

植物学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (6): 733-743.DOI: 10.11983/CBB18235 cstr: 32102.14.CBB18235
收稿日期:2018-11-04
接受日期:2019-02-11
出版日期:2019-11-01
发布日期:2020-07-09
通讯作者:
陈学森,吴树敬
基金资助:
Na Zhang1,2,Xiuxia Liu1,Xuesen Chen1,*( ),Shujing Wu1,*(
),Shujing Wu1,*( )
)
Received:2018-11-04
Accepted:2019-02-11
Online:2019-11-01
Published:2020-07-09
Contact:
Xuesen Chen,Shujing Wu
摘要: 为阐明外源茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)诱导的苹果(Malus domestica)抗病分子机制, 以生长30天的Gala组培苗为试材, 用100 μmol∙L -1MeJA处理叶片12小时, 通过转录组测序, 结合生物信息学分析鉴定出苹果叶片中受MeJA诱导表达的基因。结果表明, 外源MeJA主要影响苹果叶片倍半萜类、三萜和类黄酮的生物合成, 以及芸薹素(BR)信号转导途径间接诱导的抗病性; 倍半萜类、三萜及类黄酮生物合成途径中的关键基因为MDP0000702120和MDP0000692178; MDP0000123379是联系芸薹素信号转导途径和植物-病原菌互作途径的关键调控基因。
张娜,刘秀霞,陈学森,吴树敬. 基于转录组分析鉴定苹果茉莉素响应基因. 植物学报, 2019, 54(6): 733-743.
Na Zhang,Xiuxia Liu,Xuesen Chen,Shujing Wu. Identifying Genes Responsive to Jasmonates in Apple Based on Transcriptome Analysis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2019, 54(6): 733-743.
| Sample | Total reads | Total base pairs | Total mapped reads | Perfect match | Mismatch | Unique match | Muti-position match | Total unmapped reads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL1 | 15336268 (100.00%) | 751477132 (100.00%) | 10932142 (71.28%) | 6783455 (44.23%) | 4148687 (27.05%) | 9149425 (59.66%) | 1782717 (11.62%) | 4404126 (28.72%) |
| MeJA | 15339040 (100.00%) | 751612960 (100.00%) | 11052987 (72.06%) | 6921067 (45.12%) | 4131920 (26.94%) | 9177064 (59.83%) | 1875923 (12.23%) | 4286053 (27.94%) |
表1 供试样品(Gala)与苹果(金冠)基因组序列的比对结果
Table 1 The alignment result of genome sequences between sample (Gala) and Golden Delicious apple
| Sample | Total reads | Total base pairs | Total mapped reads | Perfect match | Mismatch | Unique match | Muti-position match | Total unmapped reads |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL1 | 15336268 (100.00%) | 751477132 (100.00%) | 10932142 (71.28%) | 6783455 (44.23%) | 4148687 (27.05%) | 9149425 (59.66%) | 1782717 (11.62%) | 4404126 (28.72%) |
| MeJA | 15339040 (100.00%) | 751612960 (100.00%) | 11052987 (72.06%) | 6921067 (45.12%) | 4131920 (26.94%) | 9177064 (59.83%) | 1875923 (12.23%) | 4286053 (27.94%) |
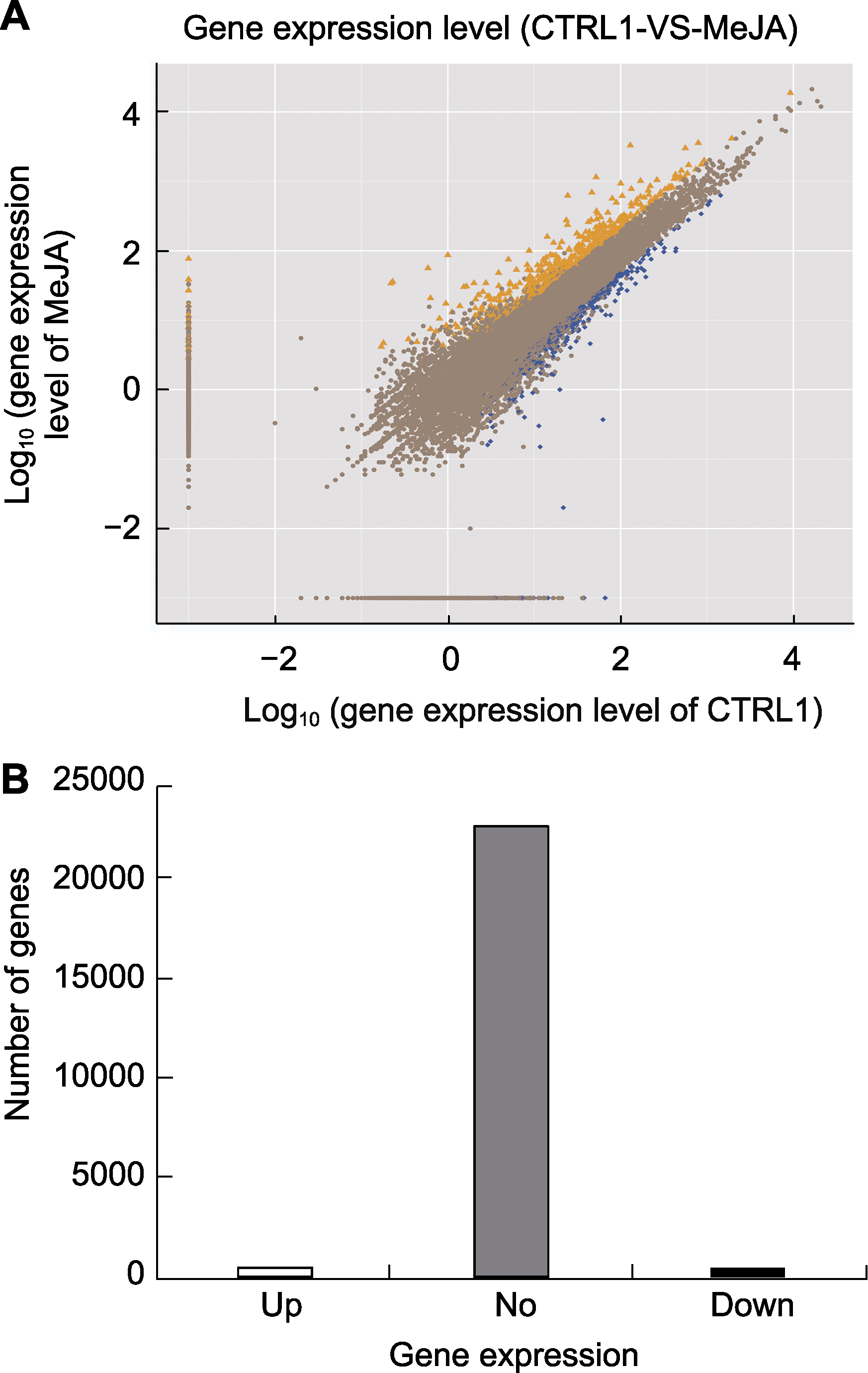
图1 茉莉酸甲酯处理下苹果叶片差异表达基因筛选 (A) 基因表达水平。横坐标表示CTRL1基因表达量的对数值, 纵坐标表示MeJA处理基因表达量的对数值(橙色三角代表上调基因, 蓝色方块代表下调基因, 褐色圆点代表非显著差异基因); (B) 基因差异表达情况。Up: 上调基因; No: 非显著差异表达基因; Down: 下调基因
Figure 1 The screening of differentially expressed genes in leaves of apple treated by MeJA (A) Gene expression level. X-axis represents log10 (gene expression level of CTRL1), Y-axis represents log10 (gene expression level of MeJA) (The orange triangle represents up-regulated genes, the blue block represents down-regu- lated genes, and the brown dot represents no significant difference genes); (B) Differentially expressed genes. Up: Up-regulated genes; No: No significant difference genes; Down: Down-regulated genes
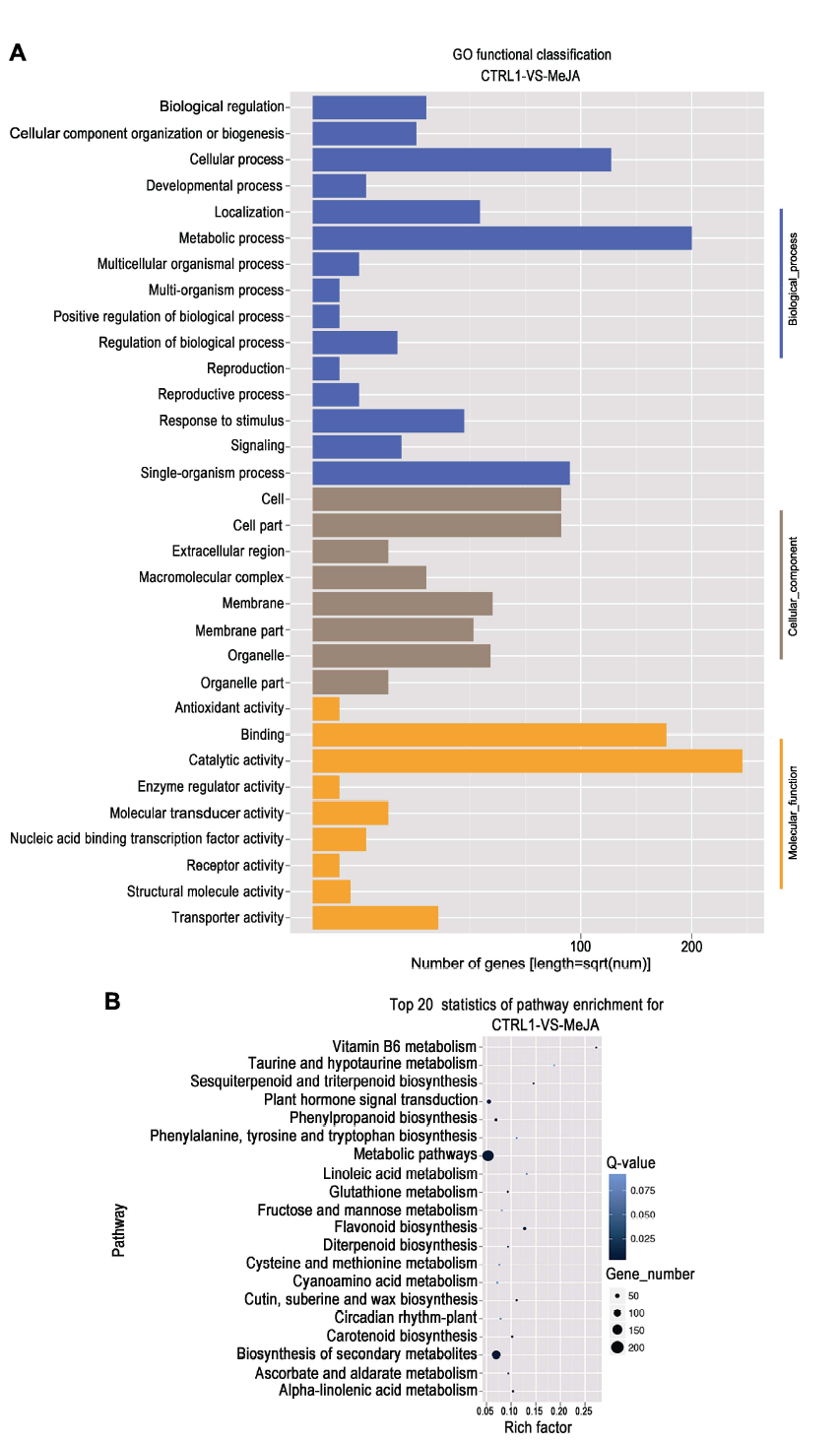
图2 茉莉酸甲酯处理苹果叶片差异表达基因的GO功能分类(A)和KEGG富集分析(B)
Figure 2 GO functional classification (A) and KEGG enrichment classification (B) of differentially expressed genes in apple leaves under MeJA treatment
| Gene ID | Log2 ratio (MeJA/CTRL1) | KEGG orthology | Blast nr | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDP0000702120 | 12.32 | K14181 | (-)-alpha-pinene synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000205617 | 7.28 | K14181 | Putative pinene synthase | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000919962 | 6.57 | K14181 | (-)-alpha-pinene synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000225361 | 3.72 | K14181 | (-)-germacrene D synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000248152 | 3.24 | K14181 | (-)-germacrene D synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000692178 | 12.12 | K00517 | Cytochrome P450 82G1-like | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000503940 | 4.67 | K05277 | Protein SRG1-like | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000225939 | 3.55 | K05277 | Flavonol synthase/flavanone 3-hydroxylase-like | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000523477 | -3.17 | K01859 | Chalcone-flavonone isomerase-like isoform X5 | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000317152 | 13.53 | K13407 | Cytochrome P450 94C1-like | Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis |
| MDP0000153822 | 3.25 | K13407 | Cytochrome P450 94B3-like | Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis |
| MDP0000218691 | 3.89 | K01183 | Acidic endochitinase-like | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism |
| MDP0000280265 | 3.22 | K01183 | Acidic endochitinase-like | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism |
| MDP0000687619 | 12.96 | K09755 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12-like | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000539956 | 3.9 | K09755 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12-like | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000313394 | 6.44 | K13267 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12-like | Isoflavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000813805 | -6.29 | K09840 | 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase NCED3, chloroplastic-like | Carotenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000228070 | -5.24 | K09840 | 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase NCED1, chloroplastic-like | Carotenoid biosynthesis |
Table 2 The regulated genes involved in biosynthesis of secondary metabolites pathway of apple leaves under MeJA treatment (Log2 (MeJA/CTRL)≥3)
| Gene ID | Log2 ratio (MeJA/CTRL1) | KEGG orthology | Blast nr | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDP0000702120 | 12.32 | K14181 | (-)-alpha-pinene synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000205617 | 7.28 | K14181 | Putative pinene synthase | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000919962 | 6.57 | K14181 | (-)-alpha-pinene synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000225361 | 3.72 | K14181 | (-)-germacrene D synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000248152 | 3.24 | K14181 | (-)-germacrene D synthase-like | Sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000692178 | 12.12 | K00517 | Cytochrome P450 82G1-like | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000503940 | 4.67 | K05277 | Protein SRG1-like | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000225939 | 3.55 | K05277 | Flavonol synthase/flavanone 3-hydroxylase-like | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000523477 | -3.17 | K01859 | Chalcone-flavonone isomerase-like isoform X5 | Flavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000317152 | 13.53 | K13407 | Cytochrome P450 94C1-like | Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis |
| MDP0000153822 | 3.25 | K13407 | Cytochrome P450 94B3-like | Cutin, suberine and wax biosynthesis |
| MDP0000218691 | 3.89 | K01183 | Acidic endochitinase-like | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism |
| MDP0000280265 | 3.22 | K01183 | Acidic endochitinase-like | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism |
| MDP0000687619 | 12.96 | K09755 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12-like | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000539956 | 3.9 | K09755 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12-like | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000313394 | 6.44 | K13267 | Cytochrome P450 CYP736A12-like | Isoflavonoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000813805 | -6.29 | K09840 | 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase NCED3, chloroplastic-like | Carotenoid biosynthesis |
| MDP0000228070 | -5.24 | K09840 | 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase NCED1, chloroplastic-like | Carotenoid biosynthesis |
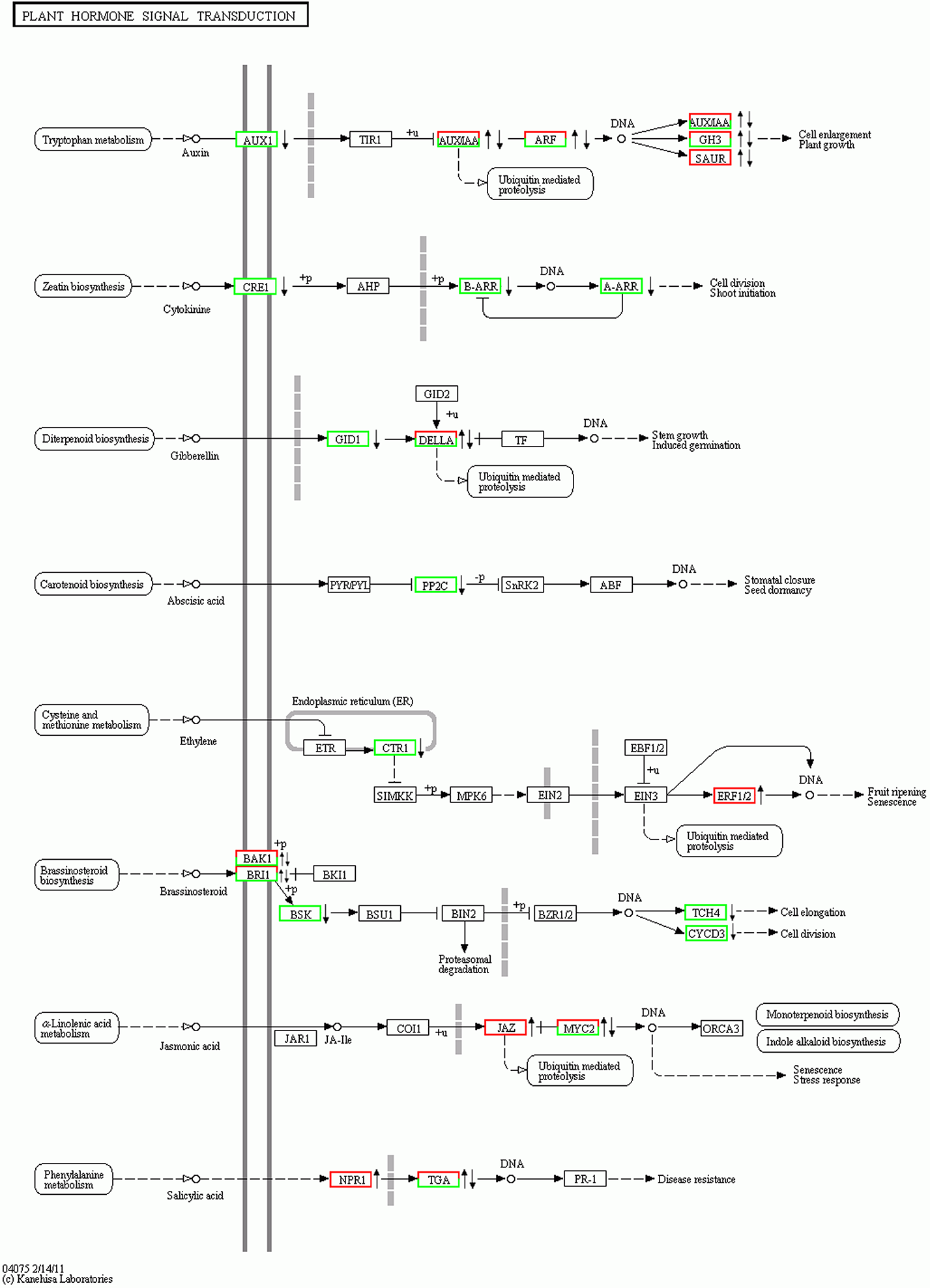
图3 茉莉酸甲酯处理对苹果叶片植物激素信号转导途径的影响 红色边框右侧: 上调; 绿色边框右侧: 下调; 红绿色边框右侧: 同时包含上调和下调基因。
Figure 3 Effect of MeJA on plant hormone signaling pathways in leaves of apple on the right side of red frame: Up-regulated; on the right side of green frame: Down-regulated; on the right side of red-green frame: Include both up-regulated and down-regulated genes.
| Plant hormone signaling pathway | Gene ID | Log2 ratio (MeJA/CTRL1) |
|---|---|---|
| Auxin | MDP0000300452 | -1.4 |
| MDP0000255223 MDP0000213864 | 1.1 -1.1 | |
| MDP0000143749 MDP0000221322 | 1.3 -1.6 | |
| MDP0000873893 MDP0000214081 | 1.5 -1.1 | |
| MDP0000786165 | 1.1 | |
| Cytokinine | MDP0000146863 | -1.1 |
| MDP0000285242 MDP0000225179 | 1.6 -1.0 | |
| MDP0000250737 | -1.5 | |
| Gibberellin | MDP0000227827 MDP0000868088 | -1.3 -1.0 |
| MDP0000284679 MDP0000227056 MDP0000397638 | 1.4 1.3 -2.2 | |
| Abscisic acid | MDP0000437033 MDP0000203818 MDP0000283274 | -1.6 -1.3 -1.2 |
| Ethylene | MDP0000275915 | -2.4 |
| MDP0000855671 MDP0000127134 MDP0000235313 MDP0000805422 MDP0000787281 | 3.1 2.5 1.8 1.2 1.0 | |
| Brassinosteroid | MDP0000123379 MDP0000319460 MDP0000319708 MDP0000904826 MDP0000196862 | 12.5 1.9 1.0 1.0 -1.8 |
| MDP0000217213 MDP0000897962 MDP0000290950 MDP0000620422 MDP0000303744 MDP0000189315 MDP0000741253 MDP0000223726 MDP0000189841 | 1.9 1.3 -2.3 -1.8 -1.6 -1.1 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 | |
| MDP0000130143 | -12.8 | |
| MDP0000320017 | -1.4 | |
| MDP0000135392 | -1.0 | |
| Jasmonic acid | MDP0000565690 MDP0000187921 MDP0000889413 MDP0000301927 | 2.8 2.6 1.7 1.2 |
| MDP0000603546 MDP0000242554 MDP0000029168 MDP0000900024 MDP0000226497 MDP0000290263 | 3.6 2.2 1.6 1.6 1.0 -1.0 | |
| Salicylic acid | MDP0000292425 | 1.8 |
| MDP0000529682 MDP0000375992 | 1.1 -4.3 |
表3 茉莉酸甲酯处理苹果叶片植物激素信号转导途径中涉及的显著差异表达基因
Table 3 The significant differentially expressed genes involved in plant hormone signaling in leaves of apple under MeJA treatment
| Plant hormone signaling pathway | Gene ID | Log2 ratio (MeJA/CTRL1) |
|---|---|---|
| Auxin | MDP0000300452 | -1.4 |
| MDP0000255223 MDP0000213864 | 1.1 -1.1 | |
| MDP0000143749 MDP0000221322 | 1.3 -1.6 | |
| MDP0000873893 MDP0000214081 | 1.5 -1.1 | |
| MDP0000786165 | 1.1 | |
| Cytokinine | MDP0000146863 | -1.1 |
| MDP0000285242 MDP0000225179 | 1.6 -1.0 | |
| MDP0000250737 | -1.5 | |
| Gibberellin | MDP0000227827 MDP0000868088 | -1.3 -1.0 |
| MDP0000284679 MDP0000227056 MDP0000397638 | 1.4 1.3 -2.2 | |
| Abscisic acid | MDP0000437033 MDP0000203818 MDP0000283274 | -1.6 -1.3 -1.2 |
| Ethylene | MDP0000275915 | -2.4 |
| MDP0000855671 MDP0000127134 MDP0000235313 MDP0000805422 MDP0000787281 | 3.1 2.5 1.8 1.2 1.0 | |
| Brassinosteroid | MDP0000123379 MDP0000319460 MDP0000319708 MDP0000904826 MDP0000196862 | 12.5 1.9 1.0 1.0 -1.8 |
| MDP0000217213 MDP0000897962 MDP0000290950 MDP0000620422 MDP0000303744 MDP0000189315 MDP0000741253 MDP0000223726 MDP0000189841 | 1.9 1.3 -2.3 -1.8 -1.6 -1.1 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 | |
| MDP0000130143 | -12.8 | |
| MDP0000320017 | -1.4 | |
| MDP0000135392 | -1.0 | |
| Jasmonic acid | MDP0000565690 MDP0000187921 MDP0000889413 MDP0000301927 | 2.8 2.6 1.7 1.2 |
| MDP0000603546 MDP0000242554 MDP0000029168 MDP0000900024 MDP0000226497 MDP0000290263 | 3.6 2.2 1.6 1.6 1.0 -1.0 | |
| Salicylic acid | MDP0000292425 | 1.8 |
| MDP0000529682 MDP0000375992 | 1.1 -4.3 |
| Gene ID | Log2 ratio (MeJA/CTRL) | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| MDP0000123379 | 12.46 | Putative serine/threonine- protein kinase |
| MDP0000603546 | 3.56 | Transcription factor MYC2- like |
| MDP0000855671 | 3.1 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 1B-like |
| MDP0000130143 | -12.82 | Probable serine/threonine- protein kinase At5g41260 |
| MDP0000375992 | -4.27 | U-box domain-containing protein 19-like |
表4 茉莉酸甲酯处理苹果叶片次生代谢途径中的调控基因(Log2 (MeJA/CTRL)≥3)
Table 4 The regulated genes involved in biosynthesis of secondary metabolites pathway in leaves of apple under MeJA treatment (Log2 (MeJA/CTRL)≥3)
| Gene ID | Log2 ratio (MeJA/CTRL) | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| MDP0000123379 | 12.46 | Putative serine/threonine- protein kinase |
| MDP0000603546 | 3.56 | Transcription factor MYC2- like |
| MDP0000855671 | 3.1 | Ethylene-responsive transcription factor 1B-like |
| MDP0000130143 | -12.82 | Probable serine/threonine- protein kinase At5g41260 |
| MDP0000375992 | -4.27 | U-box domain-containing protein 19-like |
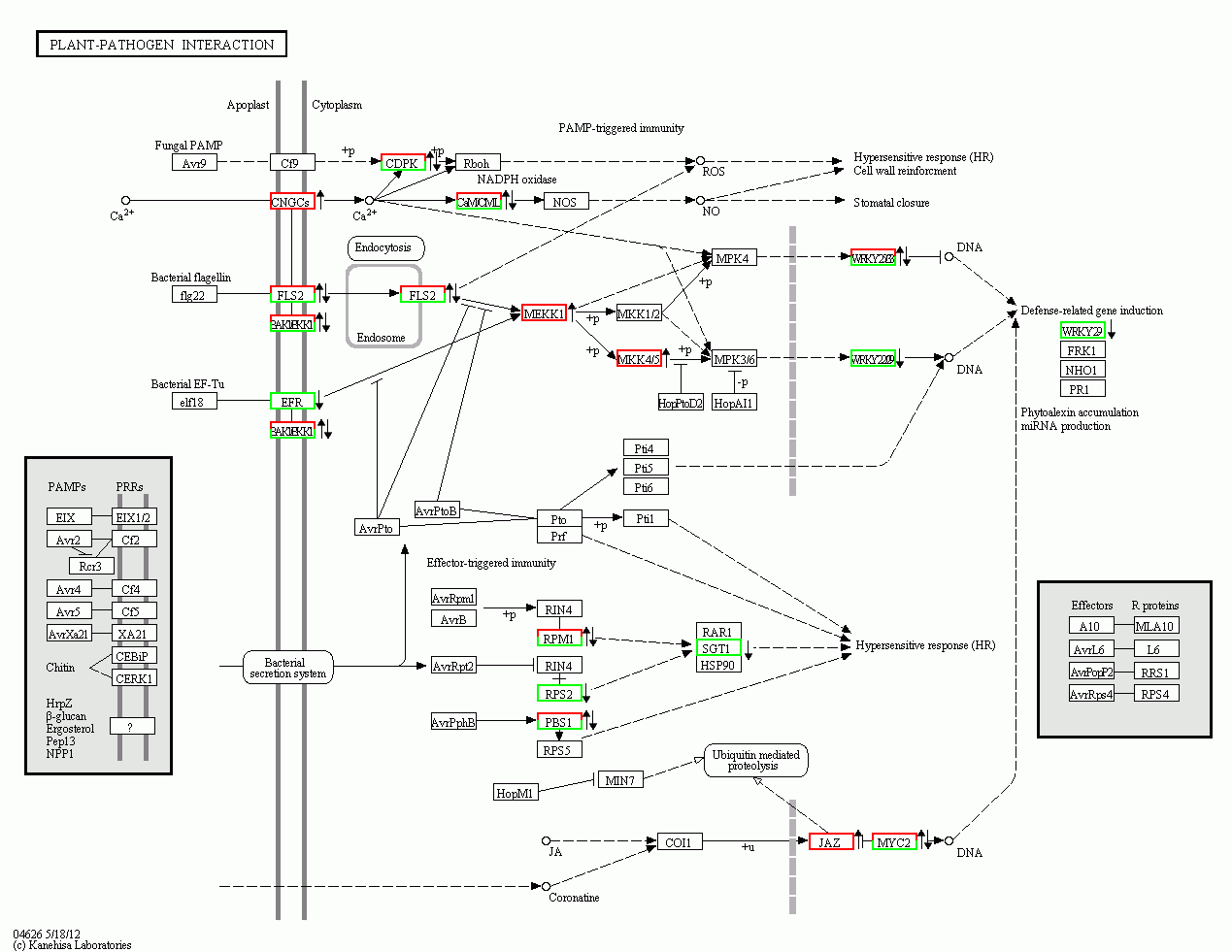
图4 茉莉酸甲酯处理对苹果叶片植物-病原菌互作途径的影响 红色边框右侧: 上调; 绿色边框右侧: 下调; 红绿色边框右侧: 同时包含上调和下调基因。
Figure 4 Effect of MeJA on plant-pathogen interaction pathway in leaves of apple on the right side of red frame: Up-regulated; on the right side of green frame: Down-regulated; on the right side of red-green frame: Include both up-regulated and down-regulated genes.
| [1] | 宾金华, 潘瑞炽 ( 1995). 茉莉酸甲酯的生理生化及在植物抗病中的作用. 植物学通报 12(4), 17-21. |
| [2] | 陈学森, 郭文武, 徐娟, 从佩华, 王力荣, 刘崇怀, 李秀根, 吴树敬, 姚玉新, 陈晓流 ( 2015). 主要果树果实品质遗传改良与提升实践. 中国农业科学 48, 3524-3540. |
| [3] | 弓德强, 谷会, 张鲁斌, 洪克前, 朱世江 ( 2013). 杧果采前喷施茉莉酸甲酯对其抗病性和采后品质的影响. 园艺学报 40, 49-57. |
| [4] | 国立耘, 李金云, 李保华, 张新忠, 周增强, 李广旭, 王英姿, 李晓军, 黄丽丽, 孙广宇, 文耀东 ( 2009). 中国苹果枝干轮纹病发生和防治情况. 植物保护 35(4), 120-123. |
| [5] | 李灿婴, 葛永红, 朱丹实, 张惠君 ( 2015). 采后茉莉酸甲酯处理对富士苹果青霉病和贮藏品质的影响. 食品科学 36(2), 255-259. |
| [6] | 李梦莎, 阎秀峰 ( 2014). 植物的环境信号分子茉莉酸及其生物学功能. 生态学报 34, 6779-6788. |
| [7] | 刘志, 张华磊, 谢兴斌, 束怀瑞, 郝玉金 ( 2009). 茉莉酸甲酯诱导的苹果悬浮细胞的防卫响应. 园艺学报 36, 171-178. |
| [8] | 罗昌国, 袁启凤, 裴晓红, 吴亚维, 郑伟, 章镇 ( 2013). 富士苹果MdWRKY40b基因克隆及其对白粉病的抗性分析. 西北植物学报 33, 2382-2387. |
| [9] | 麻宝成, 朱世江 ( 2006). 苯丙噻重氮和茉莉酸甲酯对采后香蕉果实抗病性及相关酶活性的影响. 中国农业科学 39, 1220-1227. |
| [10] | 汪开拓, 郑永华, 唐文才, 李廷君, 张卿, 尚海涛 ( 2012). 茉莉酸甲酯处理对葡萄果实NO和H2O2水平及植保素合成的影响. 园艺学报 39, 1559-1566. |
| [11] | 王英珍, 程瑞, 张绍铃, 白彬, 何子顺, 张虎平 ( 2016). 采前茉莉酸甲酯(MeJA)处理对梨果实抗病性的影响. 果树学报 33, 694-700. |
| [12] | 许晴晴, 郜海燕, 陈杭君 ( 2014). 茉莉酸甲酯对蓝莓贮藏品质及抗病相关酶活性的影响. 核农学报 28, 1226-1231. |
| [13] | 张芮 ( 2015). 苹果MdWRKY33基因在轮纹病抗性形成中的作用机制研究. 博士论文. 泰安: 山东农业大学. pp. 70-73. |
| [14] | Chen XK, Zhang JY, Zhang Z, Du XL, Du BB, Qu SC ( 2012). Overexpressing MhNPR1 in transgenic Fuji apples enhances resistance to apple powdery mildew. Mol Biol Rep 39, 8083-8089. |
| [15] | Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL ( 2009). Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10, R25. |
| [16] | Li H, Durbin R ( 2009). Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25, 1754-1760. |
| [17] | Sun X, Matus JT, Wong DCJ, Wang Z, Chai F, Zhang L, FangT, Zhao L, Wang Y, Han Y, Wang Q, Li S, Liang Z, Xin H ( 2018). The GARP/MYB-related grape transcription factor AQUILO improves cold tolerance and promotes the accumulation of raffinose family oligosaccharides. J Exp Bot 69, 1749-1764. |
| [18] | Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, Fontana P, Bhatnagar SK, Troggio M, Pruss D, Salvi S, Pindo M, Baldi P, Castelletti S, Cavaiuolo M, Coppola G, Costa F, Cova V, Dal Ri A, Goremykin V, Komjanc M, Longhi S, Magnago P, Malacarne G, Malnoy M, Micheletti D, Moretto M, Perazzolli M, Si-Ammour A, Vezzulli S, Zini E, Eldredge G, Fitzgerald LM, Gutin N, Lanchbury J, Macalma T, Mitchell JT, Reid J, Wardell B, Kodira C, Chen ZT, Desany B, Niazi F, Palmer M, Koepke T, Jiwan D, Schaeffer S, Krishnan V, Wu CJ, Chu VT, King ST, Vick J, Tao QZ, Mraz A, Stormo A, Stormo K, Bogden R, Ederle D, Stella A, Vecchietti A, Kater MM, Masiero S, Lasserre P, Lespinasse Y, Allan AC, Bus V, Chagné D, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, Lavezzo E, Fawcett JA, Proost S, Rouzé P, Sterck L, Toppo S, Lazzari B, Hellens RP, Durel CE, Gutin A, Bumgarner RE, Gardiner SE, Skolnick M, Egholm M, Van de Peer Y, Salamini F, Viola R ( 2010). The genome of the domesticated apple ( Malus × domestica Borkh.). Nat Genet 42, 833-839. |
| [19] | Xue YK, Shui GH, Wenk MR ( 2014). TPS1 drug design for rice blast disease in Magnaporthe oryzae. Springer Plus 3, 18. |
| [20] | Ye J, Fang L, Zheng HK, Zhang Y, Chen J, Zhang ZJ, Wang J, Li ST, Li RQ, Bolund L, Wang J ( 2006). WEGO: a web tool for plotting GO annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 34, W293-W297. |
| [21] | Zhang HY, Ma LC, Turner M, Xu HX, Dong Y, Jiang S ( 2009). Methyl jasmonate enhances biocontrol efficacy of Rhodotorula glutinis to postharvest blue mold decay of pears. Food Chem 117, 621-626. |
| [22] | Zhang Y, Shi XP, Li BH, Zhang QM, Liang WX, Wang CX ( 2016). Salicylic acid confers enhanced resistance to Glomerella leaf spot in apple. Plant Physiol Biochem 106, 64-72. |
| [1] | 王秀媛, 申磊, 刘婷婷, 尉雯雯, 张帅, 张伟. ‘塞外红’苹果-大豆复合系统根系时空分布与种间竞争策略[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(5): 748-759. |
| [2] | 马亮, 杨永青, 郭岩. “后绿色革命”基因——助力培育“气候智能”作物新品种[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(4): 489-498. |
| [3] | 张向歌, 陈晨, 程珊, 李春鑫, 朱雅婧, 许欣然, 王会伟. 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因鉴定及分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 33-48. |
| [4] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [5] | 周玉滢, 陈辉, 刘斯穆. 植物非典型Aux/IAA蛋白应答生长素研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(4): 651-658. |
| [6] | 蒋海港, 曾云鸿, 唐华欣, 刘伟, 李杰林, 何国华, 秦海燕, 王丽超, 姚银安. 三种藓类植物固碳耗水节律调节作用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(7): 988-997. |
| [7] | 吴楠, 覃磊, 崔看, 李海鸥, 刘忠松, 夏石头. 甘蓝型油菜EXA1的克隆及其对植物抗病的调控作用[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 385-393. |
| [8] | 王钢, 王二涛. “卫青不败由天幸”——WeiTsing的广谱抗根肿病机理被揭示[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(3): 356-358. |
| [9] | 白雪, 李玉靖, 景秀清, 赵晓东, 畅莎莎, 荆韬羽, 刘晋汝, 赵鹏宇. 谷子及其根际土壤微生物群落对铬胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(3): 418-433. |
| [10] | 路晨曦, 徐漫, 石学瑾, 赵成, 陶泽, 李敏, 司炳成. 基于贝叶斯模型MixSIAR的不同水同位素输入方法对苹果园吸水特征分析结果的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(2): 238-248. |
| [11] | 肖宇彬, 张子旭, 王玉珠, 刘欢, 陈乐天. 时空转录组研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 214-232. |
| [12] | 张宏祥, 闻志彬, 王茜. 新疆野苹果种群遗传结构及其环境适应性[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(9): 1098-1108. |
| [13] | 李聪, 齐立娟, 谷晓峰, 李继刚. 植物光信号途径重要新调控因子TZP的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 579-587. |
| [14] | 蔺海娇, 曲嘉琪, 刘祎男, 苑泽宁. 薰衣草叶片对低温胁迫的生理与分子响应机制[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(5): 611-622. |
| [15] | 李月, 胡德升, 谭金芳, 梅浩, 王祎, 李慧, 李芳, 韩燕来. 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解并调控激素响应基因表达促进玉米生长[J]. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 422-433. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||