

植物学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 497-504.DOI: 10.11983/CBB19207 cstr: 32102.14.CBB19207
收稿日期:2019-10-23
接受日期:2020-01-23
出版日期:2020-07-01
发布日期:2020-05-21
通讯作者:
夏石头
基金资助:
Chenghuizi Yang1,2,Xianyu Tang2,Wei Li1,2,Shitou Xia1,2,*( )
)
Received:2019-10-23
Accepted:2020-01-23
Online:2020-07-01
Published:2020-05-21
Contact:
Shitou Xia
摘要: 为适应丰富多变的生存环境, 植物逐渐进化出一套复杂的免疫系统来抵抗病原菌的侵染。核苷酸结合的富含亮氨酸重复蛋白(NLR)作为植物体内普遍存在的一类抗性(R)蛋白, 对植物的抗病性具有重要调控作用。该文综述了NLR蛋白结构、信号转导以及对植物抗病的调控作用近几年的研究进展。
杨程惠子,唐先宇,李威,夏石头. NLR及其在植物抗病中的调控作用. 植物学报, 2020, 55(4): 497-504.
Chenghuizi Yang,Xianyu Tang,Wei Li,Shitou Xia. NLR and Its Regulation on Plant Disease Resistance. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2020, 55(4): 497-504.
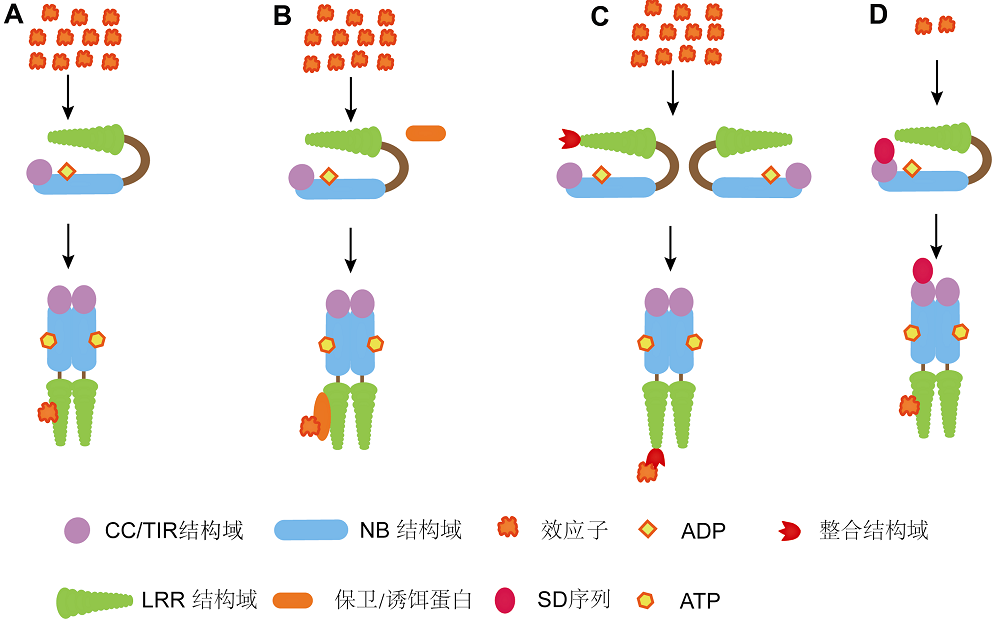
图1 NLRs的识别和激活模型 (A) 直接识别模型; (B) 保卫/诱饵模型; (C) 整合激活模型; (D) 微量识别模型
Figure 1 Models for recognition and activation of NLRs (A) Direct interaction model; (B) Guard/decoy model; (C) Integrated activation model; (D) Microrecognition model
| [1] | 夏石头, 李昕 (2019). 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体. 植物学报 54, 288-292. |
| [2] | Bent AF, Kunkel BN, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1994). RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265, 1856-1860. |
| [3] |
Bernoux M, Burdett H, Williams SJ, Zhang XX, Chen CH, Newell K, Lawrence GJ, Kobe B, Ellis JG, Anderson PA, Dodds PN (2016). Comparative analysis of the flax immune receptors L6 and L7 suggests an equilibrium- based switch activation model. Plant Cell 28, 146-159.
URL PMID |
| [4] | Boccara M, Sarazin A, Thiébeauld O, Jay F, Voinnet O, Navarro L, Colot V (2014). The Arabidopsis miR472- RDR6 silencing pathway modulates PAMP- and effector- triggered immunity through the post-transcriptional control of disease resistance genes. PLoS Pathog 10, e1003883. |
| [5] |
Canto-Pastor A, Santos BAMC, Valli AA, Summers W, Schornack S, Baulcombe DC (2019). Enhanced resistance to bacterial and oomycete pathogens by short tandem target mimic RNAs in tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 2755-2760.
URL PMID |
| [6] | Casey LW, Lavrencic P, Bentham AR, Cesari S, Ericsson DJ, Croll T, Turk D, Anderson PA, Mark AE, Dodds PN, Mobli M, Kobe B, Williams SJ (2016). The CC domain structure from the wheat stem rust resistance protein Sr33 challenges paradigms for dimerization in plant NLR proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 12856-12861. |
| [7] | Chang C, Yu DS, Jiao J, Jing SJ, Schulze-Lefert P, Shen QH (2013). Barley MLA immune receptors directly interfere with antagonistically acting transcription factors to initiate disease resistance signaling. Plant Cell 25, 1158-1173. |
| [8] | Copeland C, Ao K, Huang Y, Tong M, Li X (2016a). The evolutionarily conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase AtCHIP contributes to plant immunity. Front Plant Sci 7, 309. |
| [9] |
Copeland C, Woloshen V, Huang Y, Li X (2016b). AtCDC48A is involved in the turnover of an NLR immune receptor. Plant J 88, 294-305.
URL PMID |
| [10] | Cui XX, Yan Q, Gan SP, Xue D, Dou DL, Guo N, Xing H (2017). Overexpression of gma-miR1510a/b suppresses the expression of a NB-LRR domain gene and reduces resistance to Phytophthora sojae. Gene 621, 32-39. |
| [11] |
Deng YT, Wang JB, Tung J, Liu D, Zhou YJ, He S, Du YL, Baker B, Li F (2018). A role for small RNA in regulating innate immunity during plant growth. PLoS Pathog 14, e1006756.
URL PMID |
| [12] |
El Kasmi F, Chung EH, Anderson RG, Li JY, Wan L, Eitas TK, Gao ZY, Dangl JL (2017). Signaling from the plasma-membrane localized plant immune receptor RP- M1 requires self-association of the full-length protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E7385-E7394.
URL PMID |
| [13] |
El Kasmi F, Nishimura MT (2016). Structural insights into plant NLR immune receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 12619-12621.
DOI URL PMID |
| [14] |
Espinas NA, Saze H, Saijo Y (2016). Epigenetic control of defense signaling and priming in plants. Front Plant Sci 7, 1201.
URL PMID |
| [15] | Fujisaki K, Abe Y, Ito A, Saitoh H, Yoshida K, Kanzaki H, Kanzaki E, Utsushi H, Yamashita T, Kamoun S, Terauchi R (2015). Rice Exo70 interacts with a fungal effector, AVR-Pii, and is required for AVR-Pii-triggered immunity. Plant J 83, 875-887. |
| [16] | Gou MY, Shi ZY, Zhu Y, Bao ZL, Wang GY, Hua J (2012). The F-box protein CPR1/CPR30 negatively regulates R protein SNC1 accumulation. Plant J 69, 411-420. |
| [17] | Halter T, Navarro L (2015). Multilayer and interconnected post-transcriptional and co-transcriptional control of plant NLRs. Curr Opin Plant Biol 26, 127-134. |
| [18] |
Horsefield S, Burdett H, Zhang XX, Manik MK, Shi Y, Chen J, Qi TC, Gilley J, Lai JS, Rank MX, Casey LW, Gu WX, Ericsson DJ, Foley G, Hughes RO, Bosanac T, von Itzstein M, Rathjen JP, Nanson JD, Boden M, Dry IB, Williams SJ, Staskawicz BJ, Coleman MP, Ve T, Dodds PN, Kobe B (2019). NAD+ cleavage activity by animal and plant TIR domains in cell death pathways. Science 365, 793-799.
URL PMID |
| [19] |
Huang S, Balgi A, Pan YP, Li M, Zhang XR, Du LL, Zhou M, Roberge M, Li X (2016a). Identification of methylosome components as negative regulators of plant immunity using chemical genetics. Mol Plant 9, 1620-1633.
URL PMID |
| [20] |
Huang S, Chen X, Zhong X, Li M, Ao K, Huang J, Li X (2016b). Plant TRAF proteins regulate NLR immune receptor turnover. Cell Host Microbe 19, 204-215.
URL PMID |
| [21] | Huang Y, Minaker S, Roth C, Huang S, Hieter P, Lipka V, Wiermer M, Li X (2014). An E4 ligase facilitates poly- ubiquitination of plant immune receptor resistance pro- teins in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26, 485-496. |
| [22] |
Johnson KCM, Xia ST, Feng XQ, Li X (2015). The chromatin remodeler SPLAYED negatively regulates SNC1- mediated immunity. Plant Cell Physiol 56, 1616-1623.
URL PMID |
| [23] |
Johnson KCM, Yu Y, Gao L, Eng RC, Wasteneys GO, Chen XM, Li X (2016). A partial loss-of-function mutation in an Arabidopsis RNA polymerase III subunit leads to pleiotropic defects. J Exp Bot 67, 2219-2230.
DOI URL PMID |
| [24] | Kadota Y, Shirasu K (2012). The HSP90 complex of plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823, 689-697. |
| [25] |
Kroj T, Chanclud E, Michel-Romiti C, Grand X, Morel JB (2016). Integration of decoy domains derived from protein targets of pathogen effectors into plant immune receptors is widespread. New Phytol 210, 618-626.
DOI URL PMID |
| [26] | Kud J, Zhao ZL, Du XR, Liu YL, Zhao Y, Xiao FM (2013). SGT1 interacts with the Prf resistance protein and is required for Prf accumulation and Prf-mediated defense signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431, 501-505. |
| [27] | Le TN, Miyazaki Y, Takuno S, Saze H (2015). Epigenetic regulation of intragenic transposable elements impacts gene transcription in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 43, 3911-3921. |
| [28] |
Leibman-Markus M, Pizarro L, Schuster S, Lin ZJD, Gershony O, Bar M, Coaker G, Avni A (2018). The intracellular nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptor (SlNRC4a) enhances immune signaling elicited by extra- cellular perception. Plant Cell Environ 41, 2313-2327.
DOI URL PMID |
| [29] |
Li J, Huang HN, Zhu M, Huang S, Zhang WH, Dinesh- Kumar SP, Tao XR (2019). A plant immune receptor adopts a two-step recognition mechanism to enhance viral effector perception. Mol Plant 12, 248-262.
URL PMID |
| [30] | Liu J, Cheng XL, Liu D, Xu WH, Wise R, Shen QH (2014). The miR9863 family regulates distinct Mla alleles in barley to attenuate NLR receptor-triggered disease resistance and cell-death signaling. PLoS Genet 10, e1004755. |
| [31] |
Mindrinos M, Katagiri F, Yu GL, Ausubel FM (1994). The A. thaliana disease resistance gene RPS2 encodes a protein containing a nucleotide-binding site and leucine- rich repeats. Cell 78, 1089-1099.
URL PMID |
| [32] |
Nishimura MT, Anderson RG, Cherkis KA, Law TF, Liu QL, Machius M, Nimchuk ZL, Yang L, Chung EH, El Kasmi F, Hyunh M, Osborne Nishimura E, Sondek JE, Dangl JL (2017). TIR-only protein RBA1 recognizes a pathogen effector to regulate cell death in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, E2053-E2062.
URL PMID |
| [33] |
Oh SK, Kwon SY, Choi D (2014). Rpi-blb2-mediated hypersensitive cell death caused by phytophthora infestans AVRblb2 requires SGT1, but not EDS1, NDR1, salicylic acid-, jasmonic acid-, or ethylene-mediated signaling. Plant Pathol J 30, 254-260.
URL PMID |
| [34] |
Ortiz D, de Guillen K, Cesari S, Chalvon V, Gracy J, Padilla A, Kroj T (2017). Recognition of the Magnaporthe oryzae effector AVR-Pia by the decoy domain of the rice NLR immune receptor RGA5. Plant Cell 29, 156-168.
URL PMID |
| [35] |
Padmanabhan MS, Ma SS, Burch-Smith TM, Czymmek K, Huijser P, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2013). Novel positive regulatory role for the SPL6 transcription factor in the N TIR-NB-LRR receptor-mediated plant innate immunity. PLoS Pathog 9, e1003235.
URL PMID |
| [36] |
Park CH, Shirsekar G, Bellizzi M, Chen SB, Songkumarn P, Xie X, Shi XT, Ning YS, Zhou B, Suttiviriya P, Wang M, Umemura K, Wang GL (2016). The E3 ligase APIP10 connects the effector AvrPiz-t to the NLR receptor Piz-t in rice. PLoS Pathog 12, e1005529.
DOI URL PMID |
| [37] |
Peiró A, Cañizares MC, Rubio L, López C, Moriones E, Aramburu J, Sánchez-Navarro J (2014). The movement protein (NSm) of tomato spotted wilt virus is the avirulence determinant in the tomato Sw-5 gene-based resistance. Mol Plant Pathol 15, 802-813.
URL PMID |
| [38] |
Qi D, DeYoung BJ, Innes RW (2012). Structure-function analysis of the coiled-coil and leucine-rich repeat domains of the RPS5 disease resistance protein. Plant Physiol 158, 1819-1832.
DOI URL PMID |
| [39] |
Qi D, Innes RW (2013). Recent advances in plant NLR structure, function, localization, and signaling. Front Immunol 4, 348.
URL PMID |
| [40] |
Schultink A, Qi TC, Lee A, Steinbrenner AD, Staskawicz B (2017). Roq1 mediates recognition of the Xanthomonas and Pseudomonas effector proteins XopQ and HopQ1. Plant J 92, 787-795.
DOI URL PMID |
| [41] | Slootweg E, Roosien J, Spiridon LN, Petrescu AJ, Tameling W, Joosten M, Pomp R, van Schaik C, Dees R, Borst JW, Smant G, Schots A, Bakker J, Goverse A (2010). Nucleocytoplasmic distribution is required for activation of resistance by the potato NB-LRR receptor Rx1 and is balanced by its functional domains. Plant Cell 22, 4195-4215. |
| [42] |
Tong M, Kotur T, Liang WW, Vogelmann K, Kleine T, Leister D, Brieske C, Yang SH, Lüdke D, Wiermer M, Zhang YL, Li X, Hoth S (2017). E3 ligase SAUL1 serves as a positive regulator of PAMP-triggered immunity and its homeostasis is monitored by immune receptor SOC3. New Phytol 215, 1516-1532.
URL PMID |
| [43] |
Tran DTN, Chung EH, Habring-Müller A, Demar M, Schwab R, Dangl JL, Weigel D, Chae E (2017). Activation of a plant NLR complex through heteromeric association with an autoimmune risk variant of another NLR. Curr Biol 27, 1148-1160.
URL PMID |
| [44] |
Tsuchiya T, Eulgem T (2013). An alternative polyadenylation mechanism coopted to the Arabidopsis RPP7 gene through intronic retrotransposon domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110, E3535-3543.
URL PMID |
| [45] |
van der Biezen EA, Jones JDG (1998). Plant disease- resistance proteins and the gene-for-gene concept. Trends Biochem Sci 23, 454-456.
DOI URL PMID |
| [46] |
Wan L, Essuman K, Anderson RG, Sasaki Y, Monteiro F, Chung EH, Osborne Nishimura E, DiAntonio A, Milbrandt J, Dangl JL, Nishimura MT (2019). TIR domains of plant immune receptors are NAD+-cleaving enzymes that promote cell death. Science 365, 799-803.
URL PMID |
| [47] |
Wang JZ, Hu MJ, Wang J, Qi JF, Han ZF, Wang GX, Qi YJ, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019a). Reconstitution and structure of a plant NLR resistosome conferring immunity. Science 364, eaav5870.
URL PMID |
| [48] | Wang JZ, Wang J, Hu MJ, Wu S, Qi JF, Wang GX, Han ZF, Qi YJ, Gao N, Wang HW, Zhou JM, Chai JJ (2019b). Ligand-triggered allosteric ADP release primes a plant NLR complex. Science 364, eaav5868. |
| [49] |
Wang T, Chang C, Gu C, Tang SY, Xie Q, Shen QH (2016). An E3 ligase affects the NLR receptor stability and immunity to powdery mildew. Plant Physiol 172, 2504-2515.
DOI URL PMID |
| [50] |
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994). The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78, 1101-1115.
DOI URL PMID |
| [51] |
Williams SJ, Sornaraj P, Decourcy-Ireland E, Menz RI, Kobe B, Ellis JG, Dodds PN, Anderson PA (2011). An autoactive mutant of the M flax rust resistance protein has a preference for binding ATP, whereas wild-type M protein binds ADP. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 24, 897-906.
URL PMID |
| [52] |
Xia ST, Cheng YT, Huang S, Win J, Soards A, Jinn TL, Jones JDG, Kamoun S, Chen S, Zhang YL, Li X (2013). Regulation of transcription of nucleotide-binding leucine- rich repeat-encoding genes SNC1 and RPP4 via H3K4 trimethylation. Plant Physiol 162, 1694-1705.
DOI URL PMID |
| [53] |
Xie Z, Yan BX, Shou JY, Tang J, Wang X, Zhai KR, Liu JY, Li Q, Luo MZ, Deng YW, He ZH (2019). A nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat receptor pair confers broad-spectrum disease resistance through physical association in rice. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 374, 20180308.
DOI URL PMID |
| [54] |
Xu F, Cheng YT, Kapos P, Huang Y, Li X (2014a). P-loop-dependent NLR SNC1 can oligomerize and activate immunity in the nucleus. Mol Plant 7, 1801-1804.
URL PMID |
| [55] |
Xu F, Kapos P, Cheng YT, Li M, Zhang YL, Li X (2014b). NLR-associating transcription factor bHLH84 and its paralogs function redundantly in plant immunity. PLoS Pathog 10, e1004312.
DOI URL PMID |
| [56] | Xu F, Xu SH, Wiermer M, Zhang YL, Li X (2012). The cyclin L homolog MOS12 and the MOS4-associated complex are required for the proper splicing of plant resistance genes. Plant J 70, 916-928. |
| [57] |
Xu F, Zhu CP, Cevik V, Johnson K, Liu YN, Sohn K, Jones JD, Holub EB, Li X (2015). Autoimmunity conferred by chs3-2D relies on CSA1, its adjacent TNL-encoding neighbour. Sci Rep 5, 8792.
DOI URL PMID |
| [58] | Yang XR, Yang F, Wang WQ, Lin GZ, Hu ZH, Han ZF, Qi YJ, Zhang LM, Wang JW, Sui SF, Chai JJ (2018). Structural basis for specific flagellin recognition by the NLR protein NAIP5. Cell Res 28, 35-47. |
| [59] |
Zhai KR, Deng YW, Liang D, Tang J, Liu J, Yan BX, Yin X, Lin H, Chen FD, Yang DY, Xie Z, Liu JY, Li Q, Zhang L, He ZH (2019). RRM transcription factors interact with NLRs and regulate broad-spectrum blast resistance in rice. Mol Cell 74, 996-1009.
DOI URL PMID |
| [60] | Zhang SX, Liu YH, Yu B (2014). PRL1, an RNA-binding protein, positively regulates the accumulation of miRNAs and siRNAs in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 10, e1004841. |
| [61] |
Zhang Y, Xia R, Kuang HH, Meyers BC (2016). The diversification of plant NBS-LRR defense genes directs the evolution of microRNAs that target them. Mol Biol Evol 33, 2692-2705.
URL PMID |
| [62] |
Zhang ZB, Liu YN, Huang H, Gao MH, Wu D, Kong Q, Zhang YL (2017). The NLR protein SUMM2 senses the disruption of an immune signaling MAP kinase cascade via CRCK3. EMBO Rep 18, 292-302.
DOI URL PMID |
| [63] |
Zhu ZH, Xu F, Zhang YX, Cheng YT, Wiermer M, Li X, Zhang YL (2010). Arabidopsis resistance protein SNC1 activates immune responses through association with a transcriptional corepressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 13960-13965.
URL PMID |
| [64] |
Zou BH, Sun Q, Zhang WL, Ding Y, Yang DL, Shi ZY, Hua J (2017). The Arabidopsis chromatin-remodeling factor CHR5 regulates plant immune responses and nucleosome occupancy. Plant Cell Physiol 58, 2202-2216.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 马亮, 杨永青, 郭岩. “后绿色革命”基因——助力培育“气候智能”作物新品种[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 489-498. |
| [2] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [3] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [4] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [5] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [6] | 覃磊, 彭志红, 夏石头. 植物NLR免疫受体的识别、免疫激活与信号调控[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 12-23. |
| [7] | 周俭民. 免疫信号轴揭示水稻与病原菌斗争的秘密[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(5): 513-515. |
| [8] | 崔晓敏, 季东超, 陈彤, 田世平. 类受体激酶FER调节植物与病原菌相互作用的分子机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 339-346. |
| [9] | 王伟, 唐定中. 两类免疫受体强强联手筑牢植物免疫防线[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 142-146. |
| [10] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东. 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 218-231. |
| [11] | 崔亚宁, 钱虹萍, 赵艳霞, 李晓娟. 模式识别受体的胞内转运及其在植物免疫中的作用[J]. 植物学报, 2020, 55(3): 329-339. |
| [12] | 张娜,刘秀霞,陈学森,吴树敬. 基于转录组分析鉴定苹果茉莉素响应基因[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 733-743. |
| [13] | 李伟滔, 贺闽, 陈学伟. ZmFBL41 Chang7-2: 玉米抗纹枯病的关键利器[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(5): 547-549. |
| [14] | 夏石头, 李昕. 开启防御之门: 植物抗病小体[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 288-292. |
| [15] | 胡孔琴, 丁兆军. 非TIR1受体依赖型激活生长素信号的新机制[J]. 植物学报, 2019, 54(3): 293-295. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||