

植物学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 250-263.DOI: 10.11983/CBB17148 cstr: 32102.14.CBB17148
收稿日期:2017-08-08
接受日期:2017-12-01
出版日期:2018-03-01
发布日期:2018-08-10
通讯作者:
侯岁稳
基金资助:
Yan Jia, Liu Yaqiong, Hou Suiwen*( )
)
Received:2017-08-08
Accepted:2017-12-01
Online:2018-03-01
Published:2018-08-10
Contact:
Hou Suiwen
摘要: 为了应对外界复杂的环境变化, 植物进化出一套复杂而精细的免疫应答调控机制。植物抗病蛋白能够特异地识别病原微生物分泌的效应蛋白, 触发免疫响应以对抗病原微生物的侵扰。该文综述了植物抗病蛋白的结构与功能及对病原菌的识别方式、在免疫响应过程中抗病蛋白的动态平衡机制及其介导的防御反应信号转导。开展植物抗病蛋白研究可为定向培育抗病作物奠定理论基础。
闫佳, 刘雅琼, 侯岁稳. 植物抗病蛋白研究进展. 植物学报, 2018, 53(2): 250-263.
Yan Jia, Liu Yaqiong, Hou Suiwen. Recent Advances in Disease Resistance Proteins in Plant Immunity. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2018, 53(2): 250-263.
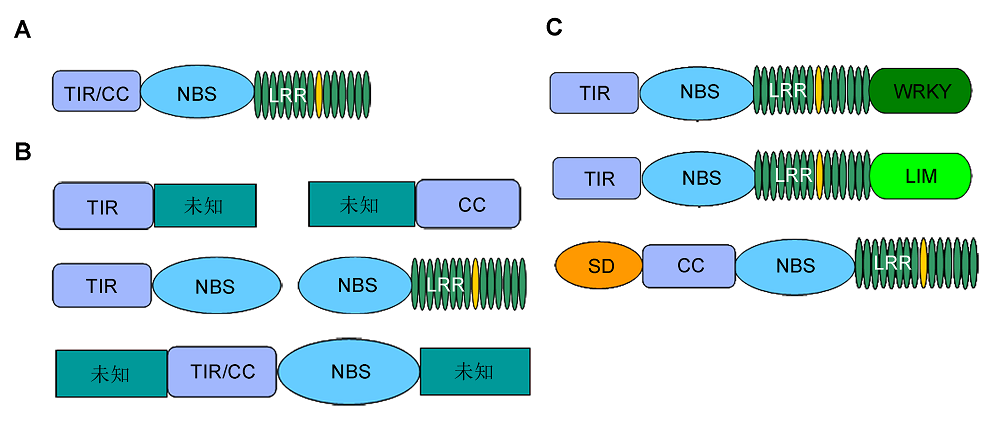
图1 NB-LRR抗病蛋白结构(A) 典型NB-LRR抗病蛋白; (B) 非典型NB-LRR抗病蛋白; (C) 含特殊结构域的NB-LRR抗病蛋白
Figure 1 Architecture of NB-LRR proteins(A) Typical NB-LRR protein; (B) Atypical NB-LRR protein; (C) NB-LRR protein with special domains
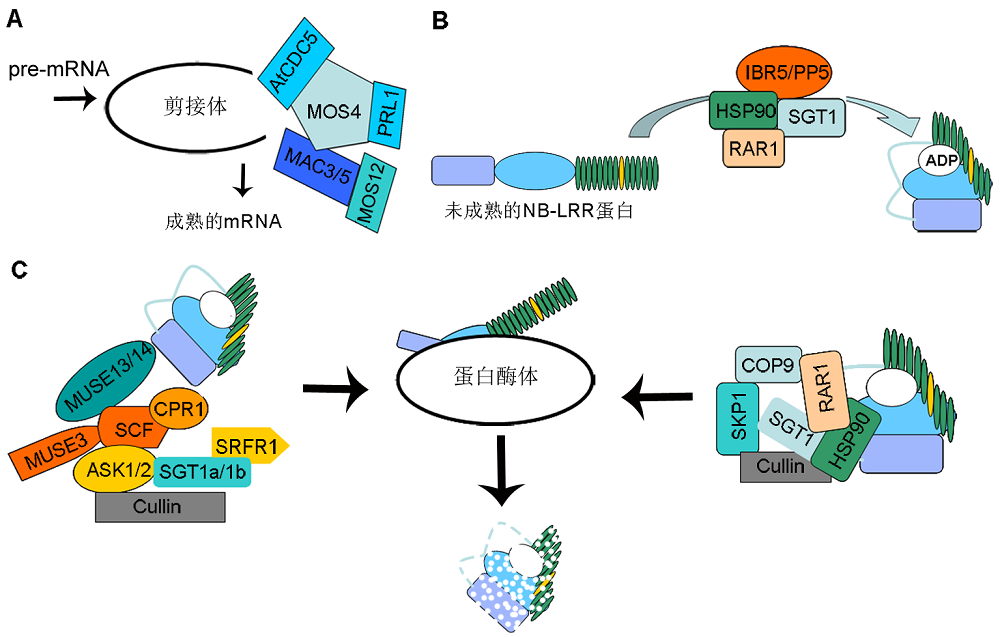
图2 抗病蛋白稳定性调控(A) 抗病基因的转录后调控; (B) 抗病蛋白的装配与成熟; (C) 抗病蛋白的降解
Figure 2 The homeostasis regulation of R proteins(A) Post-transcriptional regulation of R genes; (B) Chaperone-mediated R protein complex assembly; (C) R protein degradation
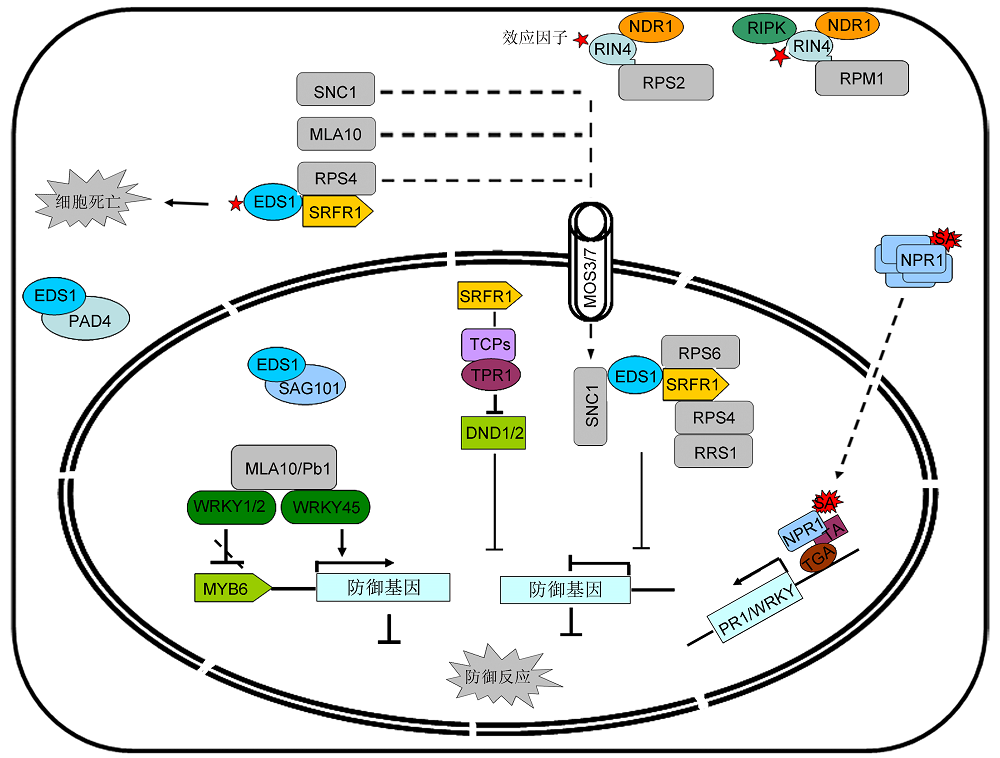
图3 抗病蛋白介导的植物免疫响应过程抗病蛋白激活触发的信号转导过程, 包括抗病信号激活、转录因子调控以及水杨酸(SA)信号通路激活。
Figure 3 R protein mediated plant immune response pathwayThe regulation mechanisms of R protein involved signaling components, including the activation of R-related proteins, transcription regulators and salicylic acid (SA) dependent signaling.
| [1] | Anderson JC, Bartels S, González Besteiro MA, Shaho- llari B, Ulm R, Peck SC (2011). Arabidopsis MAP kinase phosphatase 1 (AtMKP1) negatively regulates MPK6-me- diated PAMP responses and resistance against bacteria.Plant J 67, 258-268. |
| [2] | Axtell MJ, Staskawicz BJ (2003). Initiation of RPS2-speci- fied disease resistance in Arabidopsis is coupled to the AvrRpt2-directed elimination of RIN4. Cell 112, 369-377. |
| [3] | Azevedo C, Sadanandom A, Kitagawa K, Freialdenhoven A, Shirasu K, Schulze-Lefert P (2002). The RAR1 inter- actor SGT1, an essential component of R gene-triggered disease resistance. Science 295, 2073-2076. |
| [4] | Bartels S, Anderson JC, Besteiro MAG, Carreri A, Hirt H, Buchala A, Métraux JP, Peck SC, Ulm R (2009). MAP kinase phosphatase1 and protein tyrosine phosphatase1 are repressors of salicylic acid synthesis and SNC1- mediated responses in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 21, 2884-2897. |
| [5] | Belkhadir Y, Nimchuk Z, Hubert DA, Mackey D, Dangl JL (2004). Arabidopsis RIN4 negatively regulates disease resistance mediated by RPS2 and RPM1 downstream or independent of the NDR1 signal modulator and is not required for the virulence functions of bacterial type III effectors AvrRpt2 or AvrRpm1.Plant Cell 16, 2822-2835. |
| [6] | Bernoux M, Ve T, Williams S, Warren C, Hatters D, Valkov E, Zhang XX, Ellis JG, Kobe B, Dodds PN (2011). Structural and functional analysis of a plant resistance protein TIR domain reveals interfaces for self-association, signaling, and autoregulation.Cell Host Microbe 9, 200-211. |
| [7] | Césari S, Kanzaki H, Fujiwara T, Bernoux M, Chalvon V, Kawano Y, Shimamoto K, Dodds P, Terauchi R, Kroj T (2014). The NB-LRR proteins RGA4 and RGA5 interact functionally and physically to confer disease resistance.EMBO J 33, 1941-1959. |
| [8] | Chandra-Shekara AC, Navarre D, Kachroo A, Kang HG, Klessig D, Kachroo P (2004). Signaling requirements and role of salicylic acid in HRT- and rrt-mediated resistance to turnip crinkle virus in Arabidopsis. Plant J 40, 647-659. |
| [9] | Chang C, Yu DS, Jiao J, Jing SJ, Schulze-Lefert P, Shen QH (2013). Barley MLA immune receptors directly interfere with antagonistically acting transcription factors to initiate disease resistance signaling.Plant Cell 25, 1158-1173. |
| [10] | Chen QF, Xu L, Tan WJ, Chen L, Qi H, Xie LJ, Chen MX, Liu BY, Yu LJ, Yao N, Zhang JH, Shu WS, Xiao S (2015). Disruption of the Arabidopsis defense regulator genes SAG101, EDS1, and PAD4 confers enhanced free- zing tolerance. Mol Plant 8, 1536-1549. |
| [11] | Cheng YT, Germain H, Wiermer M, Bi DL, Xu F, García AV, Wirthmueller L, Després C, Parker JE, Zhang YL, Li X (2009). Nuclear pore complex component MOS7/ Nup88 is required for innate immunity and nuclear accu- mulation of defense regulators in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 21, 2503-2516. |
| [12] | Cheng YT, Li YZ, Huang S, Huang Y, Dong XN, Zhang YL, Li X (2011). Stability of plant immune-receptor resistance proteins is controlled by SKP1-CULLIN1-F-box (SCF)- mediated protein degradation.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 14694-14699. |
| [13] | Chung EH, da Cunha L, Wu AJ, Gao ZY, Cherkis K, Afzal AJ, Mackey D, Dangl JL (2011). Specific threonine phos- phorylation of a host target by two unrelated type III effectors activates a host innate immune receptor in plants.Cell Host Microbe 9, 125-136. |
| [14] | Dangl JL, Horvath DM, Staskawicz BJ (2013). Pivoting the plant immune system from dissection to deployment.Sci- ence 341, 746-751. |
| [15] | Day B, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz BJ (2006). NDR1 interac- tion with RIN4 mediates the differential activation of multiple disease resistance pathways in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 18, 2782-2791. |
| [16] | De Bruyne L, Höfte M, De Vleesschauwer D (2014). Con- necting growth and defense: the emerging roles of brassinosteroids and gibberellins in plant innate immunity.Mol Plant 7, 943-959. |
| [17] | De La Fuente Bentem van S, Vossen JH, de Vries KJ, van Wees S, Tameling WIL, Dekker HL, de Koster CG, Haring MA, Takken FLW, Cornelissen BJC (2005). Heat shock protein 90 and its co-chaperone protein phospha- tase 5 interact with distinct regions of the tomato I-2 disease resistance protein.Plant J 43, 284-298. |
| [18] | Deng YW, Zhai KR, Xie Z, Yang DY, Zhu XD, Liu JZ, Wang X, Qin P, Yang YZ, Zhang GM, Li Q, Zhang JF, Wu SQ, Milazzo J, Mao BZ, Wang ET, Xie HA, Tharreau D, He ZH (2017). Epigenetic regulation of antagonistic receptors confers rice blast resistance with yield balance.Science 355, 962-965. |
| [19] | Deslandes L, Olivier J, Peeters N, Feng DX, Khounlotham M, Boucher C, Somssich I, Genin S, Marco Y (2003). Physical interaction between RRS1-R, a protein conferring resistance to bacterial wilt, and PopP2, a type III effector targeted to the plant nucleus.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 8024-8029. |
| [20] | Dodds PN, Lawrence GJ, Catanzariti AM, Teh T, Wang CIA, Ayliffe MA, Kobe B, Ellis JG (2006). Direct protein interaction underlies gene-for-gene specificity and coevo- lution of the flax resistance genes and flax rust avirulence genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 8888-8893. |
| [21] | Du XR, Miao M, Ma XR, Liu YS, Kuhl JC, Martin GB, Xiao FM (2012). Plant programmed cell death caused by an autoactive form of Prf is suppressed by co-expression of the Prf LRR domain.Mol Plant 5, 1058-1067. |
| [22] | Fei QL, Xia R, Meyers BC (2013). Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory net- works.Plant Cell 25, 2400-2415. |
| [23] | Feys BJ, Moisan LJ, Newman MA, Parker JE (2001). Direct interaction between the Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling proteins, EDS1 and PAD4.EMBO J 20, 5400-5411. |
| [24] | Fu ZQ, Yan SP, Saleh A, Wang W, Ruble J, Oka N, Mohan R, Spoel SH, Tada Y, Zheng N, Dong XN (2012). NPR3 and NPR4 are receptors for the immune signal salicylic acid in plants.Nature 486, 228-232. |
| [25] | Genot B, Lang J, Berriri S, Garmier M, Gilard F, Pateyron S, Haustraete K, Van Der Straeten D, Hirt H, Colcombet J (2017). Constitutively active Arabidopsis MAP kinase 3 triggers defense responses involving salicylic acid and SUMM2 resistance protein.Plant Physiol 174, 1238-1249. |
| [26] | Goritschnig S, Zhang YL, Li X (2007). The ubiquitin path- way is required for innate immunity in Arabidopsis.Plant J 49, 540-551. |
| [27] | Gu YN, Zebell SG, Liang ZZ, Wang S, Kang BH, Dong XN (2016). Nuclear pore permeabilization is a convergent signaling event in effector-triggered immunity.Cell 166, 1526-1538. |
| [28] | Guo YL, Fitz J, Schneeberger K, Ossowski S, Cao J, Weigel D (2011). Genome-wide comparison of Nucleotide- Binding Site-Leucine-Rich Repeat-encoding genes in Ara- bidopsis.Plant Physiol 157, 757-769. |
| [29] | Gutierrez JR, Balmuth AL, Ntoukakis V, Mucyn TS, Gimenez-Ibanez S, Jones AME, Rathjen JP (2010). Prf immune complexes of tomato are oligomeric and contain multiple Pto-like kinases that diversify effector recognition.Plant J 61, 507-518. |
| [30] | Hao W, Collier SM, Moffett P, Chai J (2013). Structural basis for the interaction between the potato virus X resistance protein (Rx) and its cofactor Ran GTPase- activating protein 2 (RanGAP2).J Biol Chem 288, 35868-35876. |
| [31] | Heidrich K, Wirthmueller L, Tasset C, Pouzet C, Des- landes L, Parker JE (2011). Arabidopsis EDS1 connects pathogen effector recognition to cell compartment-specific immune responses.Science 334, 1401-1404. |
| [32] | Holt III BF, Belkhadir Y, Dangl JL (2005). Antagonistic control of disease resistance protein stability in the plant immune system.Science 309, 929-932. |
| [33] | Howden AJM, Huitema E (2012). Effector-triggered post- translational modifications and their role in suppression of plant immunity.Front Plant Sci 3, 160. |
| [34] | Hua J, Grisafi P, Cheng SH, Fink GR (2001). Plant growth homeostasis is controlled by the Arabidopsis BON1 and BAP1 genes. Genes Dev 15, 2263-2272. |
| [35] | Huang CL, Hwang SY, Chiang YC, Lin TP (2008). Mole- cular evolution of the Pi-ta gene resistant to rice blast in wild rice(Oryza rufipogon). Genet 179, 1527-1538. |
| [36] | Huang S, Chen X, Zhong XH, Li M, Ao K, Huang JH, Li X (2016). Plant TRAF proteins regulate NLR immune recep- tor turnover.Cell Host Microbe 19, 204-215. |
| [37] | Huang S, Monaghan J, Zhong XH, Lin L, Sun TJ, Dong OX, Li X (2014).a HSP90s are required for NLR immune receptor accumulation in Arabidopsis.Plant J 79, 427-439. |
| [38] | Huang Y, Minaker S, Roth C, Huang S, Hieter P, Lipka V, Wiermer M, Li X (2014).b An E4 ligase facilitates polyubi- quitination of plant immune receptor resistance proteins in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 26, 485-496. |
| [39] | Hubert DA, Tornero P, Belkhadir Y, Krishna P, Takahashi A, Shirasu K, Dangl JL (2003). Cytosolic HSP90 asso- ciates with and modulates the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance protein.EMBO J 22, 5679-5689. |
| [40] | Inoue H, Hayashi N, Matsushita A, Liu XQ, Nakayama A, Sugano S, Jiang CJ, Takatsuji H (2013). Blast resistance of CC-NB-LRR protein Pb1 is mediated by WRKY45 th- rough protein-protein interaction.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, 9577-9582. |
| [41] | Jia YL, McAdams SA, Bryan GT, Hershey HP, Valent B (2000). Direct interaction of resistance gene and aviru- lence gene products confers rice blast resistance.EMBO J 19, 4004-4014. |
| [42] | Johnson KCM, Zhao J, Wu ZS, Roth C, Lipka V, Wiermer M, Li X (2017). The putative kinase substrate MUSE7 negatively impacts the accumulation of NLR proteins.Plant J 89, 1174-1183. |
| [43] | Jones JDG, Dangl JL (2006). The plant immune system.Nature 444, 323-329. |
| [44] | Jones JDG, Vance RE, Dangl JL (2016). Intracellular innate immune surveillance devices in plants and animals. Sci- ence 354, aaf6395. |
| [45] | Kim SH, Gao F, Bhattacharjee S, Adiasor JA, Nam JC, Gassmann W (2010). The Arabidopsis resistance-like gene SNC1 is activated by mutations in SRFR1 and con- tributes to resistance to the bacterial effector AvrRps4. PLoS Pathog 6, e1001172. |
| [46] | Kim SH, Kwon SI, Saha D, Anyanwu NC, Gassmann W (2009) Resistance to the Pseudomonas syringae Effector HopA1 is governed by the TIR-NBS-LRR protein RPS6 and is enhanced by mutations in SRFR1. Plant Physiol 150, 1723-1732. |
| [47] | Kim SH, Qi D, Ashfield T, Helm M, Innes RW (2016). Using decoys to expand the recognition specificity of a plant disease resistance protein.Science 351, 684-687. |
| [48] | Kim SH, Son GH, Bhattacharjee S, Kim HJ, Nam JC, Nguyen PDT, Hong JC, Gassmann W (2014). The Arabidopsis immune adaptor SRFR1 interacts with TCP transcription factors that redundantly contribute to effector- triggered immunity.Plant J 78, 978-989. |
| [49] | Kong Q, Qu N, Gao MH, Zhang ZB, Ding XJ, Yang F, Li YZ, Dong OX, Chen S, Li X, Zhang YL (2012). The MEKK1-MKK1/MKK2-MPK4 kinase cascade negatively regulates immunity mediated by a mitogen-activated pro- tein kinase kinase kinase in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 24, 2225-2236. |
| [50] | Krasileva KV, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz BJ (2010). Activa- tion of an Arabidopsis resistance protein is specified by the in planta association of its leucine-rich repeat domain with the cognate oomycete effector.Plant Cell 22, 2444-2458. |
| [51] | Le Roux C, Huet G, Jauneau A, Camborde L, Trém- ousaygue D, Kraut A, Zhou BB, Levaillant M, Adachi H, Yoshioka H, Raffaele S, Berthomé R, Couté Y, Parker JE, Deslandes L (2015). A receptor pair with an integrated decoy converts pathogen disabling of transcription factors to immunity.Cell 161, 1074-1088. |
| [52] | Li F, Pignatta D, Bendix C, Brunkard JO, Cohn MM, Tung J, Sun HY, Kumar P, Baker B (2012). MicroRNA regula- tion of plant innate immune receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 1790-1795. |
| [53] | Li YZ, Dong O, Johnson K, Zhang YL (2011). MOS1 epigenetically regulates the expression of plant resistance gene SNC1. Plant Signal Behav 6, 434-436. |
| [54] | Li YZ, Li SX, Bi DL, Cheng YT, Li X, Zhang YL (2010).a SRFR1 negatively regulates plant NB-LRR resistance protein accumulation to prevent autoimmunity.PLoS Pa- thog 6, e1001111. |
| [55] | Li YZ, Tessaro MJ, Li X, Zhang YL (2010).b Regulation of the expression of plant Resistance gene SNC1 by a protein with a conserved BAT2 domain. Plant Physiol 153, 1425-1434. |
| [56] | Liu J, Elmore JM, Lin ZJD, Coaker G (2011). A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase phosphorylates the host target RIN4, leading to the activation of a plant innate immune receptor.Cell Host Microbe 9, 137-146. |
| [57] | Liu JY, Yang HB, Bao F, Ao K, Zhang XY, Zhang YL, Yang SH (2015). IBR5 modulates temperature-dependent, R protein CHS3-mediated defense responses in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet 11, e1005784. |
| [58] | Liu N, Hake K, Wang W, Zhao T, Romeis T, Tang DZ (2017). Calcium-dependent protein kinase 5 associates with the truncated NLR protein TIR-NBS2 to contribute to exo70B1-mediated immunity. Plant Cell 29, 746-759. |
| [59] | Lukasik-Shreepaathy E, Slootweg E, Richter H, Goverse A, Cornelissen BJC, Takken FLW (2012). Dual regula- tory roles of the extended N terminus for activation of the tomato Mi-1.2 resistance protein.Mol Plant Microbe In- teract 25, 1045-1057. |
| [60] | Mackey D, Belkhadir Y, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Dangl JL (2003). Arabidopsis RIN4 is a target of the type III vir- ulence effector AvrRpt2 and modulates RPS2-mediated resistance.Cell 112, 379-389. |
| [61] | Mackey D, Holt III BF, Wiig A, Dangl JL (2002). RIN4 interacts with Pseudomonas syringae type III effector molecules and is required for RPM1-mediated resistance in Arabidopsis. Cell 108, 743-754. |
| [62] | Maekawa T, Cheng W, Spiridon LN, Töller A, Lukasik E, Saijo Y, Liu PY, Shen QH, Micluta MA, Somssich IE, Takken FLW, Petrescu AJ, Chai JJ, Schulze-Lefert P (2011). Coiled-coil domain-dependent homodimerization of intracellular barley immune receptors defines a minimal functional module for triggering cell death.Cell Host Mi- crobe 9, 187-199. |
| [63] | Mang HG, Qian WQ, Zhu Y, Qian J, Kang HG, Klessig DF, Hua J (2012). Abscisic acid deficiency antagonizes high- temperature inhibition of disease resistance through en- hancing nuclear accumulation of resistance proteins SNC1 and RPS4 in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24, 1271-1284. |
| [64] | Monaghan J, Zipfel C (2012). Plant pattern recognition receptor complexes at the plasma membrane.Curr Opin Plant Biol 15, 349-357. |
| [65] | Mucyn TS, Clemente A, Andriotis VME, Balmuth AL, Oldroyd GED, Staskawicz BJ, Rathjen JP (2006). The tomato NBARC-LRR protein Prf interacts with Pto kinase in vivo to regulate specific plant immunity. Plant Cell 18, 2792-2806. |
| [66] | Narusaka M, Shirasu K, Noutoshi Y, Kubo Y, Shiraishi T, Iwabuchi M, Narusaka Y (2009). RRS1 and RPS4 provide a dual Resistance-gene system against fungal and bacterial pathogens. Plant J 60, 218-226. |
| [67] | Noutoshi Y, Ito T, Seki M, Nakashita H, Yoshida S, Marco Y, Shirasu K, Shinozaki K (2005). A single amino acid insertion in the WRKY domain of the Arabidopsis TIR- NBS-LRR-WRKY-type disease resistance protein SLH1 (sensitive to low humidity 1) causes activation of defense responses and hypersensitive cell death.Plant J 43, 873-888. |
| [68] | Ntoukakis V, Balmuth AL, Mucyn TS, Gutierrez JR, Jones AME, Rathjen JP (2013). The tomato Prf complex is a molecular trap for bacterial effectors based on Pto transphosphorylation.PLoS Pathog 9, e1003123. |
| [69] | Pajerowska-Mukhtar KM, Emerine DK, Mukhtar MS (2013). Tell me more: roles of NPRs in plant immunity.Trends Plant Sci 18, 402-411. |
| [70] | Qi D, DeYoung BJ, Innes RW (2012). Structure-function analysis of the coiled-coil and leucine-rich repeat domains of the RPS5 disease resistance protein.Plant Physiol 158, 1819-1832. |
| [71] | Qi D, Dubiella U, Kim SH, Sloss DI, Dowen RH, Dixon JE, Innes RW (2014). Recognition of the protein kinase AVRPPHB SUSCEPTIBLE1 by the disease resistance protein RESISTANCE TO PSEUDOMONAS SYRINGAE5 is dependent on s-acylation and an exposed loop in AVRPPHB SUSCEPTIBLE1.Plant Physiol 164, 340-351. |
| [72] | Rairdan GJ, Moffett P (2006). Distinct domains in the ARC region of the potato resistance protein Rx mediate LRR binding and inhibition of activation.Plant Cell 18, 2082-2093. |
| [73] | Roux ME, Rasmussen MW, Palma K, Lolle S, Regué ÀM, Bethke G, Glazebrook J, Zhang WP, Sieburth L, Larsen MR, Mundy J, Petersen M (2015). The mRNA decay factor PAT1 functions in a pathway including MAP kinase 4 and immune receptor SUMM2.EMBO J 34, 593-608. |
| [74] | Sarris PF, Duxbury Z, Huh SU, Ma Y, Segonzac C, Sklenar J, Derbyshire P, Cevik V, Rallapalli G, Saucet SB, Wirthmueller L, Menke FLH, Sohn KH, Jones JDG (2015). A plant immune receptor detects pathogen eff- ectors that target WRKY transcription factors.Cell 161, 1089-1100. |
| [75] | Schweighofer A, Kazanaviciute V, Scheikl E, Teige M, Doczi R, Hirt H, Schwanninger M, Kant M, Schuurink R, Mauch F, Buchala A, Cardinale F, Meskiene I (2007). The PP2C-type phosphatase AP2C1, which negatively regulates MPK4 and MPK6, modulates innate immunity, jasmonic acid, and ethylene levels in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 19, 2213-2224. |
| [76] | Schwessinger B, Ronald PC (2012). Plant innate immunity: perception of conserved microbial signatures.Annu Rev Plant Biol 63, 451-482. |
| [77] | Sela H, Spiridon LN, Petrescu AJ, Akerman M, Mandel- Gutfreund Y, Nevo E, Loutre C, Keller B, Schulman AH, Fahima T (2012). Ancient diversity of splicing motifs and protein surfaces in the wild emmer wheat (Triticum dicoc- coides) LR10 coiled coil (CC) and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains. Mol Plant Pathol 13, 276-287. |
| [78] | Slootweg EJ, Spiridon LN, Roosien J, Butterbach P, Pomp R, Westerhof L, Wilbers R, Bakker E, Bakker J, Petrescu AJ, Smant G, Goverse A (2013). Structural determinants at the interface of the ARC2 and Leucine-rich repeat domains control the activation of the plant immune receptors Rx1 and Gpa2.Plant Physiol 162, 1510-1528. |
| [79] | Sohn KH, Segonzac C, Rallapalli G, Sarris PF, Woo JY, Williams SJ, Newman TE, Paek KH, Kobe B, Jones JDG (2014). The nuclear immune receptor RPS4 is required for RRS1SLH1-dependent constitutive defense activation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet 10, e1004655. |
| [80] | Swiderski MR, Birker D, Jones JDG (2009). The TIR domain of TIR-NB-LRR resistance proteins is a signaling domain involved in cell death induction.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22, 157-165. |
| [81] | Tameling WIL, Baulcombe DC (2007). Physical association of the NB-LRR resistance protein Rx with a Ran GTPase- activating protein is required for extreme resistance to Potato virus X. Plant Cell 19, 1682-1694. |
| [82] | Tsuda K, Katagiri F (2010). Comparing signaling mecha- nisms engaged in pattern-triggered and effector-triggered immunity.Curr Opin Plant Biol 13, 459-465. |
| [83] | Van Der Biezen EA, Jones JDG (1998). Plant disease- resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept.Trends Biochem Sci 23, 454-456. |
| [84] | Wang GF, Ji JB, El-Kasmi F, Dangl JL, Johal G, Balint- Kurti PJ (2015). Molecular and functional analyses of a maize autoactive NB-LRR protein identify precise struc- tural requirements for activity.PLoS Pathog 11, e1004674. |
| [85] | Wang W, Barnaby JY, Tada Y, Li HR, Tör M, Caldelari D, Lee DU, Fu XD, Dong XN (2011). Timing of plant immune responses by a central circadian regulator.Nature 470, 110-114. |
| [86] | Wang YC, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhang XY, Yang SH (2013). A missense mutation in CHS1, a TIR-NB protein, induces chilling sensitivity in Arabidopsis. Plant J 75, 553-565. |
| [87] | Wiermer M, Feys BJ, Parker JE (2005). Plant immunity: the EDS1 regulatory node.Curr Opin Plant Biol 8, 383-389. |
| [88] | Willhoft O, Kerr R, Patel D, Zhang WJ, Al-Jassar C, Daviter T, Millson SH, Thalassinos K, Vaughan CK (2017). The crystal structure of the Sgt1-Skp1 complex: the link between Hsp90 and both SCF E3 ubiquitin ligases and kinetochores.Sci Rep 7, 41626. |
| [89] | Williams SJ, Sohn KH, Wan L, Bernoux M, Sarris PF, Segonzac C, Ve T, Ma Y, Saucet SB, Ericsson DJ, Casey LW, Lonhienne T, Winzor DJ, Zhang XX, Coerdt A, Parker JE, Dodds PN, Kobe B, Jones JDG (2014). Structural basis for assembly and function of a hetero- dimeric plant immune receptor.Science 344, 299-303. |
| [90] | Williams SJ, Sornaraj P, Decourcy-Ireland E, Menz RI, Kobe B, Ellis JG, Dodds PN, Anderson PA (2011). An autoactive mutant of the M flax rust resistance protein has a preference for binding ATP, whereas wild-type M protein binds ADP.Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24, 897-906. |
| [91] | Wu CH, Belhaj K, Bozkurt TO, Birk MS, Kamoun S (2016). Helper NLR proteins NRC2a/b and NRC3 but not NRC1 are required for Pto-mediated cell death and resistance in Nicotiana benthamiana. New Phytol 209, 1344-1352. |
| [92] | Wu Y, Zhang D, Chu JY, Boyle P, Wang Y, Brindle ID, De Luca V, Després C (2012). The Arabidopsis NPR1 protein is a receptor for the plant defense hormone salicylic acid.Cell Rep 1, 639-647. |
| [93] | Xia ST, Cheng YT, Huang S, Win J, Soards A, Jinn TL, Jones JDG, Kamoun S, Chen S, Zhang YL, Li X (2013). Regulation of transcription of nucleotide-binding leucine- rich repeat-encoding genes SNC1 and RPP4 via H3K4 trimethylation. Plant Physiol 162, 1694-1705. |
| [94] | Xu F, Kapos P, Cheng YT, Li M, Zhang YL, Li X (2014). NLR-associating transcription factor bHLH84 and its para- logs function redundantly in plant immunity.PLoS Pathog 10, e1004312. |
| [95] | Xu F, Xu SH, Wiermer M, Zhang YL, Li X (2012). The cyclin L homolog MOS12 and the MOS4-associated complex are required for the proper splicing of plant resistance genes.Plant J 70, 916-928. |
| [96] | Xu GY, Yuan M, Ai CR, Liu LJ, Zhuang E, Karapetyan S, Wang SP, Dong XN (2017). uORF-mediated translation allows engineered plant disease resistance without fitness costs.Nature 545, 491-494. |
| [97] | Xu SH, Zhang ZB, Jing BB, Gannon P, Ding JM, Xu F, Li X, Zhang YL (2011). Transportin-SR is required for proper splicing of resistance genes and plant immunity.PLoS Genet 7, e1002159. |
| [98] | Yang HB, Shi YT, Liu JY, Guo L, Zhang XY, Yang SH (2010). A mutant CHS3 protein with TIR-NB-LRR-LIM domains modulates growth, cell death and freezing toler ance in a temperature-dependent manner in Arabidopsis.Plant J 63, 283-296. |
| [99] | Yang SH, Hua J (2004). A haplotype-specific resistance gene regulated by BONZAI1 mediates temperature-depe- ndent growth control in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 1060-1071. |
| [100] | Yao CP, Wu YY, Nie HZ, Tang DZ (2012). RPN1a, a 26S proteasome subunit, is required for innate immunity in Arabidopsis.Plant J 71, 1015-1028. |
| [101] | Zbierzak AM, Porfirova S, Griebel T, Melzer M, Parker JE, Dörmann P (2013). A TIR-NBS protein encoded by Ara- bidopsis Chilling Sensitive 1 (CHS1) limits chloroplast da- mage and cell death at low temperature. Plant J 75, 539-552. |
| [102] | Zhang YL, Li X (2005). A putative nucleoporin 96 is required for both basal defense and constitutive resistance res- ponses mediated by suppressor of npr1-1, constitutive 1.Plant Cell 17, 1306-1316. |
| [103] | Zhang ZB, Liu YN, Huang H, Gao MH, Wu D, Kong Q, Zhang YL (2017). The NLR protein SUMM2 senses the disruption of an immune signaling MAP kinase cascade via CRCK3.EMBO Rep 18, 292-302. |
| [104] | Zhang ZB, Wu YL, Gao MH, Zhang J, Kong Q, Liu YN, Ba HP, Zhou JM, Zhang YL (2012). Disruption of PAMP- induced MAP Kinase cascade by a Pseudomonas sy- ringae effector activates plant immunity mediated by the NB-LRR protein SUMM2. Cell Host Microbe 11, 253-263. |
| [105] | Zhou FS, Menke FLH, Yoshioka K, Moder W, Shirano Y, Klessig DF (2004). High humidity suppresses ssi4-media- ted cell death and disease resistance upstream of MAP kinase activation, H2O2 production and defense gene ex- pression. Plant J 39, 920-932. |
| [106] | Zhu ZH, Xu F, Zhang YX, Cheng YT, Wiermer M, Li X, Zhang YL (2010). Arabidopsis resistance protein SNC1 activates immune responses through association with a transcriptional corepressor.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 13960-13965. |
| [107] | Zou BH, Yang DL, Shi ZY, Dong HS, Hua J (2014). Monou- biquitination of Histone 2B at the disease resistance gene locus regulates its expression and impacts immune res- ponses in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol 165, 309-318. |
| [1] | 史君星, 闫一嘉, 董汝, 陶轩, 孙晓龙, 黄聪聪. 拟南芥HSP1调节CERK1蛋白水平影响几丁质激发的防御反应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 712-719. |
| [2] | 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头. 植物NLR免疫受体的识别、免疫激活与信号调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 12-23. |
| [3] | 周俭民. 免疫信号轴揭示水稻与病原菌斗争的秘密[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [4] | 石添添, 高英, 王欢, 刘君. 细胞核质转运及其受体在植物抗病防御反应中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(4): 480-487. |
| [5] | 王姝瑶, 郝鑫, 曲悦, 陈迎迎, 沈应柏. 反式-2-己烯醛在植物防御反应中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 232-240. |
| [6] | 王伟, 唐定中. 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [7] | 杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504. |
| [8] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [9] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [10] | 夏石头, 李昕. 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 288-292. |
| [11] | 张静 杨洪强 魏钦平. 几丁质及其衍生物的生物活性与在农业中的应用[J]. 植物学报, 2003, 20(02): 178-183. |
| [12] | 蔡以滢 陈珈. 植物防御反应中活性氧的产生和作用[J]. 植物学报, 1999, 16(02): 107-112. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||