

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (4): 622-637.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22087 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22087
许亚楠1, 闫家榕1, 孙鑫2, 王晓梅3, 刘玉凤1, 孙周平1, 齐明芳1, 李天来1,4,5,6, 王峰1,4,5,6( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-24
接受日期:2022-08-24
出版日期:2023-07-01
发布日期:2022-08-30
通讯作者:
*E-mail: fengwang@syau.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yanan Xu1, Jiarong Yan1, Xin Sun2, Xiaomei Wang3, Yufeng Liu1, Zhouping Sun1, Mingfang Qi1, Tianlai Li1,4,5,6, Feng Wang1,4,5,6( )
)
Received:2022-04-24
Accepted:2022-08-24
Online:2023-07-01
Published:2022-08-30
Contact:
*E-mail: fengwang@syau.edu.cn
摘要: 光作为重要的环境因子之一, 不仅为植物光合作用提供能量, 而且作为信号影响植物对外界环境的响应。该文综述了红光和远红光对植物生长发育和非生物胁迫响应的调控作用, 重点阐述了光敏色素及下游光信号转录因子整合激素等内源信号调控植物种子萌发、下胚轴伸长、芽发育及开花的分子机制, 以及红光和远红光在植物响应盐、干旱及温度胁迫中的作用机制。在挖掘植物感知和响应光环境机理的基础上, 利用LED光谱技术对作物进行精确补光, 有望提高作物产量、品质和抗逆性, 同时推进实现“双碳”目标, 减少能源消耗和环境污染。
许亚楠, 闫家榕, 孙鑫, 王晓梅, 刘玉凤, 孙周平, 齐明芳, 李天来, 王峰. 红光和远红光在调控植物生长发育及应答非生物胁迫中的作用. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 622-637.
Yanan Xu, Jiarong Yan, Xin Sun, Xiaomei Wang, Yufeng Liu, Zhouping Sun, Mingfang Qi, Tianlai Li, Feng Wang. Red and Far-red Light Regulation of Plant Growth, Development, and Abiotic Stress Responses. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(4): 622-637.
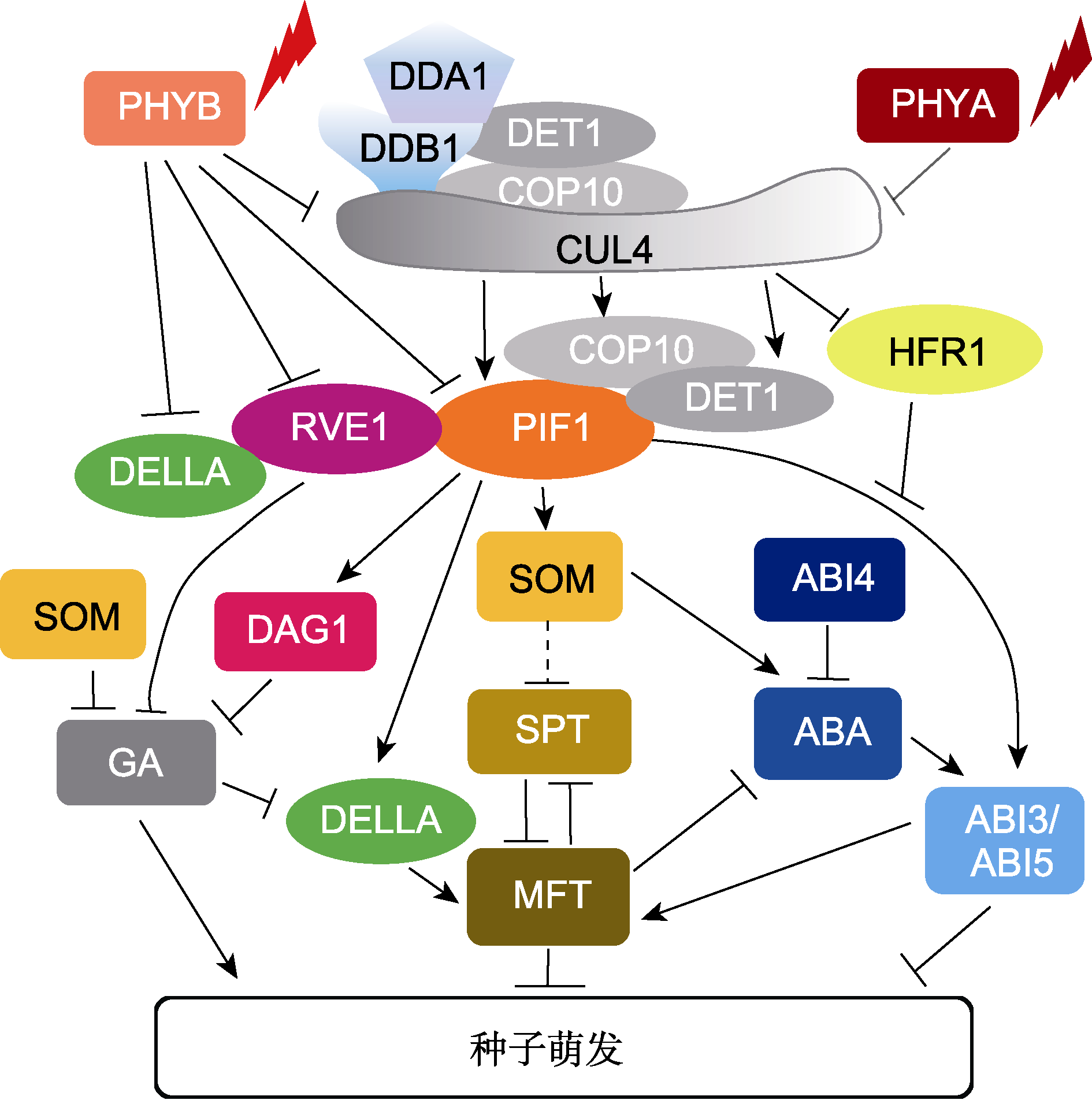
图1 光敏色素调控种子萌发 PHYA: 光敏色素A; PHYB: 光敏色素B; ABA: 脱落酸; GA: 赤霉素。箭头代表促进作用, 带有终止符号的线条表示抑制作用, 虚线代表不明确的途径。
Figure 1 Regulation of seed germination by phytochromes PHYA: PHYTOCHROME A; PHYB: PHYTOCHROME B; ABA: Abscisic acid; GA: Gibberellic acid. Arrows indicate positive regulation, bars indicate negative regulation, and dotted lines indicate the ambiguous pathways.
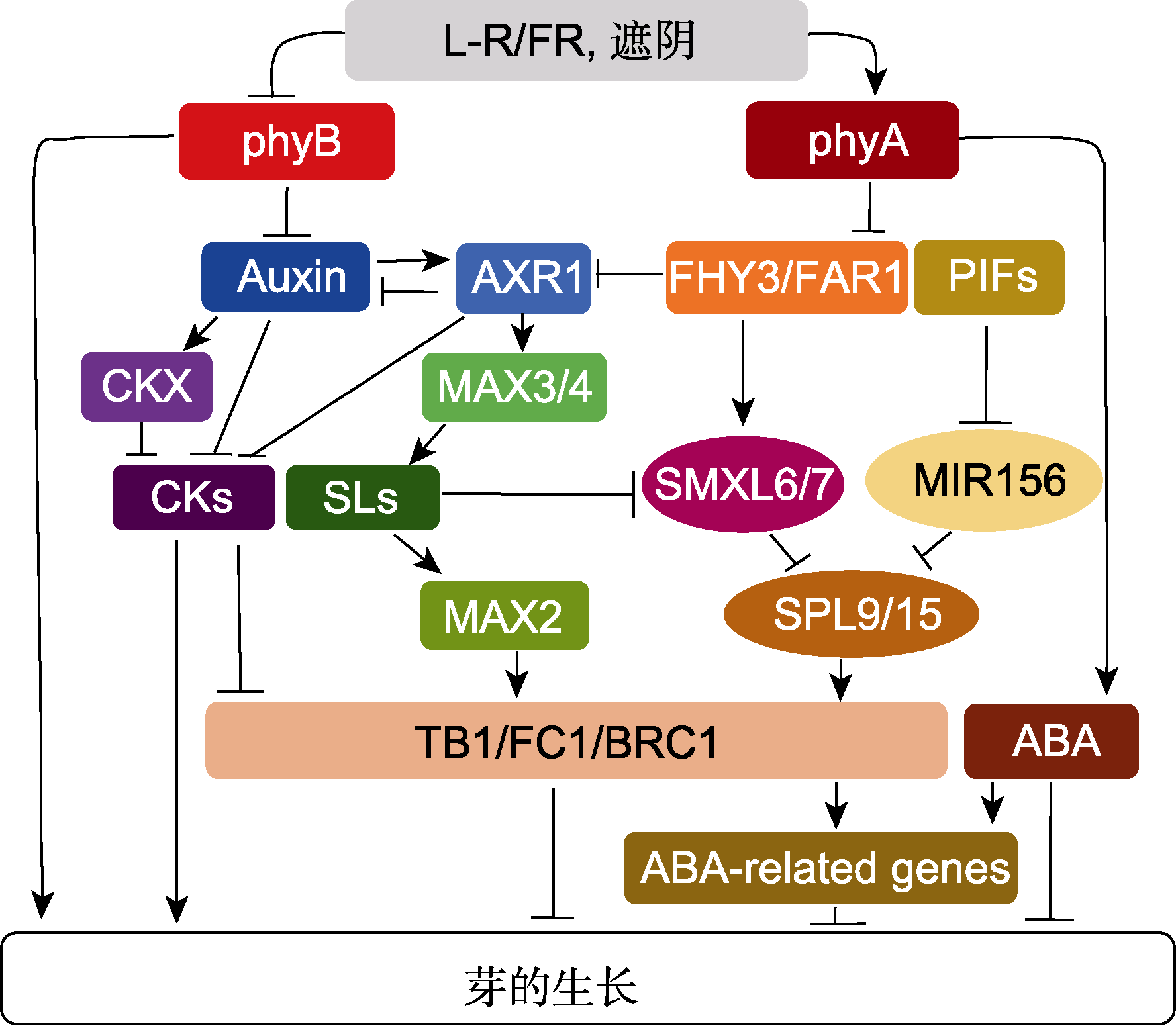
图2 光敏色素调控芽生长的信号网络 L-R/FR: 低比例的红光/远红光; phyB: 光敏色素B; phyA: 光敏色素A; PIFs: 光敏色素互作因子; CKs: 细胞分裂素; CKX: 细胞分裂素氧化酶; SLs: 独脚金内酯; ABA: 脱落酸。箭头代表促进作用, 带有终止符号的线条表示抑制作用。
Figure 2 The signaling network of phytochrome-regulation of bud outgrowth L-R/FR: Low red to far-red light ratios; phyB: Phytochrome B; phyA: Phytochrome A; PIFs: Phytochrome-interacting factors; CKs: Cytokinins; CKX: CYTOKININ OXIDASE; SLs: Strigolactones; ABA: Abscisic acid. Arrows indicate positive regulation, bars indicate negative regulation.
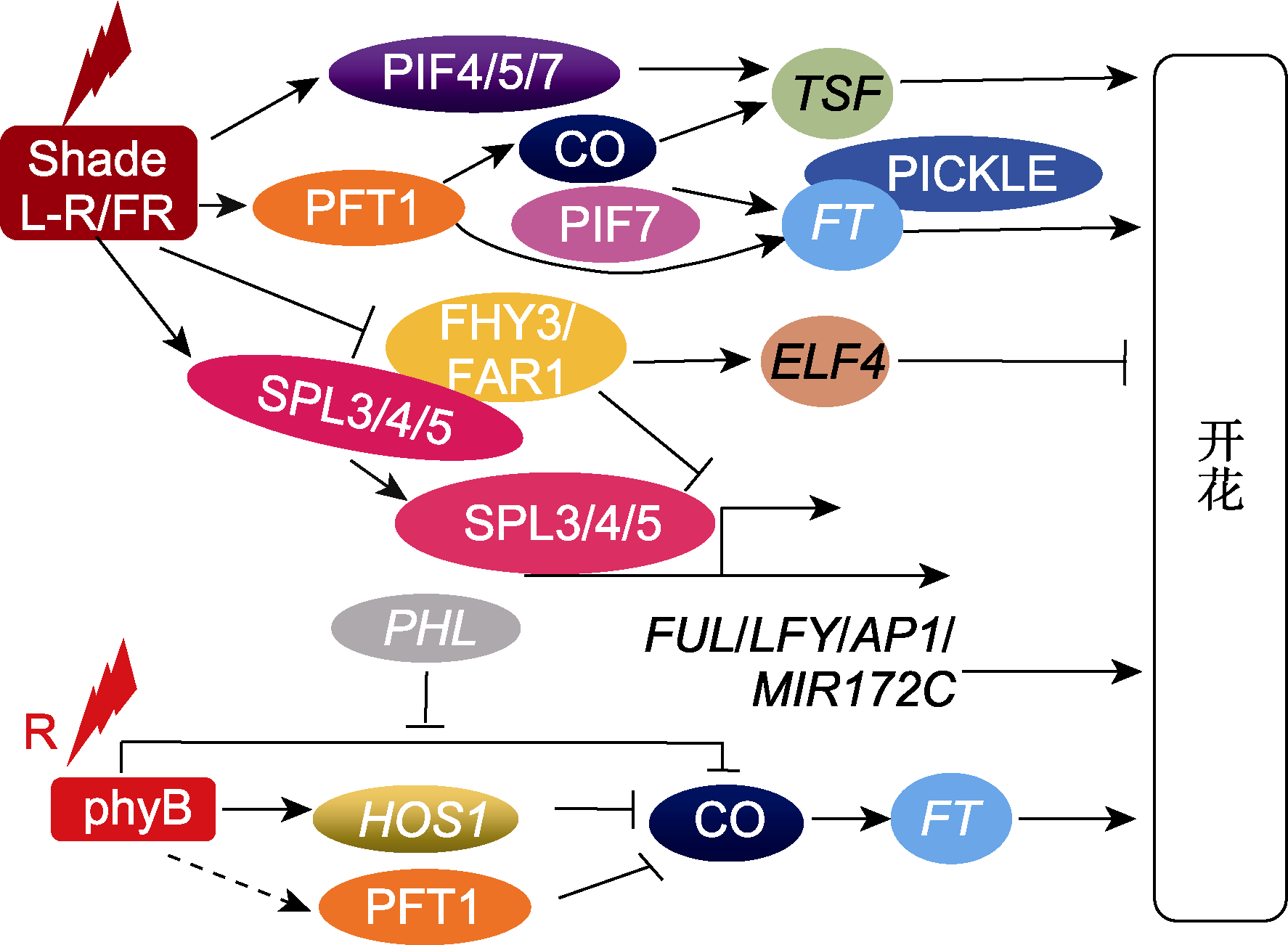
图3 光敏色素调控植物开花 phyB: 光敏色素B; L-R/FR: 低比例的红光/远红光; R: 红光。箭头代表促进作用, 带有终止符号的线条表示抑制作用, 虚线代表不明确的途径。
Figure 3 Regulation of flowering time by phytochromes phyB: Phytochrome B; L-R/FR: Low red to far-red light ratios; R: Red light. Arrows indicate positive regulation, bars indicate negative regulation, and dotted lines indicate the ambiguous pathways.
| 非生物胁迫 | 光信号因子 | 调控机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盐害 | phyB | 红光通过phyB诱导脯氨酸合成基因P5CS1和代谢途径基因PDH1的表达, 促进脯氨酸的积累, 提高植物的耐盐性 | Hayashi et al., |
| phyB | phyB突变体气孔关闭速度减慢, 水分损失增加, 抗旱性降低 | González et al., | |
| 干旱 | OsPIL1 | 水稻OsPIL1通过DREB1A正调控植物的耐旱性 | Todaka et al., |
| ZmPIF3 | ZmPIF3促进脱落酸介导的气孔关闭, 减少水分损失, 增强抗旱性 | Gao et al., | |
| 高温 | phyB | 高温使phyB失活, 促进PIF4-BES1复合物通过生长素信号诱导叶片伸长; phyB正调控高温抗性 | Mart?nez et al., |
| HY5 | 热形态建成中HY5与PIF4竞争与靶蛋白的结合 | Delker et al., | |
| COP1 | 高温使COP1进入细胞核, 通过26S蛋白酶体途径降解HY5 | Park et al., | |
| PIF4 | 高温诱导PIF4过度磷酸化, 增强蛋白的稳定性; 高温诱导PIF4蛋白的积累依赖于DET1和COP1 | Foreman et al., | |
| TCP5/17 | 高温下, TCP5/17通过调控PIF4活性诱导下胚轴伸长 | Han et al., | |
| BBX18/23 | 高温下, BBX18/23通过招募XBAT31/35泛素降解ELF3, 进而促进PIF4活性, 诱导下胚轴伸长 | Ding et al., | |
| PIF4/5 | 高温下, PIF4/5通过直接转录激活NAC019和SAG113, 介导热胁迫诱导的叶片衰老过程 | Li et al., | |
| SlBBX17 | 高温下, 通过促进SlHSF和SlHSP等基因的表达以及抗氧化物酶活性增高, 增强番茄的耐热性 | Xu et al., | |
| 低温 | PIF4/7 | PIF4和PIF7负调控CBF的表达和耐低温性 | Lee and Thomashow, |
| PIF3 | PIF3负调控植物低温抗性; 低温下, CBF蛋白与PIF3互作, 抑制phyB、EBF1和EBF2对PIF3蛋白的降解 | Jiang et al., | |
| SlphyA | SlphyA通过脱落酸与茉莉酸等激素途径正调控番茄的耐低温性 | Wang et al., | |
| SlphyB | SlphyB通过负调控CBFs等基因的表达以及光保护抑制番茄的耐低温性 | Wang et al., | |
| SlHY5 | SlHY5通过CBF、激素及光保护途径正调控耐低温性 | Wang et al., | |
| SlFHY3 | SlFHY3通过肌醇途径正调控番茄的耐低温性 | Wang et al., |
表1 光信号因子对植物非生物胁迫的调控作用
Table 1 Regulatory mechanisms of light signaling factors in response to abiotic stress
| 非生物胁迫 | 光信号因子 | 调控机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 盐害 | phyB | 红光通过phyB诱导脯氨酸合成基因P5CS1和代谢途径基因PDH1的表达, 促进脯氨酸的积累, 提高植物的耐盐性 | Hayashi et al., |
| phyB | phyB突变体气孔关闭速度减慢, 水分损失增加, 抗旱性降低 | González et al., | |
| 干旱 | OsPIL1 | 水稻OsPIL1通过DREB1A正调控植物的耐旱性 | Todaka et al., |
| ZmPIF3 | ZmPIF3促进脱落酸介导的气孔关闭, 减少水分损失, 增强抗旱性 | Gao et al., | |
| 高温 | phyB | 高温使phyB失活, 促进PIF4-BES1复合物通过生长素信号诱导叶片伸长; phyB正调控高温抗性 | Mart?nez et al., |
| HY5 | 热形态建成中HY5与PIF4竞争与靶蛋白的结合 | Delker et al., | |
| COP1 | 高温使COP1进入细胞核, 通过26S蛋白酶体途径降解HY5 | Park et al., | |
| PIF4 | 高温诱导PIF4过度磷酸化, 增强蛋白的稳定性; 高温诱导PIF4蛋白的积累依赖于DET1和COP1 | Foreman et al., | |
| TCP5/17 | 高温下, TCP5/17通过调控PIF4活性诱导下胚轴伸长 | Han et al., | |
| BBX18/23 | 高温下, BBX18/23通过招募XBAT31/35泛素降解ELF3, 进而促进PIF4活性, 诱导下胚轴伸长 | Ding et al., | |
| PIF4/5 | 高温下, PIF4/5通过直接转录激活NAC019和SAG113, 介导热胁迫诱导的叶片衰老过程 | Li et al., | |
| SlBBX17 | 高温下, 通过促进SlHSF和SlHSP等基因的表达以及抗氧化物酶活性增高, 增强番茄的耐热性 | Xu et al., | |
| 低温 | PIF4/7 | PIF4和PIF7负调控CBF的表达和耐低温性 | Lee and Thomashow, |
| PIF3 | PIF3负调控植物低温抗性; 低温下, CBF蛋白与PIF3互作, 抑制phyB、EBF1和EBF2对PIF3蛋白的降解 | Jiang et al., | |
| SlphyA | SlphyA通过脱落酸与茉莉酸等激素途径正调控番茄的耐低温性 | Wang et al., | |
| SlphyB | SlphyB通过负调控CBFs等基因的表达以及光保护抑制番茄的耐低温性 | Wang et al., | |
| SlHY5 | SlHY5通过CBF、激素及光保护途径正调控耐低温性 | Wang et al., | |
| SlFHY3 | SlFHY3通过肌醇途径正调控番茄的耐低温性 | Wang et al., |
| [1] |
景艳军, 林荣呈 (2017). 我国植物光信号转导研究进展概述. 植物学报 52, 257-270.
DOI |
| [2] |
马朝峰, 戴思兰 (2019). 光受体介导信号转导调控植物开花研究进展. 植物学报 54, 9-22.
DOI |
| [3] |
任桂萍, 王小菁, 朱根发 (2016). 不同光质的LED对蝴蝶兰组织培养增殖及生根的影响. 植物学报 51, 81-88.
DOI |
| [4] | 王峰 (2017). PhyA、HY5和PIF4在光质调控番茄低温抗性中的机制研究. 博士论文. 杭州: 浙江大学. pp. 1-163. |
| [5] |
王峰, 王秀杰, 赵胜男, 闫家榕, 卜鑫, 张颖, 刘玉凤, 许涛, 齐明芳, 齐红岩, 李天来 (2020). 光对园艺植物花青素生物合成的调控作用. 中国农业科学 53, 4904-4917.
DOI |
| [6] |
王峰, 闫家榕, 陈雪玉, 姜程浩, 孟思达, 刘玉凤, 许涛, 齐明芳, 李天来 (2019). 光调控植物叶绿素生物合成的研究进展. 园艺学报 46, 975-994.
DOI |
| [7] |
Abbas N, Maurya JP, Senapati D, Gangappa SN, Chattopadhyay S (2014). Arabidopsis CAM7 and HY5 physically interact and directly bind to the HY5 promoter to regulate its expression and thereby promote photomorphogenesis. Plant Cell 26, 1036-1052.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Ábrahám E, Rigó G, Székely G, Nagy R, Koncz C, Szabados L (2003). Light-dependent induction of proline biosynthesis by abscisic acid and salt stress is inhibited by brassinosteroid in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 51, 363-372.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Amasino RM, Michaels SD (2010). The timing of flowering. Plant Physiol 154, 516-520.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Arana MV, Sánchez-Lamas M, Strasser B, Ibarra SE, Cerdán PD, Botto JF, Sánchez RA (2014). Functional diversity of phytochrome family in the control of light and gibberellin-mediated germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 37, 2014-2023.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Arico D, Legris M, Castro L, Garcia CF, Laino A, Casal JJ, Mazzella MA (2019). Neighbour signals perceived by phytochrome B increase thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 42, 2554-2566.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Bai MY, Shang JX, Oh E, Fan M, Bai Y, Zentella R, Sun TP, Wang ZY (2012). Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 14, 810-817.
DOI |
| [13] |
Barros-Galvão T, Dave A, Gilday AD, Harvey D, Vaistij FE, Graham IA (2020). ABA INSENSITIVE4 promotes rather than represses PHYA-dependent seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 226, 953-956.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Bernardo-García S, De Lucas M, Martínez C, Espinosa- Ruiz A, Davière JM, Prat S (2014). BR-dependent phosphorylation modulates PIF4 transcriptional activity and shapes diurnal hypocotyl growth. Genes Dev 28, 1681-1694.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Bu X, Wang XJ, Yan JR, Zhang Y, Zhou SY, Sun X, Yang YX, Ahammed GJ, Liu YF, Qi MF, Wang F, Li TL (2021). Genome-wide characterization of B-box gene family and its roles in responses to light quality and cold stress in tomato. Front Plant Sci 12, 698525.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Cao K, Yu J, Xu DW, Ai KQ, Bao EC, Zou ZR (2018). Exposure to lower red to far-red light ratios improve tomato tolerance to salt stress. BMC Plant Biol 18, 92.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Carabelli M, Possenti M, Sessa G, Ciolfi A, Sassi M, Morelli G, Ruberti I (2007). Canopy shade causes a rapid and transient arrest in leaf development through auxin- induced cytokinin oxidase activity. Genes Dev 21, 1863-1868.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Casal JJ (2013). Photoreceptor signaling networks in plant responses to shade. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 403-427.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Casal JJ, Balasubramanian S (2019). Thermomorphogenesis. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70, 321-346.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Catalá R, Medina J, Salinas J (2011). Integration of low temperature and light signaling during cold acclimation response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 16475-16480.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Chattopadhyay S, Ang LH, Puente P, Deng XW, Wei N (1998). Arabidopsis bZIP protein HY5 directly interacts with light-responsive promoters in mediating light control of gene expression. Plant Cell 10, 673-683.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Chen HD, Huang X, Gusmaroli G, Terzaghi W, Lau OS, Yanagawa Y, Zhang Y, Li JG, Lee JH, Zhu DM, Deng XW (2010). Arabidopsis CULLIN4-damaged DNA binding protein 1 interacts with CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-SUPPRESSOR of PHYA complexes to regulate photomorphogenesis and flowering time. Plant Cell 22, 108-123.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Chen XJ, Xia XJ, Guo X, Zhou YH, Shi K, Zhou J, Yu JQ (2016). Apoplastic H2O2 plays a critical role in axillary bud outgrowth by altering auxin and cytokinin homeostasis in tomato plants. New Phytol 211, 1266-1278.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Cheng MC, Kathare PK, Paik I, Huq E (2021). Phytochrome signaling networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 217-244.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Cho JN, Ryu JY, Jeong YM, Park J, Song JJ, Amasino RM, Noh B, Noh YS (2012). Control of seed germination by light-induced histone arginine demethylation activity. Dev Cell 22, 736-748.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Cordeiro AM, Figueiredo DD, Tepperman J, Borba AR, Lourenço T, Abreu IA, Ouwerkerk PBF, Quail PH, Oliveira MM, Saibo NJM (2016). Rice phytochrome-interacting factor protein OsPIF14 represses OsDREB1B gene expression through an extended N-box and interacts preferentially with the active form of phytochrome B. Biochim Biophys Acta 1859, 393-404.
DOI PMID |
| [27] |
de Lucas M, Davière JM, Rodríguez-Falcón M, Pontin M, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Lorrain S, Fankhauser C, Blázquez MA, Titarenko E, Prat S (2008). A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 451, 480-484.
DOI |
| [28] |
de Lucas M, Prat S (2014). PIFs get BRright: PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORs as integrators of light and hormonal signals. New Phytol 202, 1126-1141.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Delker C, Sonntag L, James GV, Janitza P, Ibañez C, Ziermann H, Peterson T, Denk K, Mull S, Ziegler J, Davis SJ, Schneeberger K, Quint M (2014). The DET1- COP1-HY5 pathway constitutes a multipurpose signaling module regulating plant photomorphogenesis and thermomorphogenesis. Cell Rep 9, 1983-1989.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Ding L, Wang S, Song ZT, Jiang YP, Han JJ, Lu SJ, Li L, Liu JX (2018). Two B-box domain proteins, BBX18 and BBX23, interact with ELF3 and regulate thermomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep 25, 1718-1728.
DOI PMID |
| [31] |
Djakovic-Petrovic T, De Wit M, Voesenek LACJ, Pierik R (2007). DELLA protein function in growth responses to canopy signals. Plant J 51, 117-126.
PMID |
| [32] | Domagalska MA, Leyser O (2011). Signal integration in the control of shoot branching. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12, 211-221. |
| [33] | Dong XJ, Yan Y, Jiang BC, Shi YT, Jia YX, Cheng JK, Shi YH, Kang JQ, Li H, Zhang D, Qi LJ, Han R, Zhang SM, Zhou YY, Wang XJ, Terzaghi W, Gu HY, Kang DM, Yang SH, Li JG (2020). The cold response regulator CBF1 promotes Arabidopsis hypocotyl growth at ambient temperatures. EMBO J 39, e103630. |
| [34] |
Endo M, Tanigawa Y, Murakami T, Araki T, Nagatani A (2013). PHYTOCHROME-DEPENDENT LATE-FLOWERING accelerates flowering through physical interactions with phytochrome B and CONSTANS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 18017-18022.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Finch-Savage WE, Footitt S (2017). Seed dormancy cycling and the regulation of dormancy mechanisms to time germination in variable field environments. J Exp Bot 68, 843-856.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Finlayson SA, Krishnareddy SR, Kebrom TH, Casal JJ (2010). Phytochrome regulation of branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152, 1914-1927.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Foreman J, Johansson H, Hornitschek P, Josse EM, Fankhauser C, Halliday KJ (2011). Light receptor action is critical for maintaining plant biomass at warm ambient temperatures. Plant J 65, 441-452.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Franklin KA, Praekelt U, Stoddart WM, Billingham OE, Halliday KJ, Whitelam GC (2003). Phytochromes B, D, and E act redundantly to control multiple physiological responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 131, 1340-1346.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Franklin KA, Whitelam GC (2007). Light-quality regulation of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 39, 1410-1413.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Gabriele S, Rizza A, Martone J, Circelli P, Costantino P, Vittorioso P (2010). The Dof protein DAG1 mediates PIL5 activity on seed germination by negatively regulating GA biosynthetic gene AtGA3ox1. Plant J 61, 312-323.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Galvão VC, Fankhauser C (2015). Sensing the light environment in plants: photoreceptors and early signaling steps. Curr Opin Neurobiol 34, 46-53.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Galvāo VC, Fiorucci AS, Trevisan M, Franco-Zorilla JM, Goyal A, Schmid-Siegert E, Solano R, Fankhauser C (2019). PIF transcription factors link a neighbor threat cue to accelerated reproduction in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 10, 4005.
DOI |
| [43] |
Gao Y, Jiang W, Dai Y, Xiao N, Zhang CQ, Li H, Lu Y, Wu MQ, Tao XY, Deng DX, Chen JM (2015). A maize phytochrome-interacting factor 3 improves drought and salt stress tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 87, 413-428.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
Gao Y, Wu MQ, Zhang MJ, Jiang W, Ren XY, Liang EX, Zhang DP, Zhang CQ, Xiao N, Li Y, Dai Y, Chen JM (2018). A maize phytochrome-interacting factors protein ZmPIF1 enhances drought tolerance by inducing stomatal closure and improves grain yield in Oryza sativa. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 1375-1387.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
González CV, Ibarra SE, Piccoli PN, Botto JF, Boccalandro HE (2012). Phytochrome B increases drought tolerance by enhancing ABA sensitivity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 35, 1958-1968.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
González-Grandío E, Poza-Carrión C, Sorzano COS, Cubas P (2013). BRANCHED1 promotes axillary bud dormancy in response to shade in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 834-850.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Gu DC, Ji RJ, He CM, Peng T, Zhang MY, Duan J, Xiong CY, Liu XC (2019). Arabidopsis histone methyltransferase SUVH5 is a positive regulator of light-mediated seed germination. Front Plant Sci 10, 841.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Han X, Yu H, Yuan RR, Yang Y, An FY, Qin GJ (2019). Arabidopsis transcription factor TCP5 controls plant thermomorphogenesis by positively regulating PIF4 activity. iScience 15, 611-622.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Hayashi F, Ichino T, Osanai M, Wada K (2000). Oscillation and regulation of proline content by P5CS and ProDH gene expressions in the light/dark cycles in Arabidopsis thaliana L. Plant Cell Physiol 41, 1096-1101.
PMID |
| [50] |
Hayes S, Pantazopoulou CK, van Gelderen K, Reinen E, Tween AL, Sharma A, de Vries M, Prat S, Schuurink RC, Testerink C, Pierik R (2019). Soil salinity limits plant shade avoidance. Curr Biol 29, 1669-1676.
DOI PMID |
| [51] |
Hornitschek P, Kohnen MV, Lorrain S, Rougemont J, Ljung K, López-Vidriero I, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Solano R, Trevisan M, Pradervand S, Xenarios I, Fankhauser C (2012). Phytochrome interacting factors 4 and 5 control seedling growth in changing light conditions by directly controlling auxin signaling. Plant J 71, 699-711.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Ibarra SE, Auge G, Sánchez RA, Botto JF (2013). Transcriptional programs related to phytochrome A function in Arabidopsis seed germination. Mol Plant 6, 1261-1273.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Jang S, Marchal V, Panigrahi KCS, Wenkel S, Soppe W, Deng XW, Valverde F, Coupland G (2008). Arabidopsis COP1 shapes the temporal pattern of CO accumulation conferring a photoperiodic flowering response. EMBO J 27, 1277-1288.
DOI URL |
| [54] | Jiang BC, Shi YT, Zhang XY, Xin XY, Qi LJ, Guo HW, Li JG, Yang SH (2017). PIF3 is a negative regulator of the CBF pathway and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E6695-E6702. |
| [55] |
Jiang JS, Xiao YM, Chen H, Hu W, Zeng LP, Ke HY, Ditengou FA, Devisetty U, Palme K, Maloof J, Dehesh K (2020). Retrograde induction of phyB orchestrates ethylene-auxin hierarchy to regulate growth. Plant Physiol 183, 1268-1280.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Jiang ZM, Xu G, Jing YJ, Tang WJ, Lin RC (2016). Phytochrome B and REVEILLE1/2-mediated signaling controls seed dormancy and germination in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 7, 12377.
DOI |
| [57] |
Jing YJ, Guo Q, Zha P, Lin RC (2019). The chromatin-remodelling factor PICKLE interacts with CONSTANS to promote flowering in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 42, 2495-2507.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Kang MY, Kwon HY, Kim NY, Sakuraba Y, Paek NC (2015). CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 10 (COP10)contributes to floral repression under non-inductive short days in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 16, 26493-26505.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Kebrom TH, Brutnell TP, Finlayson SA (2010). Suppression of sorghum axillary bud outgrowth by shade, phyB and defoliation signaling pathways. Plant Cell Environ 33, 48-58. |
| [60] |
Kim DH, Yamaguchi S, Lim S, Oh E, Park J, Hanada A, Kamiya Y, Choi G (2008a). SOMNUS, a CCCH-type zinc finger protein in Arabidopsis, negatively regulates light- dependent seed germination downstream of PIL5. Plant Cell 20, 1260-1277.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Kim SY, Yu XH, Michaels SD (2008b). Regulation of CONSTANS and FLOWERING LOCUS T expression in response to changing light quality. Plant Physiol 148, 269-279.
DOI URL |
| [62] | Kim W, Zeljković SĆ, Piskurewicz U, Megies C, Tarkowski P, Lopez-Molina L (2019). put2) and decaying seeds enhance phyA-media- ted germination by overcoming PIF1 repression of germination. PLoS Genet 15, e1008292. |
| [63] |
Koini MA, Alvey L, Allen T, Tilley CA, Harberd NP, White- lam GC, Franklin KA (2009). High temperature-mediated adaptations in plant architecture require the bHLH transcription factor PIF4. Curr Biol 19, 408-413.
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
Kovács H, Aleksza D, Baba AI, Hajdu A, Király AM, Zsigmond L, Tóth SZ, Kozma-Bognár L, Szabados L (2019). Light control of salt-induced proline accumulation is mediated by ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10, 1584.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
Kudo M, Kidokoro S, Yoshida T, Mizoi J, Todaka D, Fernie AR, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2017). Double overexpression of DREB and PIF transcription factors improves drought stress tolerance and cell elongation in transgenic plants. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 458-471.
DOI PMID |
| [66] |
Lau OS, Song ZJ, Zhou ZM, Davies KA, Chang J, Yang X, Wang SQ, Lucyshyn D, Tay IHZ, Wigge PA, Bergmann DC (2018). Direct control of SPEECHLESS by PIF4 in the high-temperature response of stomatal development. Curr Biol 28, 1273-1280.
DOI |
| [67] |
Laubinger S, Marchal V, Gentilhomme J, Wenkel S, Adrian J, Jang S, Kulajta C, Braun H, Coupland G, Hoecker U (2006). Arabidopsis SPA proteins regulate photoperiodic flowering and interact with the floral inducer CONSTANS to regulate its stability. Development 133, 3213-3222.
PMID |
| [68] |
Lee CM, Thomashow MF (2012). Photoperiodic regulation of the C-repeat binding factor (CBF) cold acclimation pathway and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 15054-15059.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Lee KP, Piskurewicz U, Tureckova V, Carat S, Chappuis R, Strnad M, Fankhauser C, Lopez-Molina L (2012). Spatially and genetically distinct control of seed germination by phytochromes A and B. Genes Dev 26, 1984-1996.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Legris M, Klose C, Burgie ES, Rojas CCR, Neme M, Hiltbrunner A, Wigge PA, Schäfer E, Vierstra RD, Casal JJ (2016). Phytochrome B integrates light and temperature signals in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 897-900.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
Li C, Qi LJ, Zhang SM, Dong XJ, Jing YJ, Cheng JK, Feng ZY, Peng J, Li H, Zhou YY, Wang XJ, Han R, Duan J, Terzaghi W, Lin RC, Li JG (2022). Mutual upregulation of HY5 and TZP in mediating phytochrome A signaling. Plant Cell 34, 633-654.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Li G, Siddiqui H, Teng YB, Lin RC, Wan XY, Li JG, Lau OS, Ouyang XH, Dai MQ, Wan JM, Devlin PF, Deng XW, Wang HY (2011). Coordinated transcriptional regulation underlying the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 13, 616-622.
DOI |
| [73] |
Li J, Terzaghi W, Gong YY, Li CR, Ling JJ, Fan YY, Qin NX, Gong XQ, Zhu DM, Deng XW (2020). Modulation of BIN2 kinase activity by HY5 controls hypocotyl elongation in the light. Nat Commun 11, 1592.
DOI PMID |
| [74] |
Li JM, Nagpal P, Vitart V, McMorris TC, Chory J (1996). A role for brassinosteroids in light-dependent development of Arabidopsis. Science 272, 398-401.
DOI PMID |
| [75] |
Li N, Bo CP, Zhang YY, Wang L (2021). PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORS PIF4 and PIF5 promote heat stress induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 72, 4577-4589.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Lin RC, Ding L, Casola C, Ripoll DR, Feschotte C, Wang HY (2007). Transposase-derived transcription factors regulate light signaling in Arabidopsis. Science 318, 1302-1305.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Liu J, Zhang F, Zhou JJ, Chen F, Wang BS, Xie XZ (2012). Phytochrome B control of total leaf area and stomatal density affects drought tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol 78, 289-300.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Mao ZL, He SB, Xu F, Wei XX, Jiang L, Liu Y, Wang WX, Li T, Xu PB, Du SS, Li L, Lian HL, Guo TT, Yang HQ (2020). Photoexcited CRY1 and phyB interact directly with ARF6 and ARF8 to regulate their DNA-binding activity and auxin-induced hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 225, 848-865.
DOI URL |
| [79] | Martínez C, Espinosa-Ruíz A, de Lucas M, Bernardo- García S, Franco-Zorrilla JM, Prat S (2018). PIF4-induced BR synthesis is critical to diurnal and thermomorphogenic growth. EMBO J 37, e99552. |
| [80] |
Murata Y, Mori IC, Munemasa S (2015). Diverse stomatal signaling and the signal integration mechanism. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66, 369-392.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Nir I, Shohat H, Panizel I, Olszewski N, Aharoni A, Weiss D (2017). The tomato DELLA protein PROCERA acts in guard cells to promote stomatal closure. Plant Cell 29, 3186-3197.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
Oh E, Kang H, Yamaguchi S, Park J, Lee D, Kamiya Y, Choi G (2009). Genome-wide analysis of genes targeted by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3-LIKE5 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21, 403-419.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
Oh E, Yamaguchi S, Hu JH, Yusuke J, Jung B, Paik I, Lee HS, Sun TP, Kamiya Y, Choi G (2007). PIL5, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH protein, regulates gibberellin responsiveness by binding directly to the GAI and RGA promoters in Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell 19, 1192-1208.
DOI URL |
| [84] | Oh E, Zhu JY, Bai MY, Arenhart RA, Sun Y, Wang ZY (2014). Cell elongation is regulated through a central circuit of interacting transcription factors in the Arabidopsis hypocotyl. eLife 3, e03031. |
| [85] |
Oh J, Park E, Song K, Bae G, Choi G (2020). PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR8 inhibits phytochrome A-mediated far-red light responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32, 186-205.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
Park J, Lee N, Kim W, Lim S, Choi G (2011). ABI3 and PIL5 collaboratively activate the expression of SOMNUS by directly binding to its promoter in imbibed Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell 23, 1404-1415.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
Park YJ, Lee HJ, Gil KE, Kim JY, Lee JH, Lee H, Cho HT, Vu LD, de Smet I, Park CM (2019). Developmental programming of thermonastic leaf movement. Plant Physiol 180, 1185-1197.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Park YJ, Lee HJ, Ha JH, Kim JY, Park CM (2017). COP1 conveys warm temperature information to hypocotyl thermomorphogenesis. New Phytol 215, 269-280.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Pham VN, Kathare PK, Huq E (2018). Phytochromes and phytochrome interacting factors. Plant Physiol 176, 1025-1038.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Piskurewicz U, Turečková V, Lacombe E, Lopez-Molina L (2009). Far-red light inhibits germination through DELLA- dependent stimulation of ABA synthesis and ABI3 activity. EMBO J 28, 2259-2271.
DOI PMID |
| [91] |
Qiu YJ, Li MN, Kim RJA, Moore CM, Chen M (2019). Daytime temperature is sensed by phytochrome B in Arabidopsis through a transcriptional activator HEMERA. Nat Commun 10, 140.
DOI |
| [92] |
Qu GP, Li H, Lin XL, Kong XX, Hu ZL, Jin YH, Liu Y, Song HL, Kim DH, Lin RC, Li JG, Jin JB (2020). Reversible sumoylation of FHY1 regulates phytochrome a signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 13, 879-893.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Quint M, Delker C, Franklin KA, Wigge PA, Halliday KJ, van Zanten M (2016). Molecular and genetic control of plant thermomorphogenesis. Nat Plants 2, 15190.
DOI PMID |
| [94] |
Reddy SK, Holalu SV, Casal JJ, Finlayson SA (2013). Abscisic acid regulates axillary bud outgrowth responses to the ratio of red to far-red light. Plant Physiol 163, 1047-1058.
DOI PMID |
| [95] |
Reymond MC, Brunoud G, Chauvet A, Martínez-Garcia JF, Martin-Magniette ML, Monéger F, Scutt CP (2012). A light-regulated genetic module was recruited to carpel development in Arabidopsis following a structural change to SPATULA. Plant Cell 24, 2812-2825.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Rolauffs S, Fackendahl P, Sahm J, Fiene G, Hoecker U (2012). Arabidopsis COP1 and SPA genes are essential for plant elongation but not for acceleration of flowering time in response to a low red light to far-red light ratio. Plant Physiol 160, 2015-2027.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Sakuraba Y, Bülbül S, Piao WL, Choi G, Paek NC (2017). Arabidopsis EARLY FLOWERING3 increases salt tolerance by suppressing salt stress response pathways. Plant J 92, 1106-1120.
DOI URL |
| [98] | Schwartz CJ, Lee J, Amasino R (2017). Variation in shade- induced flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana results from FLOWERING LOCUS T allelic variation. PLoS One 12, e0187768. |
| [99] |
Schwarz S, Grande AV, Bujdoso N, Saedler H, Huijser P (2008). The microRNA regulated SBP-box genes SPL9 and SPL15control shoot maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67, 183-195.
DOI PMID |
| [100] |
Seaton DD, Toledo-Ortiz G, Ganpudi A, Kubota A, Imaizumi T, Halliday KJ (2018). Dawn and photoperiod sensing by phytochrome A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 10523-10528.
DOI PMID |
| [101] |
Shi H, Wang X, Mo XR, Tang C, Zhong SW, Deng XW (2015). Arabidopsis DET1 degrades HFR1 but stabilizes PIF1 to precisely regulate seed germination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 3817-3822.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
Shi H, Zhong SW, Mo XR, Liu N, Nezames CD, Deng XW (2013). HFR1 sequesters PIF1 to govern the transcriptional network underlying light-initiated seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 3770-3784.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Shinomura T, Nagatani A, Hanzawa H, Kubota M, Watanabe M, Furuya M (1996). Action spectra for phytochrome A- and B-specific photoinduction of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 8129-8133.
PMID |
| [104] |
Shu K, Liu XD, Xie Q, He ZH (2016). Two faces of one seed: hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination. Mol Plant 9, 34-45.
DOI PMID |
| [105] | Soy J, Leivar P, González-Schain N, Sentandreu M, Prat S, Quail PH, Monte E (2012). Phytochrome-imposed oscillations in PIF3 protein abundance regulate hypocotyl growth under diurnal light/dark conditions in Arabidopsis. Plant J 71, 390-401. |
| [106] |
Stirnberg P, Zhao SQ, Williamson L, Ward S, Leyser O (2012). FHY3 promotes shoot branching and stress tole- rance in Arabidopsis in an AXR1-dependent manner. Plant J 71, 907-920.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001). The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4, 447-456.
DOI PMID |
| [108] |
Strasser B, Sánchez-Lamas M, Yanovsky MJ, Casal JJ, Cerdán PD (2010). Arabidopsis thaliana life without phytochromes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 4776-4781.
DOI PMID |
| [109] |
Sweere U, Eichenberg K, Lohrmann J, Mira-Rodado V, Bäurle I, Kudla J, Nagy F, Schäfer E, Harter K (2001). Interaction of the response regulator ARR4 with phytochrome B in modulating red light signaling. Science 294, 1108-1111.
PMID |
| [110] |
Tao Y, Ferrer JL, Ljung K, Pojer F, Hong FX, Long JA, Li L, Moreno JE, Bowman ME, Ivans LJ, Cheng YF, Lim J, Zhao YD, Ballaré CL, Sandberg G, Noel JP, Chory J (2008). Rapid synthesis of auxin via a new tryptophan- dependent pathway is required for shade avoidance in plants. Cell 133, 164-176.
DOI PMID |
| [111] |
Todaka D, Nakashima K, Maruyama K, Kidokoro S, Osakabe Y, Ito Y, Matsukura S, Fujita Y, Yoshiwara K, Ohme-Takagi M, Kojima M, Sakakibara H, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012). Rice phytochrome-interacting factor-like protein OsPIL1 functions as a key regulator of internode elongation and induces a morphological response to drought stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 15947-15952.
PMID |
| [112] | Toledo-Ortiz G, Johansson H, Lee KP, Bou-Torrent J, Stewart K, Steel G, Rodríguez-Concepción M, Halliday KJ (2014). The HY5-PIF regulatory module coordinates light and temperature control of photosynthetic gene transcription. PLoS Genet 10, e1004416. |
| [113] |
Vaistij FE, Gan YB, Penfield S, Gilday AD, Dave A, He ZS, Josse EM, Choi G, Halliday KJ, Graham IA (2013). Differential control of seed primary dormancy in Arabidopsis ecotypes by the transcription factor SPATULA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 10866-10871.
DOI PMID |
| [114] |
Valverde F, Mouradov A, Soppe W, Ravenscroft D, Samach A, Coupland G (2004). Photoreceptor regulation of CONSTANS protein in photoperiodic flowering. Science 303, 1003-1006.
DOI PMID |
| [115] |
Wang F, Chen XX, Dong SJ, Jiang XC, Wang LY, Yu JQ, Zhou YH (2020a). Crosstalk of PIF4 and DELLA modulates CBF transcript and hormone homeostasis in cold response in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J 18, 1041-1055.
DOI URL |
| [116] |
Wang F, Guo ZX, Li HZ, Wang MM, Onac E, Zhou J, Xia XJ, Shi K, Yu JQ, Zhou YH (2016). Phytochrome A and B function antagonistically to regulate cold tolerance via abscisic acid-dependent jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol 170, 459-471.
DOI PMID |
| [117] |
Wang F, Wang XJ, Zhang Y, Yan JR, Ahammed GJ, Bu X, Sun X, Liu YF, Xu T, Qi HY, Qi MF, Li TL (2022a). SlFHY3 and SlHY5 act compliantly to enhance cold tolerance through the integration of myo-inositol and light signaling in tomato. New Phytol 233, 2127-2143.
DOI URL |
| [118] |
Wang F, Wu N, Zhang LY, Ahammed GL, Chen XX, Xiang X, Zhou J, Xia XJ, Shi K, Yu JQ, Foyer CH, Zhou YH (2018). Light signaling-dependent regulation of photoinhibition and photoprotection in tomato. Plant Physiol 176, 1311-1326.
DOI PMID |
| [119] |
Wang F, Yan JR, Ahammed GJ, Wang XJ, Bu X, Xiang HZ, Li YB, Lu JZ, Liu YF, Qi HY, Qi MF, Li TL (2020b). PGR5/PGRL1 and NDH mediate far-red light-induced photoprotection in response to chilling stress in tomato. Front Plant Sci 11, 669.
DOI URL |
| [120] |
Wang F, Zhang LY, Chen XX, Wu XD, Xiang X, Zhou J, Xia XJ, Shi K, Yu JQ, Foyer CH, Zhou YH (2019a). SlHY5 integrates temperature, light, and hormone signaling to balance plant growth and cold tolerance. Plant Physiol 179, 749-760.
DOI URL |
| [121] |
Wang L, Wang B, Jiang L, Liu X, Li XL, Lu ZF, Meng XB, Wang YH, Smith SM, Li JY (2015). Strigolactone signaling in Arabidopsis regulates shoot development by targeting D53-like SMXL repressor proteins for ubiquitination and degradation. Plant Cell 27, 3128-3142.
DOI URL |
| [122] |
Wang M, Le Moigne MA, Bertheloot J, Crespel L, Perez- Garcia MD, Ogé L, Demotes-Mainard S, Hamama L, Davière JM, Sakr S (2019b). BRANCHED1: a key hub of shoot branching. Front Plant Sci 10, 76.
DOI URL |
| [123] |
Wang Y, Su C, Yu YJ, He YQ, Wei H, Li N, Li H, Duan J, Li B, Li JG, Davis SJ, Wang L (2022b). Time FOR COFFEE regulates phytochrome A-mediated hypocotyl growth through dawn-phased signaling. Plant Cell 34, 2907-2924.
DOI URL |
| [124] | Woods DP, Ream TS, Minevich G, Hobert O, Amasino RM (2014). PHYTOCHROME C is an essential light receptor for photoperiodic flowering in the temperate grass, Brachypodium distachyon. Genetics 198, 397-408. |
| [125] |
Xiao YM, Savchenko T, Baidoo EE, Chehab WE, Hayden DM, Tolstikov V, Corwin JA, Kliebenstein DJ, Keasling JD, Dehesh K (2012). Retrograde signaling by the plastidial metabolite MEcPP regulates expression of nuclear stress-response genes. Cell 149, 1525-1535.
DOI PMID |
| [126] |
Xie YR, Liu Y, Wang H, Ma XJ, Wang BB, Wu GX, Wang HY (2017). Phytochrome-interacting factors directly suppress MIR156 expression to enhance shade-avoidance syndrome in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 8, 348.
DOI |
| [127] |
Xie YR, Zhou Q, Zhao YP, Li QQ, Liu Y, Ma MD, Wang BB, Shen RX, Zheng ZG, Wang HY (2020). FHY3 and FAR1 integrate light signals with the miR156-SPL module-mediated aging pathway to regulate Arabidopsis flowering. Mol Plant 13, 483-498.
DOI URL |
| [128] |
Xu X, Wang Q, Li WQ, Hu TX, Wang QQ, Yin Y, Liu XH, He S, Zhang MK, Liang Y, Zhu JH, Zhan XQ (2022). Overexpression of SlBBX17 affects plant growth and enhances heat tolerance in tomato. Int J Biol Macromol 206, 799-811.
DOI URL |
| [129] |
Yamaguchi A, Kobayashi Y, Goto K, Abe M, Araki T (2005). TWIN SISTER OF FT (TSF) acts as a floral pathway integrator redundantly with FT. Plant Cell Physiol 46, 1175-1189.
DOI PMID |
| [130] |
Yan Y, Li C, Dong XJ, Li H, Zhang D, Zhou YY, Jiang BC, Peng J, Qin XY, Cheng JK, Wang XJ, Song PY, Qi LJ, Zheng Y, Li BS, Terzaghi W, Yang SH, Guo Y, Li JG (2020). MYB30 is a key negative regulator of Arabidopsis photomorphogenic development that promotes PIF4 and PIF5 protein accumulation in the light. Plant Cell 32, 2196-2215.
DOI URL |
| [131] |
Yang LW, Jiang ZM, Jing YJ, Lin RC (2020). PIF1 and RVE1 form a transcriptional feedback loop to control light- mediated seed germination in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 1372-1384.
DOI URL |
| [132] | Yu YW, Wang J, Zhang ZJ, Quan RD, Zhang HW, Deng XW, Ma LG, Huang RF (2013). Ethylene promotes hypocotyl growth and HY5 degradation by enhancing the movement of COP1 to the nucleus in the light. PLoS Genet 9, e1004025. |
| [133] |
Yuan CQ, Ahmad S, Cheng TR, Wang J, Pan HT, Zhao LJ, Zhang QX (2018a). Red to far-red light ratio modulates hormonal and genetic control of axillary bud outgrowth in chrysanthemum (Dendranthema grandiflorum ‘Jinba’). Int J Mol Sci 19, 1590.
DOI URL |
| [134] |
Yuan TT, Xu HH, Zhang Q, Zhang LY, Lu YT (2018b). The COP1 target SHI-RELATED SEQUENCE5 directly activates photomorphogenesis-promoting genes. Plant Cell 30, 2368-2382.
DOI URL |
| [135] | Zhang LL, Shao YJ, Ding L, Wang MJ, Davis SJ, Liu JX (2021). XBAT31 regulates thermoresponsive hypocotyl growth through mediating degradation of the thermosensor ELF3 in Arabidopsis. Sci Adv 7, eabf4427. |
| [136] |
Zhang RS, Yang CW, Jiang YP, Li L (2019). A PIF7-CONSTANS-centered molecular regulatory network underlying shade-accelerated flowering. Mol Plant 12, 1587-1597.
DOI PMID |
| [137] |
Zhang SM, Li C, Zhou YY, Wang XJ, Li H, Feng ZY (2018). TANDEM ZINC-FINGER/PLUS3 is a key component of phytochrome A signaling. Plant Cell 30, 835-852.
DOI URL |
| [138] |
Zhang XY, Huai JL, Shang FF, Xu G, Tang WJ, Jing YJ, Lin RC (2017). A PIF1/PIF3-HY5-BBX23 transcription factor cascade affects photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol 174, 2487-2500.
DOI PMID |
| [139] |
Zhong SW, Shi H, Xue C, Wei N, Guo HW, Deng XW (2014). Ethylene-orchestrated circuitry coordinates a seedling’s response to soil cover and etiolated growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 3913-3920.
DOI URL |
| [140] |
Zhou Y, Xun QQ, Zhang DZ, Lv MH, Ou Y, Li J (2019). TCP transcription factors associate with PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4 and CRYPTOCHROME 1 to regulate thermomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. iScience 15, 600-610.
DOI PMID |
| [141] | Zhou YY, Yang L, Duan J, Cheng JK, Shen YP, Wang XJ, Han R, Li H, Li Z, Wang LH, Terzaghi W, Zhu DM, Chen HD, Deng XW, Li JG (2018). Hinge region of Arabidopsis phyA plays an important role in regulating phyA function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E11864-E11873. |
| [1] | 上官瑶瑶, 苏世平, 顾雪丹, 张正中, 赵祜, 李毅, 魏星宇. 红砂幼苗对光周期和光质配比的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 788-800. |
| [2] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [3] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [4] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [5] | 周文杰, 张文瀚, 贾玮, 许自成, 黄五星. 植物miRNA响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 810-833. |
| [6] | 罗燕, 刘奇源, 吕元兵, 吴越, 田耀宇, 安田, 李振华. 拟南芥光敏色素突变体种子萌发的光温敏感性[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 752-762. |
| [7] | 陈艳晓, 李亚萍, 周晋军, 解丽霞, 彭永彬, 孙伟, 和亚男, 蒋聪慧, 王增兰, 郑崇珂, 谢先芝. 拟南芥光敏色素B氨基酸位点突变对其结构与功能的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 481-494. |
| [8] | 顾家琦, 朱福慧, 谢沛豪, 孟庆营, 郑颖, 张献龙, 袁道军. 棉属光敏色素PHY基因家族的全基因组鉴定与驯化选择分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 34-53. |
| [9] | 仲昭暄, 张冬瑞, 李璐, 苏颖, 王黛宁, 王泽冉, 刘洋, 常缨. 香鳞毛蕨dfr-miR160a和靶基因DfARF10的生物信息学及表达模式分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 22-33. |
| [10] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [11] | 曾鑫海, 陈锐, 师宇, 盖超越, 范凯, 李兆伟. 植物SPL转录因子的生物功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 982-997. |
| [12] | 张嘉, 李启东, 李翠, 王庆海, 侯新村, 赵春桥, 李树和, 郭强. 植物MATE转运蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 461-474. |
| [13] | 任晓童, 张冉冉, 魏绍巍, 罗晓峰, 徐佳慧, 舒凯. 种子际微生物研究展望[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 499-509. |
| [14] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [15] | 吴霖升, 张永光, 章钊颖, 张小康, 吴云飞. 日光诱导叶绿素荧光遥感及其在陆地生态系统监测中的应用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(10): 1167-1199. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||