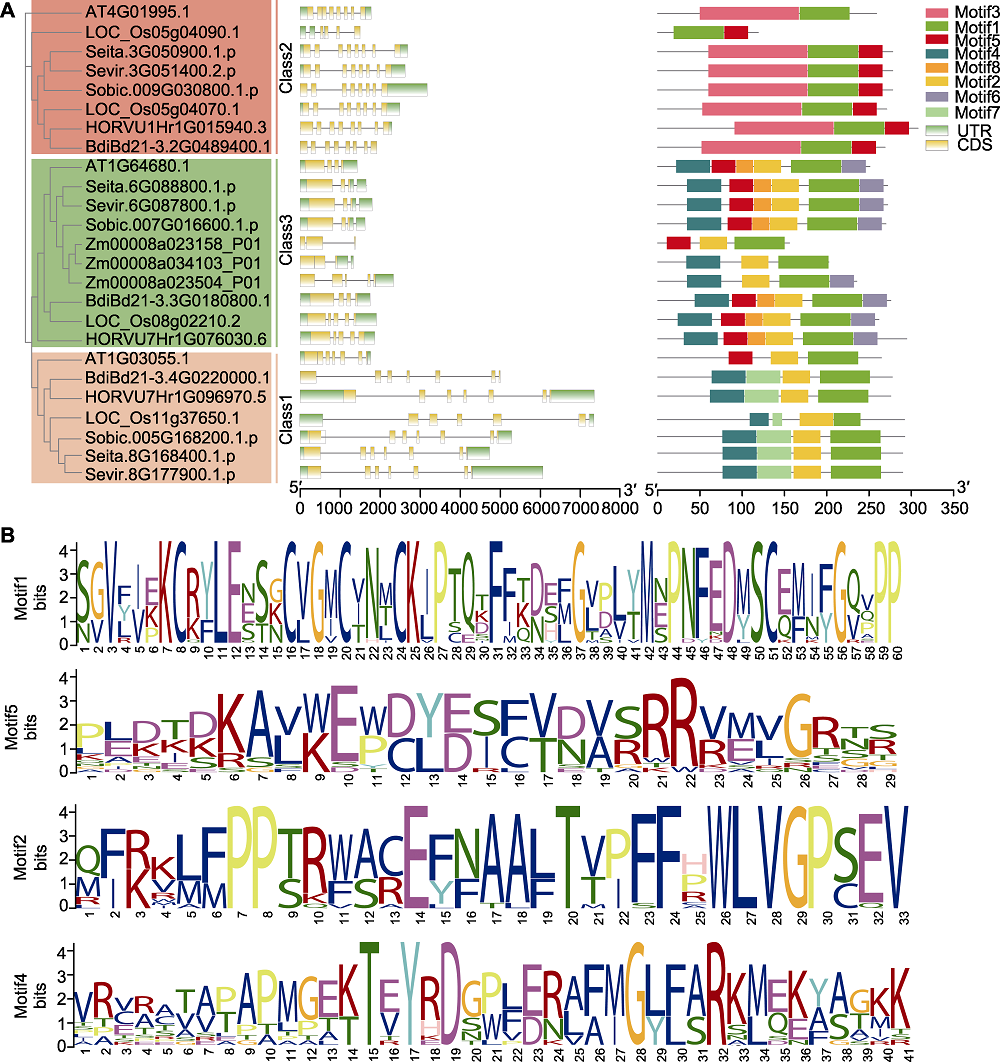
图3 D27s基因的结构及其编码蛋白质的保守基序分析 (A) D27s基因的结构及其编码蛋白的保守结构域分析(基于进化树分类(左侧), 对25个D27s基因的结构(中间)及其编码蛋白的保守结构域(右侧)进行了分析; 中间部分横线代表内含子, 右侧部分的不同颜色代表不同保守结构域; 下方比例尺代表基因或蛋白长度); (B) 25个D27s成员序列比对生成的保守基序logo。UTR: 非翻译区; CDS: 编码序列
Figure 3 A gene structures of D27s genes and conserved motifs in the D27s (A) Analysis of D27s gene structure and D27 protein conserved domains (based on evolutionary tree (left), 25 D27s genes were analyzed for gene structure (middle) and protein conserved domains (right); horizontal lines in the middle represent introns, different colors in the right part represent different conserved domains; the lower scale represents gene or protein length); (B) The conservative motif logo generated by comparison of amino acid sequences of 25 D27s members. UTR: Untranslated region; CDS: Coding sequence
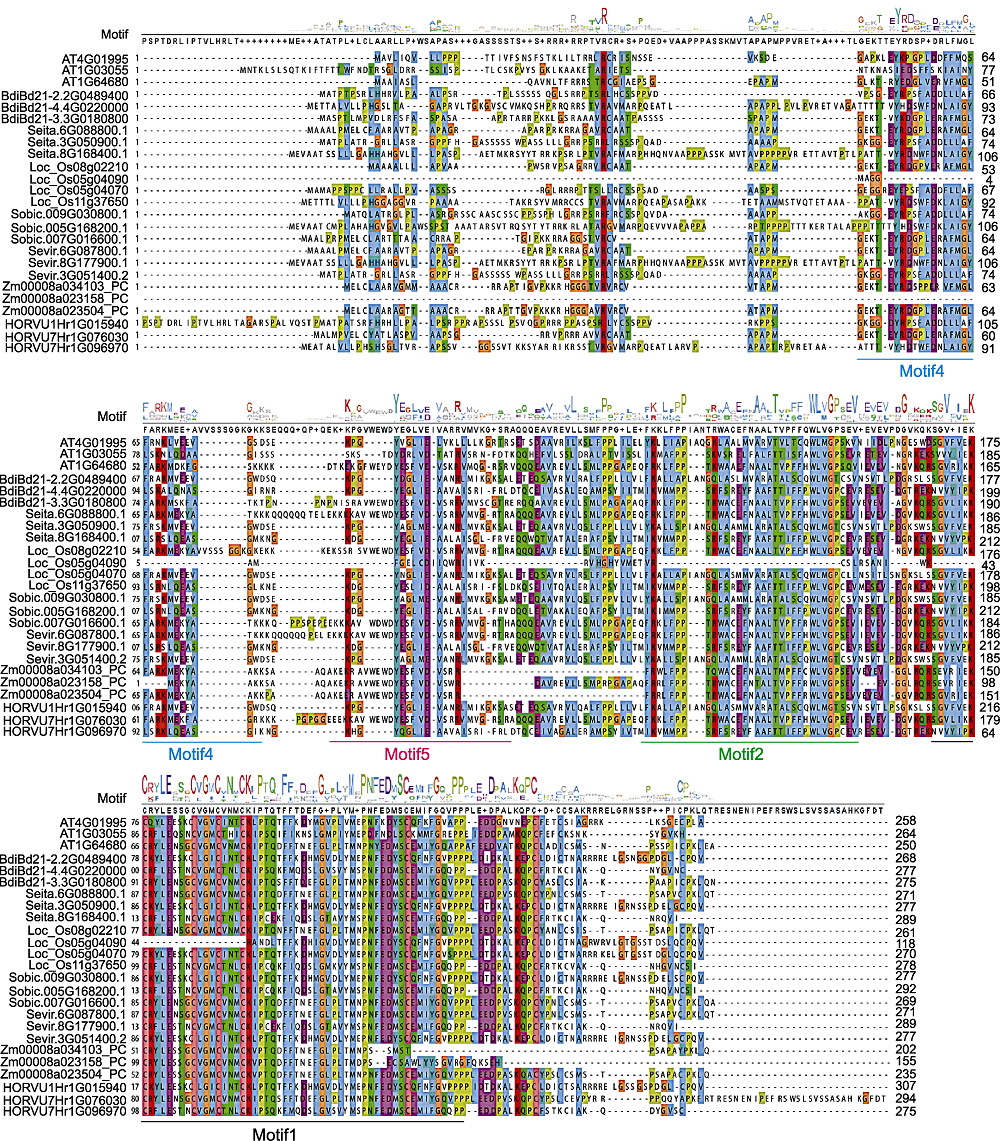
图4 8个不同物种D27氨基酸序列的多重比对 8个物种的25个D27s成员蛋白序列均存在motif1、motif2、motif4和motif5, 其中motif1用黑色标注; motif2用绿色标注; motif4用蓝色标注; motif5用红色标注。
Figure 4 Alignment of amino acid sequences of D27s from 8 different species Motif1, motif2, motif4 and motif5 are found in 25 D27s sequences of 8 species, and motif1 is marked in black; motif2 is marked in green; motif4 is marked in blue; motif5 is marked in red.
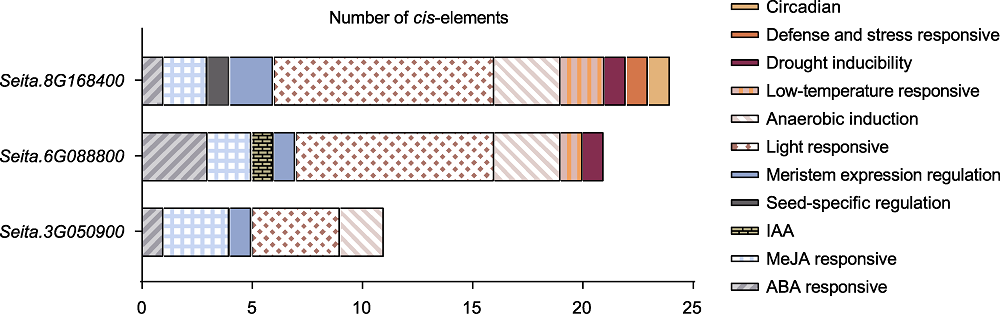
图5 D27s顺式作用元件预测 谷子D27基因上游2 000 bp启动子区顺式作用元件示意图。不同颜色的矩形框代表不同的顺式作用元件。
Figure 5 Prediction of D27s cis-element Diagram of cis-acting elements in the 2 000 bp upstream promoter regions of foxtail millet D27 genes. Rectangular boxes with different colors represent different cis-elements.
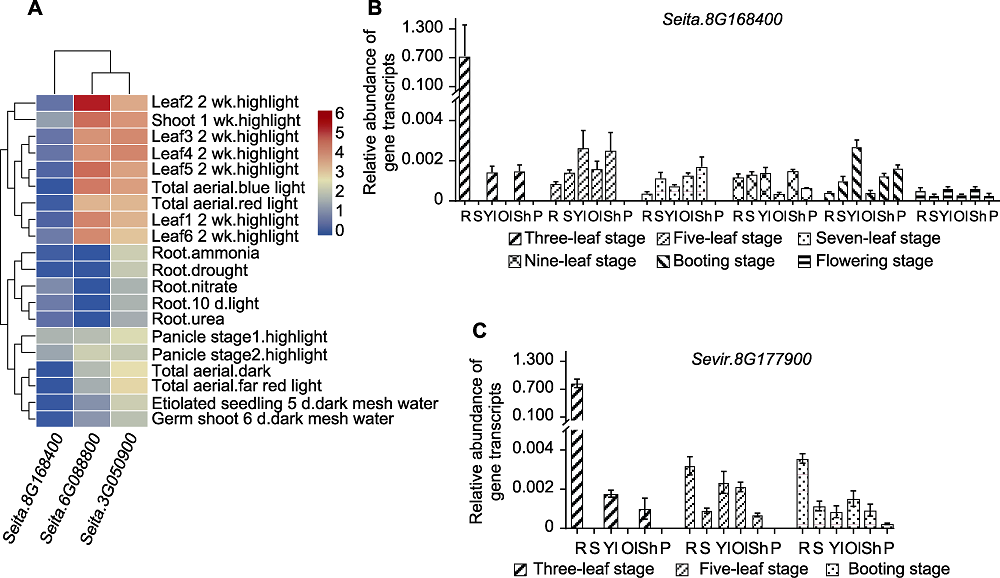
图6 D27s基因在不同分蘖材料中的全生育期表达谱 (A) D27s基因在豫谷1号不同组织中的表达模式; (B) SiD27-1在少分蘖材料豫谷1号全生育期不同组织中的表达; (C) SvD27-1在多分蘖材料A10全生育期不同组织中的表达。R代表根, S代表茎, Yl代表幼叶, Ol代表老叶, Sh代表叶鞘, P代表穗。
Figure 6 Expression of D27s genes throughout the reproductive period in different tiller materials (A) Expression patterns of D27s genes in different tissues of Yugu1; (B) Expression of SiD27-1 in different tissues of less tiller material Yugu1 reproductive period; (C) Expression of SvD27-1 in different tissues of multi-tiller material A10 reproductive period. R stand for root, S stand for stem, Yl stand for young leaf, Ol stand for old leaf, Sh stand for leaf sheath, and P stand for spike.
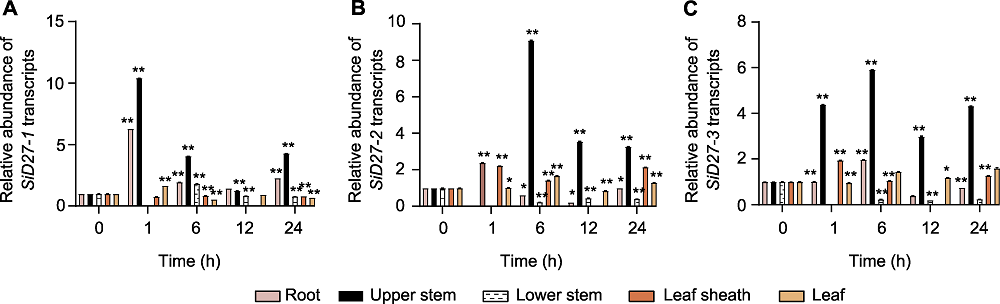
图7 D27s在缺磷条件下不同组织中的响应模式 (A) Seita.8G168400 (SiD27-1); (B) Seita.6G088800 (SiD27-2); (C) Seita.3G050900 (SiD27-3)。* P<0.05; ** P<0.01
Figure 7 Responsive pattern of D27s in different tissues under phosphorus (P) deficiency treatment (A) Seita.8G168400 (SiD27-1); (B) Seita.6G088800 (SiD27-2); (C) Seita.3G050900 (SiD27-3). * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
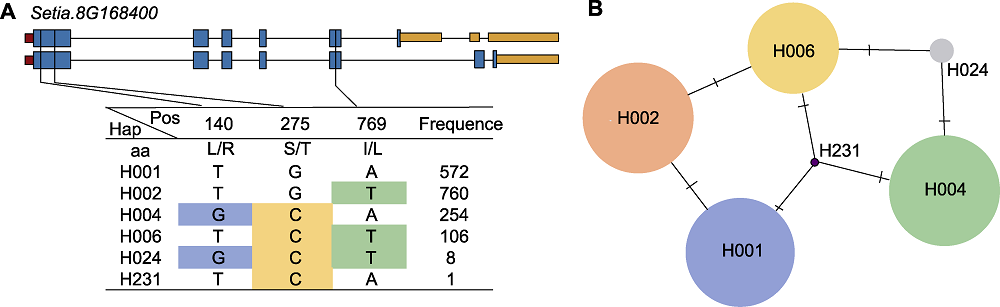
图9 SiD27-1序列多态性分析 (A) SiD27-1的基因结构和单倍型分析; (B) 单倍型变异分析(圆的大小表示每个Hap中的品种数量; 导线表示2个Haps之间的变化程度)
Figure 9 Sequence polymorphism analysis of SiD27-1 (A) The gene structure of SiD27-1 and its haplotypes; (B) Haplotype variation analysis (circle size indicate the number of varieties in each Hap; traverse lines represent the extent of variation between two Haps)
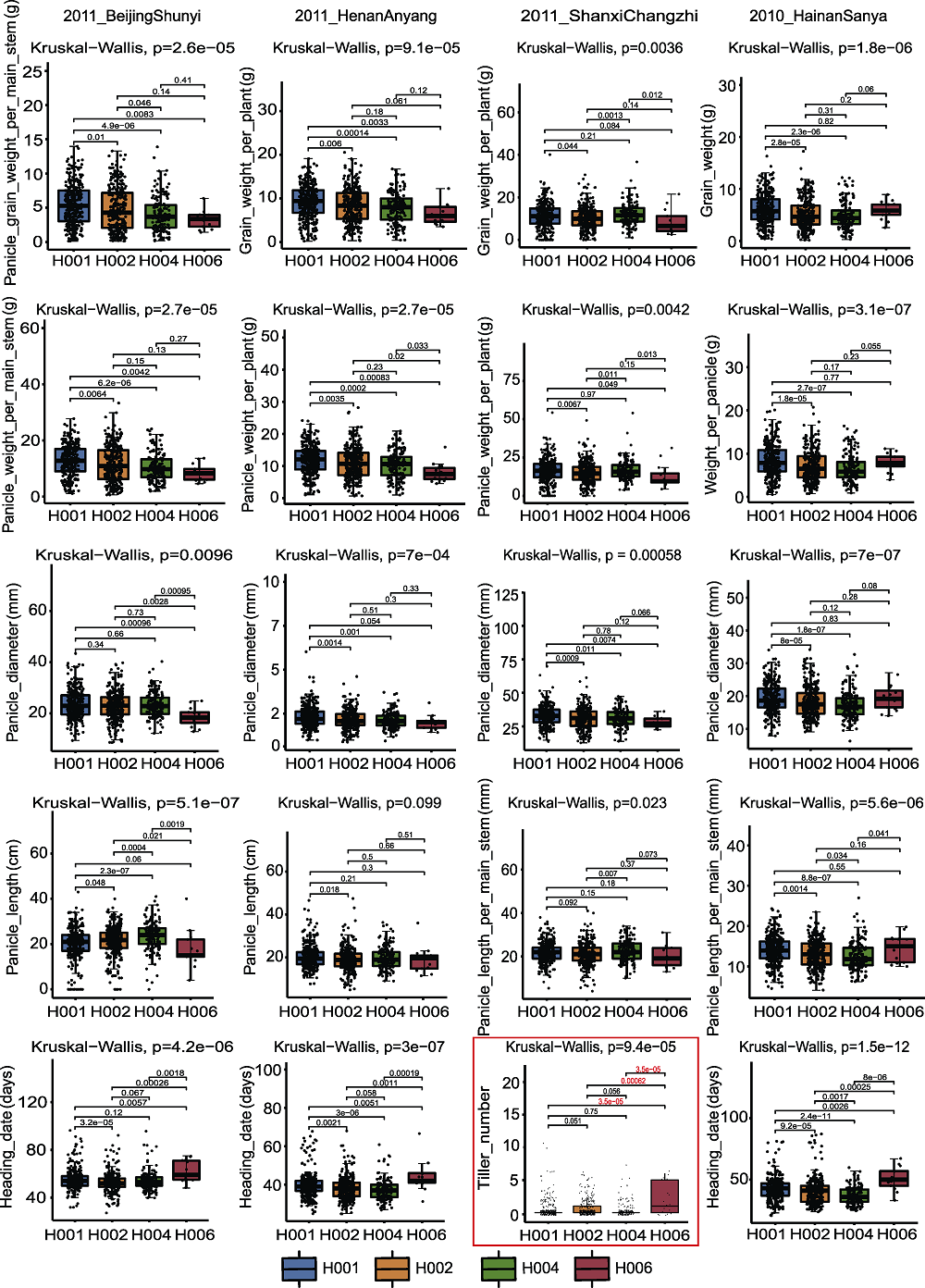
图10 SiD27-1与不同年份表型数据关联的箱式图 红框代表SiD27-1基因型与分蘖表型的关联分析
Figure 10 Box plot of SiD27-1 associated with phenotypic data in different years The red box represent the association analysis between SiD27-1 genotype and tiller phenotype
| [1] |
常金科, 黎家 (2017). 独脚金内酯信号感知揭示配体-受体作用新机制. 植物学报 52, 123-127.
DOI |
| [2] |
刁现民 (2019). 禾谷类杂粮作物耐逆和栽培技术研究新进展. 中国农业科学 52, 3943-3949.
DOI |
| [3] | 贾冠清, 刁现民 (2017). 谷子(Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.)作为功能基因组研究模式植物的发展现状及趋势. 生命科学 29, 292-301. |
| [4] | 黎家 (2018). 植物激素——植物学研究永恒的话题. 生物技术通报 34, 5-6. |
| [5] |
黎舒佳, 高谨, 李家洋, 王永红 (2015). 独脚金内酯调控水稻分蘖的研究进展. 植物学报 50, 539-548.
DOI |
| [6] | 李学勇, 钱前, 李家洋 (2003). 水稻分蘖的分子机理研究. 中国科学院院刊 18, 274-276. |
| [7] | 刘艳, 彭晓丹, 李洋 (2016). 几种水培液对香根草生长情况的影响. 农技服务 33, 23-25. |
| [8] | 王闵霞, 彭鹏, 龙海馨, 王平, 白玉路, 李学勇 (2014). 独脚金内酯途径相关基因的研究进展. 分子植物育种 12, 603-609. |
| [9] |
吴转娣, 刘新龙, 刘家勇, 昝逢刚, 李旭娟, 刘洪博, 林秀琴, 陈学宽, 苏火生, 赵培方, 吴才文 (2017). 甘蔗独脚金内酯生物合成关键基因ScD27的克隆与表达分析. 作物学报 43, 31-41.
DOI |
| [10] | 许智宏, 李家洋 (2006). 中国植物激素研究: 过去, 现在和未来. 植物学报 23, 433. |
| [11] |
Abuauf H, Haider I, Jia KP, Ablazov A, Mi JN, Blilou I, Al-Babili S (2018). The Arabidopsis DWARF27 gene encodes an all-trans-/9-cis-β-carotene isomerase and is induced by auxin, abscisic acid and phosphate deficiency. Plant Sci 277, 33-42.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW (2006). MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 34, W369-W373.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Brewer PB, Dun EA, Ferguson BJ, Rameau C, Beveridge CA (2009). Strigolactone acts downstream of auxin to regulate bud outgrowth in pea and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 150, 482-493.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Chen CJ, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He YH, Xia R (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit de- veloped for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13, 1194-1202.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Cook CE, Whichard LP, Turner B, Wall ME, Egley GH (1966). Germination of witchweed (Striga lutea Lour.): isolation and properties of a potent stimulant. Science 154, 1189-1190.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Fang ZM, Ji YY, Hu J, Guo RK, Sun SY, Wang XL (2020). Strigolactones and brassinosteroids antagonistically regu- late the stability of the D53-OsBZR1 complex to determi- ne FC1 expression in rice tillering. Mol Plant 13, 586-597.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Gao HB, Wang WG, Wang YH, Liang Y (2019). Molecular mechanisms underlying plant architecture and its environ- mental plasticity in rice. Mol Breeding 39, 167.
DOI |
| [18] |
Gomez-Roldan V, Fermas S, Brewer PB, Puech-Pagès V, Dun EA, Pillot JP, Letisse F, Matusova R, Danoun S, Portais JC, Bouwmeester H, Bécard G, Beveridge CA, Rameau C, Rochange S (2008). Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature 455, 189-194.
DOI |
| [19] |
Hammond JP, White PJ (2011). Sugar signaling in root responses to low phosphorus availability. Plant Physiol 156, 1033-1040.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Ito S, Ito K, Abeta N, Takahashi R, Sasaki Y, Yajima S (2016). Effects of strigolactone signaling on Arabidopsis growth under nitrogen deficient stress condition. Plant Signaling Behav 11, e1126031. |
| [21] |
Kebrom TH, Mullet JE (2016). Transcriptome profiling of tiller buds provides new insights into PhyB regulation of tillering and indeterminate growth in sorghum. Plant Physiol 170, 2232-2250.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Koltai H, Beveridge CA (2013). Strigolactones and the coordinated development of shoot and root. In: Baluška F, ed. Long-Distance Systemic Signaling and Communication in Plants. Berlin: Springer. pp. 189-204. |
| [23] |
Koltai H, Cohen M, Chesin O, Mayzlish-Gati E, Bécard G, Puech V, Dor BB, Resnick N, Wininger S, Kapulnik Y (2011). Light is a positive regulator of strigolactone levels in tomato roots. J Plant Physiol 168, 1993-1996.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Kronzucker HJ, Kirk GJD, Siddiqi MY, Glass ADM (1998). Effects of hypoxia on 13NH4+ fluxes in rice roots: kinetics and compartmental analysis. Plant Physiol 116, 581-587.
PMID |
| [25] | Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van De Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30, 325-327. |
| [26] |
Li B, Du X, Fei YY, Wang FQ, Xu Y, Li X, Li WQ, Chen ZH, Fan FJ, Wang J, Tao YJ, Jiang YJ, Zhu QH, Yang J (2021). Efficient breeding of early-maturing rice cultivar by editing PHYC via CRISPR/Cas9. Rice 14, 86.
DOI |
| [27] |
Liao ZG, Yu H, Duan JB, Yuan K, Yu CJ, Meng XB, Kou LQ, Chen MJ, Jing YH, Liu GF, Smith SM, Li JY (2019). SLR1 inhibits MOC1 degradation to coordinate tiller number and plant height in rice. Nat Commun 10, 2738.
DOI PMID |
| [28] |
Lin H, Wang RX, Qian Q, Yan MX, Meng XB, Fu ZM, Yan CY, Jiang B, Su Z, Li JY, Wang YH (2009). DWARF27, an iron-containing protein required for the biosynthesis of strigolactones, regulates rice tiller bud outgrowth. Plant Cell 21, 1512-1525.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
López-Ráez JA, Charnikhova T, Gómez-Roldán V, Mausova R, Kohlen W, De Vos R, Verstappen F, Puech- Pages V, Bécard G, Mulder P, Bouwmeester H (2008). Tomato strigolactones are derived from carotenoids and their biosynthesis is promoted by phosphate starvation. New Phytol 178, 863-874.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Marro N, Lidoy J, Chico MÁ, Rial C, García J, Varela RM, Macías FA, Pozo MJ, Janoušková M, López-Ráez JA (2022). Strigolactones: new players in the nitrogen-phosphorus signaling interplay. Plant Cell Environ 45, 512-527.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Matusova R, Rani K, Verstappen FWA, Franssen MCR, Beale MH, Bouwmeester HJ (2005). The strigolactone germination stimulants of the plant-parasitic Striga and Orobanche spp. are derived from the carotenoid pathway. Plant Physiol 139, 920-934.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, Von Haeseler A, Lanfear R (2020). IQ- TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol Evol 37, 1530-1534.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Umehara M, Hanada A, Magome H, Takeda-Kamiya N, Yamaguchi S (2010). Contribution of strigolactones to the inhibition of tiller bud outgrowth under phosphate defici- ency in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 1118-1126.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Umehara M, Hanada A, Yoshida S, Akiyama K, Arite T, Takeda-Kamiya N, Magome H, Kamiya Y, Shirasu K, Yoneyama K, Kyozuka J, Yamaguchi S (2008). Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature 455, 195-200.
DOI |
| [35] |
Wang B, Smith SM, Li JY (2018). Genetic regulation of shoot architecture. Annu Rev Plant Biol 69, 437-468.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Wang YX, Shang LG, Yu H, Zeng LJ, Hu J, Ni S, Rao YC, Li SF, Chu JF, Meng XB, Wang L, Hu P, Yan JJ, Kang SJ, Qu MH, Lin H, Wang T, Wang Q, Hu XM, Chen HQ, Wang B, Gao ZY, Guo LB, Zeng DL, Zhu XD, Xiong GS, Li JY, Qian Q (2020). A strigolactone biosynthesis gene contributed to the green revolution in rice. Mol Plant 13, 923-932.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Waters MT, Brewer PB, Bussell JD, Smith SM, Beveridge CA (2012). The Arabidopsis ortholog of rice DWARF27 acts upstream of MAX1 in the control of plant development by strigolactones. Plant Physiol 159, 1073-1085.
DOI PMID |
| [38] |
Wen C, Zhao QC, Nie J, Liu GQ, Shen L, Cheng CX, Xi L, Ma N, Zhao LJ (2016). Physiological controls of chrysanthemum DgD27 gene expression in regulation of shoot branching. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1053-1070.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Yoneyama K, Yoneyama K, Takeuchi Y, Sekimoto H (2007). Phosphorus deficiency in red clover promotes exudation of orobanchol, the signal for mycorrhizal symbionts and germination stimulant for root parasites. Planta 225, 1031-1038.
PMID |
| [40] |
Zhang L, Yu H, Ma B, Liu GF, Wang JJ, Wang JM, Gao RC, Li JJ, Liu JY, Xu J, Zhang YY, Li Q, Huang XH, Xu JL, Li JM, Qian Q, Han B, He ZH, Li JY (2017). A natural tandem array alleviates epigenetic repression of IPA1 and leads to superior yielding rice. Nat Commun 8, 14798.
DOI |
| [41] |
Zhao B, Wu TT, Ma SS, Jiang DJ, Bie XM, Sui N, Zhang XS, Wang F (2020). TaD27-B gene controls the tiller number in hexaploid wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 513-525.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 王子韵, 吕燕文, 肖钰, 吴超, 胡新生. 植物基因表达调控与进化机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 杨莉, 曲茜彤, 陈子航, 邹婷婷, 王全华, 王小丽. 菠菜AT-hook基因家族鉴定与表达谱分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 377-392. |
| [3] | 曹婕, 卢秋连, 翟健平, 刘宝辉, 方超, 李世晨, 苏彤. 大豆TPS基因家族在盐胁迫下的表达变化及单倍型选择规律分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 172-185. |
| [4] | 曹雪敏, 包颖, 张悦新, 李瑞杰, 苏健馨, 张蔚. 野蔷薇组培快繁和高效瞬时表达体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 235-245. |
| [5] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [6] | 张向歌, 陈晨, 程珊, 李春鑫, 朱雅婧, 许欣然, 王会伟. 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因鉴定及分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 33-48. |
| [7] | 何花, 谭敦炎, 杨晓琛. 被子植物隐性雌雄异株性系统的多样性、系统演化及进化意义[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(6): 24149-. |
| [8] | 赵来鹏, 王柏柯, 杨涛, 李宁, 杨海涛, 王娟, 闫会转. SlHVA22l基因调节番茄耐旱性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 558-573. |
| [9] | 顾磊, 张棋, 张霞, 杨冰冰, 王芳岚, 刘文, 陈发菊. 盐肤木APETALA3/DEFICIENS同源基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 533-543. |
| [10] | 赵晗茜, 宋佳怡, 杨洁, 赵永晶, 夏文念, 顾伟卓, 汪仲毅, 杨楠, 胡慧贞. 金鱼草XTH家族基因鉴定及抗核盘菌和雄蕊瓣化相关基因筛选[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 188-203. |
| [11] | 段政勇, 丁敏, 王宇卓, 丁艺冰, 陈凌, 王瑞云, 乔治军. 糜子SBP基因家族全基因组鉴定及表达分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 231-244. |
| [12] | 顾家琦, 朱福慧, 谢沛豪, 孟庆营, 郑颖, 张献龙, 袁道军. 棉属光敏色素PHY基因家族的全基因组鉴定与驯化选择分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 34-53. |
| [13] | 董小云, 魏家萍, 崔俊美, 武泽峰, 郑国强, 李辉, 王莹, 田海燕, 刘自刚. 植物抗冻蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 966-981. |
| [14] | 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| [15] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||