

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (5): 810-833.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24020 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24020
收稿日期:2024-02-18
接受日期:2024-05-04
出版日期:2024-09-10
发布日期:2024-08-19
通讯作者:
黄五星
基金资助:
Wenjie Zhou, Wenhan Zhang, Wei Jia, Zicheng Xu, Wuxing Huang*( )
)
Received:2024-02-18
Accepted:2024-05-04
Online:2024-09-10
Published:2024-08-19
Contact:
Wuxing Huang
摘要: 干旱、极端温度、盐和重金属等非生物胁迫导致植物产量和品质下降。miRNA是一类长约20-24个核苷酸的内源性非编码小分子RNA, 通过形成miRNA介导的沉默复合物(RISC)剪切靶mRNA并抑制靶基因的翻译, 在转录后水平负调控真核生物基因表达。高通量测序技术的快速发展使得植物物种中大量响应非生物胁迫的miRNA得到鉴定和表征。非生物胁迫下植物miRNA与其靶基因结合, 构成了控制各种生命活动的大型基因调控网络, 包括生长发育、营养吸收与分配、信号转导与氧化应激, 从而提高植物的抗逆性。深入理解miRNA的功能及其调控机制对于通过基因工程进行作物改良和抗逆育种至关重要。该文综述了近年来miRNA的生物合成及其作用机制研究进展, 重点探讨了参与调控植物响应非生物胁迫miRNA的鉴定及功能, 并展望了该领域可能的研究方向。
周文杰, 张文瀚, 贾玮, 许自成, 黄五星. 植物miRNA响应非生物胁迫研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 810-833.
Wenjie Zhou, Wenhan Zhang, Wei Jia, Zicheng Xu, Wuxing Huang. Advances in Plant miRNAs Responses to Abiotic Stresses. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(5): 810-833.
| 名称 | 取样部位 | 胁迫处理类型和时间 | miRNA差异 表达数量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | 全幼苗 | 200 mmol·L-1甘露醇7天(干旱胁迫) | 123 | Pegler et al., |
| 全幼苗 | 昼夜温度为32°C/28°C 7天(高温胁迫) | 121 | Pegler et al., | |
| 全幼苗 | 150 mmol·L-1氯化钠7天(盐胁迫) | 118 | Pegler et al., | |
| 叶片通气组织 | 放置4°C下4小时(低温胁迫) | 93 | Tiwari et al., | |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | 叶片组织 | 放置4°C下5小时(低温胁迫) | 23 | Shen et al., |
| 叶片 | 不浇水直至出现典型症状(干旱胁迫) | 64 | Cheah et al., | |
| 茎 | 不浇水直至出现典型症状(干旱胁迫) | 71 | Cheah et al., | |
| 全幼苗 | 200 mmol·L-1氯化钠2天(盐胁迫) | 164 | Chen et al., | |
| 具有乳熟期颖果的小穗 | 昼夜温度为38°C/22°C 6小时(高温胁迫) | 96 | Payne et al., | |
| 全幼苗 | 昼夜温度为10°C/8°C 5天(低温胁迫) | 26 | Zhao et al., | |
| 玉米 (Zea mays) | 每株第4片叶 | 昼夜温度为25°C/4°C, 直至该叶片完全成熟(低温胁迫) | 65 | Aydinoglu, |
| 每株第10片叶中部 | 昼夜温度为40°C/25°C 5天(高温胁迫) | 102 | Zhang et al., | |
| 叶片 | 16%聚乙二醇24小时(干旱胁迫) | 68 | Wei et al., | |
| 根系 | 200 mmol·L-1氯化钠24小时(盐胁迫) | 98 | Ding et al., | |
| 马铃薯 (Solanum tuberosum) | 第3片完全展开的叶片 | 放置0°C下4小时(低温胁迫) | 136 | Yan et al., |
| 全植株 | 去除培养液6小时(干旱胁迫) | 230 | Shin et al., | |
| 叶片组织 | 放置35°C下1小时(高温胁迫) | 204 | 张国栋, | |
| 根系 | 50 mmol·L-1 NaHCO3 24小时(盐胁迫) | 169 | 康益晨, | |
| 番茄(S. lycopersicum) | 长度为6.0-6.5 mm的花蕾雄蕊 | 昼夜温度为35°C/30°C 2天(高温胁迫) | 69 | Pan et al., |
| 长度为6.0-6.5 mm的花蕾雌蕊 | 昼夜温度为35°C/30°C 12天(高温胁迫) | 30 | Pan et al., | |
| 根系 | 5%聚乙二醇7天(干旱胁迫) | 101 | Candar-Cakir et al., | |
| 茎顶端第3片叶 | 放置4°C下48小时(低温胁迫) | 49 | Cao et al., | |
| 根系 | 200 mmol·L-1氯化钠12小时(盐胁迫) | 145 | Wang et al., | |
| 烟草 (Nicotiana tabacum) | 叶片 | 放置6°C下24小时(低温胁迫) | 25 | Hu et al., |
| 叶片 | 不浇水10天(干旱胁迫) | 32 | Chen et al., | |
| 叶片 | 100 mmol·L-1氯化钠24小时(盐胁迫) | 33 | Xu et al., | |
| 小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | 幼穗 | 放置0°C下48小时(低温胁迫) | 39 | Song et al., |
| 叶片组织 | 放置37°C下5天(高温胁迫) | 79 | Ragupathy et al., | |
| 旗叶 | 保持土壤含水率为田间容量的一半(6%) (干旱胁迫) | 54 | Liu et al., | |
| 全植株 | 150 mmol·L-1氯化钠24小时(盐胁迫) | 222 | Feng et al., | |
| 根和叶组织 | 脱水处理8小时(干旱胁迫) | 141 | Kantar et al., | |
| 冠状组织 | 自然条件下冬季生育期(低温胁迫) | 92 | Wang et al., |
表1 响应植物非生物胁迫miRNAs的测序鉴定
Table 1 Sequencing and identification of plant abiotic stress response miRNAs
| 名称 | 取样部位 | 胁迫处理类型和时间 | miRNA差异 表达数量 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | 全幼苗 | 200 mmol·L-1甘露醇7天(干旱胁迫) | 123 | Pegler et al., |
| 全幼苗 | 昼夜温度为32°C/28°C 7天(高温胁迫) | 121 | Pegler et al., | |
| 全幼苗 | 150 mmol·L-1氯化钠7天(盐胁迫) | 118 | Pegler et al., | |
| 叶片通气组织 | 放置4°C下4小时(低温胁迫) | 93 | Tiwari et al., | |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | 叶片组织 | 放置4°C下5小时(低温胁迫) | 23 | Shen et al., |
| 叶片 | 不浇水直至出现典型症状(干旱胁迫) | 64 | Cheah et al., | |
| 茎 | 不浇水直至出现典型症状(干旱胁迫) | 71 | Cheah et al., | |
| 全幼苗 | 200 mmol·L-1氯化钠2天(盐胁迫) | 164 | Chen et al., | |
| 具有乳熟期颖果的小穗 | 昼夜温度为38°C/22°C 6小时(高温胁迫) | 96 | Payne et al., | |
| 全幼苗 | 昼夜温度为10°C/8°C 5天(低温胁迫) | 26 | Zhao et al., | |
| 玉米 (Zea mays) | 每株第4片叶 | 昼夜温度为25°C/4°C, 直至该叶片完全成熟(低温胁迫) | 65 | Aydinoglu, |
| 每株第10片叶中部 | 昼夜温度为40°C/25°C 5天(高温胁迫) | 102 | Zhang et al., | |
| 叶片 | 16%聚乙二醇24小时(干旱胁迫) | 68 | Wei et al., | |
| 根系 | 200 mmol·L-1氯化钠24小时(盐胁迫) | 98 | Ding et al., | |
| 马铃薯 (Solanum tuberosum) | 第3片完全展开的叶片 | 放置0°C下4小时(低温胁迫) | 136 | Yan et al., |
| 全植株 | 去除培养液6小时(干旱胁迫) | 230 | Shin et al., | |
| 叶片组织 | 放置35°C下1小时(高温胁迫) | 204 | 张国栋, | |
| 根系 | 50 mmol·L-1 NaHCO3 24小时(盐胁迫) | 169 | 康益晨, | |
| 番茄(S. lycopersicum) | 长度为6.0-6.5 mm的花蕾雄蕊 | 昼夜温度为35°C/30°C 2天(高温胁迫) | 69 | Pan et al., |
| 长度为6.0-6.5 mm的花蕾雌蕊 | 昼夜温度为35°C/30°C 12天(高温胁迫) | 30 | Pan et al., | |
| 根系 | 5%聚乙二醇7天(干旱胁迫) | 101 | Candar-Cakir et al., | |
| 茎顶端第3片叶 | 放置4°C下48小时(低温胁迫) | 49 | Cao et al., | |
| 根系 | 200 mmol·L-1氯化钠12小时(盐胁迫) | 145 | Wang et al., | |
| 烟草 (Nicotiana tabacum) | 叶片 | 放置6°C下24小时(低温胁迫) | 25 | Hu et al., |
| 叶片 | 不浇水10天(干旱胁迫) | 32 | Chen et al., | |
| 叶片 | 100 mmol·L-1氯化钠24小时(盐胁迫) | 33 | Xu et al., | |
| 小麦 (Triticum aestivum) | 幼穗 | 放置0°C下48小时(低温胁迫) | 39 | Song et al., |
| 叶片组织 | 放置37°C下5天(高温胁迫) | 79 | Ragupathy et al., | |
| 旗叶 | 保持土壤含水率为田间容量的一半(6%) (干旱胁迫) | 54 | Liu et al., | |
| 全植株 | 150 mmol·L-1氯化钠24小时(盐胁迫) | 222 | Feng et al., | |
| 根和叶组织 | 脱水处理8小时(干旱胁迫) | 141 | Kantar et al., | |
| 冠状组织 | 自然条件下冬季生育期(低温胁迫) | 92 | Wang et al., |
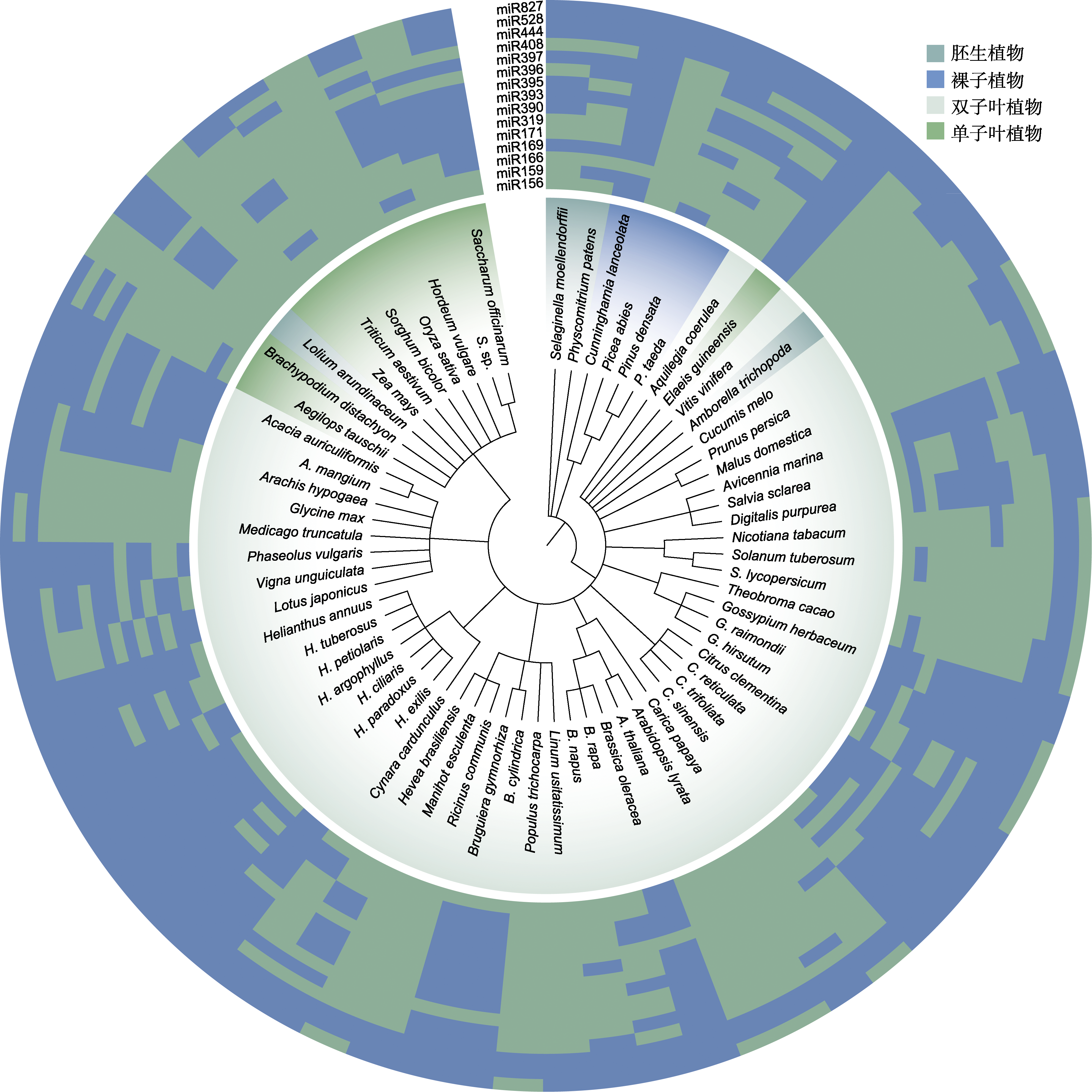
图2 响应植物非生物胁迫miRNAs在不同植物物种中的分布 含有miRNA的植物物种按照NCBI分类进化树进行排列, 热图基质中的绿色元素表示该miRNA在该物种中存在, 蓝色元素表示该miRNA在该物种中不存在。
Figure 2 Distribution of miRNAs responding to plant abiotic stress in different plant species Plant species containing miRNA are arranged according to the NCBI taxonomic evolutionary tree. In the heat map, green elements matrix indicate that the miRNA is present in the species, while the blue elements indicate that the miRNA is not present in the species.
| miRNA | 靶基因 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR156 | SPLs | 调节植物生长时期的转变, 促进生长发育和果实成熟, 增强光合作用, 提高作物产量 | 芦梦荻, |
| miR159 | MYB33、MYB65和MYB101 | 促进种子萌发, 转导激素信号, 调节气孔数量 | Guo et al., |
| miR166 | HD-ZipIII家族 | 维持渗透平衡, 改善养分吸收, 促进根系生长, 调节脱落酸和生长素信号转导 | Li et al., |
| miR169 | NF-YA家族 | 调节种子发芽和根系伸长, 提高光合速率 | Jiao et al., |
| miR171 | SCL6 | 促进植物根系发育, 转导光化学信号和激素信号 | Sun et al., |
| miR319 | TCP4/14/21和PCF5/6/8 | 控制叶片形态, 调节植物发育和昼夜节律 | Fang et al., |
| miR390 | TAS3和ARF2/3/4 | 控制侧根发育, 转导激素信号 | Lin et al., |
| miR393 | TIR1和AFBs | 转导生长素信号, 调节气孔开闭 | Yuan et al., |
| miR395 | SULTR2;1、SULTR2;2和APS1/3/4 | 调节植物硫代谢, 促进光合作用, 减少氧化损伤 | Sunkar et al., |
| miR396 | GRFs | 促进营养吸收, 调节生长发育, 调节氮代谢 | 何彬等, |
| miR397 | LACs | 调控木质素合成及细胞壁厚度 | Huang et al., |
| miR408 | LACs和铜氧还蛋白编码基因 | 调节铜稳态, 参与光合作用和光形态发生, 维持活性氧平衡 | Hu et al., |
| miR444 | MADS23/25/27/57/61 | 调控营养元素吸收, 参与激素信号转导, 调节根系发育 | 黄圣, |
| miR528 | LAC3/5和AO | 调节抗氧化酶活性, 减少氧化损伤 | Guo et al., |
| miR827 | SPX结构域基因和WRKY48 | 调节营养发育, 控制气孔密度 | Lin et al., |
表2 响应植物非生物胁迫miRNAs的靶基因及功能
Table 2 Target genes and functions of miRNAs in plant response to abiotic stresses
| miRNA | 靶基因 | 功能 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR156 | SPLs | 调节植物生长时期的转变, 促进生长发育和果实成熟, 增强光合作用, 提高作物产量 | 芦梦荻, |
| miR159 | MYB33、MYB65和MYB101 | 促进种子萌发, 转导激素信号, 调节气孔数量 | Guo et al., |
| miR166 | HD-ZipIII家族 | 维持渗透平衡, 改善养分吸收, 促进根系生长, 调节脱落酸和生长素信号转导 | Li et al., |
| miR169 | NF-YA家族 | 调节种子发芽和根系伸长, 提高光合速率 | Jiao et al., |
| miR171 | SCL6 | 促进植物根系发育, 转导光化学信号和激素信号 | Sun et al., |
| miR319 | TCP4/14/21和PCF5/6/8 | 控制叶片形态, 调节植物发育和昼夜节律 | Fang et al., |
| miR390 | TAS3和ARF2/3/4 | 控制侧根发育, 转导激素信号 | Lin et al., |
| miR393 | TIR1和AFBs | 转导生长素信号, 调节气孔开闭 | Yuan et al., |
| miR395 | SULTR2;1、SULTR2;2和APS1/3/4 | 调节植物硫代谢, 促进光合作用, 减少氧化损伤 | Sunkar et al., |
| miR396 | GRFs | 促进营养吸收, 调节生长发育, 调节氮代谢 | 何彬等, |
| miR397 | LACs | 调控木质素合成及细胞壁厚度 | Huang et al., |
| miR408 | LACs和铜氧还蛋白编码基因 | 调节铜稳态, 参与光合作用和光形态发生, 维持活性氧平衡 | Hu et al., |
| miR444 | MADS23/25/27/57/61 | 调控营养元素吸收, 参与激素信号转导, 调节根系发育 | 黄圣, |
| miR528 | LAC3/5和AO | 调节抗氧化酶活性, 减少氧化损伤 | Guo et al., |
| miR827 | SPX结构域基因和WRKY48 | 调节营养发育, 控制气孔密度 | Lin et al., |
| [1] | Achkar NP, Cho SK, Poulsen C, Arce AL, Re DA, Giudicatti AJ, Karayekov E, Ryu MY, Choi SW, Harholt J, Casal JJ, Yang SW, Manavella PA (2018). A quick HYL1- dependent reactivation of microRNA production is required for a proper developmental response after extended periods of light deprivation. Dev Cell 46, 236-247. |
| [2] | Ali S, Huang SL, Zhou JJ, Bai YS, Liu Y, Shi LY, Liu S, Hu ZL, Tang YL (2023). MiR397-LACs mediated cadmium stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 113, 415-430. |
| [3] | Aukerman MJ, Sakai H (2003). Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 15, 2730-2741. |
| [4] | Aydinoglu F (2020). Elucidating the regulatory roles of microRNAs in maize (Zea mays L.) leaf growth response to chilling stress. Planta 251, 38. |
| [5] | Bai B, Bian HW, Zeng ZH, Hou N, Shi B, Wang JH, Zhu MY, Han N (2017). MiR393-mediated auxin signaling regulation is involved in root elongation inhibition in response to toxic aluminum stress in barley. Plant Cell Physiol 58, 426-439. |
| [6] | Bajczyk M, Jarmolowski A, Jozwiak M, Pacak A, Pietrykowska H, Sierocka I, Swida-Barteczka A, Szewc L, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2023). Recent insights into plant miRNA biogenesis: multiple layers of miRNA level regulation. Plants 12, 342. |
| [7] | Balyan S, Kansal S, Jajo R, Behere PR, Chatterjee R, Raghuvanshi S (2023). Delineating the tissue-mediated drought stress governed tuning of conserved miR408 and its targets in rice. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 187. |
| [8] | Bao WL, O'Malley DM, Whetten R, Sederoff RR (1993). A laccase associated with lignification in loblolly pine xylem. Science 260, 672-674. |
| [9] | Baranauskė S, Mickutė M, Plotnikova A, Finke A, Venclovas Č, Klimašauskas S, Vilkaitis G (2015). Functional mapping of the plant small RNA methyltransferase: HEN1 physically interacts with HYL1 and DICER-LIKE 1 proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 43, 2802-2812. |
| [10] | Barrera-Rojas CH, Braga Rocha GH, Polverari L, Pinheiro Brito DA, Batista DS, Notini MM, Ferreira da Cruz AC, Ortiz Morea EG, Sabatini S, Otoni WC, Silveira Nogueira FT (2020). MiR156-targeted SPL10 controls Arabidopsis root meristem activity and root-derived de novo shoot regeneration via cytokinin responses. J Exp Bot 71, 934-950. |
| [11] | Barrera-Rojas CH, Vicente MH, Brito DAP, Silva EM, Lopez AM, Ferigolo LF, do Carmo RM, Silva CMS, Silva GFF, Correa JPO, Notini MM, Freschi L, Cubas P, Nogueira FTS (2023). Tomato miR156-targeted SlSBP15 represses shoot branching by modulating hormone dynamics and interacting with GOBLET and BRANCHED1b. J Exp Bot 74, 5124-5139. |
| [12] | Baulies JL, Bresso EG, Goldy C, Palatnik JF, Schommer C (2022). Potent inhibition of TCP transcription factors by miR319 ensures proper root growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 108, 93-103. |
| [13] | Baumberger N, Baulcombe DC (2005). Arabidopsis ARGONAUT1 is an RNA slicer that selectively recruits microRNAs and short interfering RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 11928-11933. |
| [14] | Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J, Doerks T, Stark A, Bork P, Izaurralde E (2006). MRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4: NOT deadenylase and DCP1: DCP2 decapping complexes. Genes Dev 20, 1885- 1898. |
| [15] | Bologna NG, Iselin R, Abriata LA, Sarazin A, Pumplin N, Jay F, Grentzinger T, Dal Peraro M, Voinnet O (2018). Nucleo-cytosolic shuttling of ARGONAUTE1 prompts a revised model of the plant microRNA pathway. Mol Cell 69, 709-719. |
| [16] | Bologna NG, Mateos JL, Bresso EG, Palatnik JF (2009). A loop-to-base processing mechanism underlies the biogenesis of plant microRNAs miR319 and miR159. EMBO J 28, 3646-3656. |
| [17] | Braun JE, Huntzinger E, Fauser M, Izaurralde E (2011). GW182 proteins directly recruit cytoplasmic deadenylase complexes to miRNA targets. Mol Cell 44, 120-133. |
| [18] | Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto YY, Sieburth L, Voinnet O (2008). Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 320, 1185-1190. |
| [19] | Cai XW, Zhang LF, Xiao L, Wen Z, Hou QD, Yang K (2022). Genome-wide identification of GRF gene family and their contribution to abiotic stress response in pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus). Int J Biol Macromol 223, 618- 635. |
| [20] | Cai ZM, Wang YN, Zhu L, Tian YP, Chen L, Sun ZX, Ullah I, Li X (2017). GmTIR1/GmAFB3-based auxin perception regulated by miR393 modulates soybean nodulation. New Phytol 215, 672-686. |
| [21] | Candar-Cakir B, Arican E, Zhang BH (2016). Small RNA and degradome deep sequencing reveals drought- and tissue-specific micrornas and their important roles in drought-sensitive and drought-tolerant tomato genotypes. Plant Biotechnol J 14, 1727-1746. |
| [22] | Cao X, Wu Z, Jiang FL, Zhou R, Yang ZE (2014). Identification of chilling stress-responsive tomato microRNAs and their target genes by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. BMC Genomics 15, 1130. |
| [23] | Cheah BH, Nadarajah K, Divate MD, Wickneswari R (2015). Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage. BMC Genomics 16, 692. |
| [24] | Chen CYA, Zheng DH, Xia ZF, Shyu AB (2009). Ago- TNRC6 triggers microRNA-mediated decay by promoting two deadenylation steps. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16, 1160- 1166. |
| [25] | Chen L, Luan YS, Zhai JM (2015). Sp-miR396a-5p acts as a stress-responsive genes regulator by conferring tolerance to abiotic stresses and susceptibility to Phytophthora nicotianae infection in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 34, 2013-2025. |
| [26] | Chen QS, Li M, Zhang ZC, Tie WW, Chen X, Jin LF, Zhai N, Zheng QX, Zhang JF, Wang R, Xu GY, Zhang H, Liu PP, Zhou HN (2017). Integrated mRNA and microRNA analysis identifies genes and small miRNA molecules associated with transcriptional and post-transcriptional- level responses to both drought stress and re-watering treatment in tobacco. BMC Genomics 18, 62. |
| [27] | Chen XM (2004). A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 303, 2022-2025. |
| [28] | Chen Y, Yang WL, Gao RF, Chen YL, Zhou Y, Xie JK, Zhang FT (2023). Genome-wide analysis of microRNAs and their target genes in dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) responding to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci 24, 4069. |
| [29] | Chen ZH, Bao ML, Sun YZ, Yang YJ, Xu XH, Wang JH, Han N, Bian HW, Zhu MY (2011). Regulation of auxin response by miR393-targeted transport inhibitor response protein 1 is involved in normal development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 77, 619-629. |
| [30] | Chendrimada TP, Finn KJ, Ji XJ, Baillat D, Gregory RI, Liebhaber SA, Pasquinelli AE, Shiekhattar R (2007). MicroRNA silencing through RISC recruitment of eIF6. Nature 447, 823-828. |
| [31] | Chu Y, Bai WL, Wang P, Li FG, Zhan JJ, Ge XY (2022). The mir390-GhCEPR2 module confers salt tolerance in cotton and Arabidopsis. Ind Crops Prod 190, 115865. |
| [32] | Dalmadi Á, Gyula P, Bálint J, Szittya G, Havelda Z (2019). AGO-unbound cytosolic pool of mature miRNAs in plant cells reveals a novel regulatory step at AGO1 loading. Nucleic Acids Res 47, 9803-9817. |
| [33] | Dastidar MG, Scarpa A, Mägele I, Ruiz-Duarte P, von Born P, Bald L, Jouannet V, Maizel A (2019). ARF5/ MONOPTEROS directly regulates miR390 expression in the Arabidopsis thaliana primary root meristem. Plant Direct 3, e00116. |
| [34] | de Felippes FF, Marchais A, Sarazin A, Oberlin S, Voinnet O (2017). A single miR390 targeting event is sufficient for triggering TAS3-tasiRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 5539-5554. |
| [35] | Denver JB, Ullah H (2019). MiR393s regulate salt stress response pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana through scaffold protein RACK1A mediated ABA signaling pathways. Plant Signal Behav 14, 1600394. |
| [36] | Ding BS, Yue Y, Chen X, Long XH, Zhou ZS (2024). Identification and expression analysis of miR396 and its target genes in Jerusalem artichoke under temperature stress. Gene 893, 147908. |
| [37] | Ding D, Zhang LF, Wang H, Liu ZJ, Zhang ZX, Zheng YL (2009). Differential expression of miRNAs in response to salt stress in maize roots. Ann Bot 103, 29-38. |
| [38] | Dong XX, Guan YH, Zhang ZH, Li H (2022). MiR390-tasiRNA3-ARF4 pathway is involved in regulating flowering time in woodland strawberry. Plant Cell Rep 41, 921-934. |
| [39] | Dong ZC, Han MH, Fedoroff N (2008). The RNA-binding proteins HYL1 and SE promote accurate in vitro processing of pri-miRNA by DCL1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 9970-9975. |
| [40] | Du H, Liu HB, Xiong LZ (2013). Endogenous auxin and jasmonic acid levels are differentially modulated by abiotic stresses in rice. Front Plant Sci 4, 397. |
| [41] | Elbashir SM, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001). RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs. Genes Dev 15, 188-200. |
| [42] | Fang YJ, Zheng YQ, Lu W, Li J, Duan YJ, Zhang S, Wang YP (2021). Roles of miR319-regulated TCPs in plant development and response to abiotic stress. Crop J 9, 17- 28. |
| [43] | Feng JP, Hu Z, Zhang MM, Wang XL, Yi Q, Zhu SP, Zhao XC (2023). Effect of Cre-miR171 on drought stress response in citrus. J Southwest Univer (Nat Sci Edi) 45 (7), 123-137. (in Chinese) |
| 冯继鹏, 胡洲, 张曼曼, 汪小利, 易倩, 朱世平, 赵晓春 (2023). Cre-miR171在柑橘响应干旱胁迫中的作用. 西南大学学报(自然科学版) 45(7),123-137. | |
| [44] | Feng KW, Nie XJ, Cui LC, Deng PC, Wang MX, Song WN (2017). Genome-wide identification and characterization of salinity stress-responsive miRNAs in wild emmer wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. dicoccoides). Genes 8, 156. |
| [45] | Feyissa BA, Renaud J, Nasrollahi V, Kohalmi SE, Hannoufa A (2020). Transcriptome-IPMS analysis reveals a tissue-dependent miR156/SPL13 regulatory mechanism in alfalfa drought tolerance. BMC Genomics 21, 721. |
| [46] | Fire A, Xu SQ, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC (1998). Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391, 806-811. |
| [47] | Fracasso A, Vallino M, Staropoli A, Vinale F, Amaducci S, Carra A (2021). Increased water use efficiency in miR396-downregulated tomato plants. Plant Sci 303, 110729. |
| [48] | Fukaya T, Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y (2014). MicroRNAs block assembly of eIF4F translation initiation complex in Drosophila. Mol Cell 56, 67-78. |
| [49] | Gallardo K, Courty PE, Le Signor C, Wipf D, Vernoud V (2014). Sulfate transporters in the plant’s response to drought and salinity: regulation and possible functions. Front Plant Sci 5, 580. |
| [50] | Gandikota M, Birkenbihl RP, Höhmann S, Cardon GH, Saedler H, Huijser P (2007). The miRNA156/157 recognition element in the 3′UTR of the Arabidopsis SBP box gene SPL3 prevents early flowering by translational inhibition in seedlings. Plant J 49, 683-693. |
| [51] | Gao P, Bai X, Yang L, Lv DK, Li Y, Cai H, Ji W, Guo DJ, Zhu YM (2010). Over-expression of osa-MIR396c decreases salt and alkali stress tolerance. Planta 231, 991- 1001. |
| [52] | Gao Y, Feng BH, Gao CX, Zhang HQ, Wen FT, Tao LX, Fu GF, Xiong J (2022). The evolution and functional roles of miR408 and its targets in plants. Int J Mol Sci 23, 530. |
| [53] | German MA, Pillay M, Jeong DH, Hetawal A, Luo SJ, Janardhanan P, Kannan V, Rymarquis LA, Nobuta K, German R, De Paoli E, Lu C, Schroth G, Meyers BC, Green PJ (2008). Global identification of microRNA-target RNA pairs by parallel analysis of RNA ends. Nat Biotechnol 26, 941-946. |
| [54] | Ghorecha V, Patel K, Ingle S, Sunkar R, Krishnayya NSR (2014). Analysis of biochemical variations and microRNA expression in wild (Ipomoea campanulata) and cultivated (Jacquemontia pentantha) species exposed to in vivo water stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 20, 57-67. |
| [55] | Gonzalo L, Tossolini I, Gulanicz T, Cambiagno DA, Kasprowicz-Maluski A, Smolinski DJ, Mammarella MF, Ariel FD, Marquardt S, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Jarmolowski A, Manavella PA (2022). R-loops at microRNA encoding loci promote co-transcriptional processing of pri-miRNAs in plants. Nat Plants 8, 402-418. |
| [56] | Gu M, Meng DQ, Xu GH (2016). Identification and expression analysis of tobacco microRNA827 and their target genes. J Nanjing Agricul Univer 39, 965-972. (in Chinese) |
| 顾冕, 孟大千, 徐国华 (2016). 烟草microRNA827及其靶基因的鉴定与分析. 南京农业大学学报 39, 965-972. | |
| [57] | Guo CK, Jiang YQ, Shi M, Wu X, Wu G (2021). ABI5 acts downstream of miR159 to delay vegetative phase change in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 231, 339-350. |
| [58] | Guo LL, Shen JJ, Zhang CJ, Guo Q, Liang HY, Hou XG (2022a). Characterization and bioinformatics analysis of ptc-miR396g-5p in response to drought stress of Paeonia ostii. Noncoding RNA Res 7, 150-158. |
| [59] | Guo XR, Niu JF, Cao XY (2018). Heterologous expression of Salvia miltiorrhiza microRNA408 enhances tolerance to salt stress in Nicotiana benthamiana. Int J Mol Sci 19, 3985. |
| [60] | Guo Y, Wang YF, Chen H, Du QG, Wang ZH, Gong XP, Sun Q, Li WX (2023). Nitrogen supply affects ion homeostasis by modifying root casparian strip formation through the miR528-LAC3module in maize. Plant Commun 4, 100553. |
| [61] | Guo ZL, Kuang Z, Zhao YX, Deng Y, He H, Wan MM, Tao YH, Wang D, Wei JH, Li L, Yang XZ (2022b). PmiREN2.0: from data annotation to functional exploration of plant microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 50, D1475-D1482. |
| [62] | Hackenberg M, Shi BJ, Gustafson P, Langridge P (2013). Characterization of phosphorus-regulated miR399 and miR827 and their isomirs in barley under phosphorus- sufficient and phosphorus-deficient conditions. BMC Plant Biol 13, 214. |
| [63] | Hamza NB, Sharma N, Tripathi A, Sanan-Mishra N (2016). MicroRNA expression profiles in response to drought stress in Sorghum bicolor. Gene Expr Patterns 20, 88-98. |
| [64] | Han H, Zhou Y (2022). Function and regulation of microRNA171 in plant stem cell homeostasis and developmental programing. Int J Mol Sci 23, 2544. |
| [65] | Han MH, Goud S, Song L, Fedoroff N (2004). The Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA-binding protein HYL1 plays a role in microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 1093-1098. |
| [66] | Han XY, Tang SJ, Ma X, Liu WW, Yang RJ, Zhang SB, Wang NN, Song XW, Fu CX, Yang RX, Cao XF (2024). Blocking miR528 function promotes tillering and regrowth in switchgrass. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 712-721. |
| [67] | Hang N, Shi TR, Liu YR, Ye WX, Taier G, Sun Y, Wang KH, Zhang WJ (2021). Overexpression of Os-microRNA408 enhances drought tolerance in perennial ryegrass. Physiol Plant 172, 733-747. |
| [68] | Hasan MN, Mosharaf MP, Uddin KS, Das KR, Sultana N, Noorunnahar M, Naim D, Mollah MNH (2023). Genome-wide identification and characterization of major RNAi genes highlighting their associated factors in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.). BioMed Res Int 2023, 8832406. |
| [69] | He B, Wang YD, Song SW (2022). Research progress on miR396-GRF module regulating plant stress response. Plant Sci J 40, 437-447. (in Chinese) |
| 何彬, 王俞丹, 宋世威 (2022). miR396-GRF模块参与植物逆境胁迫响应的研究进展. 植物科学学报 40, 437-447. | |
| [70] | He F, Long RC, Wei CX, Zhang YX, Li MN, Kang JM, Yang QC, Wang Z, Chen L (2022). Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the SPL gene family and its important role in salt stress in Medicago sativa L. BMC Plant Biol 22, 295. |
| [71] | He F, Xu CZ, Fu XK, Shen Y, Guo L, Leng M, Luo KM (2018). The MicroRNA390/TRANS-ACTING SHORT INTERFERING RNA3 module mediates lateral root growth under salt stress via the auxin pathway. Plant Physiol 177, 775-791. |
| [72] | Höck J, Meister G (2008). The Argonaute protein family. Genome Biol 9, 210. |
| [73] | Hou QC, Ufer G, Bartels D (2016). Lipid signaling in plant responses to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ 39, 1029-1048. |
| [74] | Hsieh LC, Lin SI, Shih ACC, Chen JW, Lin WY, Tseng CY, Li WH, Chiou TJ (2009). Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol 151, 2120-2132. |
| [75] | Hu RS, Li ZM, Xiang SP, Li YY, Yi PF, Xiao MQ, Zhang XW (2019). Comparative microRNA profiling reveals the cold response mechanisms in two contrasting tobacco cultivars. Int J Agric Biol 22, 757-762. |
| [76] | Hu YJ, Ji JY, Cheng H, Luo RL, Zhang J, Li WJ, Wang XS, Zhang J, Yao YC (2023). The miR408a-BBP-LAC3/ CSD1 module regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis mediated by crosstalk between copper homeostasis and ROS homeostasis during light induction in Malus plants. J Adv Res 51, 27-44. |
| [77] | Huang JH, Zhang LY, Lin XJ, Gao Y, Zhang J, Huang WL, Zhao DQ, Ferrarezi RS, Fan GC, Chen LS (2022). CsiLAC4 modulates boron flow in Arabidopsis and Citrus via high-boron-dependent lignification of cell walls. New Phytol 233, 1257-1273. |
| [78] | Huang S (2022). MiR444f Regulates Rice Root Development Through Gibberellin. Master’s thesis. Jinan: Shandong Normal University. pp. 53-75. (in Chinese) |
| 黄圣 (2022). miR444f通过赤霉素调控水稻根系的发育. 硕士论文. 济南: 山东师范大学. pp. 53-75. | |
| [79] | Huang SL, Zhou JJ, Gao L, Tang YL (2021). Plant miR397 and its functions. Funct Plant Biol 48, 361-370. |
| [80] | Huang TS, Xing ZT, Wu SH, Duan WH, Li L, Wang Q, Song HM, Meng LH, Xu XB (2023). Silencing of miR171d/e in tomato enhances salt tolerance of plant and improves fruit nutritional quality. Preprints. [2023-07-11]. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202307.0733.v1. |
| [81] | Huang W, Peng SY, Xian ZQ, Lin DB, Hu GJ, Yang L, Ren MZ, Li ZG (2017). Overexpression of a tomato miR171 target gene SlGRAS24 impacts multiple agronomical traits via regulating gibberellin and auxin homeostasis. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 472-488. |
| [82] | Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E (2011). Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet 12, 99-110. |
| [83] | Iki T, Yoshikawa M, Nishikiori M, Jaudal MC, Matsumoto-Yokoyama E, Mitsuhara I, Meshi T, Ishikawa M (2010). In vitro assembly of plant RNA-induced silencing complexes facilitated by molecular chaperone HSP90. Mol Cell 39, 282-291. |
| [84] | Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y (2013). Molecular insights into microRNA-mediated translational repression in plants. Mol Cell 52, 591-601. |
| [85] | Jagadeeswaran G, Li YF, Sunkar R (2014). Redox signaling mediates the expression of a sulfate-deprivation-inducible microRNA395 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 77, 85-96. |
| [86] | Jia HY, Aadland K, Kolaczkowski O, Kolaczkowski B (2021). Direct molecular evidence for an ancient, conserved developmental toolkit controlling posttranscriptional gene regulation in land plants. Mol Biol Evol 38, 4765-4777. |
| [87] | Jiang JJ, Zhu HT, Li N, Batley J, Wang YP (2022a). The miR393-target module regulates plant development and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 23, 9477. |
| [88] | Jiang SL, Chen QJ, Zhang QL, Zhang Y, Hao NN, Ou CQ, Wang F, Li TZ (2018). Pyr-miR171f-targeted PyrSCL6 and PyrSCL22 genes regulate shoot growth by responding to IAA signaling in pear. Tree Genet Genomes 14, 20. |
| [89] | Jiang YQ, Wu X, Shi M, Yu J, Guo CK (2022b). The miR159-MYB33-ABI5 module regulates seed germination in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 174, e13659. |
| [90] | Jiao XM, Wang HC, Yan JJ, Kong XY, Liu YW, Chu JF, Chen XY, Fang RX, Yan YS (2020). Promotion of BR biosynthesis by miR444 is required for ammonium-triggered inhibition of root growth. Plant Physiol 182, 1454- 1466. |
| [91] | Jiao ZY, Lian CL, Han S, Huang MB, Shen C, Li Q, Niu MX, Yu X, Yin WL, Xia XL (2021). PtmiR169o plays a positive role in regulating drought tolerance and growth by targeting the PtNF-YA6 gene in poplar. Environ Exp Bot 189, 104549. |
| [92] | Jing WK, Gong FF, Liu GQ, Deng YL, Liu JQ, Yang WJ, Sun XM, Li YH, Gao JP, Zhou XF, Ma N (2023). Petal size is controlled by the MYB73/TPL/HDA19-miR159- CKX6 module regulating cytokinin catabolism in Rosa hybrida. Nat Commun 14, 7106. |
| [93] | Joshi GAN, Chauhan C, Das S (2021). Sequence and functional analysis of MIR319 promoter homologs from Brassica juncea reveals regulatory diversification and altered expression under stress. Mol Genet Genomics 296, 731-749. |
| [94] | Kang YC (2021). Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Solanum tuberosum L. in Response to Alkaline Salt Stress. PhD dissertation. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural Uni- versity. pp. 68-82. (in Chinese) |
| 康益晨 (2021). 马铃薯响应碱性盐胁迫的生理及分子机制研究. 博士论文. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. pp. 68-82. | |
| [95] | Kantar M, Lucas SJ, Budak H (2011). MiRNA expression patterns of Triticum dicoccoides in response to shock drought stress. Planta 233, 471-484. |
| [96] | Kawashima CG, Matthewman CA, Huang SQ, Lee BR, Yoshimoto N, Koprivova A, Rubio-Somoza I, Todesco M, Rathjen T, Saito K, Takahashi H, Dalmay T, Kopriva S (2011). Interplay of SLIM1 and miR395 in the regulation of sulfate assimilation in Arabidopsis. Plant J 66, 863- 876. |
| [97] | Kiriakidou M, Tan GS, Lamprinaki S, De Planell-Saguer M, Nelson PT, Mourelatos Z (2007). An mRNA m7G cap binding-like motif within human Ago2 represses translation. Cell 129, 1141-1151. |
| [98] | Kozomara A, Birgaoanu M, Griffiths-Jones S (2019). MiRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res 47, D155-D162. |
| [99] | Kumar RS, Sinha H, Datta T, Asif MH, Trivedi PK (2023). microRNA408 and its encoded peptide regulate sulfur assimilation and arsenic stress response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 192, 837-856. |
| [100] | Kuzuoğlu-Öeztüerk D, Huntzinger E, Schmidt S, Izaurralde E (2012). The Caenorhabditis elegans GW182 protein AIN-1 interacts with PAB-1 and subunits of the PAN2-PAN3 and CCR4-NOT deadenylase complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 40, 5651-5665. |
| [101] | Lan ZX (2022). Mechanism Associated to MiR159- 3p Mediated Low Temperature Resistance of Graft Watermelon. Master’s thesis. Yangling: Northwest A&F University. pp. 8-20. (in Chinese) |
| 兰治香 (2022). miR159-3p调控嫁接西瓜低温抗性的作用机制解析. 硕士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. pp. 8-20. | |
| [102] | Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993). The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843-854. |
| [103] | Leyva-González MA, Ibarra-Laclette E, Cruz-Ramírez A, Herrera-Estrella L (2012). Functional and transcriptome analysis reveals an acclimatization strategy for abiotic stress tolerance mediated by Arabidopsis NF-YA family members. PLoS One 7, e48138. |
| [104] | Li HY, Wang J, Yan R, Wang CX, Sun HM (2021). Functional characterization of the MiR171a promoter and endogenous target mimics identification in Lilium pumilum DC. Fisch. during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 144, 345-357. |
| [105] | Li LC, Yang KB, Wang SN, Lou YF, Zhu CL, Gao ZM (2020a). Genome-wide analysis of laccase genes in moso bamboo highlights PeLAC10 involved in lignin biosynthesis and in response to abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 39, 751-763. |
| [106] | Li LH, Wang ZN, Xu RH (2022). Research progress on AGL17-like clade family in rice (Oryza sativa). J Agricul Biotechnol 30, 1606-1613. (in Chinese) |
| 李鲁华, 王忠妮, 徐如宏 (2022). 水稻AGL17-like亚家族研究进展. 农业生物技术学报 30, 1606-1613. | |
| [107] | Li M, Yu B (2021). Recent advances in the regulation of plant miRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol 18, 2087-2096. |
| [108] | Li N, Yang TX, Guo ZY, Wang QS, Chai M, Wu MB, Li XQ, Li WY, Li GX, Tang JH, Tang GL, Zhang ZH (2020b). Maize microRNA166 inactivation confers plant development and abiotic stress resistance. Int J Mol Sci 21, 9506. |
| [109] | Li SB, Liu L, Zhuang XH, Yu Y, Liu XG, Cui X, Ji LJ, Pan ZQ, Cao XF, Mo BX, Zhang FC, Raikhel N, Jiang LW, Chen XM (2013). MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 153, 562-574. |
| [110] | Li Y, Vasupalli N, Cai O, Lin XF, Wu HY (2023a). Network of miR396-mRNA in tissue differentiation in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Plants 12, 1103. |
| [111] | Li YN, Wang XL, Guo QX, Zhang XS, Zhou LX, Zhang Y, Zhang CY (2022). Conservation and diversity of miR166 family members from highbush blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) and their potential functions in abiotic stress. Front Genet 13, 919856. |
| [112] | Li YY, Liu Y, Gao ZH, Wang F, Xu T, Qi MF, Liu YF, Li TL (2023b). MicroRNA162 regulates stomatal conductance in response to low night temperature stress via abscisic acid signaling pathway in tomato. Front Plant Sci 14, 1045112. |
| [113] | Lin SI, Santi C, Jobet E, Lacut E, El Kholti N, Karlowski WM, Verdeil JL, Breitler JC, Perin C, Ko SS, Guiderdoni E, Chiou TJ, Echeverria M (2010). Complex regulation of two target genes encoding SPX-MFS proteins by rice miR827 in response to phosphate starvation. Plant Cell Physiol 51, 2119-2131. |
| [114] | Lin WY, Lin YY, Chiang SF, Syu C, Hsieh LC, Chiou TJ (2018). Evolution of microRNA827 targeting in the plant kingdom. New Phytol 217, 1712-1725. |
| [115] | Lin YL, Lin LX, Lai RL, Liu WH, Chen YK, Zhang ZH, Xu XH, Lai ZX (2015). MicroRNA390-directed TAS3 cleavage leads to the production of tasiRNA-ARF3/4 during somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Front Plant Sci 6, 1119. |
| [116] | Liu C, Cai J, Chu HL, Gao Y, Wu LF, Han LH (2022). Molecular characteristics of miR395 and its research progress in regulating plant sulfur homeostasis. Plant Physiol J 58, 1629-1638. (in Chinese) |
| 刘潮, 蔡建, 褚洪龙, 高永, 吴丽芳, 韩利红 (2022). miR395分子特征及其在调控植物硫稳态中的研究进展. 植物生理学报 58, 1629-1638. | |
| [117] | Liu HH, Tian X, Li YJ, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2008). Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 14, 836-843. |
| [118] | Liu HP, Able AJ, Able JA (2020). Integrated analysis of small RNA, transcriptome, and degradome sequencing reveals the water-deficit and heat stress response network in durum wheat. Int J Mol Sci 21, 6017. |
| [119] | Liu P, Wu XL, Gong BB, Lü GY, Li JR, Gao HB (2022). Review of the mechanisms by which transcription factors and exogenous substances regulate ROS metabolism under abiotic stress. Antioxidants 11, 2106. |
| [120] | Liu QP, Hu HC, Zhu LY, Li RC, Feng Y, Zhang LQ, Yang YY, Liu XQ, Zhang HM (2015). Involvement of miR528 in the regulation of arsenite tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Agric Food Chem 63, 8849-8861. |
| [121] | Liu TY, Huang TK, Yang SY, Hong YT, Huang SM, Wang FN, Chiang SF, Tsai SY, Lu WC, Chiou TJ (2016). Identification of plant vacuolar transporters mediating phosphate storage. Nat Commun 7, 11095. |
| [122] | Liu WW (2016). The Mechanisms of miR827-NLA-NRT1.7 Circuit Regulates Source-to-sink Remobilization of Nitrate in Arabidopsis. PhD dissertation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. pp. 30-44. (in Chinese) |
| 刘文文 (2016). miR827-NLA-NRT1.7通路调控拟南芥硝态氮由源到库的机制研究. 博士论文. 北京: 中国农业科学院. pp. 30-44. | |
| [123] | Liu XW, Xia B, Purente N, Chen B, Zhou YW, He M (2021). Transgenic Chrysanthemum indicum overexpressing cin- miR396a exhibits altered plant development and reduced salt and drought tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 168, 17-26. |
| [124] | Liu YR, Wang KX, Li DY, Yan JP, Zhang WJ (2017). Enhanced cold tolerance and tillering in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) by heterologous expression of Osa- miR393a. Plant Cell Physiol 58, 2226-2240. |
| [125] | Llave C, Xie ZX, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2002). Cleavage of Scarecrow-like mRNA targets directed by a class of Arabidopsis miRNA. Science 297, 2053-2056. |
| [126] | Lobbes D, Rallapalli G, Schmidt DD, Martin C, Clarke J (2006). Serrate: a new player on the plant microRNA scene. EMBO Rep 7, 1052-1058. |
| [127] | Lu HC, Chen L, Du MJ, Lu HQ, Liu J, Ye SH, Tao BL, Li RH, Zhao L, Wen J, Yi B, Tu JX, Fu TD, Shen JX (2023). MiR319 and its target TCP4 involved in plant architecture regulation in Brassica napus. Plant Sci 326, 111531. |
| [128] | Lu L, Luo WR, Yu WJ, Zhou JG, Wang XF, Sun YD (2022). Identification and characterization of csa-miR395s reveal their involvements in fruit expansion and abiotic stresses in cucumber. Front Plant Sci 13, 907364. |
| [129] | Lu MD (2021). Screening Upstream Transcription Factors of Mir156/miR171 and Functional Verification of AKIN10 in Citrus Somatic Embryogenesis. Master’s thesis. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University. pp. 22-34. |
| 芦梦荻 (2021). 调控柑橘体细胞胚发生的miR156和miR171上游转录因子筛选及AKIN10功能验证. 硕士论文. 武汉: 华中农业大学. pp. 22-34. | |
| [130] | Lu YZ, Feng Z, Liu XY, Bian LY, Xie H, Zhang CL, Mysore KS, Liang JS (2018). MiR393 and miR390 synergistically regulate lateral root growth in rice under different conditions. BMC Plant Biol 18, 261. |
| [131] | Luan MD, Xu MY, Lu YM, Zhang L, Fan YL, Wang L (2015). Expression of zma-miR169 miRNAs and their target ZmNF-YA genes in response to abiotic stress in maize leaves. Gene 555, 178-185. |
| [132] | Ma C, Burd S, Lers A (2015). miR408 is involved in abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 84, 169-187. |
| [133] | Ma Y, Xue H, Zhang F, Jiang Q, Yang S, Yue PT, Wang F, Zhang YY, Li LG, He P, Zhang ZH (2021). The miR156/ SPL module regulates apple salt stress tolerance by activating MdWRKY100 expression. Plant Biotechnol J 19, 311-323. |
| [134] | Marin E, Jouannet V, Herz A, Lokerse AS, Weijers D, Vaucheret H, Nussaume L, Crespi MD, Maizel A (2010). MiR390, Arabidopsis TAS3 tasiRNAs, and their AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR targets define an autoregulatory network quantitatively regulating lateral root growth. Plant Cell 22, 1104-1117. |
| [135] | Mathonnet G, Fabian MR, Svitkin YV, Parsyan A, Huck L, Murata T, Biffo S, Merrick WC, Darzynkiewicz E, Pillai RS, Filipowicz W, Duchaine TF, Sonenberg N (2007). MicroRNA inhibition of translation initiation in vitro by targeting the cap-binding complex eIF4F. Science 317, 1764-1767. |
| [136] | Mi SJ, Cai T, Hu YG, Chen YM, Hodges E, Ni FR, Wu L, Li S, Zhou HY, Long CZ, Chen S, Hannon GJ, Qi YJ (2008). Sorting of small RNAs into Arabidopsis argonaute complexes is directed by the 5′ terminal nucleotide. Cell 133, 116-127. |
| [137] | Millar AA, Lohe A, Wong G (2019). Biology and function of miR159 in plants. Plants 8, 255. |
| [138] | Millar AA, Waterhouse PM (2005). Plant and animal microRNAs: similarities and differences. Funct Integr Genomics 5, 129-135. |
| [139] | Muchate NS, Nikalje GC, Rajurkar NS, Suprasanna P, Nikam TD (2016). Plant salt stress: adaptive responses, tolerance mechanism and bioengineering for salt tolerance. Bot Rev 82, 371-406. |
| [140] | Murphy D, Dancis B, Brown JR (2008). The evolution of core proteins involved in microRNA biogenesis. BMC Evol Biol 8, 92. |
| [141] | Nguyen DQ, Brown CW, Pegler JL, Eamens AL, Grof CPL (2020). Molecular manipulation of microRNA397 abundance influences the development and salt stress response of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 21, 7879. |
| [142] | Nottrott S, Simard MJ, Richter JD (2006). Human let-7a miRNA blocks protein production on actively translating polyribosomes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13, 1108-1114. |
| [143] | O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C (2018). Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol 9, 402. |
| [144] | Pachamuthu K, Hari Sundar V, Narjala A, Singh RR, Das S, Avik Pal HCY, Shivaprasad PV (2022). Nitrate-dependent regulation of miR444-OsMADS27 signaling cascade controls root development in rice. J Exp Bot 73, 3511- 3530. |
| [145] | Pan CT, Ye L, Zheng Y, Wang Y, Yang DD, Liu X, Chen LF, Zhang YW, Fei ZJ, Lu G (2017). Identification and expression profiling of microRNAs involved in the stigma exsertion under high-temperature stress in tomato. BMC Genomics 18, 843. |
| [146] | Park W, Li JJ, Song RT, Messing J, Chen XM (2002). CARPEL FACTORY, a dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol 12, 1484-1495. |
| [147] | Payne D, Li YF, Govindan G, Kumar A, Thomas J, Addo- Quaye CA, Pereira A, Sunkar R (2023). High daytime temperature responsive microRNA profiles in developing grains of rice varieties with contrasting chalkiness. Int J Mol Sci 24, 11631. |
| [148] | Pegler JL, Nguyen DQ, Grof CPL, Eamens AL (2020). Profiling of the salt stress responsive microRNA landscape of C4 genetic model species Setaria viridis (L.). Beauv. Agronomy 10, 837. |
| [149] | Pegler JL, Nguyen DQ, Oultram JMJ, Grof CPL, Eamens AL (2021a). Molecular manipulation of the miR396/GRF expression module alters the salt stress response of Arabidopsis thaliana. Agronomy 11, 1751. |
| [150] | Pegler JL, Nguyen DQ, Oultram JMJ, Grof CPL, Eamens AL (2021b). Molecular manipulation of the miR396 and miR399 expression modules alters the response of Arabidopsis thaliana to phosphate stress. Plants 10, 2570. |
| [151] | Pegler JL, Oultram JMJ, Grof CPL, Eamens AL (2019). Profiling the abiotic stress responsive microRNA landscape of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 8, 58. |
| [152] | Pei LL, Zhang LL, Liu X, Jiang J (2023). Role of microRNA miR171 in plant development. PeerJ 11, e15632. |
| [153] | Pietrykowska H, Sierocka I, Zielezinski A, Alisha A, Carrasco-Sanchez JC, Jarmolowski A, Karlowski WM, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2022). Biogenesis, conservation, and function of miRNA in liverworts. J Exp Bot 73, 4528-4545. |
| [154] | Qi YJ, Denli AM, Hannon GJ (2005). Biochemical specialization within Arabidopsis RNA silencing pathways. Mol Cell 19, 421-428. |
| [155] | Qin RD, Hu YM, Chen H, Du QG, Yang J, Li WX (2023). MicroRNA408 negatively regulates salt tolerance by affecting secondary cell wall development in maize. Plant Physiol 192, 1569-1583. |
| [156] | Ragupathy R, Ravichandran S, Mahdi MSR, Huang D, Reimer E, Domaratzki M, Cloutier S (2016). Deep sequencing of wheat sRNA transcriptome reveals distinct temporal expression pattern of miRNAs in response to heat, light and UV. Sci Rep 6, 39373. |
| [157] | Ranocha P, Chabannes M, Chamayou S, Danoun S, Jauneau A, Boudet AM, Goffner D (2002). Laccase down-regulation causes alterations in phenolic metabolism and cell wall structure in poplar. Plant Physiol 129, 145-155. |
| [158] | Rao S, Balyan S, Jha S, Mathur S (2020). Novel insights into expansion and functional diversification of MIR169 family in tomato. Planta 251, 55. |
| [159] | Rao S, Gupta A, Bansal C, Sorin C, Crespi M, Mathur S (2022). A conserved HSF: miR169: NF-YA loop involved in tomato and Arabidopsis heat stress tolerance. Plant J 112, 7-26. |
| [160] | Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002). MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16, 1616-1626. |
| [161] | Ren GD, Xie M, Zhang SX, Vinovskis C, Chen XM, Yu B (2014). Methylation protects microRNAs from an AGO1- associated activity that uridylates 5' RNA fragments generated by AGO1 cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 6365-6370. |
| [162] | Rhaman MS, Imran S, Karim MM, Chakrobortty J, Mahamud MA, Sarker P, Tahjib-Ul-Arif M, Robin AHK, Ye WX, Murata Y, Hasanuzzaman M (2021). 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated plant adaptive responses to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Rep 40, 1451-1469. |
| [163] | Shen JQ, Xie KB, Xiong LZ (2010). Global expression profiling of rice microRNAs by one-tube stem-loop reverse transcription quantitative PCR revealed important roles of microRNAs in abiotic stress responses. Mol Genet Genomics 284, 477-488. |
| [164] | Shen XX, Ping YK, Bao CN, Liu C, Tahir MM, Li XW, Song Y, Xu WR, Ma FW, Guan QM (2023). Mdm-miR160- MdARF17-MdWRKY33 module mediates freezing tolerance in apple. Plant J 114, 262-278. |
| [165] | Shi QF, Tian DD, Wang JY, Chen AL, Miao YQ, Chen YM, Li J, Wu XM, Zheng B, Guo WW, Shi XP (2023). Overexpression of miR390b promotes stem elongation and height growth in Populus. Hortic Res 10, uhac258. |
| [166] | Shin SJ, Lee JH, Kwon HB (2017). Genome-wide identification and characterization of drought responsive microRNAs in Solanum tuberosum L. Genes Genomics 39, 1193-1203. |
| [167] | Silvestro D, Bacon CD, Ding WN, Zhang QY, Donoghue PCJ, Antonelli A, Xing YW (2021). Fossil data support a pre-cretaceous origin of flowering plants. Nat Ecol Evol 5, 449-457. |
| [168] | Singh A, Gandhi N, Mishra V, Yadav S, Rai V, Sarkar AK (2020). Role of abiotic stress responsive miRNAs in Arabidopsis root development. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 29, 733-742. |
| [169] | Singh A, Roy S, Singh S, Das SS, Gautam V, Yadav S, Kumar A, Singh A, Samantha S, Sarkar AK (2017). Phytohormonal crosstalk modulates the expression of miR166/165s, target Class III HD-ZIPs, and KANADI genes during root growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Rep 7, 3408. |
| [170] | Siré C, Moreno AB, Garcia-Chapa M, López-Moya JJ, Segundo BS (2009). Diurnal oscillation in the accumulation of Arabidopsis microRNAs, miR167, miR168, miR171 and miR398. FEBS Lett 583, 1039-1044. |
| [171] | Song GQ, Zhang RZ, Zhang SJ, Li YL, Gao J, Han XD, Chen ML, Wang J, Li W, Li GY (2017). Response of microRNAs to cold treatment in the young spikes of common wheat. BMC Genomics 18, 212. |
| [172] | Sorin C, Declerck M, Christ A, Blein T, Ma LN, Lelandais-Brière C, Njo MF, Beeckman T, Crespi M, Hartmann C (2014). A miR169 isoform regulates specific NF-YA targets and root architecture in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 202, 1197-1211. |
| [173] | Souret FF, Kastenmayer JP, Green PJ (2004). AtXRN4 degrades mRNA in Arabidopsis and its substrates include selected miRNA targets. Mol Cell 15, 173-183. |
| [174] | Stepien A, Knop K, Dolata J, Taube M, Bajczyk M, Barciszewska-Pacak M, Pacak A, Jarmolowski A, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2017). Posttranscriptional coordination of splicing and miRNA biogenesis in plants. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 8, e1403. |
| [175] | Su ZX, Di YF, Li JX, Wang X, Zhang F, Yi HL (2023). Identification and functional analysis of miR156 family and its target genes in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Plant Growth Regul 99, 149-160. |
| [176] | Sun MZ, Yang JK, Cai XX, Shen Y, Cui N, Zhu YM, Jia BW, Sun XL (2018). The opposite roles of OsmiR408 in cold and drought stress responses in Oryza sativa. Mol Breed 38, 120. |
| [177] | Sun XD, Wang CD, Xiang N, Li X, Yang SH, Du JC, Yang YP, Yang YQ (2017). Activation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis by miR319-targeted TCP4 transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 1284-1294. |
| [178] | Sun XZ (2022). Tae-miR444a Mediates Target TaMADS57 Regulating Winter Wheat Response to Low Temperature Stress. Master’s thesis. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural Uni- versity. pp. 27-52. (in Chinese) |
| 孙仙泽 (2022). 冬小麦tae-miR444a调控其靶基因TaMADS57响应低温胁迫的分子机制. 硕士论文. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学. pp. 27-52. | |
| [179] | Sun ZC, Kumar RMS, Li JS, Yang GM, Xie Y (2022). In silico search and biological validation of MicroR171 family related to abiotic stress response in mulberry (Morus alba). Hortic Plant J 8, 184-194. |
| [180] | Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu JH, Zhu JK (2007). Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci 12, 301-309. |
| [181] | Thiebaut F, Rojas CA, Almeida KL, Grativol C, Domiciano GC, Lamb CRC, De Almeida Engler J, Hemerly AS, Ferreira PCG (2012). Regulation of miR319 during cold stress in sugarcane. Plant Cell Environ 35, 502-512. |
| [182] | Tian CY, Zhou CZ, Zhu C, Chen L, Shi BY, Lin YL, Lai ZX, Guo YQ (2022). Genome-wide investigation of the miR166 family provides new insights into its involvement in the drought stress responses of tea plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze). Forests 13, 628. |
| [183] | Tiwari B, Habermann K, Arif MA, Weil HL, Garcia-Molina A, Kleine T, Mühlhaus T, Frank W (2020). Identification of small RNAs during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 20, 298. |
| [184] | Tomassi AH, Re DA, Romani F, Cambiagno DA, Gonzalo L, Moreno JE, Arce AL, Manavella PA (2020). The intrinsically disordered protein CARP9 bridges HYL1 to AGO1 in the nucleus to promote microRNA activity. Plant Physiol 184, 316-329. |
| [185] | Um T, Choi J, Park T, Chung PJ, Jung SE, Shim JS, Kim YS, Choi IY, Park SC, Oh SJ, Seo JS, Kim JK (2022). Rice microRNA171f/SCL6 module enhances drought tole- rance by regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis genes. Plant Direct 6, e374. |
| [186] | Valiollahi E, Farsi M, Kakhki AM (2014). Sly-miR166 and Sly-miR319 are components of the cold stress response in Solanum lycopersicum. Plant Biotechnol Rep 8, 349- 356. |
| [187] | Vanesa Hobecker K, Alberto Reynoso M, Bustos-Sanmamed P, Wen JQ, Mysore KS, Crespi M, Antonio Blanco F, Eugenia Zanetti M (2017). The microRNA390/TAS3 pathway mediates symbiotic nodulation and lateral root growth. Plant Physiol 174, 2469-2486. |
| [188] | Vaucheret H, Vazquez F, Crété P, Bartel DP (2004). The action of ARGONAUTE1 in the miRNA pathway and its regulation by the miRNA pathway are crucial for plant development. Genes Dev 18, 1187-1197. |
| [189] | Velandia-Huerto CA, Yazbeck AM, Schor J, Stadler PF (2022). Evolution and phylogeny of microRNAs-protocols, pitfalls, and problems. In: AllmerJ, YousefM,eds. miRNomics:MicroRNA Biology and Computational Analysis. New York: Humana. pp. 211-233. |
| [190] | Volkov V (2015). Salinity tolerance in plants. Quantitative approach to ion transport starting from halophytes and stepping to genetic and protein engineering for manipulating ion fluxes. Front Plant Sci 6, 873. |
| [191] | Wang C, Yue WH, Ying YH, Wang SD, Secco D, Liu Y, Whelan J, Tyerman SD, Shou HX (2015). Rice SPX- major facility Superfamily3, a vacuolar phosphate efflux transporter, is involved in maintaining phosphate homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiol 169, 2822-2831. |
| [192] | Wang J, Zhou ZS, Tao Q, Chen XP, Shui C, Ren XY, Yu L, Liang MX (2022). Brassica napus miR169 regulates BnaNF-YA in salinity, drought and ABA responses. Environ Exp Bot 199, 104882. |
| [193] | Wang JL, Mei J, Ren GD (2019). Plant microRNAs: biogenesis, homeostasis, and degradation. Front Plant Sci 10, 360. |
| [194] | Wang KX, Liu YR, Teng FK, Cen HF, Yan JP, Lin SW, Li DY, Zhang WJ (2021a). Heterogeneous expression of Osa-MIR156bc increases abiotic stress resistance and forage quality of alfalfa. Crop J 9, 1135-1144. |
| [195] | Wang KY, Chen FQ, Shao HF, Han D, Xu ZC, Huang WX (2018). Research progress in plant cuticles. Chin Bull Bot 53, 556-564. (in Chinese) |
| 王凯悦, 陈芳泉, 邵惠芳, 韩丹, 许自成, 黄五星 (2018). 植物角质膜研究进展. 植物学报 53, 556-564. | |
| [196] | Wang M, Guo WP, Li J, Pan XJ, Pan LH, Zhao J, Zhang YW, Cai ST, Huang X, Wang A, Liu QP (2021b). The miR528-AO module confers enhanced salt tolerance in rice by modulating the ascorbic acid and abscisic acid metabolism and ROS scavenging. J Agric Food Chem 69, 8634-8648. |
| [197] | Wang ML, Yang CH, Wei KN, Zhao M, Shen LQ, Ji J, Wang L, Zhang DJ, Guo JQ, Zheng Y, Yu JJ, Zhu M, Liu HY, Li YF (2021c). Temporal expression study of miRNAs in the crown tissues of winter wheat grown under natural growth conditions. BMC Genomics 22, 793. |
| [198] | Wang RQ, Wang YT, Gu YM, Yan PY, Zhao WN, Jiang TB (2023a). Genome-wide identification of miR169 family in response to ABA and salt stress in poplar. Forests 14, 961. |
| [199] | Wang YF, Chen YL, Peng MY, Yang C, Yang ZM, Gong MJ, Yin YQ, Zeng Y (2023b). Identification of microRNA and analysis of target genes in Panax ginseng. Chin Herb Med 15, 69-75. |
| [200] | Wang YJ, Luo Z, Zhao X, Cao HN, Wang LH, Wang W, Liu SY, Wang CY, Liu MJ, Wang LX, Liu ZG (2023c). Superstar microRNA, miR156, involved in plant biological processes and stress response: a review. Sci Hortic 316, 112010. |
| [201] | Wang ZY, Li N, Yu QH, Wang H (2021d). Genome-wide characterization of salt-responsive miRNAs, circRNAs and associated ceRNA networks in tomatoes. Int J Mol Sci 22, 12238. |
| [202] | Wei HB, Luo MT, Deng J, Xiao Y, Yan HT, Liu HJ, Li Y, Song Q, Xiao XY, Shen JL, Kong HY, Sun F, Luo KM (2024). SPL16 and SPL23 mediate photoperiodic control of seasonal growth in Populus trees. New Phytol 241, 1646-1661. |
| [203] | Wei LY, Zhang DF, Xiang F, Zhang ZX (2009). Differentially expressed miRNAs potentially involved in the regulation of defense mechanism to drought stress in maize seedlings. Int J Plant Sci 170, 979-989. |
| [204] | Wei TP, Tang Y, Jia P, Zeng YM, Wang BT, Wu P, Quan YG, Chen AM, Li YC, Wu JH (2021a). A cotton lignin biosynthesis gene, GhLAC4, fine-tuned by ghr-miR397 modulates plant resistance against Verticillium dahliae. Front Plant Sci 12, 743795. |
| [205] | Wei XB, Ke HH, Wen AJ, Gao B, Shi J, Feng Y (2021b). Structural basis of microRNA processing by dicer-like 1. Nat Plants 7, 1389-1396. |
| [206] | Wen FL, Yue Y, He TF, Gao XM, Zhou ZS, Long XH (2020). Identification of miR390-TAS3-ARF pathway in response to salt stress in Helianthus tuberosus L. Gene 738, 144460. |
| [207] | Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G (1993). Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 media- tes temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75, 855-862. |
| [208] | Wójcik AM, Gaj MD (2016). miR393 contributes to the embryogenic transition induced in vitro in Arabidopsis via the modification of the tissue sensitivity to auxin treatment. Planta 244, 231-243. |
| [209] | Wu JG, Yang RX, Yang ZR, Yao SZ, Zhao SS, Wang Y, Li PC, Song XW, Jin L, Zhou T, Lan Y, Xie LH, Zhou XP, Chu CC, Qi YJ, Cao XF, Li Y (2017). ROS accumulation and antiviral defence control by microRNA528 in rice. Nat Plants 3, 16203. |
| [210] | Wu L, Qi YJ (2020). Small RNA, no small feat: plants deploy 22 nt siRNAs to cope with environmental stress. Chin Bull Bot 55, 270-273. (in Chinese) |
| 武亮, 戚益军 (2020). 小RNA, 大本领: 22 nt siRNAs在植物适应逆境中的重要作用. 植物学报 55, 270-273. | |
| [211] | Wu P, Wang L, Guo QQ, Fan MY, Ding CQ (2022). Progress in the regulation of plant miR397 and their target genes. Mol Plant Breed. [2022-03-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220322.1149.006.html. (in Chinese) |
| 吴鹏, 王丽, 郭茜茜, 范明玉, 丁楚琦 (2022). 植物miR397及其靶基因调控的研究进展. 分子植物育种. [2022-03-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220322.1149.006.html. | |
| [212] | Xia R, Xu J, Meyers BC (2017). The emergence, evolution, and diversification of the miR390-TAS3-ARF pathway in land plants. Plant Cell 29, 1232-1247. |
| [213] | Xie DQ, Chen M, Niu JR, Wang L, Li Y, Fang XF, Li PL, Qi YJ (2021). Phase separation of SERRATE drives dicing body assembly and promotes miRNA processing in Arabidopsis. Nat Cell Biol 23, 32-39. |
| [214] | Xie J, Wang M, Ding HY, Li Q, Wang WX, Xiong XY, Qin YZ (2019). Expression and structural analysis of ScmiR390-5p and its target genes in potato response to low temperature. Sci Agricul Sin 52, 2295-2308. (in Chinese) |
| 谢洁, 王明, 丁红映, 李青, 王万兴, 熊兴耀, 秦玉芝 (2019). 马铃薯低温响应的ScmiR390-5p及其靶基因表达与结构分析. 中国农业科学 52, 2295-2308. | |
| [215] | Xie J, Wang M, Li Q, Pan F, Xiong XY, Qin YZ (2018). Research progress on plant miR390. Biotechnol Bull 34 (6), 1-10. (in Chinese) |
| 谢洁, 王明, 李青, 潘妃, 熊兴耀, 秦玉芝 (2018). 植物miR390的研究进展. 生物技术通报 34(6), 1-10. | |
| [216] | Xing XH, Cao CX, Xu ZJ, Qi YJ, Fei T, Jiang HD, Wang X (2023). Reduced soybean water stress tolerance by miR393a-mediated repression of GmTIR1 and abscisic acid accumulation. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 1067-1083. |
| [217] | Xu JY, Chen QS, Liu PP, Jia W, Chen Z, Xu ZC (2019). Integration of mRNA and miRNA analysis reveals the molecular mechanism underlying salt and alkali stress tolerance in tobacco. Int J Mol Sci 20, 2391. |
| [218] | Xu XB (2022). Analysis and Validation of miRNA Related to Cadmium Stress in N. tabacum and N. rustica. Master’s thesis. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University. pp. 34- 38. (in Chinese) |
| 许肖博 (2022). 红花烟草和黄花烟草镉胁迫相关miRNA分析与验证. 硕士论文. 郑州: 河南农业大学. pp. 34-38. | |
| [219] | Yadav A, Kumar S, Verma R, Lata C, Sanyal I, Rai SP (2021). microRNA166: an evolutionarily conserved stress biomarker in land plants targeting HD-ZIP family. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27, 2471-2485. |
| [220] | Yadav A, Kumar S, Verma R, Rai SP, Lata C, Sanyal I (2023). Target cleavage mapping and tissue-specific expression analysis of PGPR responsive miR166 under abiotic stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 154, 415-432. |
| [221] | Yan CC, Zhang N, Wang QQ, Fu YY, Wang F, Su YB, Xue BJ, Zhou L, Liao HJ (2021). The effect of low temperature stress on the leaves and microRNA expression of potato seedlings. Front Ecol Evol 9, 727081. |
| [222] | Yang JW, Zhang N, Bai JP, Duan XQ, Zhang LH, Liu SY, Tang X, Jin X, Li SG, Si HJ (2022a). Stu-miR827-targeted StWRKY48 transcription factor negatively regulates drought tolerance of potato by increasing leaf stomatal density. Int J Mol Sci 23, 14805. |
| [223] | Yang ZY, Ebright YW, Yu B, Chen XM (2006). HEN1 recognizes 21-24 nt small RNA duplexes and deposits a methyl group onto the 2' OH of the 3' terminal nucleotide. Nucleic Acids Res 34, 667-675. |
| [224] | Yang ZY, Hui SG, Lv Y, Zhang MJ, Chen D, Tian JJ, Zhang HT, Liu HB, Cao JB, Xie WY, Wu CY, Wang SP, Yuan M (2022b). miR395-regulated sulfate metabolism exploits pathogen sensitivity to sulfate to boost immunity in rice. Mol Plant 15, 671-688. |
| [225] | Yao SZ, Kang JR, Guo G, Yang ZR, Huang Y, Lan Y, Zhou T, Wang LY, Wei CH, Xu ZH, Li Y (2022). The key micronutrient copper orchestrates broad-spectrum virus resistance in rice. Sci Adv 8, eabm0660. |
| [226] | Yao SZ, Yang ZR, Yang RX, Huang Y, Guo G, Kong XY, Lan Y, Zhou T, Wang H, Wang WM, Cao XF, Wu JG, Li Y (2019). Transcriptional regulation of miR528 by OsSPL9 orchestrates antiviral response in rice. Mol Plant 12, 1114- 1122. |
| [227] | Yu Y, Jia TR, Chen XM (2017). The ‘how’ and ‘where’ of plant microRNAs. New Phytol 216, 1002-1017. |
| [228] | Yu ZP, Duan XB, Luo L, Dai SJ, Ding ZJ, Xia GM (2020). How plant hormones mediate salt stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 25, 1117-1130. |
| [229] | Yuan J, Wang X, Qu ST, Shen T, Li MJ, Zhu LC (2023). The roles of miR156 in abiotic and biotic stresses in plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 204, 108150. |
| [230] | Yuan SR, Zhao JM, Li ZG, Hu Q, Yuan N, Zhou M, Xia XX, Noorai R, Saski C, Li SG, Luo H (2019a). MicroRNA396-mediated alteration in plant development and salinity stress response in creeping bentgrass. Hortic Res 6, 48. |
| [231] | Yuan WY, Suo JQ, Shi B, Zhou CL, Bai B, Bian HW, Zhu MY, Han N (2019b). The barley miR393 has multiple roles in regulation of seedling growth, stomatal density, and drought stress tolerance. Plant Physiol Biochem 142, 303-311. |
| [232] | Zhang BL, You CJ, Zhang Y, Zeng LP, Hu J, Zhao ML, Chen XM (2020a). Linking key steps of microRNA biogenesis by TREX-2 and the nuclear pore complex in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 6, 957-969. |
| [233] | Zhang CJ, Mo BX, Chen XM, Cui J (2020). Advances on the molecular action mechanisms of plant miRNA. Biotechnol Bull 36(7), 1-14. (in Chinese) |
| 张翠桔, 莫蓓莘, 陈雪梅, 崔洁 (2020). 植物miRNA作用方式的分子机制研究进展. 生物技术通报 36(7), 1-14. | |
| [234] | Zhang GD (2021). Effects of High Temperature on Potato Growth, Tuberization and Dormancy and Mechanism of Heat Stress Response. PhD dissertation. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University. pp. 59-81. (in Chinese) |
| 张国栋 (2021). 高温对马铃薯生长结薯和休眠的影响及响应高温胁迫的分子机制. 博士论文. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学. pp. 59-81. | |
| [235] | Zhang JS, Zhang H, Srivastava AK, Pan YJ, Bai JJ, Fang JJ, Shi HZ, Zhu JK (2018). Knockdown of rice microRNA166 confers drought resistance by causing leaf rolling and altering stem xylem development. Plant Physiol 176, 2082-2094. |
| [236] | Zhang JS, Zhou ZY, Bai JJ, Tao XP, Wang L, Zhang H, Zhu JK (2020b). Disruption of MIR396e and MIR396f improves rice yield under nitrogen-deficient conditions. Natl Sci Rev 7, 102-112. |
| [237] | Zhang LW, Song JB, Shu XX, Zhang Y, Yang ZM (2013). miR395 is involved in detoxification of cadmium in Brassica napus. J Hazard Mater 250-251, 204-211. |
| [238] | Zhang MB, An PP, Li HP, Wang XL, Zhou JL, Dong PF, Zhao YL, Wang Q, Li CH (2019). The miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation of maize in response to high temperature. Int J Mol Sci 20, 1754. |
| [239] | Zhang MX, Qin SQ, Yan JP, Li L, Xu MZ, Liu YR, Zhang WJ (2023). Genome-wide identification and analysis of TCP family genes in Medicago sativa reveal their critical roles in Na+/K+ homeostasis. BMC Plant Biol 23, 301. |
| [240] | Zhang X, Ren C, Xue YY, Tian YX, Zhang HQ, Li N, Sheng CC, Jiang HF, Bai DM (2022). Small RNA and degradome deep sequencing reveals the roles of microRNAs in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cold response. Front Plant Sci 13, 920195. |
| [241] | Zhao JM, Yuan SR, Zhou M, Yuan N, Li ZG, Hu Q, Bethea FG, Liu HB, Li SG, Luo H (2019). Transgenic creeping bentgrass overexpressing Osa-miR393a exhibits altered plant development and improved multiple stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol J 17, 233-251. |
| [242] | Zhao PP, Wang FP, Deng YJ, Zhong FJ, Tian P, Lin DB, Deng JH, Zhang YX, Huang TB (2022a). Sly-miR159 regulates fruit morphology by modulating GA biosynthesis in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J 20, 833-845. |
| [243] | Zhao WL, Xiao WY, Sun JL, Chen MX, Ma MQ, Cao YQ, Cen WJ, Li RB, Luo JJ (2022b). An integration of microRNA and transcriptome sequencing analysis reveal regulatory roles of miRNAs in response to chilling stress in wild rice. Plants 11, 977. |
| [244] | Zhao YF, Wen HL, Teotia S, Du YX, Zhang J, Li JZ, Sun HZ, Tang GL, Peng T, Zhao QZ (2017). Suppression of microRNA159 impacts multiple agronomic traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol 17, 215. |
| [245] | Zhou J, Liu MY, Jiang J, Qiao GR, Lin S, Li HY, Xie LH, Zhuo RY (2012). Expression profile of miRNAs in Populus cathayana L. and Salix matsudana Koidz under salt stress. Mol Biol Rep 39, 8645-8654. |
| [246] | Zhou LX, Yarra R (2023). Genome-wide analysis of SPL/ miR156 module and its expression analysis in vegetative and reproductive organs of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis). Int J Mol Sci 24, 13658. |
| [247] | Zhou M, Li DY, Li ZG, Hu Q, Yang CH, Zhu LH, Luo H (2013). Constitutive expression of a miR319 gene alters plant development and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic creeping bentgrass. Plant Physiol 161, 1375-1391. |
| [248] | Zhou M, Luo H (2014). Role of microRNA319 in creeping bentgrass salinity and drought stress response. Plant Signal Behav 9, e28700. |
| [249] | Zhu H, Chen CJ, Zeng J, Yun Z, Liu YL, Qu HX, Jiang YM, Duan XW, Xia R (2020). MicroRNA528, a hub regulator modulating ROS homeostasis via targeting of a diverse set of genes encoding copper-containing proteins in mono- cots. New Phytol 225, 385-399. |
| [1] | 惠城阳, 章巧依, 刘腾腾, 刘维勇, 周丽娜, 金鑫杰, 张永华, 刘金亮. 温州大罗山主要植被类型及物种组成特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-. |
| [2] | 曹毅 张松林 王旭峰 杨安昌 任敏慧 杨浩 韩超. 兰州市南北两山植物群落数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 1-0. |
| [3] | 陈龙 郭柯 勾晓华 赵秀海 马泓若. 祁连圆柏林群落组成及特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(植被): 0-0. |
| [4] | 闫小红 胡文海. 亚热带地区3种常绿阔叶植物冬季光保护机制的差异[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 0-0. |
| [5] | 童金莲, 张博纳, 汤璐瑶, 叶琳峰, 李姝雯, 谢江波, 李彦, 王忠媛. C4植物狗尾草功能性状网络沿降水梯度带的区域分异规律[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(预发表): 1-. |
| [6] | 赵常明 熊高明 申国珍 葛结林 徐文婷 徐凯 武元帅 谢宗强. 神农架常绿落叶阔叶混交林和亚高山针叶林植物群落特征数据集[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(典型生态系统数据集): 0-0. |
| [7] | 赵珮杉 高广磊 丁国栋 张英. 林龄和生态位对樟子松人工林地下真菌群落构建的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(地上地下生态过程关联): 1-0. |
| [8] | 张子睿, 周静, 胡艳萍, 梁爽, 马永鹏, 陈伟乐. 极度濒危植物巧家五针松的根内和根际真菌群落特征[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [9] | 逯子佳, 王天瑞, 郑斯斯, 孟宏虎, 曹建国, Gregor Kozlowski, 宋以刚. 孑遗植物湖北枫杨的环境适应性遗传变异与遗传脆弱性[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [10] | 黄承玲, 黎荣瀚, 覃红玲, 杨胜雄, 田晓玲, 夏国威, 陈正仁, 周玮. 基于SNP分子标记的极小种群野生植物荔波杜鹃保护遗传学研究[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [11] | 周鑫宇, 刘会良, 高贝, 卢妤婷, 陶玲庆, 文晓虎, 张岚, 张元明. 新疆特有濒危植物雪白睡莲繁殖生物学研究[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [12] | 高雨轩, 苏艳军, 冯育才, 张军, 汪小全, 刘玲莉. 珍稀濒危孑遗植物银杉的研究与保护现状[J]. , 2025, 49(濒危植物的保护与恢复): 0-. |
| [13] | 平晓燕, 杜毅倩, 赖仕蓉, 孔梦桥, 余国杰. 植物应对食草动物采食的化学防御策略研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 667-680. |
| [14] | 朱润铖, 蔡锡安, 黄娟. 植物防御相关挥发性有机物排放及对氮沉降的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 681-696. |
| [15] | 贾妍妍, 柳华清, 解欣然, 王博, 张维, 杨允菲. 珍稀濒危植物天山梣林龄结构及种群动态[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 760-772. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||