

植物学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 257-270.DOI: 10.11983/CBB16150 cstr: 32102.14.CBB16150
收稿日期:2016-07-14
接受日期:2016-11-23
出版日期:2017-05-01
发布日期:2017-05-27
通讯作者:
林荣呈
作者简介:# 共同第一作者
基金资助:Yanjun Jing, Rongcheng Lin*
Received:2016-07-14
Accepted:2016-11-23
Online:2017-05-01
Published:2017-05-27
Contact:
Lin Rongcheng
About author:# Co-first authors
摘要: 光是影响植物的重要环境因子, 可调节植物生长和发育的各个过程, 如种子萌发、形态建成、庇荫反应、开花和衰老等。自20世纪80年代以来, 借助模式植物拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana), 科学家在光调控植物生长与发育研究领域取得了重要进展, 不仅鉴定了一系列光受体和重要蛋白因子, 而且初步建立了光信号转导的调控网络, 这其中包含中国科学家的杰出贡献。该文对近10多年来我国学者在光信号转导领域的主要研究进展进行了概述, 并对该领域发展提出展望。
景艳军, 林荣呈. 我国植物光信号转导研究进展概述. 植物学报, 2017, 52(3): 257-270.
Yanjun Jing, Rongcheng Lin. Advances in Light Signaling Transduction Research in China. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2017, 52(3): 257-270.
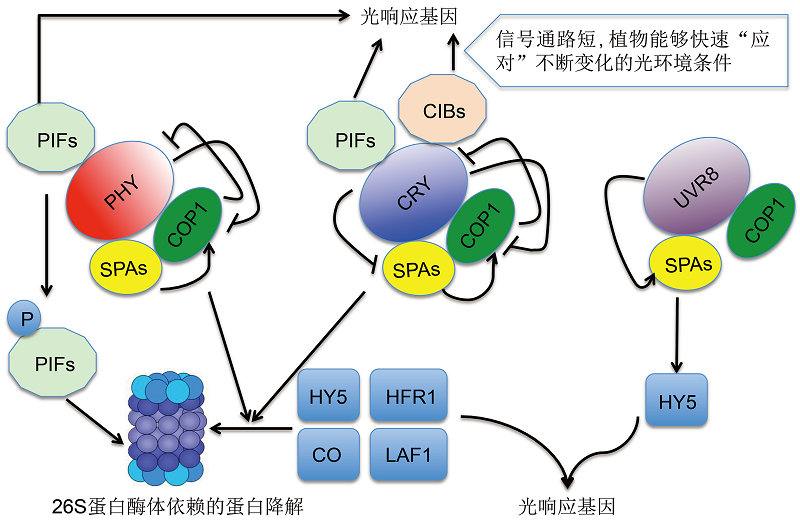
图1 光受体(光敏色素、隐花色素和紫外光受体)介导的信号转导机制的工作模型在响应外界光信号的过程中, 光受体通过两条途径调控基因表达。其一是CRY和PHY介导的光抑制COP1对转录调控因子HY5、HFR1、LAF1和CO等的降解。其二是光受体与转录因子PIFs等互作, 直接调控光响应基因的转录。在UV-B光受体UVR8介导的信号途径中, UV-B诱导形成的COP1复合体包含UVR8, 该复合体能促进HY5的稳定性和活性。COP1与光受体能够互作, 但其作用的分子机制可能不同。例如, COP1介导了PHYA和CRY2的光依赖的泛素化及降解, 但并未影响PHYB、CRY1和UVR8的稳定性。尽管CRY1和CRY2都能与SPA1直接互作, 但二者互作机制却不相同。CRY1在COP1-SPA1的互作中起竞争性抑制作用, 而CRY2-SPA1互作则增强了CRY2-COP1的互作。在这两种情况下, COP1的活性都被抑制。箭头代表促进作用, 带有终止符号的线条表示起抑制作用。
Figure 1 Simplified overview of the signal transduction pathway mediated by phytochrome, crypotochrome and UVR8 There are 2 mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by PHY and CRY. These two photoreceptors mediated light inhibition by COP1 degradation of transcription factor HY5, HFR1, LAF1 and CO etc. In addition, PHY and CRY interact with PIFs and/or CIBs which are enriched on the DNA sequence to directly modulate expression of light response genes (LRBs). In UVR8-mediated signal transduction pathway, the COP1 complex induced by UV-B contains UVR8 and promotes light signaling by stabilizing HY5. COP1 interacts with PHY, CRY and UVR8, but the molecular mechanism of these interactions seems to be different. For example, the interactions lead to ubiquitination and degradation of CRY2 and PHYA, but it seems not to affect the stability of PHYB, CRY1 and UVR8. Both CRY1 and CRY2 interact directly with SPA1 in blue light dependent manner, but the molecular outputs may be different. CRY1-SPA1 competitively inhibits COP1-SPA1 interaction, CRY2-SPA1 seems to enhance CRY2-COP1 interaction. In both cases COP1 activity is inhibited. Arrows indicate positive regulation and bars indicate negative regulation.
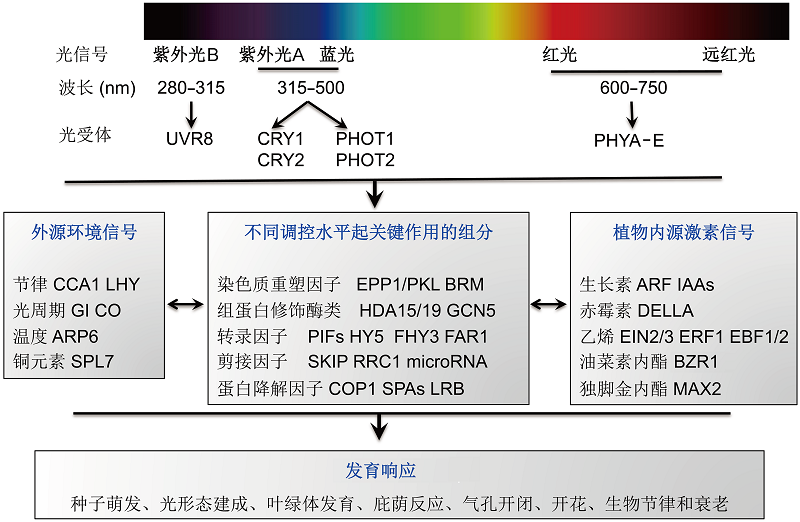
图2 光受体以及参与光信号转导途径的组分因子目前已经鉴定到在转录、转录后、翻译和翻译后各个调控水平起作用的关键组分, 由它们构成的光信号转导途径与外源环境信号和植物内源激素信号存在互作, 共同调控植物的多个发育过程。
Figure 2 Photoreceptors and potential light signaling intermediates The key regulators have been identified to regulate light-response genes at various levels, including transcriptional, posttranscriptional, translational, and posttranslational regulation. The light signaling pathway cross-talks with exogenous environmental signaling and internal phytohormone signaling to shape various developmental responses.
| [1] | Andres F, Coupland G (2012). The genetic basis of flowering responses to seasonal cues.Nat Rev Genet 13, 627-639. |
| [2] | Bai MY, Shang JX, Oh E, Fan M, Bai Y, Zentella R, Sun TP, Wang ZY (2012). Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis.Nat Cell Biol 14, 810-817. |
| [3] | Bergmann DC, Lukowitz W, Somerville CR (2004). Stomatal development and pattern controlled by a MAP- KK kinase.Science 304, 1494-1497. |
| [4] | Borthwick HA, Hendricks SB, Parker MW, Toole EH, Toole VK (1952). A reversible photoreaction controlling seed germination.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 38, 662-666. |
| [5] | Chang CS, Li YH, Chen LT, Chen WC, Hsieh WP, Shin J, Jane WN, Chou SJ, Choi G, Hu JM, Somerville S, Wu SH (2008). LZF1, a HY5-regulated transcriptional factor, functions in Arabidopsis de-etiolation.Plant J 54, 205-219. |
| [6] | Chang CS, Maloof JN, Wu SH (2011). COP1-mediated degradation of BBX22/LZF1 optimizes seedling develop- ment in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 156, 228-239. |
| [7] | Chen D, Xu G, Tang W, Jing Y, Ji Q, Fei Z, Lin R (2013). Antagonistic basic helix-loop-helix/bZIP transcription fac- tors form transcriptional modules that integrate light and reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 25, 1657-1673. |
| [8] | Chen F, Li B, Li G, Charron JB, Dai M, Shi X, Deng XW (2014). Arabidopsis phytochrome A directly targets numerous promoters for individualized modulation of genes in a wide range of pathways.Plant Cell 26, 1949-1966. |
| [9] | Chen F, Shi X, Chen L, Dai M, Zhou Z, Shen Y, Li J, Li G, Wei N, Deng XW (2012). Phosphorylation of FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL1 is a key mechanism defin- ing signaling dynamics of phytochrome A under red and far-red light in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 24, 1907-1920. |
| [10] | Chen H, Huang X, Gusmaroli G, Terzaghi W, Lau OS, Yanagawa Y, Zhang Y, Li J, Lee JH, Zhu D, Deng XW (2010). Arabidopsis CULLIN4-damaged DNA binding protein 1 interacts with CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMOR- PHOGENIC1-SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA complexes to regulate photomorphogenesis and flowering time.Plant Cell 22, 108-123. |
| [11] | Chen H, Shen Y, Tang X, Yu L, Wang J, Guo L, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Feng S, Strickland E, Zheng N, Deng XW (2006). Arabidopsis CULLIN4 forms an E3 ubiquitin ligase with RBX1 and the CDD complex in mediating light control of development.Plant Cell 18, 1991-2004. |
| [12] | Chen X, Lin WH, Wang Y, Luan S, Xue HW (2008). An inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase functions in PHO- TOTROPIN1 signaling in Arabidopsis by altering cytosolic Ca2+.Plant Cell 20, 353-366. |
| [13] | Dong J, Tang D, Gao Z, Yu R, Li K, He H, Terzaghi W, Deng XW, Chen H (2014). Arabidopsis DE-ETIOLATED1 represses photomorphogenesis by positively regulating phytochrome-interacting factors in the dark.Plant Cell 26, 3630-3645. |
| [14] | Feng S, Martinez C, Gusmaroli G, Wang Y, Zhou J, Wang F, Chen L, Yu L, Iglesias-Pedraz JM, Kircher S, Sch- afer E, Fu X, Fan LM, Deng XW (2008). Coordinated regulation ofArabidopsis thaliana development by light and gibberellins. Nature 451, 475-479. |
| [15] | Hardtke CS, Gohda K, Osterlund MT, Oyama T, Okada K, Deng XW (2000). HY5 stability and activity in Arabidopsis is regulated by phosphorylation in its COP1 binding do- main.EMBO J 19, 4997-5006. |
| [16] | Heijde M, Ulm R (2012). UV-B photoreceptor-mediated signaling in plants.Trends Plant Sci 17, 230-237. |
| [17] | Hsieh WP, Hsieh HL, Wu SH (2012). Arabidopsis bZIP16 transcription factor integrates light and hormone signaling pathways to regulate early seedling development.Plant Cell 24, 3997-4011. |
| [18] | Huang X, Ouyang X, Deng XW (2014). Beyond repression of photomorphogenesis: role switching of COP/DET/FUS in light signaling.Curr Opin Plant Biol 21, 96-103. |
| [19] | Huang X, Ouyang X, Yang P, Lau OS, Chen L, Wei N, Deng XW (2013). Conversion from CUL4-based COP1- SPA E3 apparatus to UVR8-COP1-SPA complexes un- derlies a distinct biochemical function of COP1 under UV-B.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 16669-16674. |
| [20] | Huang X, Ouyang X, Yang P, Lau OS, Li G, Li J, Chen H, Deng XW (2012). Arabidopsis FHY3 and HY5 positively mediate induction of COP1 transcription in response to photomorphogenic UV-B light.Plant Cell 24, 4590-4606. |
| [21] | Jang IC, Henriques R, Seo HS, Nagatani A, Chua NH (2010). Arabidopsis PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR proteins promote phytochrome B polyubiquitina- tion by COP1 E3 ligase in the nucleus.Plant Cell 22, 2370-2383. |
| [22] | Jang IC, Yang JY, Seo HS, Chua NH (2005). HFR1 is targeted by COP1 E3 ligase for post-translational pro- teolysis during phytochrome A signaling.Genes Dev 19, 593-602. |
| [23] | Jang K, Lee HG, Jung SJ, Paek NC, Seo PJ (2015). The E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 regulates thermosensory flower- ing by triggering GI degradation in Arabidopsis.Sci Rep 5, 12071. |
| [24] | Jiang Z, Xu G, Jing Y, Tang W, Lin R (2016). Phytochrome B and REVEILLE1/2-mediated signaling controls seed dormancy and germination in Arabidopsis.Nat Commun 7, 12377. |
| [25] | Jiao Y, Lau OS, Deng XW (2007). Light-regulated trans- criptional networks in higher plants.Nat Rev Genet 8, 217-230. |
| [26] | Jing Y, Lin R (2015). The VQ motif-containing protein family of plant-specific transcriptional regulators.Plant Physiol 169, 371-378. |
| [27] | Jing Y, Zhang D, Wang X, Tang W, Wang W, Huai J, Xu G, Chen D, Li Y, Lin R (2013). Arabidopsis chromatin remodeling factor PICKLE interacts with transcription fac- tor HY5 to regulate hypocotyl cell elongation.Plant Cell 25, 242-256. |
| [28] | Kang CY, Lian HL, Wang FF, Huang JR, Yang HQ (2009). Cryptochromes, phytochromes, and COP1 regulate light- controlled stomatal development in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 21, 2624-2641. |
| [29] | Lee J, He K, Stolc V, Lee H, Figueroa P, Gao Y, Tong- prasit W, Zhao H, Lee I, Deng XW (2007). Analysis of transcription factor HY5 genomic binding sites revealed its hierarchical role in light regulation of development.Plant Cell 19, 731-749. |
| [30] | Li G, Siddiqui H, Teng Y, Lin R, Wan XY, Li J, Lau OS, Ouyang X, Dai M, Wan J, Devlin PF, Deng XW, Wang H (2011). Coordinated transcriptional regulation underlying the circadian clock in Arabidopsis.Nat Cell Biol 13, 616-622. |
| [31] | Li J, Li G, Gao S, Martinez C, He G, Zhou Z, Huang X, Lee JH, Zhang H, Shen Y, Wang H, Deng XW (2010). Ara- bidopsis transcription factor ELONGATED HYPOCO- TYL5 plays a role in the feedback regulation of phytoch- rome A signaling.Plant Cell 22, 3634-3649. |
| [32] | Li X, Ma D, Lu SX, Hu X, Huang R, Liang T, Xu T, Tobin EM, Liu H (2016). Blue light- and low temperature- regulated COR27 and COR28 play roles in the Arabi- dopsis circadian clock.Plant Cell 28, 2755-2769. |
| [33] | Li Y, Jing Y, Li J, Xu G, Lin R (2014). Arabidopsis VQ MOTIF-CONTAINING PROTEIN29 represses seedling deetiolation by interacting with PHYTOCHROME-INTER- ACTING FACTOR1.Plant Physiol 164, 2068-2080. |
| [34] | Lian HL, He SB, Zhang YC, Zhu DM, Zhang JY, Jia KP, Sun SX, Li L, Yang HQ (2011). Blue-light-dependent interaction of cryptochrome 1 with SPA1 defines a dyna- mic signaling mechanism.Genes Dev 25, 1023-1028. |
| [35] | Lin R, Ding L, Casola C, Ripoll DR, Feschotte C, Wang H (2007). Transposase-derived transcription factors regu- late light signaling in Arabidopsis.Science 318, 1302-1305. |
| [36] | Lin XL, Niu D, Hu ZL, Kim DH, Jin YH, Cai B, Liu P, Miura K, Yun DJ, Kim WY, Lin R, Jin JB (2016). An Arabi- dopsis SUMO E3 ligase, SIZ1, negatively regulates photomorphogenesis by promoting COP1 activity.PLoS Genet 12, e1006016. |
| [37] | Ling JJ, Li J, Zhu D, Deng XW (2017). Noncanonical role of Arabidopsis COP1/SPA complex in repressing BIN2- mediated PIF3 phosphorylation and degradation in dark- ness.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 3539-3544. |
| [38] | Liu B, Zuo Z, Liu H, Liu X, Lin C (2011). Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 interacts with SPA1 to suppress COP1 activity in response to blue light.Genes Dev 25, 1029-1034. |
| [39] | Liu H, Yu X, Li K, Klejnot J, Yang H, Lisiero D, Lin C (2008a). Photoexcited CRY2 interacts with CIB1 to reg- ulate transcription and floral initiation in Arabidopsis.Science 322, 1535-1539. |
| [40] | Liu J, Zhang F, Zhou J, Chen F, Wang B, Xie X (2012). Phytochrome B control of total leaf area and stomatal density affects drought tolerance in rice.Plant Mol Biol 78, 289-300. |
| [41] | Liu LJ, Zhang YC, Li QH, Sang Y, Mao J, Lian HL, Wang L, Yang HQ (2008b). COP1-mediated ubiquitination of CONSTANS is implicated in cryptochrome regulation of flowering in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 20, 292-306. |
| [42] | Liu X, Chen CY, Wang KC, Luo M, Tai R, Yuan L, Zhao M, Yang S, Tian G, Cui Y, Hsieh HL, Wu K (2013a). PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR3 associates with the histone deacetylase HDA15 in repression of chl- orophyll biosynthesis and photosynthesis in etiolated Arabidopsis seedlings.Plant Cell 25, 1258-1273. |
| [43] | Liu Y, Li X, Li K, Liu H, Lin C (2013b). Multiple bHLH proteins form heterodimers to mediate CRY2-dependent regulation of flowering-time in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet 9, e1003861. |
| [44] | Luo Q, Lian HL, He SB, Li L, Jia KP, Yang HQ (2014). COP1 and phyB physically interact with PIL1 to regulate its stability and photomorphogenic development in Arabi- dopsis.Plant Cell 26, 2441-2456. |
| [45] | Luo XM, Lin WH, Zhu S, Zhu JY, Sun Y, Fan XY, Cheng M, Hao Y, Oh E, Tian M, Liu L, Zhang M, Xie Q, Chong K, Wang ZY (2010). Integration of light- and brass- inosteroid-signaling pathways by a GATA transcription factor in Arabidopsis.Dev Cell 19, 872-883. |
| [46] | Ma D, Li X, Guo Y, Chu J, Fang S, Yan C, Noel JP, Liu H (2016a). Cryptochrome 1 interacts with PIF4 to regulate high temperature-mediated hypocotyl elongation in res- ponse to blue light.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 224-229. |
| [47] | Ma L, Tian T, Lin R, Deng XW, Wang H, Li G (2016b). Arabidopsis FHY3 and FAR1 regulate light-inducedmyo- inositol biosynthesis and oxidative stress responses by transcriptional activation of MIPS1. Mol Plant 9, 541-557. |
| [48] | Mao J, Zhang YC, Sang Y, Li QH, Yang HQ (2005). From the cover: a role for Arabidopsis cryptochromes and COP1 in the regulation of stomatal opening.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 12270-12275. |
| [49] | Meng Y, Li H, Wang Q, Liu B, Lin C (2013). Blue light- dependent interaction between cryptochrome2 and CIB1 regulates transcription and leaf senescence in soybean.Plant Cell 25, 4405-4420. |
| [50] | Ni W, Xu SL, Tepperman JM, Stanley DJ, Maltby DA, Gross JD, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY, Quail PH (2014). A mutually assured destruction mechanism attenuates light signaling in Arabidopsis.Science 344, 1160-1164. |
| [51] | Oh E, Kim J, Park E, Kim JI, Kang C, Choi G (2004). PIL5, a phytochrome-interacting basic helix-loop-helix protein, is a key negative regulator of seed germination inAra- bidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16, 3045-3058. |
| [52] | Oh E, Zhu JY, Wang ZY (2012). Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses.Nat Cell Biol 14, 802-809. |
| [53] | Ouyang X, Li J, Li G, Li B, Chen B, Shen H, Huang X, Mo X, Wan X, Lin R, Li S, Wang H, Deng XW (2011). Genome-wide binding site analysis of FAR-RED ELONG- ATED HYPOCOTYL3 reveals its novel function in Arab- idopsis development.Plant Cell 23, 2514-2535. |
| [54] | Pedmale UV, Huang SS, Zander M, Cole BJ, Hetzel J, Ljung K, Reis PA, Sridevi P, Nito K, Nery JR, Ecker JR, Chory J (2016). Cryptochromes interact directly with PIFs to control plant growth in limiting blue light.Cell 164, 233-245. |
| [55] | Rizzini L, Favory JJ, Cloix C, Faggionato D, O'Hara A, Kaiserli E, Baumeister R, Schafer E, Nagy F, Jenkins GI, Ulm R (2011). Perception of UV-B by the Arabidopsis UVR8 protein.Science 332, 103-106. |
| [56] | Saijo Y, Sullivan JA, Wang H, Yang J, Shen Y, Rubio V, Ma L, Hoecker U, Deng XW (2003). The COP1-SPA1 interaction defines a critical step in phytochrome A- mediated regulation of HY5 activity.Genes Dev 17, 2642-2647. |
| [57] | Saijo Y, Zhu D, Li J, Rubio V, Zhou Z, Shen Y, Hoecker U, Wang H, Deng XW (2008). Arabidopsis COP1/SPA1 complex and FHY1/FHY3 associate with distinct phosp- horylated forms of phytochrome A in balancing light signa- ling.Mol Cell 31, 607-613. |
| [58] | Sang Y, Li QH, Rubio V, Zhang YC, Mao J, Deng XW, Yang HQ (2005). N-terminal domain-mediated homodi- merization is required for photoreceptor activity of Ara- bidopsis CRYPTOCHROME 1.Plant Cell 17, 1569-1584. |
| [59] | Seo HS, Yang JY, Ishikawa M, Bolle C, Ballesteros ML, Chua NH (2003). LAF1 ubiquitination by COP1 controls photomorphogenesis and is stimulated by SPA1.Nature 423, 995-999. |
| [60] | Shen Y, Zhou Z, Feng S, Li J, Tan-Wilson A, Qu LJ, Wang H, Deng XW (2009). Phytochrome A mediates rapid red light-induced phosphorylation of Arabidopsis FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL1 in a low fluence response.Plant Cell 21, 494-506. |
| [61] | Shi H, Liu R, Xue C, Shen X, Wei N, Deng XW, Zhong S (2016a). Seedlings transduce the depth and mechanical pressure of covering soil using COP1 and ethylene to regulate EBF1/EBF2 for soil emergence.Curr Biol 26, 139-149. |
| [62] | Shi H, Shen X, Liu R, Xue C, Wei N, Deng XW, Zhong S (2016b). The red light receptor phytochrome B directly enhances substrate-E3 ligase interactions to attenuate ethylene responses.Dev Cell 39, 597-610. |
| [63] | Shi H, Wang X, Mo X, Tang C, Zhong S, Deng XW (2015). Arabidopsis DET1 degrades HFR1 but stabilizes PIF1 to precisely regulate seed germination.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 3817-3822. |
| [64] | Shi H, Zhong S, Mo X, Liu N, Nezames CD, Deng XW (2013). HFR1 sequesters PIF1 to govern the transcrip- tional network underlying light-initiated seed germination in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 25, 3770-3784. |
| [65] | Song Y, Yang C, Gao S, Zhang W, Li L, Kuai B (2014). Age-triggered and dark-induced leaf senescence require the bHLH transcription factors PIF3, 4, and 5.Mol Plant 7, 1776-1787. |
| [66] | Sun J, Qi L, Li Y, Chu J, Li C (2012). PIF4-mediated activa- tion of YUCCA8 expression integrates temperature into the auxin pathway in regulating Arabidopsis hypocotyl growth.PLoS Genet 8, e1002594. |
| [67] | Sun J, Qi L, Li Y, Zhai Q, Li C (2013). PIF4 and PIF5 transcription factors link blue light and auxin to regulate the phototropic response in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 25, 2102-2114. |
| [68] | Sun N, Wang J, Gao Z, Dong J, He H, Terzaghi W, Wei N, Deng XW, Chen H (2016). Arabidopsis SAURs are critical for differential light regulation of the development of various organs.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 6071-6076. |
| [69] | Sun SY, Chao DY, Li XM, Shi M, Gao JP, Zhu MZ, Yang HQ, Luan S, Lin HX (2009). OsHAL3 mediates a new pathway in the light-regulated growth of rice.Nat Cell Biol 11, 845-851. |
| [70] | Sun W, Xu XH, Wu X, Wang Y, Lu X, Sun H, Xie X (2015). Genome-wide identification of microRNAs and their tar- gets in wild type and phyB mutant provides a key link between microRNAs and the phyB-mediated light signa- ling pathway in rice.Front Plant Sci 6, 372. |
| [71] | Tan ST, Dai C, Liu HT, Xue HW (2013). Arabidopsis casein kinase1 proteins CK1.3 and CK1.4 phosphorylate crypto- chrome2 to regulate blue light signaling.Plant Cell 25, 2618-2632. |
| [72] | Tang W, Ji Q, Huang Y, Jiang Z, Bao M, Wang H, Lin R (2013). FAR-RED ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL3 and FAR- RED IMPAIRED RESPONSE1 transcription factors inte- grate light and abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 163, 857-866. |
| [73] | Tang W, Wang W, Chen D, Ji Q, Jing Y, Wang H, Lin R (2012). Transposase-derived proteins FHY3/FAR1 inter- act with PHYTOCHROME-INTERACTING FACTOR1 to regulate chlorophyll biosynthesis by modulating HEMB1 during deetiolation in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 24, 1984-2000. |
| [74] | Tsai HL, Li YH, Hsieh WP, Lin MC, Ahn JH, Wu SH (2014). HUA ENHANCER1 is involved in posttranscriptional regulation of positive and negative regulators in Arabido- psis photomorphogenesis.Plant Cell 26, 2858-2872. |
| [75] | Wang FF, Lian HL, Kang CY, Yang HQ (2010). Phyto- chrome B is involved in mediating red light-induced sto- matal opening inArabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant 3, 246-259. |
| [76] | Wang H, Wang H (2015a). Multifaceted roles of FHY3 and FAR1 in light signaling and beyond.Trends Plant Sci 20, 453-461. |
| [77] | Wang H, Wang H (2015b). Phytochrome signaling: time to tighten up the loose ends.Mol Plant 8, 540-551. |
| [78] | Wang W, Tang W, Ma T, Niu D, Jin JB, Wang H, Lin R (2016). A pair of light signaling factors FHY3 and FAR1 regulates plant immunity by modulating chlorophyll bio- synthesis.J Integr Plant Biol 58, 91-103. |
| [79] | Wang X, Jing Y, Zhang B, Zhou Y, Lin R (2015). Glyco- syltransferase-like protein ABI8/ELD1/KOB1 promotes Arabidopsis hypocotyl elongation through regulating cellu- lose biosynthesis.Plant Cell Environ 38, 411-422. |
| [80] | Wang X, Wu F, Xie Q, Wang H, Wang Y, Yue Y, Gahura O, Ma S, Liu L, Cao Y, Jiao Y, Puta F, McClung CR, Xu X, Ma L (2012). SKIP is a component of the spliceosome linking alternative splicing and the circadian clock in Ara- bidopsis.Plant Cell 24, 3278-3295. |
| [81] | Wang Y, Wu JF, Nakamichi N, Sakakibara H, Nam HG, Wu SH (2011). LIGHT-REGULATED WD1 and PSEUDO- RESPONSE REGULATOR9 form a positive feedback re- gulatory loop in the Arabidopsis circadian clock.Plant Cell 23, 486-498. |
| [82] | Wu D, Hu Q, Yan Z, Chen W, Yan C, Huang X, Zhang J, Yang P, Deng H, Wang J, Deng X, Shi Y (2012). Structural basis of ultraviolet-B perception by UVR8.Na- ture 484, 214-219. |
| [83] | Wu S, Li Z, Yang L, Xie Z, Chen J, Zhang W, Liu T, Gao S, Gao J, Zhu Y, Xin J, Ren G, Kuai B (2016). NON- YELLOWING2 (NYE2), a close paralog of NYE1, plays a positive role in chlorophyll degradation in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant 9, 624-627. |
| [84] | Wu SH (2014). Gene expression regulation in photomor- phogenesis from the perspective of the central dogma.Annu Rev Plant Biol 65, 311-333. |
| [85] | Xie Q, Wang P, Liu X, Yuan L, Wang L, Zhang C, Li Y, Xing H, Zhi L, Yue Z, Zhao C, McClung CR, Xu X (2014). LNK1 and LNK2 are transcriptional coactivators in the Arabidopsis circadian oscillator.Plant Cell 26, 2843-2857. |
| [86] | Xu C, Liu Y, Li Y, Xu X, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, Zhang Q (2015a). Differential expression ofGS5 regulates grain size in rice. J Exp Bot 66, 2611-2623. |
| [87] | Xu D, Jiang Y, Li J, Lin F, Holm M, Deng XW (2016a). BBX21, an Arabidopsis B-box protein, directly activates HY5 and is targeted by COP1 for 26S proteasome- mediated degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 7655-7660. |
| [88] | Xu D, Li J, Gangappa SN, Hettiarachchi C, Lin F, Andersson MX, Jiang Y, Deng XW, Holm M (2014). Convergence of light and ABA signaling on the ABI5 promoter.PLoS Genet 10, e1004197. |
| [89] | Xu D, Lin F, Jiang Y, Ling J, Hettiarachchi C, Tellgren- Roth C, Holm M, Wei N, Deng XW (2015a). Arabidopsis COP1 SUPPRESSOR 2 represses COP1 E3 ubiquitin ligase activity through their Coiled-Coil domains associa- tion.PLoS Genet 11, e1005747. |
| [90] | Xu G, Guo H, Zhang D, Chen D, Jiang Z, Lin R (2015b). REVEILLE1 promotes NADPH: protochlorophyllide oxido- reductase A expression and seedling greening in Arabi- dopsis.Photosynth Res 126, 331-340. |
| [91] | Xu PB, Lian HL, Wang WX, Xu F, Yang HQ (2016b). Pivotal roles of the phytochrome-interacting factors in cryptochrome signaling.Mol Plant 9, 496-497. |
| [92] | Yang J, Lin R, Sullivan J, Hoecker U, Liu B, Xu L, Deng XW, Wang H (2005). Light regulates COP1-mediated degradation of HFR1, a transcription factor essential for light signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 17, 804-821. |
| [93] | Yu X, Klejnot J, Zhao X, Shalitin D, Maymon M, Yang H, Lee J, Liu X, Lopez J, Lin C (2007a). Arabidopsis cryptochrome 2 completes its posttranslational life cycle in the nucleus.Plant Cell 19, 3146-3156. |
| [94] | Yu X, Shalitin D, Liu X, Maymon M, Klejnot J, Yang H, Lopez J, Zhao X, Bendehakkalu KT, Lin C (2007b). Derepression of the NC80 motif is critical for the photo- activation of Arabidopsis CRY2.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 7289-7294. |
| [95] | Yu Y, Wang J, Zhang Z, Quan R, Zhang H, Deng XW, Ma L, Huang R (2013). Ethylene promotes hypocotyl growth and HY5 degradation by enhancing the movement of COP1 to the nucleus in the light.PLoS Genet 9, e100-4025. |
| [96] | Yuan S, Zhang ZW, Zheng C, Zhao ZY, Wang Y, Feng LY, Niu G, Wang CQ, Wang JH, Feng H, Xu F, Bao F, Hu Y, Cao Y, Ma L, Wang H, Kong DD, Xiao W, Lin HH, He Y (2016). Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 functions in nitrogen regulation of flowering.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 7661-7666. |
| [97] | Zhang D, Jing Y, Jiang Z, Lin R (2014a). The chromatin- remodeling factor PICKLE integrates brassinosteroid and gibberellin signaling during skotomorphogenic growth in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 26, 2472-2485. |
| [98] | Zhang D, Li Y, Zhang X, Zha P, Lin R (2017). The SWI2/SNF2 chromatin-remodeling ATPase BRAHMA re- gulates chlorophyll biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.Mol Plant 10, 155-167. |
| [99] | Zhang H, Zhao X, Li J, Cai H, Deng XW, Li L (2014b). MicroRNA408 is critical for theHY5-SPL7 gene network that mediates the coordinated response to light and cop- per. Plant Cell 26, 4933-4953. |
| [100] | Zhang Q, Li H, Li R, Hu R, Fan C, Chen F, Wang Z, Liu X, Fu Y, Lin C (2008). Association of the circadian rhythmic expression of GmCRY1a with a latitudinal cline in photo- periodic flowering of soybean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 21028-21033. |
| [101] | Zheng X, Wu S, Zhai H, Zhou P, Song M, Su L, Xi Y, Li Z, Cai Y, Meng F, Yang L, Wang H, Yang J (2013). Arabidopsis phytochrome B promotes SPA1 nuclear acc- umulation to repress photomorphogenesis under far-red light.Plant Cell 25, 115-133. |
| [102] | Zhong S, Shi H, Xue C, Wang L, Xi Y, Li J, Quail PH, Deng XW, Guo H (2012). A molecular framework of light- controlled phytohormone action in Arabidopsis.Curr Biol 22, 1530-1535. |
| [103] | Zhong S, Zhao M, Shi T, Shi H, An F, Zhao Q, Guo H (2009). EIN3/EIL1 cooperate with PIF1 to prevent photo- oxidation and to promote greening of Arabidopsis seed- lings.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 21431-21436. |
| [104] | Zhou P, Song M, Yang Q, Su L, Hou P, Guo L, Zheng X, Xi Y, Meng F, Xiao Y, Yang L, Yang J (2014). Both PHYTOCHROME RAPIDLY REGULATED1 (PAR1) and PAR2 promote seedling photomorphogenesis in multiple light signaling pathways.Plant Physiol 164, 841-852. |
| [105] | Zhu D, Maier A, Lee JH, Laubinger S, Saijo Y, Wang H, Qu LJ, Hoecker U, Deng XW (2008). Biochemical characterization of Arabidopsis complexes containing CO- NSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 and SUPPR- ESSOR OF PHYA proteins in light control of plant development.Plant Cell 20, 2307-2323. |
| [106] | Zuo Z, Liu H, Liu B, Liu X, Lin C (2011). Blue light-dep- endent interaction of CRY2 with SPA1 regulates COP1 activity and floral initiation in Arabidopsis.Curr Biol 21, 841-847. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
