

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (3): 288-292.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19035 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19035
所属专题: 逆境生物学专辑 (2019年54卷2期)
收稿日期:2019-02-23
接受日期:2019-04-03
出版日期:2019-05-01
发布日期:2019-05-20
通讯作者:
夏石头,李昕
Received:2019-02-23
Accepted:2019-04-03
Online:2019-05-01
Published:2019-05-20
Contact:
Shitou Xia,Xin Li
摘要: NLR蛋白是存在于植物和动物中的一个免疫受体大家族, 具有核苷酸结合域并富含亮氨酸重复序列。植物NLR通过识别病原菌特异效应子开启免疫信号转导。第1个植物NLR抗性蛋白于25年前克隆, 但其激活机制仍不清楚, 至今仍未获得一个完整的NLR蛋白结构。最近, 柴继杰、周俭民和王宏伟实验室合作解析了第一个植物完整NLR ZAR1激活前后的结构, 研究成果以两篇论文形式发表在“科学”杂志上, 填补了NLR介导的免疫信号转导研究领域的空白。该文简要总结了相关研究进展, 讨论了NLR免疫信号转导研究领域尚需解决的问题。
夏石头, 李昕. 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 288-292.
Shitou Xia, Xin Li. Open a Door of Defenses: Plant Resistosome. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(3): 288-292.
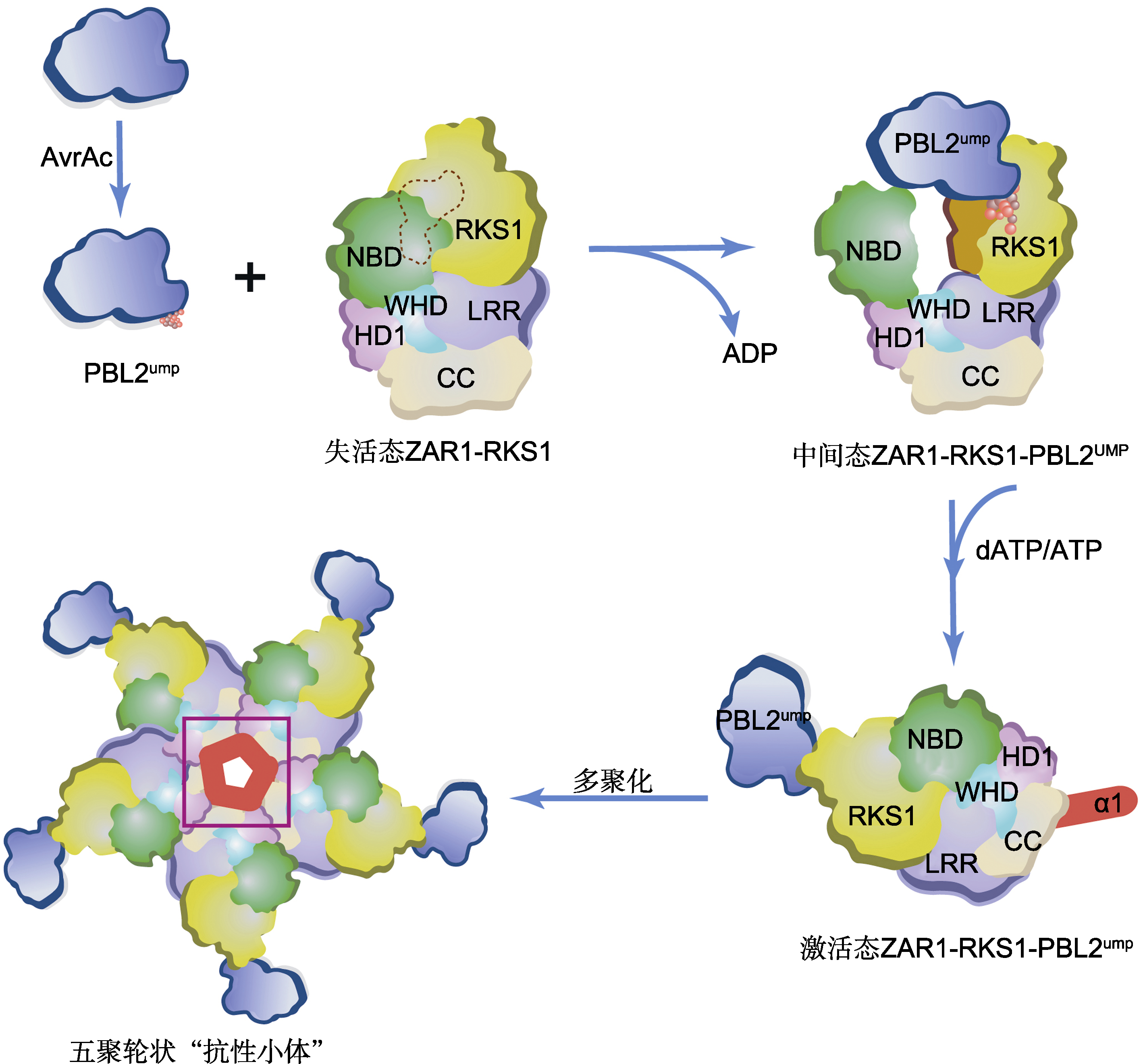
图1 PBL2UMP诱导的ZAR1抗性小体的激活与装配 野油菜黄单胞菌的效应蛋白AvrAC以尿苷酰化修饰拟南芥PBL2激酶, 尿苷酰化的PBL2UMP作为配体通过与RKS1互作而被ZAR1-RKS1复合物招募。RKS1的激活片段在与PBL2UMP的2个尿苷基部分(球形)相互作用后变得稳定(橙色表面), 并与ZAR1NBD结构域发生立体碰撞, 导致后者向外旋转, 从而释放ADP, 形成可与dATP/ATP结合的中间状态ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMP复合体。该复合物结合dATP/ATP后, 诱导ZAR1结构重塑和折叠转换, 隐藏在非活性ZAR1-RKS1复合物中的ZAR1的N顶末端α-螺旋(α1, 红色)暴露在溶剂中, 导致ZAR1完全激活(激活态ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMP), 继而通过多聚化形成五聚轮状结构的ZAR1抗性小体(紫色方框内突出显示形成的漏斗状结构)。CC、NBD、HD1、WHD和LRR为ZAR1的不同结构域。
Figure 1 PBL2UMP-induced activation and assembly of the ZAR1 resistosome Arabidopsis PBL2 is modified by uridylyl transferase AvrAC, which is an effector protein from Xanthomonas campestris. The uridylylated PBL2 (PBL2UMP) as a ligand is then recruited by the ZAR1-RKS1 complex through interaction with the pseudokinase RKS1. The activation segment of RKS1 becomes stabilized (orange surface) after interacting with the two uridylyl moieties (in sphere) of PBL2UMP, and sterically clashes with ZAR1NBD, causing the latter to rotate outward and consequently release ADP, forming an intermediate ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMP complex which allows it to bind dATP/ATP. Binding of dATP/ATP induces structural remodeling and fold switching of ZAR1. The very N-terminal helix (α1, red) of ZAR1 buried in the inactive ZAR1-RKS1 complex becomes solvent-exposed in the activated ZAR1-RKS1-PBL2UMP complex, forming a ZAR1 resistosome pentameric structure through polymerization (a funnel-shaped structure highlighted within the purple frame). CC, NBD, HD1, WHD and LRR are different structural domains of ZAR1.
| [23] |
Reubold TF, Wohlgemuth S, Eschenburg S ( 2011). Crystal structure of full-length Apaf-1: how the death signal is relayed in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Structure 19, 1074-1083.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] |
Riedl SJ, Li W, Chao Y, Schwarzenbacher R, Shi Y ( 2005). Structure of the apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 bound to ADP. Nature 434, 926-933.
DOI URL PMID |
| [25] | Schultink A, Qi T, Bally J, Staskawicz B ( 2019). Using forward genetics in Nicotiana benthamiana to uncover the immune signaling pathway mediating recognition of the Xanthomonas perforans effector XopJ4. New Phytol 221, 1001-1009. |
| [26] |
Seto D, Koulena N, Lo T, Menna A, Guttman DS, Desveaux D ( 2017). Expanded type III effector recognition by the ZAR1 NLR protein using ZED1-related 5 kinases. Nat Plants 3, 17027.
DOI URL PMID |
| [27] | Tameling WI, Elzinga SD, Darmin PS, Vossen JH, Takken FL, Haring MA, Cornelissen BJ ( 2002). The tomato R gene products I-2 and MI-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant Cell 14, 2929-2939. |
| [28] |
Wang G, Roux B, Feng F, Guy E, Li L, Li N, Zhang X, Lautier M, Jardinaud MF, Chabannes M, Arlat M, Chen S, He C, Noël LD, Zhou JM ( 2015). The decoy substrate of a pathogen effector and a pseudokinase specify pathogen-induced modified-self recognition and immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 18, 285-295.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] | Wang J, Wang J, Hu M, Qi J, Wu S, Wang G, Han Z, Qi Y, Gao N, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai J ( 2019a). Ligand-triggered allosteric ADP release primes a plant NLR complex. Science 364, eaav5868. |
| [30] | Wang J, Hu M, Wang J, Qi J, Han Z, Wang G, Qi Y, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai J ( 2019b) . Reconstitution and structure of a plant NLR resistosome conferring immunity. Science 364, eaav5870. |
| [31] |
Williams SJ, Sornaraj P, deCourcy-Ireland E, Menz RI, Kobe B, Ellis JG, Dodds PN, Anderson PA ( 2011). An autoactive mutant of the M flax rust resistance protein has a preference for binding ATP, whereas wild-type M protein binds ADP. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24, 897-906.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Wu Z, Li M, Dong OX, Xia S, Liang W, Bao Y, Wasteneys G, Li X ( 2018). Differential regulation of TNL-mediated immune signaling by redundant helper CNLs. New Phytol 222, 938-953.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Zhang L, Chen S, Ruan J, Wu J, Tong AB, Yin Q, Li Y, David L, Lu A, Wang WL, Marks C, Ouyang Q, Zhang X, Mao Y, Wu H ( 2015). Cryo-EM structure of the activated NAIP2-NLRC4 inflammasome reveals nucleated polymerization. Science 350, 404-409.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] |
施怡婷, 杨淑华 ( 2016). 中国科学家在乙烯信号转导领域取得突破性进展. 植物学报 51, 287-289.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
于倩倩, 孔祥培, 丁兆军 ( 2018). 中国科学家在生长素信号转导领域取得突破性研究进展. 植物学报 50, 535-537.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
Bernoux M, Burdett H, Williams SJ, Zhang X, Chen C, Newell K, Lawrence GJ, Kobe B, Ellis JG, Anderson PA, Dodds PN ( 2016). Comparative analysis of the flax immune receptors L6 and L7 suggests an equilibrium-ba-sed switch activation model. Plant Cell 28, 146-159.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
Bonardi V, Tang S, Stallmann A, Roberts M, Cherkis K, Dangl JL ( 2011). Expanded functions for a family of plant intracellular immune receptors beyond specific recognition of pathogen effectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 16463-16468.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | Castel B, Ngou PM, Cevik V, Redkar A, Kim DS, Yang Y, Ding P, Jones JDG ( 2018). Diverse NLR immune receptors activate defence via the RPW8-NLR NRG1. New Phytol 222, 966-980. |
| [6] |
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ ( 2006). Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 124, 803-814.
DOI URL PMID |
| [7] |
Cui H, Tsuda K, Parker JE ( 2015). Effector-triggered immunity: from pathogen perception to robust defense. Annu Rev Plant Biol 66, 487-511.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
Dodds PN, Rathjen JP ( 2010). Plant immunity: towards an integrated view of plant-pathogen interactions. Nat Rev Genet 11, 539-548.
DOI URL PMID |
| [9] |
Dong OX, Tong M, Bonardi V, El Kasmi F, Woloshen V, Wünsch LK, Dangl JL, Li X ( 2016). TNL-mediated immunity in Arabidopsis requires complex regulation of the redundant ADR1 gene family. New Phytol 210, 960-973.
DOI URL PMID |
| [10] |
Duxbury Z, Ma Y, Furzer OJ, Huh SU, Cevik V, Jones JD, Sarris PF ( 2016). Pathogen perception by NLRs in plants and animals: parallel worlds. Bioessays 38, 769-781.
DOI URL PMID |
| [11] |
Hu Z, Yan C, Liu P, Huang Z, Ma R, Zhang C, Wang R, Zhang Y, Martinon F, Miao D, Deng H, Wang J, Chang J, Chai J ( 2013). Crystal structure of NLRC4 reveals its autoinhibition mechanism. Science 341, 172-175.
DOI URL PMID |
| [12] |
Hu Z, Zhou Q, Zhang C, Fan S, Cheng W, Zhao Y, Shao F, Wang HW, Sui SF, Chai J ( 2015). Structural and biochemical basis for induced self-propagation of NLRC4. Science 350, 399-404.
DOI URL PMID |
| [13] |
Jones JDG, Dangl JL ( 2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323-329.
DOI |
| [14] | Lewis JD, Lee AH, Hassan JA, Wan J, Hurley B, Jhingree JR, Wang PW, Lo T, Youn JY, Guttman DS, Desveaux D ( 2013). The Arabidopsis ZED1 pseudokinase is required for ZAR1-mediated immunity induced by the Pseudomonas syringae type III effector HopZ1a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 18722-18727. |
| [15] | Lewis JD, Wu R, Guttman DS, Desveaux D ( 2010). Allele-specific virulence attenuation of the Pseudomonas syringae HopZ1a type III effector via the Arabidopsis ZAR1 resistance protein. PLoS Genet 6, e1000894. |
| [16] |
Lukasik E, Takken FL ( 2009). STANDing strong, resistance proteins instigators of plant defence. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12, 427-436.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
Maekawa S, Ohto U, Shibata T, Miyake K, Shimizu T ( 2016). Crystal structure of NOD2 and 35 its implications in human disease. Nat Commun 7, 11813.
DOI URL PMID |
| [18] |
Maekawa T, Kufer TA, Schulze-Lefert P ( 2011). NLR functions in plant and animal immune systems: so far and yet so close. Nat Immun 12, 817-826.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
Peart JR, Mestre P, Lu R, Malcuit I, Baulcombe DC ( 2005). NRG1, a CC-NB-LRR protein, together with N, a TIR-NB-LRR protein, mediates resistance against tobacco mosaic virus. Curr Biol 15, 968-973.
DOI URL PMID |
| [20] |
Qi D, DeYoung BJ, Innes RW ( 2012). Structure-function analysis of the coiled-coil and leucine-rich repeat domains of the RPS5 disease resistance protein. Plant Physiol 158, 1819-1832.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Qi T, Seong K, Thomazella DPT, Kim JR, Pham J, Seo E, Cho MJ, Schultink A, Staskawicz BJ ( 2018). NRG1 functions downstream of EDS1 to regulate TIR-NLR-me-diated plant immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, E10979-E10987. |
| [22] |
Rairdan GJ, Moffett P ( 2006). Distinct domains in the ARC region of the potato resistance protein Rx mediate LRR binding and inhibition of activation. Plant Cell 18, 2082-2093.
DOI URL PMID |
| [34] |
Zhou M, Li Y, Hu Q, Bai XC, Huang W, Yan C, Scheres SH, Shi Y ( 2015). Atomic structure of the apoptosome: mechanism of cytochrome c- and 25 dATP-mediated activation of Apaf-1. Genes Dev 29, 2349-2361.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头. 植物NLR免疫受体的识别、免疫激活与信号调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 12-23. |
| [2] | 周俭民. 免疫信号轴揭示水稻与病原菌斗争的秘密[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [3] | 王伟, 唐定中. 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [4] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [5] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [6] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [7] | 闫佳, 刘雅琼, 侯岁稳. 植物抗病蛋白研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2018, 53(2): 250-263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
