

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 49-61.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24019 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24019
杨柳卿,†, 王劲,†, 燕敬利, 陈芹芹, 程浩坤, 李春, 赵培玉, 杨博, 江元清*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-05
接受日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-08-22
通讯作者:
* 江元清, 男, 汉族, 湖南省桃源县人, 教授, 博士生导师。1998年6月本科毕业于湖南农业大学资环学院; 2001年6月硕士研究生毕业于中国农业大学生物学院生物化学与分子生物学专业。2001.07-2003.08在北京市农林科学院农业生物技术研究中心工作(助理研究员), 从事扁桃基因功能分析相关研究。2003.09-2007.11在加拿大阿尔伯特大学(University of Alberta)生物科学系学习(植物生物学专业), 获博士学位。2007.12-2010.11先后在阿尔伯特大学生物科学系和美国加州大学伯克利分校(University of California-Berkeley)植物与微生物学系做博士后研究。2010年12月就职于西北农林科技大学生命科学学院, 从事教学与科研工作。E-mail: jiangyq@nwafu.edu.cn作者简介:†共同第一作者。
基金资助:
Liuqing Yang,†, Jin Wang,†, Jingli Yan, Qinqin Chen, Haokun Cheng, Chun Li, Peiyu Zhao, Bo Yang, Yuanqing Jiang*( )
)
Received:2024-02-05
Accepted:2024-08-20
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-08-22
Contact:
* E-mail: About author:†These authors contributed equally to this paper
摘要: ABF转录因子是能够特异识别并结合ABA响应元件(ABRE)的碱性亮氨酸拉链蛋白的统称, 参与ABA信号转导。通过对甘蓝型油菜(Brassica napus) BnaABF2基因编码蛋白进行分析, 亚细胞定位结果显示, BnaABF2蛋白定位于细胞核; 酵母系统转录活性分析表明, BnaABF2无转录激活活性; qRT-PCR检测发现, BnaABF2在叶中的表达量最高。此外, 还发现ABA处理、模拟干旱和盐胁迫能够诱导BnaABF2的表达; BiFC结果显示, BnaMPK1/2/6/7/9/12/13能与BnaABF2相互作用。Dual-LUC结果表明, BnaMPK7可能通过磷酸化增强BnaABF2对下游靶基因的转录调控。该研究初步探索了转录因子BnaABF2的基本特性与互作蛋白, 对理解其功能与机制具有一定的理论价值。
杨柳卿, 王劲, 燕敬利, 陈芹芹, 程浩坤, 李春, 赵培玉, 杨博, 江元清. 甘蓝型油菜转录因子BnaABF2的表征分析及互作蛋白鉴定. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 49-61.
Liuqing Yang, Jin Wang, Jingli Yan, Qinqin Chen, Haokun Cheng, Chun Li, Peiyu Zhao, Bo Yang, Yuanqing Jiang. Analysis of Expression Characteristics and Identification of Interaction Proteins of BnaABF2 Transcription Factor in Brassica napus. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 49-61.
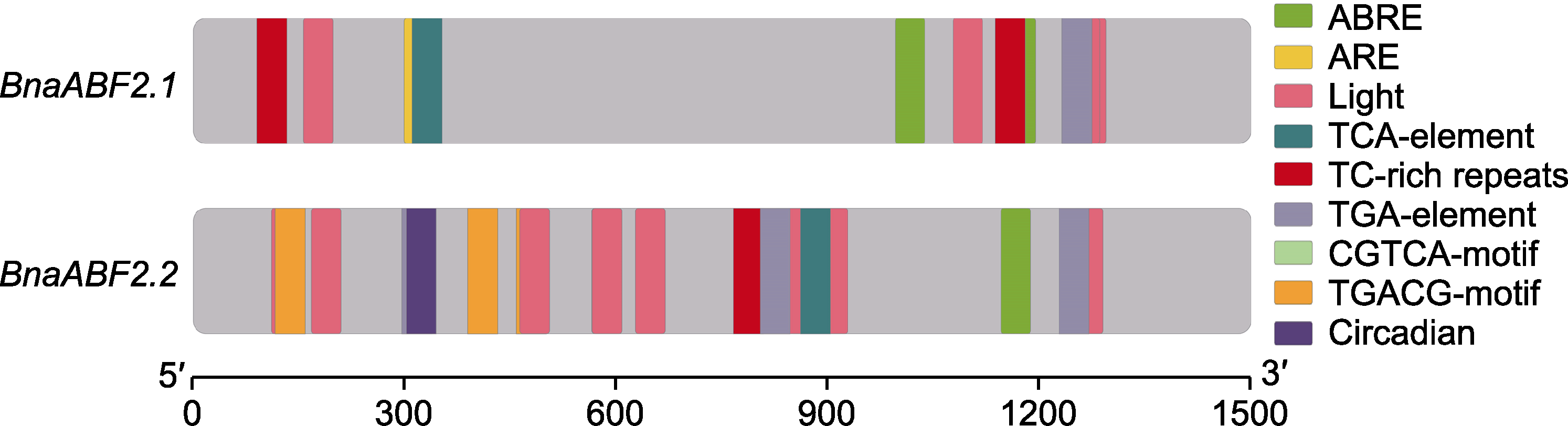
图1 2个BnaABF2基因启动子的顺式作用元件 ABRE: 脱落酸响应元件; ARE: 厌氧诱导元件; Light: 光响应元件; TCA-element: 水杨酸响应元件; TC-rich repeats: 防御和应激反应元件; TGA-element: 生长素响应元件; CGTCA-motif: 茉莉酸甲酯响应基序; TGACG-motif: 茉莉酸响应基序; Circadian: 昼夜节律
Figure 1 Cis-elements of two BnaABF2 promoters ABRE: Abscisic acid responsiveness element; ARE: Anaerobic induction element; Light: Light responsiveness element; TCA- element: Salicylic acid responsiveness element; TC-rich repeats: Defense and stress responsiveness element; TGA-element: Auxin responsiveness element; CGTCA-motif: MeJA-responsiveness motif; TGACG-motif: Jasmonic acid responsiveness motif; Circadian: Circadian rhythm
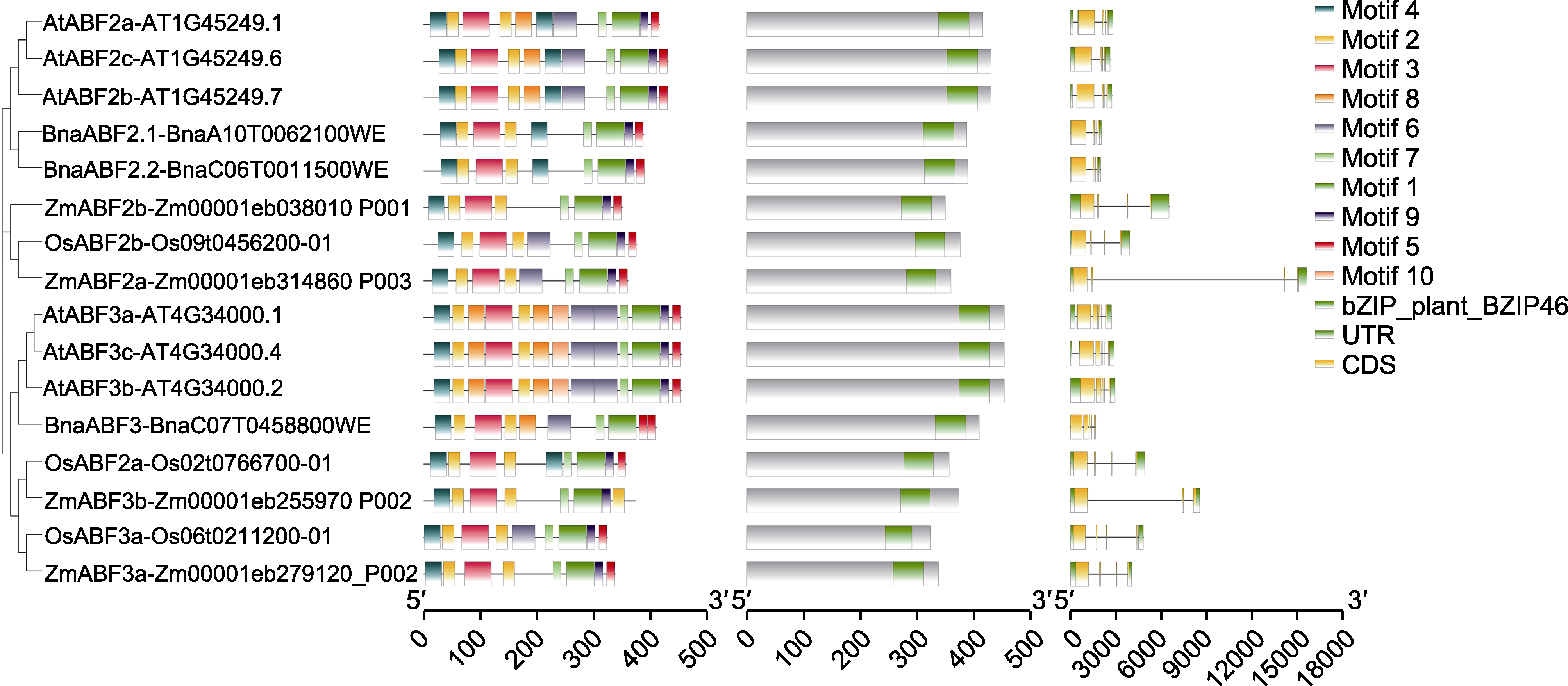
图2 BnaABF2/3与其它物种ABF保守结构域序列比对 左列: ABF2/3蛋白保守基序比对; 中列: ABF2/3蛋白保守结构域比对; 右列: ABF2/3编码区(coding sequence, CDS)与非翻译区(untranslated region, UTR)的转录本结构比对。
Figure 2 Sequence alignment of conserved domains of BnaABF2 with ABF from other species Left: Protein conserved motifs of ABF2/3 alignment; Middle: ABF2/3 protein conserved domain alignment; Right: Transcript structure alignment of coding region (CDS) and untranslated region (UTR) of ABF2/3.
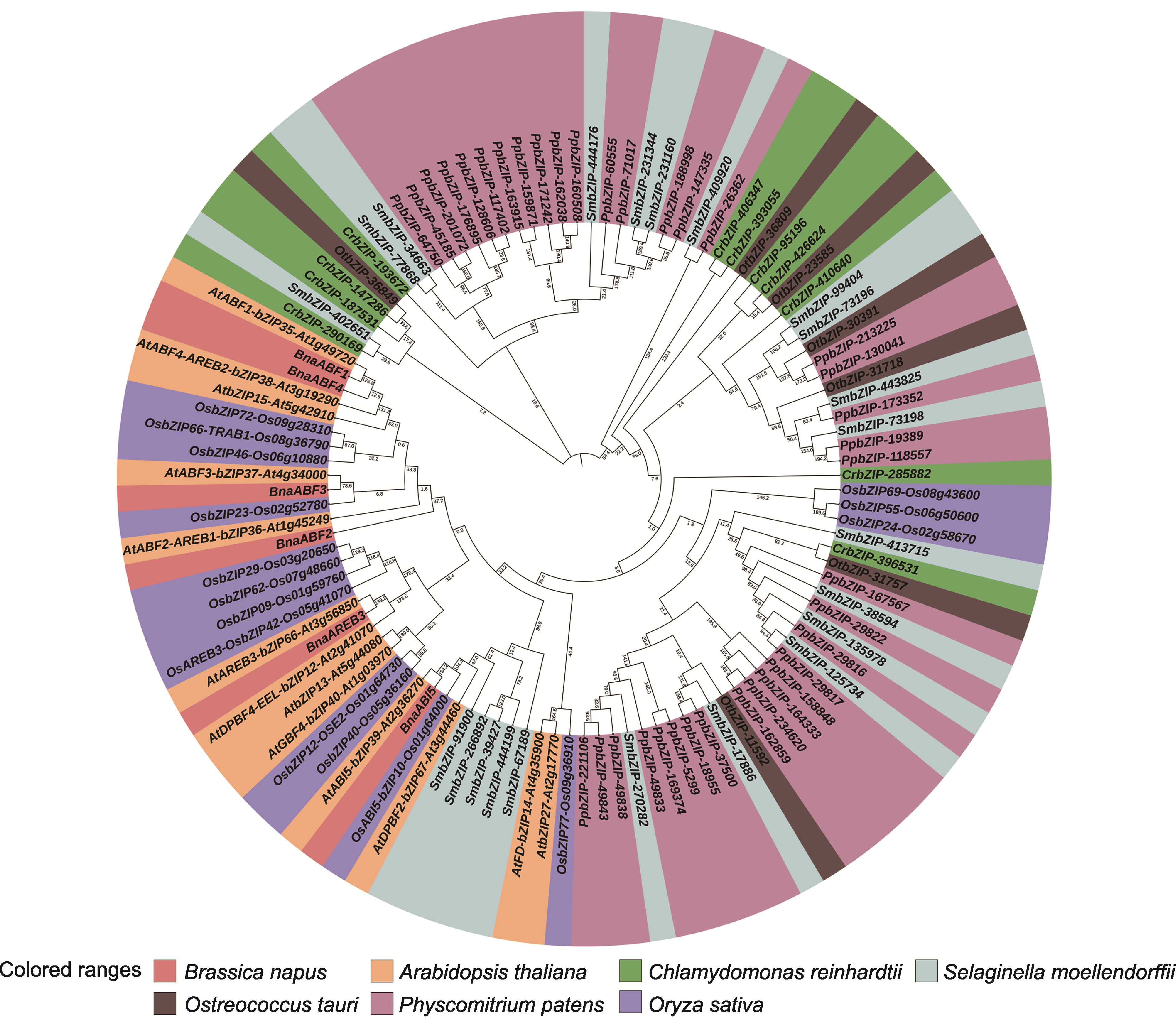
图3 BnaABF2与其它物种ABF蛋白的系统进化树 进化树分支显示遗传距离, 置信度为100。
Figure 3 A phylogenetic tree of BnaABF2 and ABF proteins from other species The branches of the evolutionary tree showed genetic distance with a confidence level of 100.
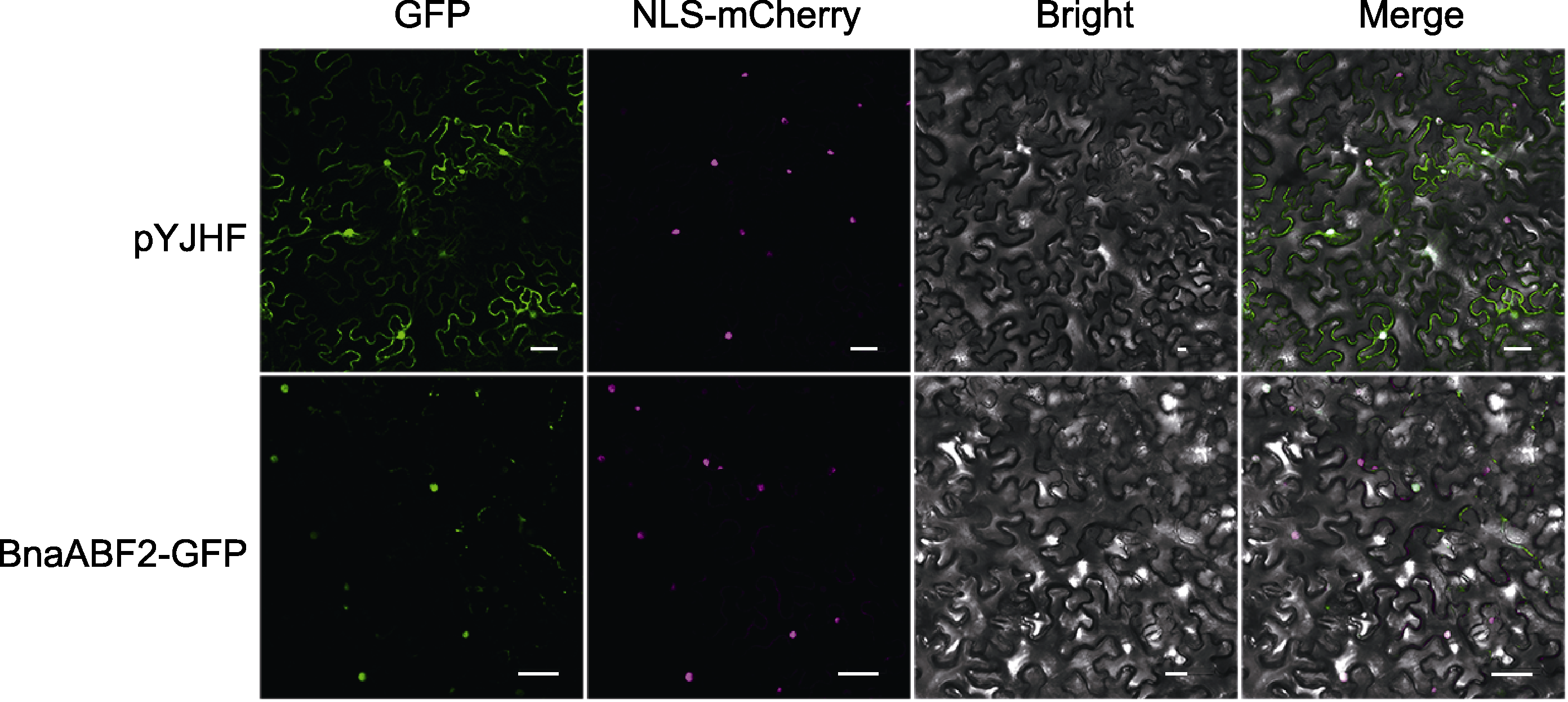
图4 BnaABF2的亚细胞定位 将重组质粒pYJHF-BnaABF2或对照质粒pYJHF转染烟草叶片, 2天后观察荧光信号。GFP: 绿色荧光蛋白信号; NLS-mCherry: 核定位标记; Bright: 明场; Merge: 叠加场。Bars=50 μm
Figure 4 Subcellular localization of BnaABF2 pYJHF-BnaABF2 or pYJHF (control) plasmid were infiltrated into tobacco leaves, and fluorescence signals were observed two days later. GFP: Green fluorescent protein signal; NLS-mCherry: Nuclear localization marker; Bright: Bright field; Merge: Superimposed field. Bars=50 μm
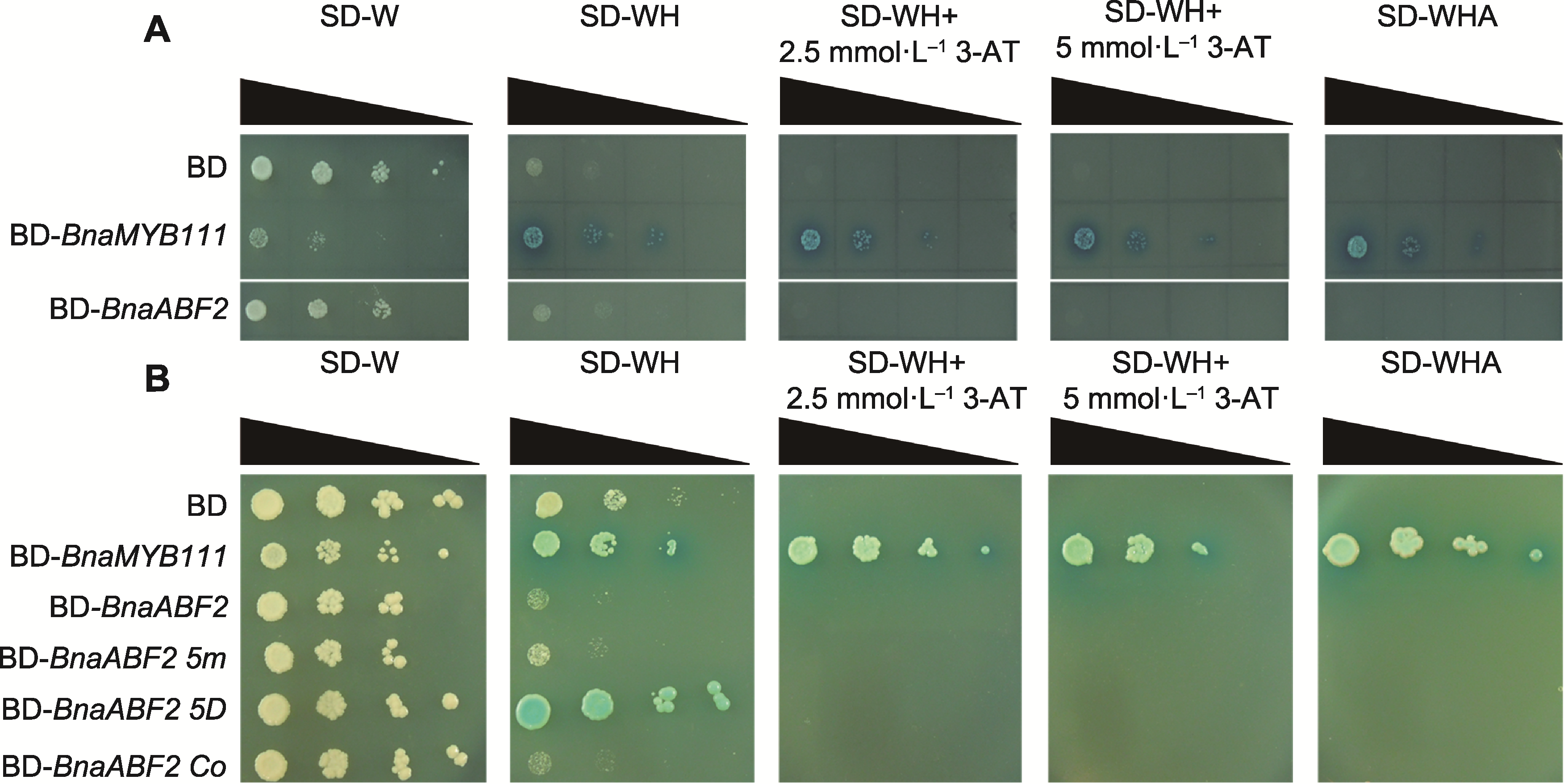
图5 BnaABF2的酵母系统转录活性分析 分别将BD (阴性对照)、BD-BnaABF2、BD-BnaMYB111 (阳性对照)、BD-BnaABF2 5m、BD-BnaABF2 5D和BD-BnaABF2 Co转入酵母进行酵母滴定实验。酵母细胞稀释梯度使用黑色三角形标示。
Figure 5 Analysis of transcriptional activity of BnaABF2 in yeast system BD (negative control), BD-BnaABF2, BD-BnaMYB111 (positive control), BD-BnaABF2 5m, BD-BnaABF2 5D and BD-BnaABF2 Co were transferred into yeast for titration experiment. The dilution gradients of yeast cells were marked with black triangles.
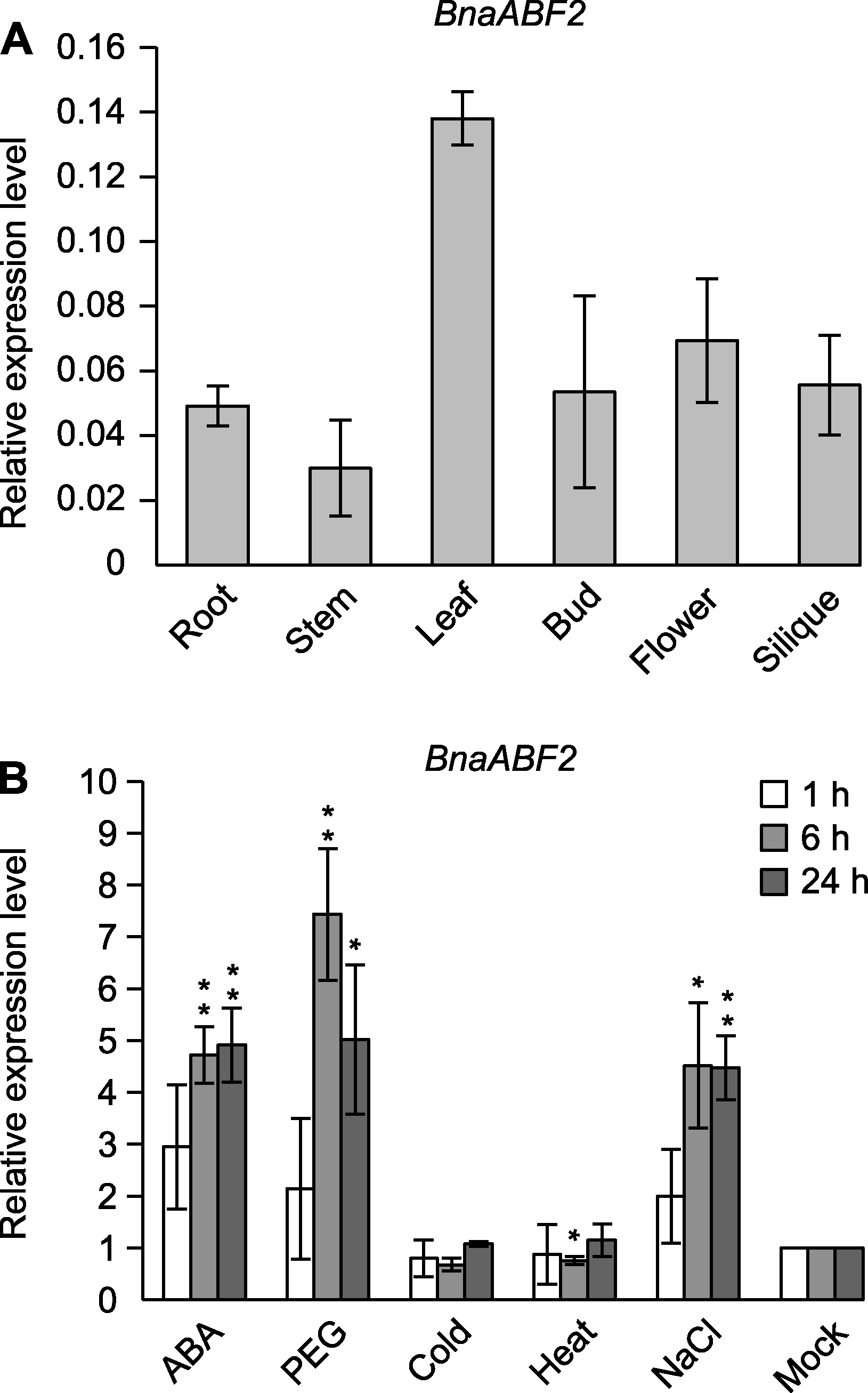
图6 BnaABF2在不同组织及多种逆境与植物生长调节剂处理下的表达分析 (A) BnaABF2在不同组织中的表达情况; (B) BnaABF2在多种逆境与植物生长调节剂处理下的表达情况, 处理条件为脱落酸(abscisic acid, ABA) (50 μmol·L-1)、模拟干旱(15% PEG8000)、冷害(4°C)、热害(38°C)和盐害(200 mmol·L-1 NaCl)。数据为平均值±标准误。星号表示t检验存在显著性差异, * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
Figure 6 Expression patterns of BnaABF2 gene in different tissues and under different stresses and plant growth regulator treatments (A) The expression of BnaABF2 in different tissues; (B) The expression of BnaABF2 under various stresses and plant growth regulator treatments, the treatments included 50 μmol·L-1 ABA, 15% PEG8000, cold (4°C), heat (38°C) and salinity (200 mmol·L-1 NaCl). Values are means±SE. The significant differences in t-test were indicated by asterisk, * P<0.05; ** P<0.01
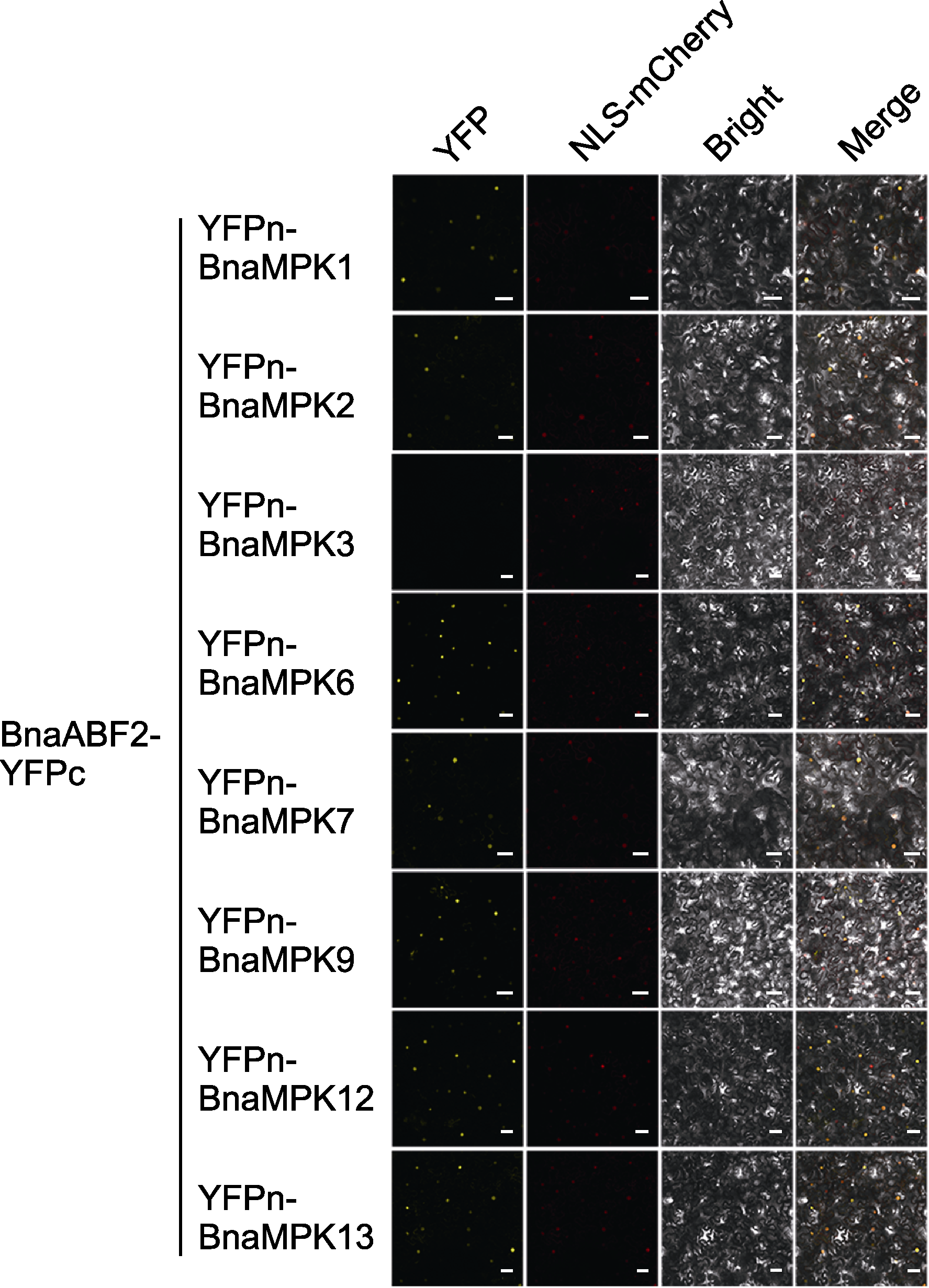
图7 双分子荧光互补实验检测油菜的BnaABF2蛋白与BnaMPKs蛋白间相互作用 将含有BnaABF2-YFPc和YFPn-BnaMPK1/2/6/7/9/12/13的质粒与NLS-mCherry共同转染28天本氏烟草, 4天后观察荧光信号。YFPn: 黄色荧光蛋白N端序列; YFPc: 黄色荧光蛋白C端序列; YFP: 黄色荧光蛋白信号; NLS-mCherry: 核定位红色荧光信号; Bright: 明场; Merge: 叠加场。Bars=50 μm
Figure 7 Screening of interaction between BnaABF2 and BnaMPK proteins through bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay The plasmids of BnaABF2-YFPc and YFPn-BnaMPK1/2/6/ 7/9/12/13 and NLS-mCherry were co-transfected into tobacco (28 d). Four days later, the fluorescence signal was observed. YFPn: Yellow fluorescent protein N-terminal sequence; YFPc: Yellow fluorescent protein C-terminal sequence; YFP: Yellow fluorescent protein signal; NLS-mCherry: Nuclear localization red fluorescence signal; Bright: Bright field; Merge: Superimposed field. Bars=50 μm
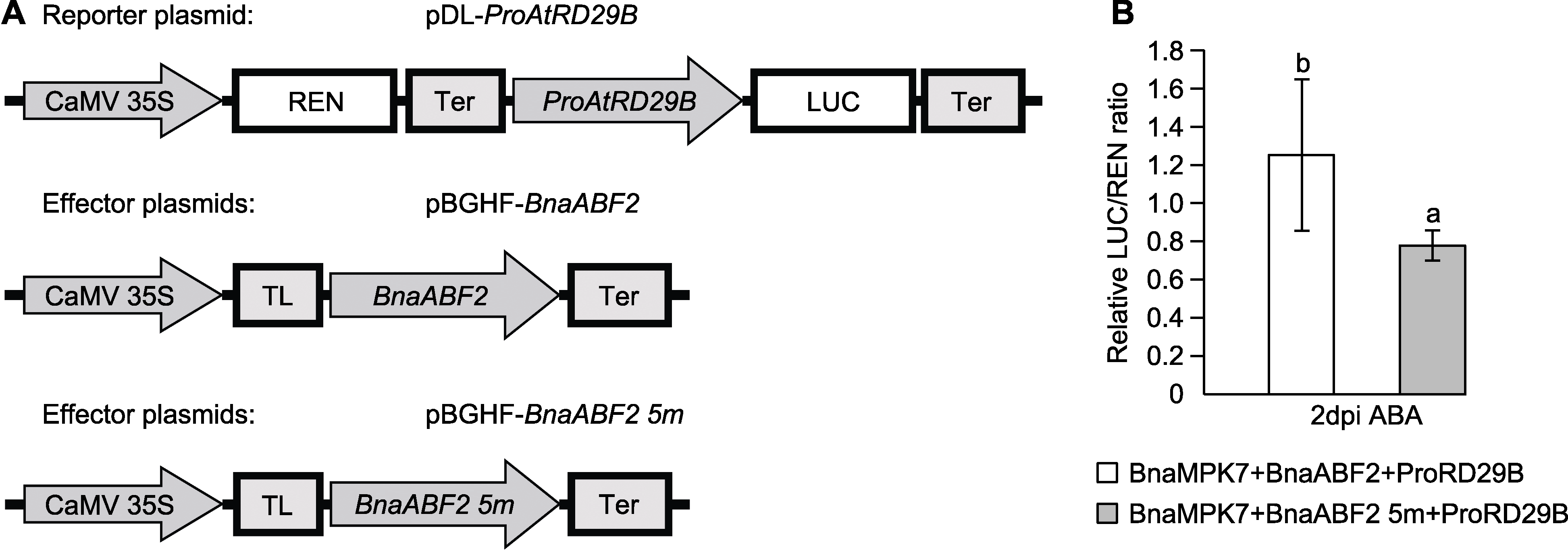
图8 双荧光素酶报告系统检测脱落酸(ABA)处理下BnaABF2对AtRD29B启动子转录活性的影响 (A) 报告子和效应子示意图; (B) LUC/REN比值表示效应子激活报告子的能力, 数值越大, 能力越强(dpi: 注射后的天数)。不同小写字母表示各处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。
Figure 8 Dual-luciferase reporter system detects the effect of BnaABF2 on the transcriptional activity of AtRD29B promoter under abscisic acid (ABA) treatment (A) A schematic diagram of the reporter and effector; (B) The LUC/REN ratio is used to indicate the ability of the effector to activate the reporter (dpi: Days post-infiltration). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between different treatments (P<0.05).
| [1] | Adachi H, Nakano T, Miyagawa N, Ishihama N, Yoshioka M, Katou Y, Yaeno T, Shirasu K, Yoshioka H (2015). WRKY transcription factors phosphorylated by MAPK regulate a plant immune NADPH oxidase in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Cell 27, 2645-2663. |
| [2] | Agarwal PK, Jha B (2010). Transcription factors in plants and ABA dependent and independent abiotic stress signaling. Biol Plant 54, 201-212. |
| [3] |
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu SY, Parkin IA, Tang HB, Wang XY, Chiquet J, Belcram H, Tong CB, Samans B, Corréa M, Da Silva C, Just J, Falentin C, Koh CS, Le Clainche I, Bernard M, Bento P, Noel B, Labadie K, Alberti A, Charles M, Arnaud D, Guo H, Daviaud C, Alamery S, Jabbari K, Zhao MX, Edger PP, Chelaifa H, Tack D, Lassalle G, Mestiri I, Schnel N, Le Paslier MC, Fan GY, Renault V, Bayer PE, Golicz AA, Manoli S, Lee TH, Thi VHD, Chalabi S, Hu Q, Fan CC, Tollenaere R, Lu YH, Battail C, Shen JX, Sidebottom CHD, Wang XF, Canaguier A, Chauveau A, Bérard A, Deniot G, Guan M, Liu ZS, Sun FM, Lim YP, Lyons E, Town CD, Bancroft I, Wang XW, Meng JL, Ma JX, Pires JC, King GJ, Brunel D, Delourme R, Renard M, Aury JM, Adams KL, Batley J, Snowdon RJ, Tost J, Edwards D, Zhou YM, Hua W, Sharpe AG, Paterson AH, Guan CY, Wincker P (2014). Plant genetics. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345, 950-953.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Choi HI, Hong JH, Ha JO, Kang JY, Kim SY (2000). ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J Biol Chem 275, 1723-1730.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008). Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signaling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413, 217-226. |
| [6] | Danquah A, de Zélicourt A, Boudsocq M, Neubauer J, dit Frey NF, Leonhardt N, Pateyron S, Gwinner F, Tamby JP, Ortiz-Masia D, Marcote MJ, Hirt H, Colcombet J (2015). Identification and characterization of an ABA-activated MAP kinase cascade in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 82, 232-244. |
| [7] | Fujita Y, Fujita M, Satoh R, Maruyama K, Parvez MM, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2005). AREB1 is a transcription activator of novel ABRE-dependent ABA signaling that enhances drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17, 3470-3488. |
| [8] | Furihata T, Maruyama K, Fujita Y, Umezawa T, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006). Abscisic acid-dependent multisite phosphorylation regulates the activity of a transcription activator AREB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 1988-1993. |
| [9] |
Johnson RR, Wagner RL, Verhey SD, Walker-Simmons MK (2002). The abscisic acid-responsive kinase PKABA1 interacts with a seed-specific abscisic acid response element-binding factor, TaABF, and phosphorylates TaABF peptide sequences. Plant Physiol 130, 837-846.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Kagale S, Links MG, Rozwadowski K (2010). Genome- wide analysis of ethylene-responsive element binding factor-associated amphiphilic repression motif-containing transcriptional regulators in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 152, 1109-1134. |
| [11] |
Kim S, Kang JY, Cho DI, Park JH, Kim SY (2004). ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor, is an essential component of glucose signaling and its overexpression affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J 40, 75-87.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Kim SH, Kim HS, Bahk S, An J, Yoo Y, Kim JY, Chung WS (2017). Phosphorylation of the transcriptional repressor MYB15 by mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 is required for freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 6613-6627. |
| [13] |
Kobayashi Y, Murata M, Minami H, Yamamoto S, Kagaya Y, Hobo T, Yamamoto A, Hattori T (2005). Abscisic acid-activated SNRK2 protein kinases function in the gene-regulation pathway of ABA signal transduction by phosphorylating ABA response element-binding factors. Plant J 44, 939-949.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | Li QY, Liu C, He L, Peng S, Ma JY, Hu ZY, Liu HB (2025). Cloning and functional analysis of BnaA02.CPSF6 gene from Brassica napus. Chin Bull Bot 60, 62-73. (in Chinese) |
|
李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波 (2025). 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析. 植物学报 60, 62-73.
DOI |
|
| [15] | Li SN, Wang WY, Gao JL, Yin KQ, Wang R, Wang CC, Petersen M, Mundy J, Qiu JL (2016). MYB75 phosphorylation by MPK4 is required for light-induced anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 28, 2866-2883. |
| [16] | Li YH, Liu K, Tong GL, Xi C, Liu J, Zhao HP, Wang YD, Ren DT, Han SC (2022). MPK3/MPK6-mediated phosphorylation of ERF72 positively regulates resistance to Botrytis cinerea through directly and indirectly activating the transcription of camalexin biosynthesis enzymes. J Exp Bot 73, 413-428. |
| [17] | Liang WW, Yang B, Yu BJ, Zhou ZL, Li C, Jia M, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Wu FF, Zhang HF, Wang BY, Deyholos MK, Jiang YQ (2013). Identification and analysis of MKK and MPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Genomics 14, 392. |
| [18] | Mao GH, Meng XZ, Liu YD, Zheng ZY, Chen ZX, Zhang SQ (2011). Phosphorylation of a WRKY transcription factor by two pathogen-responsive MAPKs drives phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23 1639-1653. |
| [19] | Niu FF, Wang C, Yan JL, Guo XH, Wu FF, Yang B, Deyholos MK, Jiang YQ (2016). Functional characterization of NAC55 transcription factor from oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) as a novel transcriptional activator modulating reactive oxygen species accumulation and cell death. Plant Mol Biol 92, 89-104. |
| [20] |
Rodriguez MSC, Petersen M, Mundy J (2010). Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61, 621-649.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Sun Y, Wang C, Yang B, Wu FF, Hao XY, Liang WW, Niu FF, Yan JL, Zhang HF, Wang BY, Deyholos MK, Jiang YQ (2014). Identification and functional analysis of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) genes in canola (Brassica napus L.). J Exp Bot 65, 2171-2188. |
| [22] |
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Yoshida R, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000). Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid- dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 11632-11637.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Wang HC, Ngwenyama N, Liu YD, Walker JC, Zhang SQ (2007). Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 63-73. |
| [24] |
Xu J, Zhang SQ (2015). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci 20, 56-64.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Yoshida T, Fujita Y, Sayama H, Kidokoro S, Maruyama K, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2010). AREB1, AREB2, and ABF3 are master transcription factors that cooperatively regulate ABRE-dependent ABA signaling involved in drought stress tolerance and require ABA for full activation. Plant J 61, 672-685. |
| [26] | Zhang HF (2019). Exploration of the Mechanisms of Two Calcium-Associated Protein Kinases Regulating ABA Signaling Transduction in Arabidopsis. PhD dissertation. Yang-ling: Northwest A&F University. (in Chinese) |
| 张翰风 (2019). 拟南芥中两个钙相关蛋白激酶调控ABA信号转导的机制研究. 博士论文. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学. | |
| [27] |
Zhang MM, Zhang SQ (2022). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 301-341.
DOI |
| [28] | Zhao BY, Hu YF, Li JJ, Yao X, Liu KD (2016). BnaABF2, a bZIP transcription factor from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.), enhances drought and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Bot Stud 57, 12. |
| [29] | Zhou YP, Yan JH, Tian CE (2022). Research progress on the regulatory mechanisms of ABA signal transduction in guard cells. Chin Bull Bot 57, 684-696. (in Chinese) |
|
周玉萍, 颜嘉豪, 田长恩 (2022). 保卫细胞中ABA信号调控机制研究进展. 植物学报 57, 684-696.
DOI |
|
| [30] | Zhu JK (2016). Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 167, 313-324. |
| [1] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [2] | 王文广, 王永红. 百年假说终获解析: 穿梭的LAZY蛋白“唤醒”植物对重力的感应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 677-681. |
| [3] | 张盈川, 吴晓明玉, 陶保龙, 陈丽, 鲁海琴, 赵伦, 文静, 易斌, 涂金星, 傅廷栋, 沈金雄. Bna-miR43介导甘蓝型油菜响应干旱胁迫[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 701-711. |
| [4] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [5] | 宋敏,张瑶,王丽莹,彭向永. 甘蓝型油菜ZF-HD基因家族的鉴定与系统进化分析[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 699-710. |
| [6] | 刘凯歌, 齐双慧, 段绍伟, 李东, 金倡宇, 高晨浩, 刘绚霞, 陈明训. 甘蓝型油菜BnTTG1-1基因的功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 713-722. |
| [7] | 高虎虎, 张云霄, 胡胜武, 郭媛. 甘蓝型油菜MADS-box基因家族的鉴定与系统进化分析[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(6): 699-712. |
| [8] | 贾乐东, 李施蒙, 许代香, 曲存民, 李加纳, 王瑞. 甘蓝型油菜BnMYB80基因的生物信息学分析[J]. 植物学报, 2016, 51(5): 620-630. |
| [9] | 刘玥, 尹悦佳, 梁重阳, 黄殿帅, 王阳, 刘艳芝, 窦瑶, 冯树丹, 郝东云. 3D-SIM结构照明超分辨率显微镜实现蛋白质在植物亚细胞器内的定位[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(4): 495-503. |
| [10] | 陈世璇, 张振南, 王波, 朱燕, 龚月桦, 孙冬梅, 邓馨. 复苏植物旋蒴苣苔J结构域蛋白编码基因BhDNAJC2的 克隆、表达与功能[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(2): 180-190. |
| [11] | 王芳. 拟南芥RabD2b蛋白氨基酸突变对定位和功能的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(6): 653-662. |
| [12] | 李春宏, 付三雄, 戚存扣. 应用基因芯片分析甘蓝型油菜柱头特异表达基因[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(3): 246-253. |
| [13] | 付三雄, 李成磊, 尼玛卓玛, 唐林, 戚存扣. 气象因子对油菜种子中油分积累的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2014, 49(1): 41-48. |
| [14] | 翟莹, 杨晓杰, 孙天国, 赵艳, 余春粉, 王秀文. 大豆转录因子GmERF5的克隆、表达及功能分析[J]. 植物学报, 2013, 48(5): 498-506. |
| [15] | 李春宏, 付三雄, 陈新军, 戚存扣. 甘蓝型油菜雌性不育突变体FS-M1乳突细胞的细胞学观察[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47(1): 36-43. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||