

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 786-803.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25108 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25108
吴玉俊1,2,*( ), 李英菊3, 罗巧玉1, 马永贵1,2
), 李英菊3, 罗巧玉1, 马永贵1,2
收稿日期:2025-06-12
接受日期:2025-07-28
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-07-30
通讯作者:
*吴玉俊, 理学博士, 兰州大学“萃英”博士后。现任青海师范大学副教授, 生物学硕士生导师。青海省“杰出青年基金”获得者, 中组部“西部之光”访问学者, 青海省“昆仑英才”。主要研究方向为植物抗病免疫信号转导及高原特色植物资源的开发利用。先后主持国家自然科学基金、博士后科学基金、青海省杰出青年基金、青海省重点研发与转化国际合作专项、甘肃省青年基金、中央高校博士后创新基金及教育部重点实验室开放课题等项目。作为第一作者、通讯作者及主要完成作者, 在Proc Natl Acad Sci USA、Cell Research、Plant Physiology和Plant Journal等国际高水平期刊发表论文20余篇。E-mail: gsyc_wyj@126.com
基金资助:
Wu Yujun1,2,*( ), Li Yingju3, Luo Qiaoyu1, Ma Yonggui1,2
), Li Yingju3, Luo Qiaoyu1, Ma Yonggui1,2
Received:2025-06-12
Accepted:2025-07-28
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-07-30
Contact:
*E-mail: gsyc_wyj@126.com
摘要: 解析植物抗病免疫机制是抗病作物育种和国家粮食安全保障的重要科学基础。光受体作为植物感知环境信号的核心组分, 不仅参与植物生长发育的精细调控, 还在植物与病原菌互作中发挥关键信号枢纽作用。现有研究表明, 植物光受体通过直接或间接的作用方式, 依赖COP1/SPA复合体、HY5和PIFs等一系列光信号调控元件, 通过调控植物抗性防御基因的时空表达以及防御激素的合成代谢等多层级途径, 实现光信号与模式触发免疫(PTI)和效应子触发免疫(ETI)信号的精密整合, 使植物在有限的资源下巧妙地协同生长与免疫的平衡。近年来, 光信号与植物免疫系统的交互作用已成为植物生物学的研究热点, 其交互机制的解析也为未来抗病作物育种提供了新方向。该文聚焦于光受体整合调控植物免疫信号的分子机制, 重点综述了光受体介导的免疫启动机制及其与免疫激素信号的时空动态整合模式, 展望了光遗传学技术在解析光信号与免疫信号交互作用机制中的应用潜力, 旨在为基于光信号调控元件的抗病作物分子设计育种提供全新的理论依据和技术路径。
吴玉俊, 李英菊, 罗巧玉, 马永贵. 光控植物免疫: 从光信号通路到免疫应答的调控网络. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 786-803.
Wu Yujun, Li Yingju, Luo Qiaoyu, Ma Yonggui. Light-regulated Plant Immunity: The Regulatory Network From Light Signaling Pathways to Immune Responses. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 786-803.
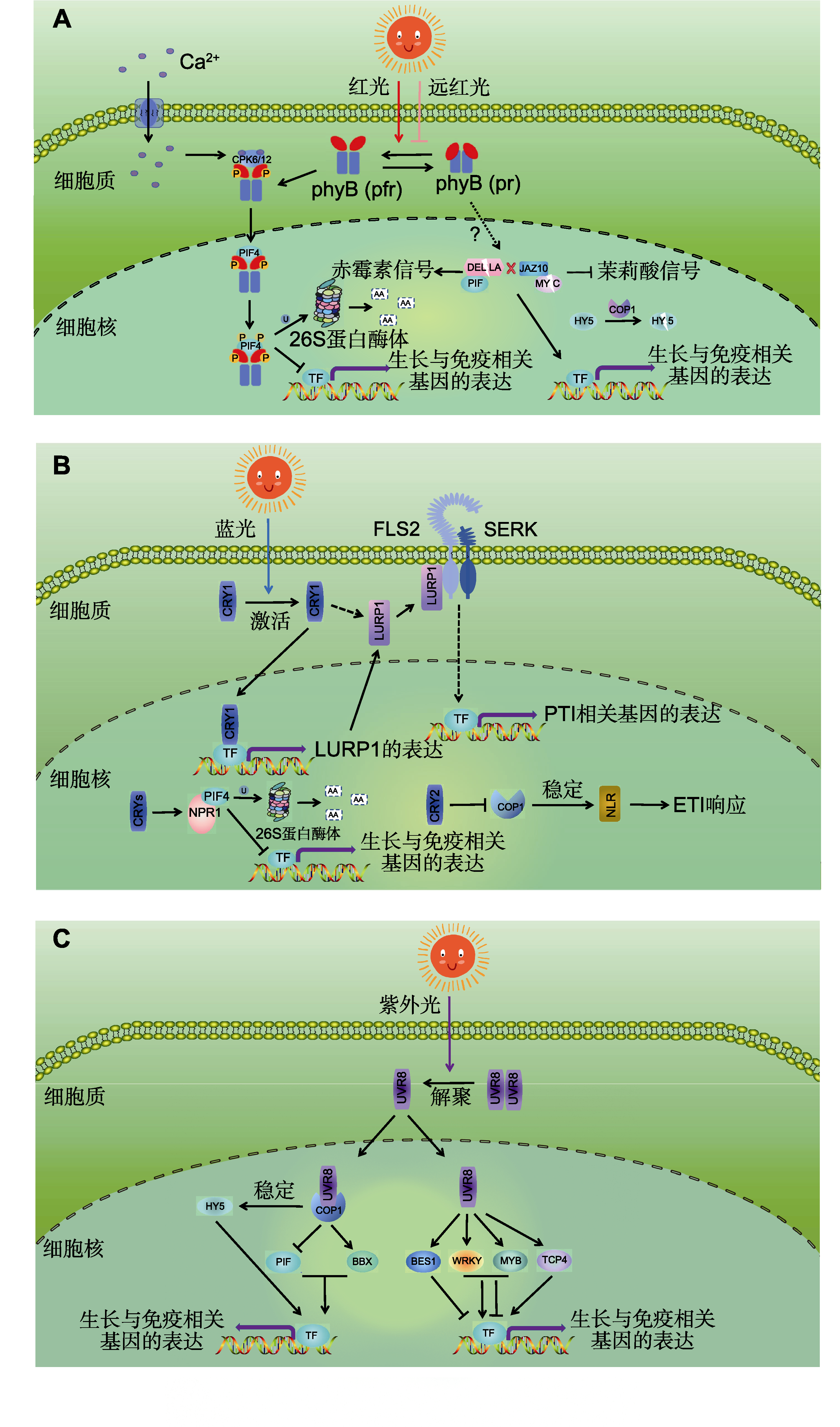
图1 光受体调控植物生长与免疫的分子模式 (A) 当植物感知红光刺激后, 细胞质中的Ca2+浓度瞬时升高, 同时光敏色素蛋白phyB发生构象重排并被激活。Ca2+信号激活的CPK随即与光活化的phyB互作, 通过磷酸化修饰促使其入核。入核的phyB进而介导下游PIF转录因子(TF)的降解, 由此调控生长与免疫相关基因的表达。在低R/FR比值的光环境或phyB缺失条件下, JAZ10蛋白稳定性增强, 同时促进DELLA蛋白及COP1介导的转录因子HY5降解, 从而抑制茉莉酸(JA)信号并激活赤霉素(GA)信号转导。最终, 通过调控生长发育以及抗性防御相关基因的表达, 实现红光诱导的光形态建成与抗病免疫的协同调控。(B) 在蓝光照射下, CRY1被激活后可诱导LURP1的转录, 为植物抵御病原体的攻击做好准备。同时蓝光介导的LURP1的棕榈酰基化修饰促使其从细胞质转移到质膜, 通过直接与细胞表面的免疫传感器复合物相互作用增强其功能, 进而调控植物的病原相关分子模式激发的免疫(PTI)响应。此外, 在蓝光作用下, 蓝光激活的CRYs家族蛋白通过增强水杨酸(SA)受体NPR1与PIF4的相互作用, 促进NPR1介导的PIF4泛素化降解, 进而协同调控下游生长与免疫相关基因的表达。其次, CRY2在蓝光下通过抑制COP1介导的泛素化降解途径, 维持NLR蛋白的稳定性, 从而确保植物效应蛋白激发的免疫(ETI)信号的正常激活。(C) 紫外光(UV-B)激活光受体UVR8后, 二聚体结构的UVB8解离为单体, 并促进单体化的UVR8在细胞核内积累, 使之能与下游的调节因子COP1作用, 进而解除其对HY5、PIF和BBX等转录因子活性的抑制, 最终影响下游生长与免疫响应基因的表达。同时, 单体化的UVB8可在细胞核内直接与BES1、WRKY、MYB和TCP4等转录因子结合, 通过抑制或增强它们的DNA结合能力, 正调控或负调控下游靶基因的表达, 从而协同平衡植物的光适应性生长与抗病免疫过程。箭头表示直接或间接激活作用, 钝线表示直接或间接抑制作用。
Figure 1 The molecular mechanism of photoreceptor in regulating plant growth and immunity (A) Upon perceiving red light, plants experience a temporary increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Simultaneously, the photoreceptor phyB undergoes conformational changes and becomes activated. Subsequently, Ca2+-activated CPK interacts with light-activated phyB, phosphorylating it to facilitate its nuclear entry. Once in the nucleus, phyB triggers the degradation of the transcription factor (TF) PIF4, thereby regulating the expression of genes related to growth and immunity. Conversely, under low R/FR light conditions or in the absence of phyB, the stability of the JAZ10 protein is enhanced and promotes the degradation of DELLA and the transcription factor HY5 via COP1-mediated processes. Consequently, jasmonic acid (JA) signaling is suppressed while gibberellin (GA) signaling is activated. Overall, these processes modulate the expression of growth-related and defense-related genes, enabling the co-regulation of plant morphogenesis and immune responses under red light. (B) Under blue light, activated CRY1 induces LURP1 transcription, priming plants to fend off pathogen assaults. Blue light also promotes LURP1 palmitoylation, redirecting it from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. As a result, modified LURP1 interacts with cell surface immune receptor complexes and regulates pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) responses. In addition, blue light-activated CRYs strengthen the interaction between the salicylic acid (SA) receptor NPR1 and PIF4. This facilitates PIF4 ubiquitination and degradation via NPR1, coordinating the expression of downstream growth- and immunity-related genes. Meanwhile, bathed in blue light, CRY2 stabilizes NLR proteins by inhibiting COP1-mediated ubiquitination, ensuring proper activation of effector-triggered immunity (ETI) signaling. (C) Upon activation by UV-B radiation, the UVR8 photoreceptor undergoes a dimer-to-monomer transition. These monomers then accumulate in the nucleus and bind to the regulatory factor COP1. This interaction inhibits COP1-mediated degradation of transcription factors such as HY5, PIF, and BBX, thereby regulating downstream genes involved in growth and immune responses. In addition, monomeric UVR8 can directly interact with transcription factors like BES1, WRKY, MYB, and TCP4 within the nucleus. By modulating their DNA-binding activities, UVR8 either enhances or suppresses the expression of target genes. This dual regulatory mechanism allows plants to coordinate and balance photoadaptive growth with disease resistance. Lines with arrows mean direct or indirect activation while blunt lines mean direct or indirect repression.
| 基因家族 | 蛋白类型 | 在光信号通路中的作用 | 在免疫信号通路中的作用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COP1 | E3泛素连接酶 | 负调控 抑制光形态建成、下胚轴伸长及气孔运动, 参与开花调控 | 调控作用待明确 影响抗病蛋白的稳定性, 参与脱落酸介导的气孔免疫 | Gangappa and Kumar, |
| PIF | 转录因子 | 负调控 抑制下胚轴伸长, 促进子叶张开, 调控开花及营养生长 | 负调控 抑制防御相关基因的表达, 抑制气孔关闭及叶绿素积累 | Gangappa et al., |
| HY5 | 转录因子 | 正调控 促进光形态建成和下胚轴伸长, 诱导去黄化 | 正调控 激活抗性防御基因的表达, 调控活性氧响应基因、水杨酸(SA)合成及响应基因以及WRKY转录因子等植物免疫相关元件的表达 | Chen et al., |
| MYB | 转录因子 | 负调控 维持PIF蛋白稳定性, 抑制 下胚轴伸长, 调控花青素生 物合成 | 既能正调控也能负调控 调控抗性基因的表达、木质素/类黄酮/角质层蜡的生物合成、多糖信号转导以及激素防御信号转导 | Kim et al., |
| CBF | 转录因子 | 负调控 维持PIF蛋白稳定性, 激活 花青素合成基因的表达 | 正调控 激活抗氧化相关基因、抗病基因及植保素合成基因的表达 | Shi et al., |
| BBX | 转录因子 | 既能正调控也能负调控 促进子叶展开和下胚轴生长, 确保叶绿素合成与光系统组装的协调 | 既能正调控也能负调控 调控气孔免疫与质外体免疫, 调控钙依赖蛋白激酶的活性, 影响模式触发免疫(PTI)、抗氧化基因及茉莉酸(JA)响应基因的表达 | Luo et al., |
| BES | 转录因子 | 负调控 调控植物激素信号转导, 影响下胚轴伸长 | 负调控 调控胼胝质合酶基因和活性氧生成基因的表达, 参与JA介导的抗性防御反应 | Kang et al., |
| TCP | 转录因子 | 负调控 抑制光形态建成相关蛋白的 合成, 抑制PIF的转录激活活 性 | 既能正调控也能负调控 诱导抗病防御相关基因的表达, 参与效应子触发免疫(ETI)信号转导 | Mukhtar et al., |
| WRKY | 转录因子 | 正调控 促进下胚轴伸长及叶片发育 | 既能正调控也能负调控 参与抗病防御相关基因、SA及JA合成基因的表达, 参与抗病次级代谢产物的合成 | Javed and Gao, |
| FHY3/FAR1 | 转录因子 | 正调控 促进叶绿素生物合成与幼苗 生长 | 负调控 依赖于HEMB1, 调控活性SA的产生 | Tang et al., |
表1 光信号通路中下游元件在光信号及免疫信号转导中的作用
Table 1 The role of downstream components in the phototransduction pathway in light and immune signaling transduction
| 基因家族 | 蛋白类型 | 在光信号通路中的作用 | 在免疫信号通路中的作用 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COP1 | E3泛素连接酶 | 负调控 抑制光形态建成、下胚轴伸长及气孔运动, 参与开花调控 | 调控作用待明确 影响抗病蛋白的稳定性, 参与脱落酸介导的气孔免疫 | Gangappa and Kumar, |
| PIF | 转录因子 | 负调控 抑制下胚轴伸长, 促进子叶张开, 调控开花及营养生长 | 负调控 抑制防御相关基因的表达, 抑制气孔关闭及叶绿素积累 | Gangappa et al., |
| HY5 | 转录因子 | 正调控 促进光形态建成和下胚轴伸长, 诱导去黄化 | 正调控 激活抗性防御基因的表达, 调控活性氧响应基因、水杨酸(SA)合成及响应基因以及WRKY转录因子等植物免疫相关元件的表达 | Chen et al., |
| MYB | 转录因子 | 负调控 维持PIF蛋白稳定性, 抑制 下胚轴伸长, 调控花青素生 物合成 | 既能正调控也能负调控 调控抗性基因的表达、木质素/类黄酮/角质层蜡的生物合成、多糖信号转导以及激素防御信号转导 | Kim et al., |
| CBF | 转录因子 | 负调控 维持PIF蛋白稳定性, 激活 花青素合成基因的表达 | 正调控 激活抗氧化相关基因、抗病基因及植保素合成基因的表达 | Shi et al., |
| BBX | 转录因子 | 既能正调控也能负调控 促进子叶展开和下胚轴生长, 确保叶绿素合成与光系统组装的协调 | 既能正调控也能负调控 调控气孔免疫与质外体免疫, 调控钙依赖蛋白激酶的活性, 影响模式触发免疫(PTI)、抗氧化基因及茉莉酸(JA)响应基因的表达 | Luo et al., |
| BES | 转录因子 | 负调控 调控植物激素信号转导, 影响下胚轴伸长 | 负调控 调控胼胝质合酶基因和活性氧生成基因的表达, 参与JA介导的抗性防御反应 | Kang et al., |
| TCP | 转录因子 | 负调控 抑制光形态建成相关蛋白的 合成, 抑制PIF的转录激活活 性 | 既能正调控也能负调控 诱导抗病防御相关基因的表达, 参与效应子触发免疫(ETI)信号转导 | Mukhtar et al., |
| WRKY | 转录因子 | 正调控 促进下胚轴伸长及叶片发育 | 既能正调控也能负调控 参与抗病防御相关基因、SA及JA合成基因的表达, 参与抗病次级代谢产物的合成 | Javed and Gao, |
| FHY3/FAR1 | 转录因子 | 正调控 促进叶绿素生物合成与幼苗 生长 | 负调控 依赖于HEMB1, 调控活性SA的产生 | Tang et al., |
| [1] | Ballaré CL, Pierik R (2017). The shade-avoidance syndrome: multiple signals and ecological consequences. Plant Cell Environ 40, 2530-2543. |
| [2] |
Baum G, Long JC, Jenkins GI, Trewavas AJ (1999). Stimulation of the blue light phototropic receptor NPH1 causes a transient increase in cytosolic Ca2+. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96, 13554-13559.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Boller T, Felix G (2009). A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60, 379-406.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Briggs WR, Christie JM (2002). Phototropins 1 and 2: versatile plant blue-light receptors. Trends Plant Sci 7, 204-210.
DOI PMID |
| [5] |
Burgie ES, Bussell AN, Walker JM, Dubiel K, Vierstra RD (2014). Crystal structure of the photosensing module from a red/far-red light-absorbing plant phytochrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 10179-10184.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Burgie ES, Vierstra RD (2014). Phytochromes: an atomic perspective on photoactivation and signaling. Plant Cell 26, 4568-4583. |
| [7] |
Cañibano E, Bourbousse C, García-León M, Garnelo Gómez B, Wolff L, García-Baudino C, Lozano-Durán R, Barneche F, Rubio V, Fonseca S (2021). DET1-mediated COP1 regulation avoids HY5 activity over second- site gene targets to tune plant photomorphogenesis. Mol Plant 14, 963-982.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Chai TT, Zhou J, Liu J, Xing D (2015). LSD1 and HY5 antagonistically regulate red light induced-programmed cell death in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 6, 292. |
| [9] |
Chen D, Lyu M, Kou XX, Li J, Yang ZX, Gao LL, Li Y, Fan LM, Shi H, Zhong SW (2022). Integration of light and temperature sensing by liquid-liquid phase separation of phytochrome B. Mol Cell 82, 3015-3029.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Chen DQ, Xu G, Tang WJ, Jing YJ, Ji Q, Fei ZJ, Lin RC (2013). Antagonistic basic helix-loop-helix/bZIP transcription factors form transcriptional modules that integrate light and reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25, 1657-1673. |
| [11] | Chen PX, Wang B, Wang ZJ, Han R (2025). The regulatory roles of the transcription factors in plant’s response to UV-B radiation. Chin Bull Bot 60, 449-459. (in Chinese) |
|
陈鹏翔, 王波, 王子俊, 韩榕 (2025). 转录因子在植物响应UV-B辐射中的调控作用. 植物学报 60, 449-459.
DOI |
|
| [12] | Chen QB, Bai L, Wang WJ, Shi HZ, Ramón Botella J, Zhan QD, Liu K, Yang HQ, Song CP (2021a). COP1 promotes ABA-induced stomatal closure by modulating the abundance of ABI/HAB and AHG3 phosphatases. New Phytol 229, 2035-2049. |
| [13] | Chen S, Lory N, Stauber J, Hoecker U (2015). Photoreceptor specificity in the light-induced and COP1-mediated rapid degradation of the repressor of photomorphogenesis SPA2 in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 11, e1005516. |
| [14] | Chen SY, Ma T, Song SR, Li XL, Fu PN, Wu W, Liu JQ, Gao Y, Ye WX, Dry IB, Lu J (2021b). Arabidopsis downy mildew effector HaRxLL470 suppresses plant immunity by attenuating the DNA-binding activity of bZIP transcription factor HY5. New Phytol 230, 1562-1577. |
| [15] | Chen YX, Li YP, Zhou JJ, Xie LX, Peng YB, Sun W, He YN, Jiang CH, Wang ZL, Zheng CK, Xie XZ (2024). Effect of amino acid point mutations on the structure and function of phytochrome B in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chin Bull Bot 59, 481-494. (in Chinese) |
|
陈艳晓, 李亚萍, 周晋军, 解丽霞, 彭永彬, 孙伟, 和亚男, 蒋聪慧, 王增兰, 郑崇珂, 谢先芝 (2024). 拟南芥光敏色素B氨基酸位点突变对其结构与功能的影响. 植物学报 59, 481-494.
DOI |
|
| [16] | Cheng MC, Kathare PK, Paik I, Huq E (2021). Phytochrome signaling networks. Annu Rev Plant Biol 72, 217-244. |
| [17] | Chico JM, Fernández-Barbero G, Chini A, Fernández- Calvo P, Díez-Díaz M, Solano R (2014). Repression of jasmonate-dependent defenses by shade involves differential regulation of protein stability of MYC transcription factors and their JAZ repressors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 1967-1980. |
| [18] |
Cortés LE, Weldegergis BT, Boccalandro HE, Dicke M, Ballaré CL (2016). Trading direct for indirect defense? Phytochrome B inactivation in tomato attenuates direct anti-herbivore defenses whilst enhancing volatile-mediated attraction of predators. New Phytol 212, 1057-1071.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Courbier S, Pierik R (2019). Canopy light quality modulates stress responses in plants. iScience 22, 441-452.
DOI PMID |
| [20] |
de Wit M, Keuskamp DH, Bongers FJ, Hornitschek P, Gommers CMM, Reinen E, Martínez-Cerón C, Fankhauser C, Pierik R (2016). Integration of phytochrome and cryptochrome signals determines plant growth during competition for light. Curr Biol 26, 3320-3326.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | de Wit M, Spoel SH, Sanchez-Perez GF, Gommers CMM, Pieterse CMJ, Voesenek LACJ, Pierik R (2013). Perception of low red:far-red ratio compromises both salicylic acid- and jasmonic acid-dependent pathogen defences in Arabidopsis. Plant J 75, 90-103. |
| [22] |
Demkura PV, Abdala G, Baldwin IT, Ballaré CL (2010). Jasmonate-dependent and -independent pathways mediate specific effects of solar ultraviolet B radiation on leaf phenolics and antiherbivore defense. Plant Physiol 152, 1084-1095.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Demkura PV, Ballaré CL (2012). UVR8 mediates UV-B- induced Arabidopsis defense responses against Botrytis cinerea by controlling sinapate accumulation. Mol Plant 5, 642-652. |
| [24] | Fei CY, Chen LJ, Yang T, Zou WS, Lin HH, Xi DH (2019). The role of phytochromes in Nicotiana tabacum against Chilli veinal mottle virus. Plant Physiol Biochem 139, 470-477. |
| [25] | Frohnmeyer H, Loyall L, Blatt MR, Grabov A (1999). Millisecond UV-B irradiation evokes prolonged elevation of cytosolic-free Ca2+ and stimulates gene expression in transgenic parsley cell cultures. Plant J 20, 109-117. |
| [26] | Gangappa SN, Berriri S, Kumar SV (2017). PIF4 coordinates thermosensory growth and immunity in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 27, 243-249. |
| [27] | Gangappa SN, Kumar SV (2018). DET1 and COP1 modulate the coordination of growth and immunity in response to key seasonal signals in Arabidopsis. Cell Rep 25, 29-37. |
| [28] | Gao GT, Zhou LL, Liu JY, Wang PW, Gong PC, Tian SP, Qin GZ, Wang WH, Wang YY (2024a). E3 ligase SlCOP1-1 stabilizes transcription factor SlOpaque2 and enhances fruit resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato. Plant Physiol 196, 1196-1213. |
| [29] | Gao H, Guo MJ, Song JB, Ma YY, Xu ZQ (2021). Signals in systemic acquired resistance of plants against microbial pathogens. Mol Biol Rep 48, 3747-3759. |
| [30] | Gao MJ, Hao ZY, Ning YS, He ZH (2024b). Revisiting growth-defence trade-offs and breeding strategies in crops. Plant Biotechnol J 22, 1198-1205. |
| [31] |
Griebel T, Zeier J (2008). Light regulation and daytime dependency of inducible plant defenses in Arabidopsis: phytochrome signaling controls systemic acquired resistance rather than local defense. Plant Physiol 147, 790-801.
DOI PMID |
| [32] | Gu JW, Liu J, Xue YJ, Zang X, Xie XZ (2011). Phytochrome functions in rice development. Chin J Rice Sci 25, 130-135. (in Chinese) |
|
顾建伟, 刘婧, 薛彦久, 臧新, 谢先芝 (2011). 光敏色素在水稻生长发育中的作用. 中国水稻科学 25, 130-135.
DOI |
|
| [33] | Guo TT, Liu MQ, Chen L, Liu Y, Li L, Li YP, Cao XL, Mao ZL, Wang WX, Yang HQ (2023). Photoexcited cryptochromes interact with ADA2b and SMC5 to promote the repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 9, 1280-1290. |
| [34] |
Hao YH, Zeng ZX, Yuan MH, Li H, Guo SS, Yang Y, Jiang SS, Hawara E, Li JX, Zhang P, Wang JW, Xin XF, Ma WB, Liu HT (2025). The blue-light receptor CRY1 serves as a switch to balance photosynthesis and plant defense. Cell Host Microbe 33, 137-150.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
Harada A, Shimazaki KI (2007). Phototropins and blue light-dependent calcium signaling in higher plants. Photochem Photobiol 83, 102-111.
PMID |
| [36] |
He J, Liu YQ, Yuan DY, Duan MJ, Liu YL, Shen ZJ, Yang CY, Qiu ZY, Li DM, Wen PZ, Huang J, Fan DJ, Xiao SZ, Xin YY, Chen XN, Jiang L, Wang HY, Yuan LP, Wan JM (2020). An R2R3 MYB transcription factor confers brown planthopper resistance by regulating the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase pathway in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117, 271-277.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Hisamatsu T, King RW, Helliwell CA, Koshioka M (2005). The involvement of gibberellin 20-oxidase genes in phytochrome-regulated petiole elongation of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138, 1106-1116.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Hoang QTN, Han YJ, Kim JI (2019). Plant phytochromes and their phosphorylation. Int J Mol Sci 20, 3450. |
| [39] |
Hua J (2013). Modulation of plant immunity by light, circadian rhythm, and temperature. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16, 406-413.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Huq E, Quail PH (2002). PIF4, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH factor, functions as a negative regulator of phytochrome B signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21, 2441-2450. |
| [41] |
Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Harmon FG, Ho LA, Kay SA (2005). FKF1 F-box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science 309, 293-297.
DOI PMID |
| [42] | Iwata T, Tokutomi S, Kandori H (2011). Light-induced structural changes of the LOV2 domains in various phototropins revealed by FTIR spectroscopy. Biophysics (Nagoya-shi) 7, 89-98. |
| [43] | Javed T, Gao SJ (2023). WRKY transcription factors in plant defense. Trends Genet 39, 787-801. |
| [44] | Jenkins GI (2014a). The UV-B photoreceptor UVR8: from structure to physiology. Plant Cell 26, 21-37. |
| [45] | Jenkins GI (2014b). Structure and function of the UV-B photoreceptor UVR8. Curr Opin Struct Biol 29, 52-57. |
| [46] | Jeong RD, Chandra-Shekara AC, Barman SR, Navarre D, Klessig DF, Kachroo A, Kachroo P (2010). Cryptochrome 2 and phototropin 2 regulate resistance protein-mediated viral defense by negatively regulating an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 13538-13543. |
| [47] | Jiang BC, Zhong ZH, Gu LF, Zhang XY, Wei JB, Ye C, Lin GF, Qu GP, Xiang X, Wen CJ, Hummel M, Bailey-Serres J, Wang Q, He C, Wang X, Lin CT (2023). Light-induced LLPS of the CRY2/SPA1/FIO1 complex regulating mRNA methylation and chlorophyll homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 9, 2042-2058. |
| [48] | Jing YJ, Lin RC (2024). Blue light receptor CRY2 transforms into a ‘dark dancer’. Chin Bull Bot 59, 878-882. (in Chinese) |
|
景艳军, 林荣呈 (2024). 蓝光受体CRY2化身“暗黑舞者”. 植物学报 59, 878-882.
DOI |
|
| [49] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329. |
| [50] | Ju LL, Yang SS, Liang XY, Zhang ZH, Wang H, Qin T, Li FY, Huang JJ, Chen D, Zheng DH, Wang P, Zhao JL, He YQ, Yu WJ, Zhang XX (2025). Ralstonia solanacearum injected protein RipH1 targets transcription factor B-box (BBX)-containing protein 31 in Arabidopsis thaliana to manipulate plant immunity. Int J Biol Macromol 318, 144718. |
| [51] |
Jung JH, Domijan M, Klose C, Biswas S, Ezer D, Gao MJ, Khattak AK, Box MS, Charoensawan V, Cortijo S, Kumar M, Grant A, Locke JCW, Schäfer E, Jaeger KE, Wigge PA (2016). Phytochromes function as thermosensors in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 886-889.
PMID |
| [52] | Kang SN, Yang F, Li L, Chen HM, Chen S, Zhang J (2015). The Arabidopsis transcription factor BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1-ETHYL METHANESULFONATE-SUPPRESSOR1 is a direct substrate of MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE6 and regulates immunity. Plant Physiol 167, 1076-1086. |
| [53] | Katagiri F, Tsuda K (2010). Understanding the plant immune system. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23, 1531-1536. |
| [54] | Kim JY, Lee JH, Park CM (2021). A multifaceted action of phytochrome B in plant environmental adaptation. Front Plant Sci 12, 659712. |
| [55] | Kim SH, Lam PY, Lee MH, Jeon HS, Tobimatsu Y, Park OK (2020). The Arabidopsis R2R3 MYB transcription factor MYB15 is a key regulator of lignin biosynthesis in effector-triggered immunity. Front Plant Sci 11, 583153. |
| [56] | Kim SH, Son GH, Bhattacharjee S, Kim HJ, Nam JC, Nguyen PDT, Hong JC, Gassmann W (2014). The Arabidopsis immune adaptor SRFR1 interacts with TCP transcription factors that redundantly contribute to effector-triggered immunity. Plant J 78, 978-989. |
| [57] | Kleine T, Lockhart P, Batschauer A (2003). An Arabidopsis protein closely related to Synechocystis cryptochrome is targeted to organelles. Plant J 35, 93-103. |
| [58] |
Konrad KR, Gao SQ, Zurbriggen MD, Nagel G (2023). Optogenetic methods in plant biology. Annu Rev Plant Biol 74, 313-339.
DOI PMID |
| [59] |
Lajeunesse G, Roussin-Léveillée C, Boutin S, Fortin É, Laforest-Lapointe I, Moffett P (2023). Light prevents pathogen-induced aqueous microenvironments via potentiation of salicylic acid signaling. Nat Commun 14, 713.
DOI PMID |
| [60] | Legris M, Klose C, Burgie ES, Rojas CCR, Neme M, Hiltbrunner A, Wigge PA, Schäfer E, Vierstra RD, Casal JJ (2016). Phytochrome B integrates light and temperature signals in Arabidopsis. Science 354, 897-900. |
| [61] | Leone M, Keller MM, Cerrudo I, Ballaré CL (2014). To grow or defend? Low red:far-red ratios reduce jasmonate sensitivity in Arabidopsis seedlings by promoting DELLA degradation and increasing JAZ10 stability. New Phytol 204, 355-367. |
| [62] | Li C, Du JC, Xu HN, Feng ZH, Chater CCC, Duan YW, Yang YP, Sun XD (2024a). UVR8-TCP4-LOX2 module regulates UV-B tolerance in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 66, 897-908. |
| [63] | Li H, Burgie ES, Gannam ZTK, Li HL, Vierstra RD (2022). Plant phytochrome B is an asymmetric dimer with unique signaling potential. Nature 604, 127-133. |
| [64] | Li JG, Li G, Wang HY, Deng XW (2011). Phytochrome signaling mechanisms. Arabidopsis Book 9, e0148. |
| [65] | Li SQ, He L, Yang YP, Zhang YX, Han X, Hu YR, Jiang YJ (2024b). INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION 1 promotes cold-enhanced immunity by directly activating salicylic acid signaling. Plant Cell 36, 2587-2606. |
| [66] | Li WT, Wang K, Chern M, Liu YC, Zhu ZW, Liu J, Zhu XB, Yin JJ, Ran L, Xiong J, He KW, Xu LT, He M, Wang J, Liu JL, Bi Y, Qing H, Li MW, Hu K, Song L, Wang L, Qi T, Hou QQ, Chen WL, Li Y, Wang WM, Chen XW (2020). Sclerenchyma cell thickening through enhanced lignification induced by OsMYB30prevents fungal penetration of rice leaves. New Phytol 226, 1850-1863. |
| [67] |
Liang T, Yang Y, Liu HT (2019). Signal transduction mediated by the plant UV-B photoreceptor UVR8. New Phytol 221, 1247-1252.
DOI PMID |
| [68] | Lim GH, Hoey T, Zhu SF, Clavel M, Yu KS, Navarre D, Kachroo A, Deragon JM, Kachroo P (2018). COP1, a negative regulator of photomorphogenesis, positively regulates plant disease resistance via double-stranded RNA binding proteins. PLoS Pathog 14, e1006894. |
| [69] | Lin RC, Liu HT, Li JG, Kong FJ, Liu B, Wang HY, Yang HQ, Zhong SW, Zhu DM, Huai JL, Li H, Liu SR, Wang F, Wang WX, Mao ZL, Deng XW (2024). Research advances in plant light signaling transduction during the past ten years. Plant Physiol J 60, 399-429. (in Chinese) |
| 林荣呈, 刘宏涛, 李继刚, 孔凡江, 刘斌, 王海洋, 杨洪全, 钟上威, 朱丹萌, 淮俊玲, 李洪, 刘双荣, 王璠, 王文秀, 茅志磊, 邓兴旺 (2024). 植物光信号转导研究领域近十年重要研究进展. 植物生理学报 60, 399-429. | |
| [70] | Liu MX, Sun M, Wang Y, Li YH (2012). Arabidopsis UV-B photoreceptor and its light signal transduction in plants. Chin Bull Bot 47, 661-669. (in Chinese) |
|
刘明雪, 孙梅, 王宇, 李玉花 (2012). 植物UV-B受体及其介导的光信号转导. 植物学报 47, 661-669.
DOI |
|
| [71] | Liu Q, Wang Q, Deng WX, Wang X, Piao M, Cai DW, Li YX, Barshop WD, Yu XL, Zhou TT, Liu B, Oka Y, Wohlschlegel J, Zuo ZC, Lin CT (2017). Molecular basis for blue light-dependent phosphorylation of Arabidopsis cryptochrome 2. Nat Commun 8, 15234. |
| [72] | Lu XD, Zhou CM, Xu PB, Luo Q, Lian HL, Yang HQ (2015). Red-light-dependent interaction of phyB with SPA1 promotes COP1-SPA1 dissociation and photomorphogenic development in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 8, 467-478. |
| [73] | Luo D, Sun WH, Cai J, Hu GY, Zhang DQ, Zhang XY, Larkin RM, Zhang JH, Yang CX, Ye ZB, Wang TT (2023). SlBBX20 attenuates JA signaling and regulates resistance to Botrytis cinerea by inhibiting SlMED25 in tomato. Plant Biotechnol J 21, 792-805. |
| [74] | Luo F, Zhang Q, Xin H, Liu HT, Yang HQ, Doblin MS, Bacic A, Li LG (2022). A Phytochrome B-PIF4-MYC2/ MYC4 module inhibits secondary cell wall thickening in response to shaded light. Plant Commun 3, 100416. |
| [75] | Ma CF, Dai SL (2019). Advances in photoreceptor-mediated signaling transduction in flowering time regulation. Chin Bull Bot 54, 9-22. (in Chinese) |
|
马朝峰, 戴思兰 (2019). 光受体介导信号转导调控植物开花研究进展. 植物学报 54, 9-22.
DOI |
|
| [76] | Más P, Kim WY, Somers DE, Kay SA (2003). Targeted degradation of TOC1 by ZTL modulates circadian function in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 426, 567-570. |
| [77] | Mukhtar MS, Carvunis AR, Dreze M, Epple P, Steinbrenner J, Moore J, Tasan M, Galli M, Hao T, Nishimura MT, Pevzner SJ, Donovan SE, Ghamsari L, Santhanam B, Romero V, Poulin MM, Gebreab F, Gutierrez BJ, Tam S, Monachello D, Boxem M, Harbort CJ, McDonald N, Gai LT, Chen HM, He YJ, European Union Effectoromics Consortium, Vandenhaute J, Roth FP, Hill DE, Ecker JR, Vidal M, Beynon J, Braun P, Dangl JL (2011). Independently evolved virulence effectors converge onto hubs in a plant immune system network. Science 333, 596-601. |
| [78] | Naqvi S, He Q, Trusch F, Qiu HS, Pham J, Sun QG, Christie JM, Gilroy EM, Birch PRJ (2022). Blue-light receptor phototropin 1 suppresses immunity to promote Phytophthora infestans infection. New Phytol 233, 2282-2293. |
| [79] | Ngou BPM, Ahn HK, Ding PT, Jones JDG (2021). Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature 592, 110-115. |
| [80] |
Ni WM, Xu SL, González-Grandío E, Chalkley RJ, Huhmer AFR, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY, Quail PH (2017). PPKs mediate direct signal transfer from phytochrome photoreceptors to transcription factor PIF3. Nat Commun 8, 15236.
DOI PMID |
| [81] | Ni WM, Xu SL, Tepperman JM, Stanley DJ, Maltby DA, Gross JD, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY, Quail PH (2014). A mutually assured destruction mechanism attenuates light signaling in Arabidopsis. Science 344, 1160-1164. |
| [82] |
Ochoa-Fernandez R, Abel NB, Wieland FG, Schlegel J, Koch LA, Miller JB, Engesser R, Giuriani G, Brandl SM, Timmer J, Weber W, Ott T, Simon R, Zurbriggen MD (2020). Optogenetic control of gene expression in plants in the presence of ambient white light. Nat Methods 17, 717-725.
DOI PMID |
| [83] | Osterlund MT, Hardtke CS, Wei N, Deng XW (2000). Targeted destabilization of HY5 during light-regulated development of Arabidopsis. Nature 405, 462-466. |
| [84] | Pham VN, Kathare PK, Huq E (2018). TDynamic regulation of PIF5 by COP1-SPA complex to optimize photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 96, 260-273. |
| [85] | Pruitt RN, Locci F, Wanke F, Zhang LS, Saile SC, Joe A, Karelina D, Hua CL, Fröhlich K, Wan WL, Hu MJ, Rao SF, Stolze SC, Harzen A, Gust AA, Harter K, Joosten MHAJ, Thomma BPHJ, Zhou JM, Dangl JL, Weigel D, Nakagami H, Oecking C, Kasmi FE, Parker JE, Nürnberger T (2021). The EDS1-PAD4-ADR1 node mediates Arabidopsis pattern-triggered immunity. Nature 598, 495-499. |
| [86] | Qiu YJ, Pasoreck EK, Reddy AK, Nagatani A, Ma WX, Chory J, Chen M (2017). Mechanism of early light signaling by the carboxy-terminal output module of Arabidopsis phytochrome B. Nat Commun 8, 1905. |
| [87] | Roden LC, Ingle RA (2009). Lights, rhythms, infection: the role of light and the circadian clock in determining the outcome of plant-pathogen interactions. Plant Cell 21, 2546-2552. |
| [88] |
Shao K, Zhang X, Li X, Hao YH, Huang XW, Ma ML, Zhang MH, Yu F, Liu HT, Zhang P (2020). The oligomeric structures of plant cryptochromes. Nat Struct Mol Biol 27, 480-488.
DOI PMID |
| [89] | Shi HT, Wei YX, He CZ (2016). Melatonin-induced CBF/ DREB1s are essential for diurnal change of disease resistance and CCA1 expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 100, 150-155. |
| [90] | Shikata H, Denninger P (2022). Plant optogenetics: applications and perspectives. Curr Opin Plant Biol 68, 102256. |
| [91] | Shin SY, Chung H, Kim SY, Nam KH (2016). BRI1- EMS-suppressor 1 gain-of-function mutant shows higher susceptibility to necrotrophic fungal infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 470, 864-869. |
| [92] | Singh P, Choudhary KK (2025). UV-B orchestration of growth, yield and grain quality traits highlights modifications of source-to-sink relationship in pearl millet cultivars. Physiol Plant 177, e70141. |
| [93] |
Suetsugu N, Wada M (2013). Evolution of three LOV blue light receptor families in green plants and photosynthetic stramenopiles: phototropin, ZTL/FKF1/LKP2 and aureochrome. Plant Cell Physiol 54, 8-23.
DOI PMID |
| [94] | Sun F, Chen Y, Luo Y, Yang F, Yu T, Han HB, Yang YX, Zhou Y (2025). Cryptochromes (CRYs) in pepper: genome-wide identification, evolution and functional analysis of the negative role of CaCRY1 under Phytophthora capsici infection. Plant Sci 355, 112460. |
| [95] |
Takemiya A, Shimazaki KI (2016). Arabidopsis phot1 and phot2 phosphorylate BLUS1 kinase with different efficiencies in stomatal opening. J Plant Res 129, 167-174.
DOI PMID |
| [96] | Takshak S, Agrawal SB (2019). Defense potential of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants under UV-B stress. J Photochem Photobiol B 193, 51-88. |
| [97] | Tang W, Wang W, Chen D, Ji Q, Jing Y, Wang H, Lin R (2012). Transposase-derived proteins FHY3/FAR1 interact with PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR1 to regulate chlorophyll biosynthesis by modulating HEMB1 during deetiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 1984-2000. |
| [98] | Vechtomova YL, Telegina TA, Kritsky MS (2020). Evolution of proteins of the DNA photolyase/cryptochrome family. Biochemistry (Mosc) 85, S131-S153. |
| [99] |
Venkatesh J, Kang BC (2019). Current views on temperature-modulated R gene-mediated plant defense responses and tradeoffs between plant growth and immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 50, 9-17.
DOI PMID |
| [100] |
Vlot AC, Dempsey DA, Klessig DF (2009). Salicylic acid, a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47, 177-206.
DOI PMID |
| [101] | Wang C, Luan S (2024). Calcium homeostasis and signaling in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 77, 102485. |
| [102] |
Wang HY, Ma LG, Li JM, Zhao HY, Deng XW (2001). Direct interaction of Arabidopsis cryptochromes with COP1 in light control development. Science 294, 154-158.
DOI PMID |
| [103] |
Wang Q, Barshop WD, Bian MD, Vashisht AA, He RQ, Yu XH, Liu B, Nguyen P, Liu XM, Zhao XY, Wohlschlegel JA, Lin CT (2015). The blue light-dependent phosphorylation of the CCE domain determines the photosensitivity of Arabidopsis CRY2. Mol Plant 8, 631-643.
DOI PMID |
| [104] | Wang Q, Zuo ZC, Wang X, Gu LF, Yoshizumi T, Yang ZH, Yang L, Liu Q, Liu W, Han YJ, Kim JI, Liu B, Wohlschlegel JA, Matsui M, Oka Y, Lin CT (2016a). Photoactivation and inactivation of Arabidopsis cryptochrome 2. Science 354, 343-347. |
| [105] | Wang WQ, Tang WJ, Ma TT, Niu D, Jin JB, Wang HY, Lin RC (2016b). A pair of light signaling factors FHY3 and FAR1 regulates plant immunity by modulating chlorophyll biosynthesis. J Integr Plant Biol 58, 91-103. |
| [106] |
Wang X, Jiang BC, Gu LF, Chen YD, Mora M, Zhu MLM, Noory E, Wang Q, Lin CT (2021). A photoregulatory mechanism of the circadian clock in Arabidopsis. Nat Plants 7, 1397-1408.
DOI PMID |
| [107] | Wang ZX, Perez V, Hua J (2025). Guard cell activity of PIF4 represses disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ 48, 1468-1478. |
| [108] | Weßling R, Epple P, Altmann S, He YJ, Yang L, Henz SR, McDonald N, Wiley K, Bader KC, Gläßer C, Mukhtar MS, Haigis S, Ghamsari L, Stephens AE, Ecker JR, Vidal M, Jones JDG, Mayer KFX, Ver Loren van Themaat E, Weigel D, Schulze-Lefert P, Dangl JL, Panstruga R, Braun P (2014). Convergent targeting of a common host protein-network by pathogen effectors from three kingdoms of life. Cell Host Microbe 16, 364-375. |
| [109] | Wu YJ, Wu WZ (2021). Pattern recognition receptors and plant innate immunity. Plant Physiol J 57, 301-312. (in Chinese) |
| 吴玉俊, 吴旺泽 (2021). 植物模式识别受体与先天免疫. 植物生理学报 57, 301-312. | |
| [110] | Xie SX, Shi BZ, Miao MZ, Zhao CC, Bai RE, Yan FM, Lei CY (2025). A B-Box (BBX) transcription factor from cucumber, CsCOL 9 positively regulates resistance of host plant to Bemisia tabaci. Int J Mol Sci 26, 324. |
| [111] | Xie XZ, Xue YJ, Zhou JJ, Zhang B, Chang H, Makoto T (2011). Phytochromes regulate SA and JA signaling pathways in rice and are required for developmentally controlled resistance to Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant 4, 688-696. |
| [112] | Xin GY, Li LP, Wang PT, Li XY, Han YJ, Zhao X (2022). The action of enhancing weak light capture via phototropic growth and chloroplast movement in plants. Stress Biol 2, 50. |
| [113] | Xiong JW, Wan XP, Ran ML, Xu XM, Chen LZ, Yang F (2022). Brassinosteroids positively regulate plant immunity via BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR 1-mediated GLUCAN SYNTHASE-LIKE 8 transcription. Front Plant Sci 13, 854899. |
| [114] | Yang YX, Li Y, Guang YL, Lin JH, Zhou Y, Yu T, Ding F, Wang YF, Chen JY, Zhou YH, Dang FF (2023). Red light induces salicylic acid accumulation by activating CaHY5 to enhance pepper resistance against Phytophthora capsici. Hortic Res 10, uhad213. |
| [115] | Yin YH, Vafeados D, Tao Y, Yoshida S, Asami T, Chory J (2005). A new class of transcription factors mediates brassinosteroid-regulated gene expression in Arabidopsis. Cell 120, 249-259. |
| [116] |
Yu X, Feng BM, He P, Shan LB (2017). From chaos to harmony: responses and signaling upon microbial pattern recognition. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55, 109-137.
DOI PMID |
| [117] | Yu XQ, Niu HQ, Zhang YM, Shan XX, Liu C, Wang HL, Yin WL, Xia XL (2024). Transcription factor PagWRKY33 regulates gibberellin signaling and immune receptor pathways in Populus. Plant Physiol 197, kiae593. |
| [118] |
Yu YB, Zhang S, Yu Y, Cui N, Yu GC, Zhao HY, Meng XN, Fan HY (2023). The pivotal role of MYB transcription factors in plant disease resistance. Planta 258, 16.
DOI PMID |
| [119] | Yuan MH, Jiang ZY, Bi GZ, Nomura K, Liu MH, Wang YP, Cai BY, Zhou JM, He SY, Xin XF (2021). Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 592, 105-109. |
| [120] | Zeng DS, Lv JQ, Li X, Liu HT (2025). The Arabidopsis blue-light photoreceptor CRY2 is active in darkness to inhibit root growth. Cell 188, 60-76. |
| [121] | Zhang X, Wang D, Zhao PZ, Sun YW, Fang RX, Ye J (2024). Near-infrared light and PIF4 promote plant antiviral defense by enhancing RNA interference. Plant Commun 5, 100644. |
| [122] |
Zhang Y, Tang M, Zhang Y, Cheng QL, Liu LJ, Chen W, Xie JT, Cheng JS, Fu YP, Li B, Jiang DH, Yu X (2025). An enhancer-promoter-transcription factor module orchestrates plant immune homeostasis by constraining camalexin biosynthesis. Mol Plant 18, 95-113.
DOI PMID |
| [123] | Zhao X, Zhao QP, Yang X, Mu SC, Zhang X (2015). Specificity and crosstalk of phototropin with cryptochrome and phytochrome in regulating hypocotyl phototropism. Chin Bull Bot 50, 122-132. (in Chinese) |
|
赵翔, 赵青平, 杨煦, 慕世超, 张骁 (2015). 向光素调节植物向光性及其与光敏色素/隐花色素的相互关系. 植物学报 50, 122-132.
DOI |
|
| [124] | Zhao Y, Shi H, Pan Y, Lyu M, Yang ZX, Kou XX, Deng XW, Zhong SW (2023a). Sensory circuitry controls cytosolic calcium-mediated phytochrome B phototransduction. Cell 186, 1230-1243. |
| [125] | Zhao Y, Zheng XJ, Zhang XJ, Wang W, Cai GH, Bi GZ, Chen S, Sun CQ, Zhou JM (2023b). PIF3 is phosphorylated by MAPK to modulate plant immunity. New Phytol 240, 372-381. |
| [126] | Zhou YY, Liu PT, Tang YQ, Liu J, Tang YR, Zhuang YM, Li XT, Xu KQ, Zhou Z, Li JG, He GM, Deng XW, Yang L (2024). NPR1 promotes blue light-induced plant photomorphogenesis by ubiquitinating and degrading PIF4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 121, e2412755121. |
| [127] | Zuo ZC, Liu HT, Liu B, Liu XM, Lin CT (2011). Blue light-dependent interaction of CRY2 with SPA1 regulates COP1 activity and floral initiation in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 21, 841-847. |
| [1] | 苏晨, 牛钰凡, 徐航, 王希岭, 于英俊, 何雨晴, 王雷. 生物钟与光温环境信号互作网络研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 315-341. |
| [2] | 景艳军, 林荣呈. 蓝光受体CRY2化身“暗黑舞者”[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(6): 878-882. |
| [3] | 王琪, 吴允哲, 刘学英, 孙丽莉, 廖红, 傅向东. 类受体激酶调控水稻生长发育和环境适应研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 199-213. |
| [4] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [5] | 王雷, 种康. 鱼和熊掌的选择: 反向重复序列变异介导的玉米环境适应与产量平衡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 555-558. |
| [6] | 石添添, 高英, 王欢, 刘君. 细胞核质转运及其受体在植物抗病防御反应中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 480-487. |
| [7] | 马朝峰,戴思兰. 光受体介导信号转导调控植物开花研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(1): 9-22. |
| [8] | 魏华, 王岩, 刘宝辉, 王雷. 植物生物钟及其调控生长发育的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(4): 456-467. |
| [9] | 景艳军, 林荣呈. 我国植物光信号转导研究进展概述[J]. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 257-270. |
| [10] | 刘明雪, 孙梅, 王宇, 李玉花. 植物UV-B受体及其介导的光信号转导[J]. 植物学报, 2012, 47(6): 661-669. |
| [11] | 王静 王艇. 高等植物光敏色素的分子结构、生理功能和进化特征[J]. 植物学报, 2007, 24(05): 649-658. |
| [12] | 赵小英 秦玉芝 刘选明 唐冬英. 植物蓝光反应突变体分子生物学研究[J]. 植物学报, 2005, 22(01): 63-69. |
| [13] | 钱善勤 王忠 莫亿伟 顾蕴洁. 植物向光性反应的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2004, 21(03): 263-272. |
| [14] | 闫海芳 周波 李玉花. 光受体及光信号转导[J]. 植物学报, 2004, 21(02): 235-246. |
| [15] | 贾燕涛. 植物抗病信号转导途径[J]. 植物学报, 2003, 20(05): 602-608. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||