

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 499-514.DOI: 10.11983/CBB24103 cstr: 32102.14.CBB24103
谢涛, 章一帆, 刘云辉, 游慧玉, 夏季奔奔, 马蓉, 张春妮, 华学军*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-13
接受日期:2024-10-14
出版日期:2025-07-10
发布日期:2024-10-16
通讯作者:
*华学军, 教授, 分别于北京大学、中国农业科学院和比利时根特大学获学士、硕士和博士学位; 经历加拿大多伦多大学博士后, 加拿大卡尔加里大学高级研究助理, 2005年入选中国科学院“百人计划”, 2018年聘为浙江理工大学生医学院教授, 专注于植物发育与逆境应答领域科学研究。主持和参加多项国家自然科学基金面上项目、973项目、863项目、转基因专项、科技部国际合作项目等。在Proc Natl Acad Sci USA、PLoS Genetics、Plant Physiology、Plant Journal、Plant Biotechnology Journal、Plant Physiology & Biochemistry和Plant & Cell Physiology等国际知名学术期刊发表论文80余篇。授权国家发明专利5项。培养硕士和博士30余名。基金资助:
Tao Xie, Yifan Zhang, Yunhui Liu, Huiyu You, Jibenben Xia, Rong Ma, Chunni Zhang, Xuejun Hua*( )
)
Received:2024-07-13
Accepted:2024-10-14
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2024-10-16
Contact:
*E-mail: xjhua@zstu.edu.cn
摘要: 铁硫[Fe-S]簇作为铁硫蛋白的辅助因子广泛参与光合作用、呼吸作用和电子传递等多种生物学过程, 并参与合成一些必需的维生素和辅助因子等。其在细胞内的生物合成受到一系列蛋白的催化和调控, 并被区隔在不同的亚细胞结构中。线粒体是细胞能量代谢的主要场所, 其中许多关键代谢酶是铁硫蛋白, 需要线粒体铁硫簇组装系统ISC (iron-sulfur cluster)提供铁硫簇。目前, 得益于细菌和酵母中的相关研究成果, 植物线粒体ISC系统中的重要催化和调控蛋白的鉴定与功能分析, 以及铁硫簇在植物生长发育中的功能研究取得了长足进步。对铁硫簇合成系统中植物特有组分的发掘与鉴定, 以及铁硫簇合成系统响应环境胁迫的机制也日益引起人们的重视。该文对植物铁硫簇合成机制特别是线粒体ISC合成系统的研究进展进行总结, 同时对ISC合成系统的重要基因在植物生长发育和非生物胁迫响应中的作用进行了简要综述。
谢涛, 章一帆, 刘云辉, 游慧玉, 夏季奔奔, 马蓉, 张春妮, 华学军. 植物线粒体铁硫簇合成系统及其调控的研究进展. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 499-514.
Tao Xie, Yifan Zhang, Yunhui Liu, Huiyu You, Jibenben Xia, Rong Ma, Chunni Zhang, Xuejun Hua. Research Progress on the Iron-sulfur Cluster Synthesis System and Regulation in Plant Mitochondria. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(4): 499-514.
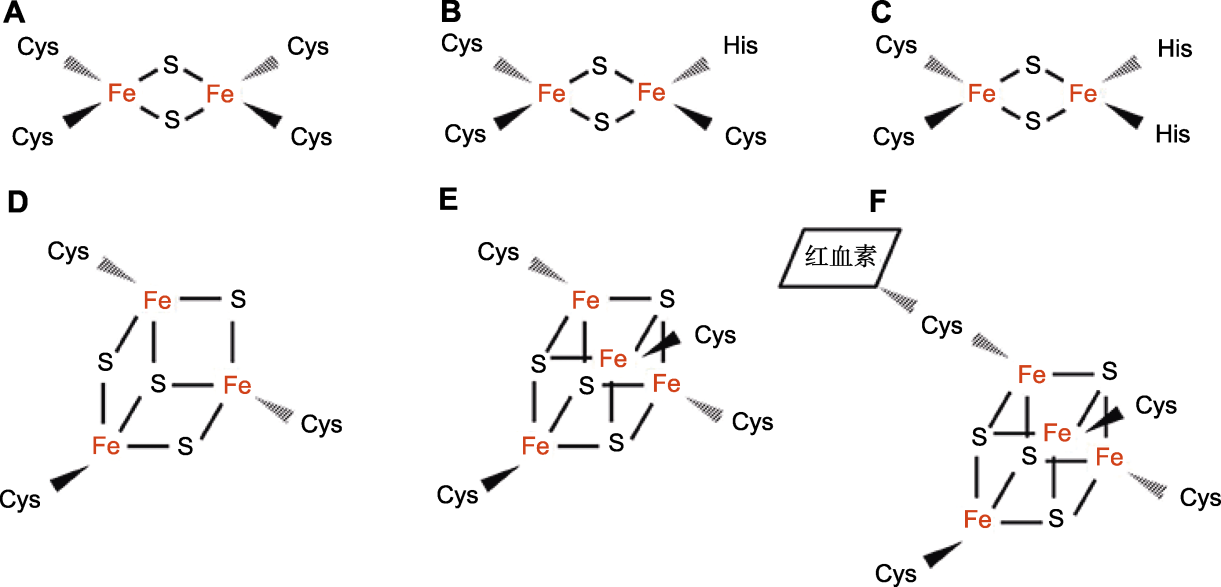
图1 铁硫簇的基本结构(参考Lu, 2018) (A) 由4个半胱氨酸连接的[2Fe-2S]型铁硫簇; (B) 由3个半胱氨酸和1个组氨酸连接的NEET类[2Fe-2S]型铁硫簇; (C) 由2个半胱氨酸和2个组氨酸连接的Rieske类[2Fe-2S]簇; (D) 由3个半胱氨酸残基连接的[3Fe-4S]簇; (E) 由4个半胱氨酸残基连接的[4Fe-4S]簇; (F) 由4个半胱氨酸残基配位的[4Fe-4S]簇, 可以硫醇配位键连接血红素。
Figure 1 The basic structure of iron-sulfur clusters (adapted from Lu, 2018) (A) [2Fe-2S] type iron-sulfur clusters linked by 4 cysteines; (B) NEET [2Fe-2S] iron-sulfur clusters connected by three cysteines and one histidine; (C) Rieske [2Fe-2S] connected by two cysteines and two histidine; (D) [3Fe-4S] connected by three cysteine residues; (E) [4Fe-4S] linked by four cysteine residues; (F) [4Fe-4S] coordinated by four cysteine residues, can bind heme with mercaptan coordination bonds.
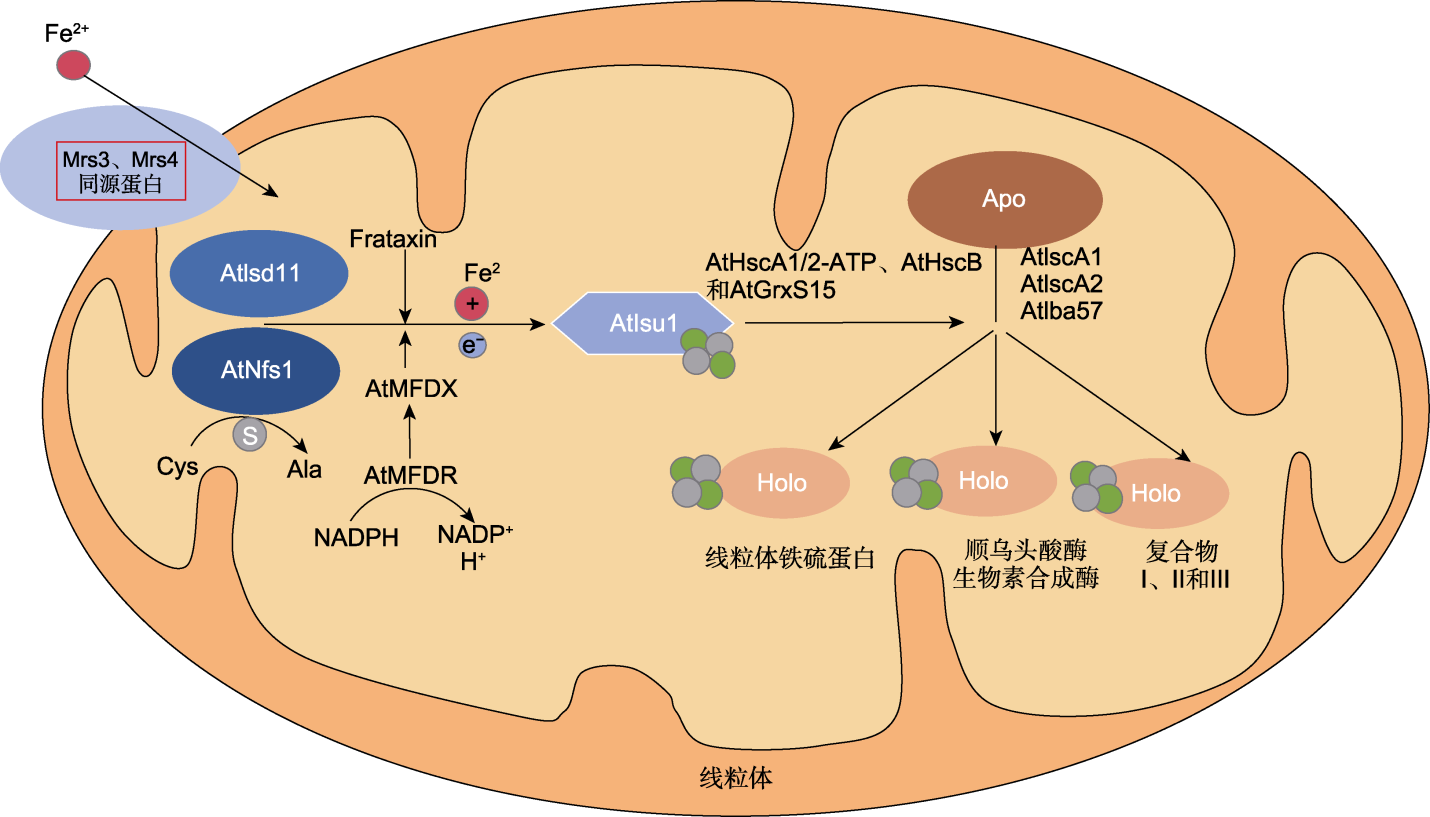
图2 拟南芥线粒体ISC合成途径模式图(参考Lill, 2009) 模式图参考自酵母线粒体ISC合成途径模型, 红色方框中的组分在拟南芥中尚未见文献报道。第1步中AtNfs1-AtIsd11复合物将半胱氨酸脱硫, Frataxin可能提供铁。未被鉴定的同源铁转运蛋白Mrs3和Mrs4可将胞质中的铁转运至线粒体与Frataxin结合, AtMFDR和AtMFDX可能帮助NADPH转移电子。铁和硫在AtIsu1上合成铁硫簇。第2步, AtHscA2和AtHscB与AtIsu1结合, 并且促进铁硫簇从AtIsu1上释放。第3步是将铁硫簇运送至不同的铁硫蛋白中, 如GrxS15、线粒体铁硫蛋白、顺乌头酸酶、生物合成酶以及电子传递链复合物I、II和III。部分铁硫蛋白转运需要铁硫簇组装因子1、组装因子2 (AtIscA1和AtIscA2)和组装因子AtIBA57参与。
Figure 2 Hypothetical model of the mitochondrial ISC biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana (adapted from Lill, 2009) The schematic diagram refers to the yeast mitochondrial ISC synthesis pathway model, and the components in the red box have not yet been reported in Arabidopsis. In the first step, the AtNfs1-AtIsd11 complex desulfurates cysteine, and Frataxin may provide iron. The unidentified homologous iron transport proteins Mrs3 and Mrs4 can transport iron from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria where it binds with Frataxin, whereas AtMFDR and AtMFDX may assist in electron transfer by NADPH. Iron and sulfur are synthesized into iron-sulfur clusters on AtIsu1. In the second step, AtHscA2 and AtHscB bind to AtIsu1, promoting the release of iron-sulfur clusters from AtIsu1. The third step involves transporting the iron-sulfur clusters to various iron-sulfur proteins, such as GrxS15, mitochondrial iron-sulfur proteins, fumarase, biosynthetic enzymes, and electron transport chain complexes I, II, and III. The transport of some iron-sulfur proteins requires the participation of iron-sulfur cluster assembly factors 1 and 2 (AtIscA1 and AtIscA2), and the assembly factor AtIBA57.
| 基因 | 突变类型 | 生长表型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frataxin | SALK_021263 | 生长迟缓、果实鲜重降低且种子数减少 | Busi et al., |
| SALK_094203 | 部分种子不育 | Busi et al., | |
| SALK_122008 | 部分种子不育, 毛绒根 | Martin et al., | |
| ISU1 | 过表达 | 提升铁的富集能力 | Song et al., |
| RNAi | 茎细, 植株矮小 | Frazzon et al., | |
| SALK_006332 | 植株矮小 | Frazzon et al., | |
| NFS1 | 过表达 | 新叶扇形边缘、杂乱花序、莲座叶和尾状叶腋下的腋 芽增多, 对病菌的抗性增强 | Frazzon et al., Fonseca et al., |
| HscB | SALK_099684 | 根的铁吸收水平降低, 铁在枝叶中积累 | Leaden et al., |
| SALK_085159 | 茎部显示出无蜡状表型, 具有光滑的外表 | Xu et al., | |
| HscA1 | SALK_081383、SALK_081385、 SALK_128982和SALK_140494 | 茎短, 莲座叶变小 | Wei et al., |
| HscA2 | SAIL_354_E09、SAIL_302_G07和 HscA2m点突变 | 无明显表型, 对外源脯氨酸具有抗性 | Wei et al., Zhang et al., |
| GrxS15 | SALK_112767、GrxS15amiR、 SALK_112767C、GK-837C05 和SAIL_431_H03 | 根短, 莲座叶变小, 根尖呼吸速率降低, 对砷胁迫的 抗性增强, 早期胚胎致死 | Moseler et al., Ströher et al., |
| SSR1 | FLAG_356A08和FLAG_571A02 | 根生长受到抑制 | Feng et al., |
表1 拟南芥中参与线粒体[Fe-S]簇组装基因的突变等位基因的表型
Table 1 Phenotypes of mutant alleles involved in mitochondrial [Fe-S] cluster assembly genes in Arabidopsis thaliana
| 基因 | 突变类型 | 生长表型 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frataxin | SALK_021263 | 生长迟缓、果实鲜重降低且种子数减少 | Busi et al., |
| SALK_094203 | 部分种子不育 | Busi et al., | |
| SALK_122008 | 部分种子不育, 毛绒根 | Martin et al., | |
| ISU1 | 过表达 | 提升铁的富集能力 | Song et al., |
| RNAi | 茎细, 植株矮小 | Frazzon et al., | |
| SALK_006332 | 植株矮小 | Frazzon et al., | |
| NFS1 | 过表达 | 新叶扇形边缘、杂乱花序、莲座叶和尾状叶腋下的腋 芽增多, 对病菌的抗性增强 | Frazzon et al., Fonseca et al., |
| HscB | SALK_099684 | 根的铁吸收水平降低, 铁在枝叶中积累 | Leaden et al., |
| SALK_085159 | 茎部显示出无蜡状表型, 具有光滑的外表 | Xu et al., | |
| HscA1 | SALK_081383、SALK_081385、 SALK_128982和SALK_140494 | 茎短, 莲座叶变小 | Wei et al., |
| HscA2 | SAIL_354_E09、SAIL_302_G07和 HscA2m点突变 | 无明显表型, 对外源脯氨酸具有抗性 | Wei et al., Zhang et al., |
| GrxS15 | SALK_112767、GrxS15amiR、 SALK_112767C、GK-837C05 和SAIL_431_H03 | 根短, 莲座叶变小, 根尖呼吸速率降低, 对砷胁迫的 抗性增强, 早期胚胎致死 | Moseler et al., Ströher et al., |
| SSR1 | FLAG_356A08和FLAG_571A02 | 根生长受到抑制 | Feng et al., |
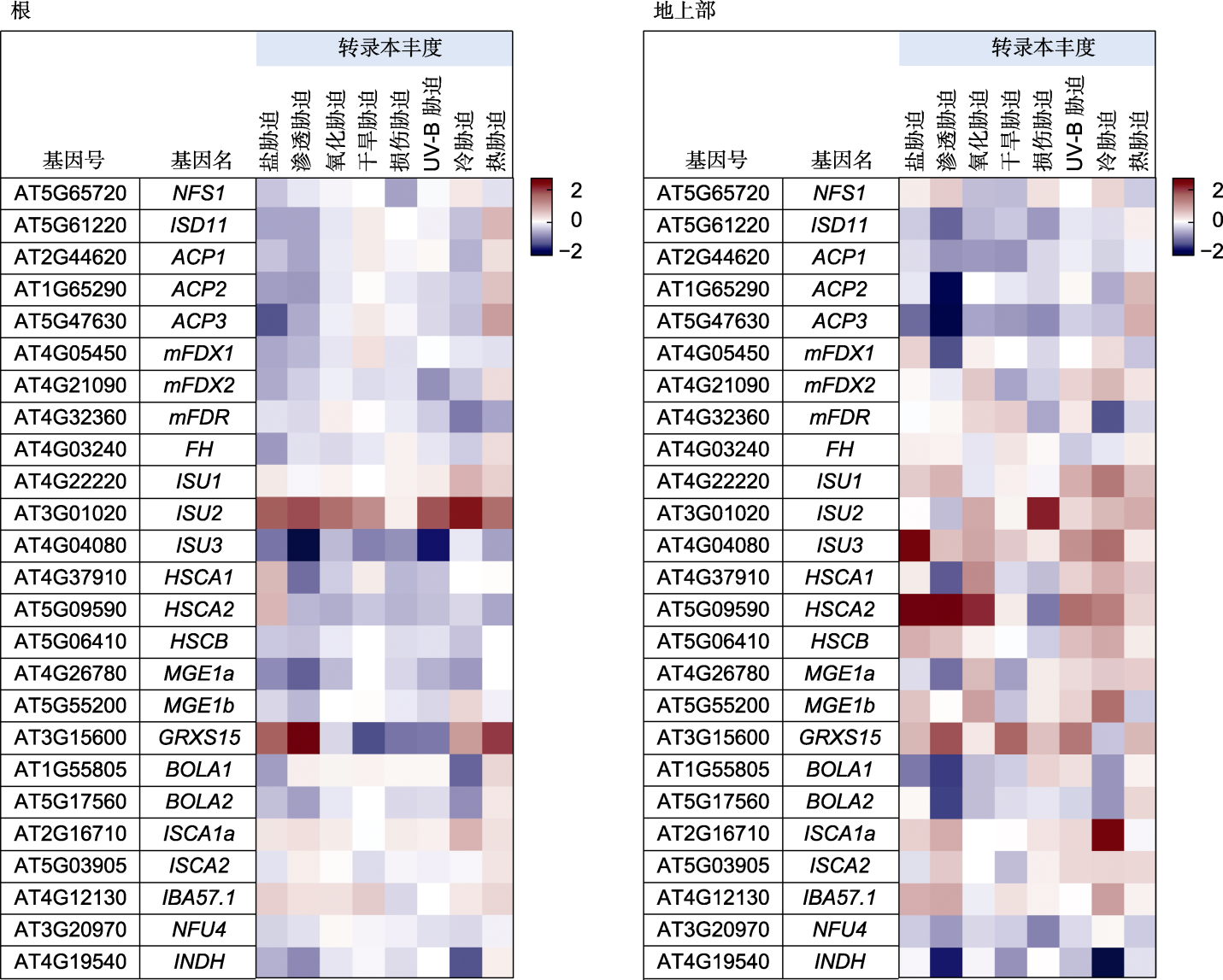
图3 拟南芥ISC合成途径相关基因在不同非生物胁迫下的表达热图 不同非生物胁迫下线粒体铁硫蛋白基因的表达热图, 数据来源于Arabidopsis eFP Browser (https://bar.utoronto.ca/efp/cgi-bin/ efpWeb.cgi)。颜色标记表示基因相对对照组的倍数关系。图中展示胁迫处理时间均为24小时。
Figure 3 Heatmap of gene expression related to the ISC synthesis pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana under various abiotic stresses Heatmap of mitochondrial iron-sulfur protein gene expression under various abiotic stresses, with data sourced from the Arabidopsis eFP Browser (https://bar.utoronto.ca/efp/cgi-bin/efpWeb.cgi). The color markings indicate the fold change in gene expression relative to that in the control group. The time of stress treatment shown in the graph is 24 h for all the samples.
| [1] |
Adam AC, Bornhövd C, Prokisch H, Neupert W, Hell K (2006). The Nfs1 interacting protein Isd11 has an essential role in Fe/S cluster biogenesis in mitochondria. EMBO J 25, 174-183.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Adinolfi S, Iannuzzi C, Prischi F, Pastore C, Iametti S, Martin SR, Bonomi F, Pastore A (2009). Bacterial Frataxin CyaY is the gatekeeper of iron-sulfur cluster formation catalyzed by IscS. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16, 390-396.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Armas AM, Balparda M, Turowski VR, Busi MV, Pagani MA, Gomez-Casati DF (2019). Altered levels of mitochondrial NFS1 affect cellular Fe and S contents in plants. Plant Cell Rep 38, 981-990.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Ayala-Castro C, Saini A, Outten FW (2008). Fe-S cluster assembly pathways in bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 72, 110-125. |
| [5] | Azam T, Przybyla-Toscano J, Vignols F, Couturier J, Rouhier N, Johnson MK (2020). [4Fe-4S] cluster trafficking mediated by Arabidopsis mitochondrial ISCA and NFU proteins. J Biol Chem 295, 18367-18378. |
| [6] |
Babcock M, de Silva D, Oaks R, Davis-Kaplan S, Jiralerspong S, Montermini L, Pandolfo M, Kaplan J (1997). Regulation of mitochondrial iron accumulation by Yfh1p, a putative homolog of Frataxin. Science 276, 1709-1712.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
Balasubramanian R, Shen GZ, Bryant DA, Golbeck JH (2006). Regulatory roles for IscA and SufA in iron homeostasis and redox stress responses in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002. J Bacteriol 188, 3182-3191.
DOI PMID |
| [8] |
Balk J, Pierik AJ, Netz DJA, Mühlenhoff U, Lill R (2004). The hydrogenase-like Nar1p is essential for maturation of cytosolic and nuclear iron-sulphur proteins. EMBO J 23, 2105-2115.
PMID |
| [9] |
Balk J, Pilon M (2011). Ancient and essential: the assembly of iron-sulfur clusters in plants. Trends Plant Sci 16, 218-226.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Balk J, Schaedler TA (2014). Iron cofactor assembly in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65, 125-153.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Barras F, Loiseau L, Py B (2005). How Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae build Fe/S proteins. Adv Microb Physiol 50, 41-101. |
| [12] | Baussier C, Fakroun S, Aubert C, Dubrac S, Mandin P, Py B, Barras F (2020). Making iron-sulfur cluster: structure, regulation and evolution of the bacterial ISC system. Advances in Microbial Physiology: Advances in Agronomy 76, 1-39. |
| [13] |
Beinert H, Holm RH, Münck E (1997). Iron-sulfur clusters: nature’s modular, multipurpose structures. Science 277, 653-659.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Brancaccio D, Gallo A, Mikolajczyk M, Zovo K, Palumaa P, Novellino E, Piccioli M, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Banci L (2014). Formation of [4Fe-4S] clusters in the mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly machinery. J Am Chem Soc 136, 16240-16250.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Braymer JJ, Lill R (2017). Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis and trafficking in mitochondria. J Biol Chem 292, 12754-12763.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Busi MV, Maliandi MV, Valdez H, Clemente M, Zabaleta EJ, Araya A, Gomez-Casati DF (2006). Deficiency of Arabidopsis thaliana Frataxin alters activity of mitochondrial Fe-S proteins and induces oxidative stress. Plant J 48, 873-882. |
| [17] | Busi MV, Zabaleta EJ, Araya A, Gomez-Casati DF (2004). Functional and molecular characterization of the Frataxin homolog from Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett 576, 141-144. |
| [18] |
Bych K, Netz DJA, Vigani G, Bill E, Lill R, Pierik AJ, Balk J (2008). The essential cytosolic iron-sulfur protein Nbp35 acts without Cfd1 partner in the green lineage. J Biol Chem 283, 35797-35804.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Cavadini P, O’Neill HA, Benada O, Isaya G (2002). Assembly and iron-binding properties of human Frataxin, the protein deficient in friedreich ataxia. Hum Mol Genet 11, 217-227.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
Chandramouli K, Unciuleac MC, Naik S, Dean DR, Huynh BH, Johnson MK (2007). Formation and properties of [4Fe-4S] clusters on the IscU scaffold protein. Biochemistry 46, 6804-6811.
PMID |
| [21] |
Ciesielski SJ, Schilke BA, Osipiuk J, Bigelow L, Mulligan R, Majewska J, Joachimiak A, Marszalek J, Craig EA, Dutkiewicz R (2012). Interaction of J-protein co-chaperone Jac1 with Fe-S scaffold Isu is indispensable in vivo and conserved in evolution. J Mol Biol 417, 1-12.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Couturier J, Touraine B, Briat JF, Gaymard F, Rouhier N (2013). The iron-sulfur cluster assembly machineries in plants: current knowledge and open questions. Front Plant Sci 4, 259.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Dean DR, Bolin JT, Zheng LM (1993). Nitrogenase metalloclusters—structures, organization, and synthesis. J Bac- teriol 175, 6737-6744. |
| [24] |
Ding HG, Clark RJ, Ding BJ (2004). IscA mediates iron delivery for assembly of iron-sulfur clusters in IscU under the limited accessible free iron conditions. J Biol Chem 279, 37499-37504.
DOI PMID |
| [25] | Du J, Li YC, Ren XY, Tan GQ, Lü JX (2015). Mechanisms of iron-sulfur clusters assemble in eukaryotes and related diseases. Chin J Cell Biol 37, 1323-1333. (in Chinese) |
| 杜璟, 李艳纯, 任雪营, 谭国强, 吕建新 (2015). 真核细胞中铁硫簇的组装机制及相关铁硫蛋白疾病. 中国细胞生物学学报 37, 1323-1333. | |
| [26] | Du KX, Shen WH, Dong AW (2018). Advances in epigenetic regulation of abiotic stress response in plants. Chin Bull Bot 53, 581-593. (in Chinese) |
|
杜康兮, 沈文辉, 董爱武 (2018). 表观遗传调控植物响应非生物胁迫的研究进展. 植物学报 53, 581-593.
DOI |
|
| [27] | Duby G, Foury F, Ramazzotti A, Herrmann J, Lutz T (2002). A non-essential function for yeast Frataxin in iron- sulfur cluster assembly. Hum Mol Genet 11, 2635-2643. |
| [28] |
Dunkley TPJ, Hester S, Shadforth IP, Runions J, Weimar T, Hanton SL, Griffin JL, Bessant C, Brandizzi F, Hawes C, Watson RB, Dupree P, Lilley KS (2006). Mapping the Arabidopsis organelle proteome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 6518-6523.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Dutkiewicz R, Nowak M, Craig EA, Marszalek J (2017). Fe-S cluster Hsp70 chaperones: the ATPase cycle and protein interactions. Methods Enzymol 595, 161-184.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Feng XJ, Hu Y, Xie T, Han HL, Bonea D, Zeng LJ, Liu J, Ying WH, Mu BN, Cai YY, Zhang M, Lu YL, Zhao RM, Hua XJ (2025). Plant-specific cochaperone SSR1 affects root elongation by modulating the mitochondrial iron- sulfur cluster assembly machinery. PLoS Genet 21, e1011597. |
| [31] |
Flint DH (1996). Escherichia coli contains a protein that is homologous in function and N-terminal sequence to the protein encoded by the nifS gene of Azotobacter vinelandii and that can participate in the synthesis of the Fe-S cluster of dihydroxy-acid dehydratase. J Biol Chem 271, 16068-16074.
PMID |
| [32] |
Fonseca JP, Lee HK, Boschiero C, Griffiths M, Lee S, Zhao P, York LM, Mysore KS (2020). Iron-sulfur cluster protein NITROGEN FIXATION S-LIKE1 and its interactor FRATAXIN function in plant immunity. Plant Physiol 184, 1532-1548.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Frazzon APG, Ramirez MV, Warek U, Balk J, Frazzon J, Dean DR, Winkel BSJ (2007). Functional analysis of Arabidopsis genes involved in mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster assembly. Plant Mol Biol 64, 225-240.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Garcia PS, D’Angelo F, Ollagnier De Choudens S, Dussouchaud M, Bouveret E, Gribaldo S, Barras F (2022). An early origin of iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis machineries before earth oxygenation. Nat Ecol Evol 6, 1564-1572.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Giel JL, Nesbit AD, Mettert EL, Fleischhacker AS, Wanta BT, Kiley PJ (2013). Regulation of iron-sulphur cluster homeostasis through transcriptional control of the Isc path- way by [2Fe-2S]-IscR in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 87, 478-492. |
| [36] | Han HL, Liu J, Feng XJ, Zhang M, Lin QF, Wang T, Qi SL, Xu T, Hua XJ (2021). SSR1 is involved in maintaining the function of mitochondria electron transport chain and iron homeostasis upon proline treatment in Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 256, 153325. |
| [37] | Huang X, Zeng J, Wang M, Liu JS, Qiu GZ (2008). Research progress on structure, function, and biosynthesis of iron-sulfur cluster. Prog Mod Biomed 8, 944-947, 951. (in Chinese) |
| 黄霞, 曾嘉, 王敏, 柳建设, 邱冠周 (2008). 铁硫簇的结构、功能及生物合成研究进展. 现代生物医学进展 8, 944-947, 951. | |
| [38] |
Ivanova A, Gill-Hille M, Huang SB, Branca RM, Kmiec B, Teixeira PF, Lehtiö J, Whelan J, Murcha MW (2019). A mitochondrial LYR protein is required for complex I assembly. Plant Physiol 181, 1632-1650.
DOI PMID |
| [39] | Jacobson MR, Cash VL, Weiss MC, Laird NF, Newton WE, Dean DR (1989). Biochemical and genetic analysis of the nifUSVWZM cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Gen Genet 219, 49-57. |
| [40] |
Kim JH, Füzéry AK, Tonelli M, Ta DT, Westler WM, Vickery LE, Markley JL (2009). Structure and dynamics of the iron-sulfur cluster assembly scaffold protein IscU and its interaction with the cochaperone HscB. Biochemistry 48, 6062-6071.
DOI PMID |
| [41] | Layer G, Ollagnier-de Choudens S, Sanakis Y, Fontecave M (2006). Iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis: characterization of Escherichia coli CYaY as an iron donor for the assembly of [2Fe-2S] clusters in the scaffold IscU. J Biol Chem 281, 16256-16263. |
| [42] | Leaden L, Busi MV, Gomez-Casati DF (2014). The mitochondrial proteins AtHscB and AtIsu1 involved in Fe-S cluster assembly interact with the Hsp70-type chaperon AtHscA2 and modulate its catalytic activity. Mitochondrion 19, 375-381. |
| [43] |
Leaden L, Pagani MA, Balparda M, Busi MV, Gomez- Casati DF (2016). Altered levels of AtHSCB disrupts iron translocation from roots to shoots. Plant Mol Biol 92, 613-628.
PMID |
| [44] | Léon S, Touraine B, Briat JF, Lobréaux S (2005). Mitochondrial localization of Arabidopsis thaliana Isu Fe-S scaffold proteins. FEBS Lett 579, 1930-1934. |
| [45] |
Lezhneva L, Amann K, Meurer J (2004). The universally conserved HCF101 protein is involved in assembly of [4Fe- 4S]-cluster-containing complexes in Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts. Plant J 37, 174-185.
PMID |
| [46] | Liang XJ, Qin L, Liu PW, Wang MH, Ye H (2014). Genes for iron-sulphur cluster assembly are targets of abiotic stress in rice, Oryza sativa. Plant Cell Environ 37, 780-794. |
| [47] | Lill R (2009). Function and biogenesis of iron-sulphur proteins. Nature 460, 831-838. |
| [48] |
Lill R, Freibert SA (2020). Mechanisms of mitochondrial iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem 89, 471-499.
DOI PMID |
| [49] |
Lill R, Mühlenhoff U (2008). Maturation of iron-sulfur proteins in eukaryotes: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Annu Rev Biochem 77, 669-700.
DOI PMID |
| [50] | López-López A, Keech O, Rouhier N (2022). Maturation and assembly of iron-sulfur cluster-containing subunits in the mitochondrial complex I from plants. Front Plant Sci 13, 916948. |
| [51] |
Lu Y (2018). Assembly and transfer of iron-sulfur clusters in the plastid. Front Plant Sci 9, 336.
DOI PMID |
| [52] | Maio N, Kim KS, Singh A, Rouault TA (2017). A single adaptable cochaperone-scaffold complex delivers nascent iron-sulfur clusters to mammalian respiratory chain complexes I-III. Cell Metabol 25, 945-953. |
| [53] | Malkin R, Rabinowitz JC (1966). The reconstitution of clostridial ferredoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 23, 822-827. |
| [54] | Marquez MD, Greth C, Buzuk A, Liu YX, Blinn CM, Beller S, Leiskau L, Hushka A, Wu K, Nur K, Netz DJA, Perlstein DL, Pierik AJ (2023). Cytosolic iron-sulfur protein assembly system identifies clients by a C-terminal tripeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120, e2311057120. |
| [55] | Martin M, Colman MJR, Gómez-Casati DF, Lamattina L, Zabaleta EJ (2009). Nitric oxide accumulation is required to protect against iron-mediated oxidative stress in Frataxin-deficient Arabidopsis plants. FEBS Lett 583, 542-548. |
| [56] | Melber A, Na U, Vashisht A, Weiler BD, Lill R, Wohlschlegel JA, Winge DR (2016). Role of Nfu1 and Bol3 in iron-sulfur cluster transfer to mitochondrial clients. eLife 5, e15991. |
| [57] |
Meyer EH, Welchen E, Carrie C (2019). Assembly of the complexes of the oxidative phosphorylation system in land plant mitochondria. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70, 23-50.
DOI PMID |
| [58] |
Moseler A, Aller I, Wagner S, Nietzel T, Przybyla-Toscano J, Mühlenhoff U, Lill R, Berndt C, Rouhier N, Schwarzländer M, Meyer AJ (2015). The mitochondrial monothiol glutaredoxin S15 is essential for iron-sulfur protein maturation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 13735-13740.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Mühlenhoff U, Richhardt N, Ristow M, Kispal G, Lill R (2002). The yeast Frataxin homolog Yfh1p plays a specific role in the maturation of cellular Fe/S proteins. Hum Mol Genet 11, 2025-2036.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Mühlenhoff U, Richter N, Pines O, Pierik AJ, Lill R (2011). Specialized function of yeast Isa1 and Isa2 proteins in the maturation of mitochondrial [4Fe-4S] proteins. J Biol Chem 286, 41205-41216.
DOI PMID |
| [61] | Murthy N, Ollagnier-de-Choudens S, Sanakis Y, Abdel- Ghany SE, Rousset C, Ye H, Fontecave M, Pilon-Smits EAH, Pilon M (2007). Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana SufE2 and SufE3: functions in chloroplast iron- sulfur cluster assembly and NAD synthesis. J Biol Chem 282, 18254-18264. |
| [62] |
Nachin L, El Hassouni M, Loiseau L, Expert D, Barras F (2001). SoxR-dependent response to oxidative stress and virulence of Erwinia chrysanthemi: the key role of SufC, an orphan ABC ATPase. Mol Microbiol 39, 960-972.
DOI PMID |
| [63] | Netz DJA, Mascarenhas J, Stehling O, Pierik AJ, Lill R (2014). Maturation of cytosolic and nuclear iron-sulfur pro- teins. Trends Cell Biol 24, 303-312 |
| [64] |
Netz DJA, Pierik AJ, Stümpfig M, Mühlenhoff U, Lill R (2007). The Cfd1-Nbp35 complex acts as a scaffold for iron-sulfur protein assembly in the yeast cytosol. Nat Chem Biol 3, 278-286.
PMID |
| [65] |
Netz DJA, Stümpfig M, Doré C, Mühlenhoff U, Pierik AJ, Lill R (2010). Tah18 transfers electrons to Dre2 in cytosolic iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. Nat Chem Biol 6, 758-765.
DOI PMID |
| [66] | Pedroletti L, Moseler A, Meyer AJ (2023). Assembly, transfer, and fate of mitochondrial iron-sulfur clusters. J Exp Bot 74, 3328-3344. |
| [67] |
Przybyla-Toscano J, Christ L, Keech O, Rouhier N (2021). Iron-sulfur proteins in plant mitochondria: roles and maturation. J Exp Bot 72, 2014-2044.
DOI PMID |
| [68] |
Przybyla-Toscano J, Roland M, Gaymard F, Couturier J, Rouhier N (2018). Roles and maturation of iron-sulfur proteins in plastids. J Biol Inorg Chem 23, 567
DOI PMID |
| [69] | Qin L, Wang MH, Zuo J, Feng XY, Liang XJ, Wu ZG, Ye H (2015). Cytosolic BolA plays a repressive role in the tolerance against excess iron and MV-induced oxidative stress in plants. PLoS One 10, e0124887. |
| [70] |
Ramelot TA, Cort JR, Goldsmith-Fischman S, Kornhaber GJ, Xiao R, Shastry R, Acton TB, Honig B, Montelione GT, Kennedy MA (2004). Solution NMR structure of the iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein U (IscU) with zinc bound at the active site. J Mol Biol 344, 567-583.
PMID |
| [71] | Raulfs EC, O’Carroll IP, Dos Santos PC, Unciuleac MC, Dean DR (2008). In vivo iron-sulfur cluster formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 8591-8596. |
| [72] | Reyda MR, Fugate CJ, Jarrett JT (2009). A complex between biotin synthase and the iron-sulfur cluster assembly chaperone HscA that enhances in vivo cluster assembly. Biochemistry 48, 10782-10792. |
| [73] |
Rouault TA (2012). Biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters in mammalian cells: new insights and relevance to human disease. Dis Model Mech 5, 155-164.
DOI PMID |
| [74] |
Schwartz CJ, Giel JL, Patschkowski T, Luther C, Ruzicka FJ, Beinert H, Kiley PJ (2001). IscR, an Fe-S cluster- containing transcription factor, represses expression of Escherichia coli genes encoding Fe-S cluster assembly proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 14895-14900.
PMID |
| [75] |
Sharma AK, Pallesen LJ, Spang RJ, Walden WE (2010). Cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly (CIA) system: factors, mechanism, and relevance to cellular iron regulation. J Biol Chem 285, 26745-26751.
DOI PMID |
| [76] |
Silberg JJ, Hoff KG, Tapley TL, Vickery LE (2001). The Fe/S assembly protein IscU behaves as a substrate for the molecular chaperone Hsc66 from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 276, 1696-1700.
DOI PMID |
| [77] | Song ZZ, Lin SZ, Fu JY, Chen YH, Zhang HX, Li JZ, Liang MX (2022). Heterologous expression of ISU1 gene from Fragaria vesca enhances plant tolerance to Fe depletion in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 184, 65-74. |
| [78] | Song ZZ, Yang Y, Xu JL, Ma RJ, Yu ML (2014). Physiological and transcriptional responses in the iron-sulphur cluster assembly pathway under abiotic stress in peach (Prunus persica L.) seedlings. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 117, 419-430. |
| [79] | Stehling O, Lill R (2013). The role of mitochondria in cellular iron-sulfur protein biogenesis: mechanisms, connected processes, and diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5, a011312. |
| [80] |
Ströher E, Grassl J, Carrie C, Fenske R, Whelan J, Millar AH (2016). Glutaredoxin S15 is involved in Fe-S cluster transfer in mitochondria influencing lipoic acid-dependent enzymes, plant growth, and arsenic tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 170, 1284-1299.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Takahashi Y, Tokumoto U (2002). A third bacterial system for the assembly of iron-sulfur clusters with homologs in archaea and plastids. J Biol Chem 277, 28380-28383.
DOI PMID |
| [82] |
Tapley TL, Cupp-Vickery JR, Vickery LE (2006). Structural determinants of HscA peptide-binding specificity. Biochemistry 45, 8058-8066.
PMID |
| [83] | Tong WH, Jameson GNL, Huynh BH, Rouault TA (2003). Subcellular compartmentalization of human Nfu, an iron- sulfur cluster scaffold protein, and its ability to assemble a [4Fe-4S] cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 9762-9767. |
| [84] | Uzarska MA, Nasta V, Weiler BD, Spantgar F, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Saviello MR, Gonnelli L, Mühlenhoff U, Banci L, Lill R (2016). Mitochondrial Bol1 and Bol3 function as assembly factors for specific iron-sulfur proteins. eLife 5, e16673. |
| [85] |
Van V, Brown JB, O’Shea CR, Rosenbach H, Mohamed I, Ejimogu NE, Bui TS, Szalai VA, Chacón KN, Span I, Zhang FL, Smith AT (2023). Iron-sulfur clusters are involved in post-translational arginylation. Nat Commun 14, 458.
DOI PMID |
| [86] |
Varadarajan J, Guilleminot J, Saint-Jore-Dupas C, Piégu B, Chabouté ME, Gomord V, Coolbaugh RC, Devic M, Delorme V (2010). ATR3 encodes a diflavin reductase essential for Arabidopsis embryo development. New Phytol 187, 67-82.
DOI PMID |
| [87] | Vickery LE, Cupp-Vickery JR (2007). Molecular chaperones HscA/Ssq1 and HscB/Jac1 and their roles in iron- sulfur protein maturation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 42, 95-111. |
| [88] | Wächtershäuser G (2006). From volcanic origins of chemoautotrophic life to bacteria, archaea and eukarya. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361, 1787-1808. |
| [89] | Wächtershäuser G (1992). Groundworks for an evolutionary biochemistry: the iron-sulphur world. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 58, 85-201. |
| [90] | Wang XK, Chen XD, Sun LH, Qian WQ (2019). Canonical cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly and non-canonical functions of DRE2 in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 15, e1008094. |
| [91] |
Ward LM, Kirschvink JL, Fischer WW (2016). Timescales of oxygenation following the evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis. Orig Life Evol Biosph 46, 51-65.
DOI PMID |
| [92] | Wei SS, Niu WT, Zhai XT, Liang WQ, Xu M, Fan X, Lv TT, Xu WY, Bai JT, Jia N, Li B (2019). Arabidopsis mtHSC70-1 plays important roles in the establishment of COX-dependent respiration and redox homeostasis. J Exp Bot 70, 5575-5590. |
| [93] | Wu QY, Lin JL, Liu JZ, Wang XF, Lim W, Oh M, Park J, Rajashekar CB, Whitham SA, Cheng NH, Hirschi KD, Park S (2012). Ectopic expression of Arabidopsis glutaredoxin AtGRXS17 enhances thermotolerance in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J 10, 945-955. |
| [94] | Xu XM, Lin H, Latijnhouwers M, Møller SG (2009). Dual localized AtHscB involved in iron sulfur protein biogenesis in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 4, e7662. |
| [95] | Xu XM, Møller SG (2011). Iron-sulfur clusters: biogenesis, molecular mechanisms, and their functional significance. Antioxid Redox Signal 15, 271-307. |
| [96] | Yabe T, Yamashita E, Kikuchi A, Morimoto K, Nakagawa A, Tsukihara T, Nakai M (2008). Structural analysis of Arabidopsis CnfU protein: an iron-sulfur cluster biosynthetic scaffold in chloroplasts. J Mol Biol 381, 160-173. |
| [97] |
Yang B, Xu CY, Cheng YT, Jia T, Hu XY (2023). Research progress on the biosynthesis and delivery of iron-sulfur clusters in the plastid. Plant Cell Rep 42, 1255-1264.
DOI PMID |
| [98] |
Ye H, Pilon M, Pilon-Smits EAH (2006). CpNifS-dependent iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis in chloroplasts. New Phytol 171, 285-292.
PMID |
| [99] | Zhang J, Bai ZC, Ouyang M, Xu XM, Xiong HB, Wang Q, Grimm B, Rochaix JD, Zhang LX (2021). The DnaJ proteins DJA6 and DJA5 are essential for chloroplast iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis. EMBO J 40, e106742. |
| [100] | Zhang M, Wang CP, Lin QF, Liu AH, Wang T, Feng XJ, Liu J, Han HL, Ma Y, Bonea D, Zhao RM, Hua XJ (2015). HSCA2 G87D point mutation enhances Arabidopsis proline tolerance via boosting mitochondrial Fe-S cluster assembly. Plant J 83, 582-599. |
| [101] | Zhang YF, Liu YH, Zhang CN, Xie T, Xia JBB, Ma R, Wang JY, You HY, Ma R, Wang JY, You HY, Ke LP, Hua XJ (2025). A tetratricopeptide repeat domain-containing protein SSR1 located in mitochondria is involved in root development and auxin polar transport in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 224, e109916 |
| [102] | Zhang YJ, Sang HT, Wang HQ, Shi ZZ, Li L, Wang X, Sun K, Zhang J, Feng HQ (2024). Research progress of plant signaling in systemic responses to abiotic stresses. Chin Bull Bot 59, 122-133. (in Chinese) |
|
张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青 (2024). 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展. 植物学报 59, 122-133.
DOI |
|
| [103] |
Zuo J, Wu ZG, Li Y, Shen ZD, Feng XY, Zhang MY, Ye H (2017). Mitochondrial ABC transporter ATM3 is essential for cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly. Plant Physiol 173, 2096-2109.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 赵洁, 李静, 李雨欣, 黄奕, 杨杰, 李霞. 活性氧在植物种子休眠释放和萌发中的作用研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 1-0. |
| [2] | 黄梦莎, 孔令蝶, 于淼, 刘畅, 王思钦, 王若涵. 不同尺度三维重建技术在植物研究中的发展及应用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 1-0. |
| [3] | 罗号东, 刘勇波. 植物卷须发生及其调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(6): 1-0. |
| [4] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张蓉菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [5] | 王笑, 徐昌文, 钱虹萍, 李思博, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 植物细胞壁参与免疫反应的机制及其原位非标记成像方法[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [6] | 刘德水, 岳宁, 刘玉乐. 植物免疫机制新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [7] | 徐羽丰, 周冕. 植物免疫的转录后调控[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [8] | 吴玉俊, 李英菊, 罗巧玉, 马永贵. 光控植物免疫:从光信号通路到免疫应答的调控网络[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [9] | 肖银燕, 于华, 万里. 植物免疫研究:机制突破和应用创新[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 1-0. |
| [10] | 王鸿梅, 袁蔚, 薛芳, 张召聪, 刘坤, 陈四龙. 植物SWEET基因参与逆境胁迫响应及其调控机制[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 640-655. |
| [11] | 魏梦璐, 李锦粤, 饶玉春. 基于“以赛促创”的植物科学领域创新型人才培养实践[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 656-663. |
| [12] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [13] | 陈鹏翔, 王波, 王子俊, 韩榕. 转录因子在植物响应UV-B辐射中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 449-459. |
| [14] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [15] | 吕加一, 李乐攻, 侯聪聪. 基于FRET原理的生物传感器: 小分子荧光探针在植物中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(2): 283-293. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||