

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 33-48.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24097 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24097
张向歌, 陈晨, 程珊, 李春鑫, 朱雅婧, 许欣然, 王会伟*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-06-28
接受日期:2024-08-20
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-08-27
通讯作者:
* 王会伟, 博士, 研究员, 河南省优秀专家, 享受国务院特殊津贴专家。河南省农业科学院经济作物研究所副所长, 油莎豆学科技术带头人。主要从事油莎豆种质资源鉴定、评价和创制, 关键性状形成机制解析, 品种遗传改良等研究。E-mail: whuiweiw@163.com基金资助:
Xiangge Zhang, Chen Chen, Shan Cheng, Chunxin Li, Yajing Zhu, Xinran Xu, Huiwei Wang*( )
)
Received:2024-06-28
Accepted:2024-08-20
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-08-27
Contact:
* E-mail: 摘要: 块茎是油莎豆(Cyperus esculentus)独特且极其重要的器官, 富含油脂且具有与种子类似的繁殖能力, 研究油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因对于解析其块茎特异性生长发育(尤其是油脂积累)的调控机理具有重要意义。通过对油莎豆主要器官(根、叶、分蘖节、匍匐茎和块茎)进行转录组测序, 全面筛选块茎特异性表达基因, 并分析相关基因的功能。结果表明, 分别以根、叶、分蘖节和匍匐茎为对照, 经过多组比对分析后共鉴定出155个块茎特异性表达基因; GO富集分析显示, 与种子发育、种子油体合成、油脂储存、脱落酸响应、非生物刺激响应和蛋白折叠相关的7个GO条目显著富集, 这些GO条目涉及的基因恰好反映出油莎豆块茎独特的类似种子的发育特性。其中, CESC_00080和CESC_16572编码油体钙蛋白, CESC_08636、CESC_12549和CESC_17828编码油体蛋白, 均参与植物油体的形成, 而油体形成是植物完成油脂储存的关键步骤, 表明这些油体形成相关基因在块茎中的特异性表达可能是油莎豆在块茎中储存大量油脂的关键所在。此外, 还筛选出8个块茎特异性表达转录因子编码基因, 如CESC_00448 (编码abscisic acid insensitive 5-like protein ABI5)和CESC_03736 (编码heat stress transcription factor C), 而在鉴定到的块茎特异性表达基因中发现一些潜在的靶基因, 表明这些转录因子可能调控各自靶基因的特异性表达。综上, 研究结果可为油莎豆块茎发育相关基因调控网络的构建以及块茎特异性基因表达的分子机制解析提供重要参考。
张向歌, 陈晨, 程珊, 李春鑫, 朱雅婧, 许欣然, 王会伟. 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因鉴定及分析. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 33-48.
Xiangge Zhang, Chen Chen, Shan Cheng, Chunxin Li, Yajing Zhu, Xinran Xu, Huiwei Wang. Identification and Analysis of Tuber-specific Expression Genes in Cyperus esculentus. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(1): 33-48.
| Gene | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CESC_13967 | ACTCTGGTGATGGTGTGAGC | CCCTCTCTCCGTCAGGATCT |
| CESC_00080 | CTACCACCTCTCCGTGCTTC | CTACCACCTCTCCGTGCTTC |
| CESC_17828 | GCACCAGAGAGAAGGACAGC | GCACCAGAGAGAAGGACAGC |
| CESC_00330 | GACAAACCATCACCACAGCG | ATCACCAGCATCTTCCCGTC |
| CESC_18197 | GCCACTCCATTCCGATTTGC | GCGTGAAGTTGCCGATGATG |
| CESC_16081 | CGGGTCAACAGAAGAAGGAGC | CGTCGACAGTCTTGTTCTCC |
| CESC_03736 | GGATTCGGTGATCTCGTGGG | CAGCTCTATCAGCCTCGCTT |
表1 qRT-PCR特异性引物序列
Table 1 Specific primer sequences of qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward primer (5′-3′) | Reverse primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| CESC_13967 | ACTCTGGTGATGGTGTGAGC | CCCTCTCTCCGTCAGGATCT |
| CESC_00080 | CTACCACCTCTCCGTGCTTC | CTACCACCTCTCCGTGCTTC |
| CESC_17828 | GCACCAGAGAGAAGGACAGC | GCACCAGAGAGAAGGACAGC |
| CESC_00330 | GACAAACCATCACCACAGCG | ATCACCAGCATCTTCCCGTC |
| CESC_18197 | GCCACTCCATTCCGATTTGC | GCGTGAAGTTGCCGATGATG |
| CESC_16081 | CGGGTCAACAGAAGAAGGAGC | CGTCGACAGTCTTGTTCTCC |
| CESC_03736 | GGATTCGGTGATCTCGTGGG | CAGCTCTATCAGCCTCGCTT |
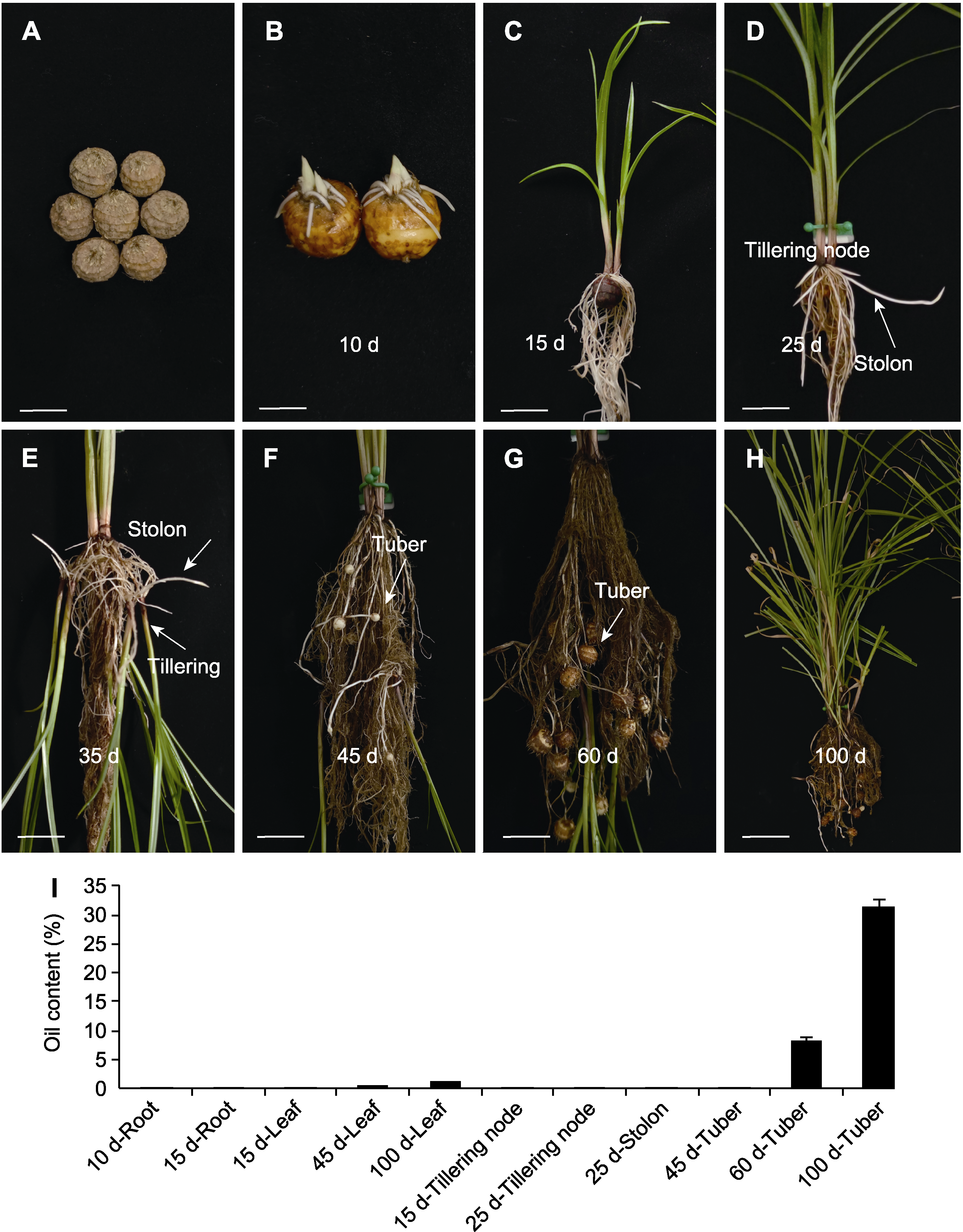
图1 油莎豆全生育期观察 (A) 干块茎(bar=20 mm); (B) 块茎发芽(bar=10 mm); (C) 幼苗生长(bar=50 mm); (D) 匍匐茎形成(bar=30 mm); (E) 分蘖形成(bar=25 mm); (F) 块茎形成(bar=25 mm); (G) 块茎变大(bar=25 mm); (H) 叶片枯黄(bar=80 mm); (I) 不同器官的油脂含量
Figure 1 Observation of the whole growth period of Cyperus esculentus (A) Dried tuber (bar=20 mm); (B) Tuber germination (bar=10 mm); (C) Seedling growth (bar=50 mm); (D) Stolon formation (bar=30 mm); (E) Tillering formation (bar=25 mm); (F) Tuber formation (bar=25 mm); (G) The enlargement of tubers (bar= 25 mm); (H) Dry yellow leaves (bar=80 mm); (I) The oil content in different organs
| Samples | Clean reads | Clean bases | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | Mapped reads | Mapped ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | 57066812 | 8330335323 | 97.86 | 93.98 | 51517757 | 90.26 |
| Leaf | 54318808 | 7949486769 | 97.59 | 93.40 | 48848097 | 89.92 |
| Tillering node | 57497577 | 8370290261 | 97.26 | 93.71 | 51548858 | 89.66 |
| Stolon | 58790213 | 8560106850 | 97.72 | 93.68 | 52822328 | 89.85 |
| Tuber | 58869179 | 8582198623 | 97.65 | 94.56 | 52938611 | 89.93 |
表2 转录组测序数据统计分析
Table 2 Statistical analysis of transcriptome sequencing data
| Samples | Clean reads | Clean bases | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | Mapped reads | Mapped ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | 57066812 | 8330335323 | 97.86 | 93.98 | 51517757 | 90.26 |
| Leaf | 54318808 | 7949486769 | 97.59 | 93.40 | 48848097 | 89.92 |
| Tillering node | 57497577 | 8370290261 | 97.26 | 93.71 | 51548858 | 89.66 |
| Stolon | 58790213 | 8560106850 | 97.72 | 93.68 | 52822328 | 89.85 |
| Tuber | 58869179 | 8582198623 | 97.65 | 94.56 | 52938611 | 89.93 |
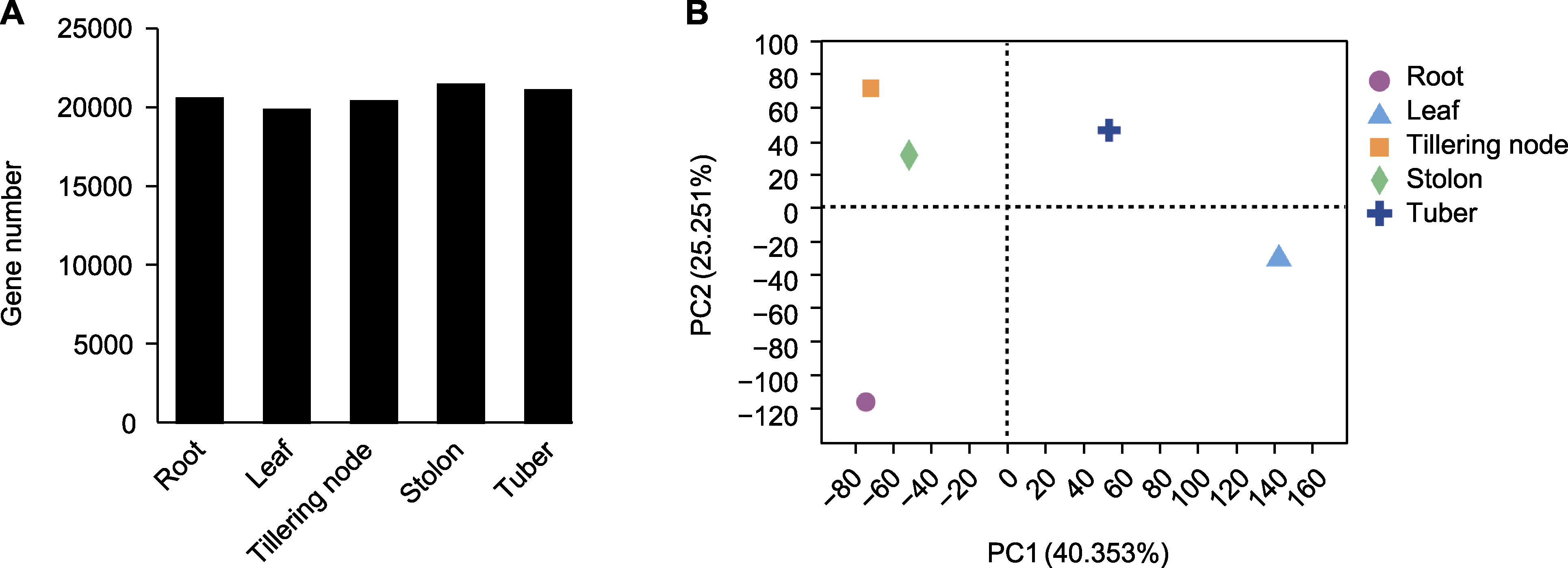
图2 油莎豆不同器官的转录组测序数据分析 (A) 不同器官中表达基因的数目; (B) 测序样品间基因表达量的主成分分析(PCA)
Figure 2 Analysis of transcriptome sequencing data of different organs of Cyperus esculentus (A) Number of expressed genes in different organs; (B) Principal component analysis (PCA) of gene expression level among sequenced samples
| Gene | Expression level (FPKM) | Gene | Expression level (FPKM) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuber | Root | Leaf | Stolon | Tillering node | Tuber | Root | Leaf | Stolon | Tillering node | ||
| CESC_17828 | 34980.30 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 9.23 | 6.20 | CESC_06642 | 449.61 | 0.00 | 3.36 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| CESC_14076 | 24917.54 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 0.54 | CESC_11684 | 424.54 | 2.11 | 0.12 | 2.17 | 0.94 |
| CESC_08636 | 23808.18 | 0.00 | 2.95 | 1.11 | 1.38 | CESC_00836 | 424.00 | 1.18 | 5.61 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| CESC_16708 | 20282.53 | 1.29 | 4.99 | 9.63 | 2.02 | CESC_04812 | 394.97 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.52 |
| CESC_14073 | 15607.24 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 1.73 | 7.62 | CESC_19053 | 392.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_10265 | 8803.59 | 0.59 | 4.34 | 0.64 | 4.16 | CESC_13856 | 384.53 | 4.48 | 1.53 | 3.09 | 2.19 |
| CESC_13913 | 6560.83 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.13 | CESC_05739 | 373.39 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_13892 | 6062.31 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.27 | CESC_15162 | 373.06 | 2.23 | 1.79 | 1.55 | 1.20 |
| CESC_14077 | 5890.09 | 1.05 | 0.06 | 0.51 | 0.77 | CESC_21269 | 357.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| CESC_00080 | 4834.92 | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.37 | CESC_12660 | 335.49 | 4.32 | 2.69 | 4.42 | 1.52 |
| CESC_12549 | 4632.55 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_15141 | 309.91 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| CESC_00832 | 3760.05 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.20 | CESC_15826 | 293.80 | 0.44 | 3.71 | 1.88 | 1.94 |
| CESC_15373 | 3721.68 | 6.39 | 6.24 | 4.11 | 6.27 | CESC_15198 | 269.77 | 2.29 | 2.45 | 5.19 | 1.98 |
| CESC_10351 | 3695.94 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.19 | CESC_03736 | 268.07 | 0.77 | 7.39 | 3.50 | 8.35 |
| CESC_18271 | 3694.18 | 1.46 | 1.25 | 3.06 | 1.59 | CESC_21099 | 239.33 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 3.22 |
| CESC_21136 | 3589.62 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.29 | CESC_15700 | 239.04 | 0.00 | 2.84 | 0.90 | 0.37 |
| CESC_07796 | 3057.85 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.09 | CESC_05388 | 226.51 | 1.01 | 5.53 | 6.37 | 2.14 |
| CESC_15694 | 2900.48 | 0.27 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 1.47 | CESC_16081 | 208.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.38 |
| CESC_03859 | 1780.16 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.92 | CESC_21299 | 202.95 | 9.12 | 0.16 | 9.83 | 9.53 |
| CESC_15801 | 1779.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | CESC_06038 | 197.18 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 1.48 |
| CESC_19612 | 1385.35 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.02 | CESC_13442 | 192.86 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.02 |
| CESC_08819 | 1367.03 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 4.98 | 3.09 | CESC_13439 | 187.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.25 |
| CESC_18197 | 1341.87 | 3.87 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.14 | CESC_16862 | 182.94 | 3.01 | 1.50 | 3.14 | 3.01 |
| CESC_08728 | 1103.89 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.04 | CESC_16946 | 174.53 | 0.28 | 1.54 | 4.13 | 6.34 |
| CESC_17427 | 906.81 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.98 | CESC_12770 | 173.37 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_17492 | 882.14 | 0.26 | 1.39 | 0.89 | 1.05 | CESC_01552 | 165.58 | 0.86 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 1.30 |
| CESC_17960 | 855.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.02 | CESC_22280 | 164.99 | 0.01 | 1.64 | 3.39 | 1.20 |
| CESC_08729 | 799.26 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_19187 | 163.80 | 0.79 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.23 |
| CESC_12402 | 780.10 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 2.10 | 0.99 | CESC_06173 | 160.18 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| CESC_14954 | 746.41 | 0.64 | 0.42 | 0.10 | 5.62 | CESC_06081 | 156.16 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 1.02 | 0.41 |
| CESC_08129 | 744.59 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 0.14 | CESC_06747 | 155.97 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_21264 | 741.47 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_12819 | 149.97 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_15594 | 641.08 | 1.91 | 1.19 | 1.34 | 3.11 | CESC_02836 | 146.94 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 2.06 | 0.23 |
| CESC_23526 | 629.26 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_05881 | 145.16 | 0.38 | 0.79 | 0.45 | 0.11 |
| CESC_08481 | 628.51 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.11 | CESC_02522 | 138.38 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| CESC_10473 | 599.12 | 3.10 | 0.03 | 5.20 | 1.41 | CESC_18879 | 122.55 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 2.88 | 1.18 |
| CESC_00650 | 581.33 | 0.21 | 1.43 | 0.48 | 0.66 | CESC_19366 | 117.03 | 2.24 | 0.67 | 4.73 | 3.77 |
| CESC_19809 | 503.39 | 3.58 | 0.51 | 2.10 | 3.52 | CESC_09038 | 116.42 | 1.54 | 0.23 | 7.88 | 2.86 |
| CESC_19929 | 496.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_16522 | 115.51 | 5.22 | 0.32 | 6.70 | 7.14 |
| CESC_02314 | 487.86 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.11 | CESC_16067 | 112.60 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.12 |
| CESC_22878 | 467.04 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 3.23 | CESC_21164 | 108.78 | 1.17 | 0.10 | 2.93 | 5.67 |
| CESC_14581 | 106.85 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.12 | CESC_20039 | 28.25 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.42 |
| CESC_00606 | 106.35 | 0.05 | 2.56 | 0.18 | 0.65 | CESC_05180 | 27.12 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 1.24 | 0.88 |
| CESC_19685 | 101.57 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.07 | CESC_08911 | 24.85 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 0.17 |
| CESC_18501 | 100.73 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.01 | CESC_14442 | 24.83 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.49 |
| CESC_13203 | 98.13 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 2.70 | 3.72 | CESC_07266 | 23.62 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| CESC_03998 | 92.03 | 1.35 | 0.80 | 1.19 | 0.84 | CESC_16550 | 23.51 | 0.59 | 2.35 | 2.13 | 0.42 |
| CESC_00033 | 91.70 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 2.20 | 0.67 | CESC_07944 | 22.65 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.73 |
| CESC_08253 | 90.37 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_09860 | 22.32 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| CESC_16780 | 89.47 | 3.47 | 0.56 | 2.98 | 2.45 | CESC_21859 | 21.75 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_17762 | 89.08 | 4.78 | 0.16 | 2.53 | 3.16 | CESC_00937 | 21.12 | 0.00 | 2.02 | 0.34 | 0.04 |
| CESC_01315 | 87.53 | 2.04 | 6.90 | 0.87 | 0.70 | CESC_22858 | 20.65 | 0.08 | 2.06 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| CESC_20841 | 87.40 | 1.66 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 3.91 | CESC_07385 | 20.53 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.26 |
| CESC_03712 | 83.29 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.06 | CESC_14874 | 20.18 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 1.12 | 0.16 |
| CESC_07763 | 77.09 | 2.08 | 3.42 | 5.30 | 2.33 | CESC_05835 | 19.57 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| CESC_15211 | 76.33 | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.09 | CESC_07703 | 19.26 | 0.76 | 0.09 | 1.76 | 1.75 |
| CESC_16572 | 74.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_09861 | 18.86 | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| CESC_00448 | 70.32 | 5.66 | 2.95 | 5.91 | 2.01 | CESC_03897 | 17.96 | 0.40 | 0.61 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| CESC_23041 | 68.12 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.45 | 1.87 | CESC_00298 | 16.93 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| CESC_00990 | 68.06 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 4.76 | 6.24 | CESC_08232 | 16.93 | 1.39 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 1.59 |
| CESC_12231 | 67.00 | 0.94 | 1.19 | 5.59 | 2.33 | CESC_07388 | 16.85 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| CESC_00330 | 66.87 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.25 | CESC_21561 | 16.68 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.81 | 0.85 |
| CESC_10266 | 65.28 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | CESC_11936 | 16.57 | 0.00 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| CESC_18500 | 59.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.02 | CESC_16352 | 16.33 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| CESC_18904 | 59.67 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.10 | CESC_04055 | 16.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
| CESC_18474 | 58.76 | 0.61 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_21332 | 16.12 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.10 |
| CESC_15687 | 58.13 | 0.72 | 4.91 | 1.77 | 0.88 | CESC_04595 | 15.92 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 1.08 |
| CESC_19611 | 56.45 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_08350 | 15.26 | 1.35 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.09 |
| CESC_16328 | 55.34 | 1.70 | 0.71 | 1.67 | 0.74 | CESC_12816 | 14.80 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 0.44 | 0.16 |
| CESC_03405 | 55.28 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.27 | CESC_15370 | 14.50 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 1.23 |
| CESC_18761 | 54.94 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 3.31 | 1.48 | CESC_19797 | 14.45 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 0.28 |
| CESC_21600 | 53.08 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.02 | CESC_01169 | 14.17 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| CESC_16965 | 52.69 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.86 | 2.69 | CESC_18475 | 13.22 | 0.60 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| CESC_04051 | 51.21 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | CESC_18599 | 12.86 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| CESC_06673 | 47.23 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.00 | CESC_00742 | 11.88 | 0.58 | 0.33 | 0.58 | 0.21 |
| CESC_05193 | 40.93 | 0.00 | 1.38 | 0.11 | 0.04 | CESC_11046 | 11.62 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.78 | 0.39 |
| CESC_21100 | 40.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | CESC_01166 | 10.25 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| CESC_21308 | 32.28 | 1.24 | 1.62 | 0.57 | 2.02 | ||||||
表3 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因的表达水平
Table 3 Expression level of tuber-specific expression genes in Cyperus esculentus
| Gene | Expression level (FPKM) | Gene | Expression level (FPKM) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuber | Root | Leaf | Stolon | Tillering node | Tuber | Root | Leaf | Stolon | Tillering node | ||
| CESC_17828 | 34980.30 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 9.23 | 6.20 | CESC_06642 | 449.61 | 0.00 | 3.36 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| CESC_14076 | 24917.54 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 1.24 | 0.54 | CESC_11684 | 424.54 | 2.11 | 0.12 | 2.17 | 0.94 |
| CESC_08636 | 23808.18 | 0.00 | 2.95 | 1.11 | 1.38 | CESC_00836 | 424.00 | 1.18 | 5.61 | 0.00 | 0.57 |
| CESC_16708 | 20282.53 | 1.29 | 4.99 | 9.63 | 2.02 | CESC_04812 | 394.97 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.52 |
| CESC_14073 | 15607.24 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 1.73 | 7.62 | CESC_19053 | 392.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_10265 | 8803.59 | 0.59 | 4.34 | 0.64 | 4.16 | CESC_13856 | 384.53 | 4.48 | 1.53 | 3.09 | 2.19 |
| CESC_13913 | 6560.83 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.13 | CESC_05739 | 373.39 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_13892 | 6062.31 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.27 | CESC_15162 | 373.06 | 2.23 | 1.79 | 1.55 | 1.20 |
| CESC_14077 | 5890.09 | 1.05 | 0.06 | 0.51 | 0.77 | CESC_21269 | 357.90 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| CESC_00080 | 4834.92 | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.37 | CESC_12660 | 335.49 | 4.32 | 2.69 | 4.42 | 1.52 |
| CESC_12549 | 4632.55 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_15141 | 309.91 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.38 | 0.06 |
| CESC_00832 | 3760.05 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.20 | CESC_15826 | 293.80 | 0.44 | 3.71 | 1.88 | 1.94 |
| CESC_15373 | 3721.68 | 6.39 | 6.24 | 4.11 | 6.27 | CESC_15198 | 269.77 | 2.29 | 2.45 | 5.19 | 1.98 |
| CESC_10351 | 3695.94 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.19 | CESC_03736 | 268.07 | 0.77 | 7.39 | 3.50 | 8.35 |
| CESC_18271 | 3694.18 | 1.46 | 1.25 | 3.06 | 1.59 | CESC_21099 | 239.33 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 3.22 |
| CESC_21136 | 3589.62 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.29 | CESC_15700 | 239.04 | 0.00 | 2.84 | 0.90 | 0.37 |
| CESC_07796 | 3057.85 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.09 | CESC_05388 | 226.51 | 1.01 | 5.53 | 6.37 | 2.14 |
| CESC_15694 | 2900.48 | 0.27 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 1.47 | CESC_16081 | 208.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.38 |
| CESC_03859 | 1780.16 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.92 | CESC_21299 | 202.95 | 9.12 | 0.16 | 9.83 | 9.53 |
| CESC_15801 | 1779.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 | CESC_06038 | 197.18 | 0.08 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 1.48 |
| CESC_19612 | 1385.35 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.02 | CESC_13442 | 192.86 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.02 |
| CESC_08819 | 1367.03 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 4.98 | 3.09 | CESC_13439 | 187.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.25 |
| CESC_18197 | 1341.87 | 3.87 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.14 | CESC_16862 | 182.94 | 3.01 | 1.50 | 3.14 | 3.01 |
| CESC_08728 | 1103.89 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 0.04 | CESC_16946 | 174.53 | 0.28 | 1.54 | 4.13 | 6.34 |
| CESC_17427 | 906.81 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.98 | CESC_12770 | 173.37 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_17492 | 882.14 | 0.26 | 1.39 | 0.89 | 1.05 | CESC_01552 | 165.58 | 0.86 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 1.30 |
| CESC_17960 | 855.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.02 | CESC_22280 | 164.99 | 0.01 | 1.64 | 3.39 | 1.20 |
| CESC_08729 | 799.26 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_19187 | 163.80 | 0.79 | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.23 |
| CESC_12402 | 780.10 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 2.10 | 0.99 | CESC_06173 | 160.18 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.00 |
| CESC_14954 | 746.41 | 0.64 | 0.42 | 0.10 | 5.62 | CESC_06081 | 156.16 | 0.12 | 0.22 | 1.02 | 0.41 |
| CESC_08129 | 744.59 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.56 | 0.14 | CESC_06747 | 155.97 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_21264 | 741.47 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_12819 | 149.97 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_15594 | 641.08 | 1.91 | 1.19 | 1.34 | 3.11 | CESC_02836 | 146.94 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 2.06 | 0.23 |
| CESC_23526 | 629.26 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_05881 | 145.16 | 0.38 | 0.79 | 0.45 | 0.11 |
| CESC_08481 | 628.51 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.11 | CESC_02522 | 138.38 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| CESC_10473 | 599.12 | 3.10 | 0.03 | 5.20 | 1.41 | CESC_18879 | 122.55 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 2.88 | 1.18 |
| CESC_00650 | 581.33 | 0.21 | 1.43 | 0.48 | 0.66 | CESC_19366 | 117.03 | 2.24 | 0.67 | 4.73 | 3.77 |
| CESC_19809 | 503.39 | 3.58 | 0.51 | 2.10 | 3.52 | CESC_09038 | 116.42 | 1.54 | 0.23 | 7.88 | 2.86 |
| CESC_19929 | 496.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_16522 | 115.51 | 5.22 | 0.32 | 6.70 | 7.14 |
| CESC_02314 | 487.86 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 0.11 | CESC_16067 | 112.60 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.39 | 0.12 |
| CESC_22878 | 467.04 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.88 | 3.23 | CESC_21164 | 108.78 | 1.17 | 0.10 | 2.93 | 5.67 |
| CESC_14581 | 106.85 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.12 | CESC_20039 | 28.25 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.42 |
| CESC_00606 | 106.35 | 0.05 | 2.56 | 0.18 | 0.65 | CESC_05180 | 27.12 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 1.24 | 0.88 |
| CESC_19685 | 101.57 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.07 | CESC_08911 | 24.85 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.00 | 0.17 |
| CESC_18501 | 100.73 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.01 | CESC_14442 | 24.83 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.49 |
| CESC_13203 | 98.13 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 2.70 | 3.72 | CESC_07266 | 23.62 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| CESC_03998 | 92.03 | 1.35 | 0.80 | 1.19 | 0.84 | CESC_16550 | 23.51 | 0.59 | 2.35 | 2.13 | 0.42 |
| CESC_00033 | 91.70 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 2.20 | 0.67 | CESC_07944 | 22.65 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.73 |
| CESC_08253 | 90.37 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_09860 | 22.32 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| CESC_16780 | 89.47 | 3.47 | 0.56 | 2.98 | 2.45 | CESC_21859 | 21.75 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| CESC_17762 | 89.08 | 4.78 | 0.16 | 2.53 | 3.16 | CESC_00937 | 21.12 | 0.00 | 2.02 | 0.34 | 0.04 |
| CESC_01315 | 87.53 | 2.04 | 6.90 | 0.87 | 0.70 | CESC_22858 | 20.65 | 0.08 | 2.06 | 0.11 | 0.12 |
| CESC_20841 | 87.40 | 1.66 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 3.91 | CESC_07385 | 20.53 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.26 |
| CESC_03712 | 83.29 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.06 | CESC_14874 | 20.18 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 1.12 | 0.16 |
| CESC_07763 | 77.09 | 2.08 | 3.42 | 5.30 | 2.33 | CESC_05835 | 19.57 | 0.06 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.14 |
| CESC_15211 | 76.33 | 0.38 | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.09 | CESC_07703 | 19.26 | 0.76 | 0.09 | 1.76 | 1.75 |
| CESC_16572 | 74.95 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | CESC_09861 | 18.86 | 0.65 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| CESC_00448 | 70.32 | 5.66 | 2.95 | 5.91 | 2.01 | CESC_03897 | 17.96 | 0.40 | 0.61 | 0.22 | 0.06 |
| CESC_23041 | 68.12 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 1.45 | 1.87 | CESC_00298 | 16.93 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| CESC_00990 | 68.06 | 0.36 | 0.42 | 4.76 | 6.24 | CESC_08232 | 16.93 | 1.39 | 0.30 | 0.44 | 1.59 |
| CESC_12231 | 67.00 | 0.94 | 1.19 | 5.59 | 2.33 | CESC_07388 | 16.85 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| CESC_00330 | 66.87 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.25 | CESC_21561 | 16.68 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.81 | 0.85 |
| CESC_10266 | 65.28 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | CESC_11936 | 16.57 | 0.00 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| CESC_18500 | 59.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.02 | CESC_16352 | 16.33 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| CESC_18904 | 59.67 | 0.59 | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.10 | CESC_04055 | 16.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.04 |
| CESC_18474 | 58.76 | 0.61 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_21332 | 16.12 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 0.10 |
| CESC_15687 | 58.13 | 0.72 | 4.91 | 1.77 | 0.88 | CESC_04595 | 15.92 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 1.08 |
| CESC_19611 | 56.45 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.00 | CESC_08350 | 15.26 | 1.35 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.09 |
| CESC_16328 | 55.34 | 1.70 | 0.71 | 1.67 | 0.74 | CESC_12816 | 14.80 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 0.44 | 0.16 |
| CESC_03405 | 55.28 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.32 | 0.27 | CESC_15370 | 14.50 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 1.23 |
| CESC_18761 | 54.94 | 0.78 | 0.12 | 3.31 | 1.48 | CESC_19797 | 14.45 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 0.28 |
| CESC_21600 | 53.08 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.02 | CESC_01169 | 14.17 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| CESC_16965 | 52.69 | 0.35 | 0.65 | 0.86 | 2.69 | CESC_18475 | 13.22 | 0.60 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| CESC_04051 | 51.21 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | CESC_18599 | 12.86 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| CESC_06673 | 47.23 | 0.00 | 0.51 | 0.02 | 0.00 | CESC_00742 | 11.88 | 0.58 | 0.33 | 0.58 | 0.21 |
| CESC_05193 | 40.93 | 0.00 | 1.38 | 0.11 | 0.04 | CESC_11046 | 11.62 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.78 | 0.39 |
| CESC_21100 | 40.35 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 | CESC_01166 | 10.25 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| CESC_21308 | 32.28 | 1.24 | 1.62 | 0.57 | 2.02 | ||||||
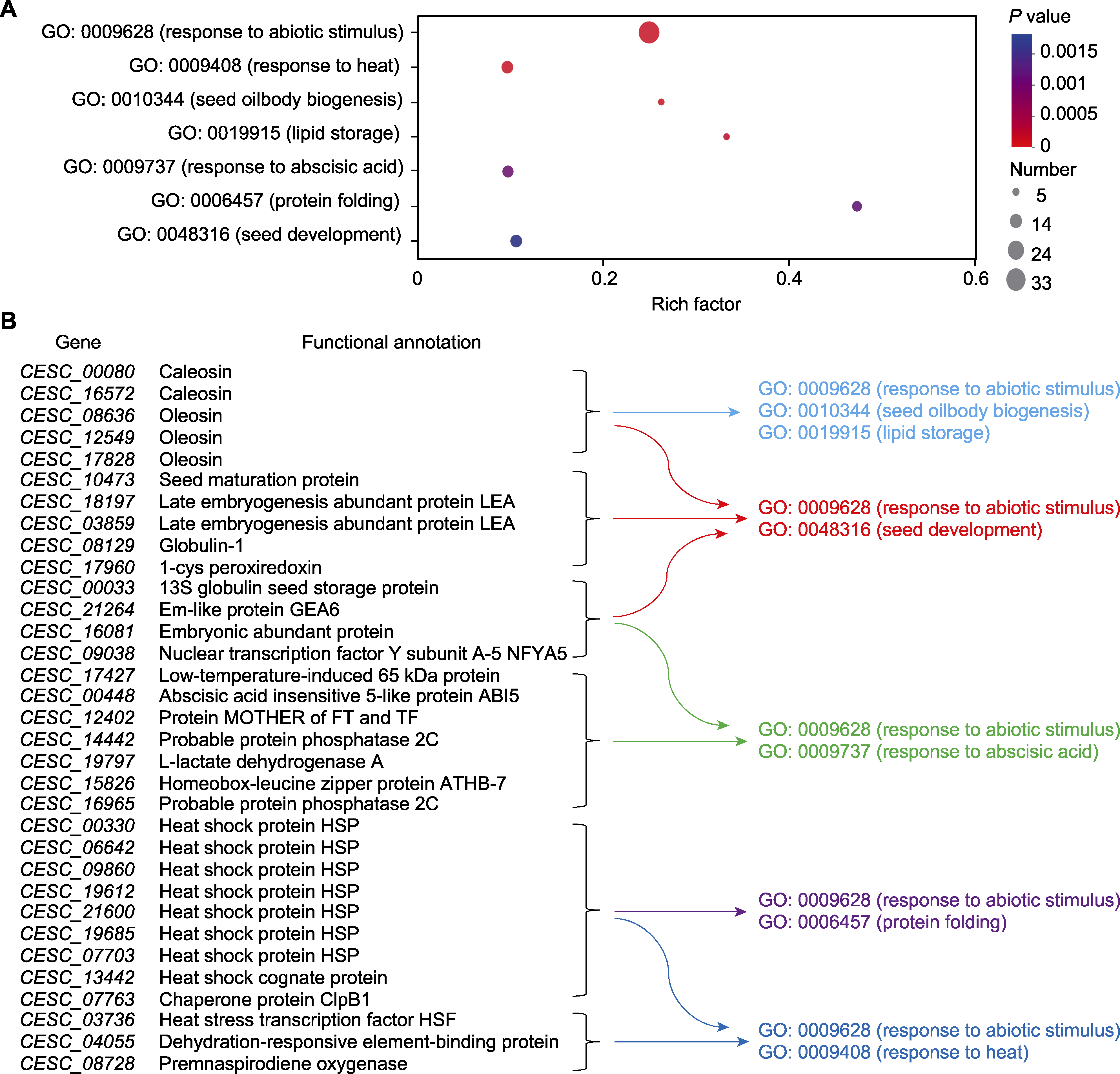
图4 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因的GO富集分析 (A) 基于分子功能(MF)的GO富集气泡图; (B) 显著富集GO条目中所有基因的功能注释
Figure 4 The GO enrichment analysis of tuber-specific expression genes in Cyperus esculentus (A) The bubble diagram of GO enrichment based on molecular function (MF); (B) The functional annotation of all genes involved in significantly enriched GO terms
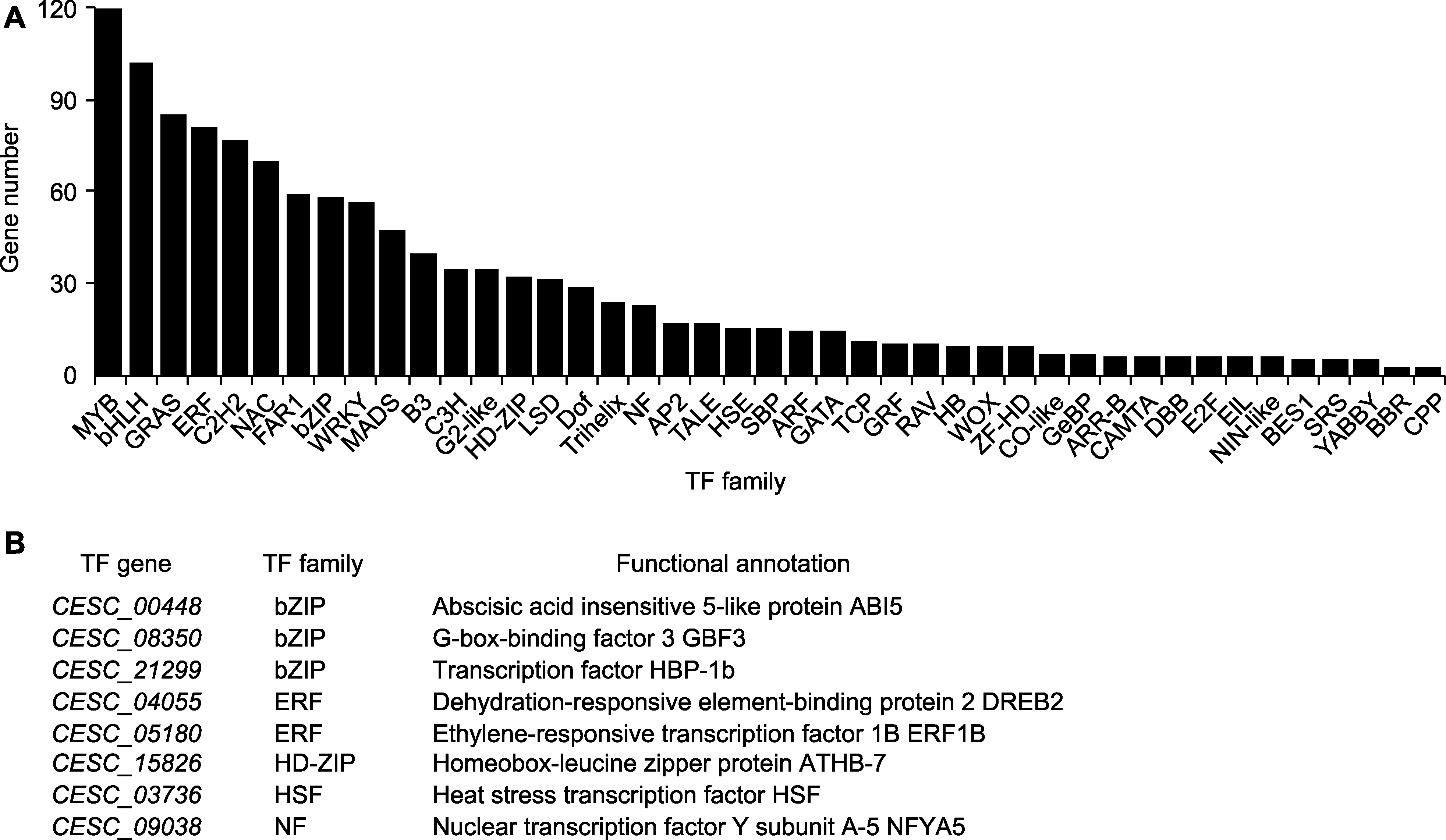
图5 油莎豆块茎特异性表达转录因子编码基因的筛选 (A) 油莎豆全基因组水平转录因子(TF)家族的鉴定; (B) 块茎特异性表达转录因子编码基因的功能注释
Figure 5 Identification of tuber-specific expression transcription factor genes in Cyperus esculentus (A) Identification of genome-wide level transcription factor (TF) family in C. esculentus; (B) The functional annotation of tuber- specific expression transcription factor genes
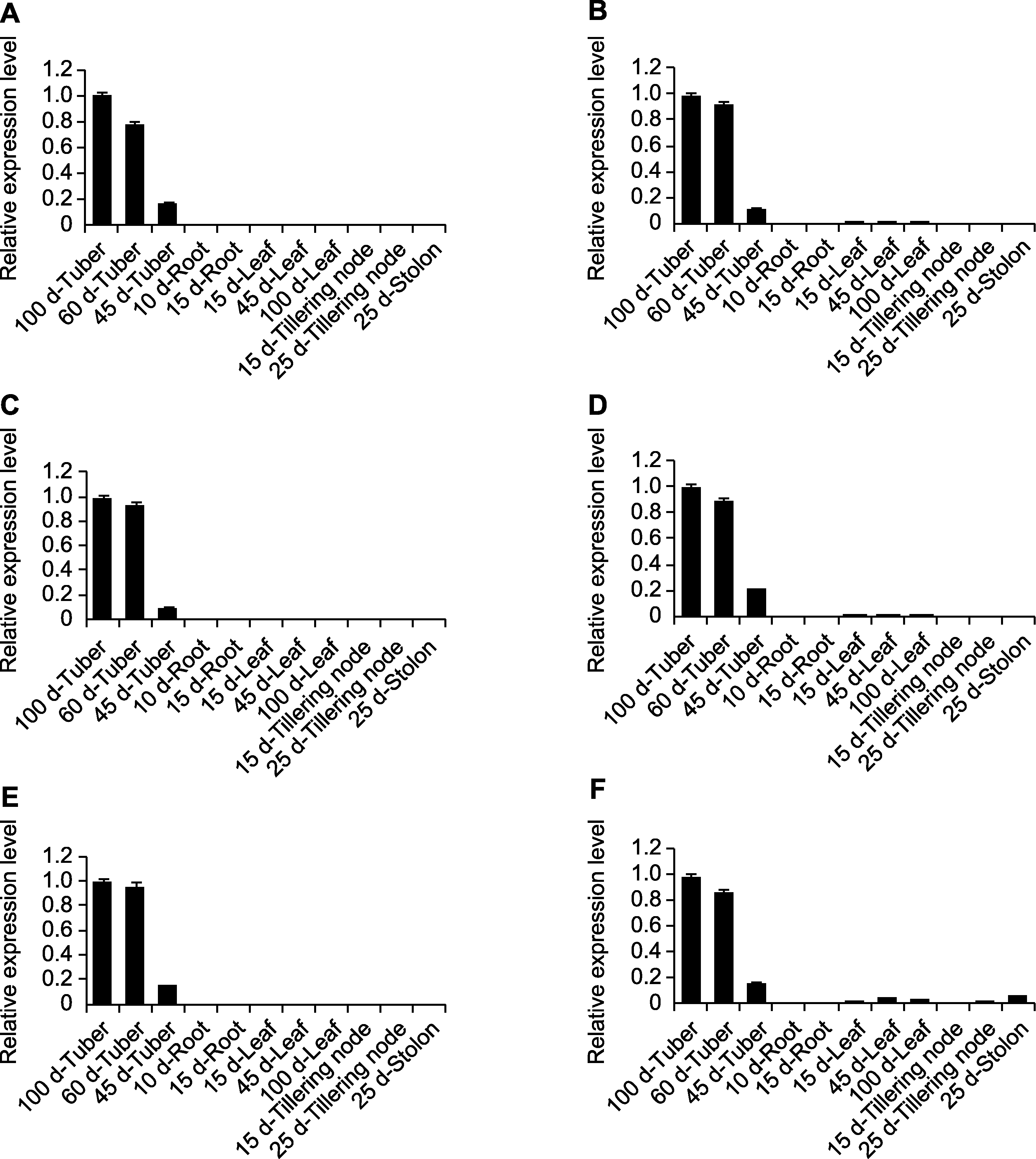
图6 油莎豆不同器官中块茎特异性表达基因的qRT-PCR分析 (A) CESC_00080; (B) CESC_17828; (C) CESC_00330; (D) CESC_18197; (E) CESC_16081; (F) CESC_03736
Figure 6 qRT-PCR analysis of tuber-specific expression genes in different organs of Cyperus esculentus (A) CESC_00080; (B) CESC_17828; (C) CESC_00330; (D) CESC_18197; (E) CESC_16081; (F) CESC_03736
| [1] | Alexa A, Rahnenfuhrer J (2010). topGO: enrichment analysis for gene ontology. R Package Version 2.0. 2010. |
| [2] | Alonso R, Oñate-Sánchez L, Weltmeier F, Ehlert A, Diaz I, Dietrich K, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Dröge-Laser W (2009). A pivotal role of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor bZIP53 in the regulation of Arabidopsis seed maturation gene expression based on heterodimerization and protein complex formation. Plant Cell 21, 1747-1761. |
| [3] |
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114-2120.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Cai ZQ, Cai ZP, Huang JL, Wang AQ, Ntambiyukuri A, Chen BM, Zheng GH, Li HF, Huang YM, Zhan J, Xiao D, He LF (2022). Transcriptomic analysis of tuberous root in two sweet potato varieties reveals the important genes and regulatory pathways in tuberous root development. BMC Genomics 23, 473.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Chen AM (2012). Research progress on stem/leaf-specific promoters in rice. Mod Agric Sci Technol (17), 16-17, 19. (in Chinese) |
| 陈爱敏 (2012). 水稻茎叶特异性启动子研究进展. 现代农业科技 (17), 16-17, 19. | |
| [6] | Chen JQ, Zhao MZ, Wang Y, Zhang MP (2023). Research progress on tissue specific promoters in plant. North Hortic (19), 128-134. (in Chinese) |
| 陈建琦, 赵明珠, 王义, 张美萍 (2023). 植物中组织特异性启动子的研究进展. 北方园艺 (19), 128-134. | |
| [7] |
Chitnis PR, Morishige DT, Nechushtai R, Thornber JP (1988). Assembly of the barley light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b proteins in barley etiochloroplasts involves processing of the precursor on thylakoids. Plant Mol Biol 11, 95-107.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Clevenger J, Chu Y, Scheffler B, Ozias-Akins P (2016). A developmental transcriptome map for allotetraploid Arachis hypogaea. Front Plant Sci 7, 1446.
PMID |
| [9] | Collin A, Daszkowska-Golec A, Szarejko I (2021). Updates on the role of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 5 (ABI5) and ABSCISIC ACID-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING FACTORs (ABFs) in ABA signaling in different developmental stages in plants. Cells 10, 1996. |
| [10] |
Cui P, Zhao YR, Yao ZP, Pang LJ, Lu GQ (2022). Starch physicochemical properties and expression levels of anabolism key genes in sweetpotato under low temperature. Sci Agric Sin 55, 3831-3840. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
崔鹏, 赵逸人, 姚志鹏, 庞林江, 陆国权 (2022). 低温对甘薯淀粉理化特性及代谢关键基因表达量的影响. 中国农业科学 55, 3831-3840.
DOI |
|
| [11] |
Fan SH, Liu N, Hua W (2021). Research advances in the biosynthesis and regulation of lipid in oil crops. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 43, 361-375. (in Chinese)
DOI |
| 范世航, 刘念, 华玮 (2021). 油料作物油脂合成调控研究进展. 中国油料作物学报 43, 361-375. | |
| [12] | Hodge A, Berta G, Doussan C, Merchan F, Crespi M (2009). Plant root growth, architecture and function. Plant Soil 321, 153-187. |
| [13] | Izadi-Darbandi A, Alameldin H, Namjoo N, Ahmad K (2023). Introducing sorghum DREB2 gene in maize (Zea mays L.) to improve drought and salinity tolerance. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 4, 1480-1488. |
| [14] | Jia Y, Yao M, He X, Xiong XH, Guan M, Liu ZS, Guan CY, Qian LW (2022). Transcriptome and regional association analyses reveal the effects of oleosin genes on the accumulation of oil content in Brassica napus. Plants 11, 3140. |
| [15] | Jiao Y, Liu XQ, Jiang HY, Chen RM (2019). Research advances of plant tissue specific promoters. J Agric Sci Technol 21, 18-28. (in Chinese) |
|
焦勇, 柳小庆, 江海洋, 陈茹梅 (2019). 植物组织特异性启动子研究进展. 中国农业科技导报 21, 18-28.
DOI |
|
| [16] |
Kim D, Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 12, 357-360.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Li JS, Xue X, Xu J, Wu B (2023). Cloning and activity comparison of eight green tissue-specific promoters. Mol Plant Breed, 1-13 [2024-05-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230524.1143.006.html. (in Chinese) |
| 李姬霜, 薛旭, 徐静, 吴斌 (2023). 八个绿色组织特异性启动子的克隆及活性比较. 分子植物育种, 1-13 [2024-05-25]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230524.1143.006.html. | |
| [18] | Li WX, Oono Y, Zhu JH, He XJ, Wu JM, Iida K, Lu XY, Cui XP, Jin HL, Zhu JK (2008). The Arabidopsis NFYA5 transcription factor is regulated transcriptionally and posttranscriptionally to promote drought resistance. Plant Cell 20, 2238-2251. |
| [19] | Li YC, Li K, Wang LN, Chen X, Li YZ, Wang WQ (2023). Cloning and identification of root tissue-specific promoter from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz.). J South Agric 54, 1925-1932. (in Chinese) |
| 李远超, 李可, 王连南, 陈新, 李有志, 王文泉 (2023). 木薯根组织特异性启动子的克隆及鉴定. 南方农业学报 54, 1925-1932. | |
| [20] | Li ZJ, Qin Y (2021). Chromatin accessibility and the gene expression regulation in plants. Chin Bull Bot 56, 664-675. (in Chinese) |
|
李占杰, 秦源 (2021). 染色质可及性与植物基因表达调控. 植物学报 56, 664-675.
DOI |
|
| [21] | Li ZX, Chen XB (2015). Research advances in plant tissue specific promoters and related cis-acting elements. J Biol 32(6), 91-95. (in Chinese) |
| 李濯雪, 陈信波 (2015). 植物组织特异性启动子及相关顺式作用元件研究进展. 生物学杂志 32(6), 91-95. | |
| [22] | Liu K, Li GJ, Yang Q (2022). Research progress in DREB/ CBF transcription factor involved in responses in plant to abiotic stress. Biotechnol Bull 38(5), 201-214. (in Chinese) |
|
刘坤, 李国婧, 杨杞 (2022). 参与植物非生物逆境响应的DREB/CBF转录因子研究进展. 生物技术通报 38(5), 201-214.
DOI |
|
| [23] | Liu YH, Li YM, Liu Z, Wang L, Lin-Wang K, Zhu JY, Bi ZZ, Sun C, Zhang JL, Bai JP (2023). Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals a dynamic regulatory network of potato tuber pigmentation. iScience 26, 105903. |
| [24] |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402-408.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Mikami K, Sakamoto A, Iwabuchi M (1994). The HBP-1 family of wheat basic/leucine zipper proteins interacts with overlapping cis-acting hexamer motifs of plant histone genes. J Biol Chem 269, 9974-9985.
PMID |
| [26] | Mudge SR, Smith FW, Richardson AE (2003). Root-specific and phosphate-regulated expression of phytase under the control of a phosphate transporter promoter enables Arabidopsis to grow on phytate as a sole P source. Plant Sci 165, 871-878. |
| [27] |
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang TC, Mendell JT, Salzberg SL (2015). StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol 33, 290-295.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | Qu AL, Ding YF, Jiang Q, Zhu C (2013). Molecular mechanisms of the plant heat stress response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 432, 203-207. |
| [29] | Ramegowda V, Gill US, Sivalingam PN, Gupta A, Gupta C, Govind G, Nataraja KN, Pereira A, Udayakumar M, Mysore KS, Senthil-Kumar M (2017). GBF3 transcription factor imparts drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci Rep 7, 9148. |
| [30] |
Schünmann PHD, Richardson AE, Smith FW, Delhaize E (2004). Characterization of promoter expression patterns derived from the Pht1 phosphate transporter genes of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J Exp Bot 55, 855-865.
PMID |
| [31] | Smolikova G, Leonova T, Vashurina N, Frolov A, Medvedev S (2021). Desiccation tolerance as the basis of long-term seed viability. Int J Mol Sci 22, 101. |
| [32] |
Söderman E, Mattsson J, Engström P (1996). The Arabidopsis homeobox gene ATHB-7 is induced by water deficit and by abscisic acid. Plant J 10, 375-381.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Song SQ, Liu J, Tang CF, Cheng HY, Wang WQ, Zhang Q, Zhang WH, Gao JD (2022). Research progress on the physiology and its molecular mechanism of seed desiccation tolerance. Sci Agric Sin 55, 1047-1063. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
宋松泉, 刘军, 唐翠芳, 程红焱, 王伟青, 张琪, 张文虎, 高家东 (2022). 种子耐脱水性的生理及分子机制研究进展. 中国农业科学 55, 1047-1063.
DOI |
|
| [34] | Song SQ, Tang CF, Lei HP, Fei ST, Chen HB (2023). Research progress on seed development regulated by ABA. Guihaia 43, 1553-1567. (in Chinese) |
| 宋松泉, 唐翠芳, 雷华平, 费思恬, 陈海波 (2023). ABA调控种子发育的研究进展. 广西植物 43, 1553-1567. | |
| [35] | Song Y, Zhou JH, Zhang YQ (2007). Research on plant tissue-specific promoters. Biotechnol Bull (6), 21-24. (in Chinese) |
| 宋扬, 周军会, 张永强 (2007). 植物组织特异性启动子研究. 生物技术通报 (6), 21-24. | |
| [36] | Song YH, Shi WL, Zhang J, Ding ZY, Peng HX, Jiang CY, Ma QQ, Li ZJ, Zhao Y, Tang DB, Zhang K, Wang JC, Liu X (2021). Development and application of an efficient method for the amylose/amylopectin ratio determination in potato tubers. Acta Hortic Sin 48, 600-608. (in Chinese) |
|
宋玉浩, 史伟玲, 张娇, 丁振宇, 彭洪娴, 蒋春燕, 马秋芹, 李芝静, 赵勇, 唐道彬, 张凯, 王季春, 刘勋 (2021). 马铃薯块茎淀粉组分高效检测体系的建立及应用. 园艺学报 48, 600-608.
DOI |
|
| [37] |
Spreitzer RJ (2003). Role of the small subunit in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 414, 141-149.
PMID |
| [38] | Sun M, Tian K, Zhang Y, Wang H, Guan DX, Yue HT (2017). Research on leaf functional traits and their environmental adaptation. Plant Sci J 35, 940-949. (in Chinese) |
| 孙梅, 田昆, 张贇, 王行, 管东旭, 岳海涛 (2017). 植物叶片功能性状及其环境适应研究. 植物科学学报 35, 940-949. | |
| [39] | Vijaybhaskar V, Subbiah V, Kaur J, Vijayakumari P, Siddiqi I (2008). Identification of a root-specific glycosyltransferase from Arabidopsis and characterization of its promoter. J Biosci 33, 185-193. |
| [40] | Wang HW, Zhu SX, Zhang XY, Wang Y, Yang TG, Zhang XG, Wang SF, Li CX (2023). Genome size, ploidy and phylogeny of Cyperus esculentus L. J Henan Agric Sci 52, 34-41. (in Chinese) |
| 王会伟, 朱世新, 张新友, 王艳, 杨铁钢, 张向歌, 王树峰, 李春鑫 (2023). 油莎豆基因组大小、倍性和系统发育分析. 河南农业科学 52, 34-41. | |
| [41] | Wang YC, Jiang HY, Mao ZL, Liu WJ, Jiang SH, Xu HF, Su MY, Zhang J, Wang N, Zhang ZY, Chen XS (2021). Ethylene increases the cold tolerance of apple via the MdERF1B-MdCIbHLH1 regulatory module. Plant J 106, 379-393. |
| [42] | Wang YY, Bai YF, Zhang DY (2010). Application of plants pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase in genetic engineering. J Shanxi Agric Sci 38(8), 88-91. (in Chinese) |
| 王原媛, 白云凤, 张定宇 (2010). 植物PPDK基因在基因工程中的应用. 山西农业科学 38(8), 88-91. | |
| [43] |
Wehmeyer N, Vierling E (2000). The expression of small heat shock proteins in seeds responds to discrete developmental signals and suggests a general protective role in desiccation tolerance. Plant Physiol 122, 1099-1108.
PMID |
| [44] | Wei H, Zhong HJ, Wang H (2004). Improvement on determination of crude oil by soxhlet extraction. China Oils Fats 29, 52-54. (in Chinese) |
| 魏红, 钟红舰, 汪红 (2004). 索氏抽提法测定粗脂肪含量的改进. 中国油脂 29, 52-54. | |
| [45] | Wei YX, Wang J, Li T, Liu LJ, Huang J, Zheng YQ (2021). Potassium application improved the agronomic properties and starch components of cassava. Chin J Trop Crops 42, 102-109. (in Chinese) |
|
魏云霞, 王娟, 李天, 刘丽娟, 黄洁, 郑永清 (2021). 施钾改善木薯农艺性状及淀粉组分. 热带作物学报 42, 102-109.
DOI |
|
| [46] | Xu DA, Zhao CQ, Zhang CH, Chen J (2015). Expression patterns of a root-specific barley aquaporin gene HvTIP2;1 and promoter. China Biotechnol 35(7), 15-21. (in Chinese) |
| 徐登安, 赵纯钦, 张赤红, 陈静 (2015). 大麦水孔蛋白基因HvTIP2;1及其启动子的表达特性分析. 中国生物工程杂志 35(7), 15-21. | |
| [47] | Xue D, Yan Q, Hu YQ, Zhou YY, Wei YW, Yuan XX, Wang XJ, Chen X (2023). Genome-scale mining of root-preferential genes from soybean and characterization of their promoter activity. Plant Physiol J 59, 55-66. (in Chinese) |
| 薛冬, 闫强, 胡亚群, 周琰琰, 韦雅雯, 袁星星, 王学军, 陈新 (2023). 大豆根系特异表达基因全基因组水平挖掘及其启动子活性鉴定. 植物生理学报 59, 55-66. | |
| [48] | Xun HW, Zhang X, Yu JM, Pang JS, Wang SC, Liu B, Dong YS, Jiang LL, Guo DQ (2021). Analysis of expression characteristics of soybean leaf and root tissue-specific promoters in Arabidopsis and soybean. Transgenic Res 30, 799-810. |
| [49] | Yamori W (2013). Improving photosynthesis to increase food and fuel production by biotechnological strategies in crops. J Plant Biochem Physiol 1, 1000113. |
| [50] | Yan J, Du J, Li C, Chen B, Shen YH (2016). Main components analysis of Cyperus esculentus in Jingbian, Shaanxi. China Oils Fats 41(3), 85-88. (in Chinese) |
| 闫军, 杜静, 李聪, 陈邦, 申烨华 (2016). 陕西靖边油莎豆主要成分分析. 中国油脂 41(3), 85-88. | |
| [51] | Yang F, Zhu WX (2020). Research status and prospect of Cyperus esculentus. Cereals Oils 33(7),4-6. (in Chinese) |
| 杨帆, 朱文学 (2020). 油莎豆研究现状及展望. 粮食与油脂 33(7), 4-6. | |
| [52] | Yang SN, Miao L, He JB, Zhang K, Li Y, Gai JY (2019). Dynamic transcriptome changes related to oil accumulation in developing soybean seeds. Int J Mol Sci 20, 2202. |
| [53] | Zhang H, Yang YJ, Li DL, Song JK, Ma CH, Wang R (2018). RNA-Seq analysis of the tissue-specific expressed genes of Pyrus betulaefolia in root, stem and leaf. Acta Hortic Sin 45, 1881-1894. (in Chinese) |
|
张欢, 杨英杰, 李鼎立, 宋健坤, 马春晖, 王然 (2018). 杜梨根茎叶特异表达基因的RNA-Seq分析. 园艺学报 45, 1881-1894.
DOI |
|
| [54] | Zhang XG, Song WX, Zhu YJ, Yu MQ, Song WX, Wang SF, Li JZ, Wang HW (2023). Content changes of endogenous hormones in Cyperus esculentus tuber during germination. Seed 42(8), 45-49. (in Chinese) |
| 张向歌, 宋万献, 朱雅婧, 于美琴, 宋雯栩, 王树峰, 李居政, 王会伟 (2023). 油莎豆茎豆萌发过程中内源激素含量的变化. 种子 42(8), 45-49. | |
| [55] | Zhang XK (2019). R & D progress report of Cyperus escu-lentus industry in China. China Rural Sci Technol (4), 67-69. (in Chinese) |
| 张学昆 (2019). 我国油莎豆产业研发进展报告. 中国农村科技 (4), 67-69. | |
| [56] | Zhao XQ, Yi LX, Ren YF, Li J, Ren W, Hou ZH, Su SF, Wang JG, Zhang YY, Dong Q, Yang XD, Cheng YC, Lu ZY (2023). Chromosome-scale genome assembly of the yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus). Genome Biol Evol 15, evad027. |
| [57] | Zhou D, Zhao JZ, Bai Y, Zhang Q, Jing W, Zhang WH (2012). Research advance in triacylglycerol synthesis, metabolism, and regulation in plants. J Nanjing Agric Univ 35(5), 77-86. (in Chinese) |
| 周丹, 赵江哲, 柏杨, 张群, 井文, 章文华 (2012). 植物油脂合成代谢及调控的研究进展. 南京农业大学学报 35(5), 77-86. |
| [1] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [2] | 孙蓉, 杨宇琭, 李亚军, 张会, 李旭凯. 谷子PLATZ转录因子基因家族的鉴定和分析[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(4): 548-559. |
| [3] | 李变变, 张凤华, 赵亚光, 孙秉楠. 不同刈割程度对油莎豆非结构性碳水化合物代谢及生物量的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(1): 101-113. |
| [4] | 徐海霞, 何静, 易航, 王丽. 镉胁迫下地钱转录组的性别特异性响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(2): 182-196. |
| [5] | 张雅楠, 黄蕾, 李佳彬, 张雷, 党振华. 基于转录组的阿拉善地区多枝柽柳多态Genic-SSRs的识别与开发[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 433-442. |
| [6] | 李俊华,刘世宇,李成龙,韩林林,董亚辉,张晓丽,赵喜亭,李明军. 铁棍山药微型块茎遗传转化体系的建立[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 72-80. |
| [7] | 刘勉, 张彩飞, 黄建勋, 马红. 利用低拷贝核基因重建菊科紫菀亚科族间系统发育关系[J]. 植物学报, 2015, 50(5): 549-564. |
| [8] | 陈开宁, 兰策介, 史龙新, 陈伟民, 许海, 包先明. 苦草繁殖生态学研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 2006, 30(3): 487-495. |
| [9] | 甘立军 曾晓春 周燮. 茉莉酸类与植物地下贮藏器官的形成[J]. 植物学报, 2001, 18(05): 546-553. |
| [10] | 柳俊 谢从华. 马铃薯块茎发育机理及其基因表达[J]. 植物学报, 2001, 18(05): 531-539. |
| [11] | 凌毅 赵武玲. 豌豆肌动蛋白异型体基因的特异性表达[J]. 植物学报, 2001, 18(01): 76-80. |
| [12] | 廖飞雄 潘瑞炽. 植物根特异性基因表达研究[J]. 植物学报, 1998, 15(02): 8-13. |
| [13] | 钱希. 扁禾旱 蔗草的生物学特性及防治研究[J]. 植物生态学报, 1988, 12(3): 205-215. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||