

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 62-73.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24068 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24068
李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-05
接受日期:2024-07-23
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-07-29
通讯作者:
* E-mail: hbliu@zafu.edu.cn基金资助:
Qingyang Li, Cui Liu, Li He, Shan Peng, Jiayin Ma, Ziyi Hu, Hongbo Liu*( )
)
Received:2024-05-05
Accepted:2024-07-23
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-07-29
Contact:
* E-mail: hbliu@zafu.edu.cn摘要: CPSF家族蛋白是植物体内mRNA前体中多聚腺苷酸化信号识别、剪切和添加poly(A)的重要因子, 对开花时间调控、环境响应和种子发育等具有重要作用。目前, 甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus) CPSF家族基因的功能尚不明确。为探究甘蓝型油菜CPSF家族基因的功能和表达模式, 从甘蓝型油菜品种中双11号中克隆得到BnaA02.CPSF6, 并对其进行生物信息学、编码蛋白质亚细胞定位、表达模式和基因功能分析。结果表明, BnaA02.CPSF6基因编码区全长1 938 bp, 编码646个氨基酸残基, 无内含子结构, 其在甘蓝型油菜中有6个同源基因; BnaA02.CPSF6启动子区存在多个参与光反应的顺式作用元件和MYB结合位点; BnaA02.CPSF6在根、茎、叶、花和不同发育时期种子中均有表达, 特别是在发育15-35天的种子中显著高表达, 其编码的蛋白定位于细胞核; BnaA02.CPSF6受盐和干旱胁迫诱导上调表达; 在ABA、IAA、GA3、SA和MeJA激素处理下, BnaA02.CPSF6基因表达先受到抑制再逐渐恢复至正常水平; 在正常条件下, 在拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中过表达BnaA02.CPSF6会出现提前抽薹开花的表型, 且莲座叶数量显著减少。综上所述, BnaA02.CPSF6参与非生物胁迫响应并受植物激素调控, 可能在开花调控中起促进作用。
李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要). 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73.
Qingyang Li, Cui Liu, Li He, Shan Peng, Jiayin Ma, Ziyi Hu, Hongbo Liu. Cloning and Functional Analysis of the BnaA02.CPSF6 Gene from Brassica napus. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 62-73.
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GGAGCTTTAAGATGGATGAAGGAG | Gene cloning |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CCTAGTCATTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCG | |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GACAGCCCAGATCAACTAGTATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Subcellular localization |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CTTGCTCACCATGGATCCTTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCGTTTC | |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-FP | GGAACAGAAGTCGATCGTCCAGAG | qRT-PCR |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-RP | GAGAGCCTTCTTTCTGTTACAAGGC | |
| BnaUBC9-FP | GCATCTGCCTCGACATCTTGA | Reference gene |
| BnaUBC9-RP | CGATAGCAGCACCTTGGAGATA | |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-FP | GGGACTCTTGACCATGGATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Vector construction |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-RP | CAATTCACACGTGACGCGTTTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCG |
表1 引物信息
Table 1 Primer information
| Primer name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GGAGCTTTAAGATGGATGAAGGAG | Gene cloning |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CCTAGTCATTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCG | |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-FP | GACAGCCCAGATCAACTAGTATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Subcellular localization |
| 35S-GFP-BnaA02.CPSF6-RP | CTTGCTCACCATGGATCCTTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCGTTTC | |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-FP | GGAACAGAAGTCGATCGTCCAGAG | qRT-PCR |
| BnaA02.CPSF6-qRT-RP | GAGAGCCTTCTTTCTGTTACAAGGC | |
| BnaUBC9-FP | GCATCTGCCTCGACATCTTGA | Reference gene |
| BnaUBC9-RP | CGATAGCAGCACCTTGGAGATA | |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-FP | GGGACTCTTGACCATGGATGGATGAAGGAGATGGGAGAGATG | Vector construction |
| 35S-BnaA02.CPSF6-NOS-RP | CAATTCACACGTGACGCGTTTATTCAGTTGTAAGCCGCCTTCG |
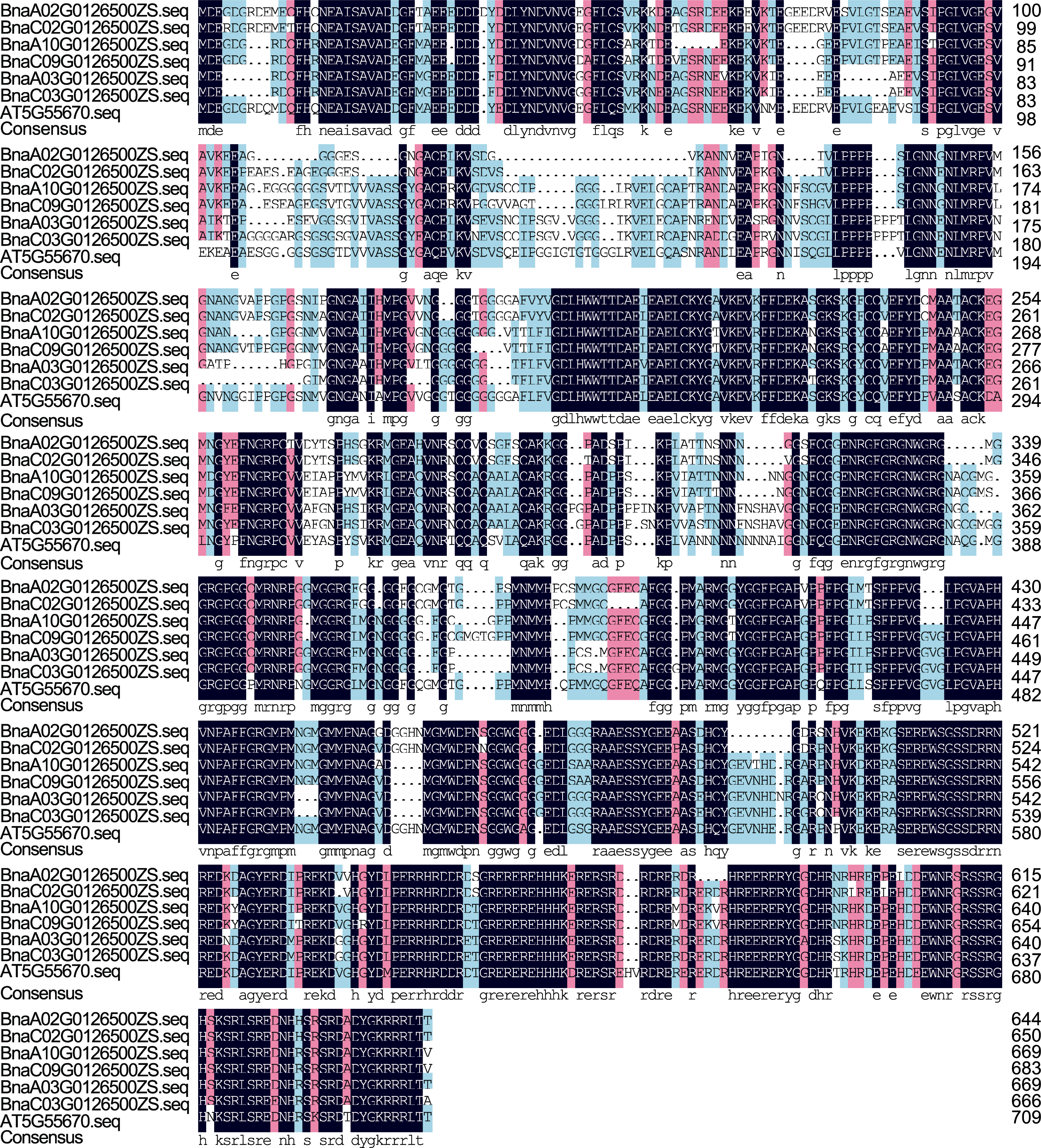
图1 BnaCPSF6s蛋白的氨基酸序列比对 图中黑紫色背景表示该位点所有序列均一致; 青蓝色和粉红色背景表示部分序列一致; 白色则表示该序列与其它样本序列不匹配。
Figure 1 Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the BnaCPSF6s protein The black-purple background in the figure indicates that all sequences at the locus are aligned; the cyan-blue and pink backgrounds indicate partial alignment; and the white color indicates that the sequence does not match other sample sequences.
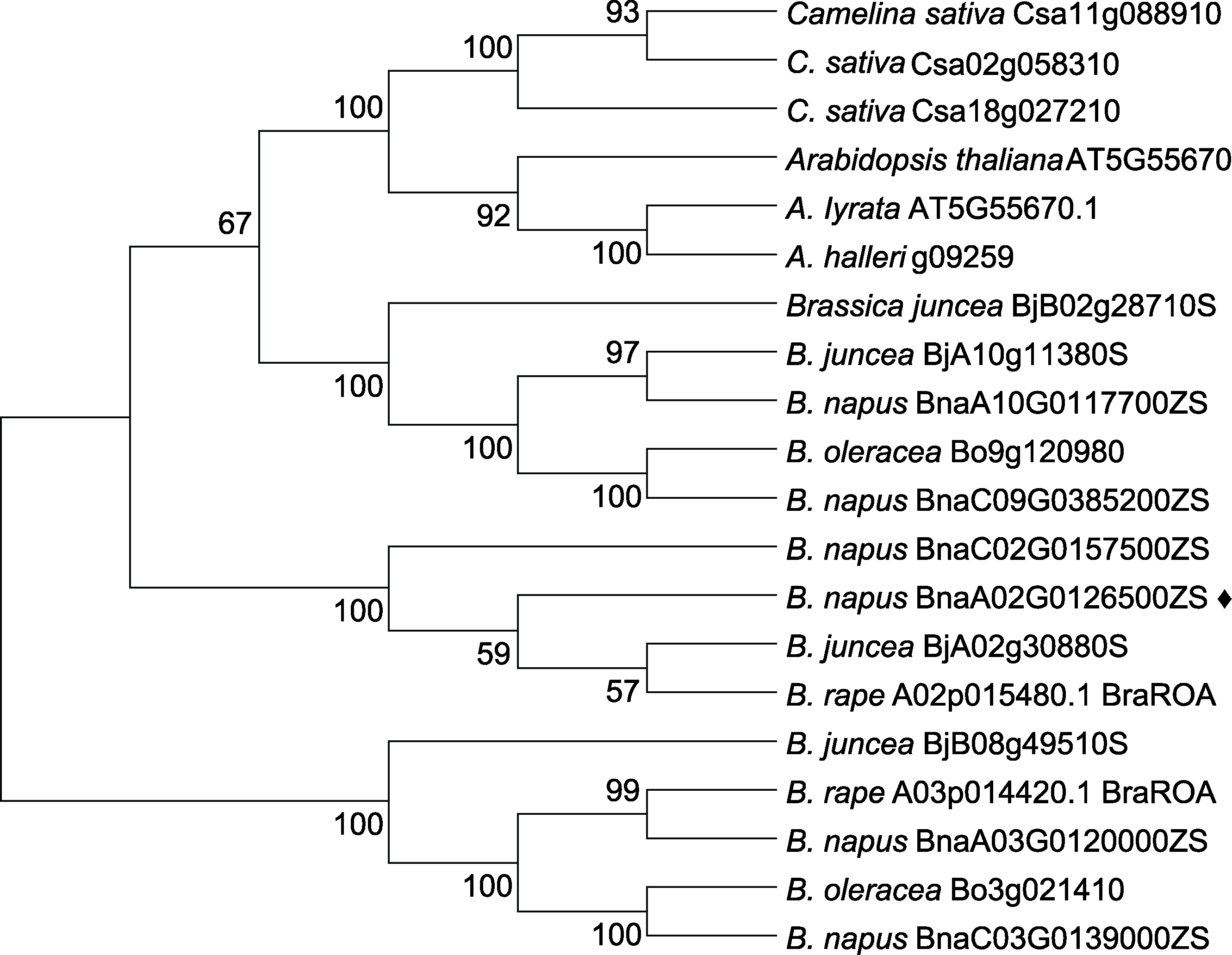

图2 BnaCPSF6s蛋白同源序列系统进化树 黑色菱形表示本研究克隆的基因。
Figure 2 Phylogenetic tree of homologous sequences of the BnaCPSF6s protein The black diamond represents the gene cloned in this study.
| Element name | Sequence | Quantity | Function | Position (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC-motif | AGTAATCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -160 (-) |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 6 | Light responsive element | -368 (-); -705 (-); -889 (-); -1225 (-); -1803 (-) |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 9 | Light responsive element | -407 (+/-); -566 (+/-); -928 (+/-); -1087 (+/-); -1292 (+/-); -1443 (+/-); -1689 (+/-); -1842 (+/-); -1992 (+/-) |
| I-box | AAGATAAGGCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -473 (-) |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 3 | Light responsive element | -1274 (+); -1372 (+); -1770 (+) |
| G-box | CACGTT | 3 | Light responsive element | -687 (-); -1207 (-); -1603 (-) |
| MYB-like sequence | TAACCA | 4 | MYB-like binding site | -367 (+); -888 (+); -1404 (+); -1802 (+) |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | 1 | MYBHv1 binding site | -1591 (-) |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 3 | Abscisic acid responsiveness | -687 (+) |
表2 BnaA02.CPSF6启动子区域顺式作用元件分析
Table 2 Analysis of cis-regulatory elements in the promoter region of BnaA02.CPSF6
| Element name | Sequence | Quantity | Function | Position (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATC-motif | AGTAATCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -160 (-) |
| GT1-motif | GGTTAA | 6 | Light responsive element | -368 (-); -705 (-); -889 (-); -1225 (-); -1803 (-) |
| Box 4 | ATTAAT | 9 | Light responsive element | -407 (+/-); -566 (+/-); -928 (+/-); -1087 (+/-); -1292 (+/-); -1443 (+/-); -1689 (+/-); -1842 (+/-); -1992 (+/-) |
| I-box | AAGATAAGGCT | 1 | Light responsive element | -473 (-) |
| TCT-motif | TCTTAC | 3 | Light responsive element | -1274 (+); -1372 (+); -1770 (+) |
| G-box | CACGTT | 3 | Light responsive element | -687 (-); -1207 (-); -1603 (-) |
| MYB-like sequence | TAACCA | 4 | MYB-like binding site | -367 (+); -888 (+); -1404 (+); -1802 (+) |
| CCAAT-box | CAACGG | 1 | MYBHv1 binding site | -1591 (-) |
| ABRE | ACGTG | 3 | Abscisic acid responsiveness | -687 (+) |
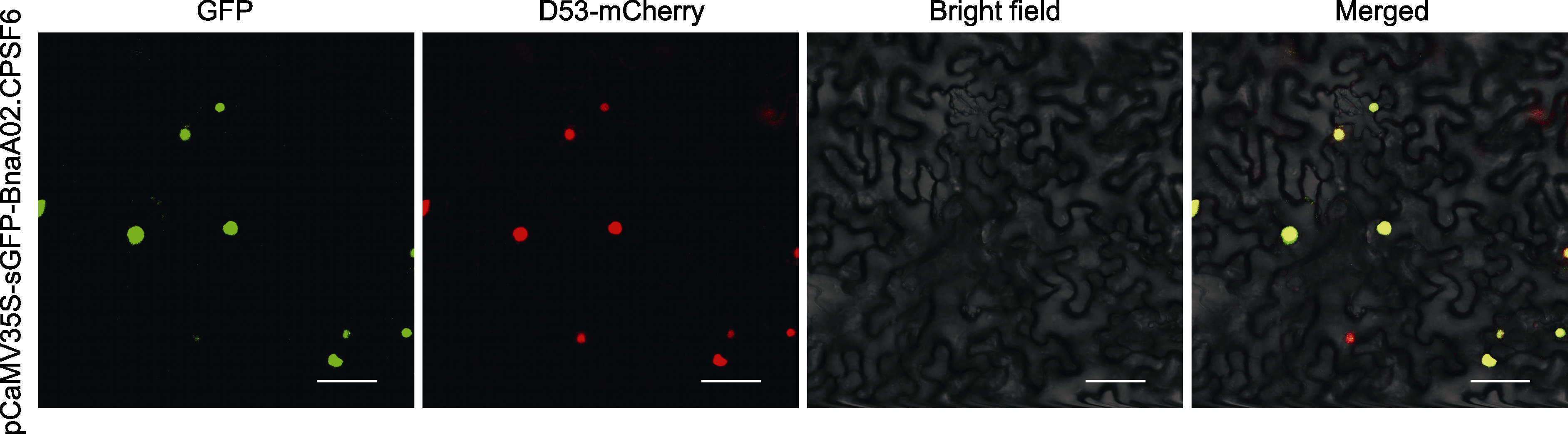
图3 BnaA02.CPSF6的亚细胞定位 GFP为BnaA02.CPSF6-GFP绿色荧光融合蛋白; D53-mCherry为核定位标记蛋白; Bright field为明场; Merged为叠加场。Bars= 50 μm
Figure 3 Subcellular localization of BnaA02.CPSF6 GFP is BnaA02.CPSF6 fusion green fluorescence protein; D53-mCherry is a nuclear marker protein; Bright field is brightfield microscope; Merged is fusion field. Bars=50 μm
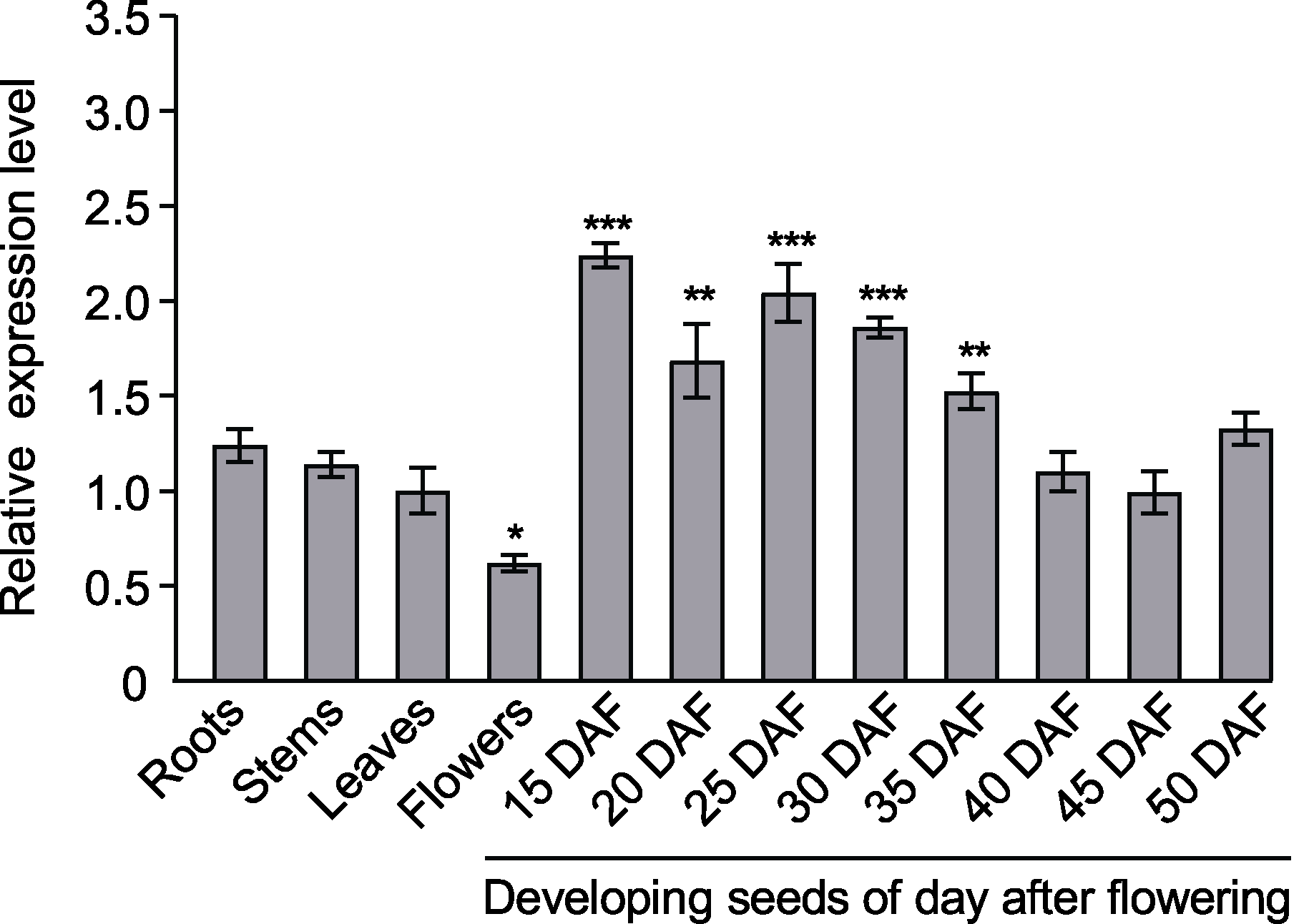
图4 BnaA02.CPSF6在甘蓝型油菜不同组织中的表达模式分析 DAF: 开花后天数; 内参基因: 甘蓝型油菜SUMO连接酶基因(BnaUBC9)。设3次生物学重复(n=3)。* P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001
Figure 4 Analysis of the expression pattern of BnaA02. CPSF6 in different tissues of Brassica napus DAF: Days after flowering; Reference gene: B. napus SUMO- conjugating enzyme gene (BnaUBC9). Three biological replicates were used (n=3). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001
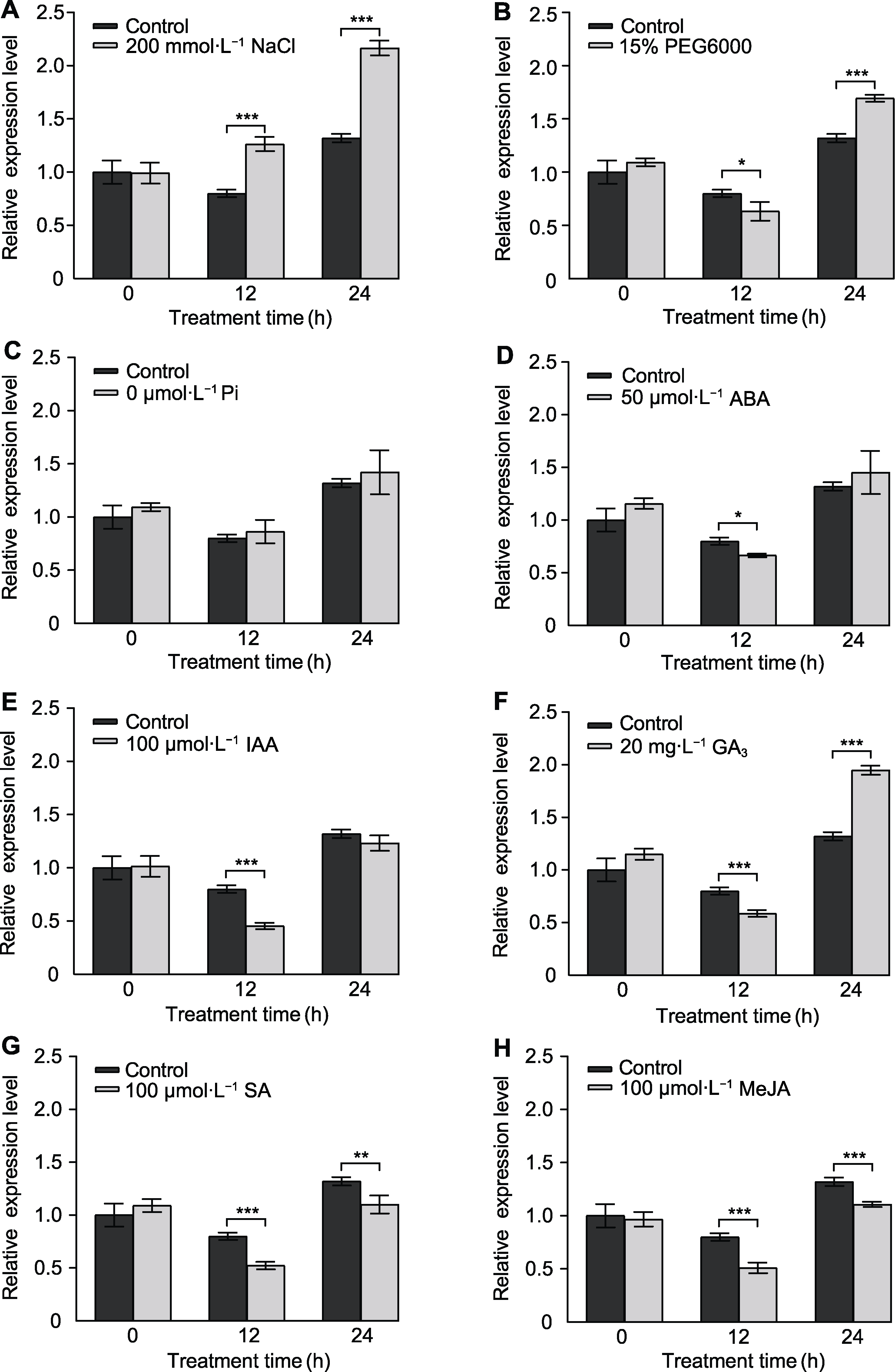
图5 BnaA02.CPSF6在非生物胁迫和外源激素处理下的表达模式分析 (A) 盐处理; (B) 干旱处理; (C) 低磷处理; (D) 脱落酸(ABA)处理; (E) 生长素(IAA)处理; (F) 赤霉素(GA3)处理; (G) 水杨酸(SA)处理; (H) 茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)处理。设3次生物学重复(n=3)。* P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001
Figure 5 Expression pattern analysis of BnaA02.CPSF6 under abiotic stress and exogenous hormone treatments (A) Salt treatment; (B) Drought treatment; (C) Low phosphorus treatment; (D) Abscisic acid (ABA) treatment; (E) Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) treatment; (F) Gibberellic acid (GA3) treatment; (G) Salicylic acid (SA) treatment; (H) Methyl jasmonate (MeJA) treatment. Three biological replicates were used (n=3). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001
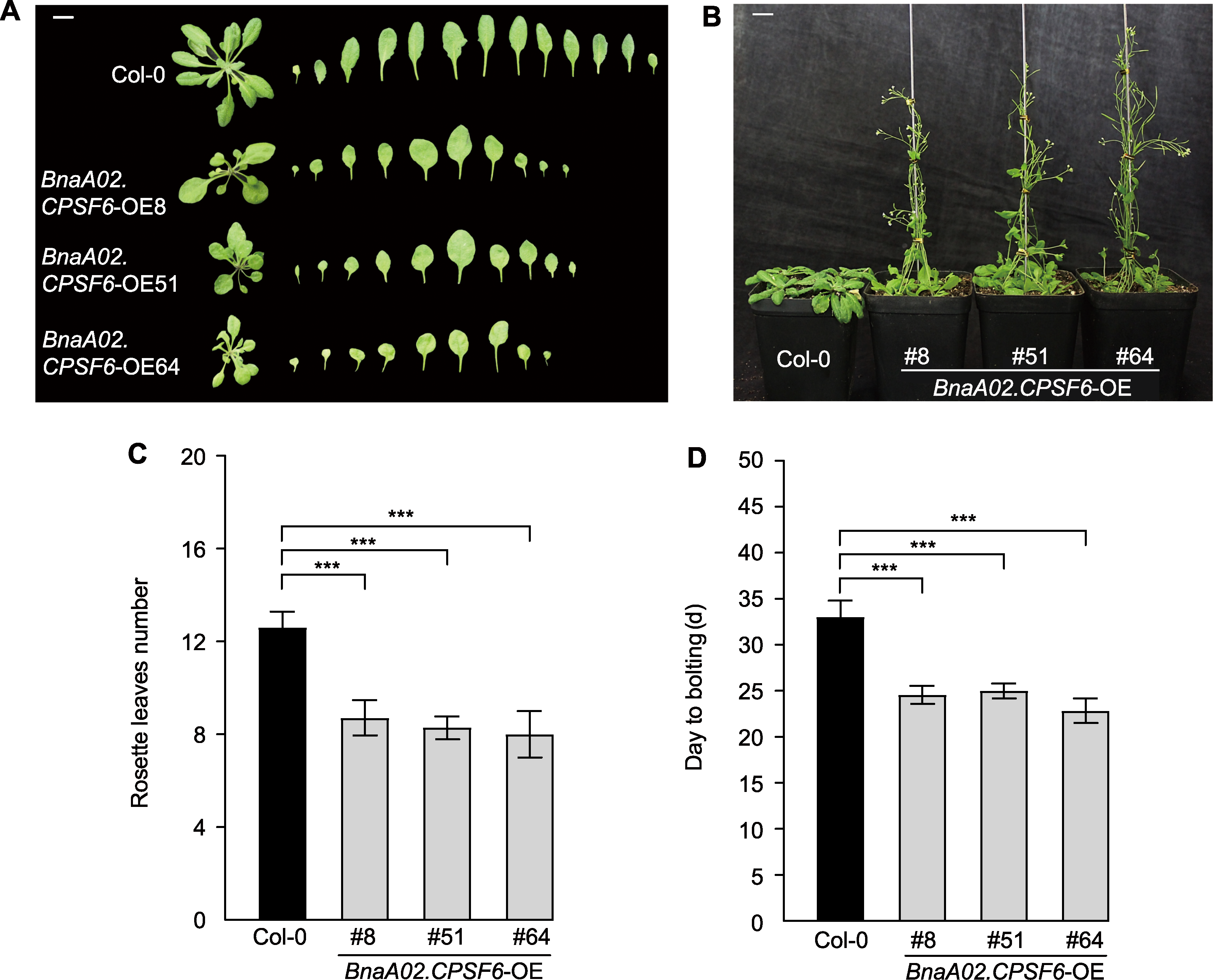
图6 BnaA02.CPSF6过表达导致拟南芥早花 (A) 开花时莲座叶表型(bar=1 cm); (B) 正常条件下30天表型(bar=1 cm); (C) 开花时莲座叶数量; (D) 抽薹时间(从播种到出现花序轴的时间)。设3次生物学重复(n=3)。各株系莲座叶分别统计5个样本重复。*** P<0.001
Figure 6 Overexpression of BnaA02.CPSF6 leads to the early-flowering of Arabidopsis thaliana (A) Rosette leaf phenotype at flowering (bar=1 cm); (B) Phenotype at 30 days under normal conditions (bar=1 cm); (C) Number of rosette leaves at flowering; (D) Bolting time (time from sowing to the appearance of the flower stalk). Three biological replicates were used (n=3). The number of rosette leaves from each genotype were counted with five replicate samples. *** P<0.001
| [1] | Bao SJ, Hua CM, Shen LS, Yu H (2020). New insights into gibberellin signaling in regulating flowering in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 62,118-131. |
| [2] |
Boreikaitė V, Passmore LA (2023). 3′-end processing of eukaryotic mRNA: machinery, regulation, and impact on gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem 92, 199-225.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Brown KM, Gilmartin GM (2003). A mechanism for the regulation of pre-mRNA 3′ processing by human cleavage factor Im. Mol Cell 12, 1467-1476.
PMID |
| [4] | Cai FF, Shao CS, Sun YQ (2022). The role of alternative splicing in floral transition. Chin Bull Bot 57, 69-79. (in Chinese) |
|
蔡芳芳, 邵长生, 孙玉强 (2022). 可变剪切在植物成花转换中的作用. 植物学报 57, 69-79.
DOI |
|
| [5] | Cui GX, Hou J, Tong L, Xu ZR (2010). Light responsive elements and binding proteins of plant genes. Plant Physiol Commun 46, 991-1000. (in Chinese) |
| 崔国新, 侯杰, 佟玲, 许志茹 (2010). 植物基因光反应元件及其结合蛋白. 植物生理学通讯 46, 991-1000. | |
| [6] | Dai YQ, Luo LJ, Zhao Z (2023). Genetic robustness control of auxin output in priming organ initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2221606120. |
| [7] |
Eckardt NA (2002). Alternative splicing and the control of flowering time. Plant Cell 14, 743-747.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Edwalds-Gilbert G, Milcarek C (1995). The binding of a subunit of the general polyadenylation factor cleavage- polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) to polyadenylation sites changes during B cell development. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (33), 229-233. |
| [9] |
Feng W, Jacob Y, Veley KM, Ding L, Yu XH, Choe G, Michaels SD (2011). Hypomorphic alleles reveal FCA- independent roles for FY in the regulation of FLOWERING LOCUS C. Plant Physiol 155, 1425-1434.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Hao SQ, Zhang LD, Zhao DH, Zhou JW, Ye CT, Qu HD, Li QQ (2023). Inhibitor AN3661 reveals biological functions of Arabidopsis CLEAVAGE and POLYADENYLATION SPECIFICITY FACTOR 73. Plant Physiol 193, 537-554. |
| [11] | Hardy JG, Norbury CJ (2016). Cleavage factor Im (CFIm) as a regulator of alternative polyadenylation. Biochem Soc Trans 44, 1051-1057. |
| [12] |
Henderson IR, Liu FQ, Drea S, Simpson GG, Dean C (2005). An allelic series reveals essential roles for FY in plant development in addition to flowering-time control. Development 132, 3597-3607.
PMID |
| [13] | Herr AJ, Molnàr A, Jones A, Baulcombe DC (2006). Defective RNA processing enhances RNA silencing and influences flowering of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 14994-15001. |
| [14] |
Hornyik C, Terzi LC, Simpson GG (2010). The spen family protein FPA controls alternative cleavage and polyadenylation of RNA. Dev Cell 18(2), 203-213.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | Hou YF, Sun J, Wu BX, Gao YY, Nie HB, Nie ZT, Quan SX, Wang Y, Cao XF, Li SS (2021). CPSF30-L-mediated recognition of mRNA m6A modification controls alternative polyadenylation of nitrate signaling-related gene transcripts in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14, 688-699. |
| [16] |
Huang Y, Zhao PS, Xie LL, Xu JS, Cheng Y, Zhang XK, Xu BB (2024). Analysis on yield composition and breeding strategy of winter rape varieties in the Yangtze River Basin. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 46, 13-18. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
黄郢, 赵培森, 谢伶俐, 徐劲松, 程勇, 张学昆, 许本波 (2024). 长江流域冬油菜品种产量构成及育种策略分析. 中国油料作物学报 46, 13-18.
DOI |
|
| [17] | Kumar A, Clerici M, Muckenfuss LM, Passmore LA, Jinek M (2019). Mechanistic insights into mRNA 3′-end processing. Curr Opin Struct Biol 59, 143-150. |
| [18] | Li GC, Niu QC, Leng BF, Ding YF, Tong T, Fan LX (2024). The decade of rapeseed industry in the new era: development and its path choice. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 46, 228-235. (in Chinese) |
|
李谷成, 牛秋纯, 冷博峰, 丁逸飞, 童婷, 范丽霞 (2024). 新时代十年: 我国油菜产业发展与路径选择. 中国油料作物学报 46, 228-235.
DOI |
|
| [19] | Li QX, Zhang L, Wang Y, Huang XX (2019). The research progress of gibberellin on the regulation of flowering and floral organ development in plant. Chin J Cell Biol 41, 746-758. (in Chinese) |
| 李巧峡, 张丽, 王玉, 黄小霞 (2019). 赤霉素调控植物开花及花器官发育的研究进展. 中国细胞生物学学报 41, 746-758. | |
| [20] | Lin JC, Xu RQ, Wu XH, Shen YJ, Li QQ (2017). Role of cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 100: anchoring poly (A) sites and modulating transcription termination. Plant J 91, 829-839. |
| [21] |
Liu YT, Wu GX, Zhao YP, Wang HHL, Dai ZY, Xue WC, Yang J, Wei HB, Shen RX, Wang HY (2021). DWARF53 interacts with transcription factors UB2/UB3/TSH4 to regulate maize tillering and tassel branching. Plant Physiol 187, 947-962.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Ma LY, Guo C, Li QQ (2014). Role of alternative polyadenylation in epigenetic silencing and antisilencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 9-10.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Macknight R, Duroux M, Laurie R, Dijkwel P, Simpson G, Dean C (2002). Functional significance of the alternative transcript processing of the Arabidopsis floral promoter FCA. Plant Cell 14, 877-888.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Mandel CR, Bai Y, Tong L (2008). Protein factors in pre- mRNA 3′-end processing. Cell Mol Life Sci 65, 1099-1122.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Mouradov A, Cremer F, Coupland G (2002). Control of flowering time: interacting pathways as a basis for diversity. Plant Cell 14, S111-S130. |
| [26] |
Proudfoot N (2004). New perspectives on connecting messenger RNA 3′ end formation to transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16, 272-278.
PMID |
| [27] |
Quesada V, Macknight R, Dean C, Simpson GG (2003). Autoregulation of FCA pre-mRNA processing controls Arabidopsis flowering time. EMBO J 22, 3142-3152.
PMID |
| [28] |
Schul W, Groenhout B, Koberna K, Takagaki Y, Jenny A, Manders EM, Raska I, van Driel R, de Jong L (1996). The RNA 3′ cleavage factors CstF 64 kDa and CPSF 100 kDa are concentrated in nuclear domains closely associated with coiled bodies and newly synthesized RNA. EMBO J 15, 2883-2892.
PMID |
| [29] | Song PZ, Yang JB, Wang CL, Lu Q, Shi LQ, Tayier S, Jia GF (2021). Arabidopsis N6-methyladenosine reader CPSF30-L recognizes FUE signals to control polyadenylation site choice in liquid-like nuclear bodies. Mol Plant 14, 571-587. |
| [30] | Thomas PE, Wu XH, Liu M, Gaffney B, Ji GL, Li QQ, Hunt AG (2012). Genome-wide control of polyadenylation site choice by CPSF30 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 4376-4388. |
| [31] | Tzafrir I, Pena-Muralla R, Dickerman A, Berg M, Rogers R, Hutchens S, Sweeney TC, McElver J, Aux G, Patton D, Meinke D (2004). Identification of genes required for embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 135, 1206-1220. |
| [32] | Venkataraman K, Brown KM, Gilmartin GM (2005). Analysis of a noncanonical poly (A) site reveals a tripartite mechanism for vertebrate poly (A) site recognition. Genes Dev 19, 1315-1327. |
| [33] | Wang XP, Niu YL, Zheng Y (2021). Multiple functions of MYB transcription factors in abiotic stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 22, 6125. |
| [34] |
Yang Q, Coseno M, Gilmartin GM, Doublié S (2011). Crystal structure of a human cleavage factor CFIm25/CFIm68/RNA complex provides an insight into poly(A) site recognition and RNA looping. Structure 19, 368-377.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Yu ZB, Lin JC, Li QQ (2019). Transcriptome analyses of FY mutants reveal its role in mRNA alternative polyadenylation. Plant Cell 31, 2332-2352. |
| [36] | Zhang CS, Wei T, Zhou YP, Fan T, Lü TX, Tian CE (2021). Progress in flowering regulation mechanisms of FLC. Chin Bull Bot 56,651-663. (in Chinese) |
|
张长生, 魏滔, 周玉萍, 范甜, 吕天晓, 田长恩 (2021). FLC调控植物成花的分子机制研究新进展. 植物学报 56, 651-663.
DOI |
|
| [37] | Zhang XJ, Nomoto M, Garcia-León M, Takahashi N, Kato M, Yura K, Umeda M, Rubio V, Tada Y, Furumoto T, Aoyama T, Tsuge T (2022). CFI 25 subunit of cleavage factor I is important for maintaining the diversity of 3′ UTR lengths in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) heynh. Plant Cell Physiol 63, 369-383. |
| [1] | 杨柳卿, 王劲, 燕敬利, 陈芹芹, 程浩坤, 李春, 赵培玉, 杨博, 江元清. 甘蓝型油菜转录因子BnaABF2的表征分析及互作蛋白鉴定[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 49-61. |
| [2] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [3] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [4] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [5] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [6] | 路笃贤, 张严妍, 刘艳, 李岩竣, 左新秀, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 非编码RNA在植物生长发育及逆境响应中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 709-725. |
| [7] | 顾磊, 张棋, 张霞, 杨冰冰, 王芳岚, 刘文, 陈发菊. 盐肤木APETALA3/DEFICIENS同源基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 533-543. |
| [8] | 曾鑫海, 陈锐, 师宇, 盖超越, 范凯, 李兆伟. 植物SPL转录因子的生物功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [9] | 张盈川, 吴晓明玉, 陶保龙, 陈丽, 鲁海琴, 赵伦, 文静, 易斌, 涂金星, 傅廷栋, 沈金雄. Bna-miR43介导甘蓝型油菜响应干旱胁迫[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 701-711. |
| [10] | 黄慧梅, 高永康, 台玉莹, 刘超, 曲德杰, 汤锐恒, 王幼宁. 硝酸盐转运蛋白NRT2在植物中的功能及分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 783-798. |
| [11] | 许亚楠, 闫家榕, 孙鑫, 王晓梅, 刘玉凤, 孙周平, 齐明芳, 李天来, 王峰. 红光和远红光在调控植物生长发育及应答非生物胁迫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 622-637. |
| [12] | 张嘉, 李启东, 李翠, 王庆海, 侯新村, 赵春桥, 李树和, 郭强. 植物MATE转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 461-474. |
| [13] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [14] | 王琪, 吴允哲, 刘学英, 孙丽莉, 廖红, 傅向东. 类受体激酶调控水稻生长发育和环境适应研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 199-213. |
| [15] | 刘德帅, 姚磊, 徐伟荣, 冯美, 姚文孔. 褪黑素参与植物抗逆功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 111-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||