

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (3): 461-474.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22092 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22092
张嘉1,2†, 李启东2,3†, 李翠2, 王庆海2, 侯新村2, 赵春桥2, 李树和1( ), 郭强2(
), 郭强2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-29
接受日期:2022-08-25
出版日期:2023-05-01
发布日期:2023-05-17
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 710580225@qq.com; guoqiang@grass-env.com
作者简介:†共同第一作者
基金资助:
Jia Zhang1,2†, Qidong Li2,3†, Cui Li2, Qinghai Wang2, Xincun Hou2, Chunqiao Zhao2, Shuhe Li1( ), Qiang Guo2(
), Qiang Guo2( )
)
Received:2022-04-29
Accepted:2022-08-25
Online:2023-05-01
Published:2023-05-17
Contact:
*E-mail: 710580225@qq.com; guoqiang@grass-env.com
About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: 多药和有毒化合物外排转运蛋白(MATE)又称解毒外排转运蛋白(DTXs), 广泛存在于真核与原核生物中。MATE是一种膜蛋白, 通常具有12个呈V型排列的跨膜区。在植物中MATE/DTXs转运蛋白主要参与铁稳态调节、无机阴离子和次生代谢物转运、外源物质和重金属解毒、植物生长发育调控以及病害与逆境胁迫响应。该文对植物MATE蛋白家族的发现、系统发育、结构及功能等研究进展进行综述, 以期为MATE/DTXs应用于作物或牧草抗逆遗传改良提供参考。
张嘉, 李启东, 李翠, 王庆海, 侯新村, 赵春桥, 李树和, 郭强. 植物MATE转运蛋白研究进展. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 461-474.
Jia Zhang, Qidong Li, Cui Li, Qinghai Wang, Xincun Hou, Chunqiao Zhao, Shuhe Li, Qiang Guo. Research Progress on MATE Transporters in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(3): 461-474.
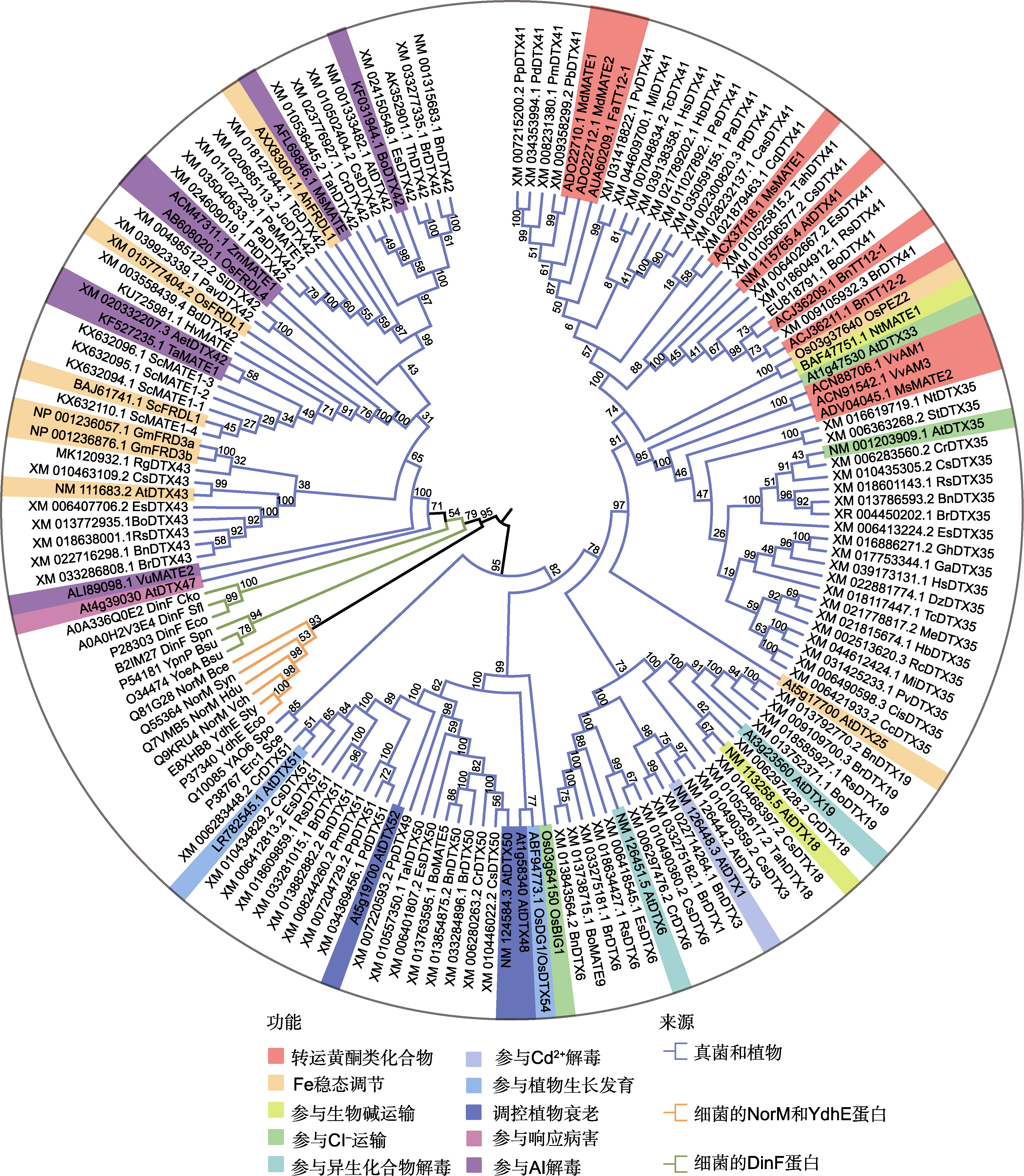
图1 MATE/DTXs蛋白系统发育树 MATE/DTXs来源: 拟南芥(At)、亚麻芥(Cs)、盐芥(Es)、小盐芥(Th)、白菜型油菜(Br)、甘蓝型油菜(Bn)、萝卜(Rs)、地黄(Rg)、醉蝶花(Tah)、黑麦(Sc)、梅(Pm)、麻风树(Jc)、胡杨(Pe)、毛果杨(Pt)、巴旦杏(Pd)、桃(Pp)、可可树(Tc)、银白杨(Pa)、二穗短柄草(Bd)、阿月浑子(Pv)、藜麦(Cq)、木槿(Hs)、小麦(Ta)、大麦(Hv)、节节麦(Aet)、柳枝稷(Pav)、谷子(Si)、橡胶树(Hb)、芒果(Mi)、白梨(Pb)、茶(Cas)、木薯(Me)、蓖麻(Rc)、陆地棉(Gh)、木本鸡脚棉(Ga)、榴莲(Dz)、甜橙(Cis)、克莱门柚(Cc)、烟草(Nt)、马铃薯(St)、水稻(Os)、大豆(Gm)、花生(Ah)、玉米(Zm)、葡萄(Vv)、蒺藜苜蓿(Mt)、苹果(Md)、苜蓿(Ms)、赤小豆(Vu)、草莓(Fa)、集胞蓝细菌(Syn)、杜克雷嗜血杆菌(Hdu)、蜡状芽孢杆菌(Bce)、霍乱弧菌(Vch)、大肠杆菌(Eco)、鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Sty)、酿酒酵母(Sce)、粟酒裂殖酵母(Spo)、弗氏志贺氏菌(Sfl)、克氏柠檬酸杆菌(Cko)、肺炎链球菌(Spn)和枯草芽孢杆菌(Bsu)。通过Clustal W方法进行多重序列比对。利用MEGA 6.0软件采用邻接法构建MATE/DTXs的系统发育树。
Figure 1 Phylogenetic tree of MATE/DTXs proteins The sources of MATE/DTXs are as follows: Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Camelina sativa (Cs), Eutrema salsugineum (Es), Thellungiella halophila (Th), Brassica rapa (Br), B. napus (Bn), Raphanus sativus (Rs), Rehmannia glutinosa (Rg), Tarenaya hassleriana (Tah), Secale cereale (Sc), Prunus mume (Pm), Jatropha curcas (Jc), Populus euphratica (Pe), P. trichocarpa (Pt), Prunus dulcis (Pd), P. persica (Pp), Theobroma cacao (Tc), P. alba (Pa), Brachypodium distachyon (Bd), Pistacia vera (Pv), Chenopodium quinoa (Cq), Hibiscus syriacus (Hs), Triticum aestivum (Ta), Hordeum vulgare (Hv), Aegilops tauschii (Aet), Panicum virgatum (Pav), Setaria italica (Si), Hevea brasiliensis (Hb), Mangifera indica (Mi), Pyrus bretschneideri (Pb), Camellia sinensis (Cas), Manihot esculenta (Me), Ricinus communis (Rc), Gossypium hirsutum (Gh), G. arboreum (Ga), Durio zibethinus (Dz), Citrus sinensis (Cis), C. clementina (Cc), Nicotiana tabacum (Nt), Solanum tuberosum (St), Oryza sativa (Os), Glycine max (Gm), Arachis hypogaea (Ah), Zea mays (Zm), Vitis vinifera (Vv), Medicago truncatula (Mt), Malus domestica (Md), M. sativa (Ms), Vigna umbellata (Vu), Fragaria x ananassa (Fa), Synechocystis sp. (Syn), Haemophilus ducreyi (Hdu), Bacillus cereus (Bce), Vibrio cholerae (Vch), Escherichia coli (Eco), Salmonella typhimurium (Sty), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sce), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Spo), Shigella flexneri (Sfl), Citrobacter koseri (Cko), Streptococcus pneumoniae (Spn), and Bacillus subtilis (Bsu). Multiple alignment was performed by the Clustal W. A phylogenetic tree of MATE/DTXs was constructed by the neighbor-joining algorithm using MEGA 6.0 software.
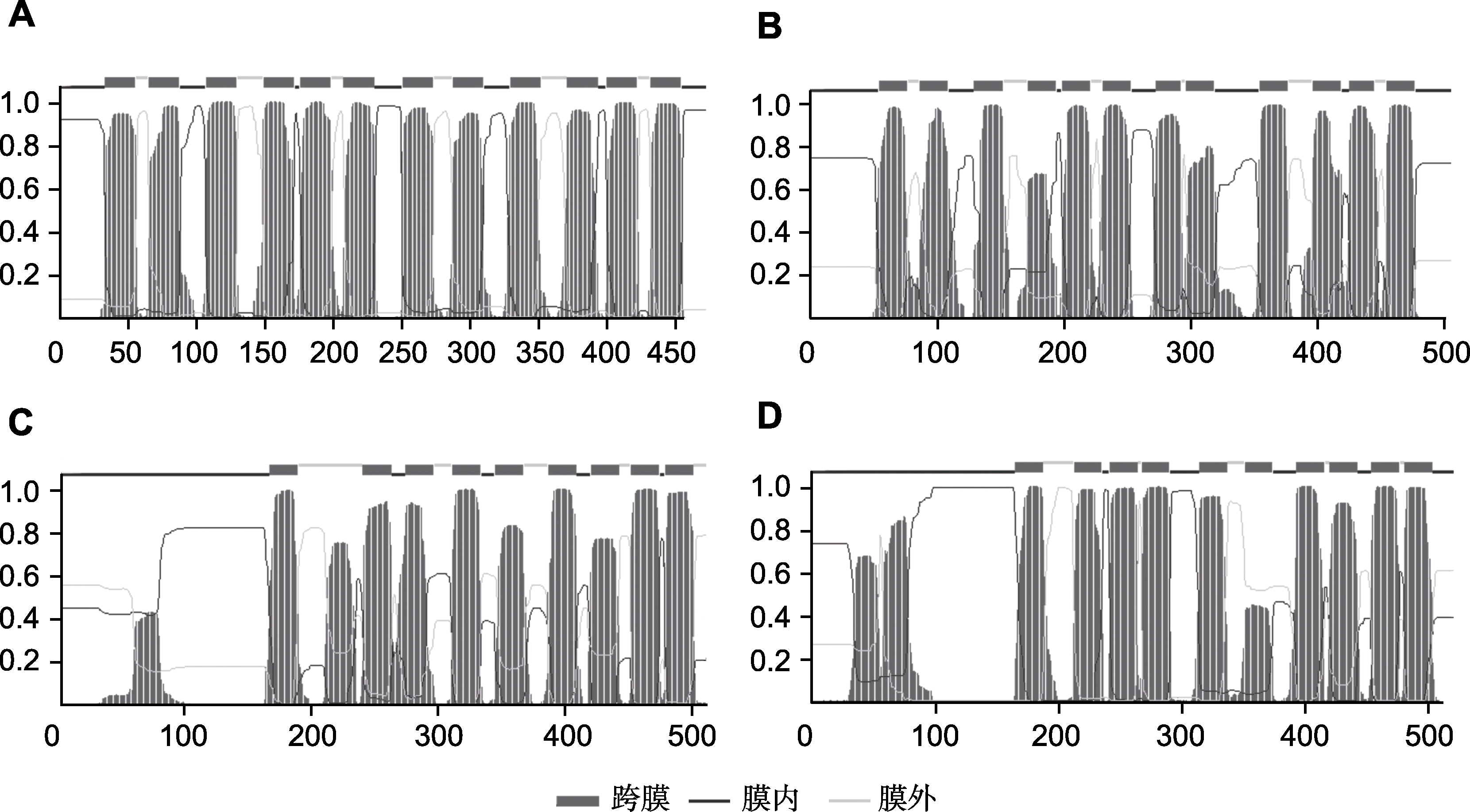
图2 MATE/DTXs蛋白跨膜结构域分析 (A) AtDTX1跨膜结构域; (B) AtDTX41跨膜结构域; (C) AtDTX42跨膜结构域; (D) AtDTX43跨膜结构域。从TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org/)数据库获得拟南芥氨基酸序列; 采用TMHMM (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM)在线工具预测跨膜结构域。
Figure 2 Analysis of MATE/DTXs transmembrane domains
| 基因名称 | 物种 | 功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtDTX43 | 拟南芥 | 调节铁稳态 | Durrett et al., | |
| OsFRDL1 | 水稻 | 调节铁稳态 | Yokosho et al., | |
| ScFRDL1 | 黑麦 | 调节铁稳态 | Yokosho et al., | |
| AtDTX25 | 拟南芥 | 调节铁稳态 | Hoang et al., | |
| AhFRDL1 | 花生 | 调节铁稳态 | Qiu et al., | |
| MsMATE1 | 苜蓿 | 调节铁稳态 | 高铭等, | |
| OsPEZ2 | 水稻 | 调节铁稳态 | Bashir et al., | |
| HvAACT1 | 大麦 | 铝解毒 | Furukawa et al., | |
| SbMATE | 高粱 | 铝解毒 | Magalhaes et al., | |
| AtDTX42 | 拟南芥 | 铝解毒 | Liu et al., | |
| PvMATEa/b | 豇豆 | 铝解毒 | Rangel et al., | |
| VuMATE2 | 赤小豆 | 铝解毒 | Liu, | |
| ZmMATE1 | 玉米 | 铝解毒 | Maron et al., | |
| ScFRDL2 | 黑麦 | 铝解毒 | Yokosho et al., | |
| OsFRDL4 | 水稻 | 铝解毒 | Yokosho et al., | |
| BoMATE | 甘蓝 | 铝解毒 | 吴新新, | |
| MsMATE | 苜蓿 | 铝解毒 | 张宝云, | |
| GmMATE2 | 丹波黑大豆 | 铝解毒 | 胡俊等, | |
| CsMATE9 | 茶树 | 铝解毒 | 陈益, | |
| GmMATE13 | 大豆 | 铝解毒 | 龚莉, | |
| AtDTX1 | 拟南芥 | 响应镉胁迫 | Li et al., | |
| AtDTX19 | 拟南芥 | 外排四甲基铵 | Diener et al., | |
| AtDTX6 | 拟南芥 | 外排百草枯 | Xia et al., | |
| AtDTX41 | 拟南芥 | 转运花青素前体 | Marinova, | |
| MtMATE1 | 蒺藜苜蓿 | 转运E3′G | Zhao and Dixon, | |
| MtMATE2 | 蒺藜苜蓿 | 转运类黄酮 | Zhao et al., | |
| FaTT12-1 | 草莓 | 转运原花青素 | Chen et al., | |
| NtMATE3 | 烟草 | 转运尼古丁 | Shitan et al., | |
| NtMATE1 | 烟草 | 转运生物碱 | Shoji et al., | |
| AtDTX18 | 拟南芥 | 参与抗病 | Dobritzsch et al., | |
| OsMATE1 | 水稻 | 参与抗病 | Tiwari et al., | |
| OsMATE2 | 水稻 | 参与抗病 | Tiwari et al., | |
| AtDTX51 | 拟南芥 | 参与生长素合成 | Li et al., | |
| AtDTX50 | 拟南芥 | 转运脱落酸 | Zhang et al., | |
| OsDTX54 | 水稻 | 转运脱落酸 | Qin et al., | |
| AtDTX47 | 拟南芥 | 转运水杨酸 | Nawrath et al., | |
| AtDTX33 | 拟南芥 | 转运Cl- | Zhang et al., | |
| AtDTX35 | 拟南芥 | 转运Cl- | Zhang et al., | |
| OsBIG1 | 水稻 | 转运Cl- | Ren et al., | |
表1 高等植物中的MATE/DTXs基因
Table 1 MATE/DTXs genes in higher plants
| 基因名称 | 物种 | 功能 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AtDTX43 | 拟南芥 | 调节铁稳态 | Durrett et al., | |
| OsFRDL1 | 水稻 | 调节铁稳态 | Yokosho et al., | |
| ScFRDL1 | 黑麦 | 调节铁稳态 | Yokosho et al., | |
| AtDTX25 | 拟南芥 | 调节铁稳态 | Hoang et al., | |
| AhFRDL1 | 花生 | 调节铁稳态 | Qiu et al., | |
| MsMATE1 | 苜蓿 | 调节铁稳态 | 高铭等, | |
| OsPEZ2 | 水稻 | 调节铁稳态 | Bashir et al., | |
| HvAACT1 | 大麦 | 铝解毒 | Furukawa et al., | |
| SbMATE | 高粱 | 铝解毒 | Magalhaes et al., | |
| AtDTX42 | 拟南芥 | 铝解毒 | Liu et al., | |
| PvMATEa/b | 豇豆 | 铝解毒 | Rangel et al., | |
| VuMATE2 | 赤小豆 | 铝解毒 | Liu, | |
| ZmMATE1 | 玉米 | 铝解毒 | Maron et al., | |
| ScFRDL2 | 黑麦 | 铝解毒 | Yokosho et al., | |
| OsFRDL4 | 水稻 | 铝解毒 | Yokosho et al., | |
| BoMATE | 甘蓝 | 铝解毒 | 吴新新, | |
| MsMATE | 苜蓿 | 铝解毒 | 张宝云, | |
| GmMATE2 | 丹波黑大豆 | 铝解毒 | 胡俊等, | |
| CsMATE9 | 茶树 | 铝解毒 | 陈益, | |
| GmMATE13 | 大豆 | 铝解毒 | 龚莉, | |
| AtDTX1 | 拟南芥 | 响应镉胁迫 | Li et al., | |
| AtDTX19 | 拟南芥 | 外排四甲基铵 | Diener et al., | |
| AtDTX6 | 拟南芥 | 外排百草枯 | Xia et al., | |
| AtDTX41 | 拟南芥 | 转运花青素前体 | Marinova, | |
| MtMATE1 | 蒺藜苜蓿 | 转运E3′G | Zhao and Dixon, | |
| MtMATE2 | 蒺藜苜蓿 | 转运类黄酮 | Zhao et al., | |
| FaTT12-1 | 草莓 | 转运原花青素 | Chen et al., | |
| NtMATE3 | 烟草 | 转运尼古丁 | Shitan et al., | |
| NtMATE1 | 烟草 | 转运生物碱 | Shoji et al., | |
| AtDTX18 | 拟南芥 | 参与抗病 | Dobritzsch et al., | |
| OsMATE1 | 水稻 | 参与抗病 | Tiwari et al., | |
| OsMATE2 | 水稻 | 参与抗病 | Tiwari et al., | |
| AtDTX51 | 拟南芥 | 参与生长素合成 | Li et al., | |
| AtDTX50 | 拟南芥 | 转运脱落酸 | Zhang et al., | |
| OsDTX54 | 水稻 | 转运脱落酸 | Qin et al., | |
| AtDTX47 | 拟南芥 | 转运水杨酸 | Nawrath et al., | |
| AtDTX33 | 拟南芥 | 转运Cl- | Zhang et al., | |
| AtDTX35 | 拟南芥 | 转运Cl- | Zhang et al., | |
| OsBIG1 | 水稻 | 转运Cl- | Ren et al., | |
| [1] | 安婷婷, 黄帝, 王浩, 张一, 陈应龙 (2021). 植物响应镉胁迫的生理生化机制研究进展. 植物学报 56, 347-362. |
| [2] | 陈益 (2019). 铝处理对茶树体内铝钾镁分布及CsMATE9表达的影响. 硕士论文. 南京: 南京农业大学. pp. 25-41. |
| [3] | 丁海燕, 温丹妮, 王苗全, 钱海丰 (2013). 水稻抗铝机制的研究进展. 生命科学 25, 532-537. |
| [4] | 董碧莹 (2019). 木豆MATE基因抗金属胁迫作用解析. 硕士论文. 北京: 北京林业大学. pp. 11-21. |
| [5] |
高铭, 周思莹, 李钧儒, 石卓, 郭长虹, 郭东林 (2021). 紫花苜蓿MsMATE1基因克隆及其抵御铁胁迫功能的鉴定. 植物遗传资源学报 22, 512-520.
DOI |
| [6] | 龚莉 (2020). GmMATE13在铝诱导大豆根系柠檬酸分泌中的作用分析. 硕士论文. 长春: 吉林大学. pp. 9-37. |
| [7] | 胡俊, 刘卢生, 韩蓉蓉, 魏运民, 汪莹, 蒋曹德, 玉永雄 (2019). 丹波黑大豆GmMATE2基因的克隆及功能鉴定. 农业生物技术学报 27, 1161-1170. |
| [8] | 李洪有, 钟长春, 蔡芳, 霍冬敖, 张晓娜, 陈庆富 (2018). 甜荞柠檬酸转运蛋白基因FeFRD3的克隆及表达分析. 西北植物学报 38, 409-415. |
| [9] | 梁俊超, 孙建, 颜廷献, 乐美旺, 饶月亮, 颜小文, 周红英 (2021). 芝麻MATE基因家族的全基因组鉴定与表达分析. 基因组学与应用生物学 40, 735-746. |
| [10] | 刘青松 (2012). 香橙CjMATE基因的克隆与功能初步分析. 硕士论文. 重庆: 西南大学. pp. 25. |
| [11] | 蒲时 (2020). 雷公藤跨膜转运蛋白TwMATE2、TwMATE3克隆与表达分析. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 2-43. |
| [12] | 王碧莹 (2018). 长春花转运基因CrMATE1的基因克隆及功能鉴定. 硕士论文. 大连: 大连工业大学. pp. 33-53. |
| [13] | 王甲水 (2010). MaMATE1基因功能的初步研究. 硕士论文. 海口: 海南大学. pp. 55. |
| [14] | 王璐, 戴思兰, 金雪花, 黄河, 洪艳 (2014). 植物花青素苷转运机制的研究进展. 生物工程学报 30, 848-863. |
| [15] | 王玉琪 (2021). 桑树多药与毒素排出蛋白MulMATE的功能及作用机制研究. 硕士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 35-44. |
| [16] | 文开新, 王成章, 严学兵, 吴鹏举, 李振田 (2010). 黄酮类化合物生物学活性研究进展. 草业科学 27(6), 115-122. |
| [17] | 吴楠 (2014). 棕色棉纤维原花青素转运蛋白基因GhTT12的克隆与表达分析. 硕士论文. 合肥: 安徽农业大学. pp. 23-36. |
| [18] | 吴平治, 栾升, 李东屏 (2006). 拟南芥中MATE基因家族的研究进展. 遗传 28, 906-910. |
| [19] | 吴新新 (2014). 甘蓝耐铝基因MATE和ALMT克隆与功能验证. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业大学. pp. 8-30. |
| [20] |
谢玲玲, 王金龙, 伍国强 (2021). 植物CBL-CIPK信号系统响应非生物胁迫的调控机制. 植物学报 56, 614-626.
DOI |
| [21] | 张宝云 (2017). 紫花苜蓿铝胁迫响应基因MsMATE与MsSTOP1的功能与表达调控研究. 博士论文. 重庆: 重庆大学. pp. 93-96. |
| [22] | 张凡 (2012). 柿单宁及花青苷跨膜相关基因的克隆与表达分析. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 28-48. |
| [23] | 张郎织, 李季肤, 黄杰, 王志勇, 陈志坚 (2021). 地毯草AcMATE1基因的克隆与表达分析. 热带作物学报 42, 1860-1867. |
| [24] |
张艳艳, 王倩, 李晓旭, 孙亭亭, 龚达平, 杨明磊, 刘贯山 (2015). 普通烟草MATE基因家族分析及功能预测. 植物遗传资源学报 16, 1307-1314.
DOI |
| [25] | 张玉倩 (2018). 文多灵在大鼠体内外代谢及对细胞色素P450酶活性影响的研究. 硕士论文. 石家庄: 河北医科大学. pp. 82-83. |
| [26] |
Baetz U, Martinoia E (2014). Root exudates: the hidden part of plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 19, 90-98.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Bashir K, Ishimaru Y, Shimo H, Kakei Y, Senoura T, Takahashi R, Sato Y, Sato Y, Uozumi N, Nakanishi H, Nishizawa NK (2011). Rice phenolics efflux transporter 2 (PEZ2) plays an important role in solubilizing apoplasmic iron. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 57, 803-812.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Blanco P, Hernando-Amado S, Reales-Calderon JA, Corona F, Lira F, Alcalde-Rico M, Bernardini A, Sanchez MB, Martinez JL (2016). Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps: much more than antibiotic resistance determinants. Microorganisms 4, 14.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Briat JF, Lebrun M (1999). Plant responses to metal toxicity. C R Acad Sci III 322, 43-54. |
| [30] |
Brown MH, Paulsen IT, Skurray RA (1999). The multidrug efflux protein NorM is a prototype of a new family of transporters. Mol Microbiol 31, 394-395.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Chai YR, Lei B, Huang HL, Li JN, Yin JM, Tang ZL, Wang R, Chen L (2009). TRANSPARENT TESTA 12 genes from Brassica napus and parental species: cloning, evolution, and differential involvement in yellow seed trait. Mol Genet Genom 281, 109-123.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Chen L, Liu YS, Liu HD, Kang LM, Geng JM, Gai YZ, Ding YL, Sun HY, Li YD (2015). Identification and expression analysis of MATE genes involved in flavonoid transport in blueberry plants. PLoS One 10, e0118578. |
| [33] |
Chen SY, Tang YM, Hu YY, Wang Y, Sun B, Wang XR, Tang HR, Chen Q (2018). FaTT12-1, a multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) member involved in proanthocyanidin transport in strawberry fruits. Sci Hortic 231, 158-165.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Coleman J, Blake-Kalff M, Davies E (1997). Detoxification of xenobiotics by plants: chemical modification and vacuolar compartmentation. Trends Plant Sci 2, 144-151.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Curie C, Alonso JM, Le Jean M, Ecker JR, Briat JF (2000). Involvement of NRAMP1 from Arabidopsis thaliana in iron transport. Biochem J 347, 749-755.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
De Angeli A, Zhang JB, Meyer S, Martinoia E (2013). AtALMT9 is a malate-activated vacuolar chloride channel required for stomatal opening in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 4, 1804.
DOI |
| [37] |
Delhaize E, Craig S, Beaton CD, Bennet RH, Jagadish VC, Randall PJ (1993). Aluminum tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) (I. Uptake and distribution of aluminum in root apices). Plant Physiol 103, 685-693.
PMID |
| [38] |
Delhaize E, Ma JF, Ryan PR (2012). Transcriptional regulation of aluminium tolerance genes. Trends Plant Sci 17, 341-348.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Diédhiou CJ, Golldack D (2006). Salt-dependent regulation of chloride channel transcripts in rice. Plant Sci 170, 793-800.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Diener AC, Gaxiola RA, Fink GR (2001). Arabidopsis ALF5, a multidrug efflux transporter gene family member, confers resistance to toxins. Plant Cell 13, 1625-1638.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Dobritzsch M, Lübken T, Eschen-Lippold L, Gorzolka K, Blum E, Matern A, Marillonnet S, Böttcher C, Dräger B, Rosahl S (2016). MATE transporter-dependent export of hydroxycinnamic acid amides. Plant Cell 28, 583-596.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Durrett TP, Gassmann W, Rogers EE (2007). The FRD3- mediated efflux of citrate into the root vasculature is necessary for efficient iron translocation. Plant Physiol 144, 197-205.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Frank S, Keck M, Sagasser M, Niehaus K, Weisshaar B, Stracke R (2011). Two differentially expressed MATE factor genes from apple complement the Arabidopsis transparent testa 12 mutant. Plant Biol 13, 42-50.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Furukawa J, Yamaji N, Wang H, Mitani N, Murata Y, Sato K, Katsuhara M, Takeda K, Ma JF (2007). An aluminum-activated citrate transporter in barley. Plant Cell Physiol 48, 1081-1091.
DOI PMID |
| [45] |
Gomez C, Terrier N, Torregrosa L, Vialet S, Fournier- Level A, Verriès C, Souquet JM, Mazauric JP, Klein M, Cheynier V, Ageorges A (2009). Grapevine MATE-type proteins act as vacuolar H+-dependent acylated anthocyanin transporters. Plant Physiol 150, 402-415.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Green LS, Rogers EE (2004). FRD3 controls iron localization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 136, 2523-2531.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Harada H, Kuromori T, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K, Leigh RA (2004). Quantitative trait loci analysis of nitrate storage in Arabidopsis leading to an investigation of the contribution of the anion channel gene, AtCLC-c, to variation in nitrate levels. J Exp Bot 55, 2005-2014.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
He X, Szewczyk P, Karyakin A, Evin M, Hong WX, Zhang QH, Chang G (2010). Structure of a cation-bound multidrug and toxic compound extrusion transporter. Nature 467, 991-994.
DOI |
| [49] |
Hoang MTT, Almeida D, Chay S, Alcon C, Corratge-Fail- alie C, Curie C, Mari S (2021). AtDTX25 a member of the multidrug and toxic compound extrusion family, is a vacuolar ascorbate transporter that controls intracellular iron cycling in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 231, 1956-1967.
DOI URL |
| [1] |
Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Tsukamoto T, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Kobayashi T, Wada Y, Watanabe S, Matsuhashi S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006). Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+-phytosiderophore and as Fe2+. Plant J 45, 335-346.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Kuroda T, Tsuchiya T (2009). Multidrug efflux transporters in the MATE family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794, 763-768.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Kusakizako T, Claxton DP, Tanaka Y, Maturana AD, Kuroda T, Ishitani R, Mchaourab HS, Nureki O (2019). Structural basis of H+-dependent conformational change in a bacterial MATE transporter. Structure 27, 293-301.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Leung J, Giraudat J (1998). Abscisic acid signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49, 199-222.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
Li LG, He ZY, Pandey GK, Tsuchiya T, Luan S (2002). Functional cloning and characterization of a plant efflux carrier for multidrug and heavy metal detoxification. J Biol Chem 277, 5360-5368.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Li RX, Li JR, Li SB, Qin GJ, Novák O, Pěnčík A, Ljung K, Aoyama T, Liu JJ, Murphy A, Gu HY, Tsuge T, Qu LJ (2014). ADP1 affects plant architecture by regulating local auxin biosynthesis. PLoS Genet 10, e1003954. |
| [7] |
Li WYF, Wong FL, Tsai SN, Phang TH, Shao GH, Lam HM (2006). Tonoplast-located GmCLC1 and GmNHX1 from soybean enhance NaCl tolerance in transgenic bright yellow (BY)-2 cells. Plant Cell Environ 29, 1122-1137.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Liu JP, Magalhaes JV, Shaff J, Kochian LV (2009). Aluminum-activated citrate and malate transporters from the MATE and ALMT families function independently to confer Arabidopsis aluminum tolerance. Plant J 57, 389-399.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Liu MY, Lou HQ, Chen WW, Piñeros MA, Xu JM, Fan W, Kochian LV, Zheng SJ, Yang JL (2018). Two citrate transporters coordinately regulate citrate secretion from rice bean root tip under aluminum stress. Plant Cell Environ 41, 809-822.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Lu M, Radchenko M, Symersky J, Nie RX, Guo Y (2013a). Structural insights into H+-coupled multidrug extrusion by a MATE transporter. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1310-1317.
DOI |
| [11] |
Lu M, Symersky J, Radchenko M, Koide A, Guo Y, Nie RX, Koide S (2013b). Structures of a Na+-coupled, substrate-bound MATE multidrug transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 2099-2104.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Lv ZY, Zhao MM, Wang WJ, Wang Q, Huang MQ, Li CQ, Lian QC, Xia JQ, Qi J, Xiang CB, Tang HR, Ge XC (2021). Changing Gly311 to an acidic amino acid in the MATE family protein DTX6 enhances Arabidopsis resistance to the dihydropyridine herbicides. Mol Plant 14, 2115-2125.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Magalhaes JV, Liu JP, Guimarães CT, Lana UGP, Alves VMC, Wang YH, Schaffert RE, Hoekenga OA, Piñeros MA, Shaff JE, Klein PE, Carneiro NP, Coelho CM, Trick HN, Kochian LV (2007). A gene in the multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family confers aluminum tolerance in sorghum. Nat Genet 39, 1156-1161.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Marinova K, Pourcel L, Weder B, Schwarz M, Barron D, Routaboul JM, Debeaujon I, Klein M (2007). The Arabidopsis MATE transporter TT12 acts as a vacuolar flavonoid/H+-antiporter active in proanthocyanidin-accumulating cells of the seed coat. Plant Cell 19, 2023-2038.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Maron LG, Piñeros MA, Guimarães CT, Magalhaes JV, Pleiman JK, Mao CZ, Shaff J, Belicuas SNJ, Kochian LV (2010). Two functionally distinct members of the MATE (multi-drug and toxic compound extrusion) family of transporters potentially underlie two major aluminum tolerance QTLs in maize. Plant J 61, 728-740.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Meyer S, Scholz-Starke J, De Angeli A, Kovermann P, Burla B, Gambale F, Martinoia E (2011). Malate transport by the vacuolar AtALMT6 channel in guard cells is subject to multiple regulation. Plant J 67, 247-257.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Miyauchi H, Moriyama S, Kusakizako T, Kumazaki K, Nakane T, Yamashita K, Hirata K, Dohmae N, Nishizawa T, Ito K, Miyaji T, Moriyama Y, Ishitani R, Nureki O (2017). Structural basis for xenobiotic extrusion by eukaryotic MATE transporter. Nat Commun 8, 1633.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Morita Y, Kodama K, Shiota S, Mine T, Kataoka A, Mizushima T, Tsuchiya T (1998). NorM, a putative multidrug efflux protein, of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its homolog in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42, 1778-1782.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Morrissey J, Guerinot ML (2009). Iron uptake and transport in plants: the good, the bad, and the ionome. Chem Rev 109, 4553-4567.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Nakamura A, Fukuda A, Sakai S, Tanaka Y (2006). Molecular cloning, functional expression and subcellular localization of two putative vacuolar voltage-gated chloride channels in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol 47, 32-42.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Nawrath C, Heck S, Parinthawong N, Métraux JP (2002). EDS5, an essential component of salicylic acid-dependent signaling for disease resistance in Arabidopsis, is a member of the MATE transporter family. Plant Cell 14, 275-286.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Pan YL, Liu ZY, Rocheleau H, Fauteux F, Wang YL, McCartney C, Ouellet T (2018). Transcriptome dynamics associated with resistance and susceptibility against fusarium head blight in four wheat genotypes. BMC Genomics 19, 642.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Poole K (2000). Efflux-mediated resistance to fluoroquinolones in gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44, 2233-2241.
DOI PMID |
| [24] | Qin P, Zhang GH, Hu BH, Wu J, Chen WL, Ren ZJ, Liu YL, Xie J, Yuan H, Tu B, Ma BT, Wang YP, Ye LM, Li LG, Xiang CB, Li SG (2021). Leaf-derived ABA regulates rice seed development via a transporter-mediated and temperature-sensitive mechanism. Sci Adv 7, eabc8873. |
| [25] |
Qiu W, Wang NQ, Dai J, Wang TQ, Kochian LV, Liu JP, Zuo YM (2019). AhFRDL1-mediated citrate secretion contributes to adaptation to iron deficiency and aluminum stress in peanuts. J Exp Bot 70, 2873-2886.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Rangel AF, Rao IM, Braun HP, Horst WJ (2010). Aluminum resistance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) involves induction and maintenance of citrate exudation from root apices. Physiol Plant 138, 176-190.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
Ren ZJ, Bai FL, Xu JW, Wang L, Wang XH, Zhang Q, Feng CX, Niu Q, Zhang LY, Song JL, Bao F, Liu LY, He YK, Ma LG, Tian W, Hou CC, Li LG (2021). A chloride efflux transporter, big rice grain 1, is involved in mediating grain size and salt tolerance in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 63, 2150-2163.
DOI |
| [28] |
Rogers EE, Guerinot ML (2002). FRD3, a member of the multidrug and toxin efflux family, controls iron deficiency responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14, 1787-1799.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Rogers EE, Wu XL, Stacey G, Nguyen HT (2009). Two MATE proteins play a role in iron efficiency in soybean. J Plant Physiol 166, 1453-1459.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Roschzttardtz H, Conéjéro G, Divol F, Alcon C, Verdeil JL, Curie C, Mari S (2013). New insights into Fe localization in plant tissues. Front Plant Sci 4, 350.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Sasaki T, Yamamoto Y, Ezaki B, Katsuhara M, Ahn SJ, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Matsumoto H (2004). A wheat gene encoding an aluminum-activated malate transporter. Plant J 37, 645-653.
DOI PMID |
| [32] |
Serrano M, Wang BJ, Aryal B, Garcion C, Abou-Mansour E, Heck S, Geisler M, Mauch F, Nawrath C, Métraux JP (2013). Export of salicylic acid from the chloroplast requires the multidrug and toxin extrusion-like transporter EDS5. Plant Physiol 162, 1815-1821.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Shitan N, Bazin I, Dan K, Obata K, Kigawa K, Ueda K, Sato F, Forestier C, Yazaki K (2003). Involvement of CjMDR1, a plant multidrug-resistance-type ATP-binding cassette protein, in alkaloid transport in Coptis japonica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 751-756.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Shitan N, Dalmas F, Dan K, Kato N, Ueda K, Sato F, Forestier C, Yazaki K (2013). Characterization of Coptis japonica CjABCB2, an ATP-binding cassette protein involved in alkaloid transport. Phytochemistry 91, 109-116.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Shitan N, Minami S, Morita M, Hayashida M, Ito S, Takanashi K, Omote H, Moriyama Y, Sugiyama A, Goossens A, Moriyasu M, Yazaki K (2014). Involvement of the leaf-specific multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) transporter Nt-JAT2 in vacuolar sequestration of nicotine in Nicotiana tabacum. PLoS One 9, e108789. |
| [36] |
Shoji T, Inai K, Yazaki Y, Sato Y, Takase H, Shitan N, Yazaki K, Goto Y, Toyooka K, Matsuoka K, Hashimoto T (2009). Multidrug and toxic compound extrusion-type transporters implicated in vacuolar sequestration of nicotine in tobacco roots. Plant Physiol 149, 708-718.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Sun XL, Gilroy EM, Chini A, Nurmberg PL, Hein I, Lacomme C, Birch PRJ, Hussain A, Yun BW, Loake GJ (2011). ADS1 encodes a MATE-transporter that negatively regulates plant disease resistance. New Phytol 192, 471-482.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Takanashi K, Shitan N, Yazaki K (2014). The multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 31, 417-430. |
| [39] |
Takahashi M, Terada Y, Nakai I, Nakanishi H, Yoshimura E, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2003). Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development. Plant Cell 15, 1263-1280.
PMID |
| [40] |
Tanaka Y, Iwaki S, Tsukazaki T (2017). Crystal structure of a plant multidrug and toxic compound extrusion family protein. Structure 25, 1455-1460.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Tiwari M, Sharma D, Singh M, Tripathi RD, Trivedi PK (2014). Expression of OsMATE1 and OsMATE2 alters development, stress responses and pathogen susceptibility in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 4, 3964.
DOI |
| [42] |
Upadhyay N, Kar D, Deepak Mahajan B, Nanda S, Rahiman R, Panchakshari N, Bhagavatula L, Datta S (2019). The multitasking abilities of MATE transporters in plants. J Exp Bot 70, 4643-4656.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Wang R, Liu XY, Liang S, Ge Q, Li YF, Shao JX, Qi YF, An LJ, Yu F (2015). A subgroup of MATE transporter genes regulates hypocotyl cell elongation in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 66, 6327-6343.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Xia JQ, Nazish T, Javaid A, Ali M, Liu QQ, Wang L, Zhang ZY, Zhang ZS, Huang YJ, Wu J, Yang ZS, Sun LF, Chen YX, Xiang CB (2021). A gain-of-function mutation of the MATE family transporter DTX6 confers paraquat resistance in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 14, 2126-2133.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2010). Isolation and characterisation of two MATE genes in rye. Funct Plant Biol 37, 296-303.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Ma JF (2011). An Al-inducible MATE gene is involved in external detoxification of Al in rice. Plant J 68, 1061-1069.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Ueno D, Mitani N, Ma JF (2009). OsFRDL1 is a citrate transporter required for efficient translocation of iron in rice. Plant Physiol 149, 297-305.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Yu F, De Luca V (2013). ATP-binding cassette transporter controls leaf surface secretion of anticancer drug components in Catharanthus roseus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 15830-15835.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Yu YQ, Assmann SM (2014). Metabolite transporter regulation of ABA function and guard cell response. Mol Plant 7, 1505-1507.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | Zhang HW, Zhao FG, Tang RJ, Yu YX, Song JL, Wang Y, Li LG, Luan S (2017). Two tonoplast MATE proteins function as turgor-regulating chloride channels in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E2036-E2045. |
| [51] |
Zhang HW, Zhu HF, Pan YJ, Yu YX, Luan S, Li LG (2014). A DTX/MATE-type transporter facilitates abscisic acid efflux and modulates ABA sensitivity and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 7, 1522-1532.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Zhao J, Dixon RA (2009). MATE transporters facilitate vacuolar uptake of epicatechin 3'-O-glucoside for proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 2323-2340.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Zhao J, Dixon RA (2010). The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of flavonoid transport. Trends Plant Sci 15, 72-80.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Zhao J, Huhman D, Shadle G, He XZ, Sumner LW, Tang YH, Dixon RA (2011). MATE2 mediates vacuolar sequestration of flavonoid glycosides and glycoside malonates in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 23, 1536-1555.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Zifarelli G, Pusch M (2010). CLC transport proteins in plants. FEBS Lett 584, 2122-2127.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 邱丹妮, 彭清清, 张慧玲, 温辉辉, 吴福忠. 中亚热带常绿阔叶林典型乔木树种对蚂蚁群落季节性动态的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [2] | 童金莲, 张博纳, 汤璐瑶, 叶琳峰, 李姝雯, 谢江波, 李彦, 王忠媛. C4植物狗尾草功能性状网络沿降水梯度带的区域分异规律[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [3] | 戴丽君, 向玲艺, 蹇陈, 王晓锋. 三峡回水扰动增强了入库小流域河岸带典型草本植物功能性状的局域分化[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 1-. |
| [4] | 张静 陈洁 李艳朋 盘李军 许涵 李意德 何海生. 南亚热带针阔混交人工林植物生物量比较及其影响因子分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 0-0. |
| [5] | 赵珮杉 高广磊 丁国栋 张英. 林龄和生态位对樟子松人工林地下真菌群落构建的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 1-0. |
| [6] | 罗敏, 杨永川, 靳程, 周礼华, 龙宇潇. 城市森林兽类组成特征及人类活动的影响——以重庆中心城区为例[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(5): 24402-. |
| [7] | 宋威, 程才, 王嘉伟, 吴纪华. 土壤微生物对植物多样性–生态系统功能关系的调控作用[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24579-. |
| [8] | 李梦琦, 苗灵凤, 李大东, 龙奕帆, 叶冰冰, 杨帆. 海南东寨港红树林植物细根功能性状对不同潮位沉积物养分变化的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 552-561. |
| [9] | 张明燡, 王晓梅, 郑言鑫, 吴楠, 李东浩, 樊恩源, 李娜, 单秀娟, 于涛, 赵春暖, 李波, 徐帅, 吴玉萍, 任利群. 黄河口典型牡蛎礁分布区资源状况和栖息地功能[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(4): 24208-. |
| [10] | 杜英杰, 范爱连, 王雪, 闫晓俊, 陈廷廷, 贾林巧, 姜琦, 陈光水. 亚热带天然常绿阔叶林乔木树种与林下灌木树种根-叶功能性状协调性及差异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(4): 585-595. |
| [11] | 刘淑琪, 崔东, 江智诚, 刘江慧, 闫江超. 短期氮、水添加和刈割减弱了苦豆子型退化草地土壤生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的联系[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(3): 24305-. |
| [12] | 刘茹, 李阳, 唐兆成, 郝婷婷, 张保龙. 甘蓝中催化NMN降解生成NR的5′-核苷酸酶基因克隆和功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 363-376. |
| [13] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [14] | 陈丁松, 刘子恺, 贺子洋, 陈伟东. 缓步动物多样性、分布特征和生态功能研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2025, 33(2): 24406-. |
| [15] | 闫小红, 傅英健, 胡文海. 亚热带地区3种常绿阔叶植物光系统II功能对冬季短暂升温的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(2): 331-342. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||