

植物学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 651-658.DOI: 10.11983/CBB23106 cstr: 32102.14.CBB23106
收稿日期:2023-08-03
接受日期:2023-11-14
出版日期:2024-07-10
发布日期:2024-07-10
通讯作者:
*陈辉, 遗传学博士, 中山火炬职业技术学院讲师。主要研究方向为植物生长素信号转导, 具体包括非典型Aux/IAA蛋白的生物学功能及其作用机制、典型Aux/IAA蛋白的特异性降解机制、生长素调控植物根重力反应的信号转导机制。此外, 还从事酵母染色质环挤出的调控机制以及硒蛋白的生物合成等方面的研究工作。在Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America、Frontiers in Plant Science、ACS Chemical Neuroscience和Nature Communications等期刊发表学术论文10篇。E-mail: chenhui2@zstp.edu.cn; 刘斯穆, 遗传学博士, 深圳大学生命与海洋科学学院讲师。主要研究方向为植物逆境响应机制和植物激素信号转导机制。主持国家自然科学基金青年项目, 在Frontiers in Plant Science、Plant Cell、Plant Journal和ACS Chemical Neuroscience等期刊发表学术论文11篇。E-mail: liusm@szu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yuying Zhou1, Hui Chen2,*( ), Simu Liu1,*(
), Simu Liu1,*( )
)
Received:2023-08-03
Accepted:2023-11-14
Online:2024-07-10
Published:2024-07-10
Contact:
*E-mail: chenhui2@zstp.edu.cn; liusm@szu.edu.cn
摘要: 植物激素生长素调控植物生长发育及环境适应的多个过程, 包括胚胎发育、器官发生和向性生长等。生长素发挥生物学功能主要依赖于经典的TIR1/AFB-auxin-Aux/IAA-ARF信号转导途径。其中, 由4个保守结构域组成的典型Aux/IAA蛋白作为TIR1/AFB的共受体在生长素信号转导过程中发挥关键作用。然而, 近年来发现缺乏保守结构域的非典型Aux/IAA蛋白也参与生长素的应答与调控作用。该文从蛋白结构、生物学功能及参与生长素信号转导等方面综述了非典型Aux/IAA蛋白的研究进展, 探讨和展望了非典型Aux/IAA蛋白的研究方向。
周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658.
Yuying Zhou, Hui Chen, Simu Liu. Research Progress on Auxin Responsive Non-canonical Aux/IAA Proteins in Plants. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2024, 59(4): 651-658.
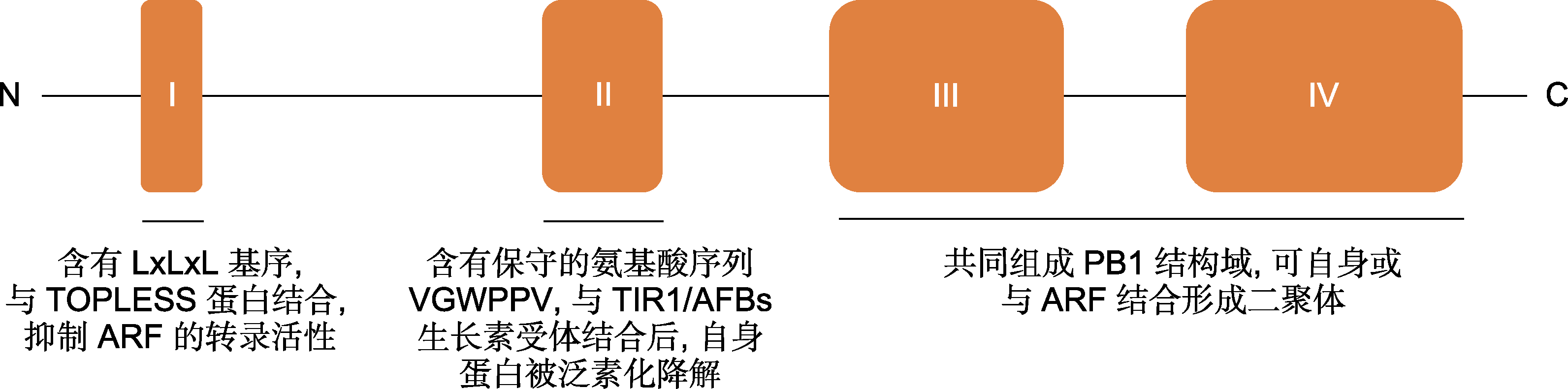
图1 典型Aux/IAA蛋白的功能结构域示意图(Tiwari et al., 2004; Szemenyei et al., 2008; Calderón Villalobos et al., 2012; Guilfoyle, 2015)
Figure 1 Functional domain diagram of canonical Aux/IAA protein (Tiwari et al., 2004; Szemenyei et al., 2008; Calderón Villalobos et al., 2012; Guilfoyle, 2015)
| 非典型Aux/ IAA蛋白 | 结构域I | 结构域II |
|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | ||
| AtIAA20 | SSSSSSIES | ···SVAAPAVEDAEYV |
| AtIAA30 | SSSSSSIES | ···EYDG··VGAAEEM |
| AtIAA31 | ········· | REARQDWPPIKSRLRD |
| AtIAA32 | NTPADFFKG | ELIDWSQPSYNSITQL |
| AtIAA33 | ········· | SSGAAG·RSFQGFGLN |
| AtIAA34 | PHPLHLVAS | GVIDLG·LSLRTIQHE |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | ||
| OsIAA4 | ········· | ················ |
| OsIAA8 | TDLRLGLTL | VVHIDGNNPSTPRSSL |
| OsIAA26 | TELTLGPPG | RGRKNGHPPPSSSM·· |
| OsIAA27 | ········· | DETTAPPPRSAAAATE |
| OsIAA28 | ········· | DRNASAGPEVKPAGLS |
| OsIAA29 | ········· | DRNASAEPVVKP·GLS |
表1 非典型Aux/IAA蛋白缺乏结构域I的LxLxL基序和/或结构域II的VGWPPV核心序列
Table 1 Non-canonical Aux/IAA proteins lack the LxLxL motif of domain I and/or the VGWPPV core amino acid resi- dues of domain II
| 非典型Aux/ IAA蛋白 | 结构域I | 结构域II |
|---|---|---|
| 拟南芥 (Arabidopsis thaliana) | ||
| AtIAA20 | SSSSSSIES | ···SVAAPAVEDAEYV |
| AtIAA30 | SSSSSSIES | ···EYDG··VGAAEEM |
| AtIAA31 | ········· | REARQDWPPIKSRLRD |
| AtIAA32 | NTPADFFKG | ELIDWSQPSYNSITQL |
| AtIAA33 | ········· | SSGAAG·RSFQGFGLN |
| AtIAA34 | PHPLHLVAS | GVIDLG·LSLRTIQHE |
| 水稻 (Oryza sativa) | ||
| OsIAA4 | ········· | ················ |
| OsIAA8 | TDLRLGLTL | VVHIDGNNPSTPRSSL |
| OsIAA26 | TELTLGPPG | RGRKNGHPPPSSSM·· |
| OsIAA27 | ········· | DETTAPPPRSAAAATE |
| OsIAA28 | ········· | DRNASAGPEVKPAGLS |
| OsIAA29 | ········· | DRNASAEPVVKP·GLS |
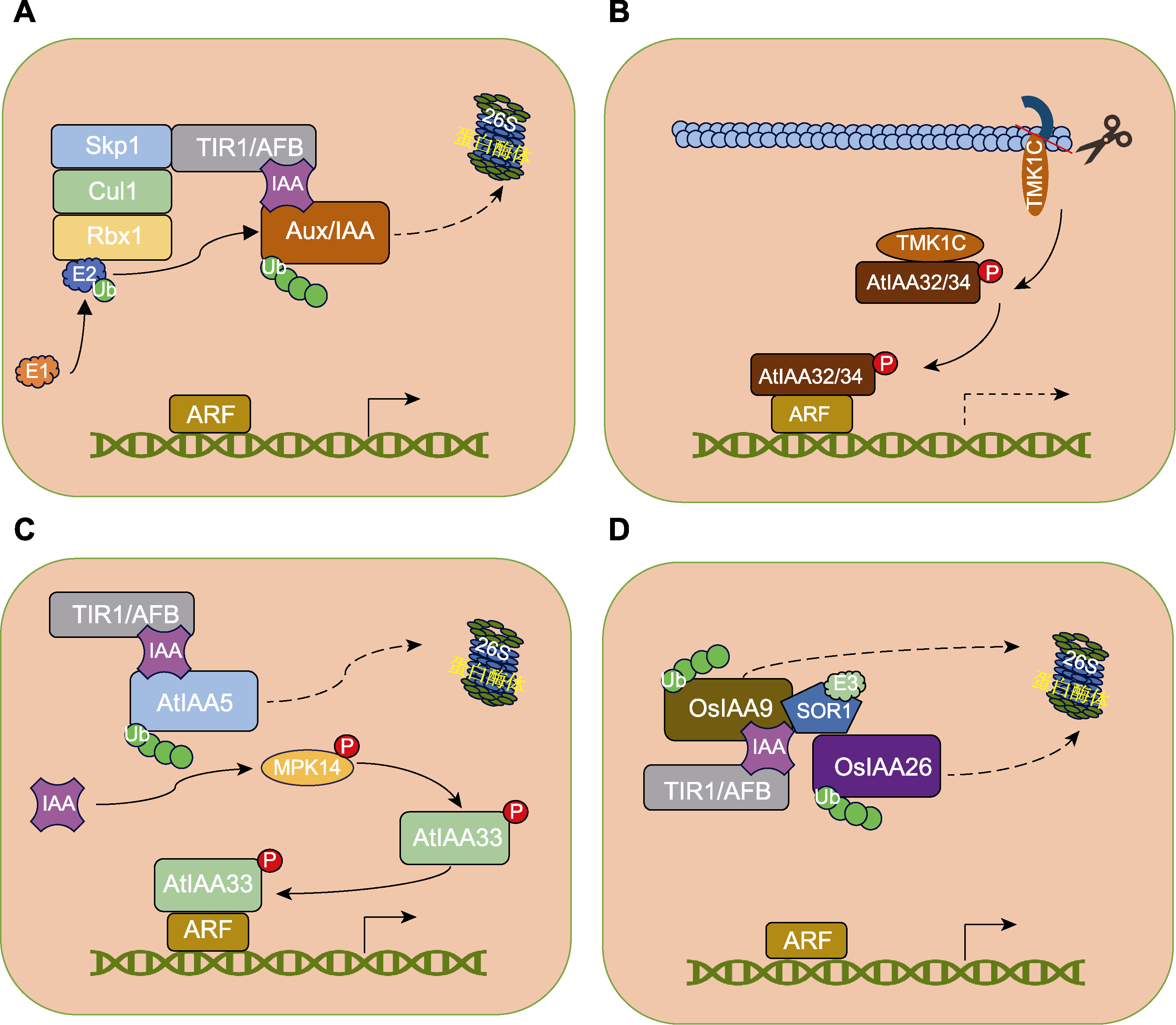
图2 Aux/IAA蛋白介导的生长素信号转导途径(Chen et al., 2018; Mutte et al., 2018; Cao et al., 2019; Lv et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2022) (A) 典型Aux/IAA蛋白介导的生长素信号转导途径; (B) 拟南芥TMK1-AtIAA32/34介导的生长素信号转导途径; (C) 拟南芥MPK14-AtIAA33介导的生长素信号转导途径; (D) 水稻SOR1-OsIAA26介导的生长素信号转导途径。
Figure 2 Aux/IAA-mediated auxin signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2018; Mutte et al., 2018; Cao et al., 2019; Lv et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2022) (A) Canonical Aux/IAA-mediated auxin signaling pathway; (B) TMK1-AtIAA32/34-mediated auxin signaling pathway in Arabidopsis; (C) MPK14-AtIAA33-mediated auxin signaling pathway in Arabidopsis; (D) SOR1-OsIAA26-mediated auxin signaling in rice.
| [1] |
Basunia MA, Nonhebel HM, Backhouse D, McMillan M (2021). Localised expression of OsIAA29 suggests a key role for auxin in regulating development of the dorsal aleurone of early rice grains. Planta 254, 40.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Béziat C, Kleine-Vehn J (2018). The road to auxin-dependent growth repression and promotion in apical hooks. Curr Biol 28, R519-R525. |
| [3] |
Calderón Villalobos LIA, Lee S, De Oliveira C, Ivetac A, Brandt W, Armitage L, Sheard LB, Tan X, Parry G, Mao HB, Zheng N, Napier R, Kepinski S, Estelle M (2012). A combinatorial TIR1/AFB-Aux/IAA co-receptor system for differential sensing of auxin. Nat Chem Biol 8, 477-485.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Cao M, Chen R, Li P, Yu YQ, Zheng R, Ge DF, Zheng W, Wang XH, Gu YT, Gelová Z, Friml J, Zhang H, Liu RY, He J, Xu TD (2019). TMK1-mediated auxin signaling regulates differential growth of the apical hook. Nature 568, 240-243. |
| [5] |
Chen H, Ma B, Zhou Y, He SJ, Tang SY, Lu X, Xie Q, Chen SY, Zhang JS (2018). E3 ubiquitin ligase SOR1 regulates ethylene response in rice root by modulating stability of Aux/IAA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 4513- 4518.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Estelle M (2005). The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. Nature 435, 441-445. |
| [7] | Ding ZJ, Friml J (2010). Auxin regulates distal stem cell differentiation in Arabidopsis roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107, 12046-12051. |
| [8] |
Dreher KA, Brown J, Saw RE, Callis J (2006). The Arabidopsis Aux/IAA protein family has diversified in degradation and auxin responsiveness. Plant Cell 18, 699-714.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Figueiredo MRA, Strader LC (2022). Intrinsic and extrinsic regulators of Aux/IAA protein degradation dynamics. Trends Biochem Sci 47, 865-874.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Friml J, Gallei M, Gelová Z, Johnson A, Mazur E, Monzer A, Rodriguez L, Roosjen M, Verstraeten I, Živanović BD, Zou MX, Fiedler L, Giannini C, Grones P, Hrtyan M, Kaufmann WA, Kuhn A, Narasimhan M, Randuch M, Rýdza N, Takahashi K, Tan ST, Teplova A, Kinoshita T, Weijers D, Rakusová H (2022). ABP1-TMK auxin perception for global phosphorylation and auxin canalization. Nature 609, 575-581. |
| [11] | Gray WM, Kepinski S, Rouse D, Leyser O, Estelle M (2001). Auxin regulates SCFTIR1-dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature 414, 271-276. |
| [12] | Guilfoyle TJ (2015). The PB1 domain in auxin response factor and Aux/IAA proteins: a versatile protein interaction module in the auxin response. Plant Cell 27, 33-43. |
| [13] | Han M, Park Y, Kim I, Kim EH, Yu TK, Rhee S, Suh JY (2014). Structural basis for the auxin-induced transcrip-tional regulation by Aux/IAA17. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 18613-18618. |
| [14] | Jain M, Kaur N, Garg R, Thakur JK, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP (2006). Structure and expression analysis of early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in rice (Oryza sati-va). Funct Integr Genomics 6, 47-59. |
| [15] | Jing HW, Yang XL, Emenecker RJ, Feng J, Zhang J, Chaisupa P, Wright RC, Holehouse AS, Strader LC, Zuo JR (2023). Nitric oxide-mediated S-nitrosylation of IAA17 protein in intrinsically disordered region represses auxin signaling. J Genet Genomics 50, 473-485. |
| [16] | Jing HW, Yang XL, Zhang J, Liu XH, Zheng HK, Dong GJ, Nian JQ, Feng J, Xia B, Qian Q, Li JY, Zuo JR (2015). Peptidyl-prolyl isomerization targets rice Aux/IAAs for proteasomal degradation during auxin signaling. Nat Com-mun 6, 7395. |
| [17] | Kepinski S, Leyser O (2005). The Arabidopsis F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. Nature 435, 446-451. |
| [18] | Li LX, Gallei M, Friml J (2022). Bending to auxin: fast acid growth for tropisms. Trends Plant Sci 27, 440-449. |
| [19] | Li YY, Qi YH (2022). Advances in biological functions of Aux/IAA gene family in plants. Chin Bull Bot 57, 30-41. (in Chinese) |
|
李艳艳, 齐艳华 (2022). 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展. 植物学报 57, 30-41.
DOI |
|
| [20] | Lin WW, Zhou X, Tang W, Takahashi K, Pan X, Dai JW, Ren H, Zhu XY, Pan SQ, Zheng HY, Gray WM, Xu TD, Kinoshita T, Yang ZB (2021). TMK-based cell-surface auxin signaling activates cell-wall acidification. Nature 599, 278-282. |
| [21] | Lv BS, Yu QQ, Liu JJ, Wen XJ, Yan ZW, Hu KQ, Li HB, Kong XP, Li CL, Tian HY, De Smet I, Zhang XS, Ding ZJ (2020). Non-canonical AUX/IAA protein IAA33 compe-tes with canonical AUX/IAA repressor IAA5 to negatively regulate auxin signaling. EMBO J 39, e101515. |
| [22] |
Mockaitis K, Estelle M (2008). Auxin receptors and plant development: a new signaling paradigm. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24, 55-80.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | Müller CJ, Valdés AE, Wang GD, Ramachandran P, Beste L, Uddenberg D, Carlsbecker A (2016). PHABULOSA mediates an auxin signaling loop to regulate vascular patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 170, 956-970. |
| [24] | Mutte SK, Kato H, Rothfels C, Melkonian M, Wong GKS, Weijers D (2018). Origin and evolution of the nuclear auxin response system. eLife 7, e33399. |
| [25] |
Nanao MH, Vinos-Poyo T, Brunoud G, Thévenon E, Mazzoleni M, Mast D, Lainé S, Wang SC, Hagen G, Li HB, Guilfoyle TJ, Parcy F, Vernoux T, Dumas R (2014). Structural basis for oligomerization of auxin transcriptional regulators. Nat Commun 5, 3617.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Park J, Kim YS, Kim SG, Jung JH, Woo JC, Park CM (2011). Integration of auxin and salt signals by the NAC transcription factor NTM2 during seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156, 537-549. |
| [27] | Piya S, Shrestha SK, Binder B, Stewart CN Jr, Hewezi T (2014). Protein-protein interaction and gene co-expression maps of ARFs and Aux/IAAs in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 5, 744. |
| [28] |
Reed JW (2001). Roles and activities of Aux/IAA proteins in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 6, 420-425.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Rouse D, Mackay P, Stirnberg P, Estelle M, Leyser O (1998). Changes in auxin response from mutations in an AUX/IAA gene. Science 279, 1371-1373.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | Salehin M, Bagchi R, Estelle M (2015). SCFTIR1/AFB-based auxin perception: mechanism and role in plant growth and development. Plant Cell 27, 9-19. |
| [31] | Sato A, Yamamoto KT (2008). Overexpression of the non-canonical Aux/IAA genes causes auxin-related aberrant phenotypes in Arabidopsis. Physiol Plant 133, 397- 405. |
| [32] |
Shimizu-Mitao Y, Kakimoto T (2014). Auxin sensitivities of all Arabidopsis Aux/IAAs for degradation in the presence of every TIR1/AFB. Plant Cell Physiol 55, 1450-1459.
DOI PMID |
| [33] | Song YL, Xu ZF (2013). Ectopic overexpression of an AUXIN/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID (Aux/IAA) gene OsIAA4 in rice induces morphological changes and reduces res-ponsiveness to auxin. Int J Mol Sci 14, 13645-13656. |
| [34] |
Szemenyei H, Hannon M, Long JA (2008). TOPLESS mediates auxin-dependent transcriptional repression during Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Science 319, 1384-1386.
DOI PMID |
| [35] | Tan X, Calderon-Villalobos LIA, Sharon M, Zheng CX, Robinson CV, Estelle M, Zheng N (2007). Mechanism of auxin perception by the TIR1 ubiquitin ligase. Nature 446, 640-645. |
| [36] | Teale WD, Paponov IA, Palme K (2006). Auxin in action: signaling, transport and the control of plant growth and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7, 847-859. |
| [37] | Teng ZN, Yu HH, Wang GQ, Meng S, Liu BH, Yi YK, Chen YK, Zheng Q, Liu L, Yang JC, Duan MJ, Zhang JH, Ye NH (2022). Synergistic interaction between ABA and IAA due to moderate soil drying promotes grain filling of infe-rior spikelets in rice. Plant J 109, 1457-1472. |
| [38] |
Tiwari SB, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (2004). Aux/IAA proteins contain a potent transcriptional repression domain. Plant Cell 16, 533-543.
DOI PMID |
| [39] |
Vain T, Raggi S, Ferro N, Barange DK, Kieffer M, Ma Q, Doyle SM, Thelander M, Pařízková B, Novák O, Ismail A, Enquist PA, Rigal A, Łangowska M, Ramans Harbo-rough S, Zhang Y, Ljung K, Callis J, Almqvist F, Kepinski S, Estelle M, Pauwels L, Robert S (2019). Selective auxin agonists induce specific AUX/IAA protein degradation to modulate plant development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 6463-6472.
DOI PMID |
| [40] |
Wang RH, Estelle M (2014). Diversity and specificity: auxin perception and signaling through the TIR1/AFB pathway. Curr Opin Plant Biol 21, 51-58.
DOI PMID |
| [41] |
Yu ZP, Zhang F, Friml J, Ding ZJ (2022). Auxin signaling: research advances over the past 30 years. J Integr Plant Biol 64, 371-392.
DOI |
| [42] | Zhong SW, Shi H, Xue C, Wei N, Guo HW, Deng XW (2014). Ethylene-orchestrated circuitry coordinates a seedling’s response to soil cover and etiolated growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 3913-3920. |
| [1] | 马亮, 杨永青, 郭岩. “后绿色革命”基因——助力培育“气候智能”作物新品种[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 489-498. |
| [2] | 冯嘉谊, 练琚愉, 冯瑜莙, 张东旭, 曹洪麟, 叶万辉. 鼎湖山南亚热带常绿阔叶林群落垂直分层对群落结构及功能的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24306-. |
| [3] | 孔祥培, 张蒙悦, 丁兆军. 柳暗花明:胞外生长素信号感受的新突破[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(6): 861-865. |
| [4] | 园园, 恩和巴雅尔, 齐艳华. 植物GH3基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(5): 770-782. |
| [5] | 周淑瑶, 李建明, 毛娟. AtGH3.17调控拟南芥生长素和油菜素甾醇的响应[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 373-384. |
| [6] | 叶青, 闫晓燕, 陈慧泽, 冯金林, 韩榕. 氮掺杂石墨烯量子点对拟南芥主根生长方向的影响[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 623-634. |
| [7] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [8] | 李彬琪, 闫佳慧, 李豪, 辛伟, 田云鹤, 杨贞标, 唐文鑫. 黄瓜卷须缠绕过程中小G蛋白活性变化[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 299-307. |
| [9] | 贾利霞, 齐艳华. 生长素代谢、运输及信号转导调控水稻粒型研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 263-275. |
| [10] | 支添添, 周舟, 韩成云, 任春梅. PAD4突变加速拟南芥酪氨酸降解缺陷突变体sscd1的程序性细胞死亡[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(3): 288-298. |
| [11] | 李艳艳, 齐艳华. 植物Aux/IAA基因家族生物学功能研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 30-41. |
| [12] | 王静文, 王兴军, 马长乐, 李膨呈. 植物核糖体应激响应机制研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(1): 80-89. |
| [13] | 崔晓敏, 季东超, 陈彤, 田世平. 类受体激酶FER调节植物与病原菌相互作用的分子机制[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(3): 339-346. |
| [14] | 宋松泉, 刘军, 杨华, 张文虎, 张琪, 高家东. 细胞分裂素调控种子发育、休眠与萌发的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 218-231. |
| [15] | 林雨晴, 齐艳华. 生长素输出载体PIN家族研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2021, 56(2): 151-165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||