

植物学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (5): 704-721.DOI: 10.11983/CBB25072 cstr: 32102.14.CBB25072
收稿日期:2025-04-22
接受日期:2025-07-01
出版日期:2025-09-10
发布日期:2025-07-07
通讯作者:
*E-mail: mianzhou@cnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xu Yufeng1,2, Zhou Mian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2025-04-22
Accepted:2025-07-01
Online:2025-09-10
Published:2025-07-07
Contact:
*E-mail: mianzhou@cnu.edu.cn
摘要: 病原体侵染严重威胁植物的正常生长发育, 是造成作物减产的主要因素之一。植物免疫系统在植物抵抗病原体侵染中发挥核心作用。自2006年提出植物免疫系统主要由模式触发的免疫(PTI)和效应子触发的免疫(ETI)两层防御体系组成以来, 大量的研究工作聚焦于解析PTI和ETI中的关键受体/共受体、PTI和ETI信号通路的组分及其作用机制、植物免疫激素水杨酸和茉莉素的合成与信号转导, 逐步形成了以病原体识别、活性氧爆发、Ca2+内流、MAPK级联信号转导及下游防御基因诱导表达为核心的复杂免疫调控网络。近年的研究表明, 植物免疫相关基因的表达不仅受到转录调控, 其mRNA的稳定性、翻译效率和翻译产物也受到多种转录后调控机制的影响, 包括可变剪接、m6A修饰、小RNA、uORF和R-motif。该文概述了植物免疫系统的组成和主要的调控通路及其组分, 详述了转录后调控对植物免疫的影响及病原体对相关调控作用的干扰机制, 梳理了转录后调控元件在作物中的应用, 为保障粮食安全、提高作物抗病性以及分子育种元件筛选提供参考。
徐羽丰, 周冕. 植物免疫的转录后调控. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 704-721.
Xu Yufeng, Zhou Mian. Post-transcriptional Regulation in Plant Immunity. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2025, 60(5): 704-721.
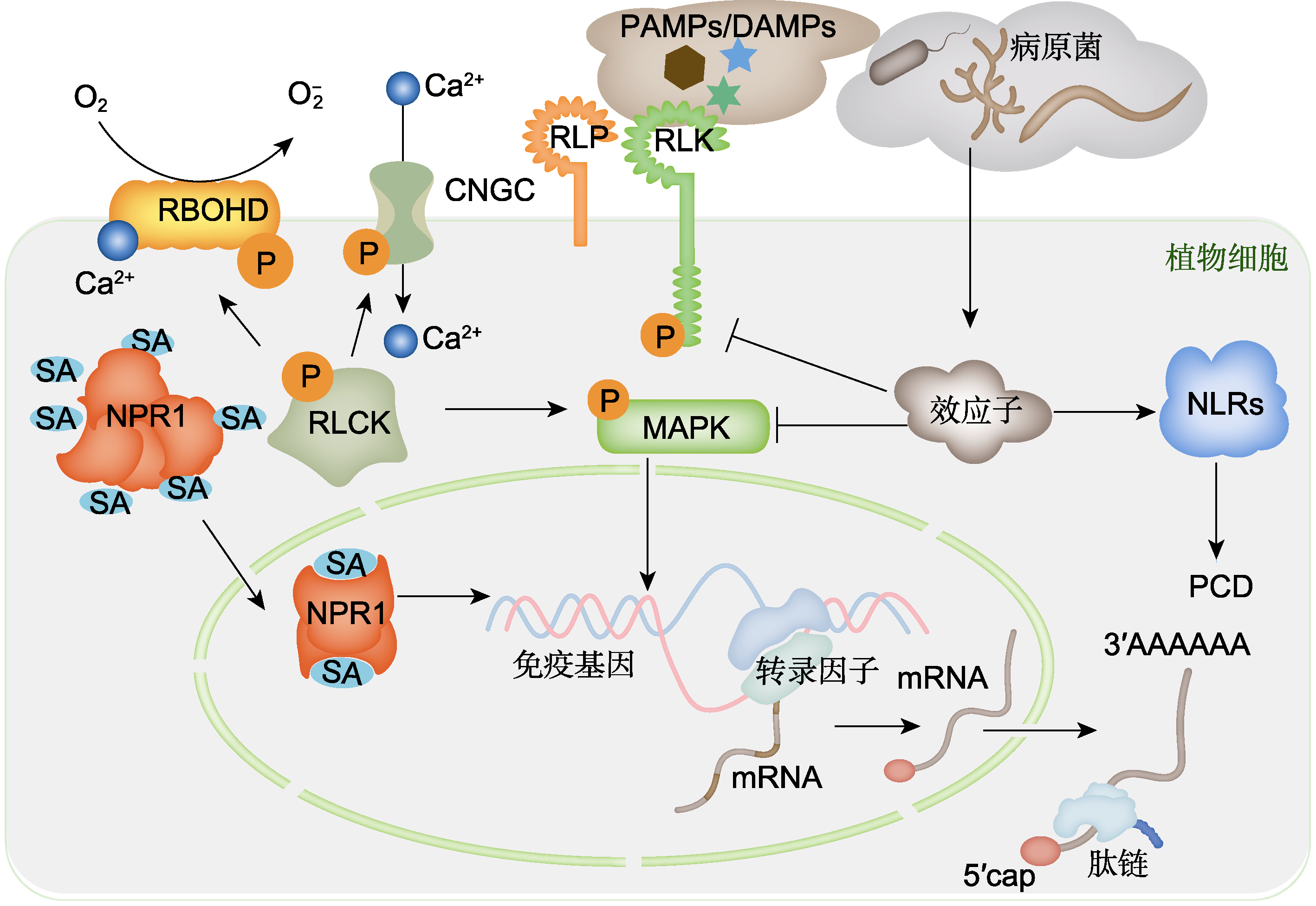
图1 植物免疫概述 植物细胞表面的PRRs识别病原菌侵染时释放的PAMPs或者产生的DAMPs后, 激活下游RLCKs, 进而激活MAPK级联激活途径, 促进免疫基因的表达。同时, RLCKs可通过其激酶活性促进ROS产生及Ca2+内流, 协同抑制病原菌侵染。病原菌可通过分泌效应子抑制PRRs及MAPK的激活。当效应子进入植物细胞后, 胞内NLR可特异性识别效应子进而诱发细胞的程序性死亡(PCD), 抑制病原菌扩散。此外, 病原菌侵染会导致水杨酸(SA)的积累, SA结合NPR1后, NPR1由多聚体形式转换为二聚体形式入核, 发挥转录共激活因子功能, 促进免疫基因的表达。PRRs: 模式识别受体; PAMPs: 病原相关分子模式; DAMPs: 损伤相关分子模式; RLCK: 受体样细胞质激酶; ROS: 活性氧; RLP: 受体样蛋白; RLK: 受体激酶; MAPK: 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶; NLR: 核苷酸结合富含亮氨酸重复序列; RBOHD: 呼吸爆发氧化酶同源蛋白D
Figure 1 Overview of plant immunity After recognition of PAMPs or DAMPs released during pathogen invasion, PRRs on plant cell surfaces activate downstream RLCKs, subsequently triggering the MAPK cascade to drive immune gene expression. Simultaneously, RLCKs enhance ROS production and Ca2+ influx through kinase activity, coordinately suppressing pathogen infection. Pathogens secrete effectors to inhibit PRRs signaling and MAPK activation. When effectors enter plant cells, intracellular NLR specifically detect these effectors, inducing Programmed Cell Death (PCD) to prevent pathogen spread. Furthermore, pathogen infection promotes salicylic acid (SA) accumulation. SA binding to NPR1 induces its transition from oligomeric to dimeric forms, enabling nuclear entry to function as a transcriptional coactivator, to potentiate the expression of immune-responsive genes. PRRs: Pattern recognition receptors; PAMPs: Pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; RLCK: Receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; RLP: Receptor-like protein; RLK: Receptor-like kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NLR: Nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat; RBOHD: Respiratory burst oxidase protein D
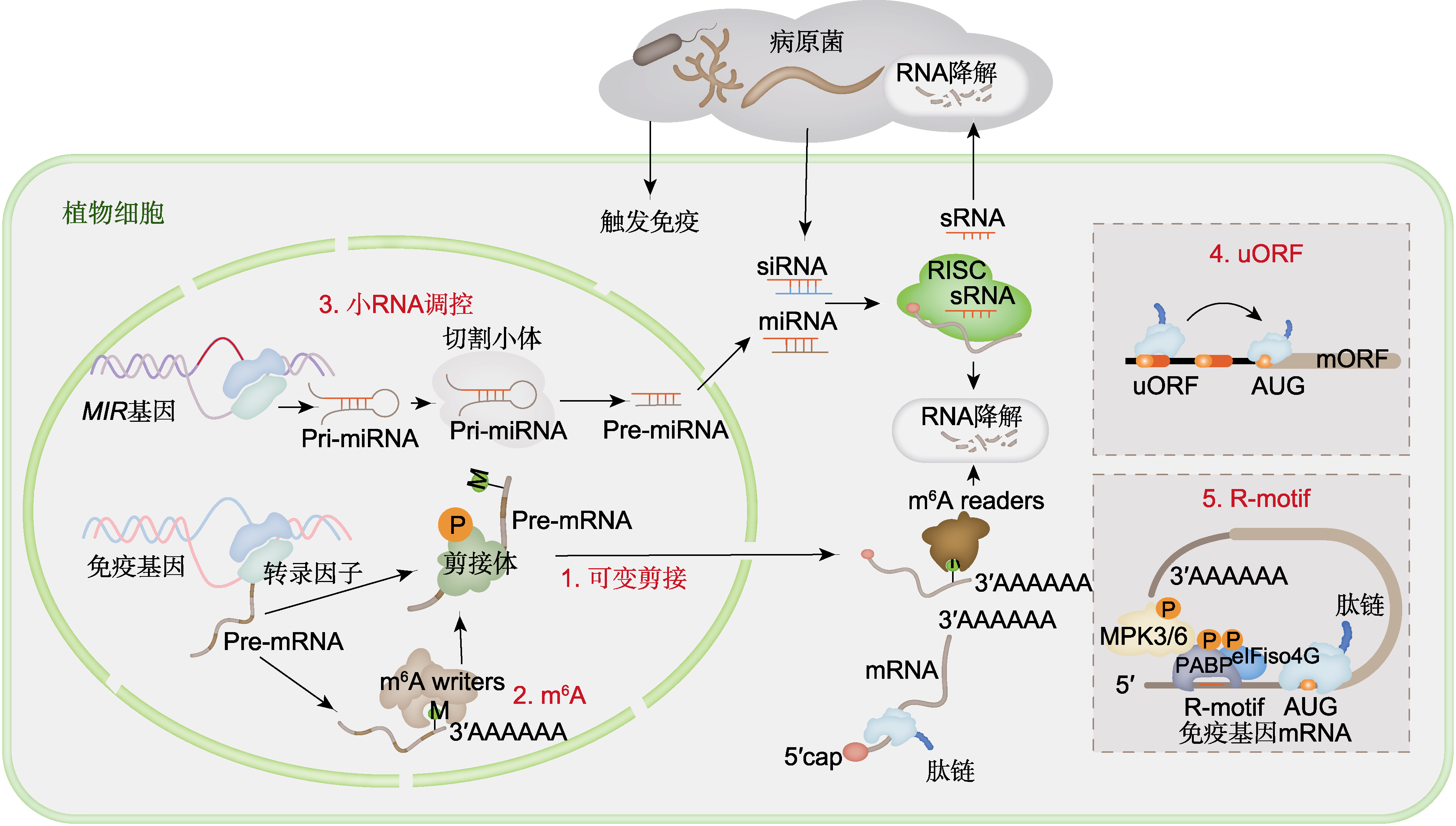
图2 植物免疫中RNA及其翻译的调控 植物免疫过程中, 剪接体组分被磷酸化促进mRNA的剪接, 此外可变剪接还可导致NLR基因转录本种类及功能多样性, 各转录本协同调控植物免疫。mRNA的腺嘌呤N6位点可发生甲基化修饰(m6A), 该修饰被特异性识别蛋白(readers)识别后调控mRNA的稳定性及核质转运, 从而参与免疫信号的精细化调控。miRNA来源于MIR基因的转录, 而siRNA来源于双链的dsRNA。二者在成熟后一条链被组装进入RISC, 另一条链降解。RISC通过与目标mRNA结合进而切割mRNA或者抑制其翻译, 部分产生的sRNA还可被运输进入病原体, 抑制病原体关键致病基因, 以抑制其侵染过程。此外, 位于mRNA 5'端的uORF通常会抑制mORF的翻译, 但是在受到胁迫时可解除uORF的翻译抑制, 启动mORF的翻译。部分免疫基因的5'端具有可作为IRES元件的R-motifs, 植物免疫激活后, R-motifs通过与PABPs结合, 替代经典通路中eIF4E的功能, 直接招募翻译起始因子启动非帽依赖翻译。此过程中, 关键调控因子PABP的磷酸化修饰可增强其与R-motifs的亲和力, 协同促进免疫蛋白的翻译。NLR: 富含亮氨酸重复序列; RISC: RNA诱导沉默复合体; uORF: 上游开放阅读框; mORF: 主开放阅读框; IRES: 内部核糖体进入位点; PABPs: 多聚腺苷酸结合蛋白; elF4E: 真核翻译起始因子4E
Figure 2 Regulation of RNA and translational control in plant immunity During plant immune responses, phosphorylation of spliceosome components enhances mRNA splicing efficiency, while alternative splicing diversifies NLR gene transcripts, enabling synergistic coordination among isoforms to regulate immunity. The m6A methylation at mRNA adenine N6 positions is recognized by reader proteins, fine-tuning immune signaling through modulating transcript stability and nucleocytoplasmic transport. miRNA originates from MIR gene transcripts, whereas siRNA derives from dsRNA. After maturation, one strand is incorporated into the RISC, while the other strand is degraded. RISC suppresses target mRNA via cleavage or translational repression. Certain sRNAs may translocate into pathogens to silence virulence genes, inhibiting infection. Moreover, uORFs at mRNA 5′ termini typically repress mORF translation, but stress conditions alleviate this inhibition to activate mORF expression. Notably, R-motifs in the 5′ regions of select immune genes function as IRES elements. Upon immune activation, R-motifs recruit translation initiation factors by interacting with PABPs, bypassing the canonical cap-dependent pathway. Phosphorylation of PABPs strengthens their binding affinity to R-motifs, synergistically boosting the translation of immune-related proteins. NLR: Nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat; RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex; uORF: Upstream open reading frames; mORF: Main open reading frame; IRES: Internal ribosome entry site; PABPs: Poly(A)- binding proteins; eIF4E: Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E
| [1] |
Aerts N, Chhillar H, Ding PT, Van Wees SCM (2022). Transcriptional regulation of plant innate immunity. Essays Biochem 66, 607-620.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Akhtar J, Lugoboni M, Junion G (2021). m6A RNA modification in transcription regulation. Transcription 12, 266-276. |
| [3] |
Anderson C, Khan MA, Catanzariti AM, Jack CA, Nemri A, Lawrence GJ, Upadhyaya NM, Hardham AR, Ellis JG, Dodds PN, Jones DA (2016). Genome analysis and avirulence gene cloning using a high-density RADseq linkage map of the flax rust fungusMelampsora lini. BMC Genomics 17, 667.
DOI PMID |
| [4] |
Axtell MJ (2013). Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64, 137-159.
DOI PMID |
| [5] | Bai YB, Liu H, Lyu HM, Su LY, Xiong JS, Cheng ZM (2022). Development of a single-cell atlas for woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca) leaves during early Botrytis cinerea infection using single-cell RNA-seq. Hortic Res 9, uhab055. |
| [6] | Bazin J, Mariappan K, Jiang YH, Blein T, Voelz R, Crespi M, Hirt H (2020). Role of MPK4 in pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered alternative splicing in Arabidopsis. PLoS Pathog 16, e1008401. |
| [7] |
Belbahri L, Boucher C, Candresse T, Nicole M, Ricci P, Keller H (2001). A local accumulation of the Ralstonia solanacearum PopA protein in transgenic tobacco renders a compatible plant-pathogen interaction incompatible. Plant J 28, 419-430.
DOI PMID |
| [8] | Bhardwaj V, Meier S, Petersen LN, Ingle RA, Roden LC (2011). Defence responses of Arabidopsis thaliana to infection by Pseudomonas syringae are regulated by the circadian clock. PLoS One 6, e26968. |
| [9] |
Bi GZ, Su M, Li N, Liang Y, Dang S, Xu JC, Hu MJ, Wang JZ, Zou MX, Deng YN, Li QY, Huang SJ, Li JJ, Chai JJ, He KM, Chen YH, Zhou JM (2021). The ZAR1 resistosome is a calcium-permeable channel triggering plant immune signaling. Cell 184, 3528-3541.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Boutrot F, Zipfel C (2017). Function, discovery, and exploitation of plant pattern recognition receptors for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 55, 257-286.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Cai Q, Qiao LL, Wang M, He BY, Lin FM, Palmquist J, Huang SD, Jin HL (2018). Plants send small RNAs in extracellular vesicles to fungal pathogen to silence virulence genes. Science 360, 1126-1129.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Champouret N, Bouwmeester K, Rietman H, van der Lee T, Maliepaard C, Heupink A, van de Vondervoort PJI, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF, van der Vossen EAG, Govers F, Vleeshouwers VGAA (2009). Phytophthora infestans isolates lacking class I ipiO variants are virulent on Rpi-blb1 potato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22, 1535-1545. |
| [13] | Chand Jha U, Nayyar H, Mantri N, Siddique KHM (2021). Non-coding RNAs in legumes: their emerging roles in regulating biotic/abiotic stress responses and plant growth and development. Cells 10, 1674. |
| [14] | Chen TY, Greene GH, Motley J, Mwimba M, Luo GZ, Xu GY, Karapetyan S, Xiang YZ, Liu C, He C, Dong XN (2024). m6A modification plays an integral role in mRNA stability and translation during pattern-triggered immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 121, e2411100121. |
| [15] |
Chinchilla D, Bauer Z, Regenass M, Boller T, Felix G (2006). The Arabidopsis receptor kinase FLS2 binds flg22 and determines the specificity of flagellin perception. Plant Cell 18, 465-476.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Cui FH, Wu SJ, Sun WX, Coaker G, Kunkel B, He P, Shan LB (2013). The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector AvrRpt2 promotes pathogen virulence via stimulating Arabidopsis auxin/indole acetic acid protein turnover. Plant Physiol 162, 1018-1029. |
| [17] | de la Fuente van Bentem S, Anrather D, Roitinger E, Djamei A, Hufnagl T, Barta A, Csaszar E, Dohnal I, Lecourieux D, Hirt H (2006). Phosphoproteomics reveals extensive in vivo phosphorylation of Arabidopsis proteins involved in RNA metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res 34, 3267-3278. |
| [18] | Després C, Chubak C, Rochon A, Clark R, Bethune T, Desveaux D, Fobert PR (2003). The Arabidopsis NPR1 disease resistance protein is a novel cofactor that confers redox regulation of DNA binding activity to the basic domain/leucine zipper transcription factor TGA1. Plant Cell 15, 2181-2191. |
| [19] |
Després C, DeLong C, Glaze S, Liu EW, Fobert PR (2000). The Arabidopsis NPR1/NIM1 protein enhances the DNA binding activity of a subgroup of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors. Plant Cell 12, 279-290.
PMID |
| [20] |
Dinesh-Kumar SP, Baker BJ (2000). Alternatively spliced N resistance gene transcripts: their possible role in tobacco mosaic virus resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97, 1908-1913.
DOI PMID |
| [21] | Duan HC, Wang Y, Jia GF (2019). Dynamic and reversible RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 10, e1507. |
| [22] | Duan HC, Wei LH, Zhang C, Wang Y, Chen L, Lu ZK, Chen PR, He C, Jia GF (2017). ALKBH10B is an RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase affecting Arabidopsis floral transition. Plant Cell 29, 2995-3011. |
| [23] |
Echevarría-Zomeño S, Yángüez E, Fernández-Bautista N, Castro-Sanz AB, Ferrando A, Castellano MM (2013). Regulation of translation initiation under biotic and abiotic stresses. Int J Mol Sci 14, 4670-4683.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
Ellis J, Dodds P, Pryor T (2000). Structure, function and evolution of plant disease resistance genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3, 278-284.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Filichkin SA, Priest HD, Givan SA, Shen RK, Bryant DW, Fox SE, Wong WK, Mockler TC (2010). Genome-wide mapping of alternative splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 20, 45-58.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Förderer A, Li ET, Lawson AW, Deng YN, Sun Y, Logemann E, Zhang XX, Wen J, Han ZF, Chang JB, Chen YH, Schulze-Lefert P, Chai JJ (2022). A wheat resistosome defines common principles of immune receptor channels. Nature 610, 532-539. |
| [27] | Fu ZQ, Guo M, Jeong BR, Tian F, Elthon TE, Cerny RL, Staiger D, Alfano JR (2007). A type III effector ADP-ribosylates RNA-binding proteins and quells plant immunity. Nature 447, 284-288. |
| [28] |
Gimenez-Ibanez S, Hann DR, Ntoukakis V, Petutschnig E, Lipka V, Rathjen JP (2009). AvrPtoB targets the LysM receptor kinase CERK1 to promote bacterial virulence on plants. Curr Biol 19, 423-429.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Göhre V, Spallek T, Häweker H, Mersmann S, Mentzel T, Boller T, de Torres M, Mansfield JW, Robatzek S (2008). Plant pattern-recognition receptor FLS2 is directed for degradation by the bacterial ubiquitin ligase AvrPtoB. Curr Biol 18, 1824-1832.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Goss EM, Tabima JF, Cooke DEL, Restrepo S, Fry WE, Forbes GA, Fieland VJ, Cardenas M, Grünwald NJ (2014). The Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans originated in central Mexico rather than the An-des. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 8791-8796. |
| [31] | Govindan G, Sharma B, Li YF, Armstrong CD, Merum P, Rohila JS, Gregory BD, Sunkar R (2022). mRNA N6- methyladenosine is critical for cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 111, 1052-1068. |
| [32] |
Heese A, Hann DR, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Jones AME, He K, Li J, Schroeder JI, Peck SC, Rathjen JP (2007). The receptor-like kinase SERK3/BAK1 is a central regulator of innate immunity in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 12217-12222.
DOI PMID |
| [33] |
Hinnebusch AG, Ivanov IP, Sonenberg N (2016). Translational control by 5'-untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 352, 1413-1416.
DOI PMID |
| [34] |
Hou SG, Liu ZY, Shen HX, Wu DJ (2019). Damage-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in plants. Front Plant Sci 10, 646.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Huang CY, Wang H, Hu P, Hamby R, Jin HL (2019). Small RNAs—big players in plant-microbe interactions. Cell Host Microbe 26, 173-182. |
| [36] |
Huang J, Lu XY, Wu HW, Xie YC, Peng Q, Gu LF, Wu JY, Wang YC, Reddy ASN, Dong SM (2020). Phytophthora effectors modulate genome-wide alternative splicing of host mRNAs to reprogram plant immunity. Mol Plant 13, 1470-1484.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Huot B, Yao J, Montgomery BL, He SY (2014). Growth-defense tradeoffs in plants: a balancing act to optimize fitness. Mol Plant 7, 1267-1287.
DOI PMID |
| [38] | Iizasa E, Mitsutomi M, Nagano Y (2010). Direct binding of a plant LysM receptor-like kinase, LysM RLK1/CERK1, to chitin in vitro. J Biol Chem 285, 2996-3004. |
| [39] |
Jones JDG, Staskawicz BJ, Dangl JL (2024). The plant immune system: from discovery to deployment. Cell 187, 2095-2116.
DOI PMID |
| [40] | Juntawong P, Girke T, Bazin J, Bailey-Serres J (2014). Translational dynamics revealed by genome-wide profiling of ribosome footprints in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, E203-E212. |
| [41] |
Kadota Y, Shirasu K, Zipfel C (2015). Regulation of the NADPH oxidase RBOHD during plant immunity. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 1472-1480.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Katiyar-Agarwal S, Morgan R, Dahlbeck D, Borsani O, Villegas Jr A, Zhu JK, Staskawicz BJ, Jin HL (2006). A pathogen-inducible endogenous siRNA in plant immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 18002-18007.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
Kazan K, Manners JM (2013). MYC2: the master in action. Mol Plant 6, 686-703.
DOI PMID |
| [44] | Kim SH, Kwon SI, Saha D, Anyanwu NC, Gassmann W (2009). Resistance to the Pseudomonas syringae effector HopA1 is governed by the TIR-NBS-LRR protein RPS6 and is enhanced by mutations in SRFR1. Plant Physiol 150, 1723-1732. |
| [45] | Kufel J, Diachenko N, Golisz A (2022). Alternative splicing as a key player in the fine-tuning of the immunity response in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant Pathol 23, 1226-1238. |
| [46] | Kumar S, Zavaliev R, Wu QL, Zhou Y, Cheng J, Dillard L, Powers J, Withers J, Zhao JS, Guan ZQ, Borgnia MJ, Bartesaghi A, Dong XN, Zhou P (2022). Structural basis of NPR1 in activating plant immunity. Nature 605, 561-566. |
| [47] | Lee KP, Liu KW, Kim EY, Medina-Puche L, Dong HH, Di MH, Singh RM, Li MP, Qi S, Meng ZL, Cho J, Zhang H, Lozano-Duran R, Kim C (2024). The m6A reader ECT1 drives mRNA sequestration to dampen salicylic acid-dependent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 36, 746-763. |
| [48] | Li HP, Li YF, Nie YF (2019). Research status of occurrence and control of Fusarium wilt banana. Hua Nan Nong Ye Da Xue Xue Bao 40(5), 128-136. (in Chinese) |
| 李华平, 李云锋, 聂燕芳 (2019). 香蕉枯萎病的发生及防控研究现状. 华南农业大学学报 40(5), 128-136. | |
| [49] | Li Y, Cao XL, Zhu Y, Yang XM, Zhang KN, Xiao ZY, Wang H, Zhao JH, Zhang LL, Li GB, Zheng YP, Fan J, Wang J, Chen XQ, Wu XJ, Zhao JQ, Dong OX, Chen XW, Chern M, Wang WM (2019). Osa-miR398b boosts H2O2 production and rice blast disease-resistance via multiple superoxide dismutases. New Phytol 222, 1507-1522. |
| [50] |
Li Y, Zhang QQ, Zhang JG, Wu L, Qi YJ, Zhou JM (2010). Identification of microRNAs involved in pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered plant innate immunity. Plant Physiol 152, 2222-2231.
DOI PMID |
| [51] | Li YJ, Chen JP, Sun ZT (2025). N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification: emerging regulators in plant-virus interactions. Virology 603, 110373. |
| [52] |
Liebrand TWH, van den Berg GCM, Zhang Z, Smit P, Cordewener JHG, America AHP, Sklenar J, Jones AME, Tameling WIL, Robatzek S, Thomma BPHJ, Joosten MHAJ (2013). Receptor-like kinase SOBIR1/EVR interacts with receptor-like proteins in plant immunity against fungal infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 10010-10015.
DOI PMID |
| [53] | Lin WW, Li B, Lu DP, Chen SX, Zhu N, He P, Shan LB (2014). Tyrosine phosphorylation of protein kinase complex BAK1/BIK1 mediates Arabidopsis innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 3632-3637. |
| [54] | Liu Q, Fang LM, Wu CJ (2022). Alternative splicing and isoforms: from mechanisms to diseases. Genes 13, 401. |
| [55] |
Lorenzo O, Chico JM, Sánchez-Serrano JJ, Solano R (2004). JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 1938-1950.
DOI PMID |
| [56] | Luo S, Tetteh C, Song ZQ, Zhang C, Jin PY, Hao XQ, Liu YJ, Ge ST, Chen J, Ye KK, Wang K, Zhang T, Zhang HJ (2025). Positive regulation of BBX11 by NAC053 confers stomatal and apoplastic immunity against bacterial infection in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 246, 1816-1833. |
| [57] | Ma SC, Lapin D, Liu L, Sun Y, Song W, Zhang XX, Logemann E, Yu DL, Wang J, Jirschitzka J, Han ZF, Schulze-Lefert P, Parker JE, Chai J (2020). Direct pathogen-induced assembly of an NLR immune receptor complex to form a holoenzyme. Science 370, eabe3069. |
| [58] | Mao GH, Meng XZ, Liu YD, Zheng ZY, Chen ZX, Zhang SQ (2011). Phosphorylation of a WRKY transcription factor by two pathogen-responsive MAPKs drives phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 23, 1639-1653. |
| [59] |
Marquez Y, Brown JWS, Simpson C, Barta A, Kalyna M (2012). Transcriptome survey reveals increased complexity of the alternative splicing landscape in Arabidopsis. Genome Res 22, 1184-1195.
DOI PMID |
| [60] |
Masachis S, Segorbe D, Turrà D, Leon-Ruiz M, Fürst U, El Ghalid M, Leonard G, López-Berges MS, Richards TA, Felix G, Di Pietro A (2016). A fungal pathogen secretes plant alkalinizing peptides to increase infection. Nat Microbiol 1, 16043.
DOI PMID |
| [61] |
McCombe CL, Catanzariti AM, Greenwood JR, Desai AM, Outram MA, Yu DS, Ericsson DJ, Brenner SE, Dodds PN, Kobe B, Jones DA, Williams SJ (2023). A rust-fungus nudix hydrolase effector decaps mRNA in vitro and interferes with plant immune pathways. New Phytol 239, 222-239.
DOI PMID |
| [62] |
McCook S, Vandermeer J (2015). The big rust and the red queen: long-term perspectives on coffee rust research. Phytopathology 105, 1164-1173.
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
Meyers BC, Morgante M, Michelmore RW (2002). TIR-X and TIR-NBS proteins: two new families related to disease resistance TIR-NBS-LRR proteins encoded in Arabidopsis and other plant genomes. Plant J 32, 77-92.
DOI PMID |
| [64] | Mou R, Niu RX, Yang RY, Xu GY (2025). Engineering crop performance with upstream open reading frames. Trends Plant Sci 30, 311-323. |
| [65] | Nadarajah KK, Abdul Rahman NSN (2022). The role of non-coding RNA in rice immunity. Agronomy 12, 39. |
| [66] |
Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones JDG (2006). A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 312, 436-439.
DOI PMID |
| [67] | Ngou BPM, Ahn HK, Ding PT, Jones JDG (2021). Mutual potentiation of plant immunity by cell-surface and intracellular receptors. Nature 592, 110-115. |
| [68] | Nicaise V, Joe A, Jeong BR, Korneli C, Boutrot F, Westedt I, Staiger D, Alfano JR, Zipfel C (2013). Pseudomonas HopU1 modulates plant immune receptor levels by blocking the interaction of their mRNAs with GRP7. EMBO J 32, 701-712. |
| [69] | Niu RX, Zhou YL, Zhang Y, Mou R, Tang ZJ, Wang Z, Zhou GL, Guo SB, Yuan M, Xu GY (2020). uORFlight: a vehicle toward uORF-mediated translational regulation mechanisms in eukaryotes. Database. (Oxford) 2020, baaa007. |
| [70] | Nobori T, Monell A, Lee TA, Sakata Y, Shirahama S, Zhou JT, Nery JR, Mine A, Ecker JR (2025). A rare PRIMER cell state in plant immunity. Nature 638, 197-205. |
| [71] | Nowara D, Gay A, Lacomme C, Shaw J, Ridout C, Douchkov D, Hensel G, Kumlehn J, Schweizer P (2010). HIGS: host-induced gene silencing in the obligate biotrophic fungal pathogen Blumeria graminis. Plant Cell 22, 3130-3141. |
| [72] |
Pajerowska-Mukhtar KM, Wang W, Tada Y, Oka N, Tucker CL, Fonseca JP, Dong XN (2012). The HSF-like transcription factor TBF1 is a major molecular switch for plant growth-to-defense transition. Curr Biol 22, 103-112.
DOI PMID |
| [73] | Panwar V, McCallum B, Bakkeren G (2013). Endogenous silencing of Puccinia triticina pathogenicity genes through in planta-expressed sequences leads to the suppression of rust diseases on wheat. Plant J 73, 521-532. |
| [74] |
Parker JE, Coleman MJ, Szabò V, Frost LN, Schmidt R, van der Biezen EA, Moores T, Dean C, Daniels MJ, Jones JD (1997). The Arabidopsis downy mildew resis-tance gene RPP5 shares similarity to the toll and interleukin-1 receptors with N and L6. Plant Cell 9, 879-894.
DOI PMID |
| [75] | Parker MT, Knop K, Sherwood AV, Schurch NJ, Mackinnon K, Gould PD, Hall AJW, Barton GJ, Simpson GG (2020). Nanopore direct RNA sequencing maps the complexity of Arabidopsis mRNA processing and m6A modification. eLife 9, e49658 |
| [76] | Prall W, Sheikh AH, Bazin J, Bigeard J, Almeida-Trapp M, Crespi M, Hirt H, Gregory BD (2023). Pathogen-induced m6A dynamics affect plant immunity. Plant Cell 35, 4155-4172. |
| [77] |
Pré M, Atallah M, Champion A, De Vos M, Pieterse CMJ, Memelink J (2008). The AP2/ERF domain transcription factor ORA59 integrates jasmonic acid and ethylene signals in plant defense. Plant Physiol 147, 1347-1357.
DOI PMID |
| [78] |
Qi JS, Wang JL, Gong ZZ, Zhou JM (2017). Apoplastic ROS signaling in plant immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 38, 92-100.
DOI PMID |
| [79] | Qi YX, Xie YX, Zhang X (2023). Progress on banana Fusarium wilt pathogen and resistance breeding. Mol Plant Breed 1-17. (in Chinese) |
| 漆艳香, 谢艺贤, 张欣 (2023). 香蕉枯萎病病原菌及其抗病育种进展. 分子植物育种 1-17. | |
| [80] |
Qiao YL, Shi JX, Zhai Y, Hou YN, Ma WB (2015). Phytophthora effector targets a novel component of small RNA pathway in plants to promote infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 5850-5855.
DOI PMID |
| [81] |
Qiao YL, Xia R, Zhai JX, Hou YN, Feng L, Zhai Y, Ma WB (2021). Small RNAs in plant immunity and virulence of filamentous pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 59, 265-288.
DOI PMID |
| [82] | Quilis J, Peñas G, Messeguer J, Brugidou C, Segundo BS (2008). The Arabidopsis AtNPR1 inversely modulates defense responses against fungal, bacterial, or viral pathogens while conferring hypersensitivity to abiotic stresses in transgenic rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21, 1215-1231. |
| [83] | Razumova E, Makariuk A, Dontsova O, Shepelev N, Rubtsova M (2025). Structural features of 5′ untranslated region in translational control of eukaryotes. Int J Mol Sci 26, 1979. |
| [84] |
Reddy ASN (2007). Alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNAs in plants in the genomic era. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58, 267-294.
PMID |
| [85] |
Roberts L, Wieden HJ (2018). Viruses, IRESs, and a universal translation initiation mechanism. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 34, 60-75.
DOI PMID |
| [86] | Rogers K, Chen XM (2013). Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 25, 2383-2399. |
| [87] | Shan LB, He P, Li JM, Heese A, Peck SC, Nürnberger T, Martin GB, Sheen J (2008). Bacterial effectors target the common signaling partner BAK1 to disrupt multiple MAMP receptor-signaling complexes and impede plant immunity. Cell Host Microbe 4, 17-27. |
| [88] | Song PZ, Wei LH, Chen ZX, Cai ZH, Lu Q, Wang CL, Tian EL, Jia GF (2023). m6A readers ECT2/ECT3/ECT4 enhance mRNA stability through direct recruitment of the poly(A) binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 24, 103. |
| [89] | Song W, Liu L, Yu DL, Bernardy H, Jirschitzka J, Huang SJ, Jia AL, Jemielniak W, Acker J, Laessle H, Wang JL, Shen QC, Chen WJ, Li PL, Parker JE, Han ZF, Schulze-Lefert P, Chai JJ (2024). Substrate-induced condensation activates plant TIR domain proteins. Nature 627, 847-853. |
| [90] | Sun BY, Huang J, Kong L, Gao CY, Zhao F, Shen JY, Wang T, Li KP, Wang LY, Wang YC, Halterman DA, Dong SM (2024). Alternative splicing of a potato disease resistance gene maintains homeostasis between growth and immunity. Plant Cell 36, 3729-3750. |
| [91] | Sun YD, Li L, Macho AP, Han ZF, Hu ZH, Zipfel C, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2013). Structural basis for flg22-induced activation of the Arabidopsis FLS2-BAK1 immune complex. Science 342, 624-628. |
| [92] | Tanaka M, Yokoyama T, Saito H, Nishimoto M, Tsuda K, Sotta N, Shigematsu H, Shirouzu M, Iwasaki S, Ito T, Fujiwara T (2024). Boric acid intercepts 80S ribosome migration from AUG-stop by stabilizing eRF1. Nat Chem Biol 20, 605-614. |
| [93] | Tang BZ, Feng L, Hulin MT, Ding PT, Ma WB (2023a). Cell-type-specific responses to fungal infection in plants revealed by single-cell transcriptomics. Cell Host Microbe 31, 1732-1747. |
| [94] | Tang J, Chen SY, Jia GF (2023b). Detection, regulation, and functions of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in plants. Plant Commun 4, 100546. |
| [95] | Tian W, Hou CC, Ren ZJ, Wang C, Zhao FG, Dahlbeck D, Hu SP, Zhang LY, Niu Q, Li LG, Staskawicz BJ, Luan S (2019). A calmodulin-gated calcium channel links pathogen patterns to plant immunity. Nature 572, 131-135. |
| [96] | Toruño TY, Shen MZ, Coaker G, Mackey D (2019). Regulated disorder: posttranslational modifications control the RIN4 plant immune signaling hub. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 32, 56-64. |
| [97] |
van der Hoorn RAL, Kamoun S (2008). From guard to decoy: a new model for perception of plant pathogen effectors. Plant Cell 20, 2009-2017.
DOI PMID |
| [98] |
von Arnim AG, Jia QD, Vaughn JN (2014). Regulation of plant translation by upstream open reading frames. Plant Sci 214, 1-12.
DOI PMID |
| [99] | Wang B, Sun YF, Song N, Zhao MX, Liu R, Feng H, Wang XJ, Kang ZS (2017). Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici microRNA-like RNA 1 (Pst-milR1), an important pathogenicity factor of Pst, impairs wheat resistance to Pst by suppressing the wheat pathogenesis-related 2 gene. New Phytol 215, 338-350. |
| [100] |
Wang D, Weaver ND, Kesarwani M, Dong XN (2005). Induction of protein secretory pathway is required for systemic acquired resistance. Science 308, 1036-1040.
PMID |
| [101] | Wang GX, Roux B, Feng F, Guy E, Li L, Li NN, Zhang XJ, Lautier M, Jardinaud MF, Chabannes M, Arlat M, Chen S, He CZ, Noël LD, Zhou JM (2015a). The decoy substrate of a pathogen effector and a pseudokinase specify pathogen-induced modified-self recognition and immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 18, 285-295. |
| [102] | Wang JE, Liu JH, Guo ZL (2024). Natural uORF variation in plants. Trends Plant Sci 29, 290-302. |
| [103] |
Wang JL, Zhang X, Greene GH, Xu GY, Dong XN (2022). PABP/purine-rich motif as an initiation module for cap-independent translation in pattern-triggered immunity. Cell 185, 3186-3200.
DOI PMID |
| [104] | Wang JZ, Hu MJ, Wang J, Qi JF, Han ZF, Wang GX, Qi YJ, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019a). Reconstitution and structure of a plant NLR resistosome conferring immunity. Science 364, eaav5870. |
| [105] | Wang JZ, Wang J, Hu MJ, Wu S, Qi JF, Wang GX, Han ZF, Qi YJ, Gao N, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019b). Ligand-triggered allosteric ADP release primes a plant NLR complex. Science 364, eaav5868. |
| [106] | Wang L, Yang T, Wang BQ, Lin QL, Zhu SR, Li CY, Ma YC, Tang J, Xing JJ, Li XS, Liao HD, Staiger D, Hu ZQ, Yu F (2020). RALF1-FERONIA complex affects splicing dynamics to modulate stress responses and growth in plants. Sci Adv 6, eaaz1622. |
| [107] | Wang W, Tang DZ (2021). Synergistic cooperation between cell surface and intracellular immune receptors potentiates to activate robust plant defense. Chin Bull Bot 56, 142-146. (in Chinese) |
| 王伟, 唐定中 (2021). 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线. 植物学报 56, 142-146. | |
| [108] | Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu ZK, Han DL, Ma HH, Weng XC, Chen K, Shi HL, He C (2015b). N6-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 161, 1388-1399. |
| [109] | Wang XY, Gao J, Zhu Z, Dong XX, Wang XL, Ren GD, Zhou X, Kuai BK (2015c). TCP transcription factors are critical for the coordinated regulation of ISOCHORISMATE SYNTHASE 1 expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 82, 151-162. |
| [110] | Wei LH, Song PZ, Wang Y, Lu ZK, Tang Q, Yu Q, Xiao Y, Zhang X, Duan HC, Jia GF (2018). The m6A reader ECT2 controls trichome morphology by affecting mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 30, 968-985. |
| [111] |
Weiberg A, Wang M, Lin FM, Zhao HW, Zhang ZH, Kaloshian I, Huang HD, Jin HL (2013). Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science 342, 118-123.
DOI PMID |
| [112] | Xiang TT, Zong N, Zou Y, Wu Y, Zhang J, Xing WM, Li Y, Tang XY, Zhu LH, Chai JJ, Zhou JM (2008). Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPto blocks innate immunity by targeting receptor kinases. Curr Biol 18, 74-80. |
| [113] | Xiang YZ, Huang WZ, Tan LM, Chen TY, He Y, Irving PS, Weeks KM, Zhang QC, Dong XN (2023). Pervasive downstream RNA hairpins dynamically dictate start-codon selection. Nature 621, 423-430. |
| [114] | Xu GY, Greene GH, Yoo H, Liu LJ, Marqués J, Motley J, Dong XN (2017b). Global translational reprogramming is a fundamental layer of immune regulation in plants. Nature 545, 487-490. |
| [115] | Xu GY, Moeder W, Yoshioka K, Shan LB (2022). A tale of many families: calcium channels in plant immunity. Plant Cell 34, 1551-1567. |
| [116] | Xu GY, Yuan M, Ai CR, Liu LJ, Zhuang E, Karapetyan S, Wang SP, Dong XN (2017a). uORF-mediated translation allows engineered plant disease resistance without fitness costs. Nature 545, 491-494. |
| [117] |
Yamashita Y, Takamatsu S, Glasbrenner M, Becker T, Naito S, Beckmann R (2017). Sucrose sensing through nascent peptide-meditated ribosome stalling at the stop codon of Arabidopsis bZIP11 uORF2. FEBS Lett 591, 1266-1277.
DOI PMID |
| [118] |
Yan SP, Dong XN (2014). Perception of the plant immune signal salicylic acid. Curr Opin Plant Biol 20, 64-68.
DOI PMID |
| [119] | Yang CHZ, Tang XY, Li W, Xia ST (2020). NLR and its regulation on plant disease resistance. Chin Bull Bot 55, 497-504. (in Chinese) |
| 杨程惠子, 唐先宇, 李威, 夏石头 (2020). NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用. 植物学报 55, 497-504. | |
| [120] |
Yang SM, Tang F, Zhu HY (2014). Alternative splicing in plant immunity. Int J Mol Sci 15, 10424-10445.
DOI PMID |
| [121] | Yin LY, Huang Z, Zhou YM, Lu MY, Zhu LX, Di RL, Duan Z, Bao YX, Hu Q, Powell CA, Chen BS, Zhang JS, Zhang MQ, Yao W (2025). Enhanced resistance to Pokkah boeng disease in sugarcane through host-induced gene silencing targeting FsCYP51 in Fusarium sacchari. Plant Cell Environ 48, 3861-3874. |
| [122] | Yu XY, Lin XX, Zhou TT, Cao LF, Hu KX, Li FZ, Qu SC (2024). Host-induced gene silencing in wild apple germ-plasm Malus hupehensis confers resistance to the fungal pathogen Botryosphaeria dothidea. Plant J 118, 1174-1193. |
| [123] | Yuan MH, Jiang ZY, Bi GZ, Nomura K, Liu MH, Wang YP, Cai BY, Zhou JM, He SY, Xin XF (2021). Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 592, 105-109. |
| [124] |
Zavaliev R, Dong XN (2024). NPR1, a key immune regulator for plant survival under biotic and abiotic stresses. Mol Cell 84, 131-141.
DOI PMID |
| [125] | Zhang C, Xie QG, Anderson RG, Ng G, Seitz NC, Peterson T, McClung CR, McDowell JM, Kong DD, Kwak JM, Lu H (2013). Crosstalk between the circadian clock and innate immunity in Arabidopsis. PLoS Pathog 9, e1003370. |
| [126] |
Zhang J, Coaker G, Zhou JM, Dong XN (2020). Plant immune mechanisms: from reductionistic to holistic points of view. Mol Plant 13, 1358-1378.
DOI PMID |
| [127] |
Zhang J, Shao F, Li Y, Cui HT, Chen LJ, Li HT, Zou Y, Long CZ, Lan LF, Chai JJ, Chen S, Tang XY, Zhou JM (2007). A Pseudomonas syringae effector inactivates MAPKs to suppress PAMP-induced immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 1, 175-185.
DOI PMID |
| [128] | Zhang XM, Xia J, Lii YE, Barrera-Figueroa BE, Zhou XF, Gao S, Lu L, Niu DD, Chen Z, Leung C, Wong T, Zhang HM, Guo JH, Li Y, Liu RY, Liang WQ, Zhu JK, Zhang WX, Jin HL (2012). Genome-wide analysis of plant nat-siRNAs reveals insights into their distribution, biogenesis and function. Genome Biol 13, R20. |
| [129] | Zhang XM, Zhao HW, Gao S, Wang WC, Katiyar-Agarwal S, Huang HD, Raikhel N, Jin HL (2011). Arabidopsis Argonaute 2 regulates innate immunity via miRNA393*- mediated silencing of a Golgi-localized SNARE gene, MEMB12. Mol Cell 42, 356-366. |
| [130] | Zhang YL, Tessaro MJ, Lassner M, Li X (2003). Knockout analysis of Arabidopsis transcription factors TGA2, TGA5, and TGA6 reveals their redundant and essential roles in systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 15, 2647-2653. |
| [131] |
Zhang YX, Xu SH, Ding PT, Wang DM, Cheng YT, He J, Gao MH, Xu F, Li Y, Zhu ZH, Li X, Zhang YL (2010). Control of salicylic acid synthesis and systemic acquired resistance by two members of a plant-specific family of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 18220-18225.
DOI PMID |
| [132] |
Zhao X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Shi Y, Yang X, Xiao W, Hao YJ, Ping XL, Chen YS, Wang WJ, Jin KX, Wang X, Huang CM, Fu Y, Ge XM, Song SH, Jeong HS, Yanagisawa H, Niu YM, Jia GF, Wu W, Tong WM, Okamoto A, He C, Danielsen JMR, Wang XJ, Yang YG (2014). FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res 24, 1403-1419.
DOI PMID |
| [133] | Zheng XY, Spivey NW, Zeng WQ, Liu PP, Fu ZQ, Klessig DF, He SY, Dong XN (2012). Coronatine promotes Pseudomonas syringae virulence in plants by activating a signaling cascade that inhibits salicylic acid accumulation. Cell Host Microbe 11, 587-596. |
| [134] | Zheng XY, Zhou M, Yoo H, Pruneda-Paz JL, Spivey NW, Kay SA, Dong XN (2015). Spatial and temporal regulation of biosynthesis of the plant immune signal salicylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 9166-9173. |
| [135] | Zhou M (2022). Molecular interplay between the circadian clock and the plant immunity. Plant Physiol J 58, 21-32. (in Chinese) |
| 周冕 (2022). 生物钟与植物免疫互作的研究进展. 植物生理学报 58, 21-32. | |
| [136] |
Zhou YL, Niu RX, Tang ZJ, Mou R, Wang Z, Zhu ST, Yang HC, Ding PT, Xu GY (2023). Plant HEM1 specifies a condensation domain to control immune gene translation. Nat Plants 9, 289-301.
DOI PMID |
| [137] | Zhu ST, Yuan S, Niu RX, Zhou YL, Wang Z, Xu GY (2024). RNAirport: a deep neural network-based database characterizing representative gene models in plants. J Genet Genomics 51, 652-664. |
| [138] | Zhu ZM, Huo FC, Zhang J, Shan HJ, Pei DS (2023). Crosstalk between m6A modification and alternative splicing during cancer progression. Clin Transl Med 13, e1460. |
| [139] |
Zipfel C, Kunze G, Chinchilla D, Caniard A, Jones JDG, Boller T, Felix G (2006). Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 125, 749-760.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 江亚楠, 徐雨青, 魏毅铤, 陈钧, 张容菀, 赵蓓蓓, 林宇翔, 饶玉春. 水稻抗病调控机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 734-748. |
| [2] | 肖银燕, 于华, 万里. 植物免疫研究: 机制突破和应用创新[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 693-703. |
| [3] | 刘德水, 岳宁, 刘玉乐. 植物免疫机制新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 669-678. |
| [4] | 王笑, 徐昌文, 钱虹萍, 李思博, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 植物细胞壁参与免疫反应的机制及其原位非标记成像方法[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(5): 773-785. |
| [5] | 熊良林, 梁国鲁, 郭启高, 景丹龙. 基因可变剪接调控植物响应非生物胁迫研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 435-448. |
| [6] | 路笃贤, 张严妍, 刘艳, 李岩竣, 左新秀, 林金星, 崔亚宁. 非编码RNA在植物生长发育及逆境响应中的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 709-725. |
| [7] | 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头. 植物NLR免疫受体的识别、免疫激活与信号调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 12-23. |
| [8] | 周俭民. 免疫信号轴揭示水稻与病原菌斗争的秘密[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [9] | 胡滨滨, 薛治慧, 张翠. 植物小RNA荧光原位杂交实验方法[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 330-338. |
| [10] | 王伟, 唐定中. 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [11] | 宋凝曦, 谢寅峰, 李霞. 干旱胁迫下表观遗传机制对转C4型PEPC基因水稻种子萌发的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(6): 677-692. |
| [12] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [13] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [14] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [15] | 夏石头, 李昕. 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 288-292. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||