

植物学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (2): 199-213.DOI: 10.11983/CBB22129 cstr: 32102.14.CBB22129
王琪1, 吴允哲2,*( ), 刘学英2, 孙丽莉1, 廖红1, 傅向东1,2,*(
), 刘学英2, 孙丽莉1, 廖红1, 傅向东1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2022-06-22
接受日期:2022-10-24
出版日期:2023-03-01
发布日期:2023-03-15
通讯作者:
*E-mail: 基金资助:
Qi Wang1, Yunzhe Wu2,*( ), Xueying Liu2, Lili Sun1, Hong Liao1, Xiangdong Fu1,2,*(
), Xueying Liu2, Lili Sun1, Hong Liao1, Xiangdong Fu1,2,*( )
)
Received:2022-06-22
Accepted:2022-10-24
Online:2023-03-01
Published:2023-03-15
Contact:
*E-mail: 摘要: 类受体激酶(RLKs)是一类数量庞大的跨膜蛋白激酶家族, 在植物细胞之间以及细胞与环境的信号交流中发挥重要作用。RLKs的胞外区能特异识别并结合胞外信号和环境刺激因子, 并通过与共受体互作将信号传递至细胞内, 从而参与调控植物生长发育及环境适应性。目前已发现水稻(Oryza sativa)基因组至少含有1 131个RLKs成员, 接近于拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)中RLKs数目的2倍。根据胞外区的基序和结构域特征, 水稻RLKs被划分为20多个亚家族。近年来, 虽然有一些RLKs胞外区的配体和激酶区的作用蛋白被相继报道, 但大多数水稻RLKs的生物学功能仍不明确。该文详细总结了近年来有关水稻RLKs结构和功能的重要研究进展, 并展望了RLKs未来的研究方向, 旨在为深入揭示RLKs的功能以及绿色高产水稻分子设计育种奠定理论基础。
王琪, 吴允哲, 刘学英, 孙丽莉, 廖红, 傅向东. 类受体激酶调控水稻生长发育和环境适应研究进展. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 199-213.
Qi Wang, Yunzhe Wu, Xueying Liu, Lili Sun, Hong Liao, Xiangdong Fu. The Rice Receptor-like Kinases Function as Key Regulators of Plant Development and Adaptation to the Environment. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2023, 58(2): 199-213.
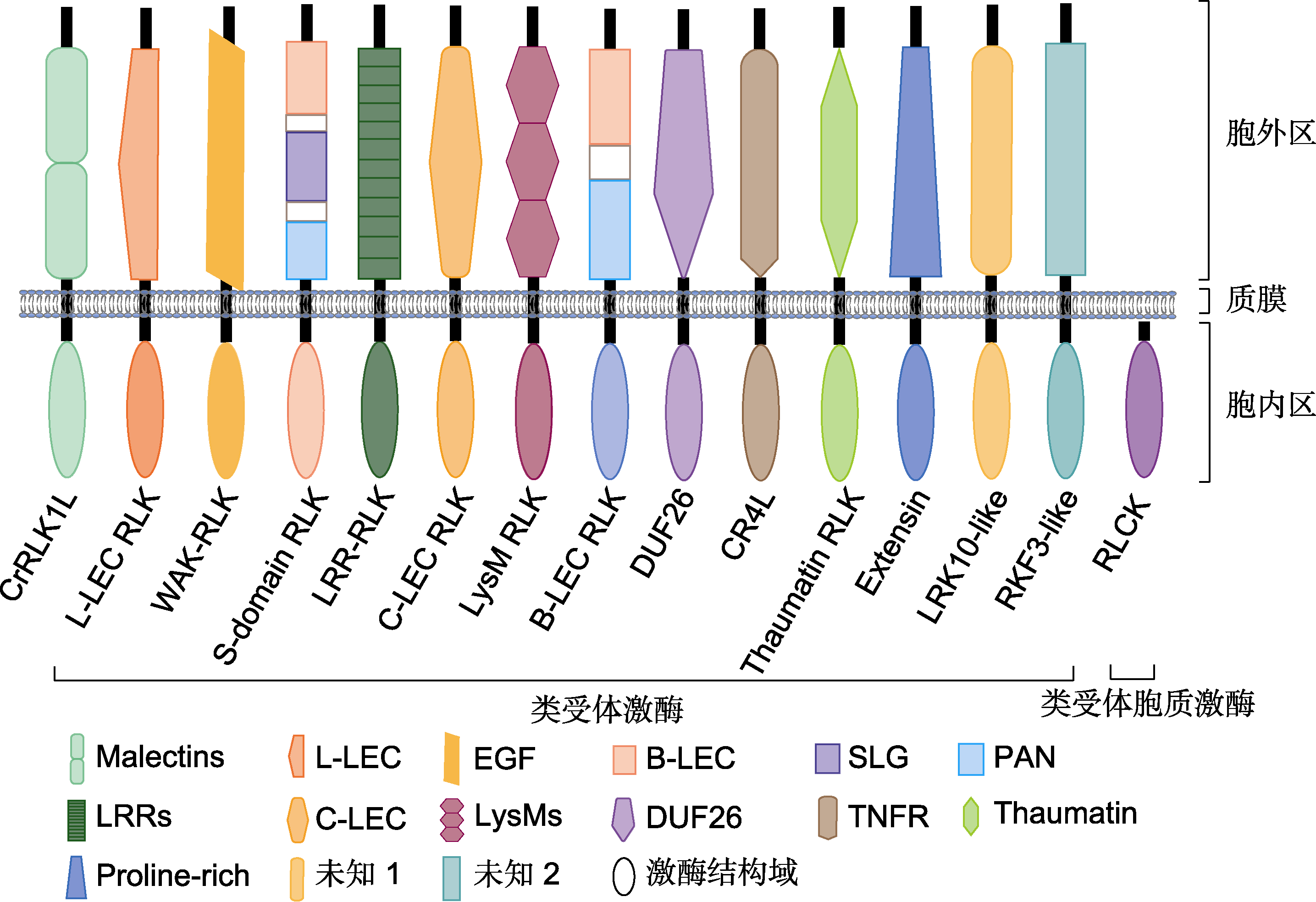
图1 水稻类受体激酶(RLKs)的主要结构基序和功能结构域 CrRLK1L: 长春花受体样激酶; L-LEC: 豆科植物凝集素; WAK: 细胞壁相关激酶; LRR: 亮氨酸富集重复; C-LEC: 钙离子依赖型凝集素; LysM: 溶素基序; B-LEC: 球茎型凝集素; DUF: 未知功能域; EGF: 类表皮生长因子; SLG: S位点糖蛋白; PAN: 纤溶酶原/苹果/线虫蛋白结构域; TNFR: 肿瘤坏死因子受体
Figure 1 The major structural motifs and functional domains of receptor-like kinases (RLKs) in rice CrRLK1L: Catharanthus roseus RLK1-like kinase; L-LEC: Legume lectin; WAK: Wall associated kinase; LRR: Leucine-rich repeat; C-LEC: Calcium dependent lectin; LysM: Lysin motif; B-LEC: Bulb-type lectin; DUF: Domain of unknown function; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; SLG: S-locus glycoprotein; PAN: Plasminogen/apple/nematode protein domain; TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor
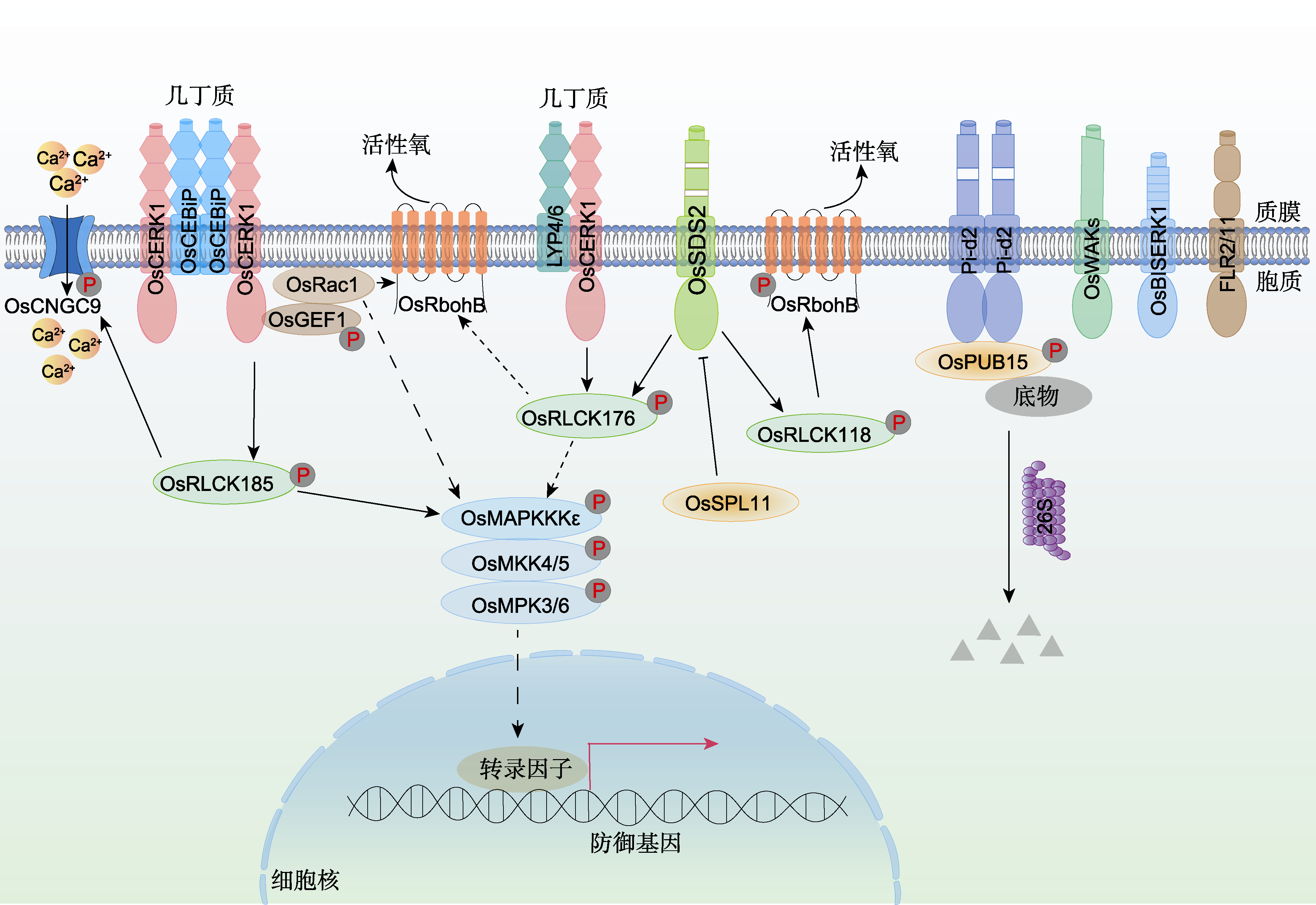
图3 水稻类受体激酶(OsRLKs)参与调控抗稻瘟病示意图 实线箭头表示直接激活作用, 虚线箭头表示间接或者未证实的激活作用, T型实线表示抑制作用, P表示磷酸化。
Figure 3 Schematic representations of OsRLKs (Oryza sativa receptor-like kinases) in regulating rice blast resistance Solid arrows indicate positive regulation, dashed arrows indicate indirect or unproven activation, T solid lines indicate negative regulation, and P indicates phosphorylation.
| [1] | 崔晓敏, 季东超, 陈彤, 田世平 (2021). 类受体激酶FER调节植物与病原菌相互作用的分子机制. 植物学报 56, 339-346. |
| [2] |
Akamatsu A, Wong HL, Fujiwara M, Okuda J, Nishide K, Uno K, Imai K, Umemura K, Kawasaki T, Kawano Y, Shimamoto K (2013). An OsCEBiP/OsCERK1-OsRacGEF1-OsRac1 module is an essential early component of chitin-induced rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 13, 465-476.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Ao Y, Li ZQ, Feng DR, Xiong F, Liu J, Li JF, Wang ML, Wang JF, Liu B, Wang HB (2014). OsCERK1 and OsRLCK176 play important roles in peptidoglycan and chitin signaling in rice innate immunity. Plant J 80, 1072-1084.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
Bettembourg M, Dal-Soglio M, Bureau C, Vernet A, Dardoux A, Portefaix M, Bes M, Meynard D, Mieulet D, Cayrol B, Perin C, Courtois B, Ma JF, Dievart A (2017). Root cone angle is enlarged in docs1LRR-RLK mutants in rice. Rice 10, 50.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Cao YL, Duan L, Li HJ, Sun XL, Zhao Y, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP (2007). Functional analysis of Xa3/Xa26 family members in rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Theor Appl Genet 115, 887-895.
DOI URL |
| [6] | Cayrol B, Delteil A, Gobbato E, Kroj T, Morel JB (2016). Three wall-associated kinases required for rice basal immunity form protein complexes in the plasma membrane. Plant Signal Behav 11, e1149676. |
| [7] | Chen JG, Jones AM (2004). AtRGS1 function in Arabidopsis thaliana. Method Enzymol 389, 338-350. |
| [8] |
Chen KY, Ke RN, Du MM, Yi YQ, Chen YC, Wang XC, Yao L, Liu H, Hou X, Xiong LZ, Yang YN, Xie KB (2022). A FLASH pipeline for arrayed CRISPR library construction and the gene function discovery of rice receptor-like kinases. Mol Plant 15, 243-257.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Chen XW, Chern M, Canlas PE, Jiang CY, Ruan DL, Cao PJ, Ronald PC (2010). A conserved threonine residue in the juxtamembrane domain of the XA21 pattern recognition receptor is critical for kinase autophosphorylation and XA21-mediated immunity. J Biol Chem 285, 10454-10463.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Chen XW, Shang JJ, Chen DX, Lei CL, Zou Y, Zhai WX, Liu GZ, Xu JC, Ling ZZ, Cao G, Ma BT, Wang YP, Zhao XF, Li SG, Zhu LH (2006). A B-lectin receptor kinase gene conferring rice blast resistance. Plant J 46, 794-804.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Chen XW, Zuo SM, Schwessinger B, Chern M, Canlas PE, Ruan DL, Zhou XG, Wang J, Daudi A, Petzold CJ, Heazlewood JL, Ronald PC (2014). An XA21-associated kinase (OsSERK2) regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors. Mol Plant 7, 874-892.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Chun Y, Fang JJ, Zafar SA, Shang JY, Zhao JF, Yuan SJ, Li XY (2020). MINI SEED 2 (MIS2) encodes a receptor- like kinase that controls grain size and shape in rice. Rice 13, 7.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
Dievart A, Gottin C, Périn C, Ranwez V, Chantret N (2020). Origin and diversity of plant receptor-like kinases. Annu Rev Plant Biol 71, 131-156.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Dievart A, Perin C, Hirsch J, Bettembourg M, Lanau N, Artus F, Bureau C, Noel N, Droc G, Peyramard M, Pereira S, Courtois B, Morel JB, Guiderdoni E (2016). The phenome analysis of mutant alleles in leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase genes in rice reveals new potential targets for stress tolerant cereals. Plant Sci 242, 240-249.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Dubouzet JG, Maeda S, Sugano S, Ohtake M, Hayashi N, Ichikawa T, Kondou Y, Kuroda H, Horii Y, Matsui M, Oda K, Hirochika H, Takatsuji H, Mori M (2011). Screening for resistance against Pseudomonas syringae in rice-FOX Arabidopsis lines identified a putative receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase gene that confers resistance to major bacterial and fungal pathogens in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Biotechnol J 9, 466-485.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Fan JB, Bai PF, Ning YS, Wang JY, Shi XT, Xiong YH, Zhang K, He F, Zhang CY, Wang RY, Meng XZ, Zhou JG, Wang M, Shirsekar G, Park CH, Bellizzi M, Liu WD, Jeon JS, Xia Y, Shan LB, Wang GL (2018). The monocot-specific receptor-like kinase SDS2 controls cell death and immunity in rice. Cell Host Microbe 23, 498-510.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Feng P, Shi JQ, Zhang T, Zhong YQ, Zhang LS, Yu GL, Zhang TQ, Zhu XY, Xing YD, Yin WZ, Sang XC, Ling YH, Zhang CW, Yang ZL, He GH, Wang N (2019). Zebra leaf 15, a receptor-like protein kinase involved in moderate low temperature signaling pathway in rice. Rice 12, 83.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Giri J, Vij S, Dansana PK, Tyagi AK (2011). Rice A20/AN1 zinc-finger containing stress-associated proteins (SAP1/11) and a receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase (OsRLCK253) interact via A20 zinc-finger and confer abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. New Phytol 191, 721-732.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Gómez-Gómez L, Boller T (2000). FLS2: an LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 5, 1003-1011. |
| [20] | Harkenrider M, Sharma R, De Vleesschauwer D, Tsao L, Zhang XT, Chern M, Canlas P, Zuo SM, Ronald PC (2016). Overexpression of rice wall-associated kinase 25 (OsWAK25) alters resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens. PLoS One 11, e0147310. |
| [21] |
Haruta M, Sabat G, Stecker K, Minkoff BB, Sussman MR (2014). A peptide hormone and its receptor protein kinase regulate plant cell expansion. Science 343, 408-411.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Hayafune M, Berisio R, Marchetti R, Silipo A, Kayama M, Desaki Y, Arima S, Squeglia F, Ruggiero A, Tokuyasu K, Molinaro A, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2014). Chitin-induced activation of immune signaling by the rice receptor CEBiP relies on a unique sandwich-type dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, E404-E413. |
| [23] |
He JM, Zhang C, Dai HL, Liu H, Zhang XW, Yang J, Chen X, Zhu YY, Wang DP, Qi XF, Li WC, Wang ZH, An GY, Yu N, He ZH, Wang YF, Xiao YL, Zhang P, Wang ET (2019). A LysM receptor heteromer mediates perception of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiotic signal in rice. Mol Plant 12, 1561-1576.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
He ZH, Wang ZY, Li JM, Zhu Q, Lamb C, Ronald P, Chory J (2000). Perception of brassinosteroids by the extracellular domain of the receptor kinase BRI1. Science 288, 2360-2363.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | He ZY, Zou T, Xiao Q, Yuan GQ, Liu MM, Tao Y, Zhou D, Zhang X, Deng QM, Wang SQ, Zheng AP, Zhu J, Liang YY, Yu XM, Wang AJ, Liu HN, Wang LX, Li P, Li SC (2021). An L-type lectin receptor-like kinase promotes starch accumulation during rice pollen maturation. Development 148, dev196378. |
| [26] |
Huang CF, Yamaji N, Ono K, Ma JF (2012). A leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase gene is involved in the specification of outer cell layers in rice roots. Plant J 69, 565-576.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Huang H, Ma H (1997). FON1, an Arabidopsis gene that terminates floral meristem activity and controls flower organ number. Plant Cell 9, 115-134.
PMID |
| [28] |
Jiang YH, Bao L, Jeong SY, Kim SK, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2012). XIAO is involved in the control of organ size by contributing to the regulation of signaling and homeostasis of brassinosteroids and cell cycling in rice. Plant J 70, 398-408.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Kang JF, Li JM, Gao S, Tian C, Zha XJ (2017). Overexpression of the leucine-rich receptor-like kinase gene LRK2 increases drought tolerance and tiller number in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 15, 1175-1185.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Kanneganti V, Gupta AK (2008). Wall associated kinases from plants—an overview. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 14, 109-118.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Kanneganti V, Gupta AK (2011). RNAi mediated silencing of a wall associated kinase, OsiWAK1 in Oryza sativa results in impaired root development and sterility due to anther indehiscence: wall associated kinases from Oryza sativa. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 17, 65-77.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Kim YJ, Kim MH, Hong WJ, Moon S, Kim ST, Park SK, Jung KH (2021). OsMTD2-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) balance is essential for intact pollen-tube elongation in rice. Plant J 107, 1131-1147.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Kishimoto K, Kouzai Y, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Minami E, Nishizawa Y (2010). Perception of the chitin oligosaccharides contributes to disease resistance to blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Plant J 64, 343-354.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Kouzai Y, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Minami E, Nishizawa Y (2013). Expression of the chimeric receptor between the chitin elicitor receptor CEBiP and the receptor-like protein kinase Pi-d2 leads to enhanced responses to the chitin elicitor and disease resistance against Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Plant Mol Biol 81, 287-295.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Kouzai Y, Mochizuki S, Nakajima K, Desaki Y, Hayafune M, Miyazaki H, Yokotani N, Ozawa K, Minami E, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Nishizawa Y (2014). Targeted gene disruption of OsCERK1 reveals its indispensable role in chitin perception and involvement in the peptidoglycan response and immunity in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 27, 975-982.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Li CH, Wang G, Zhao JL, Zhang LQ, Ai LF, Han YF, Sun DY, Zhang SW, Sun Y (2014). The receptor-like kinase SIT1 mediates salt sensitivity by activating MAPK3/6 and regulating ethylene homeostasis in rice. Plant Cell 26, 2538-2553.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Li D, Wang L, Wang M, Xu YY, Luo W, Liu YJ, Xu ZH, Li J, Chong K (2009a). Engineering OsBAK1 gene as a molecular tool to improve rice architecture for high yield. Plant Biotechnol J 7, 791-806.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Li H, Zhou SY, Zhao WS, Su SC, Peng YL (2009b). A novel wall-associated receptor-like protein kinase gene, OsWAK1, plays important roles in rice blast disease resistance. Plant Mol Biol 69, 337-346.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Li YX, Tang DY, Li L, Zhao XY, Lin JZ, Liu XM (2018). Plant stature related receptor-like kinanse2 (PSRK2) acts as a factor that determines stem elongation toward gibberellins response in rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 82, 1931-1941.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Li ZQ, Ao Y, Feng DR, Liu J, Wang JF, Wang HB, Liu B (2017). OsRLCK57, OsRLCK107 and OsRLCK118 positively regulate chitin- and PGN-induced immunity in rice. Rice 10, 6.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Limpens E, Franken C, Smit P, Willemse J, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2003). LysM domain receptor kinases regulating rhizobial nod factor-induced infection. Science 302, 630-633.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Lin FM, Li S, Wang K, Tian HR, Gao JF, Zhao QZ, Du CQ (2020). A leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, OsSTLK, modulates salt tolerance in rice. Plant Sci 296, 110465.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Liu LT, Zheng CH, Kuang B, Wei LQ, Yan LF, Wang T (2016). Receptor-like kinase RUPO interacts with potassium transporters to regulate pollen tube growth and integrity in rice. PLoS Genet 12, e1006085. |
| [44] |
Liu T, Jiang GQ, Yao XF, Liu CM (2021). The leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase OsERL plays a critical role in anther lobe formation in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 563, 85-91.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Liu TT, Liu ZX, Song CJ, Hu YF, Han ZF, She J, Fan FF, Wang JW, Jin CW, Chang JB, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2012). Chitin-induced dimerization activates a plant immune receptor. Science 336, 1160-1164.
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
Ma Y, Dai XY, Xu YY, Luo W, Zheng XM, Zeng DL, Pan YJ, Lin XL, Liu HH, Zhang DJ, Xiao J, Guo XY, Xu SJ, Niu YD, Jin JB, Zhang H, Xu X, Li LG, Wang W, Qian Q, Ge S, Chong K (2015). COLD1 confers chilling tolerance in rice. Cell 160, 1209-1221.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Maeda S, Hayashi N, Sasaya T, Mori M (2016). Overexpression of BSR1 confers broad-spectrum resistance against two bacterial diseases and two major fungal diseases in rice. Breed Sci 66, 396-406.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Markmann K, Giczey G, Parniske M (2008). Functional adaptation of a plant receptor-kinase paved the way for the evolution of intracellular root symbioses with bacteria. PLoS Biol 6, e68. |
| [49] |
Matsubayashi Y, Ogawa M, Morita A, Sakagami Y (2002). An LRR receptor kinase involved in perception of a peptide plant hormone, phytosulfokine. Science 296, 1470-1472.
DOI PMID |
| [50] |
Miyata K, Hayafune M, Kobae Y, Kaku H, Nishizawa Y, Masuda Y, Shibuya N, Nakagawa T (2016). Evaluation of the role of the LysM receptor-like kinase, OsNFR5/ OsRLK2 for AM symbiosis in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 57, 2283-2290.
PMID |
| [51] |
Miyata K, Kozaki T, Kouzai Y, Ozawa K, Ishii K, Asamizu E, Okabe Y, Umehara Y, Miyamoto A, Kobae Y, Akiyama K, Kaku H, Nishizawa Y, Shibuya N, Nakagawa T (2014). The bifunctional plant receptor, OsCERK1, regulates both chitin-triggered immunity and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 1864-1872.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Moon S, Jung KH, Lee DE, Lee DY, Lee J, An K, Kang HG, An G (2006). The rice FON1 gene controls vegetative and reproductive development by regulating shoot apical meristem size. Mol Cells 21, 147-152. |
| [53] |
Morinaka Y, Sakamoto T, Inukai Y, Agetsuma M, Kitano H, Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2006). Morphological alteration caused by brassinosteroid insensitivity increases the biomass and grain production of rice. Plant Physiol 141, 924-931.
DOI PMID |
| [54] | Nagar P, Sharma N, Jain M, Sharma G, Prasad M, Mustafiz A (2022). OsPSKR15, a phytosulfokine receptor from rice enhances abscisic acid response and drought stress tolerance. Physiol Plant 174, e13569. |
| [55] |
Nakamura A, Fujioka S, Sunohara H, Kamiya N, Hong Z, Inukai Y, Miura K, Takatsuto S, Yoshida S, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Hasegawa Y, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2006). The role of OsBRI1 and its homologous genes, OsBRL1 and OsBRL3, in rice. Plant Physiol 140, 580-590.
DOI PMID |
| [56] |
Ogawa M, Shinohara H, Sakagami Y, Matsubayashi Y (2008). Arabidopsis CLV3 peptide directly binds CLV1 ectodomain. Science 319, 294-294.
DOI PMID |
| [57] |
Ouyang SQ, Liu YF, Liu P, Lei G, He SJ, Ma B, Zhang WK, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2010). Receptor-like kinase OsSIK1 improves drought and salt stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Plant J 62, 316-329.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Park CJ, Ronald PC (2012). Cleavage and nuclear localization of the rice XA21 immune receptor. Nat Commun 3, 920.
DOI |
| [59] |
Park HS, Ryu HY, Kim BH, Kim SY, Yoon IS, Nam KH (2011). A subset of OsSERK genes, including OsBAK1, affects normal growth and leaf development of rice. Mol Cells 32, 561-569.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Passricha N, Saifi SK, Kharb P, Tuteja N (2020). Rice lectin receptor-like kinase provides salinity tolerance by ion homeostasis. Biotechnol Bioeng 117, 498-510.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
Peng H, Zhang Q, Li YD, Lei CL, Zhai Y, Sun XH, Sun DY, Sun Y, Lu TG (2009). A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase, OsBRR1, is involved in rice blast resistance. Planta 230, 377-385.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
Peng XQ, Wang ML, Li YQ, Yan W, Chang ZY, Chen ZF, Xu CJ, Yang CW, Deng XW, Wu JX, Tang XY (2020). Lectin receptor kinase OsLecRK-S.7 is required for pollen development and male fertility. J Integr Plant Biol 62, 1227-1245.
DOI |
| [63] |
Pu CX, Sun Y (2012). Rice Crinkly4 receptor-like kinase positively regulates culm elongation and amino acid K532 is not essential for its kinase activity. Plant Signal Behav 7, 1062-1064.
DOI URL |
| [64] | Sade N, Weng F, Tajima H, Zeron Y, Zhang L, Rubio Wilhelmi MDM, Day G, Peleg Z, Blumwald E (2020). A cytoplasmic receptor-like kinase contributes to salinity tolerance. Plants (Basel) 9, 1383. |
| [65] |
Sakaguchi J, Itoh JI, Ito Y, Nakamura A, Fukuda H, Sawa S (2010). COE1, an LRR-RLK responsible for commissural vein pattern formation in rice. Plant J 63, 405-416.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
Sandve SR, Rudi H, Asp T, Rognli OA (2008). Tracking the evolution of a cold stress associated gene family in cold tolerant grasses. BMC Evol Biol 8, 245.
DOI PMID |
| [67] |
Shen H, Zhong XB, Zhao FF, Wang YM, Yan BX, Li Q, Chen GY, Mao BZ, Wang JJ, Li YS, Xiao GY, He YK, Xiao H, Li JM, He ZH (2015). Overexpression of receptor-like kinase ERECTA improves thermotolerance in rice and tomato. Nat Biotechnol 33, 996-1003.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Shimizu T, Nakano T, Takamizawa D, Desaki Y, Ishii- Minami N, Nishizawa Y, Minami E, Okada K, Yamane H, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2010). Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice. Plant J 64, 204-214.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
Shin NH, Trang DT, Hong WJ, Kang K, Chuluuntsetseg J, Moon JK, Yoo YH, Jung KH, Yoo SC (2019). Rice senescence-induced receptor-like kinase (OsSRLK) is involved in phytohormone-mediated chlorophyll degradation. Int J Mol Sci 21, 260.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001). Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 10763-10768.
DOI PMID |
| [71] |
Shiu SH, Karlowski WM, Pan RS, Tzeng YH, Mayer KFX, Li WH (2004). Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 16, 1220-1234.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
Song DH, Li GJ, Song FM, Zheng Z (2008). Molecular characterization and expression analysis of OsBISERK1, a gene encoding a leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, during disease resistance responses in rice. Mol Biol Rep 35, 275-283.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL, Kim HS, Pi LY, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai WX, Zhu LH, Fauquet C, Ronald P (1995). A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 270, 1804-1806.
DOI PMID |
| [74] |
Song YJ, Niu RF, Yu HL, Guo J, Du CH, Zhang ZL, Wei Y, Li JX, Zhang SQ (2022). OsSLA1 functions in leaf angle regulation by enhancing the interaction between OsBRI1 and OsBAK1 in rice. Plant J 110, 1111-1127.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
Sun XL, Cao YL, Yang ZF, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP, Zhang QF (2004). Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J 37, 517-527.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
Suzaki T, Sato M, Ashikari M, Miyoshi M, Nagato Y, Hirano HY (2004). The gene FLORAL ORGAN NUMBER 1 regulates floral meristem size in rice and encodes a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase orthologous to Arabidopsis CLAVATA1. Development 131, 5649-5657.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
Torii KU (2004). Leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases in plants: structure, function, and signal transduction pathways. Int Rev Cytol 234, 1-46.
PMID |
| [78] |
Van der Knaap E, Song WY, Ruan DL, Sauter M, Ronald PC, Kende H (1999). Expression of a gibberellin-induced leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase in deepwater rice and its interaction with kinase-associated protein phosphatase. Plant Physiol 120, 559-570.
PMID |
| [79] |
Walker JC, Zhang R (1990). Relationship of a putative receptor protein kinase from maize to the S-locus glycoproteins of Brassica. Nature 345, 743-746.
DOI |
| [80] |
Wang B, Fang RQ, Zhang J, Han JL, Chen FM, He FR, Liu YG, Chen LT (2020). Rice LecRK5 phosphorylates a UGPase to regulate callose biosynthesis during pollen development. J Exp Bot 71, 4033-4041.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Wang C, Wang G, Zhang C, Zhu PK, Dai HL, Yu N, He ZH, Xu L, Wang ET (2017). OsCERK1-mediated chitin perception and immune signaling requires receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 185 to activate an MAPK cascade in rice. Mol Plant 10, 619-633.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Wang J, Qu BY, Dou SJ, Li LY, Yin DD, Pang ZQ, Zhou ZZ, Tian MM, Liu GZ, Xie Q, Tang DZ, Chen XW, Zhu LH (2015). The E3 ligase OsPUB15 interacts with the receptor-like kinase PID2 and regulates plant cell death and innate immunity. BMC Plant Biol 15, 49.
DOI PMID |
| [83] |
Wang N, Huang HJ, Ren ST, Li JJ, Sun Y, Sun DY, Zhang SQ (2012). The rice wall-associated receptor-like kinase gene OsDEES1 plays a role in female gametophyte development. Plant Physiol 160, 696-707.
DOI PMID |
| [84] |
Wang YS, Pi LY, Chen XH, Chakrabarty PK, Jiang JD, De Leon AL, Liu GZ, Li LC, Benny U, Oard J, Ronald PC, Song WY (2006). Rice XA21 binding protein 3 is a ubiquitin ligase required for full Xa21-mediated disease resistance. Plant Cell 18, 3635-3646.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
Wu FQ, Sheng PK, Tan JJ, Chen XL, Lu GW, Ma WW, Heng YQ, Lin QB, Zhu SS, Wang JL, Wang J, Guo XP, Zhang X, Lei CL, Wan JM (2015). Plasma membrane receptor-like kinase leaf panicle 2 acts downstream of the DROUGHT AND SALT TOLERANCE transcription factor to regulate drought sensitivity in rice. J Exp Bot 66, 271-281.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Xiang Y, Cao YL, Xu CG, Li XH, Wang SP (2006). Xa3, conferring resistance for rice bacterial blight and encoding a receptor kinase-like protein, is the same as Xa26. Theor Appl Genet 113, 1347-1355.
DOI PMID |
| [87] |
Xu L, Wang JZ, Xiao Y, Han ZF, Chai JJ (2022). Structural insight into chitin perception by chitin elicitor receptor kinase 1 of Oryza sativa. J Integr Plant Biol 65, 235-248.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
Xu WH, Wang YS, Liu GZ, Chen XH, Tinjuangjun P, Pi LY, Song WY (2006). The autophosphorylated Ser686, Thr688, and Ser689 residues in the intracellular juxtamembrane domain of XA21 are implicated in stability control of rice receptor-like kinase. Plant J 45, 740-751.
DOI URL |
| [89] |
Yamaguchi K, Yamada K, Ishikawa K, Yoshimura S, Hayashi N, Uchihashi K, Ishihama N, Kishi-Kaboshi M, Takahashi A, Tsuge S, Ochiai H, Tada Y, Shimamoto K, Yoshioka H, Kawasaki T (2013). A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase targeted by a plant pathogen effector is directly phosphorylated by the chitin receptor and mediates rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 13, 347-357.
DOI PMID |
| [90] |
Yamamuro C, Ihara Y, Wu X, Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Ashikari M, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2000). Loss of function of a rice brassinosteroid insensitive1 homolog prevents internode elongation and bending of the lamina joint. Plant Cell 12, 1591-1606.
DOI PMID |
| [91] |
Yang Z, Sun X, Wang S, Zhang Q (2003). Genetic and physical mapping of a new gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 106, 1467-1472.
PMID |
| [92] |
Yang ZH, Xing JJ, Wang L, Liu Y, Qu JN, Tan Y, Fu XQ, Lin QL, Deng HF, Yu F (2020). Mutations of two FERONIA-like receptor genes enhance rice blast resistance without growth penalty. J Exp Bot 71, 2112-2126.
DOI URL |
| [93] |
Yu JP, Han JJ, Kim YJ, Song M, Yang Z, He Y, Fu RF, Luo ZJ, Hu JP, Liang WQ, Zhang DB (2017). Two rice receptor-like kinases maintain male fertility under changing temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 12327-12332.
DOI PMID |
| [94] |
Yuan MH, Ngou BPM, Ding PT, Xin XF (2021). PTI-ETI crosstalk: an integrative view of plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 62, 102030.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
Yue ZL, Liu N, Deng ZP, Zhang Y, Wu ZM, Zhao JL, Sun Y, Wang ZY, Zhang SW (2022). The receptor kinase OsWAK11 monitors cell wall pectin changes to fine-tune brassinosteroid signaling and regulate cell elongation in rice. Curr Biol 32, 2454-2466.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
Zeng DD, Yang CC, Qin R, Alamin M, Yue EK, Jin XL, Shi CH (2018). A guanine insert in OsBBS1 leads to early leaf senescence and salt stress sensitivity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 37, 93 3-946.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
Zhang BW, Wang XL, Zhao ZY, Wang RJ, Huang XH, Zhu YL, Yuan L, Wang YC, Xu XD, Burlingame AL, Gao YJ, Sun Y, Tang WQ (2016). OsBRI1 activates BR signaling by preventing binding between the TPR and kinase domains of OsBSK3 via phosphorylation. Plant Physiol 170, 1149-1161.
DOI PMID |
| [98] | Zhang C, He JM, Dai HL, Wang G, Zhang XW, Wang C, Shi JC, Chen X, Wang DP, Wang ET (2021a). Discriminating symbiosis and immunity signals by receptor competition in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 118, e2023738118. |
| [99] |
Zhang H, Zhai N, Ma X, Zhou HN, Cui YC, Wang C, Xu GY (2021b). Overexpression of OsRLCK241 confers enhanced salt and drought tolerance in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Gene 768, 145278.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
Zhang HT, Cao YL, Zhao J, Li XH, Xiao JH, Wang SP (2011). A pair of orthologs of a leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase-like disease resistance gene family regulates rice response to raised temperature. BMC Plant Biol 11, 160.
DOI PMID |
| [101] | Zhang X, Zhao GC, Tan Q, Yuan H, Betts N, Zhu L, Zhang DB, Liang WQ (2020). Rice pollen aperture formation is regulated by the interplay between OsINP1 and OsDAF1. Nat Plants 6, 394-403. |
| [102] |
Zhang XW, Dong WT, Sun J, Feng F, Deng YW, He ZH, Oldroyd GED, Wang ET (2015). The receptor kinase CERK1 has dual functions in symbiosis and immunity signaling. Plant J 81, 258-267.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
Zhang ZY, Li JJ, Pan YH, Li JL, Zhou L, Shi HL, Zeng YW, Guo HF, Yang SM, Zheng WW, Yu JP, Sun XM, Li GL, Ding YL, Ma L, Shen SQ, Dai LY, Zhang HL, Yang SH, Guo Y, Li ZC (2017). Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats. Nat Commun 8, 14788.
DOI |
| [104] |
Zhao JL, Zhang LQ, Liu N, Xu SL, Yue ZL, Zhang LL, Deng ZP, Burlingame AL, Sun DY, Wang ZY, Sun Y, Zhang SW (2019). Mutual regulation of receptor-like kinase SIT1 and B'κ-PP2A shapes the early response of rice to salt stress. Plant Cell 31, 2131-2151.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
Zhao XA, de Palma J, Oane R, Gamuyao R, Luo M, Chaudhury A, Hervé P, Xue QZ, Bennett J (2008). OsTDL1A binds to the LRR domain of rice receptor kinase MSP1, and is required to limit sporocyte numbers. Plant J 54, 375-387.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
Zhou YB, Liu C, Tang DY, Yan L, Wang D, Yang YZ, Gui JS, Zhao XY, Li LG, Tang XD, Yu F, Li JL, Liu LL, Zhu YH, Lin JZ, Liu XM (2018). The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase STRK1 phosphorylates and activates CatC, thereby regulating H2O2 homeostasis and improving salt tolerance in rice. Plant Cell 30, 1100-1118.
DOI URL |
| [107] |
Zou XH, Qin ZR, Zhang CY, Liu B, Liu J, Zhang CS, Lin CT, Li HY, Zhao T (2015). Over-expression of an S-domain receptor-like kinase extracellular domain improves panicle architecture and grain yield in rice. J Exp Bot 66, 7197-7209.
DOI PMID |
| [108] |
Zou Y, Liu XY, Wang Q, Chen Y, Liu C, Qiu Y, Zhang W (2014). OsRPK1, a novel leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, negatively regulates polar auxin transport and root development in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840, 1676-1685.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 叶灿, 姚林波, 金莹, 高蓉, 谭琪, 李旭映, 张艳军, 陈析丰, 马伯军, 章薇, 张可伟. 水稻水杨酸代谢突变体高通量筛选方法的建立与应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 1-0. |
| [2] | 赵凌, 管菊, 梁文化, 张勇, 路凯, 赵春芳, 李余生, 张亚东. 基于高密度Bin图谱的水稻苗期耐热性QTL定位[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 342-353. |
| [3] | 苏晨, 牛钰凡, 徐航, 王希岭, 于英俊, 何雨晴, 王雷. 生物钟与光温环境信号互作网络研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 315-341. |
| [4] | 李新宇, 谷月, 徐非非, 包劲松. 水稻胚乳淀粉合成相关蛋白的翻译后修饰研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 256-270. |
| [5] | 李建国, 张怡, 张文君. 水稻根系铁膜形成及对磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 132-143. |
| [6] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [7] | 李青洋, 刘翠, 何李, 彭姗, 马嘉吟, 胡子祎, 刘宏波. 甘蓝型油菜BnaA02.CPSF6基因的克隆及功能分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 62-73. |
| [8] | 姚瑞枫, 谢道昕. 水稻独脚金内酯信号感知的激活和终止[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 873-877. |
| [9] | 闫恒宇, 李朝霞, 李玉斌. 高温对玉米生长的影响及中国耐高温玉米筛选研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 1007-1023. |
| [10] | 杜庆国, 李文学. lncRNA调控玉米生长发育和非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 950-962. |
| [11] | 王涛, 冯敬磊, 张翠. 高温胁迫影响玉米生长发育的分子机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 963-977. |
| [12] | 连锦瑾, 唐璐瑶, 张伊诺, 郑佳兴, 朱超宇, 叶语涵, 王跃星, 商文楠, 傅正浩, 徐昕璇, 吴日成, 路梅, 王长春, 饶玉春. 水稻抗氧化性状遗传位点挖掘及候选基因分析[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 738-751. |
| [13] | 路笃贤, 张严妍, 刘艳, 李岩竣, 左新秀, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 非编码RNA在植物生长发育及逆境响应中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 709-725. |
| [14] | 黄佳慧, 杨惠敏, 陈欣雨, 朱超宇, 江亚楠, 胡程翔, 连锦瑾, 芦涛, 路梅, 张维林, 饶玉春. 水稻突变体pe-1对弱光胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 574-584. |
| [15] | 周俭民. 收放自如的明星战车[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(3): 343-346. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||