

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 594-602.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17114 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17114
收稿日期:2017-06-07
接受日期:2017-10-07
出版日期:2018-09-01
发布日期:2018-11-29
通讯作者:
袁政
作者简介: 作者简介: 路安民(图中左), 植物系统分类学家。20世纪60-70年代编著《中国植物志》等, 后从事植物系统发育和进化研究。“七五”以来主持了4项中科院、国家自然科学基金委重大和重点项目。1991年获国务院颁发的有突出贡献科学家荣誉证书。1987年8月-1990年12月担任中科院植物所所长。
作者简介: 路安民(图中左), 植物系统分类学家。20世纪60-70年代编著《中国植物志》等, 后从事植物系统发育和进化研究。“七五”以来主持了4项中科院、国家自然科学基金委重大和重点项目。1991年获国务院颁发的有突出贡献科学家荣誉证书。1987年8月-1990年12月担任中科院植物所所长。
基金资助:
Lu Dan, Wang Li, Song Fan, Tao Juhong, Zhang Dabing, Yuan Zheng*( )
)
Received:2017-06-07
Accepted:2017-10-07
Online:2018-09-01
Published:2018-11-29
Contact:
Yuan Zheng
About author:† These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 可选择性多聚腺苷酸化是真核生物重要的基因调控机制之一, 通过形成不同长度的3'端非翻译区影响信使RNA的稳定性、定位和翻译效率, 从而增加转录本的复杂度。已有研究表明, 拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中参与DNA去甲基化调控IBM1基因的可选择性多聚腺苷酸化加工受染色质调节因子EDM2调控, 从而影响拟南芥基因组数千基因的CHG甲基化水平, 但该类调控机制是否在其它物种中同样存在仍然未知。以水稻(Oryza sativa)基因组中IBM1同源基因OsJMJ718为研究对象, 利用生物信息学分析和3'RACE实验, 发现IBM1同源基因也存在可选择性多聚腺苷酸化修饰, OsJMJ718基因可能存在9个可选择性多聚腺苷酸化序列。序列比对分析表明, NCBI网站现存日本晴OsJMJ718基因组3'末端序列与9522和明辉63等其它生态型基因组序列组成可能不同。荧光实时定量PCR分析表明, OsJMJ718的9个转录本在水稻生殖发育阶段呈现不同的动态表达模式, 其中TVX5转录本表达量最高。研究获得的OsJMJ718基因可选择性多聚腺苷酸化序列信息及相关的表达模式分析为进一步揭示水稻OsJMJ718基因的可选择性多聚腺苷酸化分子机制和生物学功能奠定了基础。
鲁丹, 王丽, 宋凡, 陶菊红, 张大兵, 袁政. 水稻OsJMJ718基因可选择性多聚腺苷酸化序列的 克隆及生殖发育期表达模式. 植物学报, 2018, 53(5): 594-602.
Lu Dan, Wang Li, Song Fan, Tao Juhong, Zhang Dabing, Yuan Zheng. Cloning and Expression Pattern Analysis of Rice OsJMJ718 Alternative Polyadenylation Sequences During Reproductive Developmental Stage. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(5): 594-602.
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| qRT-F-TVX1 | GAGCTTGGATAGCCCGCCTC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX1 | TCTTTTCTTCCCGGGAGTGC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX2 | CAATAATTGAACTCTAGGTC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX2 | TAAGGAAATACAATCAGATC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX3 | ACGGACGCTGGATCGGCGAG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX3 | TAACAAGAGCAGTAGAGCAC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX4 | ACGGACGCTGGATCGGCGAG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX4 | AAGGACGGGGATGCGGCGT | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX5 | AACGACAACTTTAGGGTTCG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX5 | TCGTTACAAGAAAGATGAAC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX6 | ATCGAATTGCCACGTAAGCG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX6 | TCATCCTCACTCTCTTCTTC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX7 | GAACCACAGGGCCAAAGAAG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX7 | TAATCCAATTAAAAGTGTTG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX9 | AACTCTTCACCACGCGTATG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX9 | TAACCGGCGATGGCTGCATC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX11 | GAATAAGATGATAATCTATG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX11 | ATATCTCTAACTCTACATGC | qRT PCR |
| 3'RACE-F-OsJMJ718 | GATTACGCCAAGCTTAGTGAGACCAACAAGGGAGGTGCT | 3'RACE |
表1 本研究所用引物
Table 1 Primers used in this research
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5′-3′) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| qRT-F-TVX1 | GAGCTTGGATAGCCCGCCTC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX1 | TCTTTTCTTCCCGGGAGTGC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX2 | CAATAATTGAACTCTAGGTC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX2 | TAAGGAAATACAATCAGATC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX3 | ACGGACGCTGGATCGGCGAG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX3 | TAACAAGAGCAGTAGAGCAC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX4 | ACGGACGCTGGATCGGCGAG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX4 | AAGGACGGGGATGCGGCGT | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX5 | AACGACAACTTTAGGGTTCG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX5 | TCGTTACAAGAAAGATGAAC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX6 | ATCGAATTGCCACGTAAGCG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX6 | TCATCCTCACTCTCTTCTTC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX7 | GAACCACAGGGCCAAAGAAG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX7 | TAATCCAATTAAAAGTGTTG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX9 | AACTCTTCACCACGCGTATG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX9 | TAACCGGCGATGGCTGCATC | qRT PCR |
| qRT-F-TVX11 | GAATAAGATGATAATCTATG | qRT PCR |
| qRT-R-TVX11 | ATATCTCTAACTCTACATGC | qRT PCR |
| 3'RACE-F-OsJMJ718 | GATTACGCCAAGCTTAGTGAGACCAACAAGGGAGGTGCT | 3'RACE |
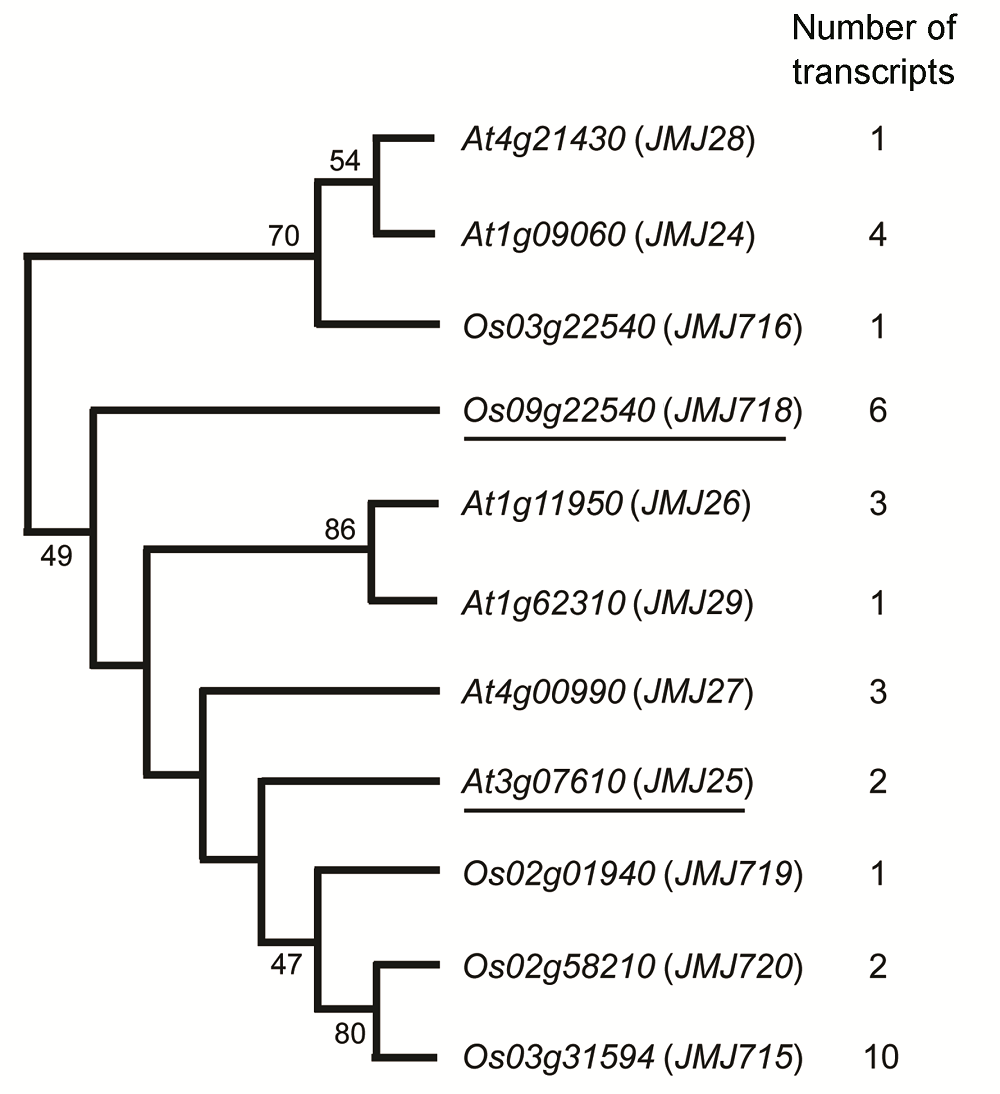
图1 拟南芥和水稻中JHDM2家族基因mRNA可选择性多聚腺苷酸化加工序列数目Os09g22540 (JMJ718)为研究对象OsJMJ718; At3g07610 (JMJ25)是拟南芥IBM1, OsJMJ718的同源基因。
Figure 1 The number of alternative polyadenylation sequences of JHDM2 family genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and riceOs09g22540 (JMJ718) is OsJMJ718, the target sequence of this study; At3g07610 (JMJ25) is IBM1, which is the homo- logous gene of OsJMJ718 in Arabidopsis thaliana.
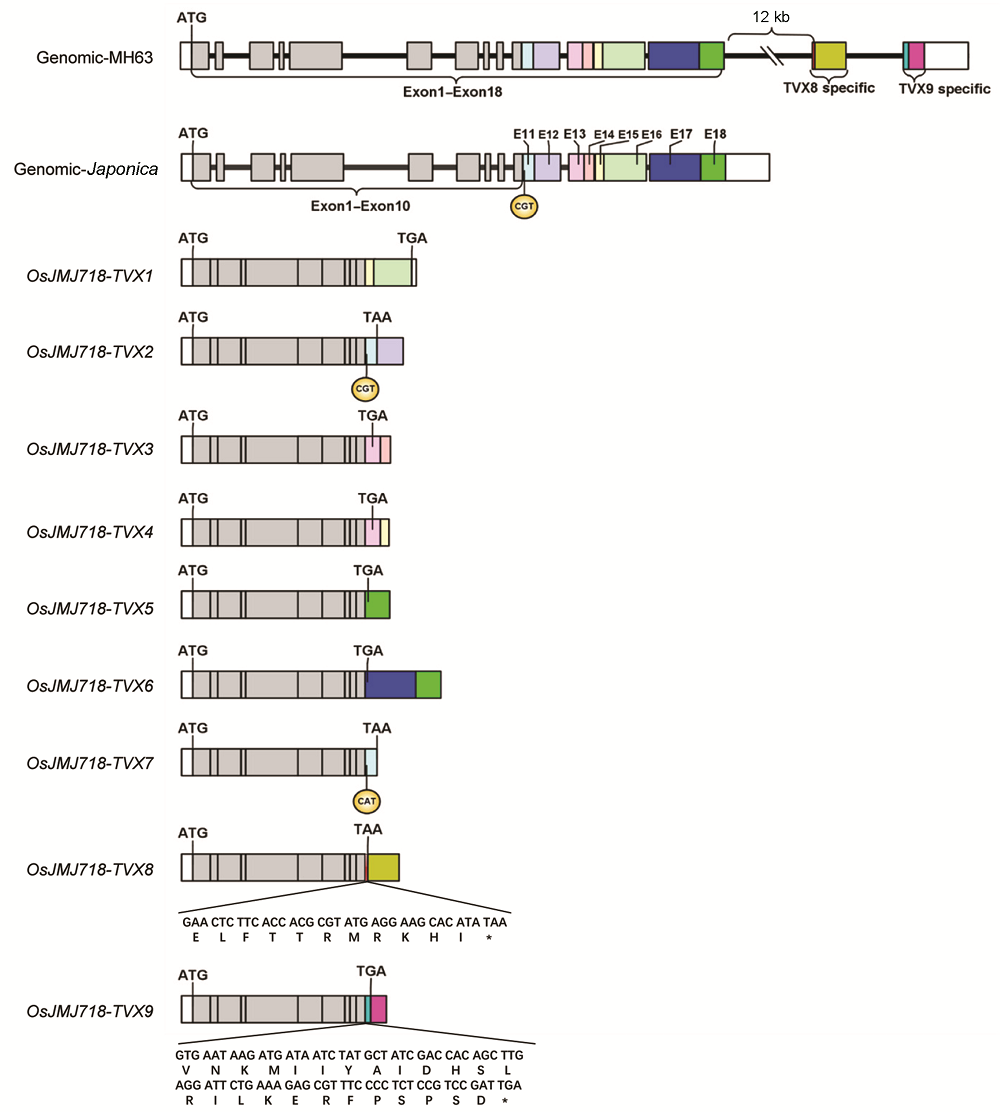
图2 OsJMJ718-TVX转录本序列9个转录本分别命名为TVX1-TVX9; Exon1-Exon10表示各转录本共有外显子序列, Exon11-Exon18为不同颜色表示基因组上的8个外显子通过可选择性多聚腺苷酸化被特异加工至TVX1-TVX7转录本。其中, TVX8和TVX9的3'端序列仅存在于明辉63 (MH63)基因组中。* 表示终止密码子
Figure 2 Sequence analysis of OsJMJ718-TVX transcriptsNine transcripts were named as TVX1-TVX9, respectively; Exon1-Exon10 represent common exon sequences for each transcript; Exon11-Exon18 were marked in different color, the 8 exons were processed in TVX1-TVX7 by alternative polyadenylation. However, 3’ terminal sequences of TVX8 and TVX9 are only exist in MH63 genomic sequences. * indicates stop codon
| 11 | Saze H, Shiraishi A, Miura A, Kakutani T (2008). Control of genic DNA methylation by a jmjC domain-containing pro- tein in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 319, 462-465. |
| 12 | Shen YJ, Venu RC, Nobuta K, Wu XH, Notibala V, Demirci C, Meyers BC, Wang GL, Ji GL, Li QQ (2011). Transcrip- tome dynamics through alternative polyadenylation in developmental and environmental responses in plants revealed by deep sequencing.Genome Res 21, 1478-1486. |
| 13 | Shi YS (2012). Alternative polyadenylation: new insights from global analyses.RNA 18, 2105-2117. |
| 14 | Simpson GG, Dijkwel PP, Quesada V, Henderson I, Dean C (2003). FY is an RNA 3′ end-processing factor that inter- acts with FCA to control the Arabidopsis floral transition.Cell 113, 777-787. |
| 15 | Sun Q, Zhou DX (2008). Rice jmjC domain-containing gene JMJ706 encodes H3K9 demethylase required for floral organ development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 13679-13684. |
| 16 | Wu XH, Liu M, Downie B, Liang C, Ji GL, Li QQ, Hunt AG (2011). Genome-wide landscape of polyadenylation in Arabidopsis provides evidence for extensive alternative polyadenylation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 12533-12538. |
| 17 | Xing DH, Li QQ (2011). Alternative polyadenylation and gene expression regulation in plants.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 2, 445-458. |
| 18 | Yao P, Potdar AA, Arif A, Ray PS, Mukhopadhyay R, Willard B, Xu YC, Yan J, Saidel GM, Fox PL (2012). Coding region polyadenylation generates a truncated tRNA synthetase that counters translation repression.Cell 149, 88-100. |
| 19 | Zhang JX, Addepalli B, Yun KY, Hunt AG, Xu RQ, Rao S, Li QQ, Falcone DL (2008). A polyadenylation factor subunit implicated in regulating oxidative signaling in Ara- bidopsis thaliana. PLoS One 3, e2410. |
| 20 | Zhang JW, Chen LL, Xing F, Kudrna DA, Yao W, Copetti D, Mu T, Li WM, Song JM, Xie WB, Lee S, Talag J, Shao L, An Y, Zhang CL, Ouyang YD, Sun S, Jiao WB, Lv F, Du BG, Luo MZ, Maldonado CE, Goicoechea JL, Xiong LZ, Wu CY, Xing YZ, Zhou DX, Yu SB, Zhao Y, Wang GW, Yu Y, Luo YJ, Zhou ZW, Hurtado BEP, Danowitz A, Wing RA, Zhang QF (2016). Extensive sequence divergence between the reference genomes of two elite indica rice varieties Zhenshan 97 and Minghui 63. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, E5163-E5171. |
| 1 | Elkon R, Ugalde AP, Agami R (2013). Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation: extent, regulation and function.Nat Rev Genet 14, 496-506. |
| 2 | Inagaki S, Miura-Kamio A, Nakamura Y, Lu FL, Cui X, Cao XF, Kimura H, Saze H, Kakutani T (2010). Autocatalytic differentiation of epigenetic modifications within the Ara- bidopsis genome.EMBO J 29, 3496-3506. |
| 3 | Itoh JI, Nonomura KI, Ikeda K, Yamaki S, Inukai Y, Yamagishi H, Kitano H, Nagato Y (2005). Rice plant development: from zygote to spikelet.Plant Cell Physiol 46, 23-47. |
| 4 | Lei MG, La HG, Lu K, Wang PC, Miki D, Ren ZZ, Duan CG, Wang XG, Tang K, Zeng L, Yang L, Zhang H, Nie WF, Liu P, Zhou JP, Liu RY, Zhong YL, Liu D, Zhu JK (2014). Arabidopsis EDM2 promotes IBM1 distal poly- adenylation and regulates genome DNA methylation pat- terns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 527-532. |
| 5 | Licatalosi DD, Darnell RB (2010). RNA processing and its regulation: global insights into biological networks.Nat Rev Genet 11, 75-87. |
| 6 | Liu Y, Cui SJ, Wu F, Yan S, Lin XL, Du XQ, Chong K, Schilling S, Theissen G, Meng Z (2013). Functional conservation of MIKC*-type MADS box genes in Ara- bidopsis and rice pollen maturation.Plant Cell 25, 1288-1303. |
| 7 | Ma LY, Guo C, Li QQ (2014). Role of alternative poly- adenylation in epigenetic silencing and antisilencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 9-10. |
| 8 | Mayr C, Bartel DP (2009). Widespread shortening of 3'UTRs by alternative cleavage and polyadenylation activates onco- genes in cancer cells.Cell 138, 673-684. |
| 9 | Rigal M, Kevei Z, Pélissier T, Mathieu O (2012). DNA methylation in an intron of the IBM1 histone demethylase gene stabilizes chromatin modification patterns.EMBO J 31, 2981-2993. |
| 10 | Rosonina E, Manley JL (2010). Alternative polyadenylation blooms.Dev Cell 18, 172-174. |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [4] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [5] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [6] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [7] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [8] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [9] | 顾磊, 张棋, 张霞, 杨冰冰, 王芳岚, 刘文, 陈发菊. 盐肤木APETALA3/DEFICIENS同源基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 533-543. |
| [10] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| [11] | 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 朱哲楠, 张芷宁, 汪理海, 陈钧, 李三峰, 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 钟芊芊, 殷文晶, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻穗部性状QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 217-230. |
| [12] | 夏婧, 饶玉春, 曹丹芸, 王逸, 柳林昕, 徐雅婷, 牟望舒, 薛大伟. 水稻中乙烯生物合成关键酶OsACS和OsACO调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(2): 291-301. |
| [13] | 朱宝, 赵江哲, 张可伟, 黄鹏. 水稻细胞分裂素氧化酶9参与调控水稻叶夹角发育[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 10-21. |
| [14] | 方妍力, 田传玉, 苏如意, 刘亚培, 王春连, 陈析丰, 郭威, 纪志远. 水稻抗细菌性条斑病基因挖掘与初定位[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 1-9. |
| [15] | 贾绮玮, 钟芊芊, 顾育嘉, 陆天麒, 李玮, 杨帅, 朱超宇, 胡程翔, 李三峰, 王跃星, 饶玉春. 水稻茎秆细胞壁相关组分含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 882-892. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||