

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 533-543.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24015 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24015
顾磊, 张棋, 张霞, 杨冰冰, 王芳岚, 刘文, 陈发菊*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-30
接受日期:2024-03-30
出版日期:2024-07-10
发布日期:2024-07-10
通讯作者:
*E-mail: chenfj616@163.com
基金资助:
Lei Gu, Qi Zhang, Xia Zhang, Bingbing Yang, Fanglan Wang, Wen Liu, Faju Chen*( )
)
Received:2024-01-30
Accepted:2024-03-30
Online:2024-07-10
Published:2024-07-10
Contact:
*E-mail: chenfj616@163.com
摘要: AP3/DEF (APETALA3/DEFICIENS)基因为MADS-box基因家族的B类基因, 在花发育过程中主要参与调控花瓣和雄蕊发育。对盐肤木(Rhus chinensis) AP3/DEF同源基因进行克隆及功能分析, 有助于探究其在盐肤木雄蕊发育过程中的作用。采用RT-PCR技术获得盐肤木AP3/DEF同源基因CDS; 利用NCBI CD Search对其序列和结构域进行比较分析; 利用酵母双杂交系统, 对AP3/DEF同源蛋白与盐肤木中其它MADS-box转录因子进行蛋白互作验证; 通过实时荧光定量PCR分析盐肤木AP3/DEF同源基因的时空表达模式; 用过表达拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)验证盐肤木AP3/DEF同源基因在花器官发育中的功能。结果表明, 克隆得到2个盐肤木AP3/DEF同源基因分别命名为RcAP3 (GenBank: OR962160)和RcTM6 (GenBank: OR962159), 根据其氨基酸保守结构域比对及系统进化分析, 发现这2个蛋白序列与漆树科的芒果(Mangifera indica)和阿月浑子(Pistacia vera) AP3/DEF同源蛋白亲缘关系最近。酵母双杂交结果表明, RcAP3和RcTM6与盐肤木B类蛋白RcPI、C类蛋白RcAG和Rcag存在互作关系, 但与A类和E类蛋白不存在互作关系。实时荧光定量PCR分析结果显示, RcAP3和RcTM6基因在不同性别盐肤木花芽快速发育期高表达, 在花芽发育早期和开花后表达水平较低; RcAP3在雌花、雄花和两性花的花芽分化过程中均维持较高的表达水平, 而RcTM6在两性花中显著表达, 在雄花和雌花中表达量很低。两性花快速生长期, RcAP3在花瓣和雄蕊中高表达且差异很小, 而RcTM6在雄蕊中的表达量显著高于其它花器官。RcAP3基因能恢复拟南芥ap3-3突变体花瓣和雄蕊的缺陷表型, RcTM6过表达则导致拟南芥花瓣、雄蕊和子房缩短, 花药败育, 表明盐肤木中同属AP3/DEF亚家族的同源基因RcAP3和RcTM6存在功能分化。RcAP3促进花瓣和雄蕊发育, 而RcTM6抑制雄蕊发育。研究结果为进一步研究盐肤木性别分化的分子机制奠定了基础。
顾磊, 张棋, 张霞, 杨冰冰, 王芳岚, 刘文, 陈发菊. 盐肤木APETALA3/DEFICIENS同源基因的克隆与功能分析. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 533-543.
Lei Gu, Qi Zhang, Xia Zhang, Bingbing Yang, Fanglan Wang, Wen Liu, Faju Chen. Cloning and Functional Analysis of APETALA3/DEFICIENS Homologous Gene from Rhus chinensis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 533-543.
| Primers | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Primer usage |
|---|---|---|
| RcAP3-CDS-F | ATGGCTCGAGGAAAGATCCAG | CDS cloning and positive plant identification |
| RcAP3-CDS-R | CTAGTCAAGCAAGGGGGAGG | |
| RcTM6-CDS-F | ATGGGTCGCGGAAAGATTG | |
| RcTM6-CDS-R | TCAACCAAGGCTGAGATTGTTG | |
| qRcAP3-CDS-F | GAAGAAGGTAAGGAGTGTGACAG | Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR |
| qRcAP3-CDS-R | AGGTGGTGAGATCTGAGCCTG | |
| qRcTM6-CDS-F | CGTCCGTGAAAGAAAGTACCATG | |
| qRcTM6-CDS-R | GCGTACAGGTTAGATGCTCC | |
| qPP2A-F | TCCACCGTCCGATCATCAGAAC | Reference gene |
| qPP2A-R | GCACGTTCCATTCCTCCACC | |
| ap3-jianceF1 | ATGGCGAGAGGGAAGATCC | Detection of ap3 gene-pure plants in Arabidopsis thaliana |
| ap3-jianceR1 | GATCAAGAGGATAGAGAACCAGACAAACAGA | |
| ap3-jianceF2 | ACAGTTTCCTCTTGGTTTCTTGC | |
| ap3-jianceR2 | CGCATCAAGAATTTAACCAACCAGCG |
表1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences used in this study
| Primers | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Primer usage |
|---|---|---|
| RcAP3-CDS-F | ATGGCTCGAGGAAAGATCCAG | CDS cloning and positive plant identification |
| RcAP3-CDS-R | CTAGTCAAGCAAGGGGGAGG | |
| RcTM6-CDS-F | ATGGGTCGCGGAAAGATTG | |
| RcTM6-CDS-R | TCAACCAAGGCTGAGATTGTTG | |
| qRcAP3-CDS-F | GAAGAAGGTAAGGAGTGTGACAG | Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR |
| qRcAP3-CDS-R | AGGTGGTGAGATCTGAGCCTG | |
| qRcTM6-CDS-F | CGTCCGTGAAAGAAAGTACCATG | |
| qRcTM6-CDS-R | GCGTACAGGTTAGATGCTCC | |
| qPP2A-F | TCCACCGTCCGATCATCAGAAC | Reference gene |
| qPP2A-R | GCACGTTCCATTCCTCCACC | |
| ap3-jianceF1 | ATGGCGAGAGGGAAGATCC | Detection of ap3 gene-pure plants in Arabidopsis thaliana |
| ap3-jianceR1 | GATCAAGAGGATAGAGAACCAGACAAACAGA | |
| ap3-jianceF2 | ACAGTTTCCTCTTGGTTTCTTGC | |
| ap3-jianceR2 | CGCATCAAGAATTTAACCAACCAGCG |
| Species | Protein | GenBank ID |
|---|---|---|
| Rhus chinensis | RcAP3 | OR962159 |
| R. chinensis | RcTM6 | OR962160 |
| Nicotiana tabacum | NtDEF | CAA65288 |
| Petunia × hybrida | PhDEF | AAQ72510 |
| Solanum lycopersicum | SolyDEF | CAJ53871 |
| Antirrhinum majus | AmDEF | P23706 |
| Torenia fournieri | TofoDEF | BAG24492 |
| Gerbera hybrid | GDEF2 | CAA08803 |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtAP3 | NP_191002 |
| Pistacia vera | PvAP3 | OR962159 |
| Mangifera indica | MinAP3 | XP_044510378 |
| Lotus japonicus | LojaAP3 | AAX13301 |
| Gongora galeata | GogaDEF | ACR16038 |
| Oncidium hybrid | OMADS9 | ADJ67235 |
| Dendrobium crumenatum | DecrAP3 | AAZ95249 |
| Spiranthes odorata | SpodDEF | ACR16049 |
| Vanilla planifolia | VaplDEF | ACR16055 |
| Asparagus officinalis | AODEF | BAC75969 |
| Muscari armeniacum | MaDEF | BAE48147 |
| Tulipa gesneriana | TGDEFA | BAC75970 |
| T. gesneriana | TGDEFB | BAC75971 |
| Lilium longiflorum | LMADS1 | AAM27456 |
| Monotropa hypopitys | MhTM6 | AQM52303 |
| Tradescantia ohiensis | TrohDEF | BAD80745 |
| Commelina communis | CocoAP3 | BAD80747 |
| Oryza sativa | OsMADS16 | Q944S9 |
| Chimonanthus praecox | ChprAP3 | ABK34952 |
| Akebia trifoliata | AktAP3-1 | AAT46097 |
| Hydrangea macrophylla | HmTM6 | AAF73932 |
| Petunia × hybrida | PhTM6 | AAS46017 |
| Helianthus annuus | HAM91 | AAO18231 |
| Rosa rugosa | MASAKO B3 | BAB63261 |
| Prunus avium | PaTM6 | BAT57494 |
| Malus domestica | MdTM6 | BAC11907 |
| Ma. domestica | MdMADS13 | CAC80856 |
| Pistacia vera | PvTM6 | XP_031264419 |
| Mangifera indica | MinTM6 | XP_044469431 |
| Philadelphus pubescens | PhpTM6 | ACY08886 |
| Vitis vinifera | VvTM6 | ABI98021 |
| Saurauia zahlbruckneri | SzTM6 | ACY08897 |
| Actinidia chinensis | AcAP3 | ADU15473 |
| Ar. thaliana | AtPI | NP_197524 |
表2 构建系统进化树蛋白序列登录号
Table 2 GenBank number of protein sequences used for constructing the phylogenetic tree
| Species | Protein | GenBank ID |
|---|---|---|
| Rhus chinensis | RcAP3 | OR962159 |
| R. chinensis | RcTM6 | OR962160 |
| Nicotiana tabacum | NtDEF | CAA65288 |
| Petunia × hybrida | PhDEF | AAQ72510 |
| Solanum lycopersicum | SolyDEF | CAJ53871 |
| Antirrhinum majus | AmDEF | P23706 |
| Torenia fournieri | TofoDEF | BAG24492 |
| Gerbera hybrid | GDEF2 | CAA08803 |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtAP3 | NP_191002 |
| Pistacia vera | PvAP3 | OR962159 |
| Mangifera indica | MinAP3 | XP_044510378 |
| Lotus japonicus | LojaAP3 | AAX13301 |
| Gongora galeata | GogaDEF | ACR16038 |
| Oncidium hybrid | OMADS9 | ADJ67235 |
| Dendrobium crumenatum | DecrAP3 | AAZ95249 |
| Spiranthes odorata | SpodDEF | ACR16049 |
| Vanilla planifolia | VaplDEF | ACR16055 |
| Asparagus officinalis | AODEF | BAC75969 |
| Muscari armeniacum | MaDEF | BAE48147 |
| Tulipa gesneriana | TGDEFA | BAC75970 |
| T. gesneriana | TGDEFB | BAC75971 |
| Lilium longiflorum | LMADS1 | AAM27456 |
| Monotropa hypopitys | MhTM6 | AQM52303 |
| Tradescantia ohiensis | TrohDEF | BAD80745 |
| Commelina communis | CocoAP3 | BAD80747 |
| Oryza sativa | OsMADS16 | Q944S9 |
| Chimonanthus praecox | ChprAP3 | ABK34952 |
| Akebia trifoliata | AktAP3-1 | AAT46097 |
| Hydrangea macrophylla | HmTM6 | AAF73932 |
| Petunia × hybrida | PhTM6 | AAS46017 |
| Helianthus annuus | HAM91 | AAO18231 |
| Rosa rugosa | MASAKO B3 | BAB63261 |
| Prunus avium | PaTM6 | BAT57494 |
| Malus domestica | MdTM6 | BAC11907 |
| Ma. domestica | MdMADS13 | CAC80856 |
| Pistacia vera | PvTM6 | XP_031264419 |
| Mangifera indica | MinTM6 | XP_044469431 |
| Philadelphus pubescens | PhpTM6 | ACY08886 |
| Vitis vinifera | VvTM6 | ABI98021 |
| Saurauia zahlbruckneri | SzTM6 | ACY08897 |
| Actinidia chinensis | AcAP3 | ADU15473 |
| Ar. thaliana | AtPI | NP_197524 |
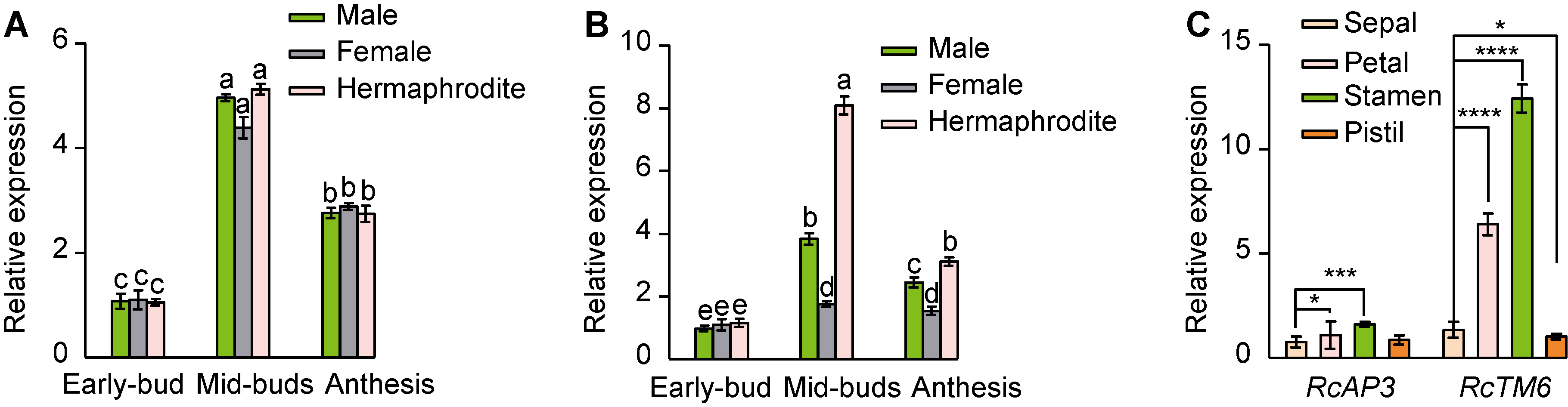
图2 RcAP3和RcTM6的相对表达模式 (A), (B) RcAP3 (A)和RcTM6 (B)在花芽不同发育时期的表达(单因素方差分析, 沃勒-邓肯检测, 不同小写字母表示在P<0.05水平差异显著); (C) RcAP3和RcTM6在两性花花芽中期不同器官中的表达水平(* P<0.05, *** P<0.001)。
Figure 2 The relative expression patterns of RcAP3 and RcTM6 (A), (B) Expression of RcAP3 and RcTM6 at different stages of flower bud development (One-way analysis of ANOVA by Waller-Duncan, different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at P<0.05); (C) Expression levels of RcAP3 and RcTM6 in different organs in the middle stage of flower buds of hermaphroditic flower (* P<0.05, *** P<0.001).
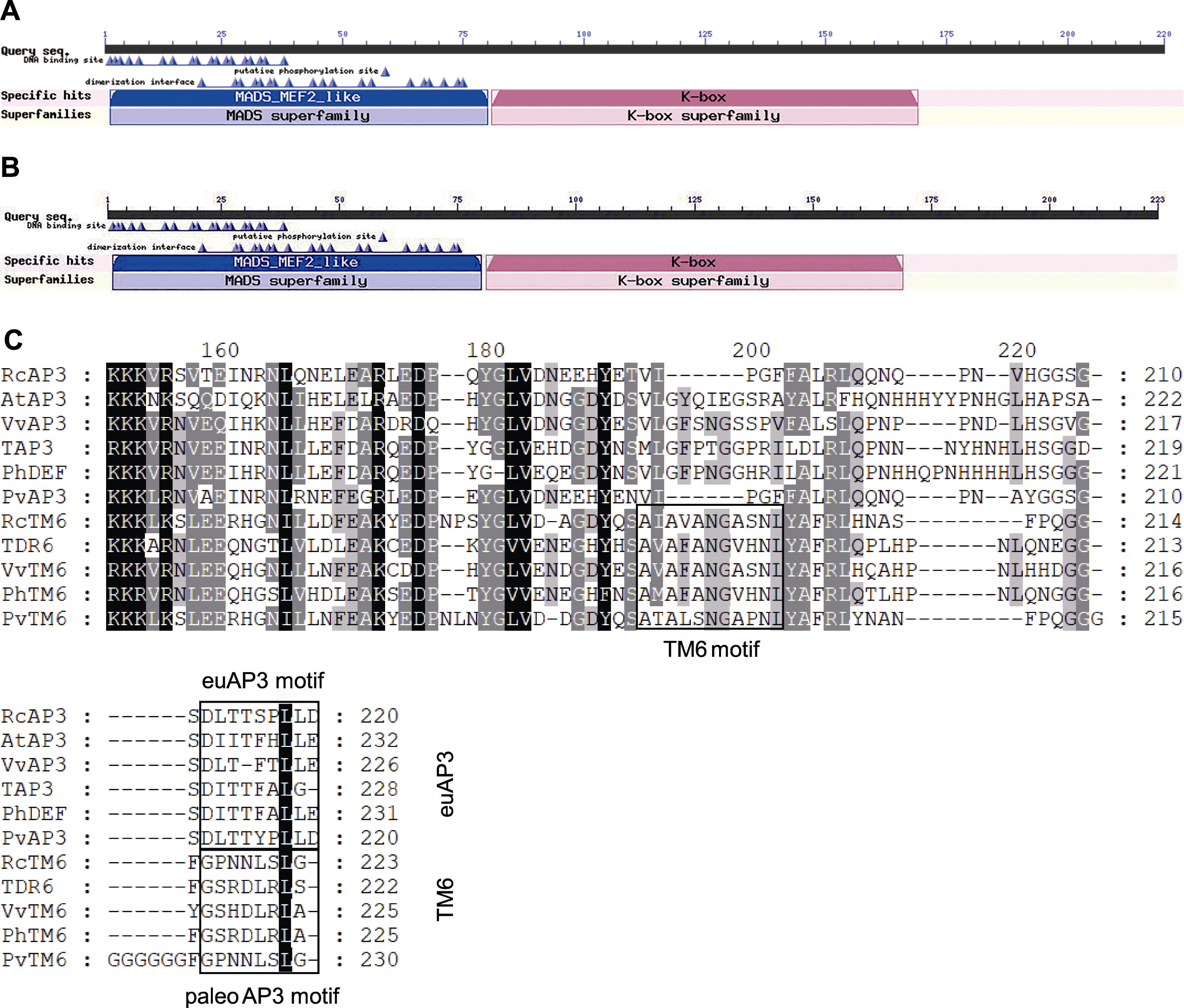
图3 RcAP3 (A)和RcTM6 (B)的蛋白质保守结构域以及与其它植物的氨基酸序列多重比对(C)
Figure 3 The protein conserved domain of RcAP3 (A), RcTM6 (B), and the alignment of amino acid sequences of RcAP3 and RcTM6 with other plants (C)
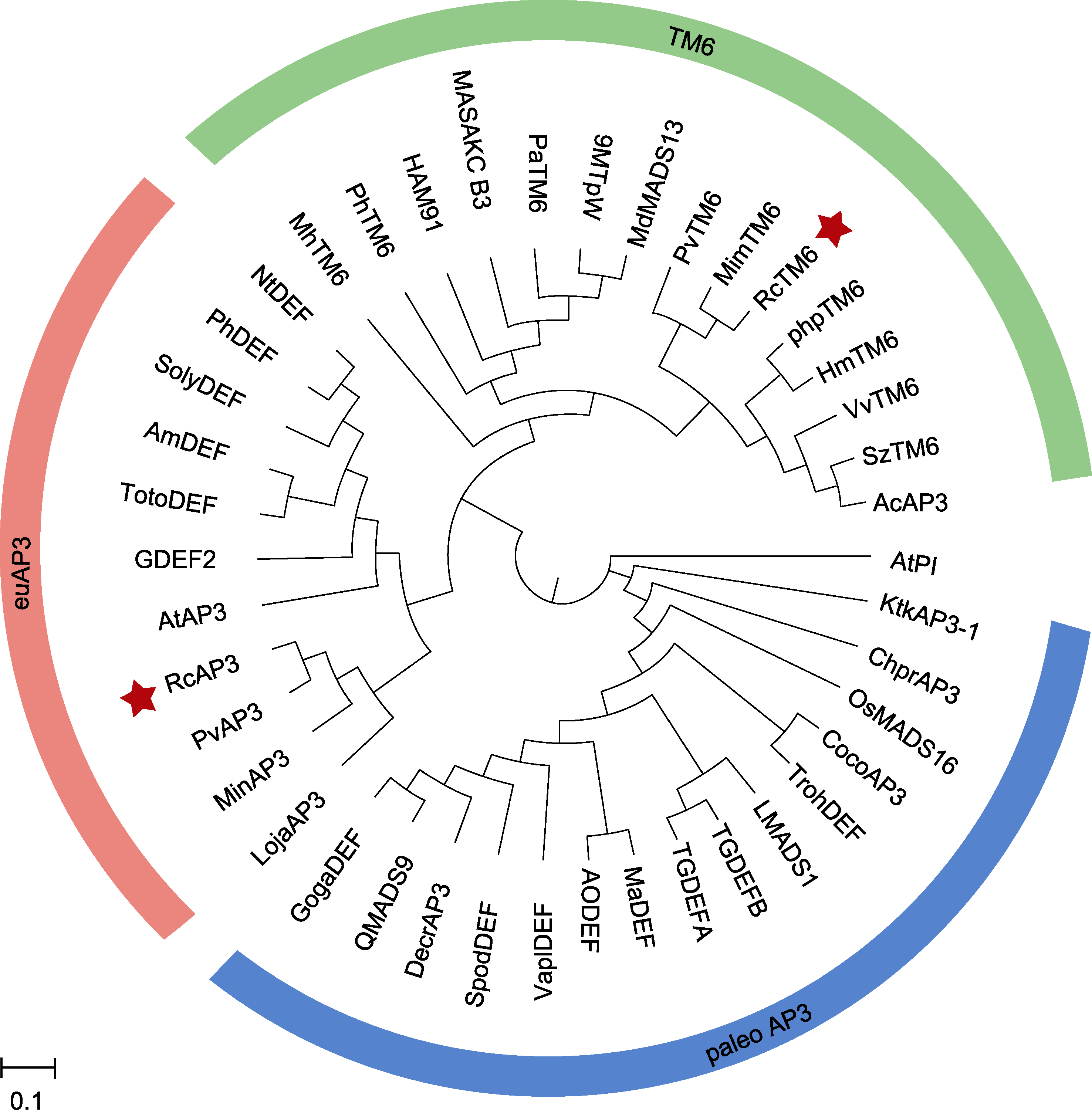
图4 基于盐肤木RcAP3和RcTM6蛋白的系统进化树 红色星号表示本研究中的蛋白。
Figure 4 Phylogenetic tree based on RcAP3 and RcTM6 proteins The red asterisk indicates the protein in this study.
| Parameter | RcAP3 | RcTM6 |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | C1118H1824N328O348S5 | C1125H1789N325O343S6 |
| Molecular mass (kDa) | 25.59 | 25.55 |
| Total number of atoms | 3623 | 3588 |
| Theoretical pI | 9.23 | 9.33 |
| Total number of negatively char- ged residues (Asp+Glu) | 30 | 29 |
| Total number of positively char- ged residues (Arg+Lys) | 35 | 36 |
| Instability index | 48.17 | 40.95 |
| Aliphatic index | 86.82 | 73.50 |
| Grand average of hydropathicity | -0.754 | -0.749 |
| Signal peptide | None | None |
| Transmembrane domain | None | None |
表3 RcAP3和RcTM6蛋白理化性质分析
Table 3 Analysis of physicochemical properties of RcAP3 and RcTM6 proteins
| Parameter | RcAP3 | RcTM6 |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | C1118H1824N328O348S5 | C1125H1789N325O343S6 |
| Molecular mass (kDa) | 25.59 | 25.55 |
| Total number of atoms | 3623 | 3588 |
| Theoretical pI | 9.23 | 9.33 |
| Total number of negatively char- ged residues (Asp+Glu) | 30 | 29 |
| Total number of positively char- ged residues (Arg+Lys) | 35 | 36 |
| Instability index | 48.17 | 40.95 |
| Aliphatic index | 86.82 | 73.50 |
| Grand average of hydropathicity | -0.754 | -0.749 |
| Signal peptide | None | None |
| Transmembrane domain | None | None |
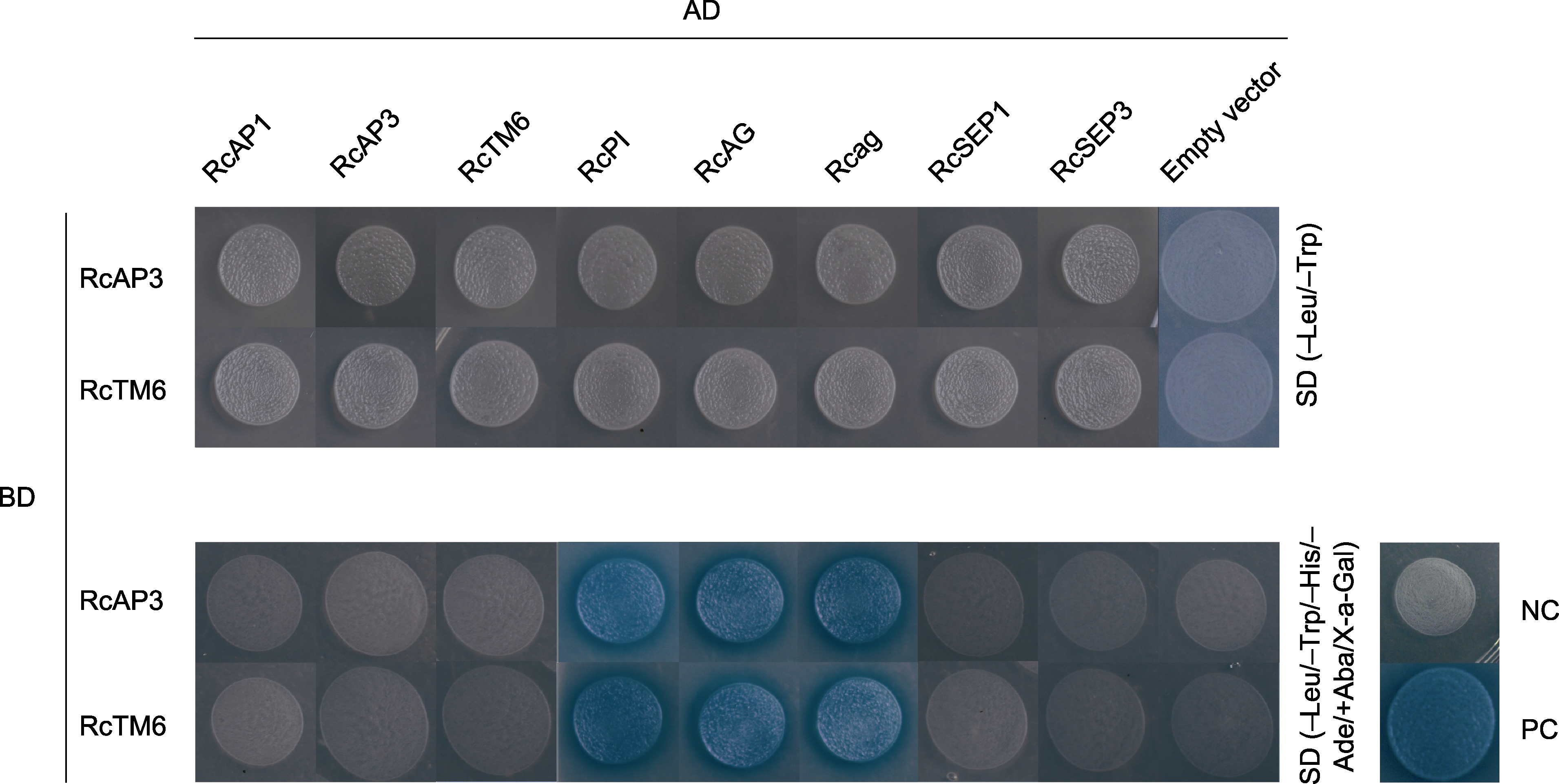
图6 酵母双杂交分析RcAP3与RcTM6蛋白的相互作用模式 AD: 激活结构域; BD: 结合结构域; NC: 阴性对照; PC: 阳性对照
Figure 6 Yeast two-hybrid analysis of RcAP3 and RcTM6 protein interaction patterns AD: Activation domain; BD: Binding domain; NC: Negative control; PC: Positive control

图7 转基因拟南芥表型比较 (A) 野生型(WT)拟南芥(Col-0); (B) 空载体pBI121转Col-0拟南芥; (C), (D) 35S::RcAP3转Col-0拟南芥; (E)-(I) 35S::RcTM6转Col-0拟南芥; (J) ap3-3突变体拟南芥; (K), (L) 35S::RcAP3转ap3-3突变体拟南芥。(A)-(H), (J)-(L) Bars=1 mm; (I) Bar=1 cm
Figure 7 Comparison of phenotypes of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana (A) Wild-type (WT) of A. thaliana (Col-0); (B) pBI121 empty vector to Arabidopsis Col-0; (C), (D) 35S::RcAP3 transgenic Arabidopsis in a Col-0 background; (E)-(I) 35S::RcTM6 transgenic Arabidopsis in a Col-0 background; (J) ap3-3 homozygous mutants; (K), (L) 35S::RcAP3 transgenic Arabidopsis in a ap3-3 homozygous background. (A)-(H), (J)-(L) Bars=1 mm; (I) Bar=1 cm
| [1] |
Broholm SK, Pöllänen E, Ruokolainen S, Tähtiharju S, Kotilainen M, Albert VA, Elomaa P, Teeri TH (2010). Functional characterization of B class MADS-box transcription factors in Gerbera hybrida. J Exp Bot 61, 75-85.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Cao X, Liu XY, Wang XT, Yang MX, van Giang T, Wang J, Liu XL, Sun S, Wei K, Wang XX, Gao JC, Du YC, Qin Y, Guo YM, Huang ZJ (2019). B-class MADS-box TM6 is a candidate gene for tomato male sterile-1526. Theor Appl Genet 132, 2125-2135. |
| [3] |
Causier B, Castillo R, Xue Y, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Davies B (2010). Tracing the evolution of the floral homeotic B- and C-function genes through genome synteny. Mol Biol Evol 27, 2651-2664.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998). Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16, 735-743.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
de Martino G, Pan I, Emmanuel E, Levy A, Irish VF (2006). Functional analyses of two tomato APETALA3 genes demonstrate diversification in their roles in regulating floral development. Plant Cell 18, 1833-1845.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Doyle JJ (1994). Evolution of a plant homeotic multigene family: toward connecting molecular systematics and molecular developmental genetics. Syst Biol 43, 307-328. |
| [7] | Fang ZW, Qi R, Li XF, Liu ZX (2014). Ectopic expression of FaesAP3, a Fagopyrum esculentum (Polygonaceae) AP3 orthologous gene rescues stamen development in an Arabidopsis ap3mutant. Gene 550, 200-206. |
| [8] | Goto K, Meyerowitz EM (1994). Function and regulation of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene PISTILLATA. Genes Dev 8, 1548-1560. |
| [9] |
Hernández-Hernández T, Martínez-Castilla LP, Alvarez- Buylla ER (2007). Functional diversification of B MADS- box homeotic regulators of flower development: adaptive evolution in protein-protein interaction domains after major gene duplication events. Mol Biol Evol 24, 465-481.
PMID |
| [10] |
Jack T, Brockman LL, Meyerowitz EM (1992). The homeotic gene APETALA3 of Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a MADS box and is expressed in petals and stamens. Cell 68, 683-697.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Jing DL, Chen WW, Shi M, Wang D, Xia Y, He Q, Dang JB, Guo QG, Liang GL (2020). Ectopic expression of an Eriobotrya japonica APETALA3 ortholog rescues the petal and stamen identities in Arabidopsis ap3-3 mutant. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 523, 33-38. |
| [12] | Jing DL, Xia Y, Zhang SG, Wang JH (2016). Expression analysis of B-class MADS-box genes from Catalpa speciosa. Chin Bull Bot 51, 210-217. (in Chinese) |
|
景丹龙, 夏燕, 张守攻, 王军辉 (2016). 黄金树B类MADS- box基因表达特征分析. 植物学报 51, 210-217.
DOI |
|
| [13] | Kim S, Yoo MJ, Albert VA, Farris JS, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2004). Phylogeny and diversification of B-function MADS- box genes in angiosperms: evolutionary and functional implications of a 260-million-year-old duplication. Am J Bot 91, 2102-2118. |
| [14] | Kramer EM, Irish VF (2000). Evolution of the petal and stamen developmental programs: evidence from comparative studies of the lower eudicots and basal angiosperms. Int J Plant Sci 161, S29-S40. |
| [15] | Lai XL, Daher H, Galien A, Hugouvieux V, Zubieta C (2019). Structural basis for plant MADS transcription factor oligomerization. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 17, 946- 953. |
| [16] | Lamb RS, Irish VF (2003). Functional divergence within the APETALA3/PISTILLATA floral homeotic gene lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 6558-6563. |
| [17] | Li B, Gao JY, Gong LM, Liu PA, Li SX (2015). Chemical constituents from Rhus chinensis fruit dregs. J Chin Medi Materials 38, 1209-1211. (in Chinese) |
| 李斌, 高洁莹, 龚力民, 刘平安, 李顺祥 (2015). 盐肤木果粕化学成分研究. 中药材 38, 1209-1211. | |
| [18] | Li MC, Wang AD, Zhang YQ, Han TT, Guan L, Fan DX, Liu JY, Xu YN (2022). A comprehensive review on ethnobotanical, phytochemical and pharmacological aspects of Rhus chinensis Mill. J Ethnopharmacol 293, 115288. |
| [19] | Li XF, Xu J, Yang R, Jia LY, Deng XJ, Xiong LJ, Zhang XP, Fang Q, Zhang W, Sun Y, Xu L (2013). Analysis of B-class genes NAP3L3 and NAP3L4 in Narcissus tazetta var. chinensis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31, 255-263. |
| [20] |
Litt A, Kramer EM (2010). The ABC model and the diversification of floral organ identity. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21, 129-137.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆CTmethod. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Ma N, Cai SB, Sun YL, Chu CQ (2024). Chinese sumac (Rhus chinensis Mill.) fruits prevent hyperuricemia and uric acid nephropathy in mice fed a high-purine yeast diet. Nutrients 16, 184. |
| [23] | Poupin MJ, Federici F, Medina C, Matus JT, Timmermann T, Arce-Johnson P (2007). Isolation of the three grape sub-lineages of B-class MADS-box TM6, PISTILLATA and APETALA3 genes which are differentially expressed during flower and fruit development. Gene 404, 10-24. |
| [24] |
Rijpkema AS, Royaert S, Zethof J, van der Weerden G, Gerats T (2006). Analysis of the Petunia TM6 MADS box gene reveals functional divergence within the DEF/AP3 lineage. Plant Cell 18, 1819-1832.
PMID |
| [25] | Rusanov K, Kovacheva N, Rusanova M, Linde M, Debener T, Atanassov I (2019). Genetic control of flower petal number in Rosa × Damascena Mill f. trigintipetala. Biotechnol Biotec Eq 33, 597-604. |
| [26] | Shen GX, Jia Y, Wang WL (2021). Evolutionary divergence of motifs in B-class MADS-box proteins of seed plants. J Biol Res-Thessalon 28, 12. |
| [27] | Shen GX, Yang CH, Shen CY, Huang KS (2019). Origination and selection of ABCDE and AGL6 subfamily MADS- box genes in gymnosperms and angiosperms. Biol Res 52, 25. |
| [28] |
Sommer H, Beltrán JP, Huijser P, Pape H, Lönnig WE, Saedler H, Schwarz-Sommer Z (1990). Deficiens, a homeotic gene involved in the control of flower morphogenesis in Antirrhinum majus: the protein shows homolo-gy to transcription factors. EMBO J 9, 605-613.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | Sun FH, Fang HY, Wen XH, Zhang LS (2023). Phylogenetic and expression analysis of MADS-box gene family in Rhododendron ovatum. Chin Bull Bot 58, 404-416. (in Chinese) |
|
孙福辉, 方慧仪, 温小蕙, 张亮生 (2023). 马银花MADS- box基因家族系统进化与表达分析. 植物学报 58, 404-416.
DOI |
|
| [30] |
Vandenbussche M, Zethof J, Royaert S, Weterings K, Gerats T (2004). The duplicated B-class heterodimer model: whorl-specific effects and complex genetic interactions in Petunia hybrida flower development. Plant Cell 16, 741-754.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Ye A, Zhang CL, Sun YL, Wang WN, He YH, Bao MZ (2017). Characterization and functional analysis of five MADS-Box B class genes related to floral organ identification in Tagetes erecta. PLoS One 12, e0169777. |
| [32] | Zhang HQ, Han W, Linghu T, Zhao ZX, Wang AZ, Zhai R, Yang CQ, Xu LF, Wang ZG (2023). Overexpression of a pear B-class MADS-box gene in tomato causes male sterility. Fruit Res 3, 1. |
| [33] | Zhang Q, Wang BG, Duan K, Wang LG, Wang M, Tang XM, Pan AH, Sui SZ, Wang GD (2011). The paleoAP3-type gene CpAP3, an ancestral B-class gene from the basal angiosperm Chimonanthus praecox, can affect stamen and petal development in higher eudicots. Dev Genes Evol 221, 83-93. |
| [1] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [2] | 鲁丹, 王丽, 宋凡, 陶菊红, 张大兵, 袁政. 水稻OsJMJ718基因可选择性多聚腺苷酸化序列的 克隆及生殖发育期表达模式[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 594-602. |
| [3] | 牛艳丽, 柏胜龙, 王麒云, 刘凌云. 单细胞组学技术及其在植物保卫细胞研究中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 788-796. |
| [4] | 韩笑, 郭凯, 李新新, 刘绪, 王炳锐, 夏涛, 彭良才, 丰胜求. 拟南芥纤维素合酶基因时空表达模式与功能预测[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(5): 539-547. |
| [5] | 佘朝文;*;蒋向辉;宋运淳. 玉米rRNA基因的组织和表达模式[J]. 植物学报, 2010, 45(03): 345-353. |
| [6] | 杨珍珍;李萍;王崇英*. T-DNA介导的基因诱捕技术及其在植物功能基因组学研究中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2008, 25(01): 112-120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||