

植物学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 57 ›› Issue (4): 422-433.DOI: 10.11983/CBB21147 cstr: 32102.14.CBB21147
李月1, 胡德升1, 谭金芳2, 梅浩1, 王祎1, 李慧1, 李芳1,*( ), 韩燕来1,*(
), 韩燕来1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-27
修回日期:2022-01-13
出版日期:2022-07-01
发布日期:2022-07-14
通讯作者:
李芳,韩燕来
作者简介:hylai@henau.edu.cn基金资助:
Li Yue1, Hu Desheng1, Tan Jinfang2, Mei Hao1, Wang Yi1, Li Hui1, Li Fang1,*( ), Han Yanlai1,*(
), Han Yanlai1,*( )
)
Received:2021-08-27
Revised:2022-01-13
Online:2022-07-01
Published:2022-07-14
Contact:
Li Fang,Han Yanlai
摘要: 为探究生防真菌单列毛壳菌(Chaetomium uniseriatum)对秸秆降解和玉米(Zea mays)生长的影响, 将单列毛壳菌接种到玉米盆栽土壤中, 其它条件不变, 以保证单一变量。于拔节期和抽雄期进行采样, 通过测定土壤有机碳、土壤可溶性碳/氮、微生物量碳/氮以及酶活性, 探究接种单列毛壳菌对土壤生物化学指标的影响。在抽雄期对秸秆降解率、地上部生物量、叶片SPAD值、玉米根系激素含量及根系转录组进行分析, 探究接种单列毛壳菌对秸秆降解和玉米植株生长发育的影响。结果表明, 接种单列毛壳菌后, 土壤养分含量未出现显著性变化, β-葡萄糖苷酶(β-GC)活性显著降低; 抽雄期玉米地上部生物量、叶片SPAD值以及秸秆降解率均显著高于对照组; 玉米根系生长激素(IAA)和玉米素(ZR)含量均显著低于对照组。不同处理下玉米根系转录组分析筛选得到990个差异表达基因(383个基因表达上调, 607个基因表达下调); 对差异基因进行GO富集分析, 得到5个植物激素相关的条目; KEGG富集分析得到1个与植物激素相关的通路(P value<0.05, Q value<0.05)。综上, 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解以及调控作物根系激素响应基因的表达, 进而促进玉米生长。
李月, 胡德升, 谭金芳, 梅浩, 王祎, 李慧, 李芳, 韩燕来. 单列毛壳菌通过促进秸秆降解并调控激素响应基因表达促进玉米生长. 植物学报, 2022, 57(4): 422-433.
Li Yue, Hu Desheng, Tan Jinfang, Mei Hao, Wang Yi, Li Hui, Li Fang, Han Yanlai. Chaetomium uniseriatum Promotes Maize Growth by Accelerating Straw Degradation and Regulating the Expression of Hormone Responsive Genes. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2022, 57(4): 422-433.
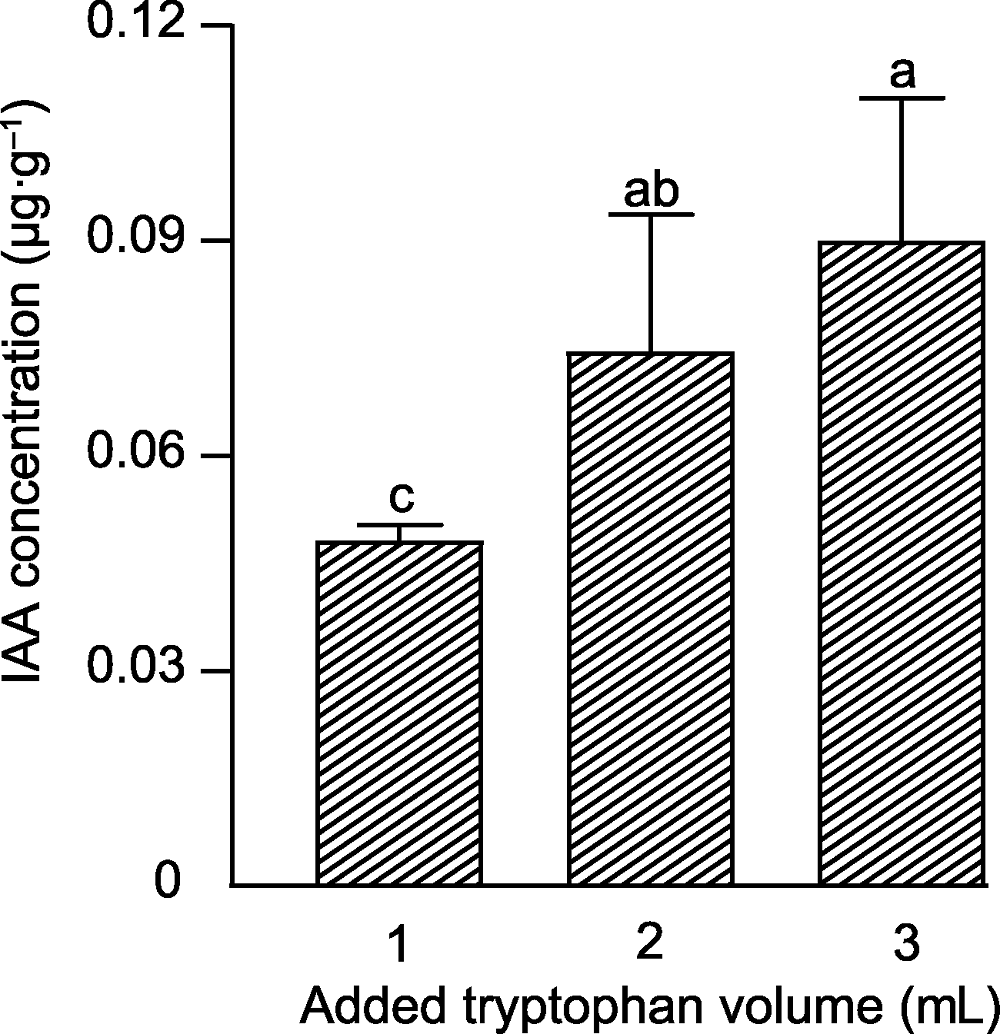
图1 不同浓度色氨酸条件下单列毛壳菌产生生长素(IAA)的浓度 不同小写字母表示在5%水平差异显著(n=4)。
Figure 1 The concentration of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) produced by Chaetomium uniseriatum with different concentrations of tryptophan Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences at 5% level (n=4).
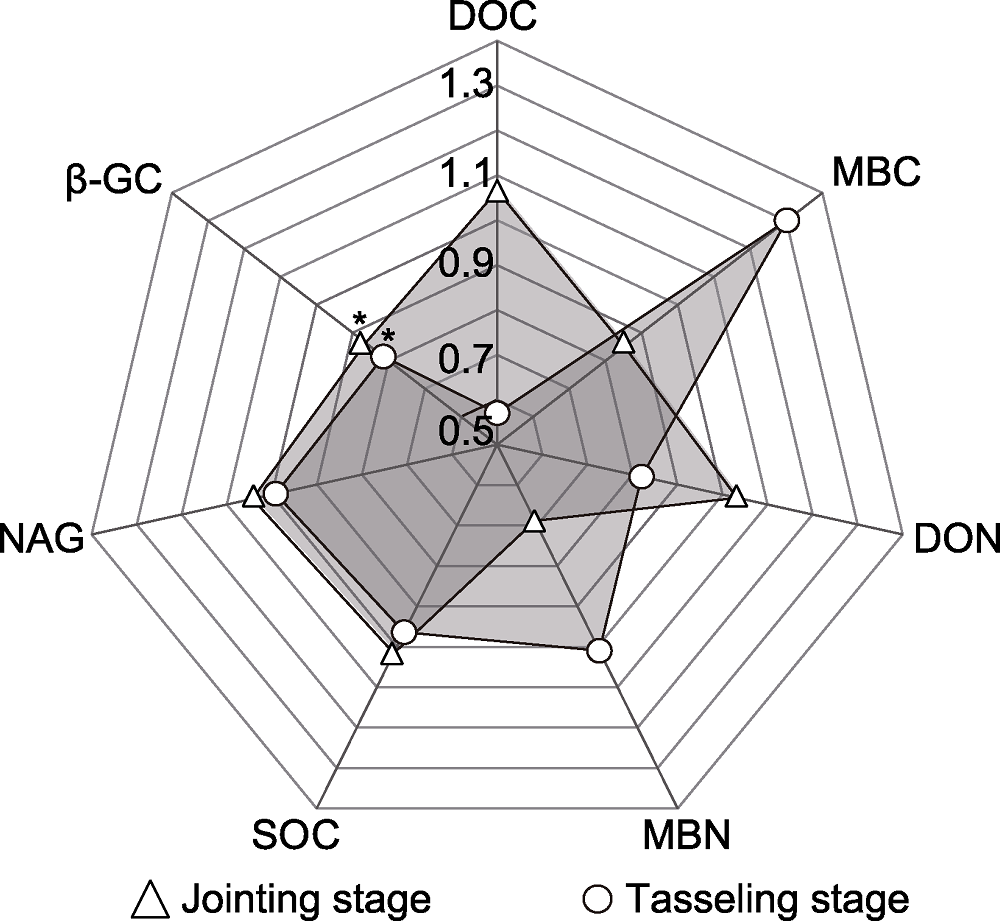
图2 不同时期土壤性质相对于对照的变化倍数 图中数值为土壤性质相对于对照的变化倍数, * 表示在5%水平差异显著。DOC: 可溶性碳; MBC: 微生物量碳; DON: 可溶性氮; MBN: 微生物量氮; NAG: N-乙酰-β,D-氨基葡萄糖苷酶; β-GC: β-葡萄糖苷酶; SOC: 土壤有机碳
Figure 2 Fold change of soil properties relative to the control in different periods The values in the figure are the change fold of soil properties relative to the control. * indicated significant differences at 5% level. DOC: Dissolved organic carbon; MBC: Microbial biomass carbon; DON: Dissolved organic nitrogen; MBN: Microbial biomass nitrogen; NAG: N-acetyl-β,D-glucosaminidase; β-GC: β-glucosidase; SOC: Soil organic carbon
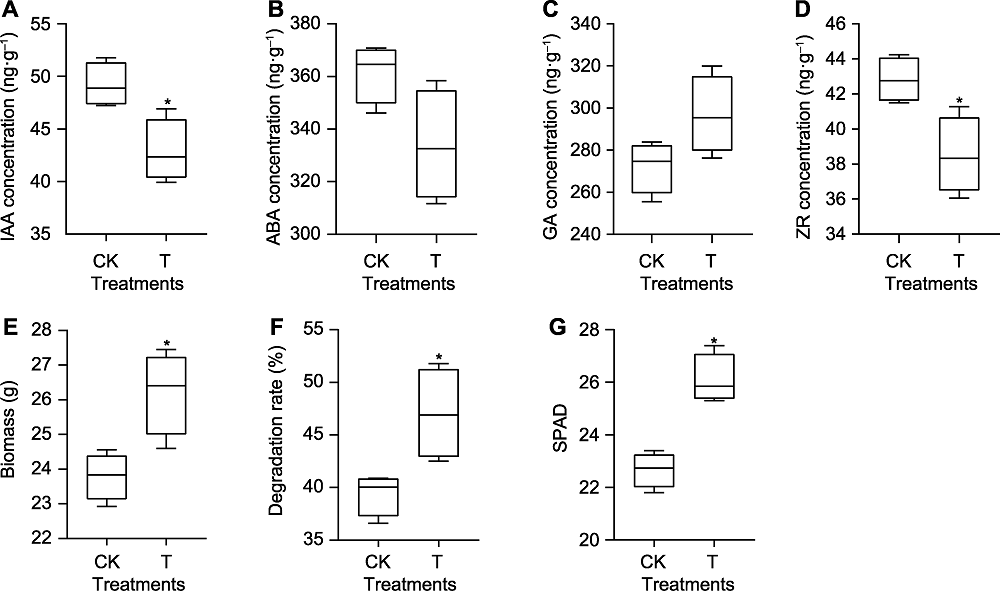
图3 接种单列毛壳菌对玉米生理特性的影响 (A) 玉米根系生长素(IAA)含量; (B) 玉米根系脱落酸(ABA)含量; (C) 玉米根系赤霉素(GA)含量; (D) 玉米根系玉米素(ZR)含量; (E) 玉米地上部生物量; (F) 网袋内秸秆降解率; (G) 玉米叶片SPAD值。* 表示5%水平差异显著(n=4)。CK表示对照处理; T表示接菌处理。
Figure 3 Effects of Chaetomium uniseriatum inoculation on maize physiological characteristics (A) Auxin (IAA) content in maize roots; (B) Abscisic acid (ABA) content in maize roots; (C) Gibberellin (GA) content in maize roots; (D) Zeatin (ZR) content in maize roots; (E) Aboveground biomass of maize; (F) Degradation rate of straw in net bag; (G) SPAD value of maize leaves. * indicated significant differences at 5% level (n=4). CK represents the control treatment; T represents the inoculation treatment.
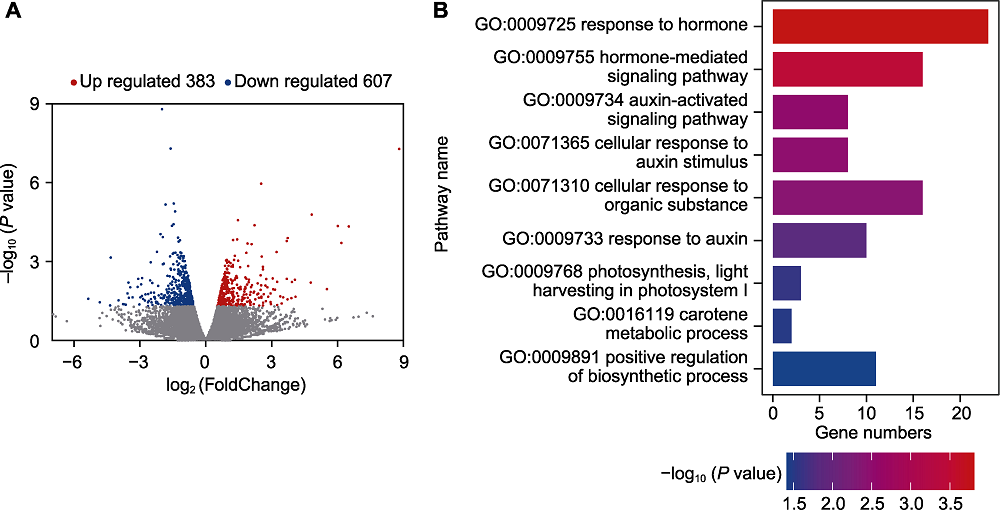
图4 接种单列毛壳菌后玉米差异表达基因分析 (A) 上调和下调基因的数量; (B) 差异表达基因的GO功能注释分类
Figure 4 Analysis of differentially expressed genes in maize after inoculation with Chaetomium uniseriatum (A) The number of up-regulated/down-regulated genes; (B) The results of GO annotation on differentially expressed genes
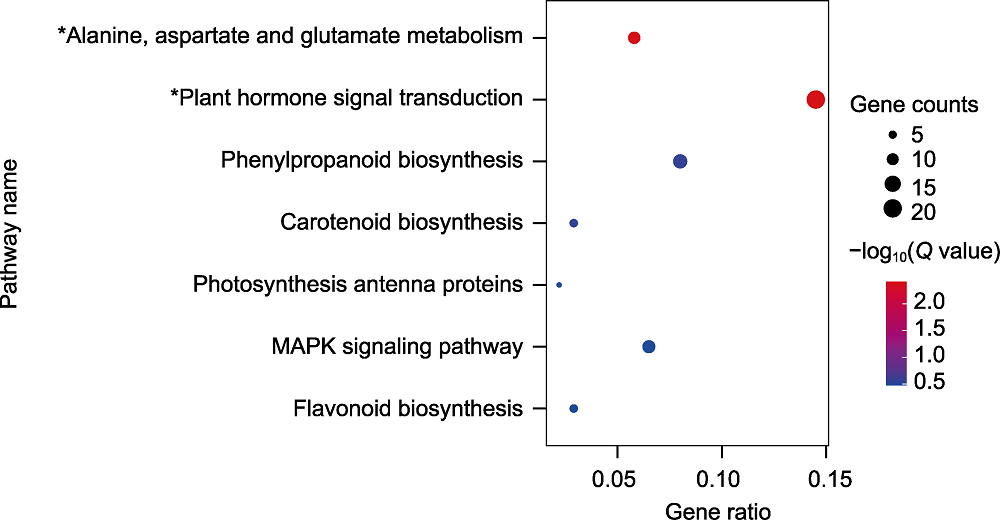
图5 差异表达基因的KEGG通路富集散点图 * 表示P value<0.05且Q value<0.05。
Figure 5 Scatter plot of KEGG enrichment of differentially expressed genes * indicated P value<0.05 and Q value<0.05.
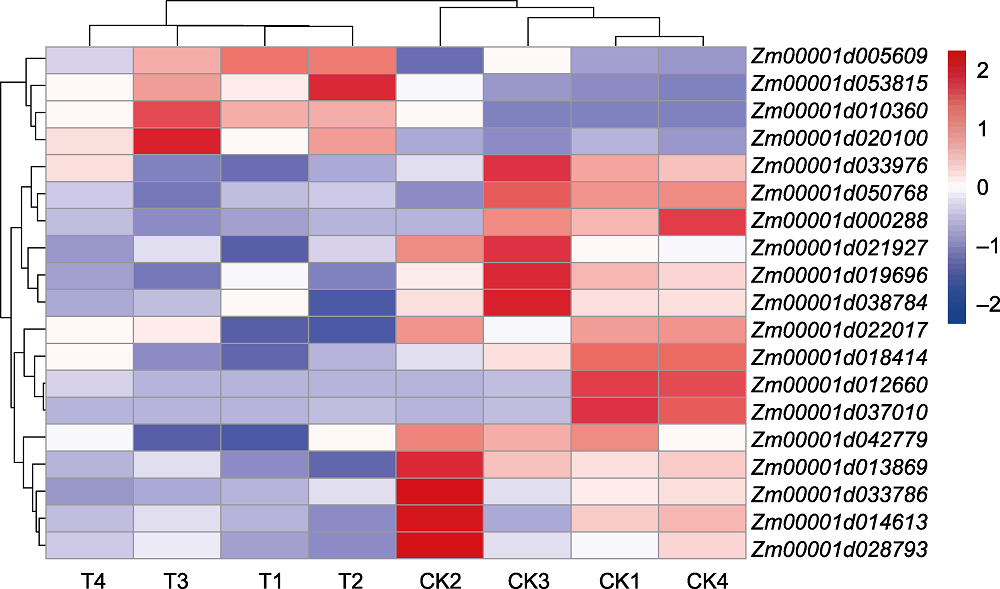
图6 植物激素信号转导通路相关基因聚类分析 CK1-CK4: 对照处理; T1-T4: 接菌处理
Figure 6 Cluster analysis of genes involved in plant hormone signal transduction pathway CK1-CK4: Control; T1-T4: Inoculation treatment
| Gene | log2(FoldChange) | P value | Gene description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zm00001d032724* | -1.541 | 0.000 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d035172* | -0.901 | 0.041 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d030888 | -0.327 | 0.227 | Probable disease resistance protein |
| Zm00001d054090 | -1.297 | 0.259 | Protein enhanced disease resistance 2 |
| Zm00001d041343 | -0.278 | 0.307 | Probable disease resistance protein |
| Zm00001d043197 | -0.549 | 0.349 | Probable disease resistance protein |
| Zm00001d052992 | -0.251 | 0.368 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d021491 | -0.267 | 0.370 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d041358 | -1.208 | 0.394 | NBS-LRR disease resistance protein-like |
| Zm00001d043233 | -0.239 | 0.407 | Disease resistance gene analog PIC21 |
| Zm00001d031711 | -0.529 | 0.435 | Disease resistance gene analog PIC15 |
| Zm00001d032510 | -0.632 | 0.473 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 1 |
| Zm00001d006873 | -0.329 | 0.517 | Disease resistance response protein-like; protein |
| Zm00001d007776 | -0.298 | 0.519 | Disease resistance protein RGA2 |
| Zm00001d024681 | -0.599 | 0.547 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d017954 | -0.179 | 0.554 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d049121 | -0.296 | 0.582 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d035973 | -0.159 | 0.601 | Protein enhanced disease resistance 2 |
| Zm00001d048663 | -0.180 | 0.611 | Disease resistance protein RGA2 |
| Zm00001d024977 | -0.376 | 0.623 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d014654 | -0.130 | 0.651 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d034555 | -0.179 | 0.653 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d006755 | -0.260 | 0.658 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d021564 | -0.936 | 0.681 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d014876 | -0.104 | 0.726 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d037648 | -0.090 | 0.753 | Disease resistance protein RPP13 |
| Zm00001d024975 | -0.111 | 0.756 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d048639 | -0.147 | 0.762 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d007935 | -0.593 | 0.781 | Disease resistance response protein 206 |
| Zm00001d007630 | -0.051 | 0.844 | Disease resistance protein RPS2 |
| Zm00001d023923 | -0.056 | 0.872 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d045512 | -0.177 | 0.886 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 3 |
| Zm00001d044172 | -0.022 | 0.903 | SGT1 disease resistance protein homolog1 |
| Zm00001d045335 | -0.027 | 0.916 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 1 |
| Zm00001d052389 | -0.094 | 0.923 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d048637 | -0.062 | 0.950 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d048635 | -0.282 | 0.971 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d032166 | -0.016 | 0.975 | Protein enhanced disease resistance 2 |
| Zm00001d053244 | -0.002 | 1.000 | Disease resistance protein (TIR-NBS class) |
| Zm00001d048613 | -0.031 | 1.000 | Disease resistance protein RGA2 |
表1 抗病相关基因表达情况
Table 1 Expression of genes associated with disease resistance
| Gene | log2(FoldChange) | P value | Gene description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zm00001d032724* | -1.541 | 0.000 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d035172* | -0.901 | 0.041 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d030888 | -0.327 | 0.227 | Probable disease resistance protein |
| Zm00001d054090 | -1.297 | 0.259 | Protein enhanced disease resistance 2 |
| Zm00001d041343 | -0.278 | 0.307 | Probable disease resistance protein |
| Zm00001d043197 | -0.549 | 0.349 | Probable disease resistance protein |
| Zm00001d052992 | -0.251 | 0.368 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d021491 | -0.267 | 0.370 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d041358 | -1.208 | 0.394 | NBS-LRR disease resistance protein-like |
| Zm00001d043233 | -0.239 | 0.407 | Disease resistance gene analog PIC21 |
| Zm00001d031711 | -0.529 | 0.435 | Disease resistance gene analog PIC15 |
| Zm00001d032510 | -0.632 | 0.473 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 1 |
| Zm00001d006873 | -0.329 | 0.517 | Disease resistance response protein-like; protein |
| Zm00001d007776 | -0.298 | 0.519 | Disease resistance protein RGA2 |
| Zm00001d024681 | -0.599 | 0.547 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d017954 | -0.179 | 0.554 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d049121 | -0.296 | 0.582 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d035973 | -0.159 | 0.601 | Protein enhanced disease resistance 2 |
| Zm00001d048663 | -0.180 | 0.611 | Disease resistance protein RGA2 |
| Zm00001d024977 | -0.376 | 0.623 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d014654 | -0.130 | 0.651 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d034555 | -0.179 | 0.653 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d006755 | -0.260 | 0.658 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d021564 | -0.936 | 0.681 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d014876 | -0.104 | 0.726 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d037648 | -0.090 | 0.753 | Disease resistance protein RPP13 |
| Zm00001d024975 | -0.111 | 0.756 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d048639 | -0.147 | 0.762 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d007935 | -0.593 | 0.781 | Disease resistance response protein 206 |
| Zm00001d007630 | -0.051 | 0.844 | Disease resistance protein RPS2 |
| Zm00001d023923 | -0.056 | 0.872 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d045512 | -0.177 | 0.886 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 3 |
| Zm00001d044172 | -0.022 | 0.903 | SGT1 disease resistance protein homolog1 |
| Zm00001d045335 | -0.027 | 0.916 | Putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein 1 |
| Zm00001d052389 | -0.094 | 0.923 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d048637 | -0.062 | 0.950 | Disease resistance RPP13-like protein 4 |
| Zm00001d048635 | -0.282 | 0.971 | Disease resistance protein RPM1 |
| Zm00001d032166 | -0.016 | 0.975 | Protein enhanced disease resistance 2 |
| Zm00001d053244 | -0.002 | 1.000 | Disease resistance protein (TIR-NBS class) |
| Zm00001d048613 | -0.031 | 1.000 | Disease resistance protein RGA2 |
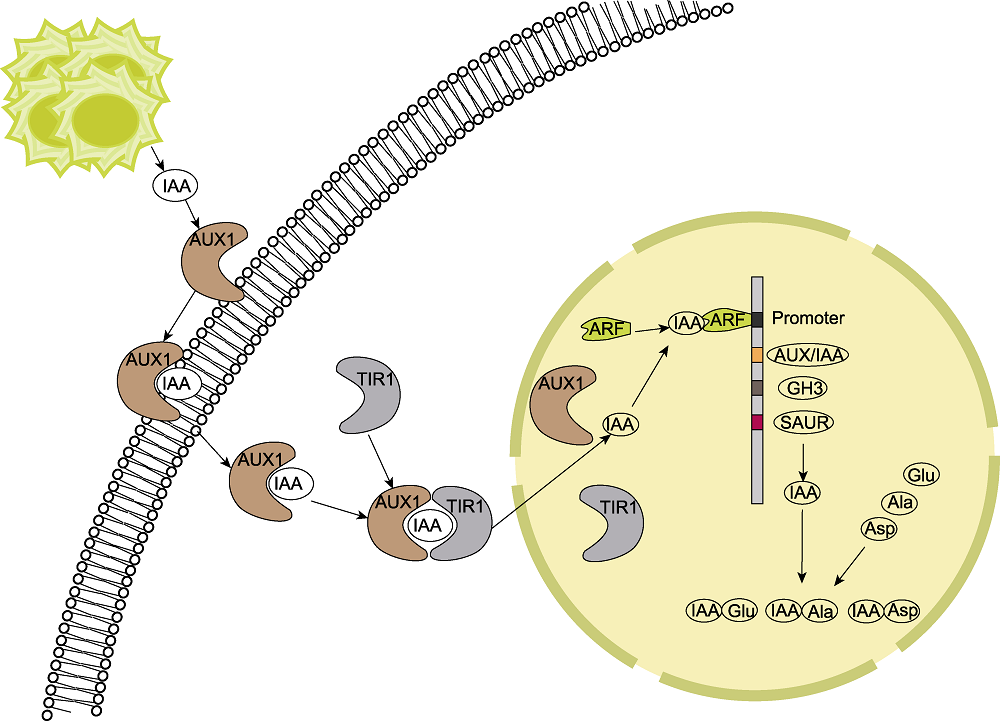
图7 单列毛壳菌促进玉米生长的机制 IAA: 生长素; Asp: 天冬氨酸; Ala: 丙氨酸; Glu: 谷氨酸
Figure 7 Mechanism of maize growth promotion by Chaetomium uniseriatum IAA: Auxin; Asp: Aspartate; Ala: Alanine; Glu: Glutamate
| [1] | 鲍士旦 (2000). 土壤农化分析(第3版). 北京: 中国农业出版社. pp. 25-38. |
| [2] | 郭栋, 杜媚, 周宝元, 刘颖慧, 赵明 (2019). 玉米SAUR基因家族的鉴定与生物信息学分析. 植物遗传资源学报 20, 90-99. |
| [3] | 何芳芳, 王海军, 王雪莹 (2020). 纤维素酶的研究进展. 造纸科学与技术 39(4), 1-8. |
| [4] | 滕青云, 乐丽娜, 宋冰倩, 陈英 (2020). 植物TIR1/AFBs基因家族研究进展. 农业工程 10, 93-97. |
| [5] |
Abdel-Azeem AM, Gherbawy YA, Sabry AM (2016). Enzyme profiles and genotyping of Chaetomium globosum isolates from various substrates. Plant Biosyst 150, 420-428.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
Allen HR, Ptashnyk M (2020). Mathematical modelling of auxin transport in plant tissues: flux meets signaling and growth. Bull Math Biol 82, 17.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Anders S, Huber W (2010). Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11, R106.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Archer SK, Shirokikh NE, Preiss T (2014). Selective and flexible depletion of problematic sequences from RNA-seq libraries at the cDNA stage. BMC Genomics 15, 401.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000). Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25, 25-29.
DOI PMID |
| [10] |
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CMJ, Bakker PAHM (2012). The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci 17, 478-486.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Berhane M, Xu M, Liang ZY, Shi JL, Wei GH, Tian XH (2020). Effects of long-term straw return on soil organic carbon storage and sequestration rate in North China upland crops: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 26, 2686-2701.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Cañizares R, Benitez E, Ogunseitan OA (2011). Molecular analyses of β-glucosidase diversity and function in soil. Eur J Soil Biol 47, 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Chen YN, Chen YR, Li YP, Wu YX, Zhu FZ, Zeng GM, Zhang JC, Li H (2018). Application of Fenton pretreatment on the degradation of rice straw by mixed culture of Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Aspergillus niger. Ind Crop Prod 112, 290-295.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Fattorini L, Falasca G, Kevers C, Mainero Rocca L, Zadra C, Altamura MM (2009). Adventitious rooting is enhanced by methyl jasmonate in tobacco thin cell layers. Planta 231, 155-168.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995). A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61, 793-796.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Guilfoyle TJ, Ulmasov T, Hagen G (1998). The ARF family of transcription factors and their role in plant hormone-responsive transcription. Cell Mol Life Sci 54, 619-627.
PMID |
| [17] |
Jaroszuk-Ściseł J, Kurek E, Trytek M (2014). Efficiency of indoleacetic acid, gibberellic acid and ethylene synthesized in vitro by Fusarium culmorum strains with different effects on cereal growth. Biologia 69, 281-292.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Jiang C, Song JZ, Zhang JZ, Yang Q (2017). New production process of the antifungal chaetoglobosin A using cornstalks. Braz J Microbiol 48, 410-418.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Jiang XZ, Du JW, He RN, Zhang ZY, Qi F, Huang JZ, Qin L (2020). Improved production of majority cellulases in Trichoderma reesei by integration of cbh1gene grom Chaetomium thermophilum. Front Microbiol 11, 1633.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T, Yamanishi Y (2008). KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 36, D480-D484.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Kang SM, Khan AL, Waqas M, You YH, Kim JH, Kim JG, Hamayun M, Lee IJ (2014). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria reduce adverse effects of salinity and osmotic stress by regulating phytohormones and antioxidants in Cucumis sativus. J Plant Interact 9, 673-682.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Kazan K, Manners JM (2009). Linking development to defense: auxin in plant-pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci 14, 373-382.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Khan AL, Shinwari ZK, Kim YH, Waqas M, Hamayun M, Kamran M, Lee IJ (2012). Role of endophyte Chaetomium globosum lk4 in growth of Capsicum annuum by producion of gibberellins and indole acetic acid. Pak J Bot 44, 1601-1607. |
| [24] |
Laothanachareon T, Bunterngsook B, Suwannarangsee S, Eurwilaichitr L, Champreda V (2015). Synergistic action of recombinant accessory hemicellulolytic and pectinolytic enzymes to Trichoderma reesei cellulase on rice straw degradation. Bioresour Technol 198, 682-690.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Leyser O (2005). Auxin distribution and plant pattern formation: how many angels can dance on the point of PIN? Cell 121, 819-822.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Li F, Zhang SQ, Wang Y, Li Y, Li PP, Chen L, Jie XL, Hu DS, Feng B, Yue K, Han YL (2020). Rare fungus, Mortierella capitata, promotes crop growth by stimulating primary metabolisms related genes and reshaping rhizosphere bacterial community. Soil Biol Biochem 151, 108017.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Li ZX, Zhang XR, Zhao YJ, Li YJ, Zhang GF, Peng ZH, Zhang JR (2018). Enhancing auxin accumulation in maize root tips improves root growth and dwarfs plant height. Plant Biotechnol J 16, 86-99.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Liu G, Yu HY, Ma J, Xu H, Wu QY, Yang JH, Zhuang YQ (2015). Effects of straw incorporation along with microbial inoculant on methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice fields. Sci Total Environ 518-519, 209-216.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Liu HW, Brettell LE, Qiu ZG, Singh BK (2020). Microbiome-mediated stress resistance in plants. Trends Plant Sci 25, 733-743.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Liu X, Zhou F, Hu GQ, Shao S, He HB, Zhang W, Zhang XD, Li LJ (2019). Dynamic contribution of microbial residues to soil organic matter accumulation influenced by maize straw mulching. Geoderma 333, 35-42.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Manirakiza E, Ziadi N, St Luce M, Hamel C, Antoun H, Karam A (2019). Nitrogen mineralization and microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen in response to co-application of biochar and paper mill biosolids. Appl Soil Ecol 142, 90-98.
DOI |
| [32] |
Millevoi S, Vagner S (2010). Molecular mechanisms of eukaryotic pre-mRNA 3′ end processing regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 38, 2757-2774.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Narukawa-Nara M, Nakamura A, Kikuzato K, Kakei Y, Sato A, Mitani Y, Yamasaki-Kokudo Y, Ishii T, Hayashi KI, Asami T, Ogura T, Yoshida S, Fujioka S, Kamakura T, Kawatsu T, Tachikawa M, Soeno K, Shimada Y (2016). Aminooxy-naphthylpropionic acid and its derivatives are inhibitors of auxin biosynthesis targeting L-tryptophan aminotransferase: structure-activity relationships. Plant J 87, 245-257.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Ortiz J, Soto J, Fuentes A, Herrera H, Meneses C, Arriagada C (2019). The endophytic fungus Chaetomium cupreum regulates expression of genes involved in the tolerance to metals and plant growth promotion in eucalyptus globulus roots. Microorganisms 7, 490.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Park JH, Choi GJ, Jang KS, Lim HK, Kim HT, Cho KY, Kim JC (2005). Antifungal activity against plant pathogenic fungi of chaetoviridins isolated from Chaetomium globosum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 252, 309-313.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Pedraza-Zapata DC, Sánchez-Garibello AM, Quevedo-Hidalgo B, Moreno-Sarmiento N, Gutiérrez-Rojas I (2017). Promising cellulolytic fungi isolates for rice straw degradation. J Microbiol 55, 711-719.
DOI PMID |
| [37] |
Raza W, Mei XL, Wei Z, Ling N, Yuan J, Wang JC, Huang QW, Shen QR (2017). Profiling of soil volatile organic compounds after long-term application of inorganic, organic and organic-inorganic mixed fertilizers and their effect on plant growth. Sci Total Environ 607-608, 326-338.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Saiya-Cork KR, Sinsabaugh RL, Zak DR (2002). The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34, 1309-1315.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Sato M, Winter JM, Kishimoto S, Noguchi H, Tang Y, Watanabe K (2016). Combinatorial generation of chemical diversity by redox enzymes in chaetoviridin biosynthesis. Org Lett 18, 1446-1449
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Shanthiyaa V, Saravanakumar D, Rajendran L, Karthikeyan G, Prabakar K, Raguchander T (2013). Use of Chaetomium globosum for biocontrol of potato late blight disease. Crop Prot 52, 33-38.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Siegel-Hertz K, Edel-Hermann V, Chapelle E, Terrat S, Raaijmakers JM, Steinberg C (2018). Comparative microbiome analysis of a Fusarium wilt suppressive soil and a Fusarium wilt conducive soil from the Châteaurenard region. Front Microbiol 9, 568.
DOI PMID |
| [42] |
Singh A, Sharma S (2002). Composting of a crop residue through treatment with microorganisms and subsequent vermicomposting. Bioresour Technol 85, 107-111.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Timmusk S, Wagner EGH (1999). The plant-growth-promoting rhizobacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa induces changes in Arabidopsis thaliana gene expression: a possible connection between biotic and abiotic stress responses. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12, 951-959.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Uddling J, Gelang-Alfredsson J, Piikki K, Pleijel H (2007). Evaluating the relationship between leaf chlorophyll concentration and SPAD-502 chlorophyll meter readings. Photosynth Res 91, 37-46.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987). Anextraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19, 703-707.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Wang B, Funakoshi D, Dalpé Y, Hamel C (2002). Phosphorus-32 absorption and translocation to host plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi at low root-zone temperature. Mycorrhiza 12, 93-96.
PMID |
| [47] |
Wang R, Zhang HC, Sun LG, Qi GF, Chen S, Zhao XY (2017). Microbial community composition is related to soil biological and chemical properties and bacterial wilt outbreak. Sci Rep 7, 343.
DOI PMID |
| [48] |
Wu JS, Joergensen RG, Pommerening B, Chaussod R (1990). Measurement of soil microbial biomass c by fumigation extraction—an automated procedure. Soil Biol Biochem 22, 1167-1169.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Xu J, Han HF, Ning TY, Li ZJ, Lal R (2019). Long-term effects of tillage and straw management on soil organic carbon, crop yield, and yield stability in a wheat-maize system. Field Crop Res 233, 33-40.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Yang HS, Zhou JJ, Weih M, Li YF, Zhai SL, Zhang Q, Chen WP, Liu J, Liu L, Hu SJ (2020). Mycorrhizal nitrogen uptake of wheat is increased by earthworm activity only under no-till and straw removal conditions. Appl Soil Ecol 155, 103672.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Yang J, Kloepper JW, Ryu CM (2009). Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci 14, 1-4.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Yun SI, Jeong CS, Chung DK, Choi HS (2001). Purification and some properties of a β-glucosidase from Trichoderma harzianum type C-4. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65, 2028-2032.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Zhang Y, Yu XX, Zhang WJ, Lang DY, Zhang XJ, Cui GC, Zhang XH (2019). Interactions between endophytes and plants: beneficial effect of endophytes to ameliorate biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. J Plant Biol 62, 1-13.
DOI |
| [54] |
Zhao XL, Yuan GY, Wang HY, Lu DJ, Chen XQ, Zhou JM (2019). Effects of full straw incorporation on soil fertility and crop yield in rice-wheat rotation for silty clay loamy cropland. Agronomy 9, 133.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Zhao XY, He XS, Xi BD, Gao RT, Tan WB, Zhang H, Li D (2016). The evolution of water extractable organic matter and its association with microbial community dynamics during municipal solid waste composting. Waste Manage 56, 79-87.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张静 陈洁 李艳朋 盘李军 许涵 李意德 何海生. 南亚热带针阔混交人工林植物生物量比较及其影响因子分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(化学计量与功能性状): 0-0. |
| [2] | 刘旭鹏, 王敏, 韩守安, 朱学慧, 王艳蒙, 潘明启, 张雯. 植物器官脱落调控因素及分子机理研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(3): 472-482. |
| [3] | 马录花, 孟宪超, 王贵强, 马子峰, 李以康, 李月梅, 周华坤, 张法伟, 林丽. 藓类结皮接种对三江源高寒草甸土壤性状和微生物的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2025, 49(1): 173-188. |
| [4] | 张向歌, 陈晨, 程珊, 李春鑫, 朱雅婧, 许欣然, 王会伟. 油莎豆块茎特异性表达基因鉴定及分析[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 33-48. |
| [5] | 王亚萍, 包文泉, 白玉娥. 单细胞转录组学在植物生长发育及胁迫响应中的应用进展[J]. 植物学报, 2025, 60(1): 101-113. |
| [6] | 龙吉兰, 蒋铮, 刘定琴, 缪宇轩, 周灵燕, 冯颖, 裴佳宁, 刘瑞强, 周旭辉, 伏玉玲. 干旱下植物根系分泌物及其介导的根际激发效应研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2024, 48(7): 817-827. |
| [7] | 陈婷欣, 符敏, 李娜, 杨蕾蕾, 李凌飞, 钟春梅. 铁甲秋海棠DNA甲基转移酶全基因组鉴定及表达分析(长英文摘要)[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(5): 726-737. |
| [8] | 杜晴晴, 任思远, Nicole Tsz Shun Yuan, 祝燕. 北京东灵山暖温带落叶阔叶林幼树及成树生产力的影响因素[J]. 生物多样性, 2024, 32(12): 24284-. |
| [9] | 张悦婧, 桑鹤天, 王涵琦, 石珍珍, 李丽, 王馨, 孙坤, 张继, 冯汉青. 植物对非生物胁迫系统性反应中信号传递的研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2024, 59(1): 122-133. |
| [10] | 蒋海港, 曾云鸿, 唐华欣, 刘伟, 李杰林, 何国华, 秦海燕, 王丽超, 姚银安. 三种藓类植物固碳耗水节律调节作用[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(7): 988-997. |
| [11] | 白雪, 李玉靖, 景秀清, 赵晓东, 畅莎莎, 荆韬羽, 刘晋汝, 赵鹏宇. 谷子及其根际土壤微生物群落对铬胁迫的响应机制[J]. 植物生态学报, 2023, 47(3): 418-433. |
| [12] | 肖宇彬, 张子旭, 王玉珠, 刘欢, 陈乐天. 时空转录组研究进展[J]. 植物学报, 2023, 58(2): 214-232. |
| [13] | 李万年, 罗益敏, 黄则月, 杨梅. 望天树人工幼林混交对土壤微生物功能多样性与碳源利用的影响[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(9): 1109-1124. |
| [14] | 孙彩丽, 仇模升, 黄朝相, 王艺伟. 黔西南石漠化过程中土壤胞外酶活性及其化学计量变化特征[J]. 植物生态学报, 2022, 46(7): 834-845. |
| [15] | 李季蔓, 靳楠, 胥毛刚, 霍举颂, 陈小云, 胡锋, 刘满强. 不同干旱水平下蚯蚓对番茄抗旱能力的影响[J]. 生物多样性, 2022, 30(7): 21488-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||